Submitted:
01 August 2023
Posted:
03 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
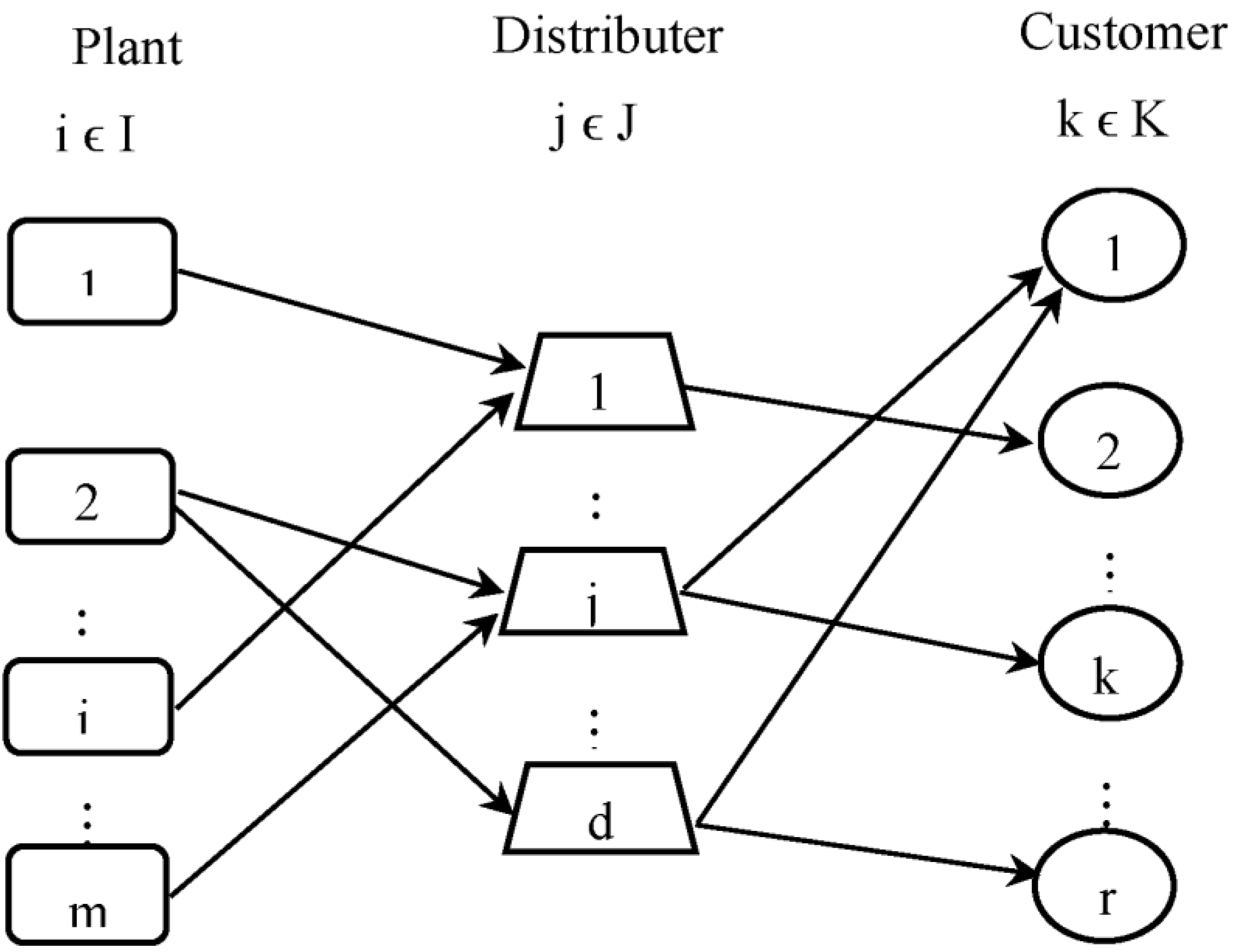
3. Problem Formulation
- Plants set,
- Distributors set,
- Retailers set,
- Plant capacity
- DistributorStorage capacity
- Retailer demand
- Transported units in 1st stage
- Transported units in 2nd stage
- Binary (specifies whether the units are transported in 1st stage)
- Binary (specifies whether the units are transported in 2nd stage)
- Binary (specifies whether a new distributor is open)
- Unit transportation cost in 1st stage
- Unit transportation cost in 2nd stage
- Fixed cost of transportation in 1st stage
- Fixed cost of transportation in 2nd stage
- Fixed opening cost for a new distributor
4. Computational Study
4.1. Numerical Simulation
4.2. Results and Discussion
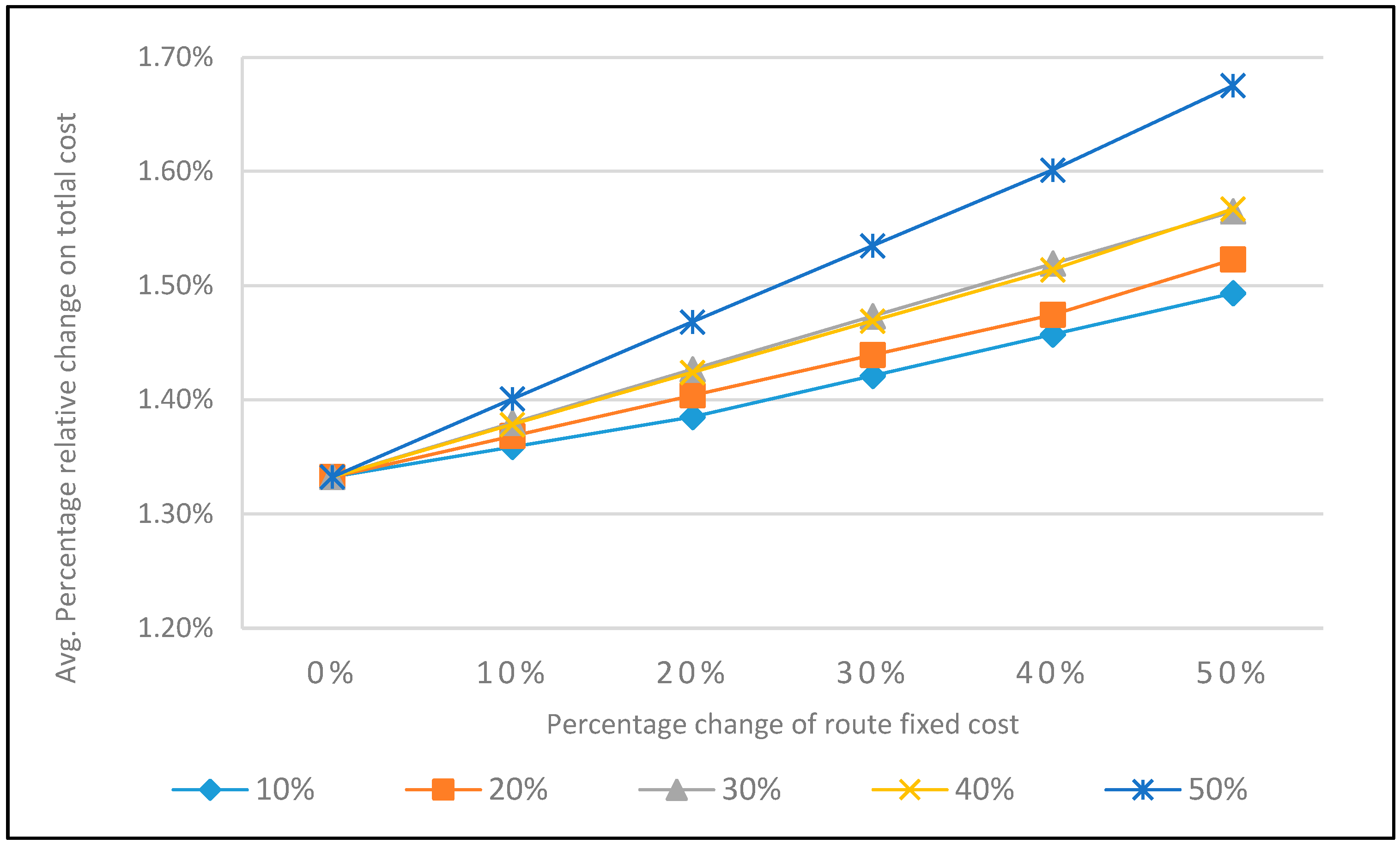
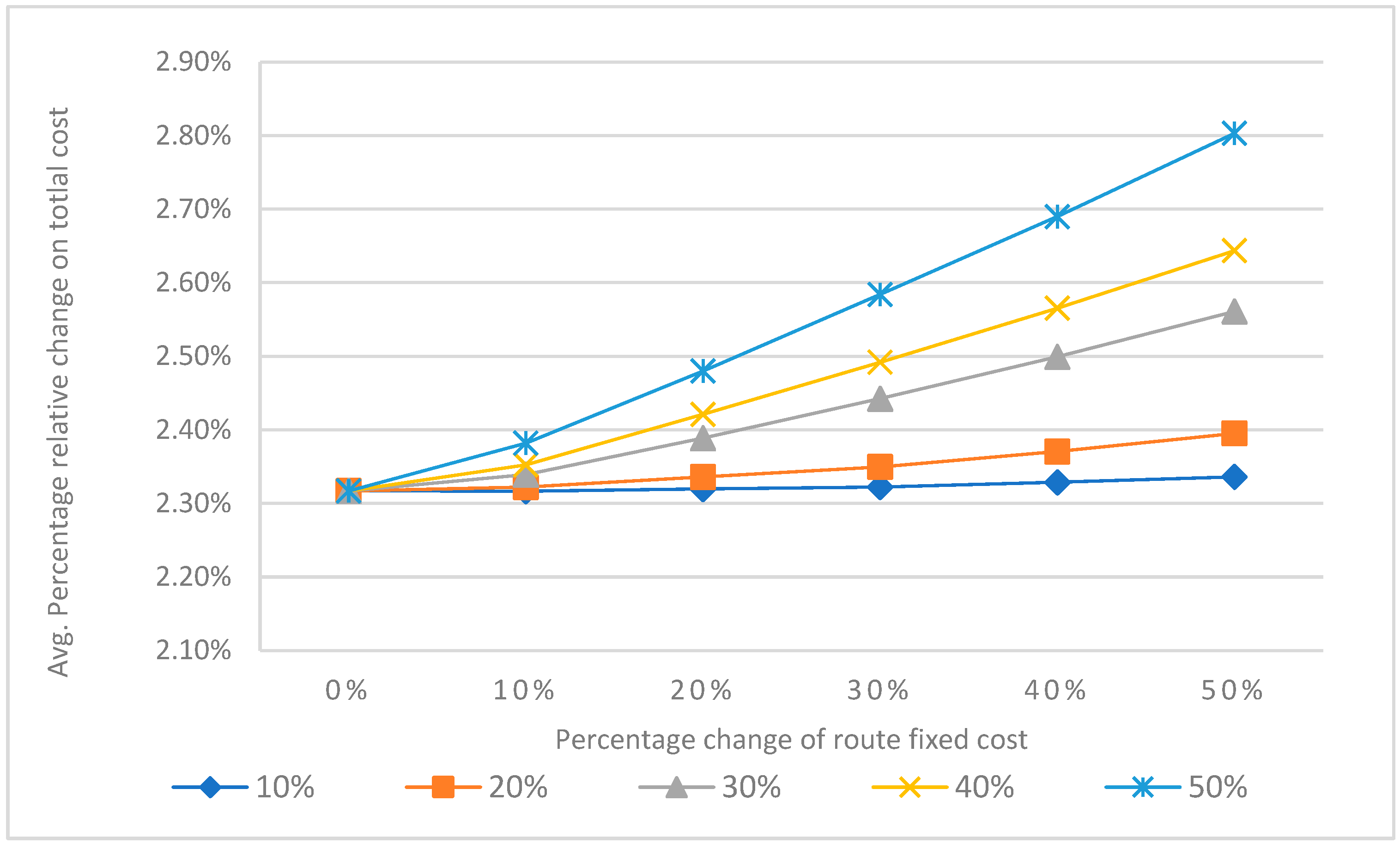
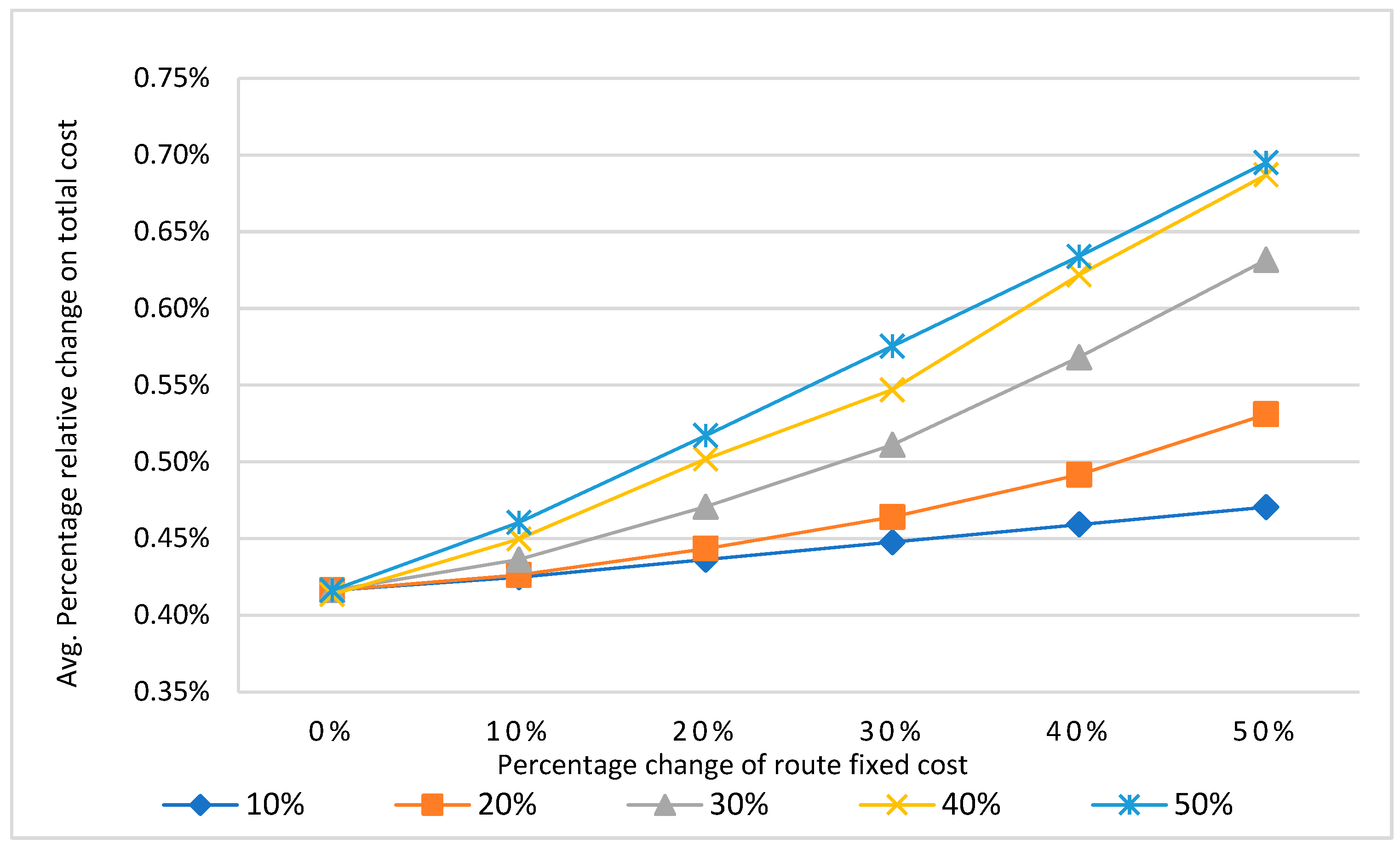
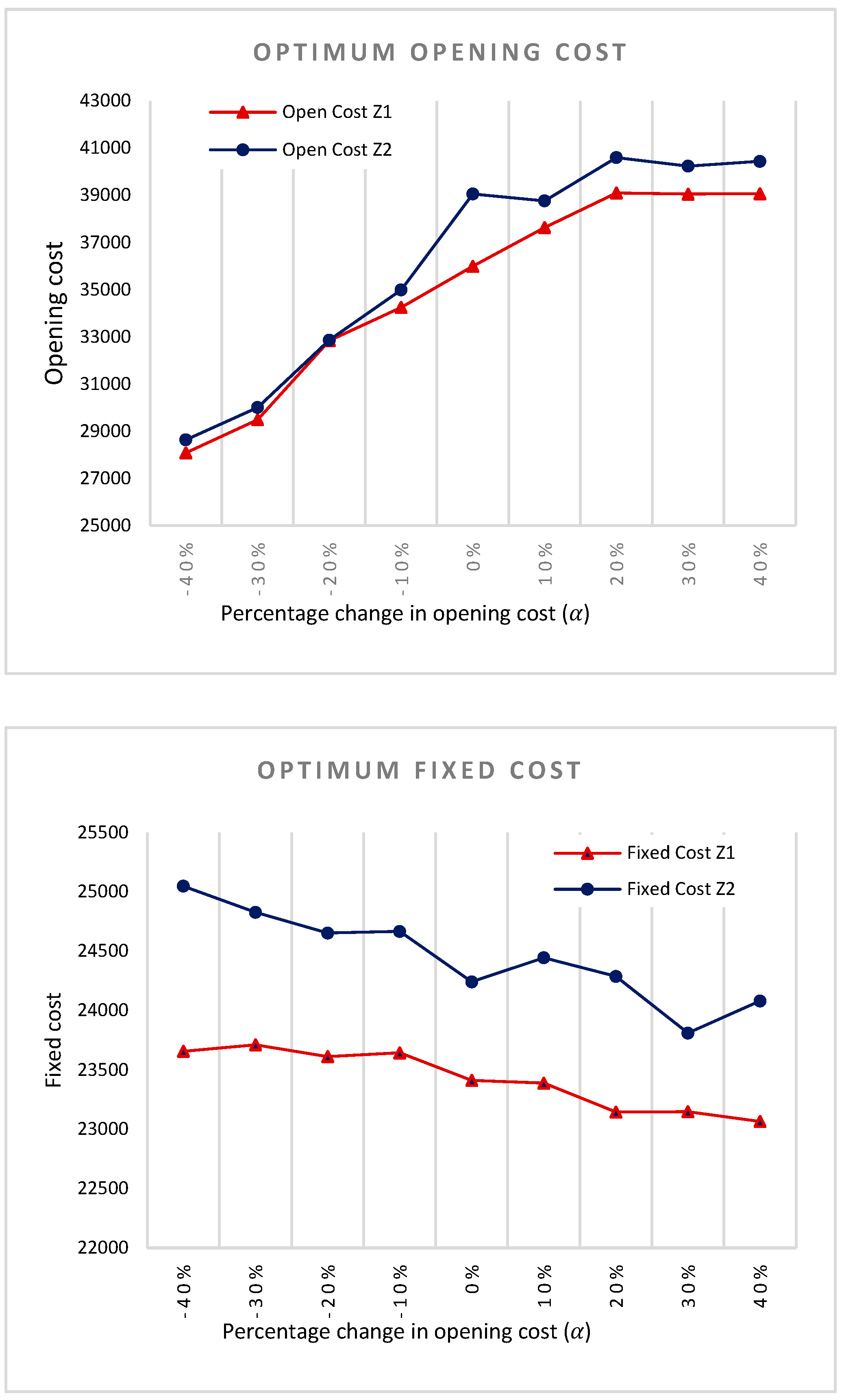
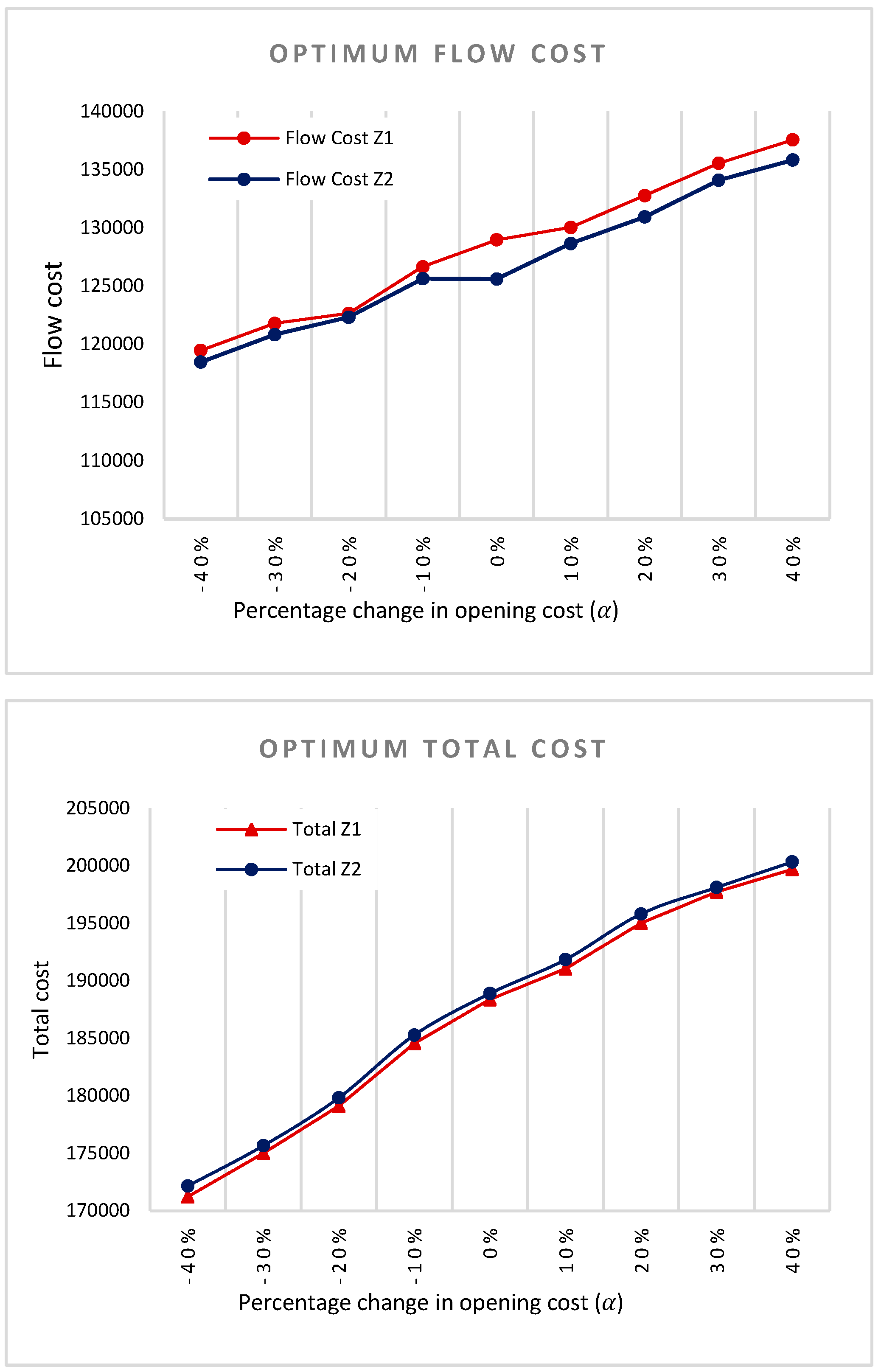
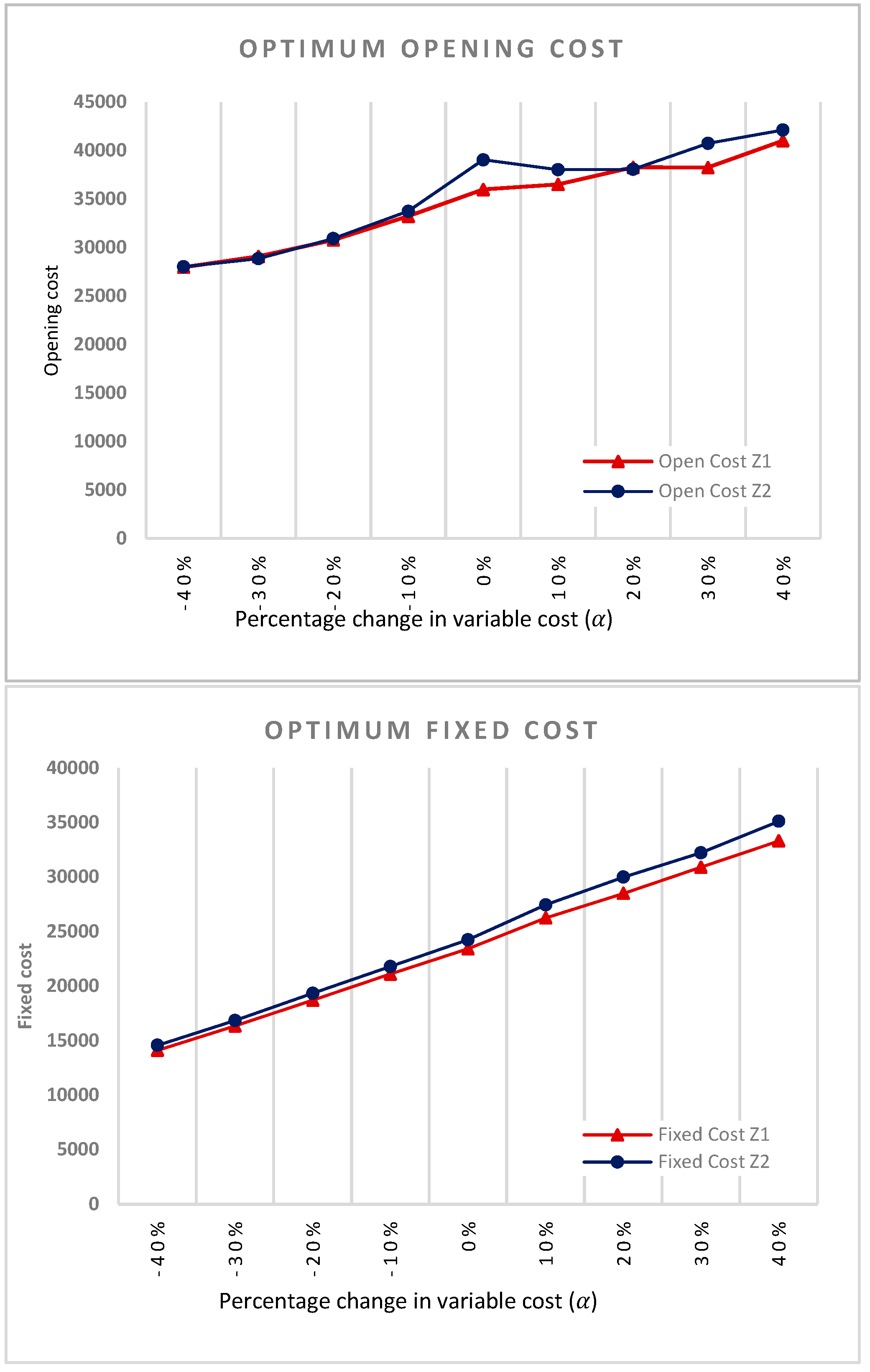
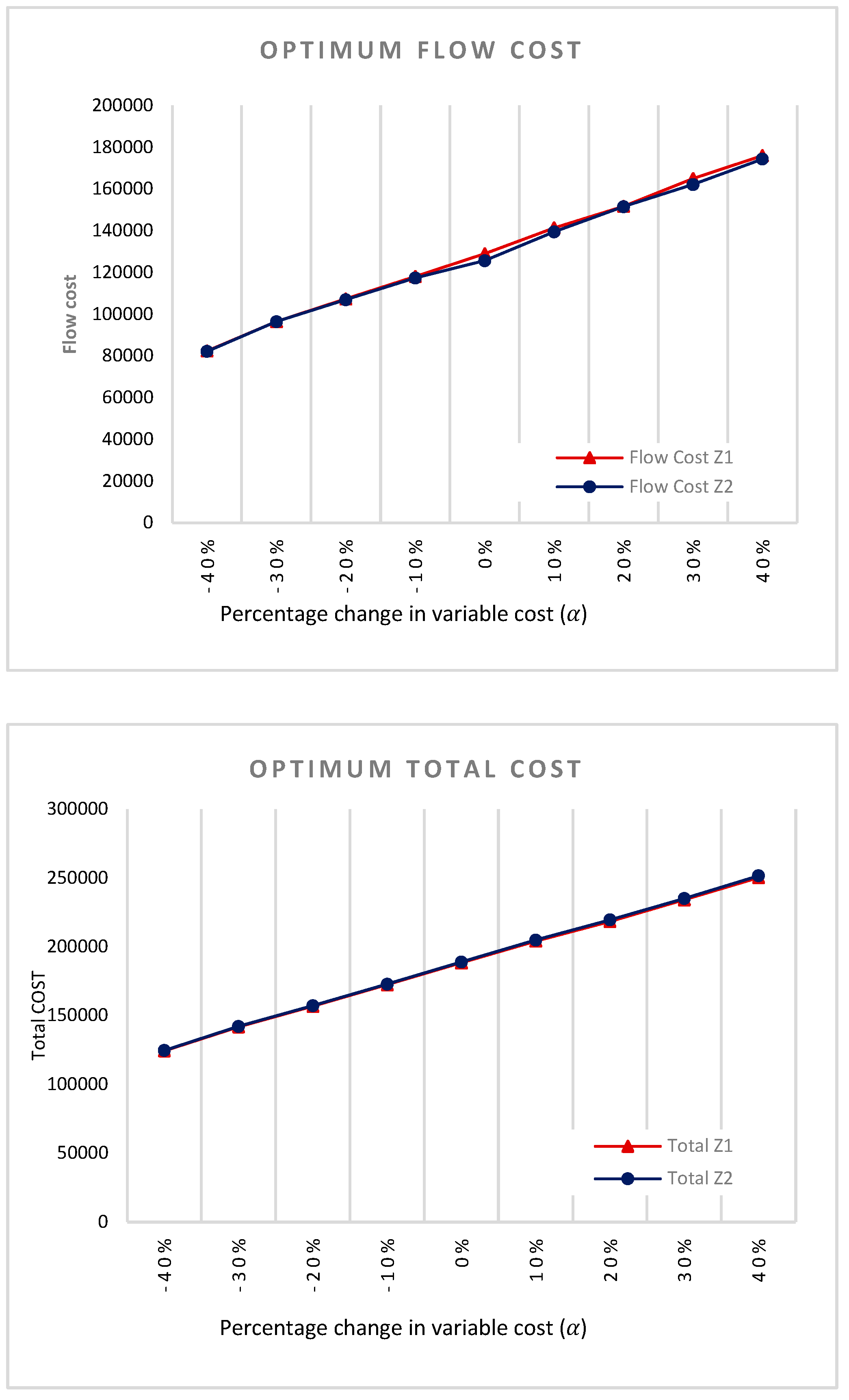
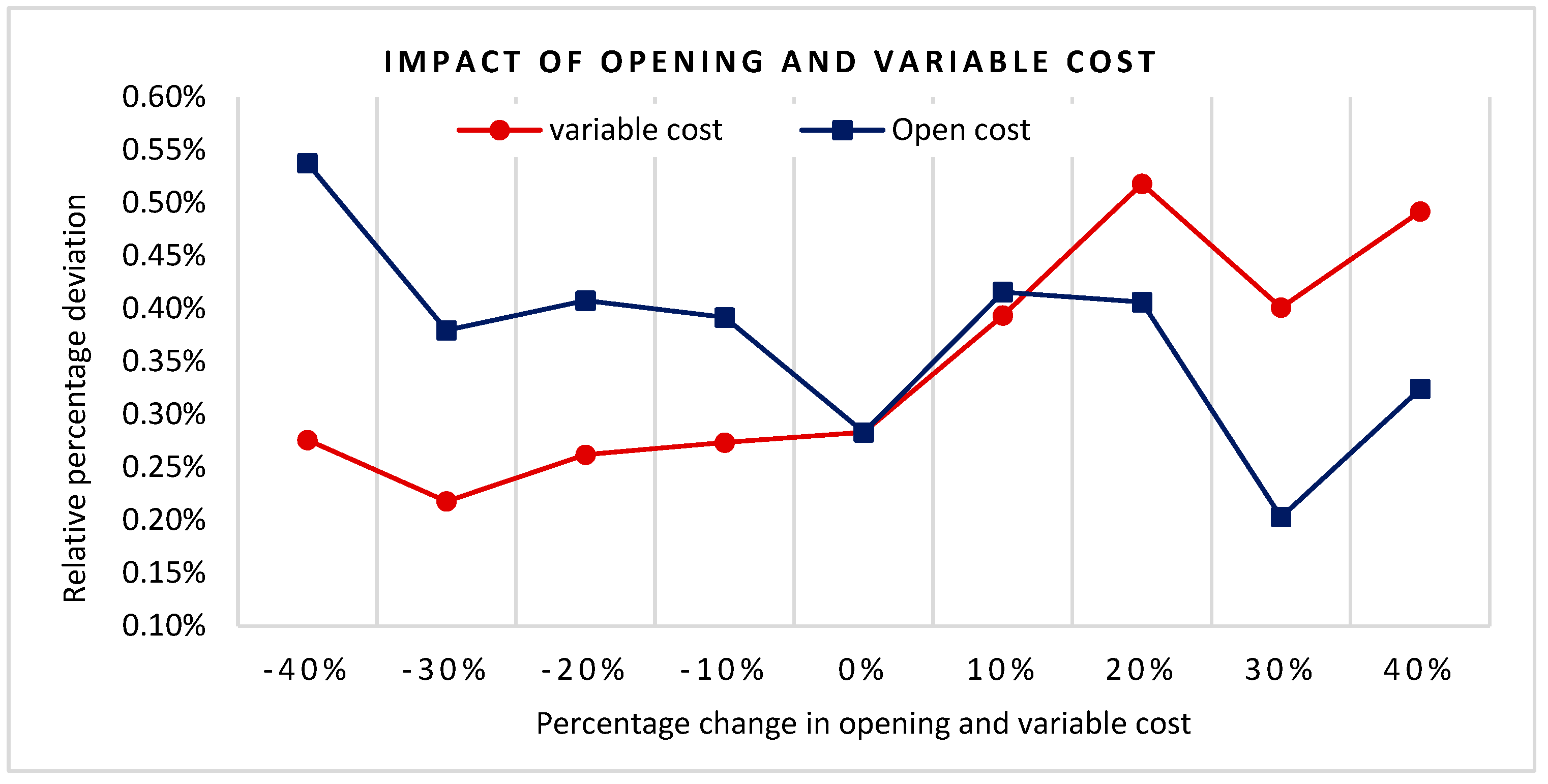
5. Sensitivity Analysis
5.1. Opening Costs
5.2. Variable Costs
5.3. Discussion
6. Conclusions and Future Work
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
Appendix B
References
- M. M. Lotfi and R. Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, “A genetic algorithm using priority-based encoding with new operators for fixed charge transportation problems,” Applied Soft Computing Journal, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 2711–2726, 2013. [CrossRef]
- V. Adlakha, K. Kowalski, R. R. Vemuganti, and B. Lev, “More-for-less algorithm for fixed-charge transportation problems,” Omega, vol. 35, no. 1, pp. 116–127, 2007. [CrossRef]
- K. Kowalski, B. Lev, W. Shen, and Y. Tu, “A fast and simple branching algorithm for solving small scale fixed-charge transportation problem,” Operations Research Perspectives, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1–5, 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Molla-Alizadeh-Zavardehi, M. Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, and R. Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, “Solving a capacitated fixed-charge transportation problem by artificial immune and genetic algorithms with a Prufer number representation,” Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 38, pp. 10462–10474, Aug. 2011. [CrossRef]
- V. V. Panicker, R. Vanga, and R. Sridharan, “Ant colony optimisation algorithm for distribution-allocation problem in a two-stage supply chain with a fixed transportation charge,” International Journal of Production Research, vol. 51, no. 3, pp. 698–717, Feb. 2013. [CrossRef]
- J. Hong, A. Diabat, V. V. Panicker, and S. Rajagopalan, “A two-stage supply chain problem with fixed costs: An ant colony optimization approach,” International Journal of Production Economics, vol. 204, no. January, pp. 214–226, 2018. [CrossRef]
- K. A. A. D. Raj and C. Rajendran, “Fast heuristic algorithms to solve a single-stage Fixed-Charge Transportation Problem,” International Journal of Operational Research, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 304–329, 2009. [CrossRef]
- K. Antony Arokia Durai Raj and C. Rajendran, “A genetic algorithm for solving the fixed-charge transportation model: Two-stage problem,” Computers and Operations Research, vol. 39, no. 9, pp. 2016–2032, 2012. [CrossRef]
- N. Jawahar, A. Gunasekaran, and N. Balaji, “A simulated annealing algorithm to the multi-period fixed charge distribution problem associated with backorder and inventory,” International Journal of Production Research, vol. 50, no. 9, pp. 2533–2554, 2012. [CrossRef]
- S. Molla-Alizadeh-Zavardehi, M. Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, and R. Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, “Solving a capacitated fixed-charge transportation problem by artificial immune and genetic algorithms with a Prufer number representation,” Expert Syst. Appl., vol. 38, pp. 10462–10474, Aug. 2011. [CrossRef]
- M. Yaghini, M. Momeni, and M. Sarmadi, “A Simplex-based simulated annealing algorithm for node-arc capacitated multicommodity network design,” Applied Soft Computing Journal, vol. 12, no. 9, pp. 2997–3003, Sep. 2012. [CrossRef]
- M. Dorigo, S. Member, and L. M. Gambardella, “Ant Colony System : A Cooperative Learning Approach to the Traveling Salesman Problem,” vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 53–66, 1997.
- N. Jawahar and A. N. Balaji, “A genetic algorithm for the two-stage supply chain distribution problem associated with a fixed charge,” European Journal of Operational Research, vol. 194, no. 2, pp. 496–537, Apr. 2009. [CrossRef]
- G. Editorial Marco Dorigo, G. Di Caro, and T. Stützle, “Special Issue on Ant Algorithms,” 1999.
- M. Sanei, A. Mahmoodirad, S. Niroomand, A. Jamalian, and S. Gelareh, “Step fixed-charge solid transportation problem: a Lagrangian relaxation heuristic approach,” Computational and Applied Mathematics, vol. 36, no. 3, pp. 1217–1237, 2017. [CrossRef]
- M. M. Lotfi and R. Tavakkoli-Moghaddam, “A genetic algorithm using priority-based encoding with new operators for fixed charge transportation problems,” Applied Soft Computing Journal, vol. 13, no. 5, pp. 2711–2726, 2013. [CrossRef]
- J. Shen and K. Zhu, “An uncertain two-echelon fixed charge transportation problem,” Soft Computing, vol. 24, no. 5, pp. 3529–3541, 2020. [CrossRef]
- K. Kowalski, B. Lev, W. Shen, and Y. Tu, “A fast and simple branching algorithm for solving small scale fixed-charge transportation problem,” Operations Research Perspectives, vol. 1, no. 1, pp. 1–5, 2014. [CrossRef]
- S. Sadeghi-Moghaddam, M. Hajiaghaei-Keshteli, and M. Mahmoodjanloo, “New approaches in metaheuristics to solve the fixed charge transportation problem in a fuzzy environment,” Neural Computing and Applications, vol. 31, pp. 477–497, 2019. [CrossRef]
- V. V. Panicker and I. V. Sarin, “Multi-product multi-period fixed charge transportation problem: An ant colony optimization approach,” IFAC-PapersOnLine, vol. 52, no. 13, pp. 1937–1942, 2019. [CrossRef]
- J. Wang, X. Wang, and M. Yu, “Multi-Period Multi-Product Supply Chain Network Design in the Competitive Environment,” Mathematical Problems in Engineering, vol. 2020, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Mostafa and R. Elshaer, “New Ant Colony Optimization Algorithms for Designing Two-Stage Supply Chain with Fixed Costs,” Journal of Advanced Manufacturing Systems, 2022. [CrossRef]
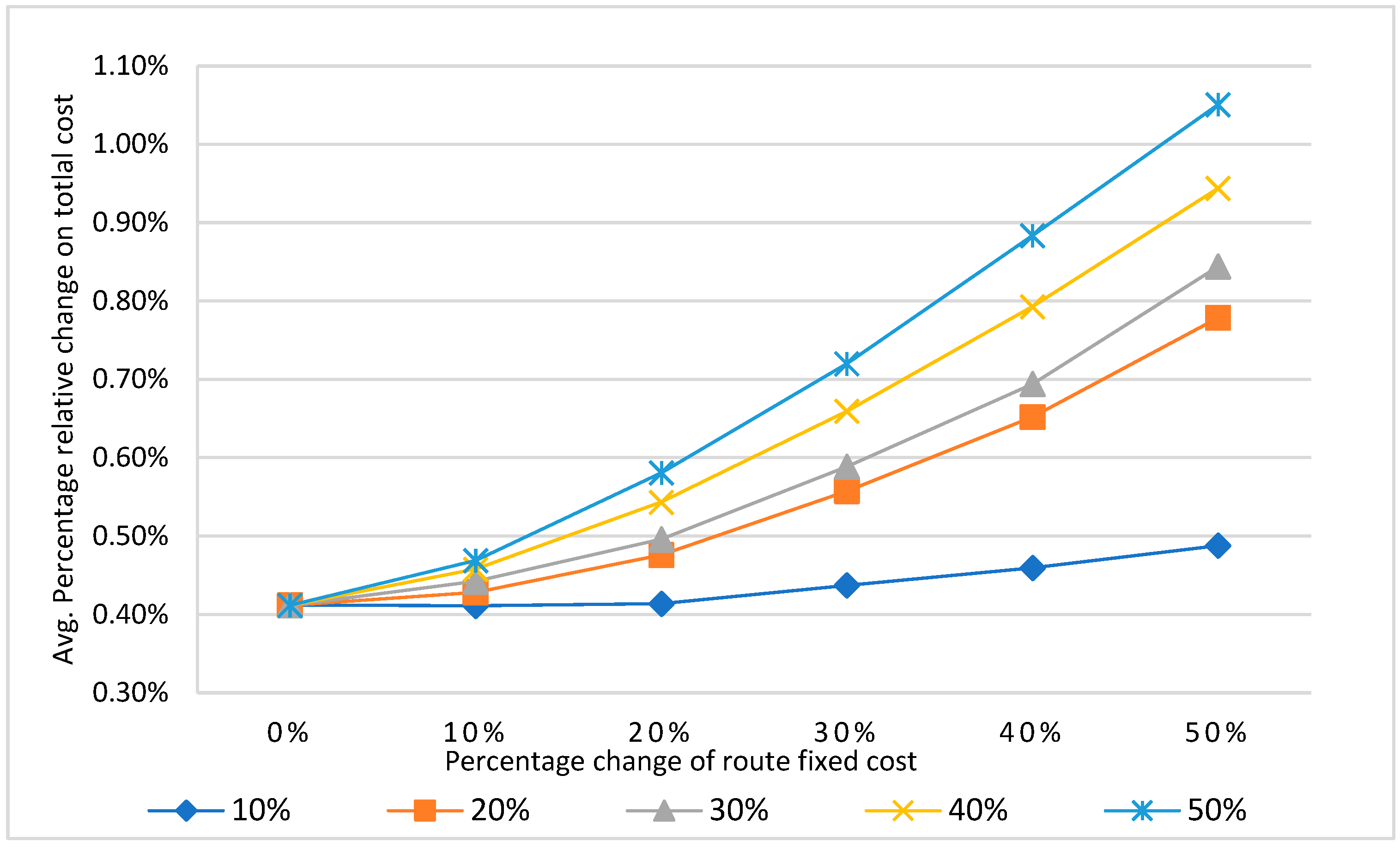
| Problem Groups | Number of Instances | Number of Plants |
Number of Distributors |
Number of Retailers |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| G_1 | 260 | 2 | 5 | 10 |
| G_2 | 260 | 4 | 8 | 15 |
| G_3 G_4 |
260 260 |
6 10 |
10 20 |
20 30 |
| Fixed cost range | Variable cost range in 1st stage | Variable cost range in 2nd stage |
|---|---|---|
| (30 - 50) x Avg. variable cost | 10 - 30 | 10 - 50 |
| Parameter | Range | |
|---|---|---|
| Retailer demand | 50 | 500 |
| Opening cost of the distribution center. | ||
| Fixed cost = 30 -50 * average variable cost | 30 | 50 |
| Variable cost = 10 -30 in stage 1 | 10 | 30 |
| Variable cost = 10 -50 in stage 2 | 10 | 50 |
| Parameter | Range | |
|---|---|---|
| Retailer demand | 50 | 500 |
| Opening cost of the distribution center. | ||
| Fixed cost = 30 -50 * average variable cost | 30 | 50 |
| Variable cost = 10 -30 in stage 1 | ||
| Variable cost = 10 -50 in stage 2 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





