1. Introduction
Peptides have emerged as a potent therapeutic candidate for several diseases, including cancer, because of their small size, facile manufacturing, easy membrane permeability, and enhanced specificity. Excessive research has supported several small therapeutic peptides, many undergoing clinical trials [
1,
2,
3]. These small peptides (20–30 amino acids) are essentially lower immunogenic and stable at room temperature than full-length proteins and antibodies [
2]. Recent research has been inclined toward studying the anticancer role of small peptides in several forms of cancer [
3]. Colon cancer (CC) is one of the most frequent malignant tumour around the globe, and in recent years, the incidence rate has risen globally [
4,
5]. Epigenetic and genetic alterations within a cell are intrinsic in CC, activating oncogenes and proliferative signals from the abnormal microenvironment surrounding the cell [
6,
7]. Adenomatous polyposis coli (APC), a tumour suppressor gene, is deregulated at the somatic and germ line levels. In CC, APC gene mutations cause the APC protein to stabilise and accumulate β-catenin in the cytoplasm. Cytoplasmic β-catenin translocates to the nucleus and upregulates genes that promote uncontrolled cell growth and division [
8]. Cellular activities, including cell adhesion, motility, differentiation, proliferation, and chromosome separation, are all influenced by APC, which is found to be mutated in about 80% of colon tumours [
9,
10,
11,
12]. For 80%–85% of sporadic CC, changes in the APC gene are an early, if not an initiating, event, except those that display a CpG island methylator phenotype (CIMP) or hypermutable microsatellite instability (MSI) phenotype because of a lack of mismatch repair (MMR) [
13,
14]. Although there are several strategies for CC treatments, the main issues with the majority of these therapies include a variety of unfavorable side effects and drug resistance, which negates their efficiency [
7].
Developments in the last few decades have shed light on the antimicrobial peptide BMAP-27, an α-helical cathelicidin peptide with a 27-residue C-terminus that is amidated. BMAP-27 demonstrated an elongated N-terminal α-helix with faces patterned into cationic and aromatic scaffolds, a central kink, and a small hydrophobic C-terminal helix [
15,
16,
17,
18]. The peptide’s cationic NH
2-terminal portion (residues 1 to 18) is predicted to create an amphipathic α-helix, followed by a hydrophobic tail (residues 19 to 27). The hydrophobic tail is discovered to be essential for the peptide to exert its cytotoxic effect. The N-terminal amphipathic helix carries out the initial binding to the anionic membrane surface. In contrast, the C-terminal hydrophobic helix is a crucial structural component for the quick and effective insertion of the peptide into the hydrophobic core of the lipid bilayer, leading to cytotoxic effects against bacteria and cancer cells [
19]. The cytotoxic activity of BMAP-27 against neoplastic cells was shown that when BMAP-27 peptide was added to different human leukemia cell lines, the cell membranes opened up, and Ca
2+ penetrated inside the membrane [
18,
20]. This was followed by DNA fragmentation, a sign of apoptosis [
21]. The current study aimed to investigate the role of the BMAP-27 in suppressing CC cell proliferation and inducing apoptosis.
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Chemicals
Primary (SW480) and metastatic (SW620) CC cell lines were purchased from NCCS, Pune, India, where Sixteen short tandem repeat (STR) profiling were done using AmpFISTR® Identifiler® Plus Amplification Kit and Applied Bio system® 3500 Genetic analyser at NCCS, Pune (
Supplementary Material 1). BMAP-27 peptide with the sequence (GRFKRFRKKFKKLFKKLSPVIPLLHL) was purchased from PRIVEEL PEPTIDES: CHENNAI, India, with >90% purity.
2.2. Cell culture conditions
Primary (SW480) and metastatic (SW620) CC cell lines were cultured in DMEM containing 10% FBS, 1% glutamine, and 1% penicillin-streptomycin at 37 °C in 5% CO2.
2.3. Dosage selection and cell proliferation analysis
2.3.1. MTT assay
MTT (3-[4,5-dimethylthiazol-2-yl]-2,5 diphenyl tetrazolium bromide) analysis was performed for dose fixation of BMAP-27 peptide for further experiments. About 2 × 103 per well of SW480 and SW620 cells were seeded in a 96-well plate. The MTT assay was performed according to standard protocol. Absorbance was taken at 546 nm with a microplate reader (Robonik Touch Well Reader, India).
2.3.2. Cell proliferation assay
The Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8, Abbkine) was used to determine cell proliferation. About 2 × 103 cells per well were seeded in a 96-well plate. After 24 hrs, the cells were treated with the selected doses of BMAP-27 peptide and allowed to proliferate for different intervals (24 hrs, 48 hrs, and 72 hrs). Absorbance was measured at 450 nm with a microplate reader (Robonik Touch Well Reader, India).
2.4. Lactate Dehydrogenase (LDH) Activity
LDH assay was performed to measure the degree of damaged cells using the EZcountTM lactate dehydrogenase cell assay kit (Cat. No: CCK036) per the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.5. Catalase activity analysis
Catalase activity was measured using a standard protocol with slight modification [
22].
2.6. Assessment of cellular senescence
2.6.1. β-galactosidase activity assay
The β-galactosidase activity is a known biomarker of cell senescence which is measured using an EZdetectTM cell senescence detection kit (Cat. No: CCK063).
2.7. Gene expression analysis by qPCR:
RNAzol (Cat. No. R4533) was used to isolate RNA from the cells. NanoDrop was used to measure the concentration of total RNA in each sample at 260 nm and 280 nm. Eurogentec Reverse Transcriptase PCR kit (Cat. No. RT-RTCK-03) was used for the reverse transcriptase. Using the cDNA samples, the qPCR was done using the pre-designed primers for the following genes (CASPASE3, BAX, BCL-2, CDK-6, PCNA, TP53, WNT11, AXIN1, CTNNB1) with Takara Bio’s RR420A Syber Green qPCR master mix (Cat. No: RR420A).
2.8. Assessment of expression of IL-6, IFN-γ and CXCL-10, human cytochrome c
The evaluation of the inflammatory markers was performed with the help of the proteins that were isolated from the cell lysate. IL-6, IFN-γ, and CXCL-10 and cytochrome c expression were studied using IL-6 ELISA kit (Cat No. KET6017), IFN-γ ELISA kit (Cat No. KET6011), and CXCL-10 ELISA kit (Cat. No. KTE62958), cytochrome c ELISA kit (Cat. No. KTE62179) according to the manufacturer’s protocol.
2.9. Statistical Analysis
The statistical significance was determined with the help of the unpaired student’s t-test and the GraphPad V8.4.2 software; a p-value less than 0.05 was taken to indicate a statistically significant difference. The data are presented as mean ± standard error. All the experiments were performed in triplicates.
2.10. Methodology for molecular docking and simulation analysis
The structure of the BMAP-27 was prepared from the peptide sequence from the Phyre2 server (
http://www.sbg.bio.ic.ac.uk/phyre2/html/page.cgi?id=index). The molecular docking study between BMAP-27, APC and β-catenin protein was then performed using the patchdock web server (
http://bioinfo3d.cs.tau.ac.il/PatchDock/php.php). Furthermore, to investigate the effect of BMAP-27 on APC-protein and β-catenin, we have performed MD-simulation studies using GROMACS (Version 2018.5), protein-peptide composite system using the amber99sb force field and TIP3P solvation model. A periodic boundary condition with a cubical box of 1 nm edge length was considered. Na
+ or Cl
− ions were added to neutralize the system. Energy minimization was carried out until the maximum force became <10 kJmol
−1nm
−1. Then isochoric-isothermal (NVT) followed by isobaric-isothermal (NPT) ensembles were used to equilibrate the system for 1000 ps at 300 K. For the NPT ensemble modified Berendsen thermostat was used. NVT and NPT equilibration 1 nm of electrostatic and van der Waals interaction cut-off was kept. Using the same electrostatic and van der Waals cut-off with the equilibrated ensembles, MD simulation for 10 ns was performed. A modified Berendsen thermostat and a Parinello-Rahman barostat were used with reference temperature and pressure at 300 K and 1 bar, respectively.
2.10.1. Molecular dynamic simulations
To re-center the protein, peptide, and other molecules within the cubical box, the trjconv tool was used. Xmgrace tool was used to plot RMSD, Radius of gyration, and solvent-accessible surface area (SASA) plots.
3. Results
3.1. MTT assay
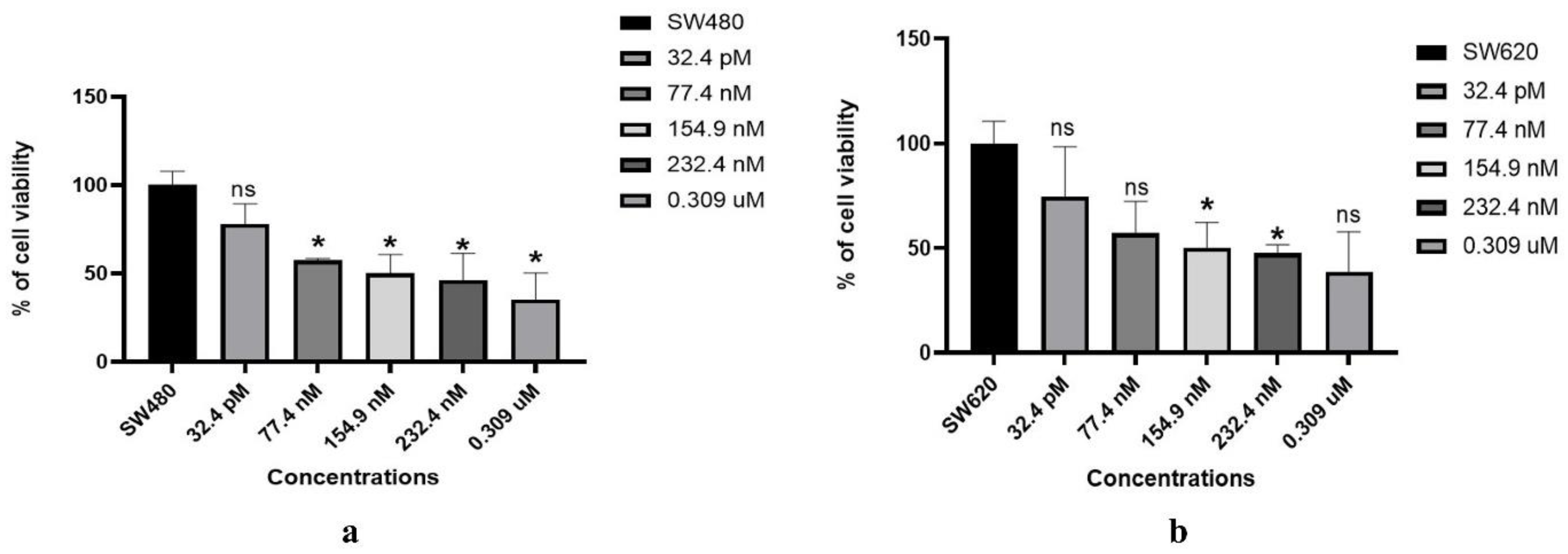
SW480 and SW620 were treated with various concentrations (32.4 pM, 77.4 nM, 154.9 nM, 232.4 nM, 0.309 µM) of BMAP-27 peptide for 72 hrs. BMAP-27 was found to exhibit a strong dose as well as time-dependent reduction of cell viability, and doses of 154.9 nM and 77.4 nM were chosen for future investigation as the other higher doses were found to be more lethal for the selected cell lines, as shown in
Figure 1a,b.
3.2. CCK-8 assay
The Cell Counting Kit-8 (CCK-8) was used to measure the proliferation of SW480 and SW620 cells. The BMAP-27 peptides (154.9 nM and 77.4 nM) showed a reduction in cell growth compared to the untreated SW480 and SW620 cells. It was found to decrease cell survival by inhibiting growth, and statistically significant data is shown in
Figure 2a,b.
3.3. Lactate dehydrogenase assay:
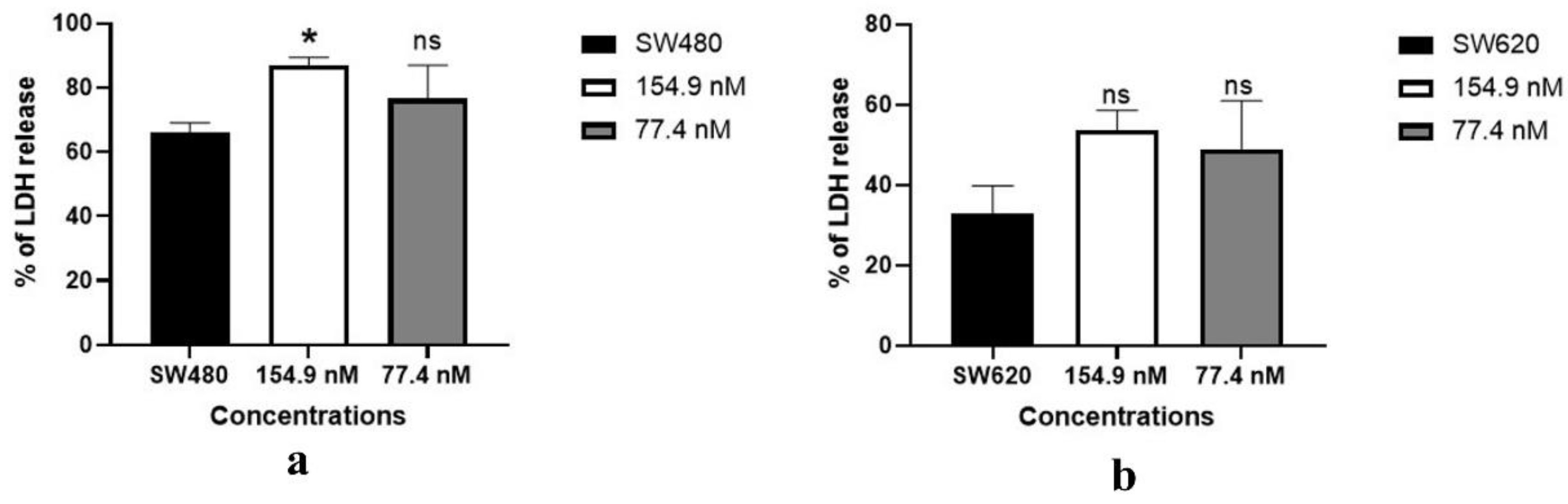
The lactate dehydrogenase (LDH) test was used to evaluate the cell-damaging potential of the BMAP-27 peptide. After 72 hrs of treatment with the peptide, cellular damage was seen as increased LDH release in peptide-treated SW480 (154.9 nM p-value = 0.0171) cells compared to non-treated cells. However, it did not show any significance in metastatic CC cells
Figure 3a,b.
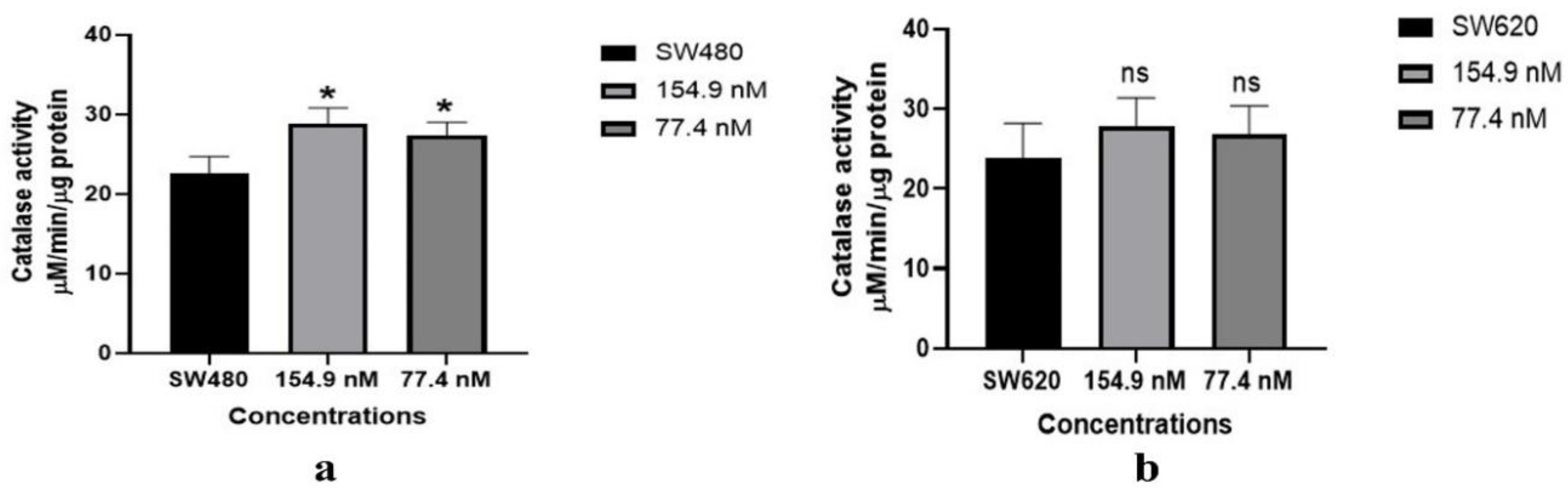
3.4. Catalase Activity
The activity of catalase was assessed in both non-treated groups as well as in the peptide-treated groups. Our findings showed that BMAP-27 peptide, at concentrations of 154.9 nM and 77.4 nM, respectively, produced a substantial increase in the catalase activity of both primary and metastatic cells, thus restoring the initial levels of catalase. However, it showed no significant difference in metastatic CC cells
Figure 4a,b.
3.5. Cell senescence assay
3.5.1. Senescence-associated-β-galactosidase (SA-β-gal) assay:
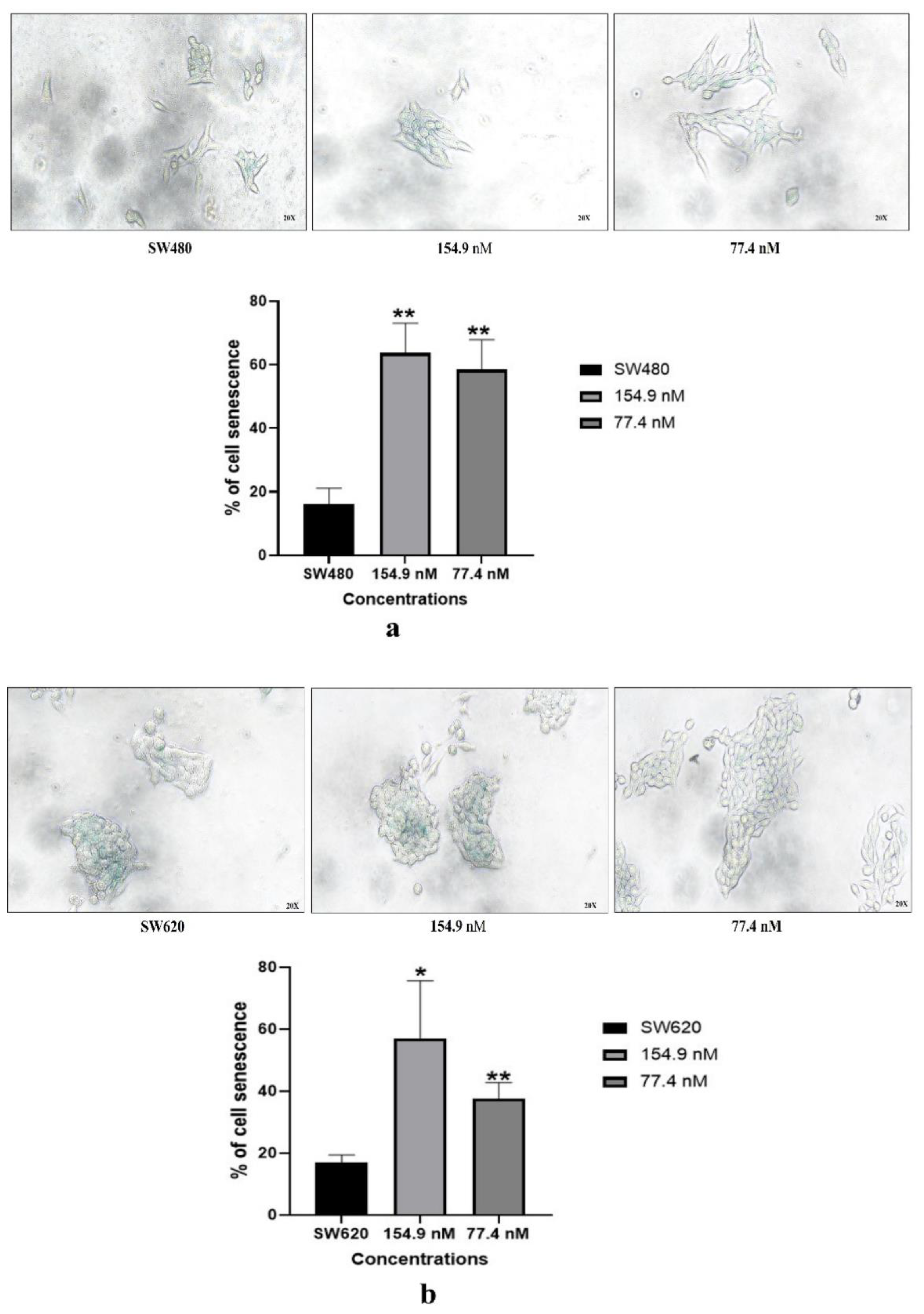
Senescence-associated-β-galactosidase staining of SW480 and SW620 cells revealed a low level of senescence. However, SW480 and SW620 cells supplemented with BMAP-27 (154.9 nM, 77.4 nM) peptide exhibited more significant number of blue-stained cells indicating significantly higher levels of senescence (SW480, 154.9 nM p-value = 0.0015; 77.4 nM p-value = 0.0024; SW620, 154.9 nM p-value = 0.0208, 77.4 nM p-value = 0.0036) as shown in
Figure 5a,b.
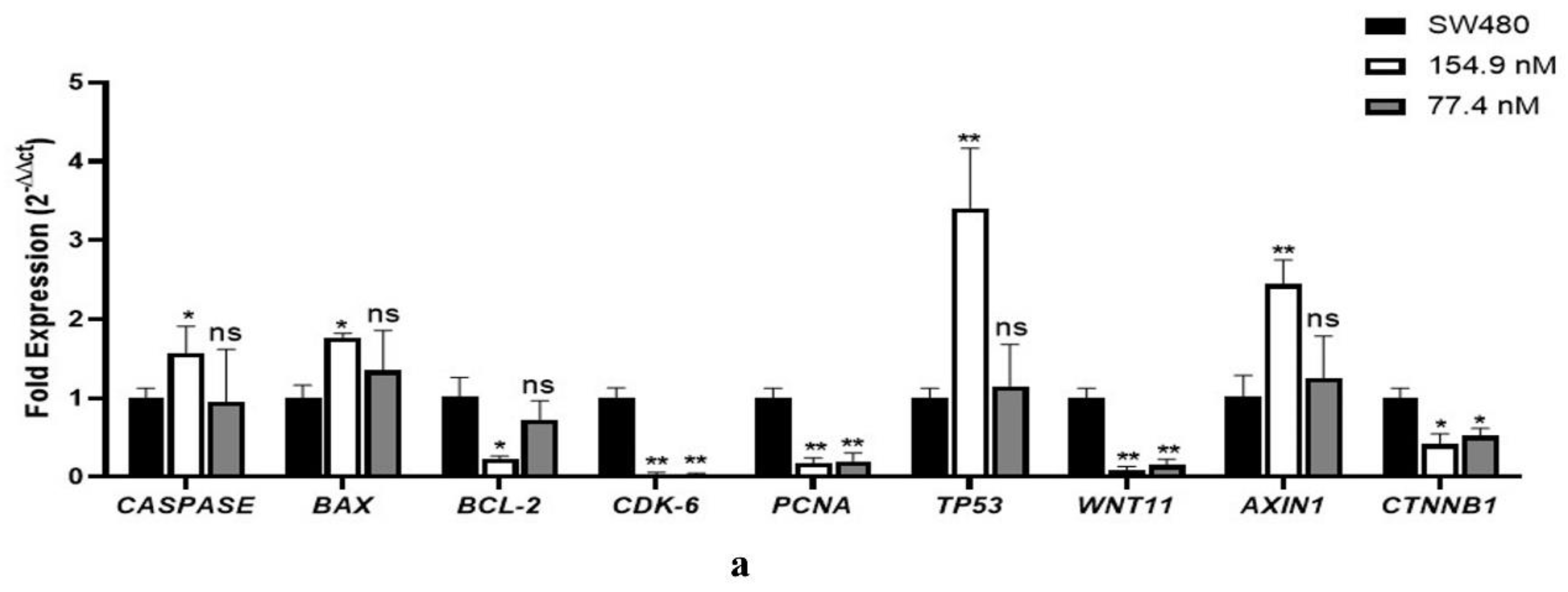
3.6. Gene expression analysis using qPCR
The expression of apoptotic markers
CASPASE3,
BAX, and
BCL-2 was analysed because their expression patterns affect tumour stage, metastasis, and survival. Prognosis is poorer with higher
BCL-2 expression or
BAX/BCL-2 ratios. Our present research on the apoptotic panel in primary and metastatic CC cells showed that BMAP-27 treatment for 72 hrs significantly regulated and directed apoptosis more effectively in primary CC cells. Further, BMAP-27 decreased
CDK6 and
PCNA expression in CC cells, indicating its cell-cycle regulatory effects in both primary and metastatic cells. Mutations in the
TP53 gene have also been associated with poor CC prognosis. However, BMAP-27 treatment for 72 hrs increased
p53 expression in primary CC cells. Additionally, BMAP-27 was also observed to regulate the Wnt signalling-related genes, which revealed a decreased expression of
WNT11 post-treatment of the primary and metastatic CC cells with BMAP-27 peptide. Similarly, BMAP-27 dramatically increases
AXIN1 expression, which may control
CTNNB1 and diminish its expression in peptide-treated CC cells
Figure 6.
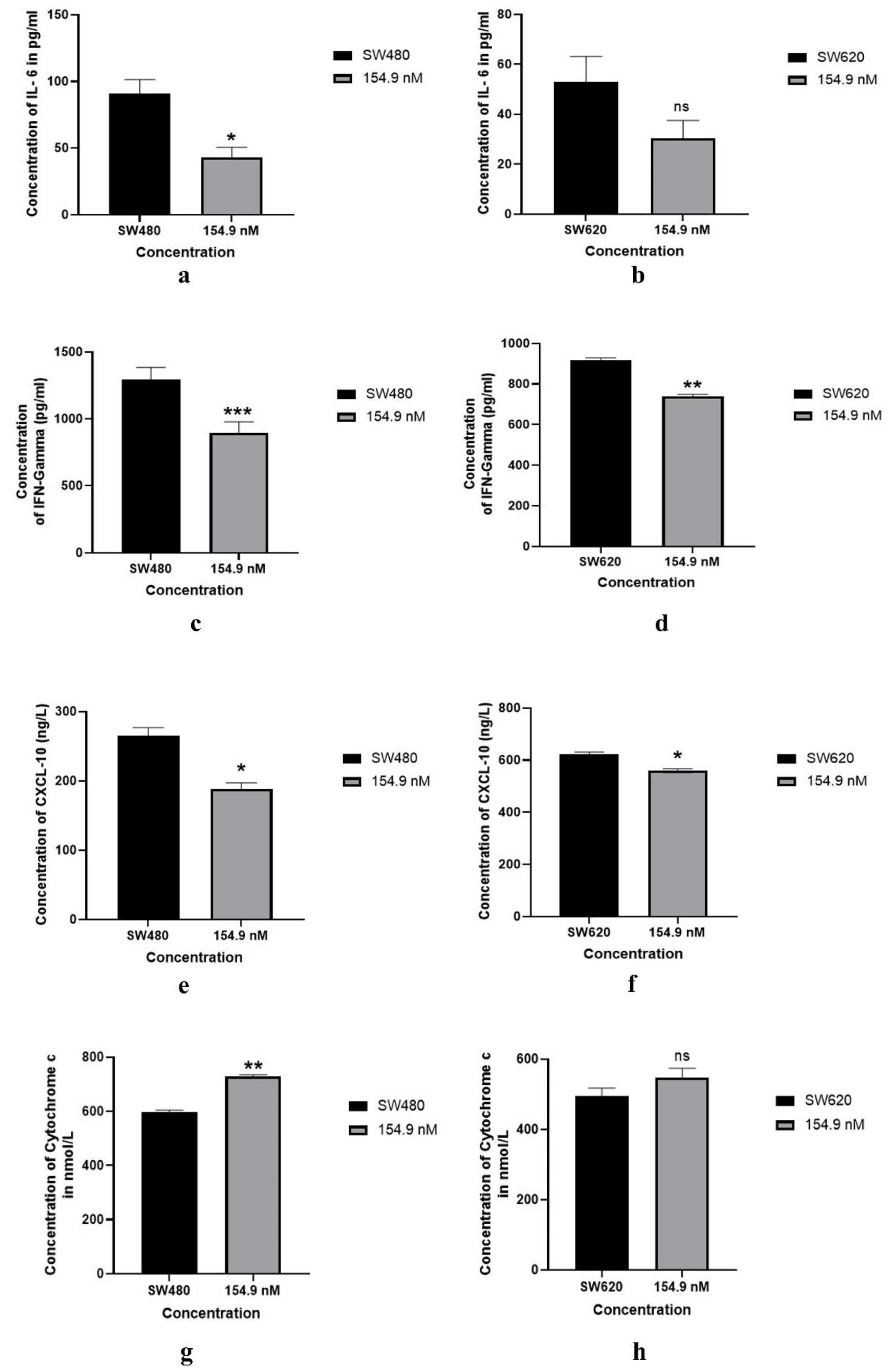
3.7. Modulation of inflammatory markers after the treatment of BMP 27
IL-6 is a cytokine that is involved in both the immune response as well as in inflammation. Our results suggested that the BMAP-27 peptide (154.9 nM) reduced the IL-6 concentration significantly in SW480 (p-value = 0.0334). However, it could not exert a significant effect on metastatic CC cells. IFN-γ is a cytokine that helps to control immune reactions, primarily by stimulating immune cells and regulating inflammation. Our results showed that the selected dose of BMAP-27 (154.9 nM) was able to reduce the IFN-γ concentration significantly in both SW480 (p-value = 0.0006) and SW620 (p-value = 0.0041) cells indicating that BMAP-27 treatment might regulate the exaggerated immune response in tumor microenvironment. Additionally, CXCL10 is known to be expressed in monocytes, fibroblasts, endothelium, and intestinal epithelial cells, and its expression is documented to be significantly elevated in pathogenic conditions. Our analysis showed that BMAP-27 could significantly decrease the expression level of CXCL-10 in BMAP-27 treated both primary (SW480, 154.9 nM p-value = 0.0153) and metastatic (SW620, 154.9 nM p-value = 0.0167) CC cells, indicating the likely induction of anti-tumour properties of BMAP-27 against cancer cells. Lower levels of cytochrome c expression or changes in its subcellular location have been linked to adverse effects such as an increased risk of metastasis and decreased lifespan. In the current investigation, we found that the cytochrome c level was increased significantly in SW480 (154.9 nM p-value = 0.0030). Although an increased level of cytochrome c was also observed in SW620, it did not show any significant difference when compared to untreated SW620 CC cells, as shown in
Figure 7a–h.
3.8. Molecular docking and Molecular simulation study
The PDB files of the crystal structure of APC protein (PDB ID: 1LUJ) and β-catenin (PDB ID: 4YJL) were retrieved from the protein data bank (
https://www.rcsb.org/). Both the structures of the proteins were cleaned using UCSF-chimers. The molecular docking study of BMAP-27 with APC protein and β-catenin was then performed using patchdock server, and the results obtained from the server were tabulated in
Table 1. It is clear from
Table 1 that the docking score between BMAP-27 and β-catenin is higher compared to APC protein. Also, the higher confidence score and lower RMSD of BMAP-27 prove more selective docking against β-catenin (4YJL).
Figure 8 represents the docked structure of BMAP-27 with APC protein (1LUJ) and β-catenin (4YJL). Due to the smaller binding cavity of both proteins, BMAP-27 has docked at the surface of the proteins. The minimum distance between BMAP-27 and 1LUJ was found 2.73 Å in the docked structure, while that between BMAP-27 and 4YJL was found 2.68 Å, which suggests a good binding affinity between BMAP-27 and 4YJL.
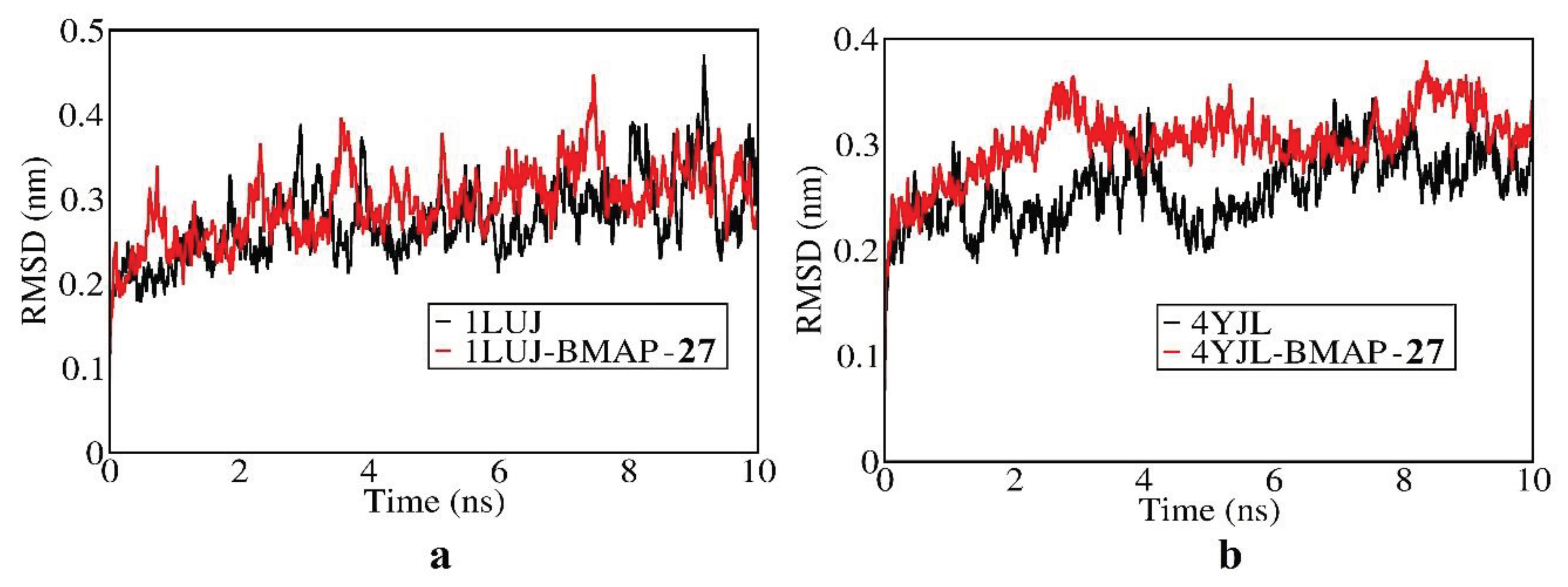
To further investigate the interaction of BMAP-27 with the proteins, MD simulation was performed for a period of 10ns with the docked and undocked structures. The RMSD plots obtained from the MD-simulation are shown in
Figure 9. It is clear from
Figure 9a that the deviation of the plot is lesser after 8ns with the BMAP-27 bind protein indicating the stabilization of the protein due to the presence of BMAP-27. While
Figure 9b indicates the stabilization of the plot after 4ns due to the presence of BMAP-27. Again, the deviation is more in the docked 1LUJ compared to 4YJL, revealing the more effectiveness of BMAP-27 against β-catenin (4YJL) compared to APC protein (1LUJ).
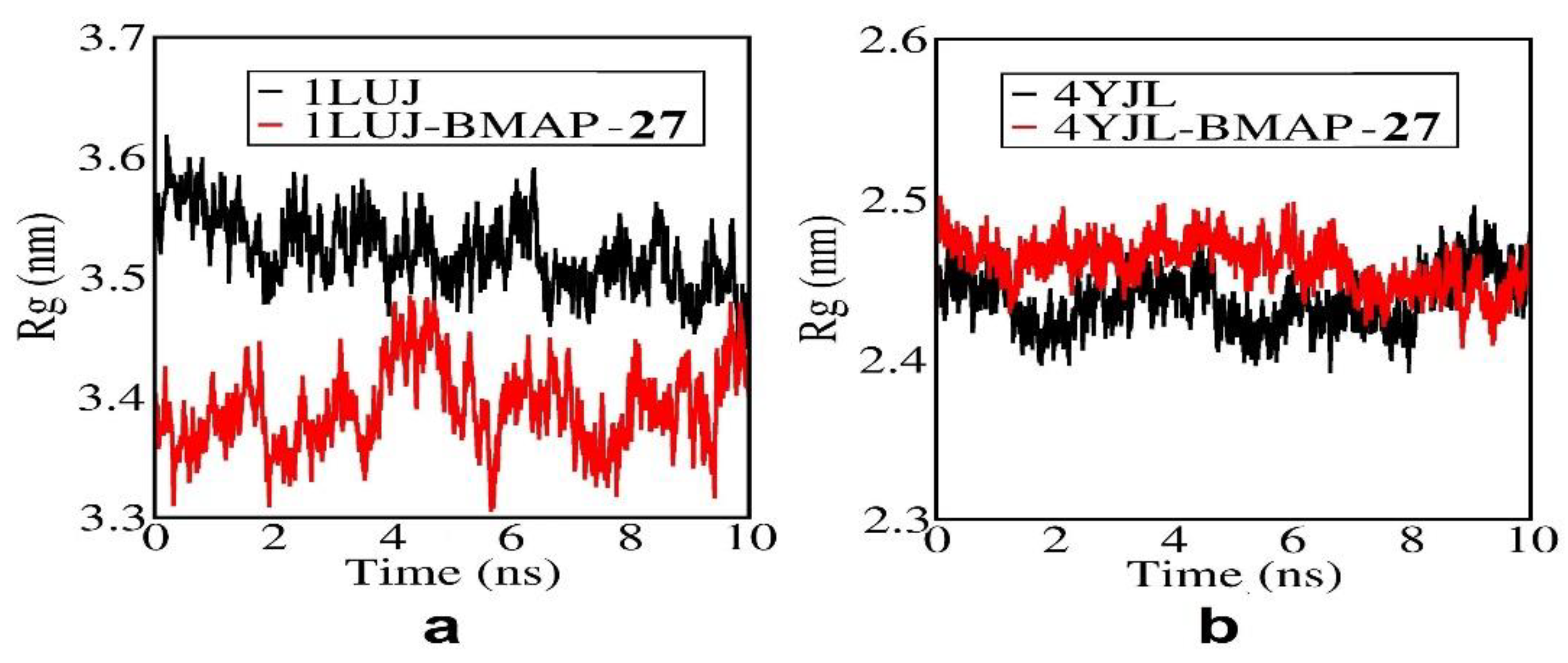
Figure 10 represents the radius of gyration (Rg) plot of BMAP-27 with APC protein and β-catenin. Rg-plots measure the compactness of the protein during MD-simulation. More the compactness of the proteins more will be binding with the BMAP-27. It is clear from
Figure 10 that the proteins are more compact in the docked structures compared to undocked structures. Again, the compactness is more in BMAP-27 docked 4YJL compared to 1LUJ.
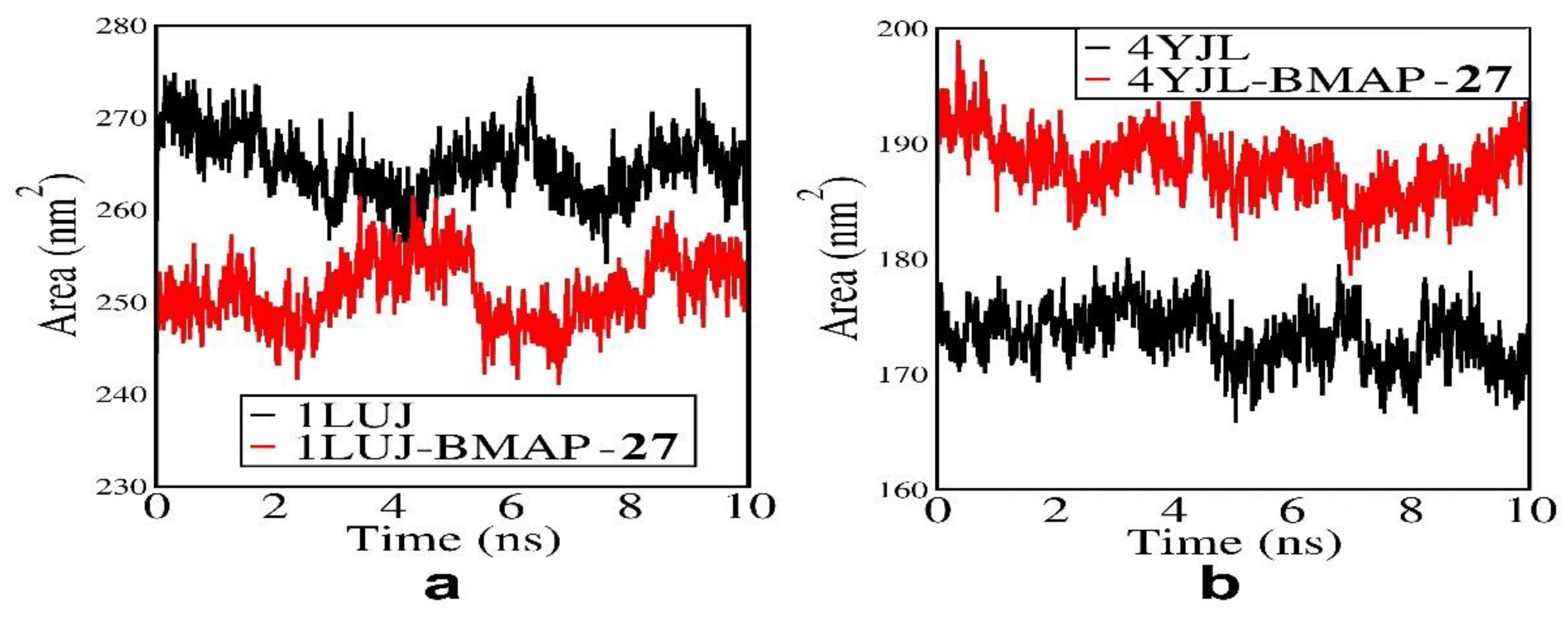
Figure 11 represents the solvent accessible surface area (SASA) plot of BMAP-27 docked 1LUJ and 4YJL which determines the stability and folding of proteins.
In both cases, BMAP-27 docked conformers show less fluctuation (for 1LUJ-BMAP within 250 nm2 and for 4YJL-BMAP within 190 nm2) compared to undocked conformation suggesting the stability of the docked conformation.
4. Discussion
BMAP-27, which belongs to the cathelicidin family of peptides, has been found to kill cancer cells without toxic hemolytic activity at lower doses [
18,
23,
24,
25,
26,
27]. The C-terminal hydrophobic helix of the peptide may be inserted into the lipid bilayer, and this contact results in membrane permeabilization and depolarization, which are crucial processes in its anticancer actions [
18,
28,
29,
30]. SW480 and SW620 cells were treated with various concentrations of BMAP-27 peptides for dose fixation. The IC
50 value was determined, and concentrations of BMAP-27 peptide at 154.9 nM and 77.4 nM were chosen for further analysis. We observed a significant reduction in cellular proliferation via CCK-8 analysis in a dose and time-dependent manner (24 hrs, 48 hrs, and 72 hrs) in which the selected concentrations of the peptides showed significant results in 72 hrs compared to 24 hrs and 48 hrs, confirming that BMAP-27 could reduce the proliferation of the CC cells. However, it is observed from the results that BMAP-27 showed a more significant impact in primary CC cells than that in metastatic cells. LDH levels are associated with tumour burden and may reflect tumour growth and invasive potential, including CC [
31,
32,
33]. Our results showed that BMAP-27 can induce cellular damage at a significant rate in primary (154.9 nM p-value = 0.0171) CC cells. However, BMAP-27 could not show a significant difference in metastatic CC cells compared to the untreated SW620 cells. Catalase enzymatic activity is found to be reduced in CC conditions. It has been demonstrated to be crucial in several different cellular processes where H
2O
2 acts as a secondary messenger [
34]. However, our results showed a significant increase in the levels of catalase activity with the peptide-treated groups in SW480 (154.9 nM p-value = 0.0200; 77.4 nM p-value = 0.0390) cells but did not show any significant difference in the metastatic CC cells. CC reduces cell senescence through several methods [
35,
36]. Senescence-associated secretory phenotype (SASP), a group of cytokines and chemokines generated by senescent cells, may cause inflammation. Thus, in SW480 (154.9 nM p-value = 0.0015; 77.4 nM p-value = 0.0024) and SW620 (154.9 nM p-value = 0.0208; 77.4 nM p-value = 0.0036) CC cells, BMAP-27 peptide dosages significantly increased the number of blue-stained cells compared to untreated SW480 and SW620 cells.
CASPASE3,
BAX, and
BCL-2 expression levels predict CC progression. Expression patterns determine tumour stage, metastasis, and survival. Increased
BCL-2 expression or
BAX/BCL-2 ratio worsens prognosis [
37,
38]. The apoptotic panel in primary and metastatic CC cells demonstrated that 72 hrs of BMAP-27 treatment greatly regulated apoptosis and caused tumour cells to undergo apoptosis more significantly in primary cells than in metastatic cells. Proliferating genes comprising
CDK6,
PCNA, and further Wnt-signalling pathway markers
Wnt11 were also found to be significantly downregulated. Earlier studies have markedly reported that TP53 mutations were always 80% in advanced CC patients with metastases [
39,
40,
41,
42,
43]. Similar to the prior investigation, CC cells had lower p53 expression. However, BMAP-27 peptide treatment CC cells showed increased p53 expression significantly in the primary CC cells. CC development is connected to
AXIN1 inactivation. In certain CC instances,
AXIN1 gene mutations increase Wnt/β-catenin signaling.
AXIN1 dysfunction causes
β-catenin nuclear accumulation and stability, upregulating target genes that promote cell proliferation, survival, and cancer [
44]. We found that post-treatment with BMAP-27 dramatically increases the expression of
AXIN1, whereas it lowers the expression of
β-catenin, which may indicate that
AXIN1 controls the expression of
β-catenin and diminish its expression in peptide-treated CC cells.
IL-6 promotes various malignancies, including CC [
45]. In agreement with earlier studies, CC cells had an increased level of IL-6, however, primary CC cells treated with BMAP-27 had considerably lower levels of IL-6. Moreover, the BMAP-27 treatment decreased the inflammatory cytokine IFN-γ at 154.9 nM in SW480 and SW620 cells, indicating that the peptide may restrict the spread of cancer. Additionally, CXCL10 promotes CC tumor development. It may promote tumor growth, migration, and invasion [
46]. BMAP-27 decreases CXCL10 expression in primary and metastatic CC cells, suggesting that CXCL10 may induce anti-tumour capabilities against cancer cells. Reduced cytochrome c expression or subcellular localization has been linked to worse outcomes, including advanced tumor stage, higher metastatic risk, and worse survival rates [
47]. In our study, SW480 and SW620 cells have lower cytochrome c levels, but SW480 and SW620 cells treated with BMAP-27 peptide increased its expression significantly in SW480 cells. However, it did not show any significant increase in SW620 cells.
The in-silico analyses on the effect of BMAP-27 peptide on APC and β-catenin proteins were conducted through molecular docking studies followed by molecular dynamics simulation. The results indicated significant binding between BMAP-27 and the selected proteins with a high binding affinity, revealing strong interactions. The MD-simulation study for 10ns in an aqueous medium further supported the effect of BMAP-27 on the conformation of both β-catenin and APC proteins. The RMSD plot showed less fluctuation in the case of docked proteins during MD-simulation, indicating their stability and compactness. The radius of the gyration plot also demonstrated increased compactness of both proteins after binding with BMAP-27. Additionally, the solvent-accessible surface area plot showed more scattered conformation in the docked state, suggesting increased stability and access to solvent molecules like water.
5. Conclusions
BMAP-27 peptide demonstrated the ability to induce cell death, inhibit cell proliferation, promote tumor suppression, and regulate Wnt signaling-associated genes for reducing CC proliferation and inducing apoptosis. Moreover, from our results, it was found that BMAP-27 activity was more in primary CC cells as compared to metastatic CC cells. The molecular docking and MD simulations further shed light on the interactions between BMAP-27 and its target proteins, APC and β-catenin, providing valuable insights into the mechanisms underlying its anti-cancer properties. Further research, including in vivo studies and clinical trials, will be necessary to validate the therapeutic potential of BMAP-27 as an anti-colon cancer agent.
Supplementary Materials
The supplementary material is provided in a PDF file separately.
Author Contributions
The study was designed by AD, DD, NB and SP; the manuscript was written by AD, DD, and NB; reviewed and edited by AB, AB1, SA, NB, SFA, ADR and SP.
Funding
This study was supported by grants from InfoGenom R&D Laboratories of Cukurova University Technopolis (Project Reference Number: 008/12-22). The funding source had no role in the publication. The authors acknowledge the Project Number (RSPD2023R709), King Saud University, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia, for providing the APC for the publication of the manuscript. The authors are thankful to the Chettinad Hospital and Research Institute (CHRI), Chettinad Academy of Research and Education (CARE) for providing the infrastructural support to complete this piece of work.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
The entire data set resulting from the studies that have been anayzed from this study are depicted in the figures and are also accessible from the corresponding author under very specific request.
Acknowledgments
The authors are thankful to Chettinad Hospital and Research Institute (CHRI), Chettinad Academy of Research and Education (CARE), for providing the infrastructural support to complete this work.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Bose, D.; Roy, L.; Chatterjee, S. Peptide therapeutics in the management of metastatic cancers. RSC Adv. 2022, 12, 21353–21373. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Adhikari, S.; Deka, D.; Bisgin, A.; Paul, S.; Balidya, N.; Pathak, S. An Updated Review on Recent Advances in the Usage of Novel Therapeutic Peptides for Breast Cancer Treatment. Int. J. Pept. Res. Ther. 2023, 29, 32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Das, A.; Deka, D.; Banerjee, A.; Radhakrishnan, A.K.; Zhang, H.; Sun, X.F.; Pathak, S. A Concise Review on the Role of Natural and Synthetically Derived Peptides in Colorectal Cancer. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2022, 22, 2571–2588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Girigoswami, K.; Girigoswami, A. A Review on the Role of Nanosensors in Detecting Cellular miRNA Expression in Colorectal Cancer. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2021, 21, 12–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ren, J.; Zhang, P.; Li, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhong, W.; Song, W.; Wang, X.; Gao, P.; Mao, C. Association of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs, Genetic Risk, and Environmental Risk Factors with Incidence of Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2022, 14, 5138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhatiya, M.; Pathak, S.; Jothimani, G.; Duttaroy, A.K.; Banerjee, A. A Comprehensive Study on the Anti-cancer Effects of Quercetin and Its Epigenetic Modifications in Arresting Progression of Colon Cancer Cell Proliferation. Arch Immunol Ther Exp (Warsz) 2023, 71, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Malayaperumal, S.; Sriramulu, S.; Banerjee, A.; Pathak, S. Over-Expression of MicroRNA-122 Inhibits Proliferation and Induces Apoptosis in Colon Cancer Cells. Microrna 2020, 9, 354–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ayala-Calvillo, E.; Mojica-Vázquez, L.H.; García-Carrancá, A.; González-Maya, L. Wnt/β-catenin pathway activation and silencing of the APC gene in HPV-positive human cervical cancer-derived cells. Mol. Med. Rep. 2018, 17, 200–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, P.; Liang, B.; Liu, M.; Lebbink, J.H.G.; Li, S.; Qian, M.; Lavrijsen, M.; Peppelenbosch, M.P.; Chen, X.; Smits, R. Oncogenic Mutations in Armadillo Repeats 5 and 6 of β-Catenin Reduce Binding to APC, Increasing Signaling and Transcription of Target Genes. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1029–1043.e10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghasemi, T.; Khalaj-Kondori, M.; Hosseinpour Feizi, M.A.; Asadi, P. Aberrant expression of lncRNAs SNHG6, TRPM2-AS1, MIR4435-2HG, and hypomethylation of TRPM2-AS1 promoter in colorectal cancer. Cell Biol. Int. 2021, 45, 2464–2478. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Wang, D.; Zhang, Z.; Wang, Y.; Yu, W.; Sun, K.; Maimela, N.R.; Sun, Z.; Liu, J.; Yuan, W.; et al. DEFB4A is a potential prognostic biomarker for colorectal cancer. Oncol. Lett. 2020, 20, 114. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Siraj, A.K.; Kumar Parvathareddy, S.; Pratheeshkumar, P.; Padmaja Divya, S.; Ahmed, S.O.; Melosantos, R.; Begum, R.; Concepcion, R.M.J.A.; Al-Sanea, N.; Ashari, L.H.; et al. APC truncating mutations in Middle Eastern Population: Tankyrase inhibitor is an effective strategy to sensitize APC mutant CRC To 5-FU chemotherapy. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2020, 121, 109572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fennell, L.J.; Kane, A.; Liu, C.; McKeone, D.; Fernando, W.; Su, C.; Bond, C.; Jamieson, S.; Dumenil, T.; Patch, A.M.; et al. APC Mutation Marks an Aggressive Subtype of BRAF Mutant Colorectal Cancers. Cancers 2020, 12, 1171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moshawih, S.; Lim, A.F.; Ardianto, C.; Goh, K.W.; Kifli, N.; Goh, H.P.; Jarrar, Q.; Ming, L.C. Target-Based Small Molecule Drug Discovery for Colorectal Cancer: A Review of Molecular Pathways and In Silico Studies. Biomolecules 2022, 12, 878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, L.R.; Hancock, R.E.; Pearson, T.W. Cationic antimicrobial peptide killing of African trypanosomes and Sodalis glossinidius, a bacterial symbiont of the insect vector of sleeping sickness. Vector Borne Zoonotic Dis. 2003, 3, 175–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGwire, B.S.; Olson, C.L.; Tack, B.F.; Engman, D.M. Killing of African trypanosomes by antimicrobial peptides. J. Infect. Dis. 2003, 188, 146–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, E.K.; Kim, Y.C.; Nan, Y.H.; Shin, S.Y. Cell selectivity, mechanism of action and LPS-neutralizing activity of bovine myeloid antimicrobial peptide-18 (BMAP-18) and its analogs. Peptides 2011, 32, 1123–1130. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Lee, C.W.; Kim, H.J.; Jung, H.H.; Kim, J.I.; Shin, S.Y.; Shin, S.H. Structural analysis and mode of action of BMAP-27, a cathelicidin-derived antimicrobial peptide. Peptides 2019, 118, 170106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoskin, D.W.; Ramamoorthy, A. Studies on anticancer activities of antimicrobial peptides. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2008, 1778, 357–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risso, A.; Zanetti, M.; Gennaro, R. Cytotoxicity and apoptosis mediated by two peptides of innate immunity. Cell Immunol. 1998, 189, 107–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Risso, A.; Braidot, E.; Sordano, M.C.; Vianello, A.; Macrì, F.; Skerlavaj, B.; Zanetti, M.; Gennaro, R.; Bernardi, P. BMAP-28, an antibiotic peptide of innate immunity, induces cell death through opening of the mitochondrial permeability transition pore. Mol. Cell Biol. 2002, 22, 1926–1935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hadwan, M.H.; Abed, H.N. Data supporting the spectrophotometric method for the estimation of catalase activity. Data Brief. 2015, 6, 194–199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liang, S.; Mao, Y.; Liao, M.; Xu, Y.; Chen, Y.; Huang, X.; Wei, C.; Wu, C.; Wang, Q.; Pan, X.; et al. Gut microbiome associated with APC gene mutation in patients with intestinal adenomatous polyps. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2020, 16, 135–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, L.; Shay, J.W. Multiple Roles of APC and its Therapeutic Implications in Colorectal Cancer. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2017, 109, djw332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lath, A.; Santal, A.R.; Kaur, N.; Kumari, P.; Singh, N.P. Anti-cancer peptides: Their current trends in the development of peptide-based therapy and anti-tumor drugs. Biotechnol. Genet Eng. Rev. 2023, 39, 45–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cragg, G.M.; Pezzuto, J.M. Natural Products as a Vital Source for the Discovery of Cancer Chemotherapeutic and Chemopreventive Agents. Med. Princ Pract. 2016, 25 (Suppl. 2), 41–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zanetti, M.; Gennaro, R.; Skerlavaj, B.; Tomasinsig, L.; Circo, R. Cathelicidin peptides as candidates for a novel class of antimicrobials. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2002, 8, 779–793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amerikova, M.; Pencheva El-Tibi, I.; Maslarska, V.; Bozhanov, S.; Tachkov, K. Antimicrobial activity, mechanism of action, and methods for stabilisation of defensins as new therapeutic agents. Biotechnol. Biotechnol. Equip. 2019, 33, 671–682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, S.A.; Lee, W.H.; Zhang, Y. Efficacy of OH-CATH30 and its analogs against drug-resistant bacteria in vitro and in mouse models. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2012, 56, 3309–3317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yadav, V.; Misra, R. A review emphasizing on utility of heptad repeat sequence as a tool to design pharmacologically safe peptide-based antibiotics. Biochimie 2021, 191, 126–139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall’Olio, F.G.; Marabelle, A.; Caramella, C.; Garcia, C.; Aldea, M.; Chaput, N.; Robert, C.; Besse, B. Tumour burden and efficacy of immune-checkpoint inhibitors. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2022, 19, 75–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bohers, E.; Viailly, P.J.; Becker, S.; Marchand, V.; Ruminy, P.; Maingonnat, C.; Bertrand, P.; Etancelin, P.; Picquenot, J.M.; Camus, V.; et al. Non-invasive monitoring of diffuse large B-cell lymphoma by cell-free DNA high-throughput targeted sequencing: Analysis of a prospective cohort. Blood Cancer J. 2018, 8, 74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tas, F.; Aykan, F.; Alici, S.; Kaytan, E.; Aydiner, A.; Topuz, E. Prognostic factors in pancreatic carcinoma: Serum LDH levels predict survival in metastatic disease. Am. J. Clin. Oncol. 2001, 24, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zińczuk, J.; Maciejczyk, M.; Zaręba, K.; Romaniuk, W.; Markowski, A.; Kędra, B.; Zalewska, A.; Pryczynicz, A.; Matowicka-Karna, J.; Guzińska-Ustymowicz, K. Antioxidant Barrier, Redox Status, and Oxidative Damage to Biomolecules in Patients with Colorectal Cancer. Can Malondialdehyde and Catalase Be Markers of Colorectal Cancer Advancement? Biomolecules 2019, 9, 637. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Özsoy, S.; Becer, E.; Kabadayı, H.; Vatansever, H.S.; Yücecan, S. Quercetin-Mediated Apoptosis and Cellular Senescence in Human Colon Cancer. Anticancer Agents Med. Chem. 2020, 20, 1387–1396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dai, L.; Wang, X.; Bai, T.; Liu, J.; Chen, B.; Li, T.; Yang, W. Identification of a novel cellular senescence-related signature for the prediction of prognosis and immunotherapy response in colon cancer. Front. Genet. 2022, 13, 961554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scopa, C.D.; Vagianos, C.; Kardamakis, D.; Kourelis, T.G.; Kalofonos, H.P.; Tsamandas, A.C. bcl-2/bax ratio as a predictive marker for therapeutic response to radiotherapy in patients with rectal cancer. Appl. Immunohistochem. Mol. Morphol. 2001, 9, 329–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khodapasand, E.; Jafarzadeh, N.; Farrokhi, F.; Kamalidehghan, B.; Houshmand, M. Is Bax/Bcl-2 ratio considered as a prognostic marker with age and tumor location in colorectal cancer? Iran Biomed. J. 2015, 19, 69–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yousuf, M.; Khan, P.; Shamsi, A.; Shahbaaz, M.; Hasan, G.M.; Haque, Q.M.R.; Christoffels, A.; Islam, A.; Hassan, M.I. Inhibiting CDK6 Activity by Quercetin Is an Attractive Strategy for Cancer Therapy. ACS Omega 2020, 5, 27480–27491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, H.; Huang, T.; Xiong, Y.; Peng, L.; Wang, R.; Zhang, G.J. The prognostic value of proliferating cell nuclear antigen expression in colorectal cancer: A meta-analysis. Medicine (Baltimore) 2018, 97, e13752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorroño-Etxebarria, I.; Aguirre, U.; Sanchez, S.; González, N.; Escobar, A.; Zabalza, I.; Quintana, J.M.; Vivanco, M.D.; Waxman, J.; Kypta, R.M. Wnt-11 as a Potential Prognostic Biomarker and Therapeutic Target in Colorectal Cancer. Cancers 2019, 11, 908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakayama, M.; Oshima, M. Mutant p53 in colon cancer. J. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019, 11, 267–276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.L.; Zhou, J.; Chen, Z.R.; Chng, W.J. P53 mutations in colorectal cancer–molecular pathogenesis and pharmacological reactivation. World J. Gastroenterol. 2015, 21, 84–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakamura, T.; Hamada, F.; Ishidate, T.; Anai, K.; Kawahara, K.; Toyoshima, K.; Akiyama, T. Axin, an inhibitor of the Wnt signalling pathway, interacts with beta-catenin, GSK-3beta and APC and reduces the beta-catenin level. Genes Cells 1998, 3, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.T.; Wang, J.Y.; Chen, M.K.; Chen, H.C.; Chang, T.H.; Su, B.W.; Chang, P.J. Colon cancer mesenchymal stem cells modulate the tumorigenicity of colon cancer through interleukin 6. Exp. Cell Res. 2013, 319, 2216–2229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Ao, X.; Shen, Z.; Ao, L.; Wu, X.; Pu, C.; Guo, W.; Xing, W.; He, M.; Yuan, H.; et al. TNF-α augments CXCL10/CXCR3 axis activity to induce Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition in colon cancer cell. Int. J. Biol. Sci. 2021, 17, 2683–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robichaux, D.J.; Harata, M.; Murphy, E.; Karch, J. Mitochondrial permeability transition pore-dependent necrosis. J. Mol. Cell Cardiol. 2023, 174, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
Bar diagram representing the viability and cytotoxicity of (a) SW480 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 cells; (b) SW620 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW620 cells at 72 hrs.
Figure 1.
Bar diagram representing the viability and cytotoxicity of (a) SW480 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 cells; (b) SW620 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW620 cells at 72 hrs.
Figure 2.
Bar diagram representing the difference in proliferation of (a) SW480 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 cells; (b) SW620 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW620 cells at 24, 48, and 72 hrs.
Figure 2.
Bar diagram representing the difference in proliferation of (a) SW480 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 cells; (b) SW620 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW620 cells at 24, 48, and 72 hrs.
Figure 3.
Bar diagram representing the percentage of LDH release by (a) SW480 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 cells; (b) SW620 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW620 cells.
Figure 3.
Bar diagram representing the percentage of LDH release by (a) SW480 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 cells; (b) SW620 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW620 cells.
Figure 4.
Bar diagram representing the catalase activity in (a) SW480 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 cells; (b) SW620 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW620 cells.
Figure 4.
Bar diagram representing the catalase activity in (a) SW480 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 cells; (b) SW620 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW620 cells.
Figure 5.
Figure representing the SA-β-Gal staining images of (a) SW480 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 cells; (b) SW620 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW620 cells.
Figure 5.
Figure representing the SA-β-Gal staining images of (a) SW480 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 cells; (b) SW620 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW620 cells.
Figure 6.
Expression profile of pro-apoptotic marker CASPASE3 and BAX, anti-apoptotic marker BCL-2, cell proliferation markers CDK-6 and PCNA, tumour suppressor marker TP53, Wnt signalling markers WNT11, AXIN1, and CTNNB1 in (a) SW480 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 cells; (b) SW620 and BMAP-27 peptide treated SW620 cells.
Figure 6.
Expression profile of pro-apoptotic marker CASPASE3 and BAX, anti-apoptotic marker BCL-2, cell proliferation markers CDK-6 and PCNA, tumour suppressor marker TP53, Wnt signalling markers WNT11, AXIN1, and CTNNB1 in (a) SW480 and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 cells; (b) SW620 and BMAP-27 peptide treated SW620 cells.
Figure 7.
Bar diagram representing the concentration of (a,b) IL-6, (c,d) IFN-γ, (e,f) CXCL-10, (g,h) cytochrome c in SW480, SW620, and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 and SW620 cells.
Figure 7.
Bar diagram representing the concentration of (a,b) IL-6, (c,d) IFN-γ, (e,f) CXCL-10, (g,h) cytochrome c in SW480, SW620, and BMAP-27 peptide-treated SW480 and SW620 cells.
Figure 8.
Docked structure of (a) 1LUJ and BMAP-27 and (b) 4YJL and BMAP-27.
Figure 8.
Docked structure of (a) 1LUJ and BMAP-27 and (b) 4YJL and BMAP-27.
Figure 9.
RMSD plot of (a) 1LUJ and BMAP-27 and (b) 4YJL and BMAP-27.
Figure 9.
RMSD plot of (a) 1LUJ and BMAP-27 and (b) 4YJL and BMAP-27.
Figure 10.
Radius of gyration plot of (a) 1LUJ and BMAP-27 and (b) 4YJL and BMAP-27.
Figure 10.
Radius of gyration plot of (a) 1LUJ and BMAP-27 and (b) 4YJL and BMAP-27.
Figure 11.
Solvent-accessible surface area of (a) 1LUJ and BMAP-27 and (b) 4YJL and BMAP-27.
Figure 11.
Solvent-accessible surface area of (a) 1LUJ and BMAP-27 and (b) 4YJL and BMAP-27.
Table 1.
Molecular docking results between BMAP-27 of APC-protein and β-catenin.
Table 1.
Molecular docking results between BMAP-27 of APC-protein and β-catenin.
| System |
Docking Score |
Confidence Score |
BMAP RMSD ( Å) |
| 1LUJ-BMAP-27 |
-249.43 |
0.8796 |
29.79 |
| 4YJL-BMAP-27 |
-284.80 |
0.9368 |
22.56 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).