Submitted:
03 August 2023
Posted:
04 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study population and design
2.2. Clinical characteristics
2.3. Blood samples and LDL purification
2.4. Biochemistry analysis
2.5. Lipids analyses
2.5.1. Z-scan technique
2.5.2. UV-visible spectroscopy
2.5.3. Lipoprotein subfractions analysis
2.5.4. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Clinical and Biochemistry parameters
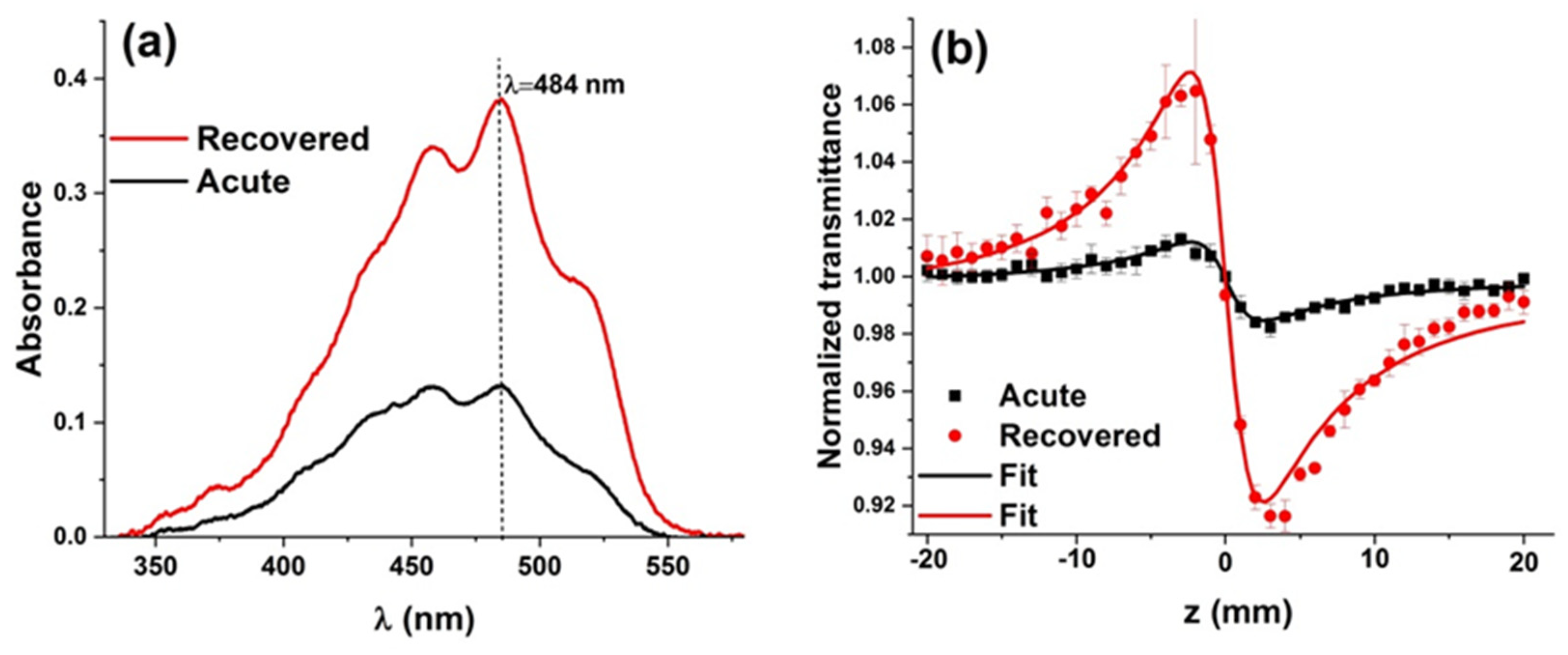
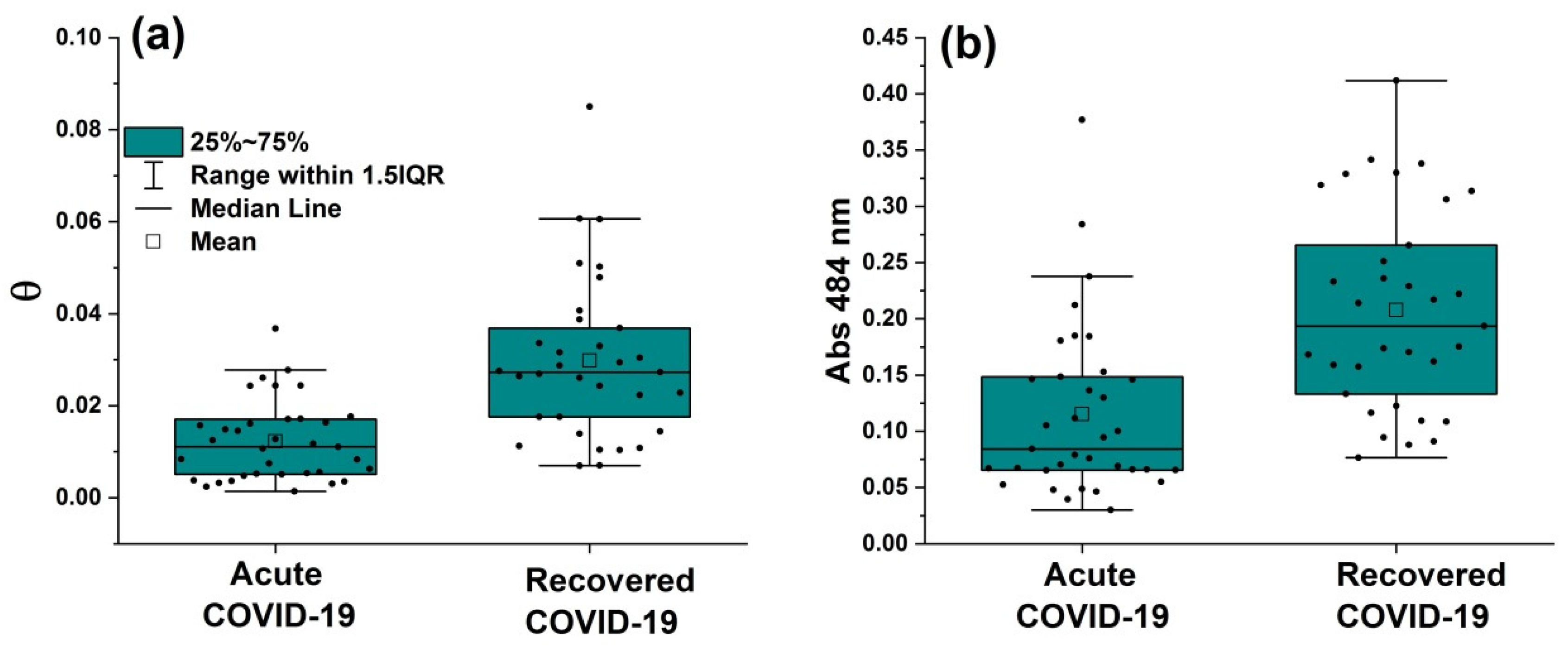
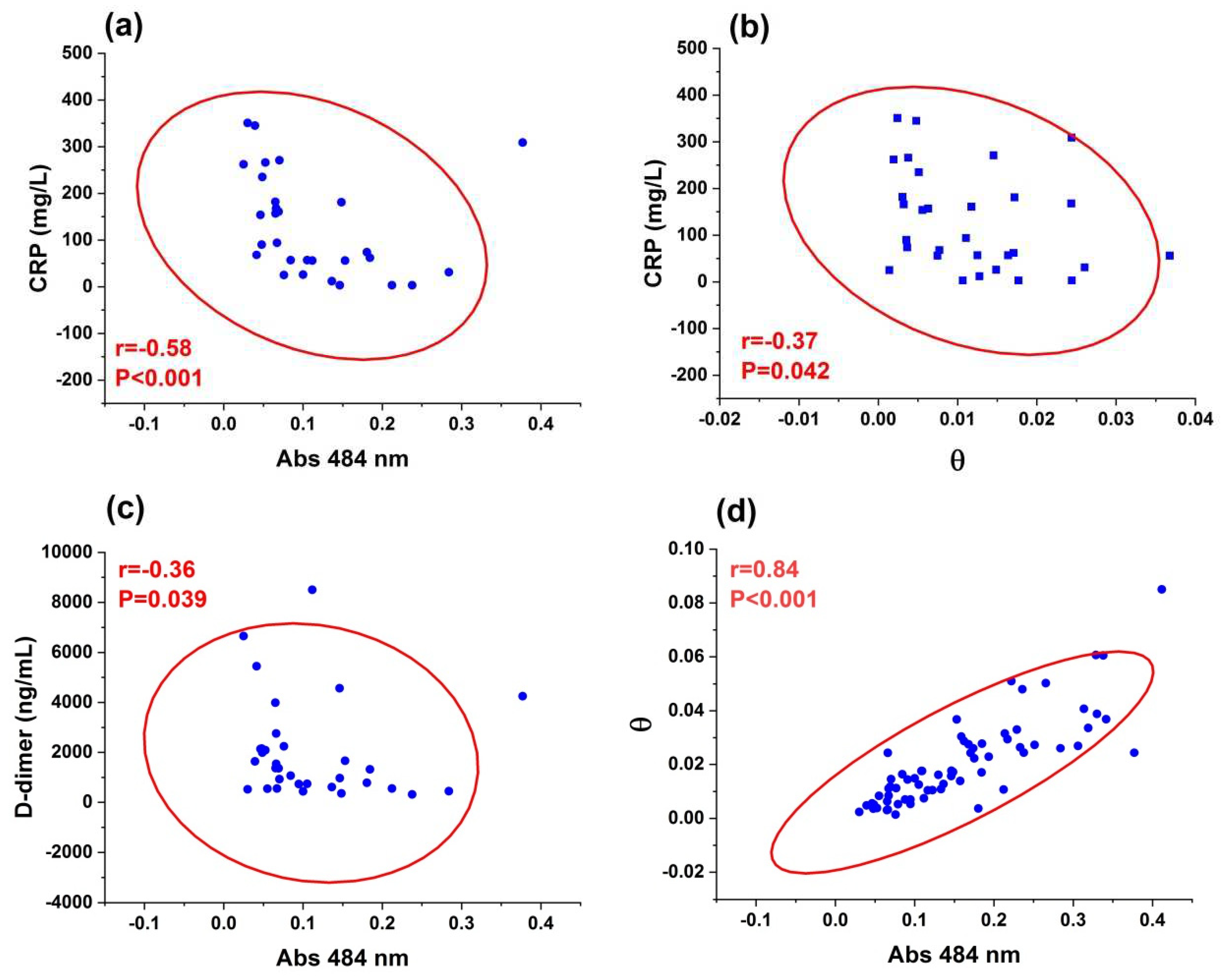
3.2. Z-scan and UV-visible results
3.3. Lipoprotein subfractions analysis
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Abu-Farha, M.; Thanaraj, T.A.; Qaddoumi, M.G.; Hashem, A.; Abubaker, J.; Al-Mulla, F. The role of lipid metabolism in COVID-19 virus infection and as a drug target. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirillo, A.; Casula, M.; Olmastroni, E.; Norata, G.D.; Catapano, A.L. Global epidemiology of dyslipidaemias. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2021, 18, 689–700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santos, R.D.; Bensenor, I.M.; Pereira, A.C.; Lotufo, P.A. Dyslipidemia according to gender and race: the Brazilian Longitudinal Study of Adult Health (ELSA-Brasil). J. Clin. Lipidol. 2016, 10, 1362–1368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, X.; Zeng, W.; Su, J.; Wan, H.; Yu, X.; Cao, X.; Tan, W.; Wang, H. Hypolipidemia is associated with the severity of COVID-19. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2020, 14, 297–304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, J.; Wang, H.; Ye, G.; Cao, X.; Xu, X.; Tan, W.; Zhang, Y. Low-density lipoprotein is a potential predictor of poor prognosis in patients with coronavirus disease 2019. Metab. 2020, 107, 154243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feingold, K.R. Lipid and lipoprotein levels in patients with COVID-19 infections. 2020, MDText.com, Inc., South Dartmouth (MA). https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/sites/books/NBK564657/.
- Jin, X.; Yang, S.; Lu, J.; Wu, M. Small, dense low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol and atherosclerosis: relationship and therapeutic strategies. Front. Cardiovasc. Med. 2022, 8, 1–14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Du, L.; Cao, X.; Wei, X.; Jiang, Y.; Lin, Y.; Nguyen, V.; Tan, W.; Wang, H. Follow-up study on serum cholesterol profiles and potential sequelae in recovered COVID-19 patients. BMC Infect. Dis. 2021, 21, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Changaripour, S.; Sarvazad, H.; Barghi, M.; Sajadi, E.; Sadeghian, M.H.; Roozbahani, N.E. Lipid profile changes in patients with COVID-19 referred to medical centers in Kermanshah, Iran; a case–control study. J. Int. Med. Res. 2022, 85, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesan, A.; Gopalakrishnan, S.; Purandhar, S. A study of relationship between lipid profile and severity of SARS-CoV-2. Rom J Diabetes Nutr Metab Dis 2022, 29, 289–292. [Google Scholar]
- Novack, V.; Eisinger, M.; Frenkel, A.; Terblanche, M.; Adhikari, N.K.; Douvdevani, A.; Amichay, D.; Almog, Y. The effects of statin therapy on inflammatory cytokines in patients with bacterial infections: a randomized double-blind placebo controlled clinical trial. Intensive Care Med INTENS 2009, 35, 1255–1260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Papazian, L.; Roch, A.; Charles, P.E.; Penot-Ragon, C.; Perrin, G.; Roulier, P.; Goutorbe, P.; Lefrant, J.Y.; Wiramus, S.; Jung, B.; Perbet, S. Effect of statin therapy on mortality in patients with ventilator-associated pneumonia: a randomized clinical trial. Jama 2013, 310, 1692–1700. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pertzov, B.; Eliakim-Raz, N.; Atamna, H.; Trestioreanu, A.Z.; Yahav, D.; Leibovici, L. Hydroxymethylglutaryl-CoA reductase inhibitors (statins) for the treatment of sepsis in adults–a systematic review and meta-analysis. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2019, 25, 280–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Otvos, J.D.; Mora, S.; Shalaurova, I.; Greenland, P.; Mackey, R.H.; Goff Jr, D.C. Clinical implications of discordance between low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and particle number. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2011, 5, 105–113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Packard, C.; Caslake, M.; Shepherd, J. The role of small, dense low density lipoprotein (LDL): a new look. Int. J. Cardiol. 2000, 74, S17–S22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ivanova, E.A.; Myasoedova, V.A.; Melnichenko, A.A.; Grechko, A.V.; Orekhov, A.N. Small dense low-density lipoprotein as biomarker for atherosclerotic diseases. Oxidative Med. Cell. Longev. 2017, 2017, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mello, A.P.Q.; da Silva, I.T.; Abdalla, D.S.P.; Damasceno, N.R.T. Electronegative low-density lipoprotein: origin and impact on health and disease. Atherosclerosis 2011, 215, 257–265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Queiroz Mello, A.P.; Albattarni, G.; Espinosa, D.H.; Reis, D.; Figueiredo Neto, A.M. Structural and Nonlinear Optical Characteristics of In Vitro Glycation of Human Low-Density Lipoprotein, as a Function of Time. Braz. J. Phys. 2018, 48, 560–570. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.M.; Jardini, M.A.; Giampaoli, V.; Alves, S.; Figueiredo Neto, A.M.; Gidlund, M. Measurement of the nonlinear optical response of low-density lipoprotein solutions from patients with periodontitis before and after periodontal treatment: evaluation of cardiovascular risk markers. J. Biomed. Opt. 2012, 17, 115004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfollahi, Z.; Mello, A.P.D.Q.; Costa, E.S.; Oliveira, C.L.; Damasceno, N.R.; Izar, M.C.; Neto, A.M.F. Green-banana biomass consumption by diabetic patients improves plasma low-density lipoprotein particle functionality. Sci. Rep. 2020, 10, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lotfollahi, Z.; Mello, A.P.; Fonseca, F.A.; Machado, L.O.; Mathias, A.F.; Izar, M.C.; Damasceno, N.R.; Oliveira, C.L.; Neto, A.M.F. Changes in lipoproteins associated with lipid-lowering and antiplatelet strategies in patients with acute myocardial infarction. PloS one 2022, 17, e0273292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Monteiro, A.M.; Jardini, M.A.; Alves, S.; Giampaoli, V.; Aubin, E.C.; Figueiredo Neto, A.M.; Gidlund, M. Cardiovascular disease parameters in periodontitis. J. Periodontol. 2009, 80, 378–388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alves, S.; Figueiredo Neto, A.M. Advances in the non-linear optical investigation of lyotropic-like low-density human lipoproteins in the native and oxidised states. Liq. Cryst. 2014, 41, 465–470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pedroso, J.D.F.; Lotfollahi, Z.; Albattarni, G.; Arrruda Schulz, M.; Monteiro, A.; Sehnem, A.L.; Gidlund, M.A.; Figueiredo Neto, A.M.; Jardini, M.A.N. Influence of Periodontal Disease on cardiovascular markers in Diabetes Mellitus patients. Sci. Rep. 2019, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Friedewald, W.T.; Levy, R.I.; Fredrickson, D.S. Estimation of the concentration of low-density lipoprotein cholesterol in plasma, without use of the preparative ultracentrifuge. Clin. Chem. 1972, 18, 499–502. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanders, D.W.; Jumper, C.C.; Ackerman, P.J.; Bracha, D.; Donlic, A.; Kim, H.; Kenney, D.; Castello-Serrano, I.; Suzuki, S.; Tamura, T.; Tavares, A.H. SARS-CoV-2 requires cholesterol for viral entry and pathological syncytia formation. Elife 2021, 10, e65962. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gill, M.R.S.; Ambrose, J.A. COVID-19 Infection and Myocardial Infarction Pathophysiology and Therapy. CARDIOLOGY 2021, 99. [Google Scholar]
- Rhoads, J.P.; Major, A.S. How oxidized low-density lipoprotein activates inflammatory responses. CRC crit. rev. immunol. 2018, 38, 333–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tekin, I.O.; Orem, A.; Shiri-Sverdlov, R. Oxidized LDL in inflammation: from bench to bedside. Mediators Inflamm. 2013, 2013, 762759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Memon, R.A.; Staprans, I.; Noor, M.; Holleran, W.M.; Uchida, Y.; Moser, A.H.; Feingold, K.R.; Grunfeld, C. Infection and inflammation induce LDL oxidation in vivo. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Biol. 2000, 20, 1536–1542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Silva, I.T.; Mello, A.P.; Damasceno, N.R. Antioxidant and inflammatory aspects of lipoprotein-associated phospholipase A2 (Lp-PLA2): a review. Lipids Health Dis. 2011, 10, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Freitas, M.C.P.; Neto, A.M.F.; Damasceno, N.R. Nonlinear optical responses of oxidized low-density lipoprotein: Cutoff point for z-scan peak-valley distance. Photodiagnosis Photodyn Ther. 2020, 30, 101689. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- da Silva, I.T.; de Queiroz Mello, A.P.; Sanches, L.B.; Abdalla, D.S.P.; Damasceno, N.R.T. Is plasma alpha-tocopherol associated with electronegative LDL in obese adolescents? J. Nutr. Sci. Vitaminol. 2013, 59, 100–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, H.K.; Hong, J.; Ahn, S.; Lee, W.; Chun, S.; Min, W.K. Association between measured or calculated small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol and oxidized low-density lipoprotein in subjects with or without type 2 diabetes mellitus. J. Clin. Lab. Anal. 2022, 37, e24807. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pfützner, A.; Efstrathios, K.; Löbig, M.; Armbruster, F.P.; Hanefeld, M.; Forst, T. Differences in the results and interpretation of oxidized LDL cholesterol by two ELISA assays--an evaluation with samples from the PIOstat study. Clin. Lab. 2009, 55, 275–281. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Erol, A. Role of oxidized LDL-induced “trained macrophages” in the pathogenesis of COVID-19 and benefits of pioglitazone: A hypothesis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. 2020, 14, 713–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stringer, D.; Braude, P.; Myint, P.K.; Evans, L.; Collins, J.T.; Verduri, A.; Quinn, T.J.; Vilches-Moraga, A.; Stechman, M.J.; Pearce, L.; Moug, S. The role of C-reactive protein as a prognostic marker in COVID-19. Int. J. Epidemiol. 2021, 50, 420–429. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J. Tackle the free radicals damage in COVID-19. Nitric Oxide. 2020, 102, 39–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chernyak, B.V.; Popova, E.N.; Prikhodko, A.S.; Grebenchikov, O.A.; Zinovkina, L.A.; Zinovkin, R.A. COVID-19 and oxidative stress. Biochem. (Mosc.) 2020, 85, 1543–1553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Walston, J.; Xue, Q.; Semba, R.D.; Ferrucci, L.; Cappola, A.R.; Ricks, M.; Guralnik, J.; Fried, L.P. Serum antioxidants, inflammation, and total mortality in older women. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2006, 163, 18–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johra, F.T.; Bepari, A.K.; Bristy, A.T.; Reza, H.M. A mechanistic review of β-carotene, lutein, and zeaxanthin in eye health and disease. Antioxidants 2020, 9, 1046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bae, M.; Kim, H. The role of vitamin C, vitamin D, and selenium in immune system against COVID-19. Molecules 2020, 25, 5346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Iddir, M.; Brito, A.; Dingeo, G.; Fernandez Del Campo, S.S.; Samouda, H.; La Frano, M.R.; Bohn, T. Strengthening the immune system and reducing inflammation and oxidative stress through diet and nutrition: considerations during the COVID-19 crisis. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1562. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Griffin, B.A. Lipoprotein atherogenicity: an overview of current mechanisms. Proc. Nutr. Soc. 1999, 58, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Taskinen, M.-R. LDL-cholesterol, HDL-cholesterol or triglycerides—which is the culprit? Diabetes Res. Clin. Pract. 2003, 61, S19–S26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perugini, C.; Seccia, M.; Bagnati, M.; Cau, C.; Albano, E.; Bellomo, G. Different mechanisms are progressively recruited to promote Cu (II) reduction by isolated human low-density lipoprotein undergoing oxidation. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 1998, 25, 519–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tsai, M.Y.; Steffen, B.T.; Guan, W.; McClelland, R.L.; Warnick, R.; McConnell, J.; Hoefner, D.M.; Remaley, A.T. New automated assay of small dense low-density lipoprotein cholesterol identifies risk of coronary heart disease: the Multi-ethnic Study of Atherosclerosis. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Bio. 2014, 34, 196–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoogeveen, R.C.; Gaubatz, J.W.; Sun, W.; Dodge, R.C.; Crosby, J.R.; Jiang, J.; Couper, D.; Virani, S.S.; Kathiresan, S.; Boerwinkle, E.; Ballantyne, C.M. Small dense low-density lipoprotein-cholesterol concentrations predict risk for coronary heart disease: the Atherosclerosis Risk in Communities (ARIC) study. Arterioscler. Thromb. Vasc. Bio. 2014, 2014. 34, 1069–1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Janovsky, C.C.P.S.; Goulart, A.C.; Generoso, G.; Santos, R.D.; Blaha, M.J.; Jones, S.; Toth, P.P.; Lotufo, P.A.; Bittencourt, M.S.; Benseñor, I.M. Substantially elevated TSH, not traditional clinical subclinical thyroid disorder groupings, are associated with smaller LDL-P mean size: ELSA-Brasil. J. Clin. Lipidol. 2022, 16, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeljkovic, A.; Vekic, J.; Spasojevic-Kalimanovska, V. Jelic-Ivanovic, Z.; Bogavac-Stanojevic, N.; Gulan, B.; Spasic, S. LDL and HDL subclasses in acute ischemic stroke: prediction of risk and short-term mortality. Atherosclerosis 2010, 210, 548–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Acute COVID-19 (n=33) |
Recovered COVID-19 (n=30) |
P-value | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Age, years | 60±19 | 53±15 | 0.101 |
| Sex, male | 21(63) | 13 (43) | 0.45 |
| Race, white | 25 (75) | 20 (66) | 0.89 |
| Smoking | 2 (6) | 3 (10) | 0.66 |
| Alcoholism | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 1.00 |
| Comorbidities | 20 (61) | 18 (60) | 0.99 |
| DM | 9 (27) | 6 (20) | 0.93 |
| Stroke | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 1.00 |
| SARS | 28 (84) | 20 (66) | 0.41 |
| Dyslipidaemia | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 1.00 |
| SAH | 12 (36) | 13 (43) | 0.95 |
| CVD | 1 (3) | 0 (0) | 1.00 |
| CRP (mg/L) | 92 (49-195) | 87 (56-175) | 0.84 |
| D-dimer (ng/mL) | 1,362 (579-2,201) | 656 (451-1,529) | 0.0248* |
| Variables | Acute COVID-19 (n=33) |
Recovered COVID-19 (n=30) |
P-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| LDL-1 (%) | 14.1 (2.6-26.5) | 17.0 (2.0-31.7) | 0.266 |
| LDL-2 (%) | 8.9 (0.0-23.0) | 12.9 (0.0-24.7) | 0.008* |
| LDL-3 (%) | 1.8 (0.0-9.4) | 3.1 (0.0-12.5) | 0.060 |
| LDL-4 (%) | 0.0 (0.0-4.7) | 0.0 (0.0-8.4) | 0.261 |
| LDL-5 (%) | 0.0 (0.0-1.2) | 0.0 (0.0-5.0) | 0.046* |
| LDL-6 (%) | 0.0 (0.0-2.2) | 0.0 (0.0-2.2) | 0.502 |
| LDL-7 (%) | 0.0 (0.0-30.6) | 0.0 (0.0-11.0) | 0.657 |
| Large LDL (%) | 23.1 (2.6-39.0) | 29.9 (2.0-50.2) | 0.025* |
| Small LDL (%) | 3.2 (0.0-32.8) | 4.8 (0.0-25.1) | 0.153 |
| LDL-1 (mg/dL) | 23.9 (2.5-58.2) | 35 (4.5-70.1) | 0.009* |
| LDL-2 (mg/dL) | 24.6 (0.0-47.6) | 27.1 (0.0-53.2) | 0.489 |
| LDL-3 (mg/dL) | 8.1 (0.0-39.8) | 6.3 (0.0-28.1) | 0.548 |
| LDL-4 (mg/dL) | 0.0 (0.0-13.9) | 0.0 (0.0-17.8) | 0.753 |
| LDL-5 (mg/dL) | 0.0 (0.0-3.4) | 0.0 (0.0-10.7) | 0.039* |
| LDL-6 (mg/dL) | 0.0 (0.0-0.0) | 0.0 (4.3) | 0.195 |
| LDL-7 (mg/dL) | 0.0 (0.0-8.5) | 0.0 (0.0-25.2) | 0.029* |
| Large LDL (mg/dL) | 49.4 (2.5-94.6) | 60.9 (4.5-108.3) | 0.040* |
| Small LDL (mg/dL) | 8.3 (0.0-53.7) | 10.1 (0.0-53.6) | 0.595 |
| LDL size (nm) | 267 (205-276) | 266 (201-275) | 0.336 |
| Phenotype A (%) | 24(43) | 11(41) | 0.996 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





