1. Introduction
Scientist have been studied extensively motion profiles for several decades, since it has uncountable applications related to motion control, robotics, and commercial machinery, such as robot manipulators [
1,
2], conveyor belts, computer numerical control (CNC) machinery, 3D printers, and any system that needs to control movement based on electric motors [
3,
4,
5]. The motion profiles define not only the position of the motor shaft but also the velocity, acceleration, and the third derivative of position (jerk) along the path or entire movement [
6]. With constant movement phases, it is possible to generate smooth trajectories that reduce mechanical wear and aggressive current peaks to improve movements’ precision [
7,
8]. So, motion profiles are focused on obtaining a function of time, which returns at each instant the position that the mechanical system must follow [
9]. Constantly it is sought to have at least continuous acceleration [
10], since discontinuities in acceleration, such as in a trapezoidal profile, can cause the jerk to be too large and residual vibrations are generated [
11], which, in addition to affecting the precision of the movement, also degrade valuable life of the mechanical system [
12]. On the other hand, in mechatronics systems, motion profiles are applied to execute point-to-point movements [
13]. For instance, to move from an initial point to a final point, the trajectory must be smooth, according to the cinematic magnitude restrictions of the system, with which an exceeding of the speed, acceleration, or jerk limits supported by the motor is avoided [
14].
Another aspect to consider besides the motion profiles is the control algorithm , which is designed to keep the tracking error as low as possible, guaranteeing efficiency in the execution of the movement [
15]. The most commonly used control technique is the classical Proportional-Integral-Derivative (PID) and PD controllers as observed in [
16]. However, technological changes demand new control strategies that present a better response than traditional controllers. For example, in [
17], the implementation of a controller based on fuzzy logic for a robot manipulator shows better performance in terms of robustness and trajectory following; in [
18] an adaptive controller with neural networks is used, which improves the precision of the movement at the cost of greater computational demands.
In recent years, several works have been proposed that allow smooth movements to be executed using functions of the polynomial, exponential, trigonometric type, or a combination of these [
19,
20,
21,
22]. The study of the motion profiles has shown that, depending on the path implemented, it is possible to minimize execution times, reduce vibrations by minimizing the jerk (which translates into less wear on the mechanical structure), as well as reduce energy consumption [
23]. Fang Y. et al. use a 15-segment s-curve trajectory formed by pieces of sigmoid functions, which allows for obtaining successive continuous derivatives [
24]. This results in a trajectory with vibration and reduced tracking error verified experimentally in a robotic arm. Similarly, Wu et al. propose a 15-segment trajectory with a shorter execution time. It is made up of pieces of functions of the trigonometric type, with constant motion phases [
1]. Alpers employs a 7-segment motion profile based on chunks of polynomial functions [
25]. However, discontinuities in successive derivatives can cause unwanted vibrations; [
10] proposes an improvement with a 15-segment path, in which the snap is a continuous piece-wise function; Due to the complexity of the expressions, the time required to calculate the trajectory is longer compared to classical profiles. Lee and Han use nth-order polynomial motion profiles to achieve fast motion and minimal vibration in an industrial robot [
12]; the motion controller is implemented on a 32-bit MCU. Jerk minimization has been achieved through the use of degree 7 polynomials, as shown by Wu and Zhang in [
4], which is implemented in a robot manipulator. Similarly, Boryga et al. use polynomials of degrees 5 to 9 to obtain phases of continuous motion [
3]. However, experimental results still need to be presented. For their part, Wang H. et al. propose a methodology for using degree 4 polynomials in an industrial robot [
26]. On the other hand, the reduction of energy consumption has been analyzed in point-to-point movements using trapezoidal and cycloid profiles [
2], as well as trajectories based on Chebyshev polynomials [
15]. A review and classification on energy-saving optimization strategies for robotic and automatic systems is presented in [
27], being the software approach based on the motion planning an effective and economical technique easy to implement on existing system [
28]. Montalvo et al. conducted a comparative analysis of the energy consumption of the trapezoidal and parabolic motion profiles on a Field-Programmable Gate Array (FPGA)-based motion control system [
29]. A similar study was conducted by Carabani G. and Vidoni R. adding higher-order polynomial and modified s-curve profiles [
30], however, Hosseini, S., and Hahn obtained better energy saving with third-degree polynomials than with higher degree trajectories [
31]. Other authors have developed a hybrid approach. For instance, Nshama, E. W. seeks, in addition to decreasing execution times, to reduce energy consumption in industrial feed drive systems [
32] and Halinga M. S. with the same hybrid approach proposed a modified s-curve trajectory introducing harmonic functions into the constant jerk phases [
33].
This work’s motivation is to design a motion controller for precise tracking to reduce energy consumption through appropriate motion profiles; A trajectory generator and a motion controller were embedded in a 32-bit microcontroller with ARM architecture to calculate the trajectories in real-time.
The main contributions of this paper are:
An analysis of 3 smooth trajectories in a point-to-point motion control system to decrease energy consumption in DC motors.
A novel approach for designing a motion control system from the embedded system selection to the motion control implementation.
Development of a software-based strategy that can be implemented in any microcontroller to control a linear platform with a motion controller using a sampling time of 0.001 s.
The rest of this paper is organized as follows: We presented and explain the velocity profiles in
Section 2, next, we describe the materials we used and the methodology we followed for conducting the experiments in
Section 3; Also, we discuss relevant implementation guidelines in
Section 4. We present the experimental results in
Section 5. Finally, we present our conclusions in
Section 6 and the relevant references.
3. Materials and methods
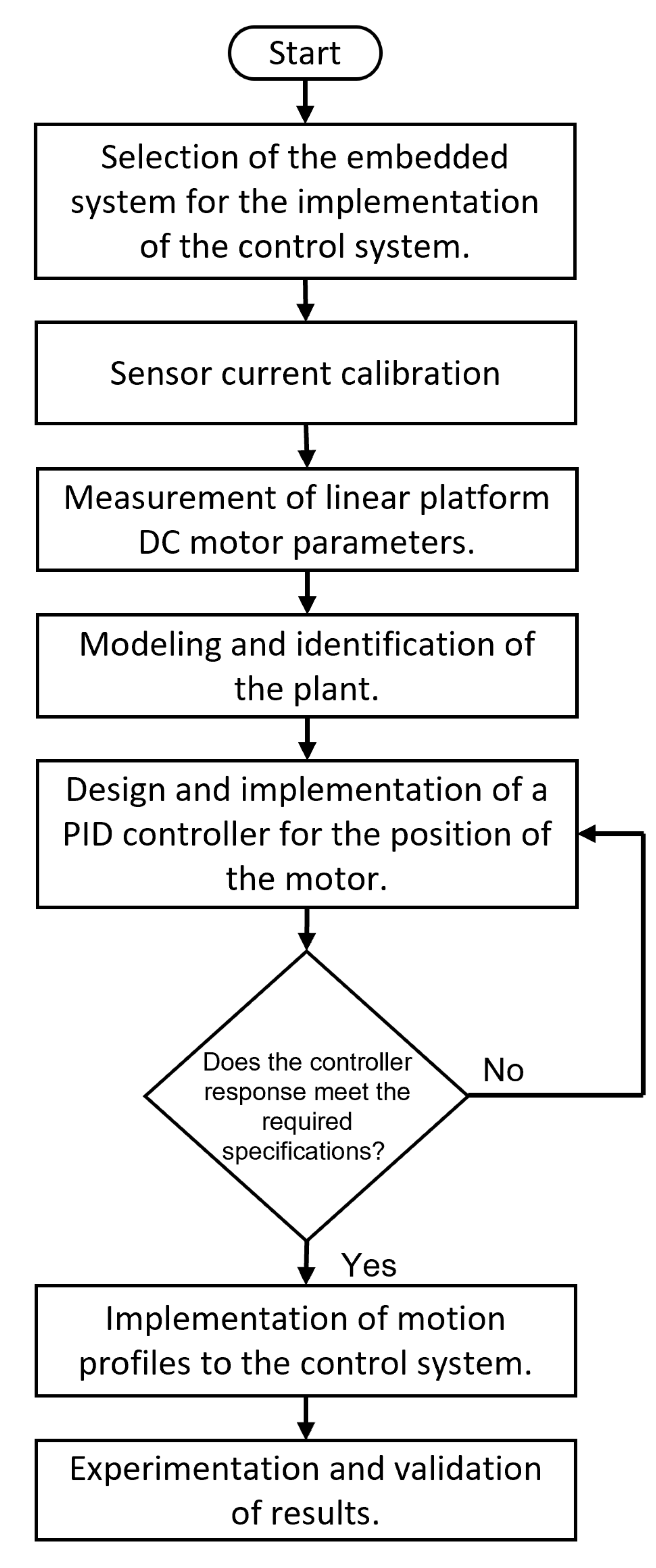
An approach to selecting the embedded system, sensors calibration, plant identification, and motion controller design is presented in
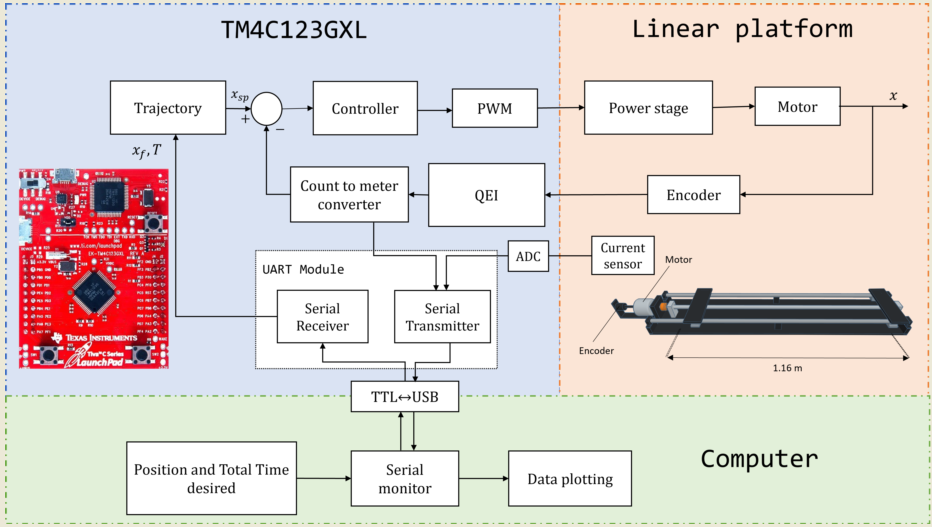
Figure 4. The first step is selecting the most suitable embedded system according to the design constraints. The proper selection of embedded systems is of utmost importance since it is crucial to understand the capabilities of these devices to determine if they are suitable to solve a given problem. Thus, it is essential to analyze cost-benefit trade-offs during the selection process of an embedded system to properly balance the costs associated with its implementation and the benefits achieved.
Once the designer selects an embedded system, the next step is obtaining the parameters for the motor voltage, current, and kinematic magnitudes. This is crucial to enforce that the platform operates within its limits. In the case of having information on these parameters in advance, they can be used directly. However, such values are missing in some cases; in that cases, designers require determining them experimentally.
The third step involves the designer deriving a mathematical model of the DC motor. This step, known as identification, involves obtaining a transfer function through experimentation to determine the system’s dynamic response. To reach this goal, designers must follow a rigorous and methodological approach, comparing motor input and output data, such as applied voltage and resulting angular velocity converted in linear position over time, then use this data to determine the motor’s mathematical model. When designers assess the closed-loop model of the DC motor, they can design a controller to ensure the system’s stability. This controller, which is usually proportional in action, plays a crucial role in rejecting disturbances that may affect the proper behavior of the motor. The proportional action of the controller also allows errors to be corrected and deviations to be mitigated, which contributes to maintaining stability and improving the dynamic response of the plant.
Figure 5 shows a block diagram of the system used for the identification process. The input is the target position the DC motor should reach, denoted as
. On the other hand, the system’s output is the carriage’s real position, denoted by
. A control mechanism computes the control signal
. In this case, it is the voltage applied to the motor to get the carriage as close to the target position as possible.
The closed-loop transfer function of the block diagram in
Figure 5 is given by Equation (
24).
is the transfer function of a second-order system with the parameters presented in Equations (
25) and (
26).
According to modern control theory, when a step input is applied to a second-order system, the system response exhibits specific characteristics, such as rise time
and overshoot
, especially in the case of an overdamped system, where the damping coefficient is in the range
. To achieve this overdamped behavior, it is necessary to adjust the value of the proportional coefficient
to be large enough. The parameters to be calculated based on the transient response are the damping constant
, the undamped natural frequency
, and the damped natural frequency
, expressed in Equations (
27)–(
29).
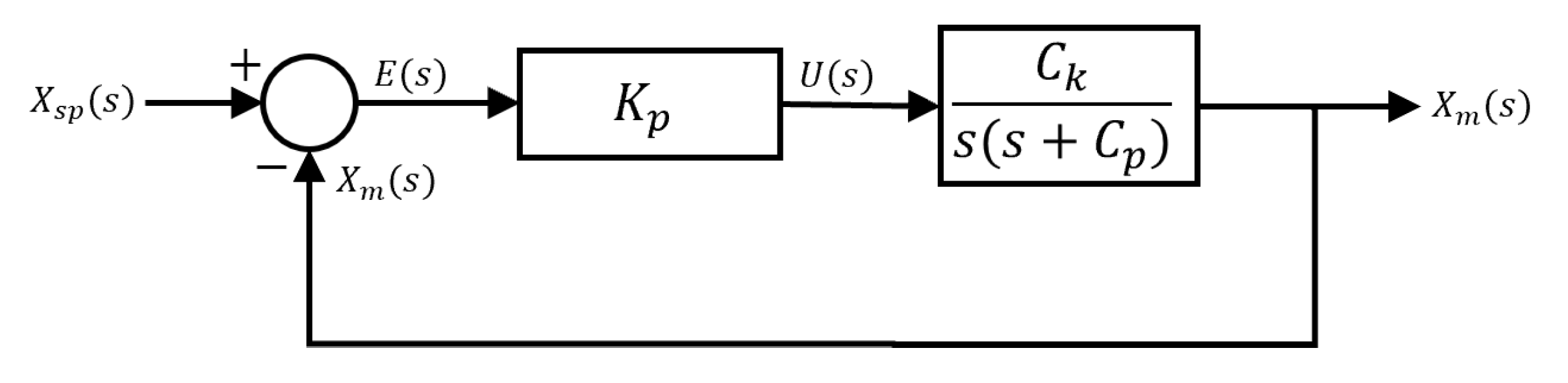
The fourth step consists of the design of the controller, a classic PID type controller shown in
Figure 6 is proposed to eliminate errors in steady state.
The controller parameters are obtained using the pole assignment method. This approach consists of selecting the desired poles of the closed-loop system and calculating the controller parameters so that these poles are located at the desired positions. By assigning the poles appropriately, a desired behavior of the system in terms of stability, response time, and damping can be achieved. The closed-loop transfer function of the system is determined from the controller parameters. This transfer function, represented by Equation (
30), describes the relationship between the system’s input and output in the frequency domain.
The controller gains are selected to place specific poles in the denominator of Equation (
30). The poles are calculated using the characteristic equation of a second-order system that meets the required design criteria, given in Equation (
31).
Adding a non-dominant pole at
to the Equation (
31) gives the Equation (
32).
For the response of the third-order system to approximate that of the desired second-order system, the non-dominant pole is located 10 times further away than the real part of the dominant poles in the standard form given by Equation (
31). From the equalization of the coefficients with the same power in
s of Equation (
32) and the denominator of Equation (
30), the Equations (
33), (
34) and (
35), with which the controller gains are calculated.
The proposed criteria for controller design are rise time and maximum overshoot. Once the controller meets the specifications, the previously described motion profiles are added to the control system. The function of the trajectory generator is to generate a series of values that specify the position that the motor must assume at each instant of time. Calculating the trajectory requires defining the magnitude of the displacement and the time to execute the movement. The last step consists of experimentation and validation of results, which is addressed in a later section.
4. Methodology of implementation
4.1. Selecting an Embedded System
Following the process described in
Figure 4, the
C series TM4C123 evaluation platform has been selected. This low-cost platform includes two TM4C123GH6PM high-performance 32-bit microcontrollers based on the ARM Cortex-M4F architecture. The choice of this embedded system is based on its essential capabilities for implementing the project, such as motion controller, path generation, and accurate current measurement through the 12-bit analog-to-digital converter (ADC). On the other hand, it has a dedicated module for reading the encoder, significantly simplifying the system configuration process, and making it robust for control applications. Another essential advantage of this microcontroller is its ability to operate in real-time with a sampling rate of
. This ensures that the entire system can respond quickly and accurately to the demands of the environment in which it is located, which is especially relevant for applications that require real-time interaction. In addition, it allows connection to a computer via serial protocol, which facilitates efficient data collection from the plant. This communication capacity is invaluable for monitoring and analyzing the results obtained during the operation of the embedded system. The main characteristics of this microcontroller are presented in
Appendix A.
4.2. Embedded Motion Controller Implementation
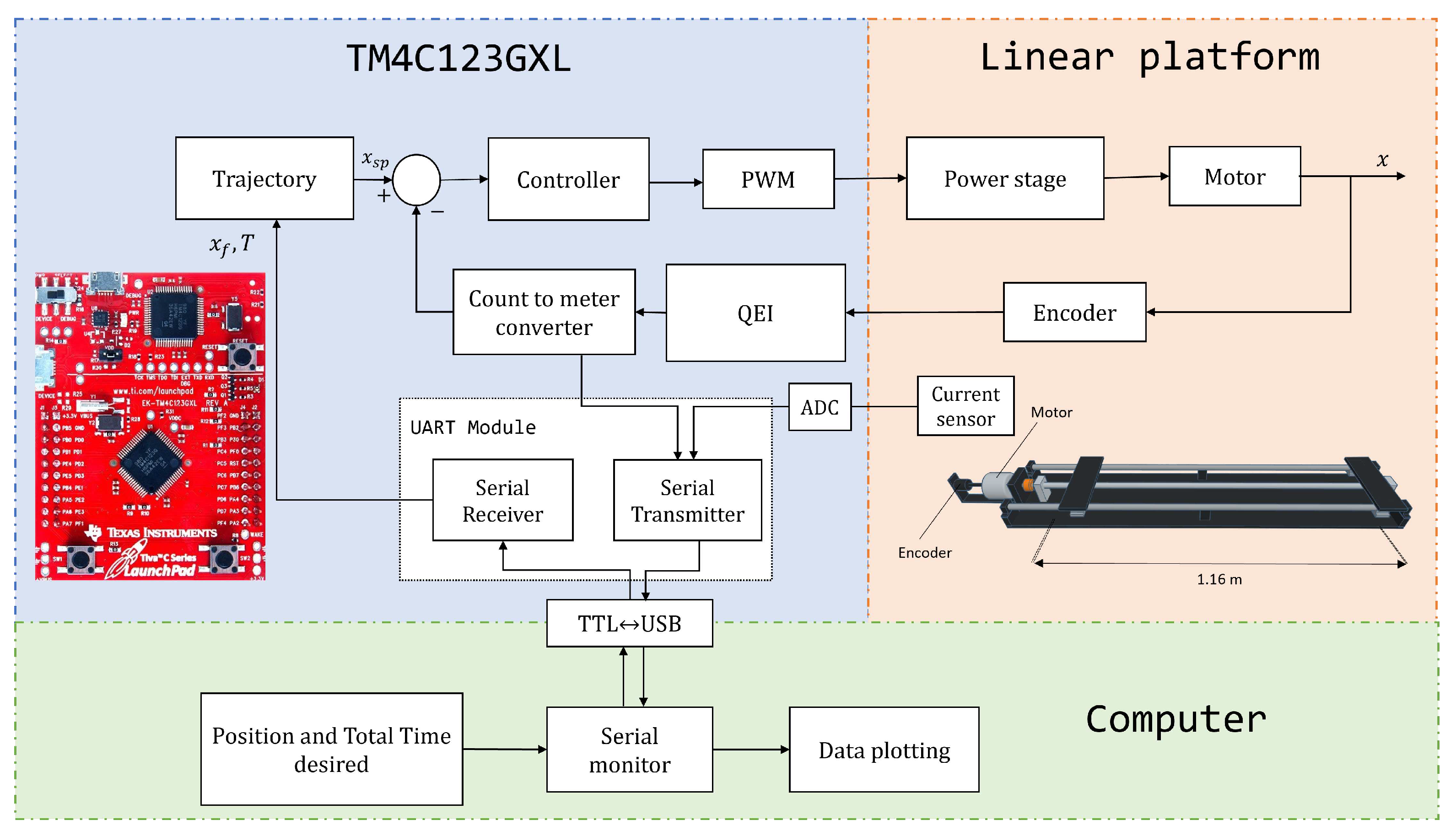
This section describes the implementation of the motion control system that has been made. In this system, a classic PID controller and a motion profile generator have been integrated into a microcontroller to control the position of the carriage of a linear platform. To allow configuration and adjustment of the motion profile parameters, serial communication is established between the microcontroller and a computer.
Figure 7 shows the general diagram of the blocks that comprise the proposed system.
The first block consists of the plant described in the last section. The second block is the embedded system. In this stage, the microcontroller schedules sensing tasks for measuring both the current and the position of the encoder, which allows for obtaining information on the state of the motor. In addition, the microcontroller computes the motion profile using the received data to determine the carriage’s speed, acceleration, and displacement. Once the motion profile has been calculated, PID controller adjusts the trajectory using the position information. The control signal is applied to the motor driver, the HW-039 BTS7960, via a Pulse-Width-Modulation (PWM) signal.
The third component of the system is a computer, which is linked to the ARM microcontroller using the PL2303HX TTL-USB converter. During the tests, the computer sends data to the embedded system regarding the required displacement and the total time for the execution of the movement. These data define the parameters of the movement profile and the duration of the operation. On the other hand, the microcontroller sends data to the computer about the current position of the motor, the computed control signal, and the current consumed by the motor. These data allow real-time monitoring and visualization of the status and performance of the control system.
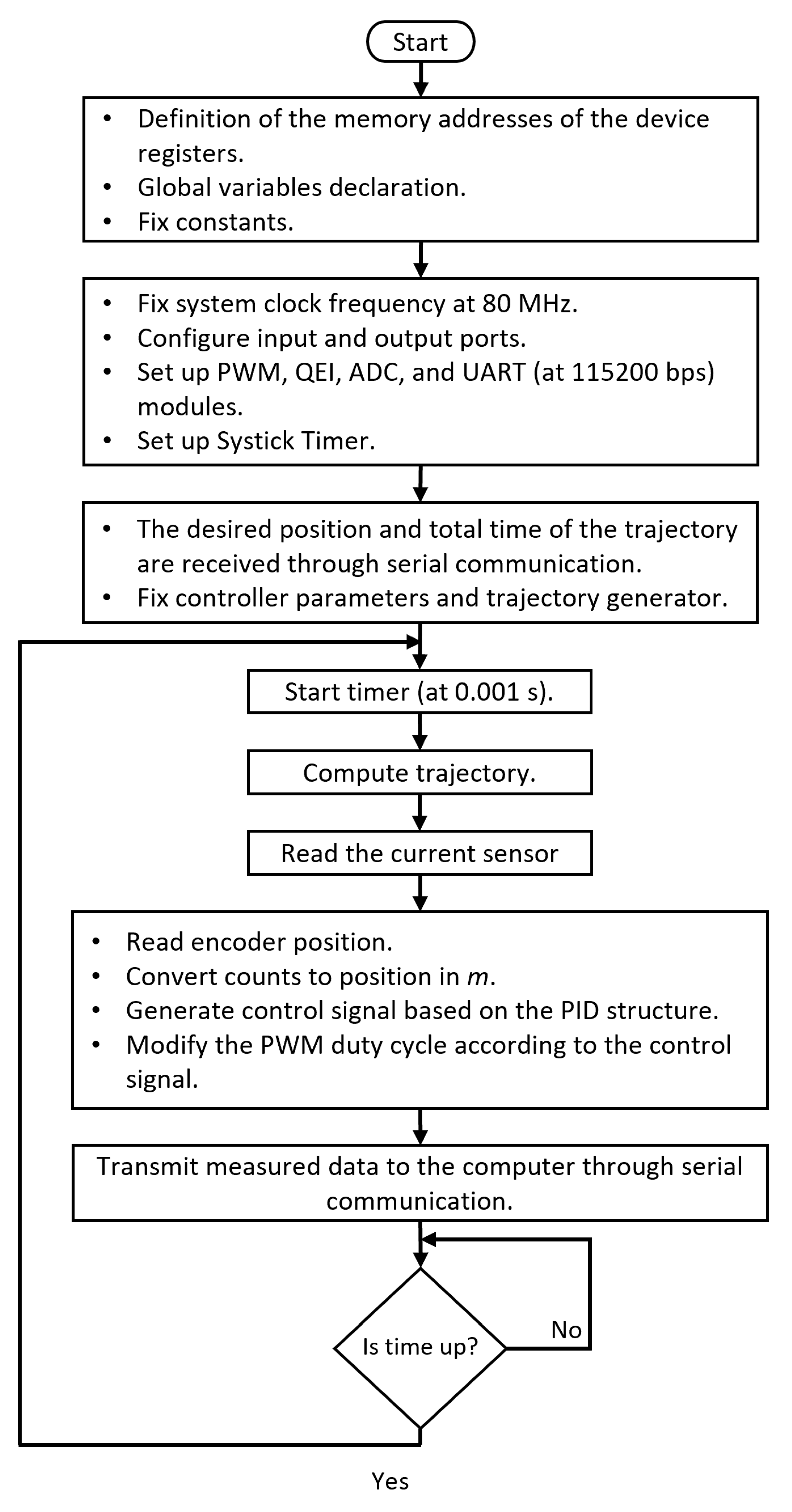
The direct manipulation of the microcontroller registers provides greater control and optimization of the system, adapting it to the specific needs of this project, one of which is the sampling time of the entire proposed system. The flowchart in
Figure 8 shows the algorithm used to program the embedded system.
4.3. Initial definitions of the microcontroller memory addresses
In the initial stage of the programming process, the memory addresses of the registers related to the device’s configuration are defined. These registers are essential to establish and control the behavior of the different components of the microcontroller. In addition to memory addresses, global variables, and constant values are established. Global variables can be accessed and used anywhere in the program, making exchanging information between code sections easy. On the other hand, constant values are those that do not change throughout the execution of the program and are used to establish parameters or static configurations.
4.4. Initial configuration
In this subsection, the configuration of the necessary registers for the correct operation of the microcontroller is carried out. By default, the microcontroller operates at a frequency of 16 MHz, but by appropriately modifying the corresponding registers, it is possible to reach a maximum operating frequency of 80 MHz. Once the operating frequency has been configured, proceed to the activation and configuration of input/output ports. These ports allow communication and connection with other external devices, facilitating the interaction of the microcontroller with its environment. In addition to the input/output ports, other necessary peripheral modules must be initialized. For example, the Quadrature Encoder Interface (QEI) module is configured to allow quadrature reading of the encoder, which provides greater accuracy in motor position measurement. In addition, the PWM module is configured to generate two PWM signals at a frequency of 5 kHz, allowing efficient control of the speed and power supplied to the motor. In the same way, the initialization of the ADC module is performed, which enables the conversion of analog signals to digital for further processing. On the other hand, the Universal Asynchronous Receivers/Transmitter (UART) module is configured to operate at a speed of 115200 baud, which facilitates serial communication with other devices. The last module to configure is the Systick Timer. This 24-bit timer is loaded with RELOAD_VALUE, a value given by the Equation (
36) to generate an interrupt every
t seconds, which allows ensuring a time-fixed sampling. However, before starting the timer count,
and
T are set according to the information received by serial communication.
Within the program’s main loop, a series of tasks are carried out periodically every , corresponding to the system sampling time. First, the trajectory calculation is performed, which involves determining the desired position or the path that the system should follow. Next, the current is measured, an important parameter to evaluate the performance and load of the motor. This measurement is carried out through an ACS712 model current sensor. Subsequently, the control algorithm is executed, which uses the trajectory information to generate the appropriate control signal. The control algorithm is based on a discrete PID controller. Finally, the measured data is sent to the computer using the UART module.
4.5. Implementation of motion profiles
For the implementation of the velocity profiles, in each iteration,
k, a point of the trajectory, is calculated for the current time instant
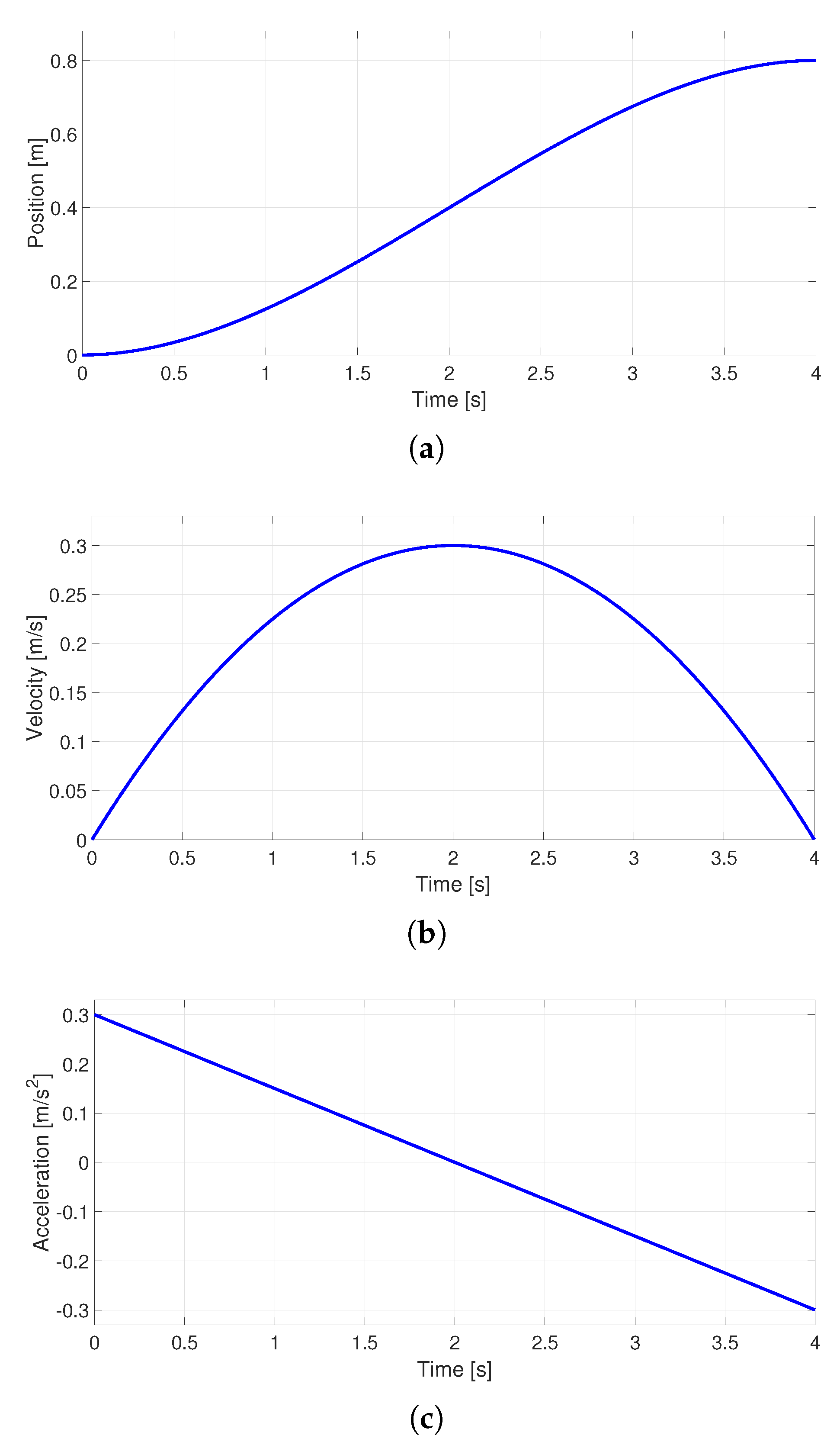
. In the case of the parabolic profile, the trajectory is calculated in the microcontroller with Equation (
37), which is a simplification of Equation (
4) in which
is considered and
.
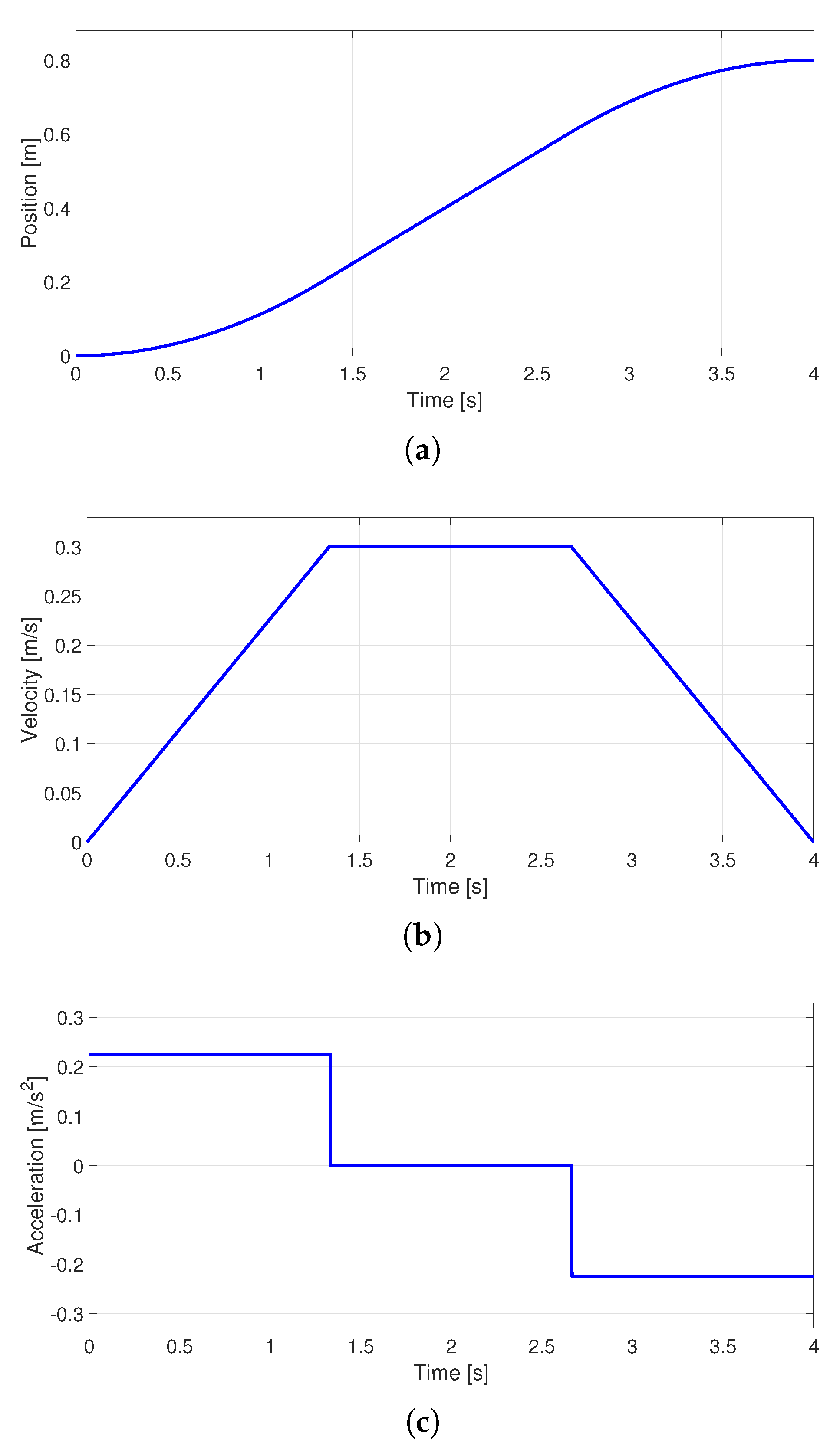
Regarding the trapezoidal profile, Equation (
10) is reduced to Equation (
38) considering the initial position and time equal to 0.
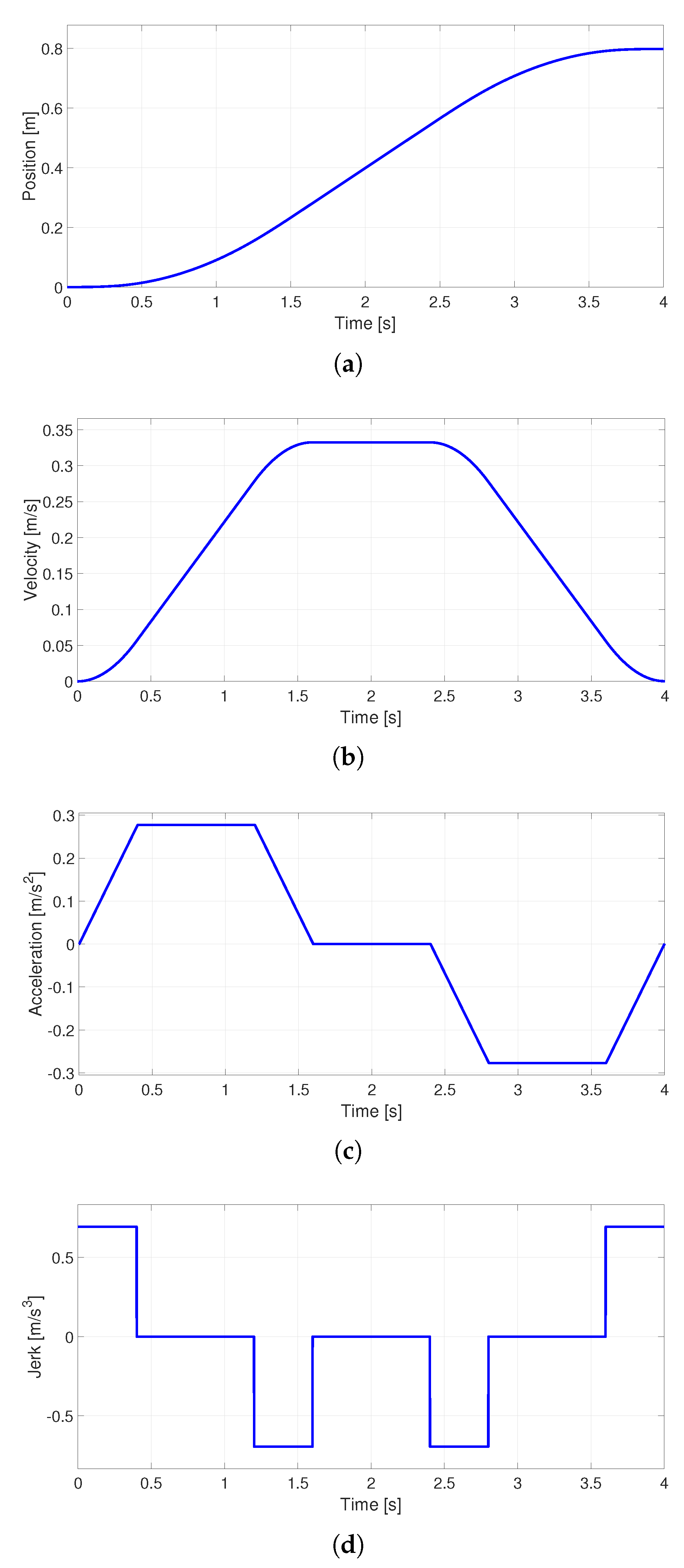
The s-curve velocity profile is calculated with the Equations (
39), (
40) and (
41), obtained after the discretization of the Equations (
21), (
22) and (
23) by Euler’s method backward.
Where k is the sample number, whereas , , and are the current jerk, acceleration, velocity and position, respectively.
4.6. Implementation of the control algorithm
The control algorithm starts with the encoder reading. The value is converted to meters by multiplying the count by
. The error is calculated as the deviation between the position in meters and the actual set point given by the trajectory generator. The control signal
is generated with Equations (
43) and (
42), obtained from the discretization of the PID controller by Euler’s backward method.
The value obtained by the control signal represents a voltage in the
V range, which is the DC motor’s operating range. The control signal is scaled to the microcontroller’s operating range
V by modifying the duty cycle of the PWM signal, given by Equation (
44).
Where PWM_LOAD is the value to load to the configuration register to generate a 5 kHz PWM signal, is the maximum voltage (in this case 24 V), is the control signal and PWM_CMP is the value to load in the register that modifies the duty cycle.
4.7. Timer ended
After sending the measurements to the computer, wait for the timer to expire. To do this, the account status indicator is checked. When it reaches zero, the counter resets, and the loop starts again.
6. Conclusions
This paper presented a methodology that allows designing and implementing open architecture motion controllers, from selecting the embedded system to implementing it in a linear platform composed of a direct current motor coupled to an endless screw to measure the energy consumption of trajectories. The control algorithm is based on a classic PID controller whose reference signal is given by a motion profile generator. The selected embedded system allowed a sampling time of 0.001 s, with which an adequate system response for controlling direct current motors is obtained. The motion profiles used in this work were of the polynomial type: trapezoidal, parabolic, and S-curve. The same displacement length
h was considered for calculating each of the trajectories and the exact total movement time
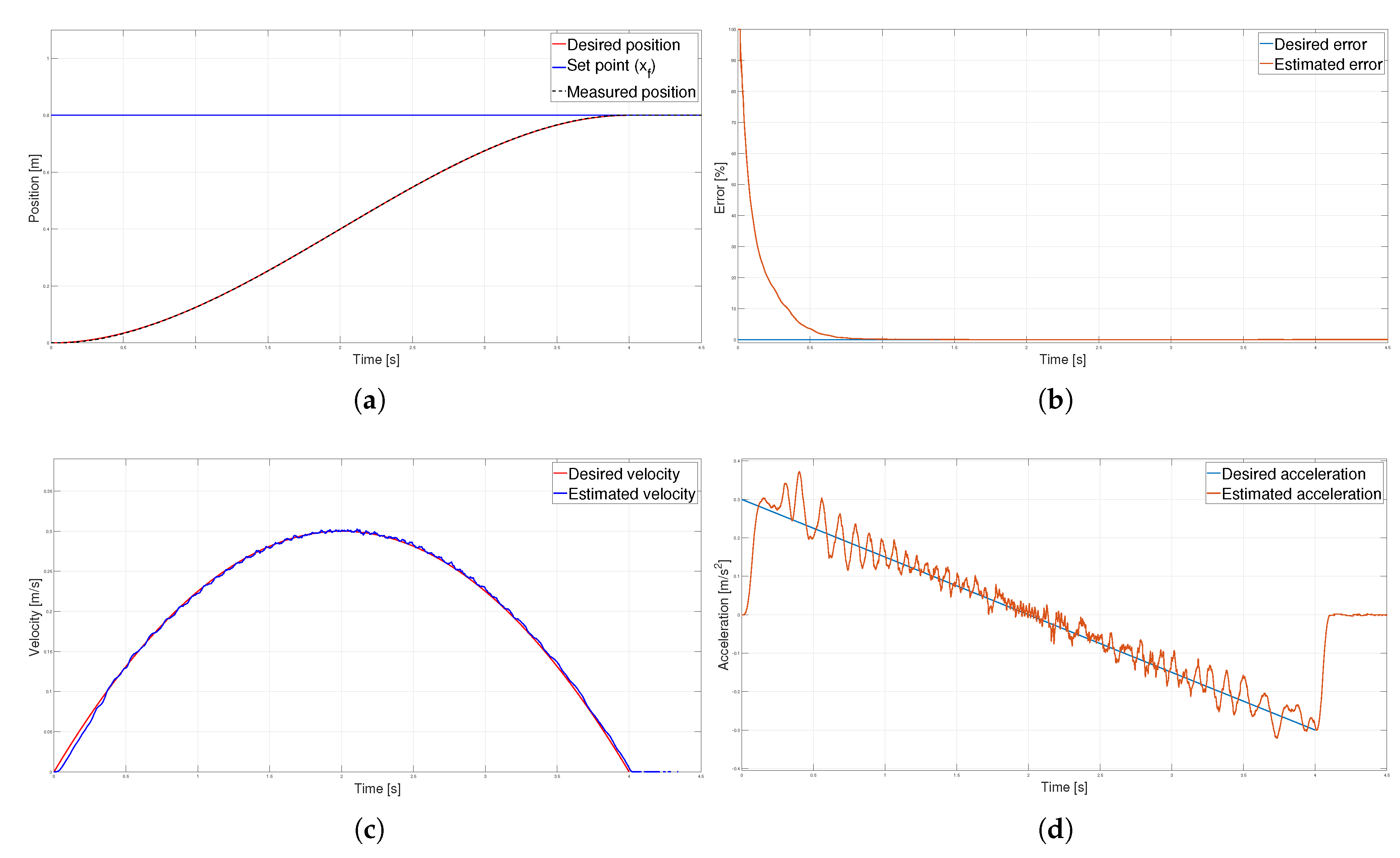
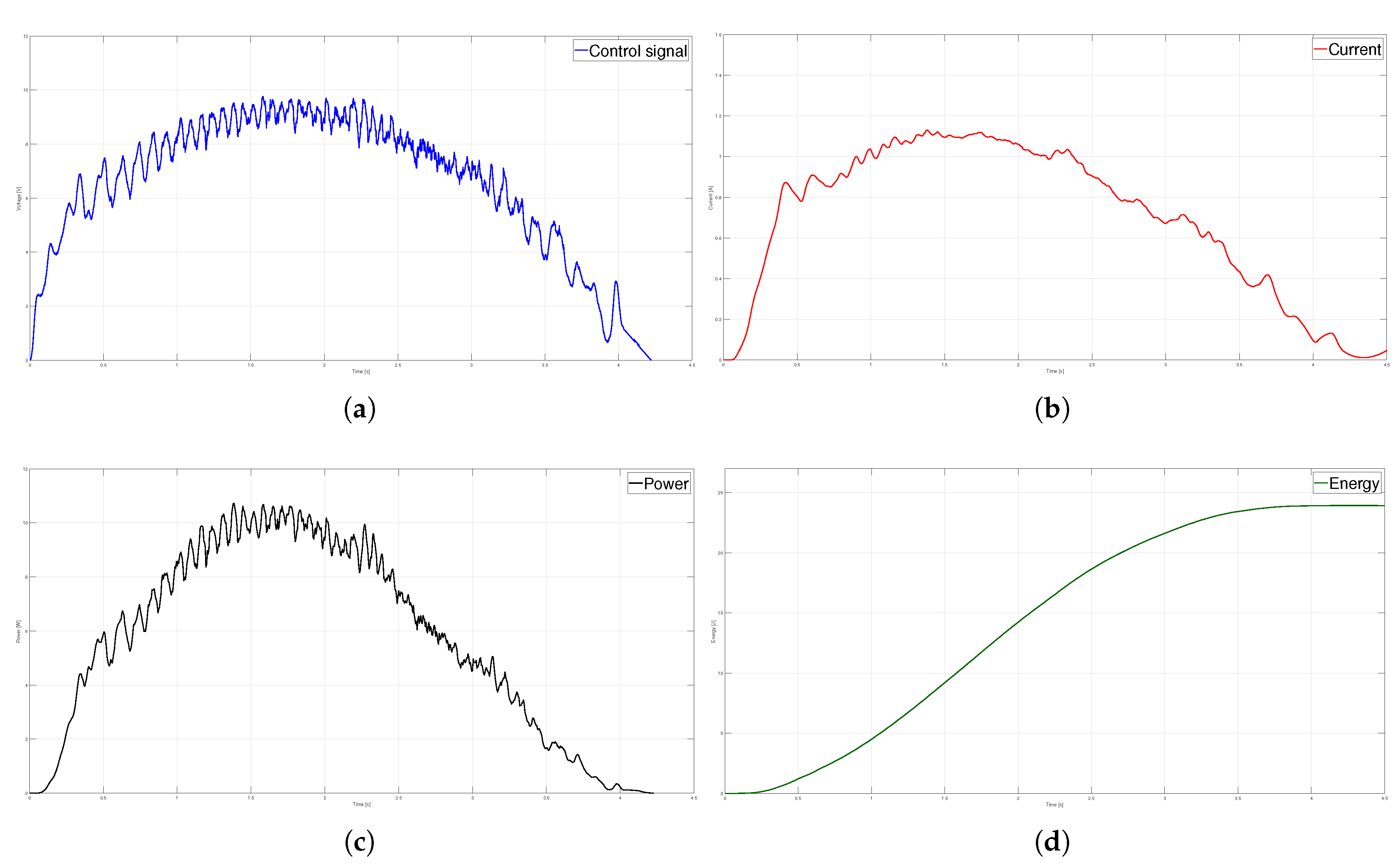
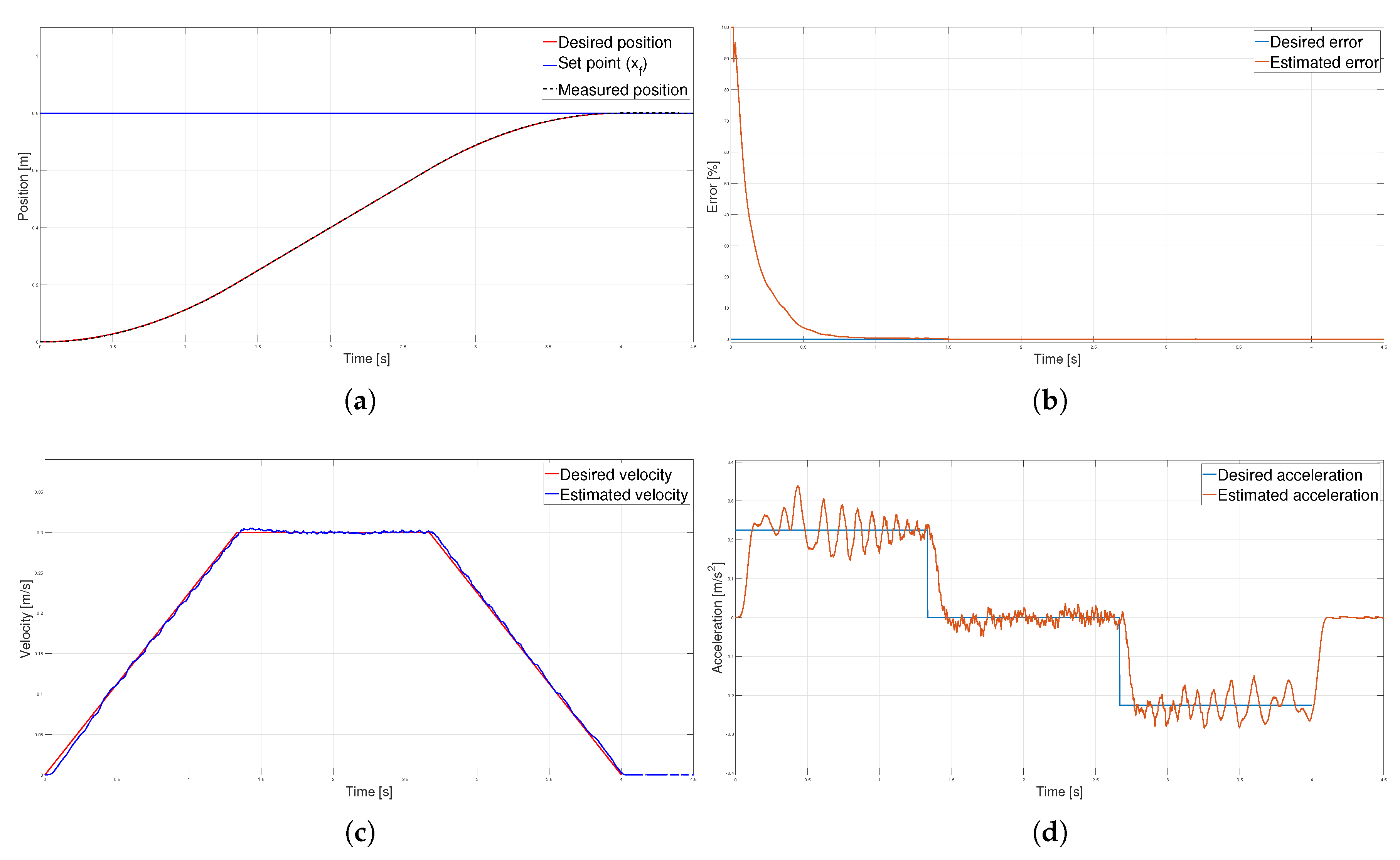
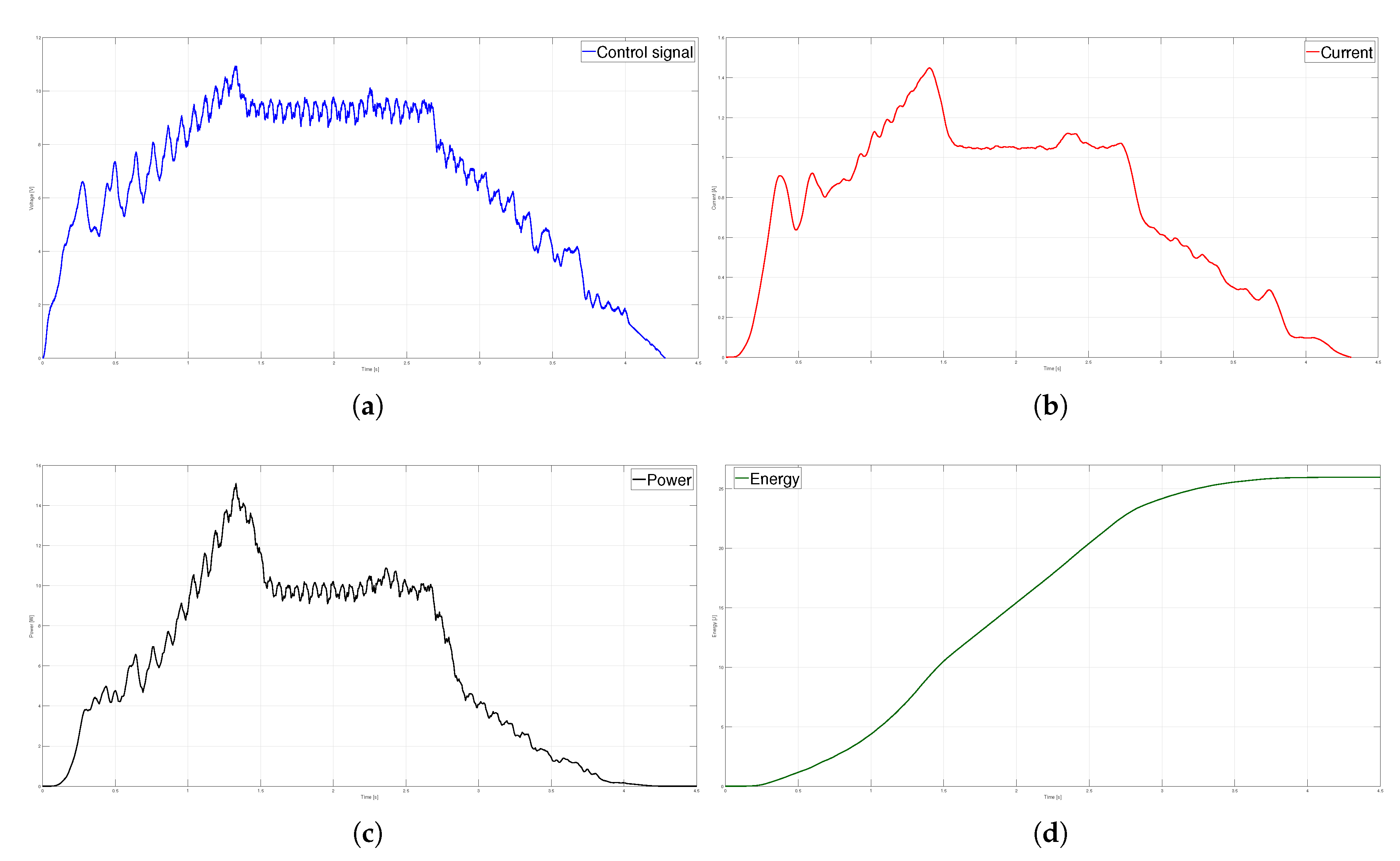
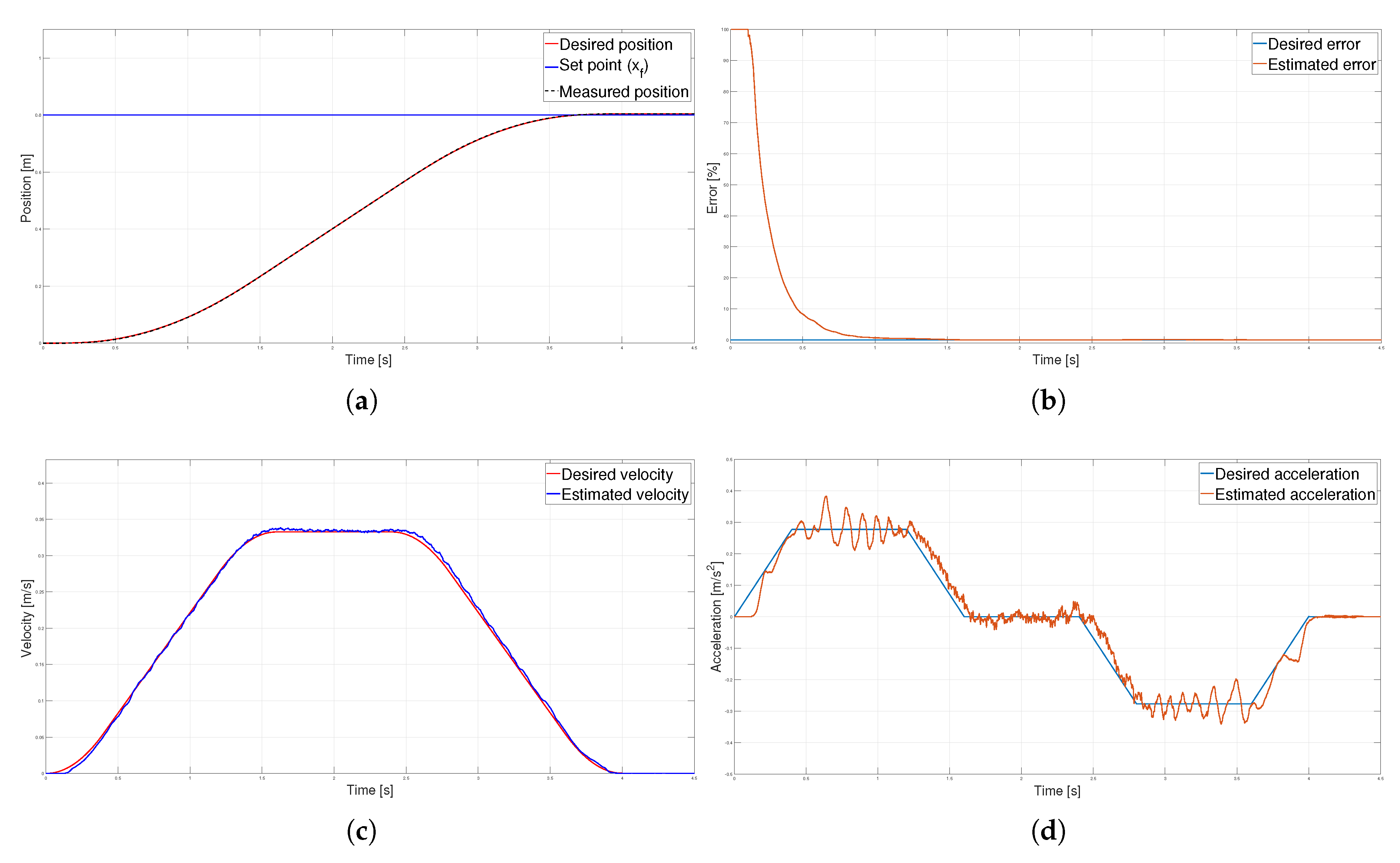
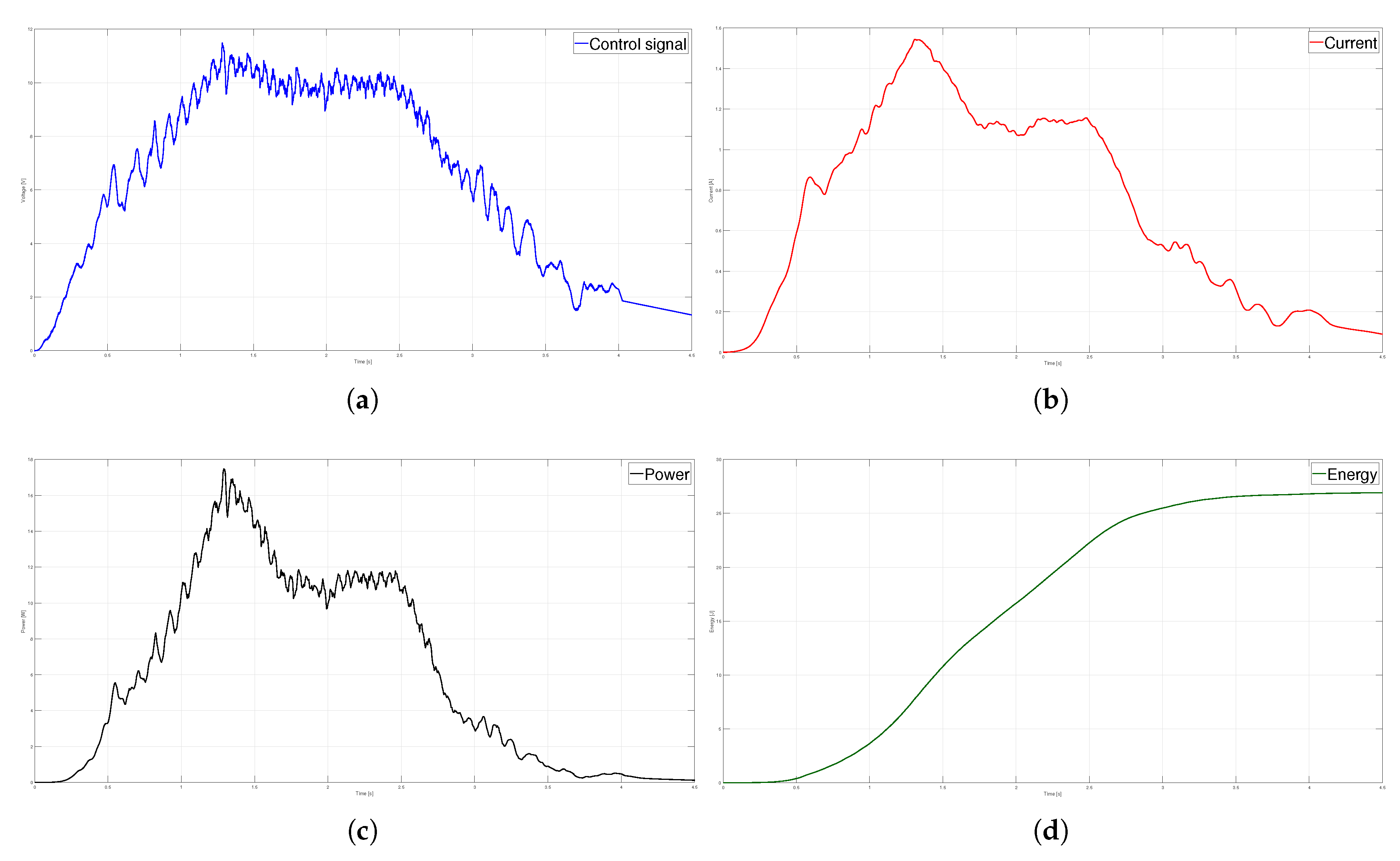
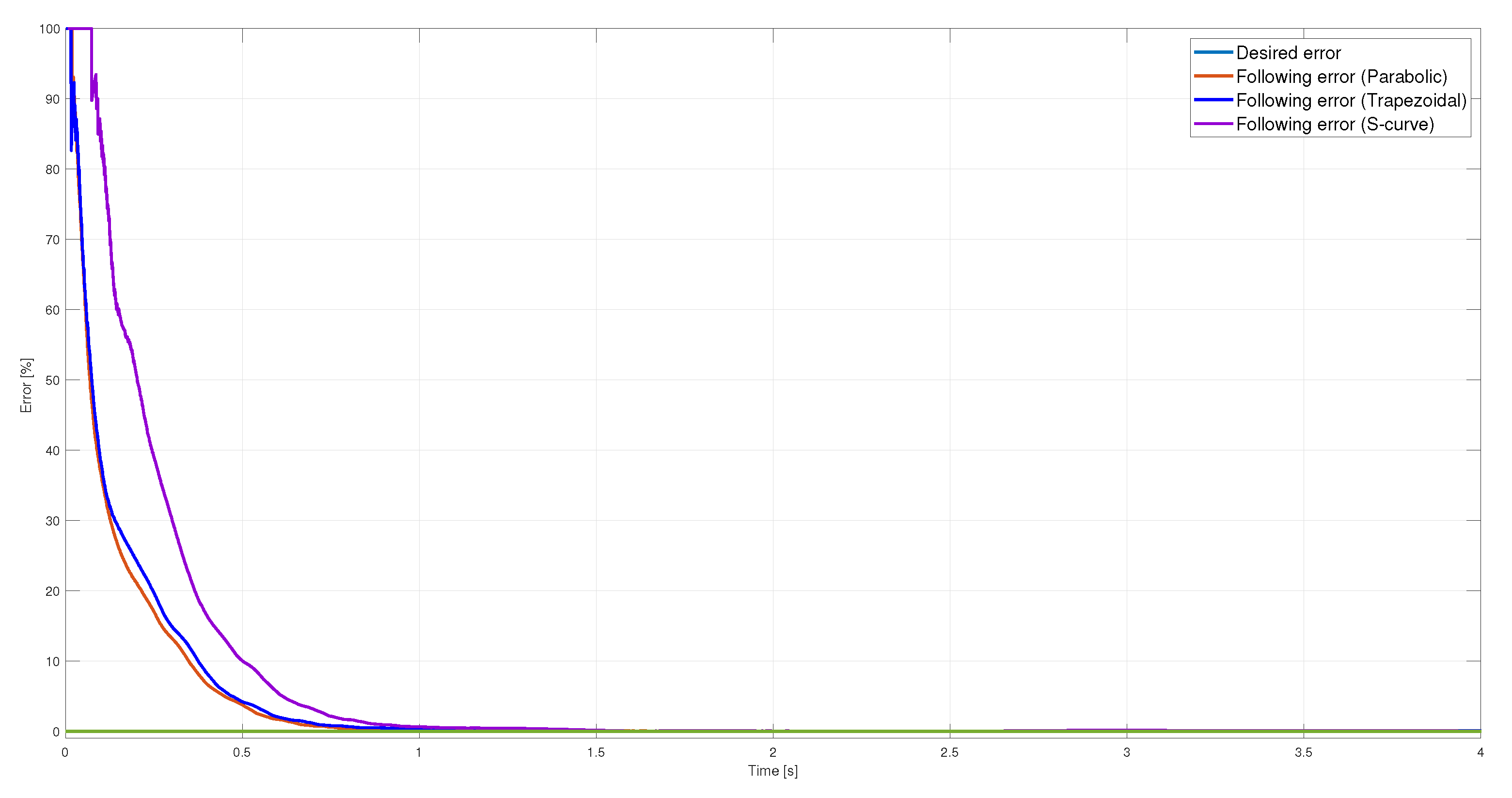
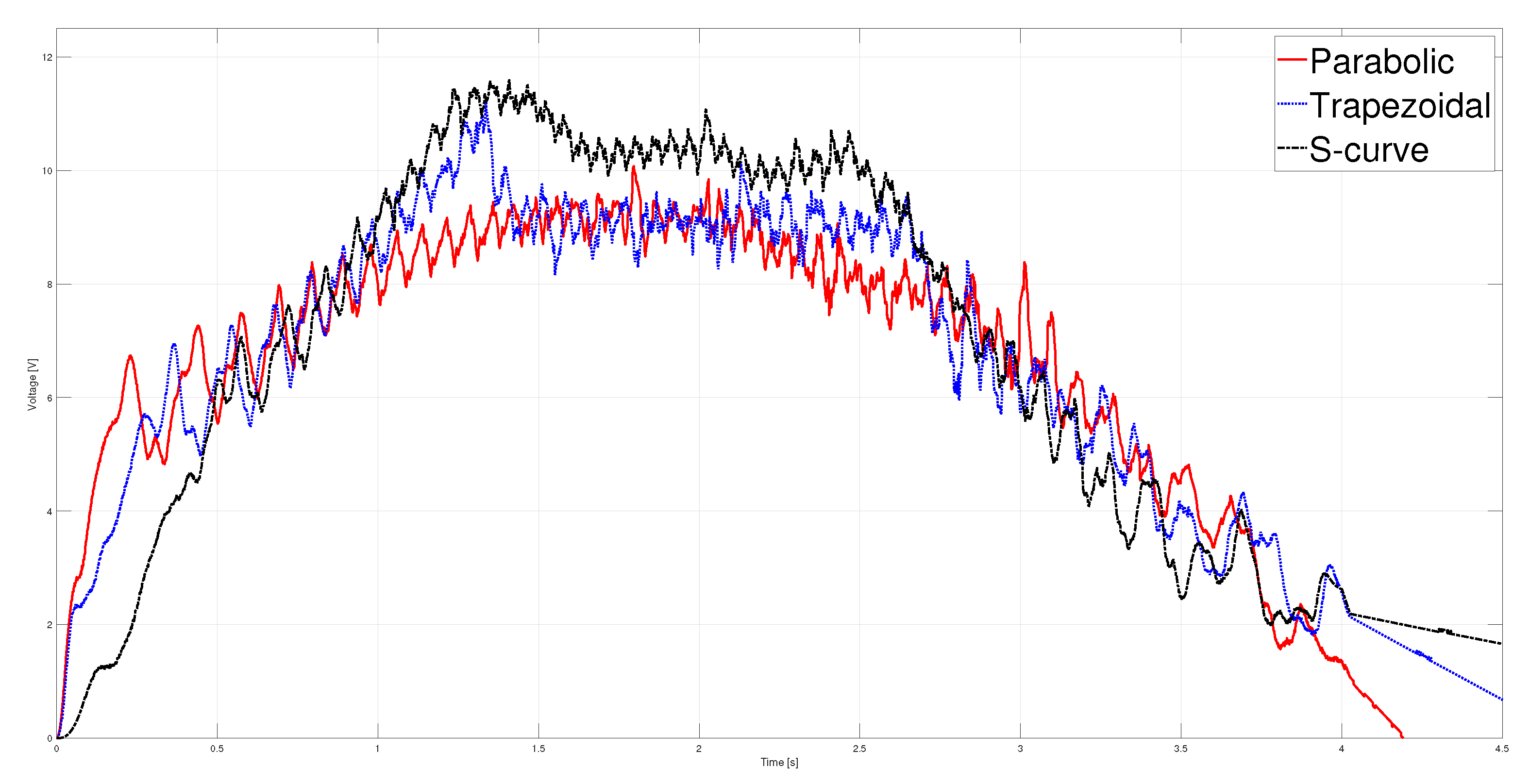
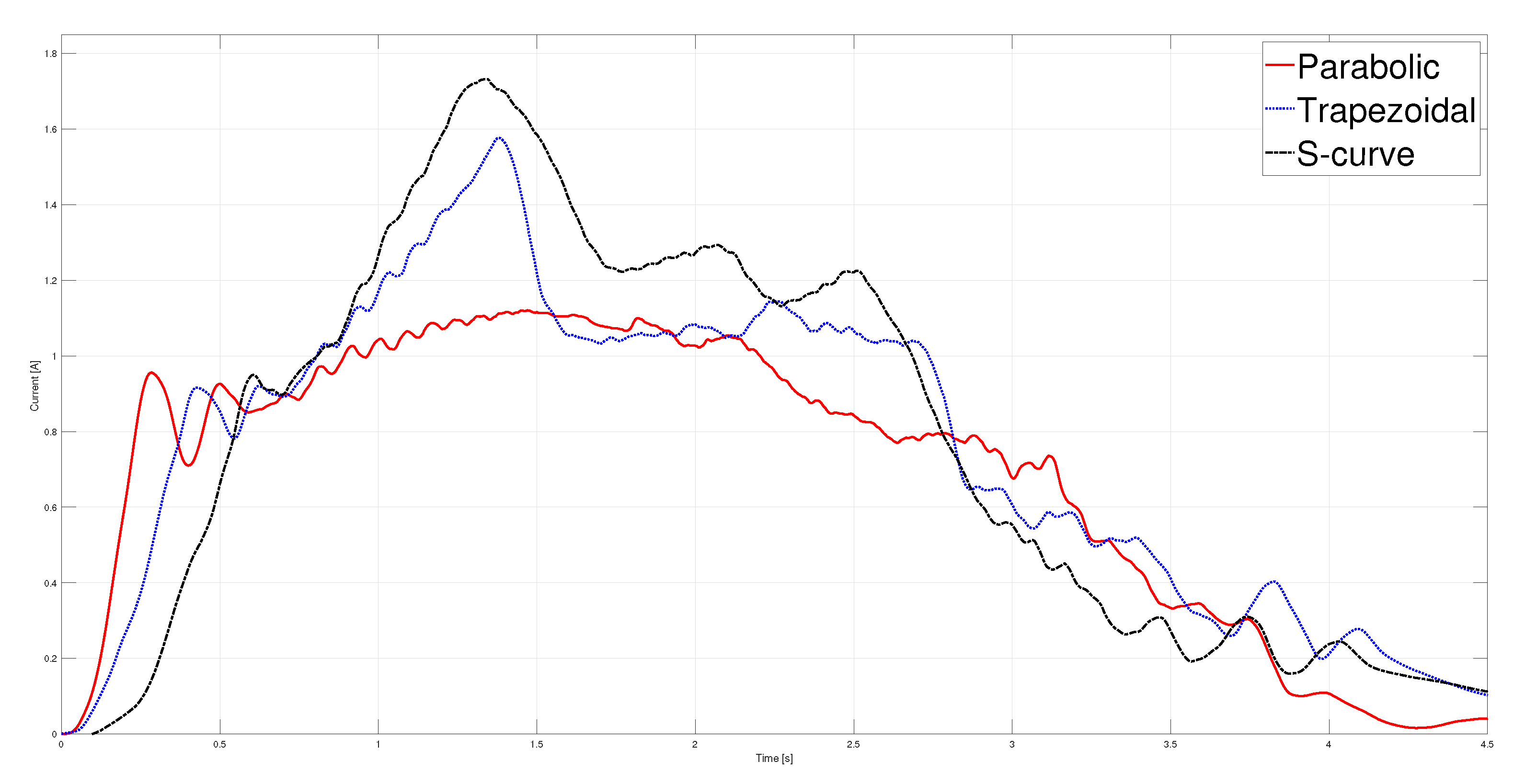
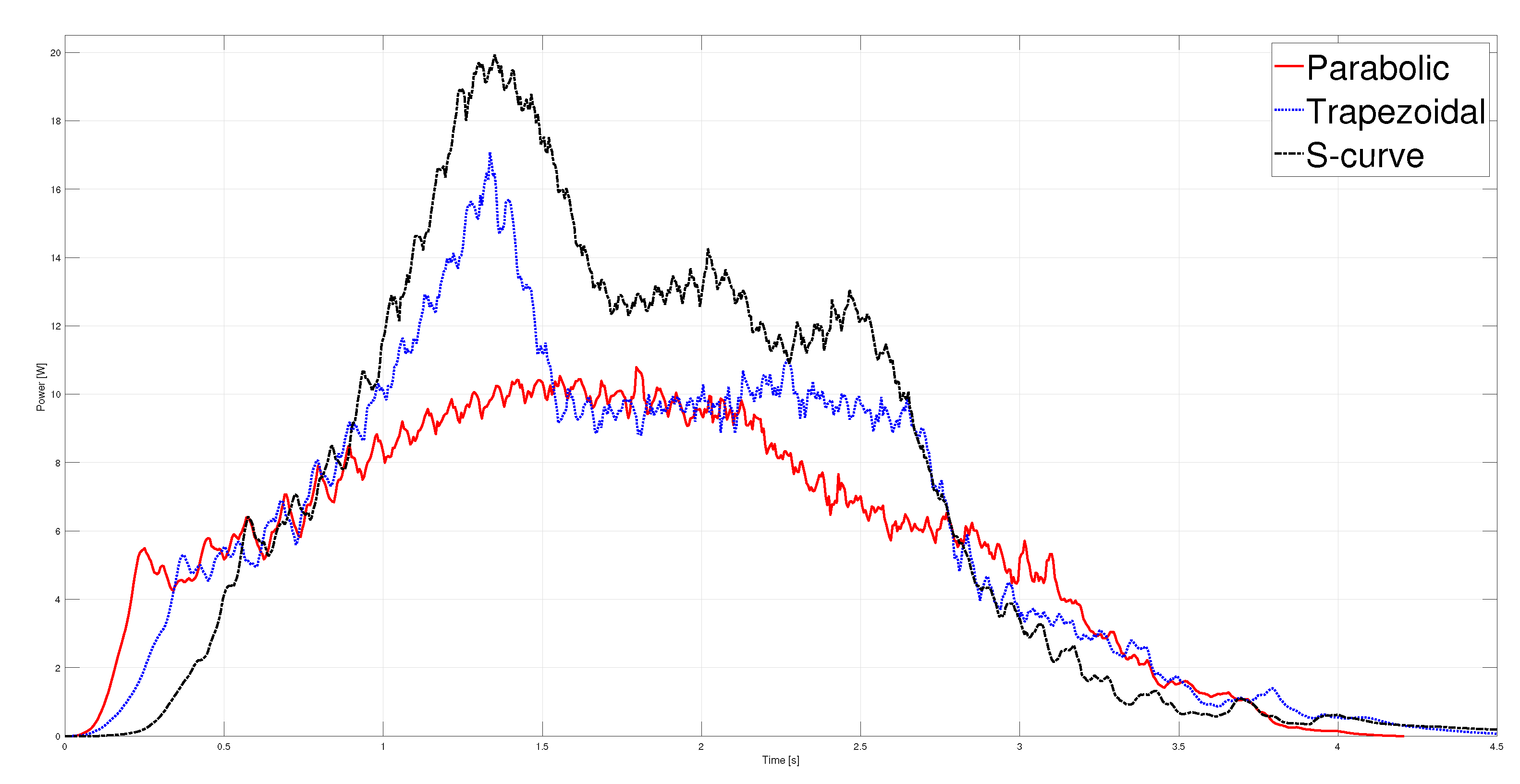
T. The kinematic magnitudes of the three profiles, such as position, velocity, and acceleration, were compared during the experimentation. The S-curve profile presented the most significant magnitude in speed, and the parabolic profile had the highest acceleration. However, the main characteristic analyzed was the energy consumption, which required analyzing the control signal, the measured current, and the instantaneous power to be estimated using numerical integration techniques. The results showed that the parabolic speed profile presented the lowest amplitude in the control signal, current, and power. In contrast, the S-curve speed profile was the one that presented the highest amplitude in the same magnitudes mentioned.
Table 4 shows that the highest energy consumption was dissipated using the S-curve profile, while the parabolic trajectory consumed less than the other two. In fact, after carrying out 40 tests for each profile, the energy consumption in the parabolic profile was
% less than the trapezoidal profile and
% less than the s-curve profile. In a second case, the same analysis was carried out, placing a load of 9
on the carriage; the robustness of the controller allowed for obtaining similar results in position, velocity, and acceleration for each profile compared to the case with no load. The difference identified was in the control signal and current consumed, translating into higher energy consumption. Nevertheless, from
Table 4, it is clear that the parabolic velocity profile also had the lowest energy consumption despite adding the load. Based on the results, trajectory planning is an effective technique easy to implement in low-cost microcontrollers to reduce energy consumption in motion control systems. In future studies, the S-curve parameters will be modified to reduce the maximum velocity and analyze the energy consumption behavior. Finally, a fuzzy controller will be used so as not to require the mathematical model of the plant.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.F.O-G and J.R.G-M; methodology, L.F.O-G; software, L.F.O-G and E.E.C-M; validation, L.F.O-G, J.R.G-M and E.E.C-M.; formal analysis, J.R.G-M; investigation, L.F.-G and O.A.B-V; resources, J.R.G-M, E.E.-C, O.A.B-V, M.G-L and T.M-S; data curation, M.G-L and T.M-S; writing—original draft preparation, J.R.G-M, M.G-L and T.M-S; writing—review and editing, J.R.G-M; visualization, M.G-L and T.M-S; supervision, J.R.G-M; project administration, J.R.G-M and L.F.O-G.
Figure 1.
Parabolic velocity profile (a) Position, (b) Velocity and (c) Acceleration.
Figure 1.
Parabolic velocity profile (a) Position, (b) Velocity and (c) Acceleration.
Figure 2.
Trapezoidal velocity profile (a) Position, (b) Velocity and (c) Acceleration.
Figure 2.
Trapezoidal velocity profile (a) Position, (b) Velocity and (c) Acceleration.
Figure 3.
S-curve velocity profile (a) Position, (b) Velocity, (c) Acceleration and (d) Jerk.
Figure 3.
S-curve velocity profile (a) Position, (b) Velocity, (c) Acceleration and (d) Jerk.
Figure 4.
Design stages of a motion controller.
Figure 4.
Design stages of a motion controller.
Figure 5.
Block diagram of the system used for identification.
Figure 5.
Block diagram of the system used for identification.
Figure 6.
PID algorithm structure.
Figure 6.
PID algorithm structure.
Figure 7.
Approach of the entire system implementation.
Figure 7.
Approach of the entire system implementation.
Figure 8.
Flowchart of the algorithm used for the microntroller programming.
Figure 8.
Flowchart of the algorithm used for the microntroller programming.
Figure 9.
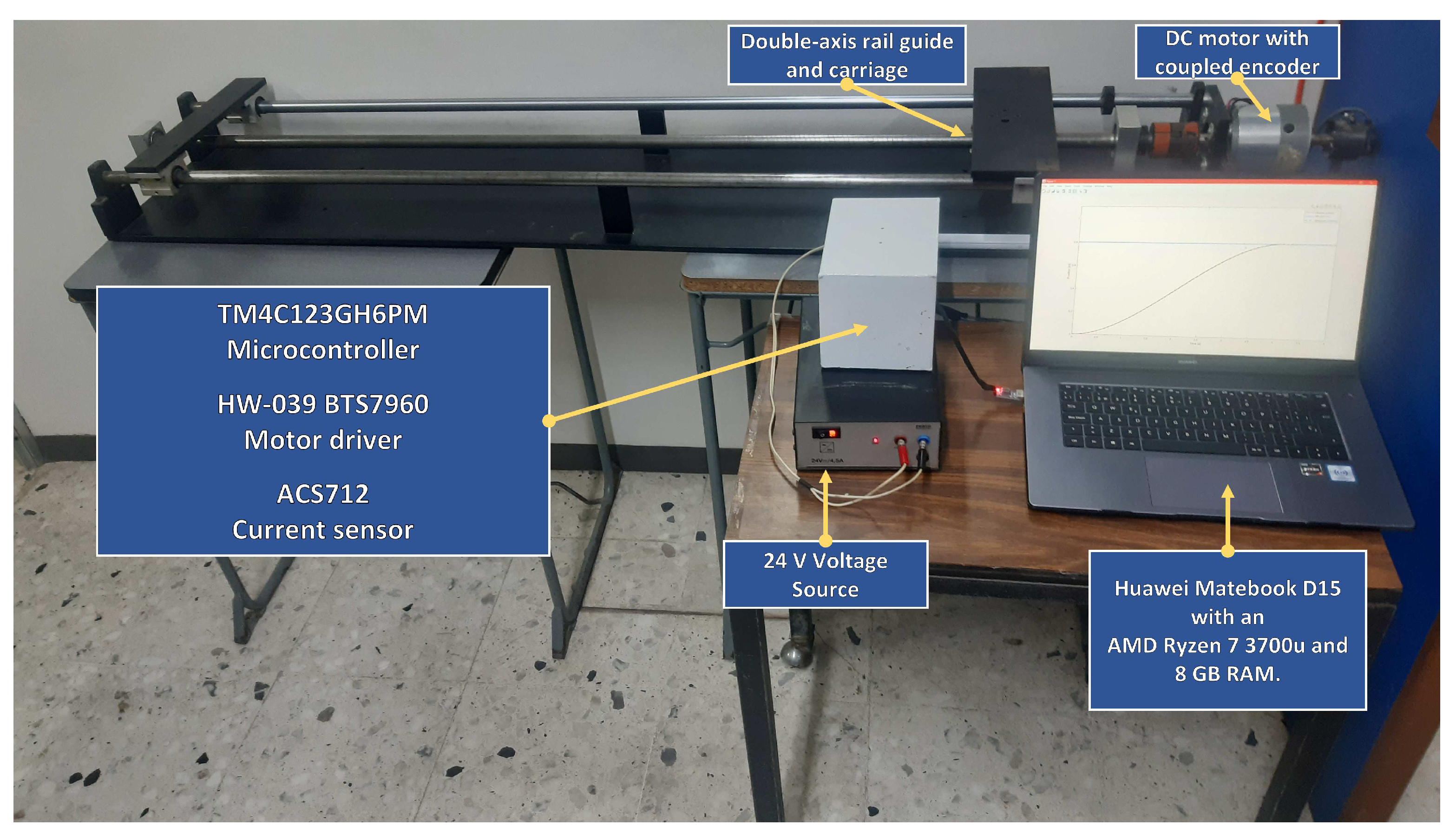
Linear plant used for the experimentation.
Figure 9.
Linear plant used for the experimentation.
Figure 10.
Parabolic velocity profile (a) Position, (b) Error (c) Velocity and (d) Acceleration.
Figure 10.
Parabolic velocity profile (a) Position, (b) Error (c) Velocity and (d) Acceleration.
Figure 11.
Parabolic velocity profile (a) Control signal, (b) Current (c) Power and (d) Energy.
Figure 11.
Parabolic velocity profile (a) Control signal, (b) Current (c) Power and (d) Energy.
Figure 12.
Trapezoidal velocity profile (a) Position, (b) Error (c) Velocity and (d) Acceleration.
Figure 12.
Trapezoidal velocity profile (a) Position, (b) Error (c) Velocity and (d) Acceleration.
Figure 13.
Trapezoidal velocity profile (a) Control signal, (b) Current (c) Power and (d) Energy.
Figure 13.
Trapezoidal velocity profile (a) Control signal, (b) Current (c) Power and (d) Energy.
Figure 14.
S-curve velocity profile (a) Position, (b) Error (c) Velocity and (d) Acceleration.
Figure 14.
S-curve velocity profile (a) Position, (b) Error (c) Velocity and (d) Acceleration.
Figure 15.
S-curve velocity profile (a) Control signal, (b) Current (c) Power and (d) Energy.
Figure 15.
S-curve velocity profile (a) Control signal, (b) Current (c) Power and (d) Energy.
Figure 16.
Error with a load of the three position profiles.
Figure 16.
Error with a load of the three position profiles.
Figure 17.
Control signal with a load of .
Figure 17.
Control signal with a load of .
Figure 18.
Current measured with a load of .
Figure 18.
Current measured with a load of .
Figure 19.
Power estimated with a load of .
Figure 19.
Power estimated with a load of .
Figure 20.
Energy estimated with a load of .
Figure 20.
Energy estimated with a load of .
Table 1.
Parameters used to implement the parabolic motion profile.
Table 1.
Parameters used to implement the parabolic motion profile.
| Parameter |
Value |
| Final position () |
m |
| Total time for displacement (T) |
4 s |
| Maximum velocity () |
|
| Maximum acceleration () |
0.3
|
Table 2.
Parameters used to implement the trapezoidal motion profile.
Table 2.
Parameters used to implement the trapezoidal motion profile.
| Parameter |
Value |
| Final position () |
m |
| Total time for displacement (T) |
4 s |
| Acceleration Time () |
s |
| Maximum velocity () |
|
| Maximum acceleration () |
|
Table 3.
Parameters used to implement the S-curve velocity profile.
Table 3.
Parameters used to implement the S-curve velocity profile.
| Parameter |
Value |
| Final position () |
m
|
| Total time for displacement (T) |
4 s
|
| Time factor for acceleration () |
|
| Time factor for jerk phase () |
|
| Acceleration Time () |
s
|
| Jerk pulse width () |
s
|
| Maximum velocity () |
|
| Maximum acceleration () |
|
| Maximum jerk () |
|
Table 4.
Energy comparison of the three motion profiles.
Table 4.
Energy comparison of the three motion profiles.
| Motion profile |
Energy (without load) |
Energy (with load) |
| Parabolic |
23.7044 J |
23.845 J |
| Trapezoidal |
25.9644 J |
26.7616 J |
| S-curve |
26.9525 J |
30.6456 J |