Submitted:
31 July 2023
Posted:
02 August 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
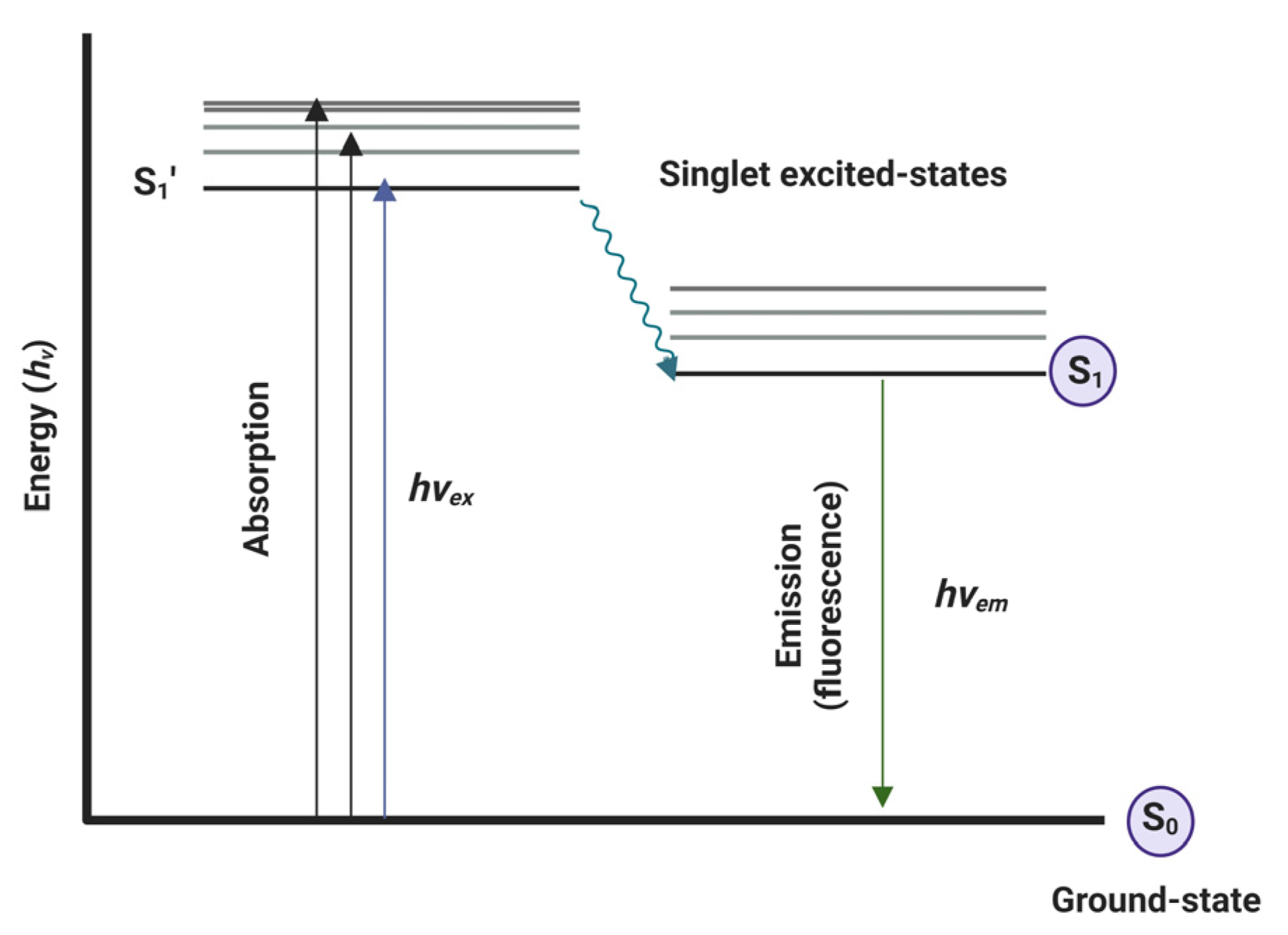
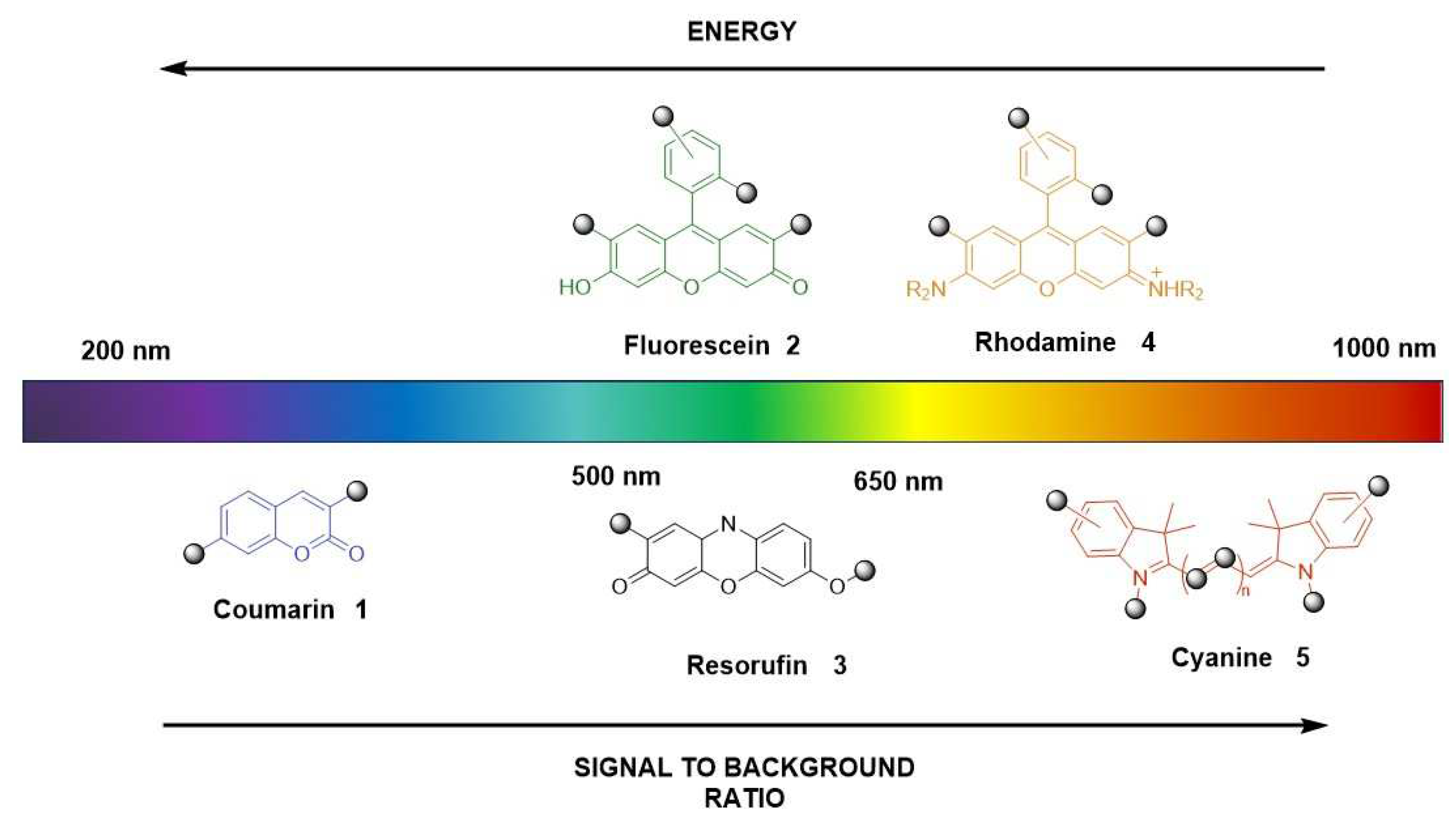
2. Optical fluorescence technique and fluorescent probes
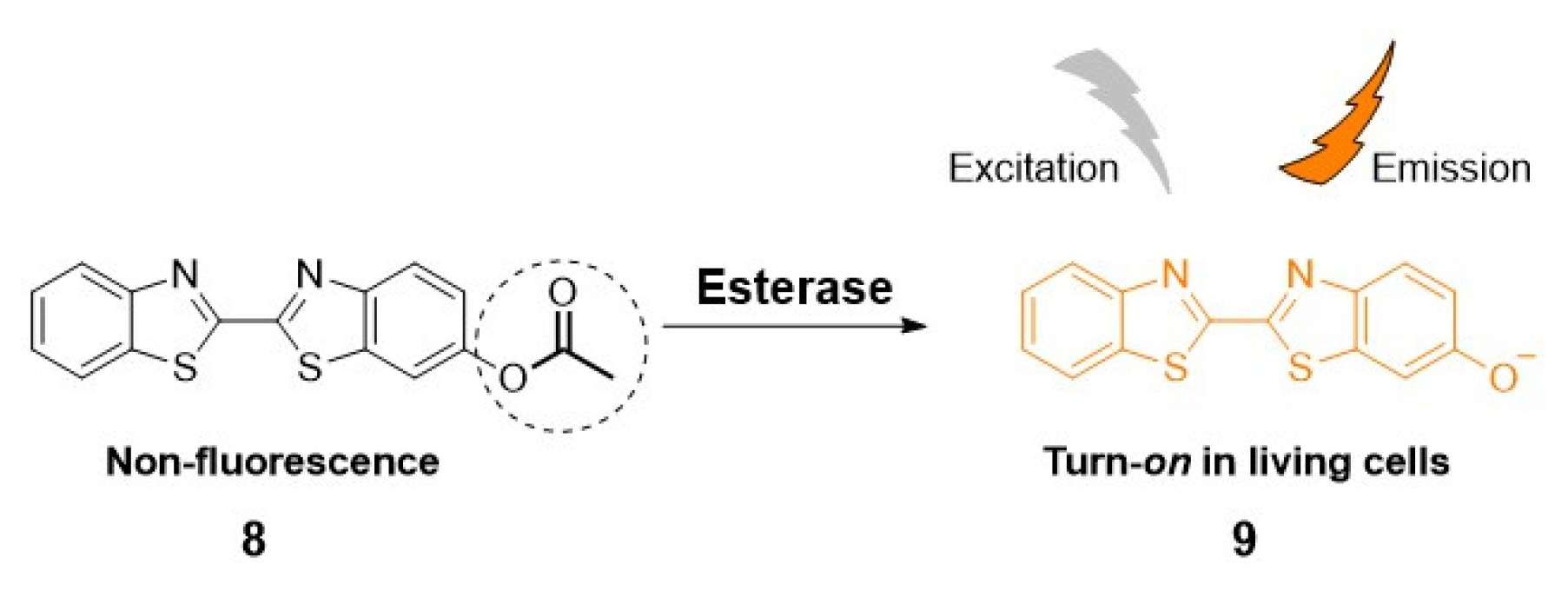
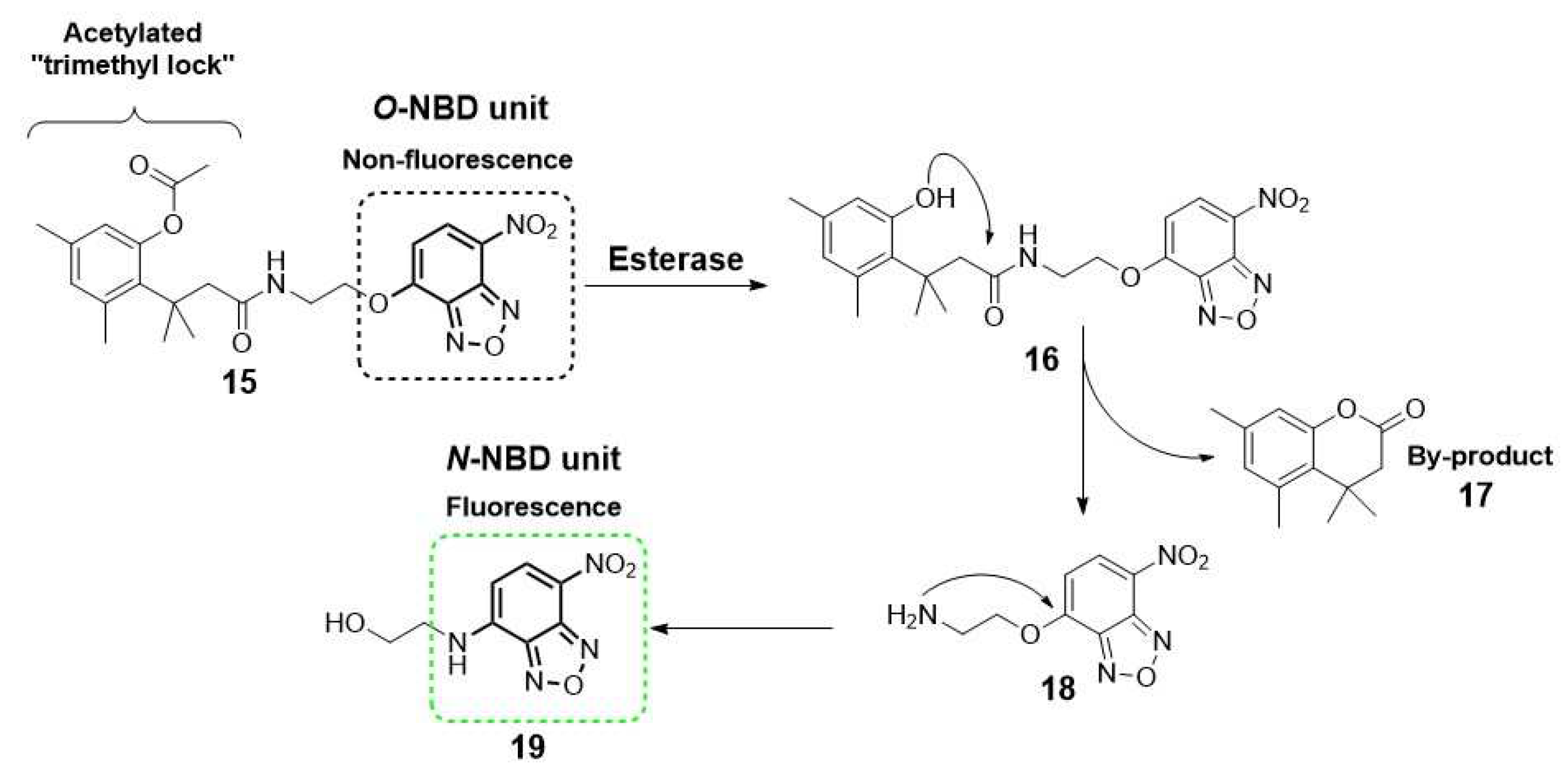
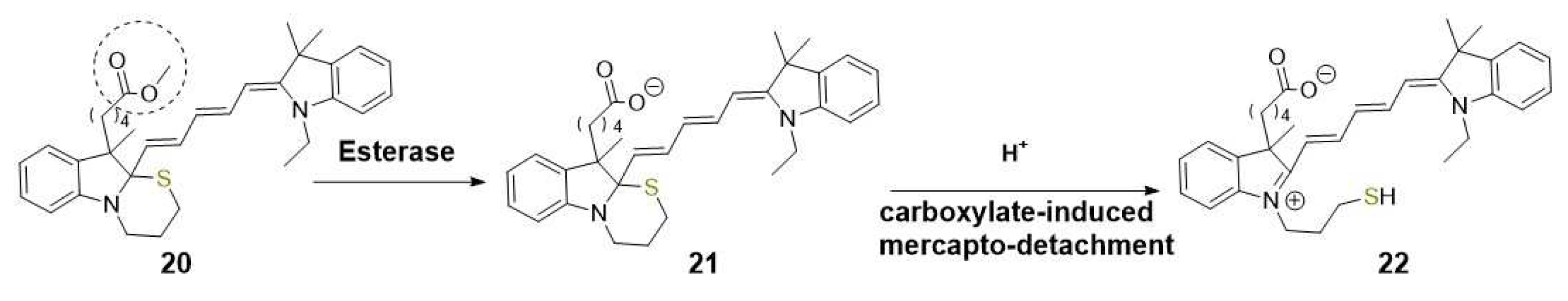
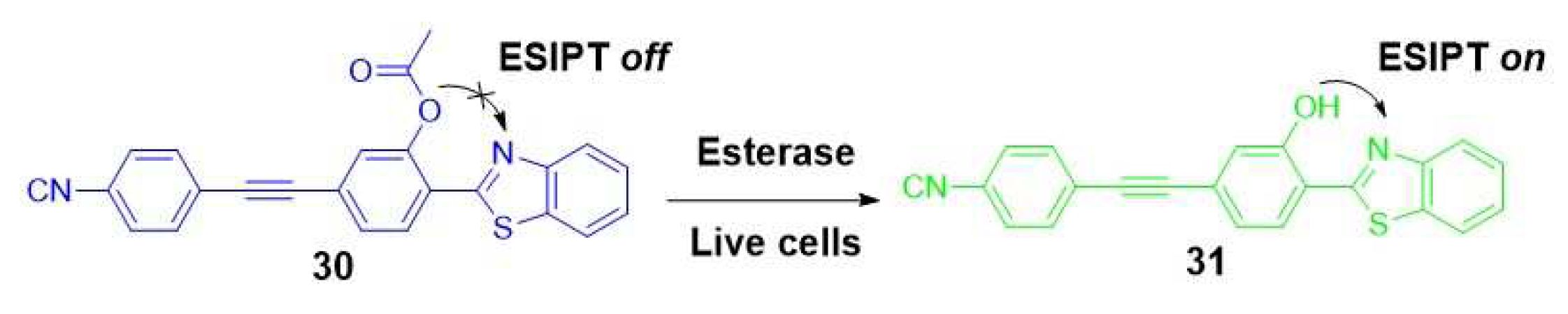
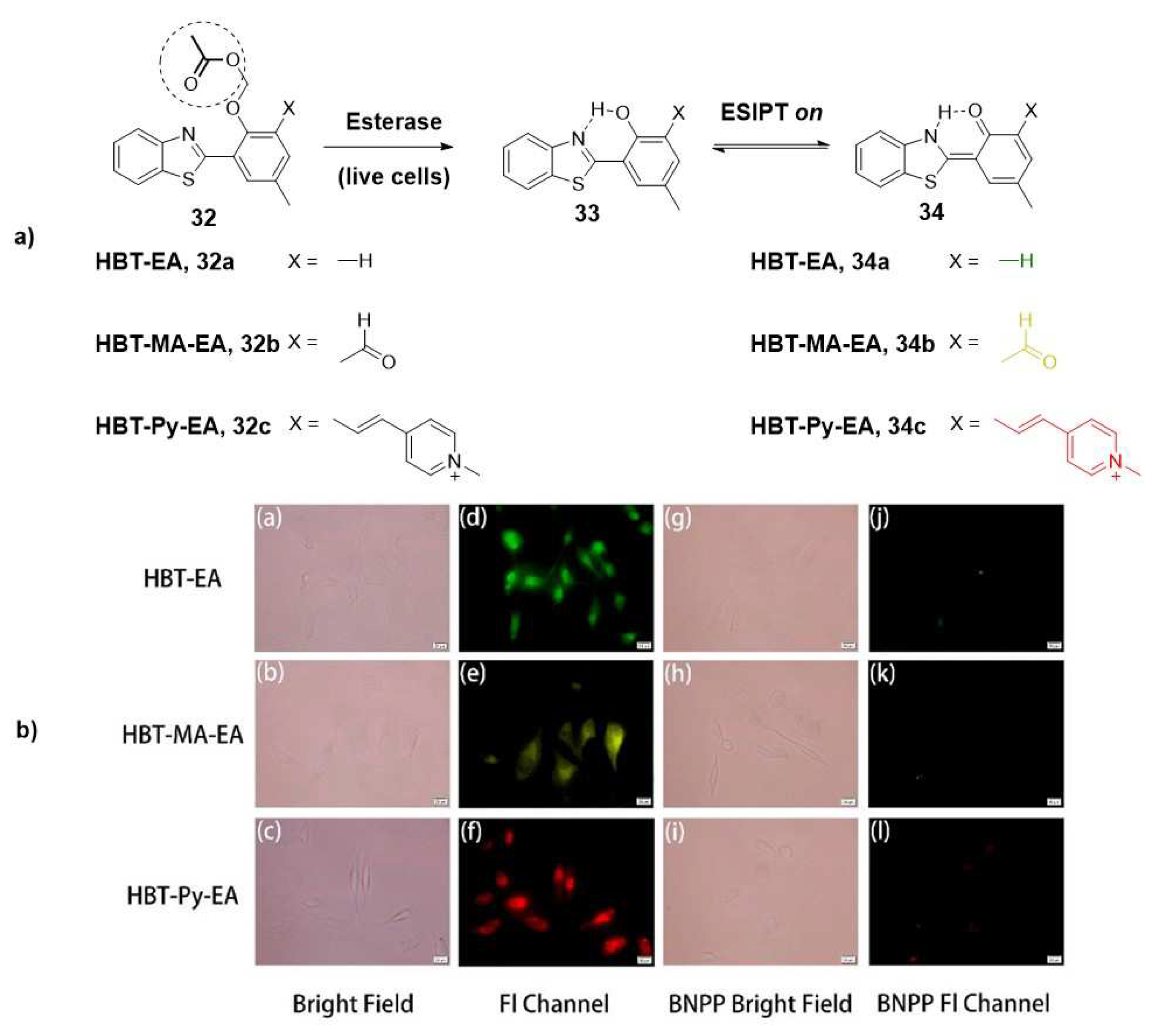
2.1. Imaging and therapy: fluorescent probes for esterases
2.1.1. Cells viability
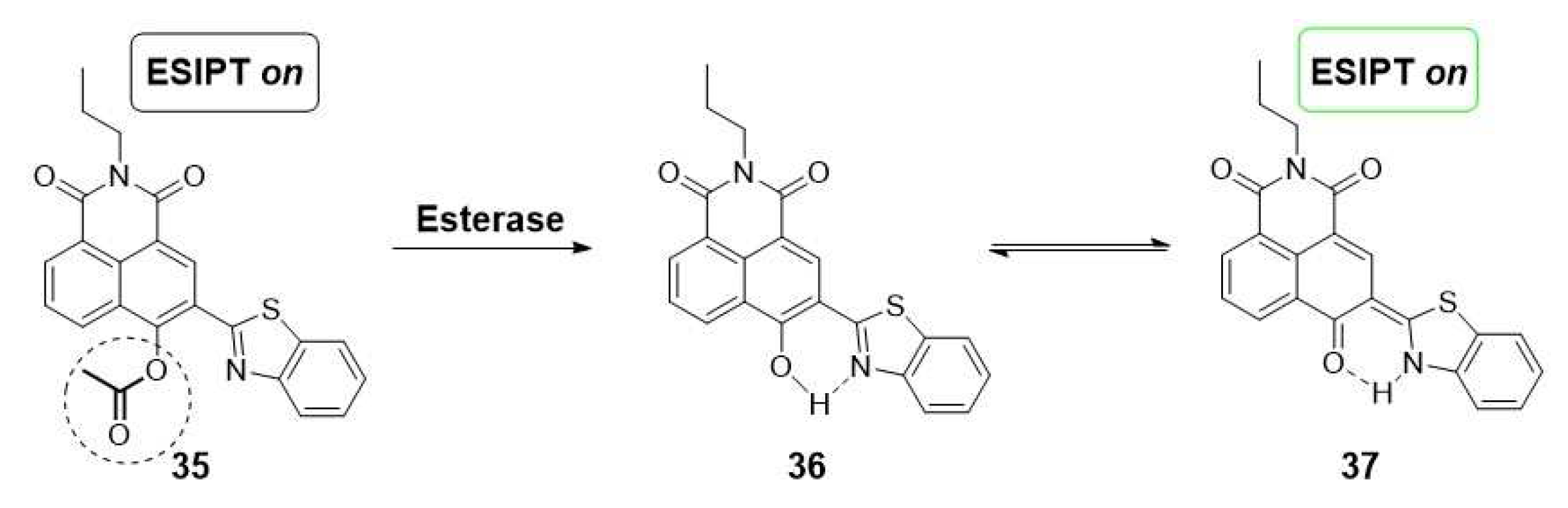
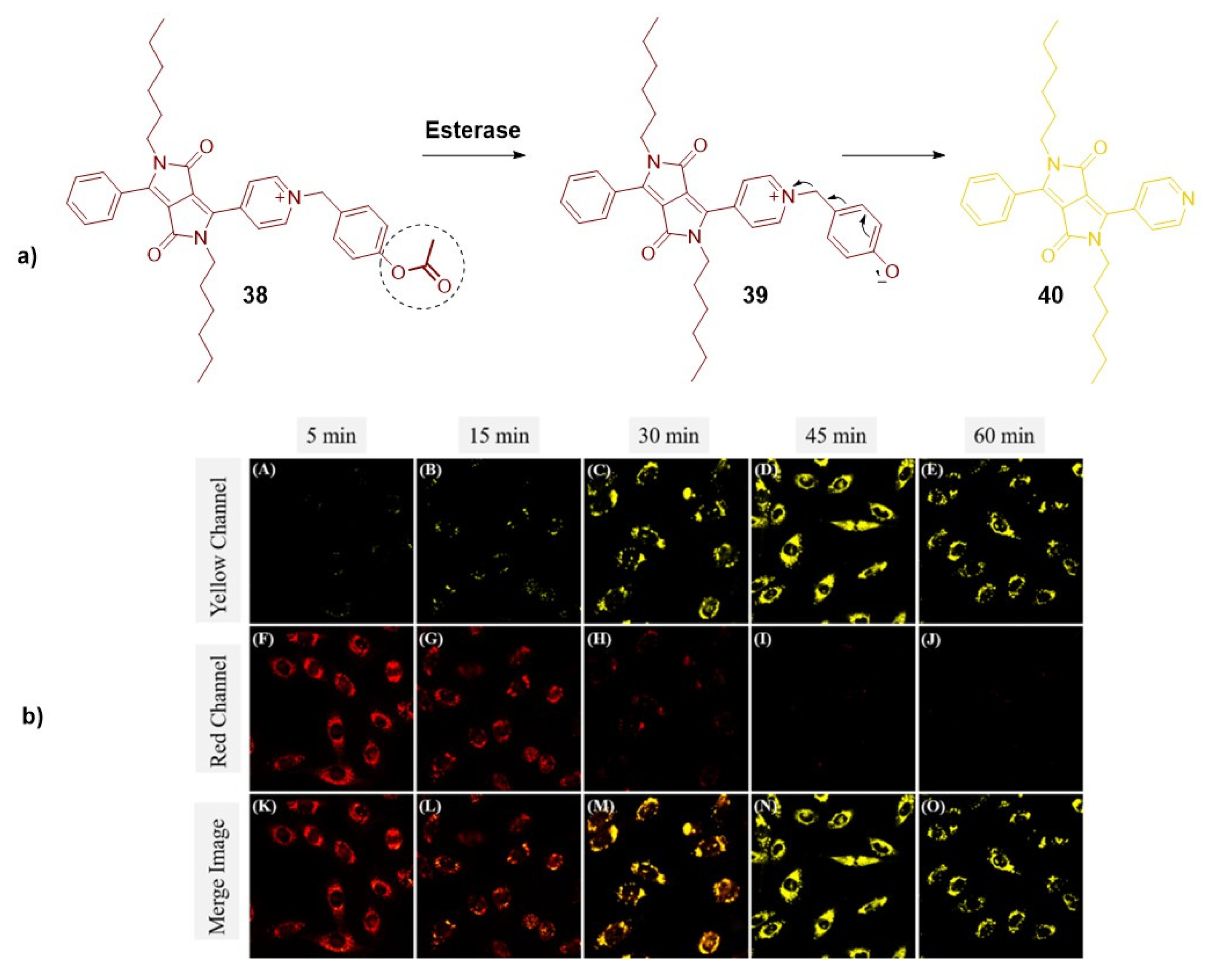
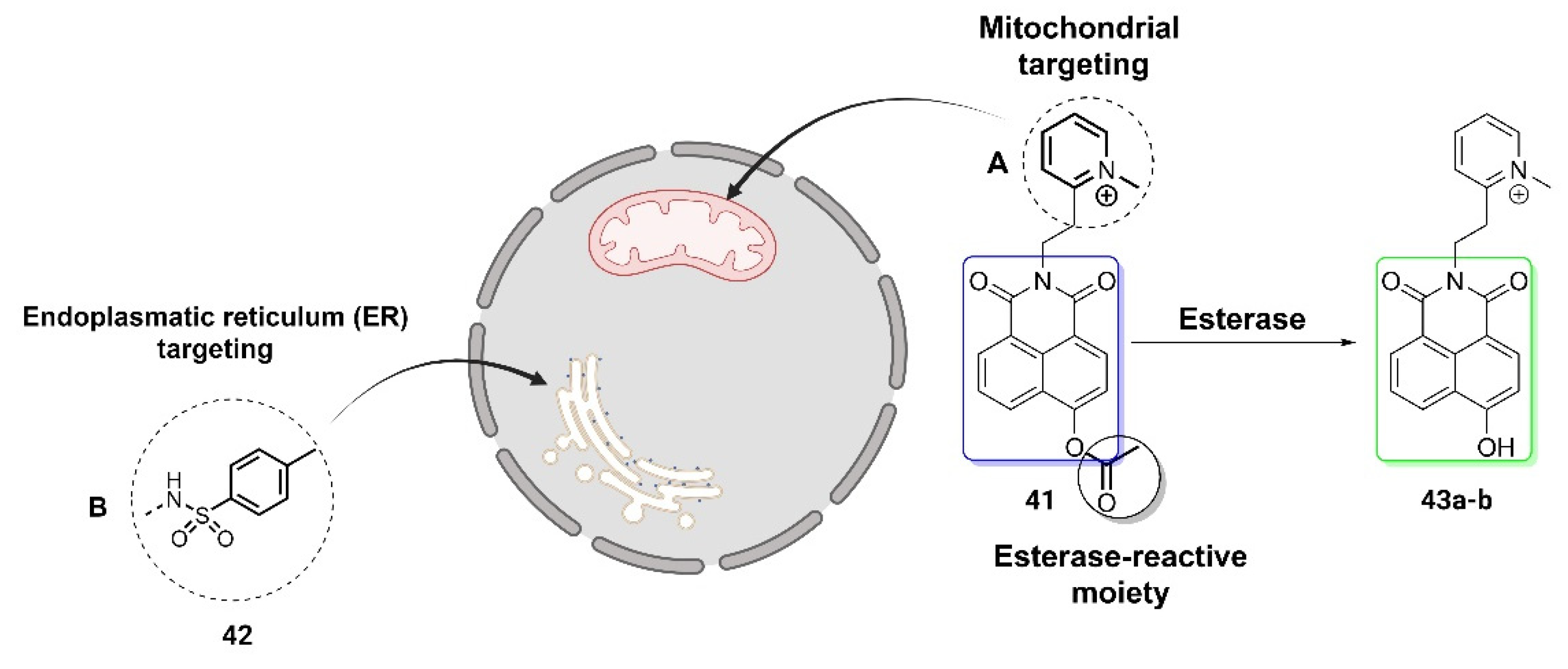
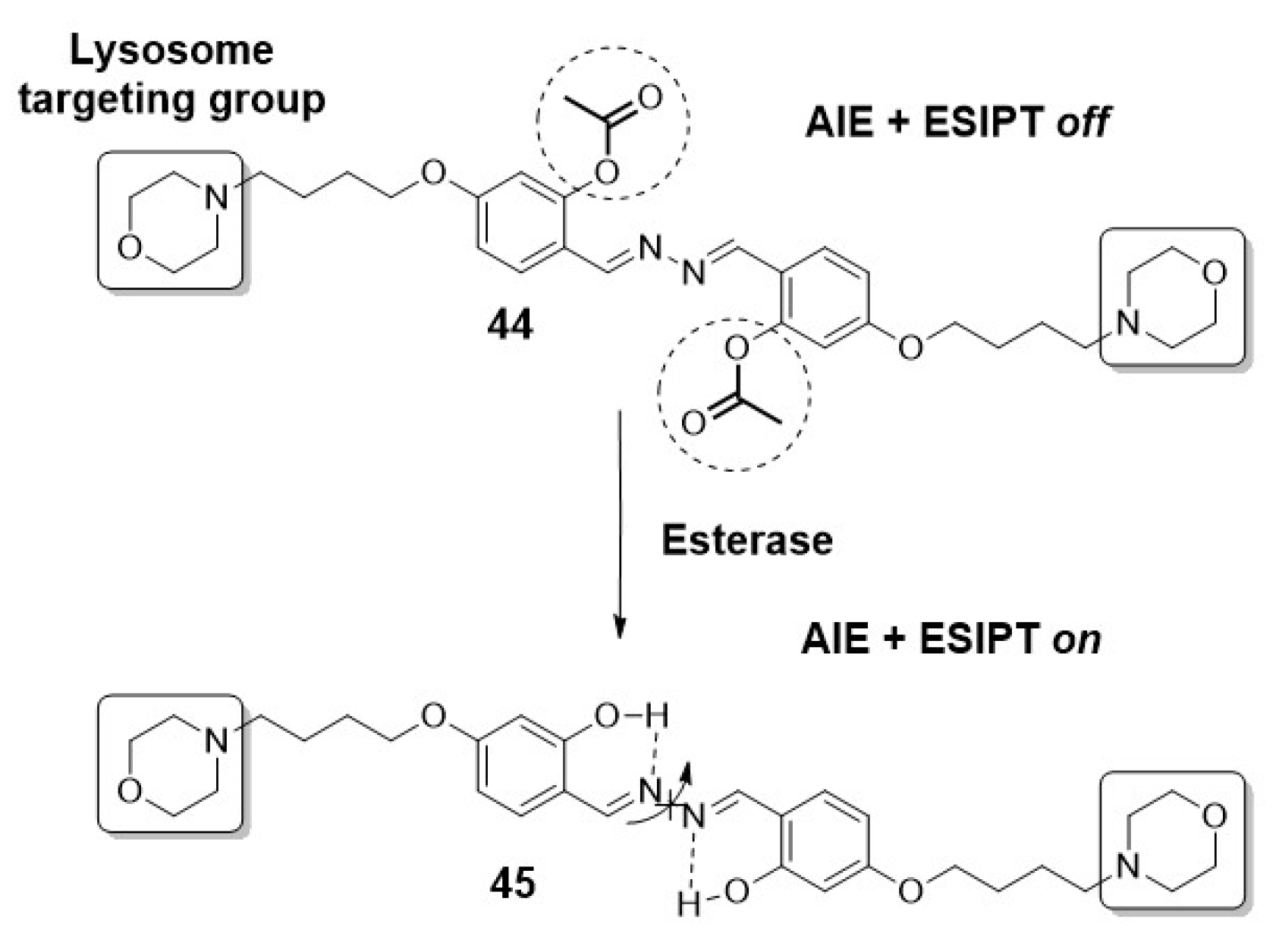
2.1.2. Organelles-targeted fluorescent probes.
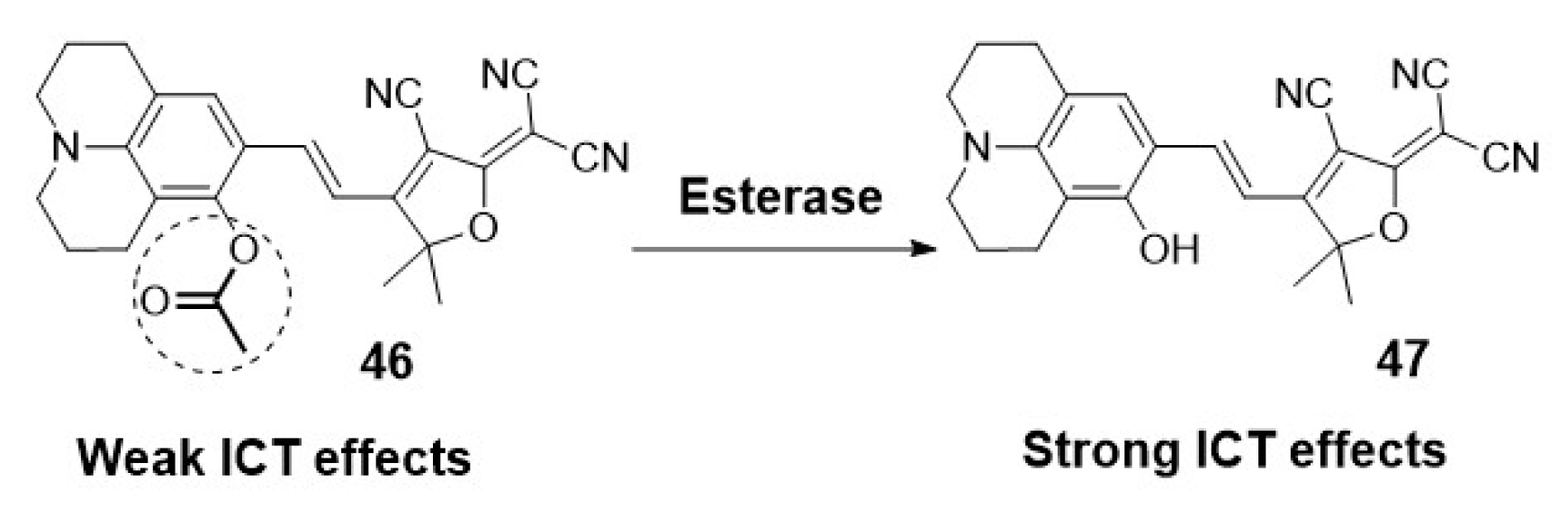
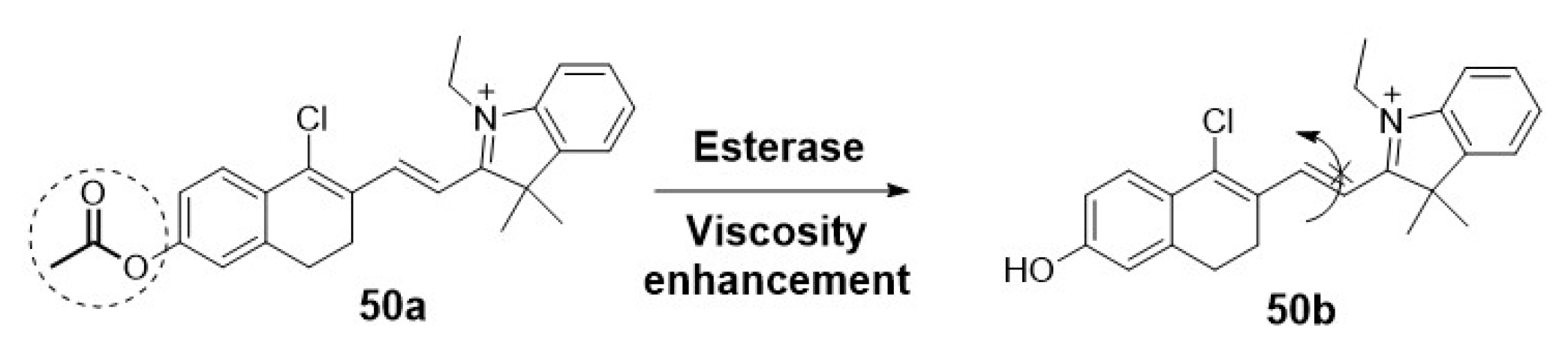
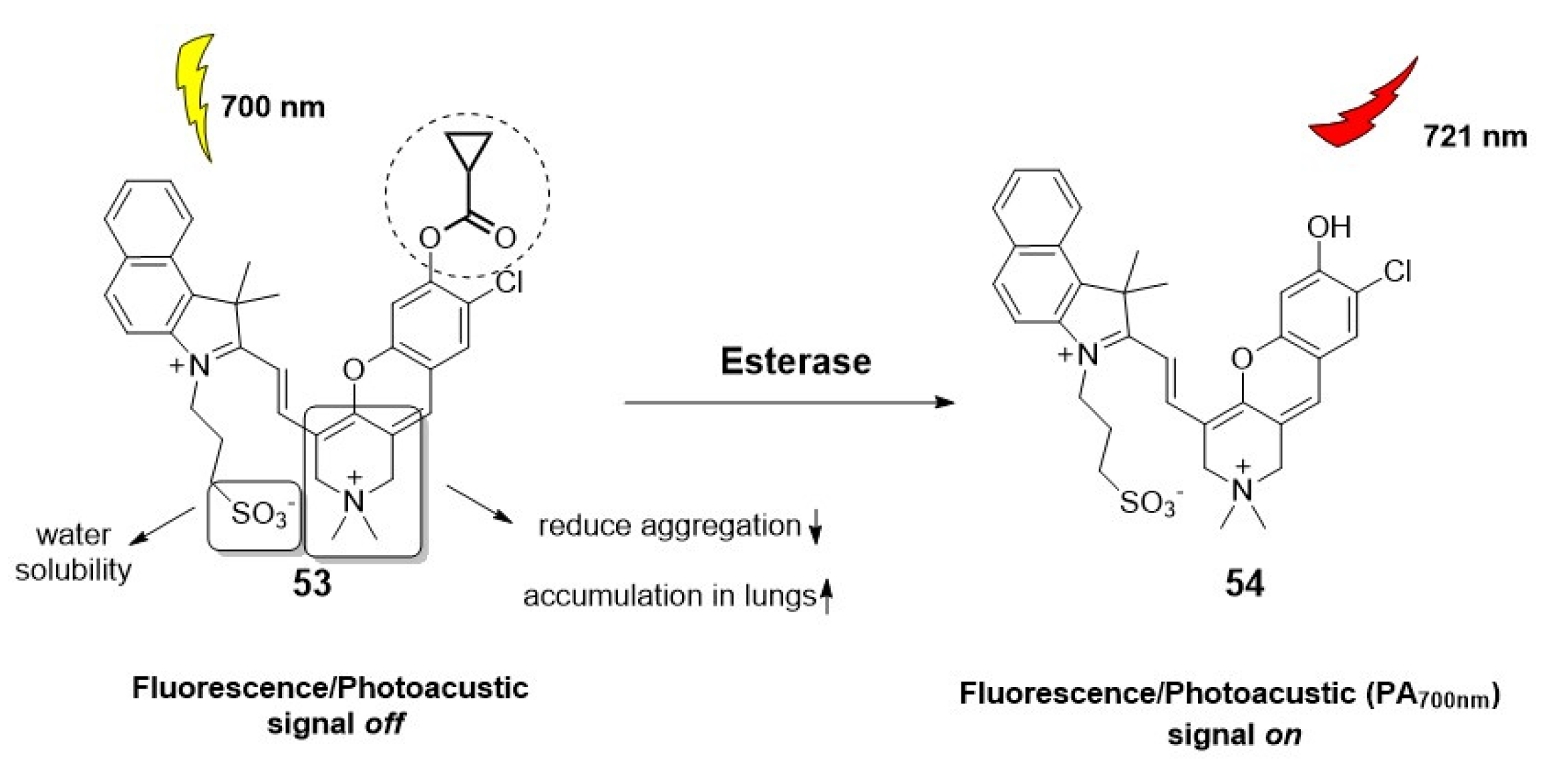
2.1.3. Fluorescent probes for tissues and organs.
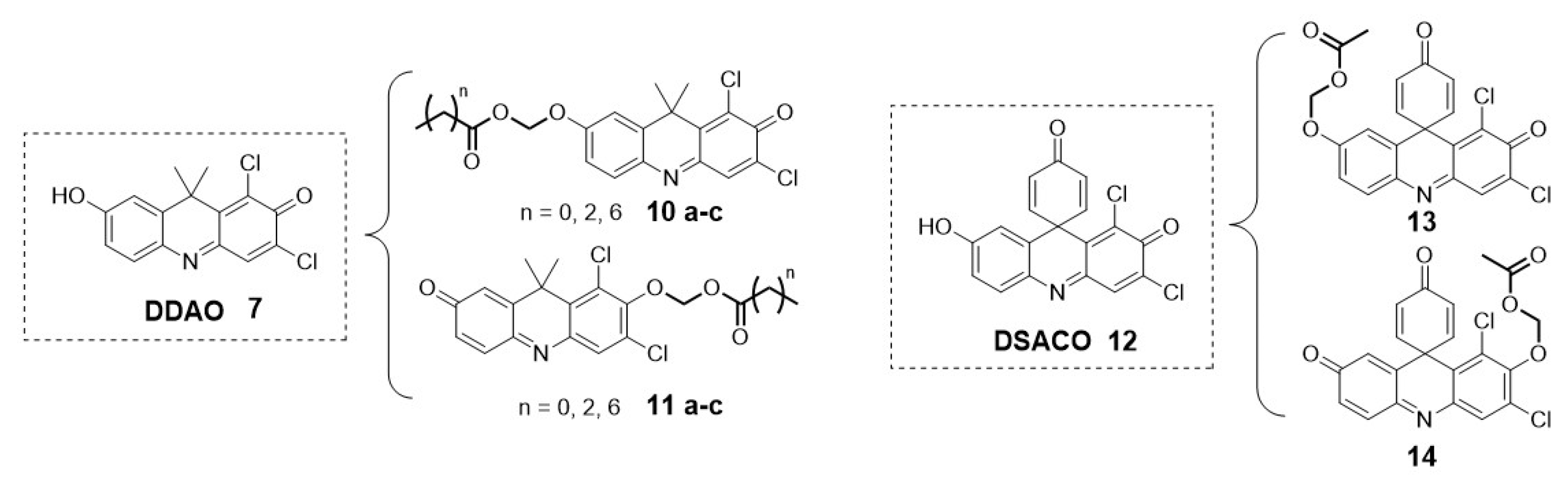
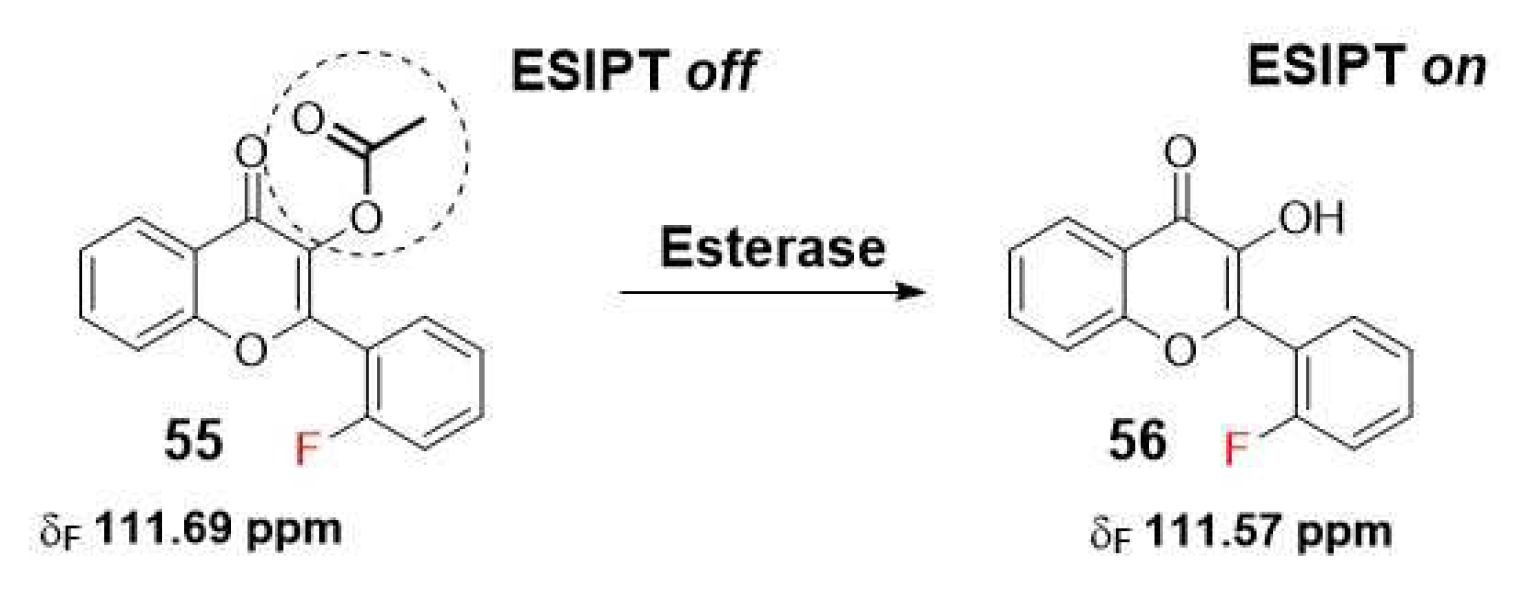
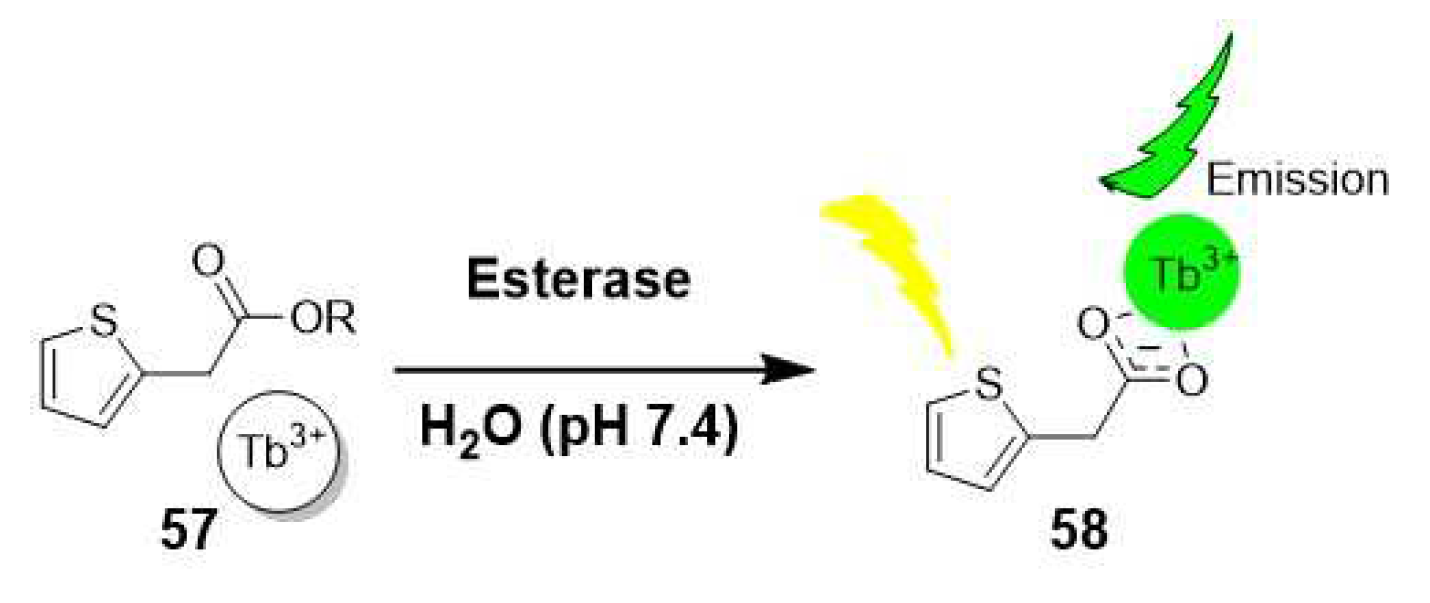
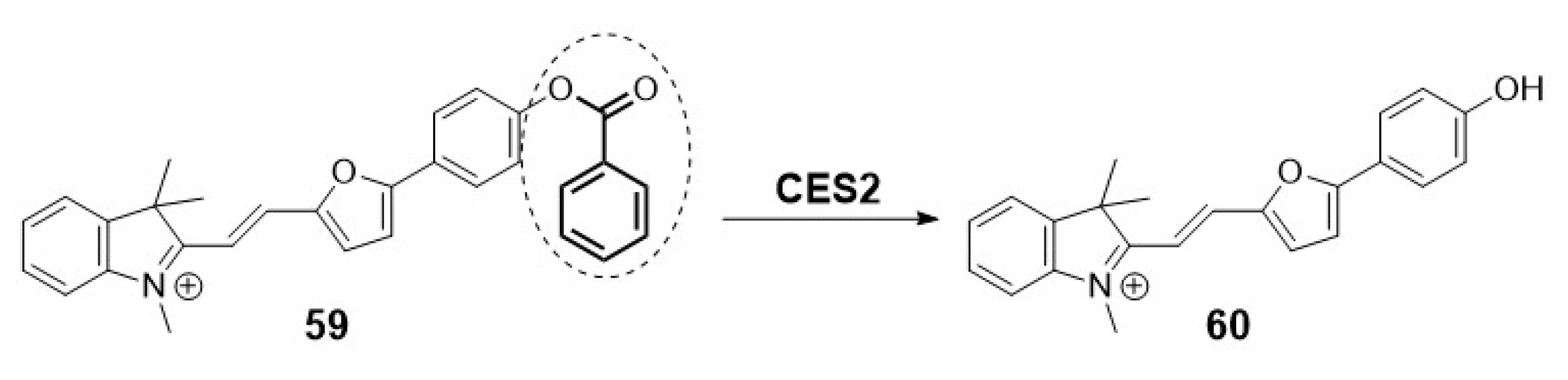
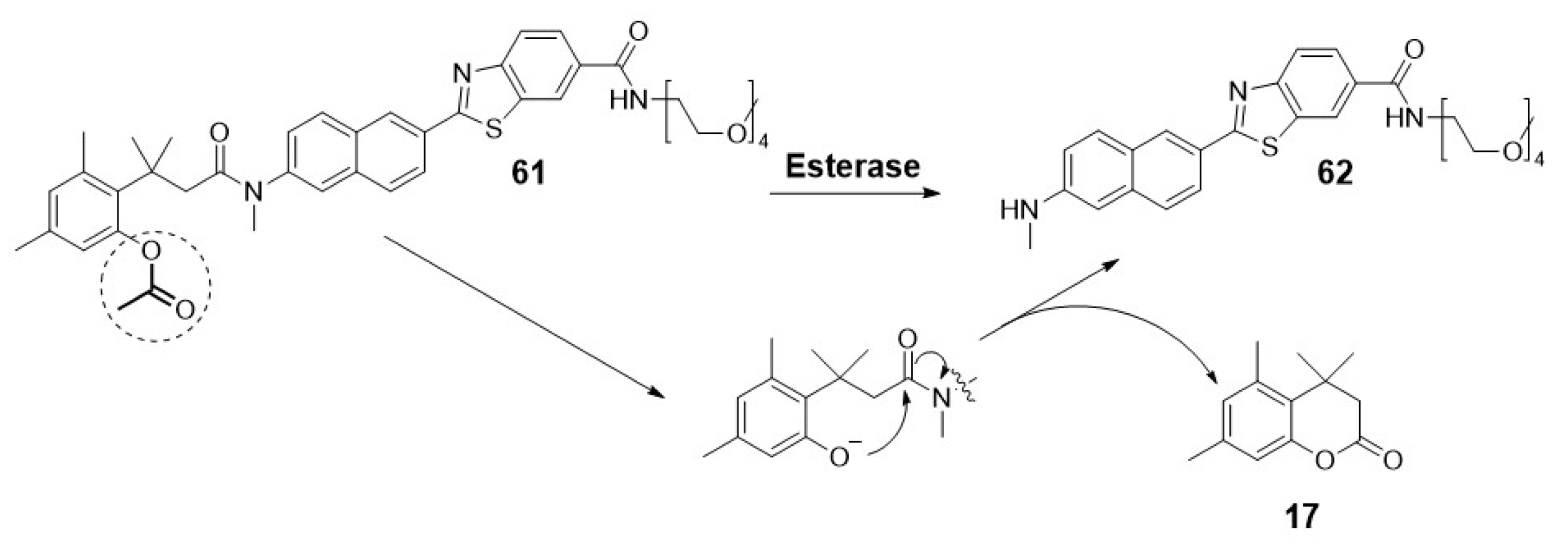
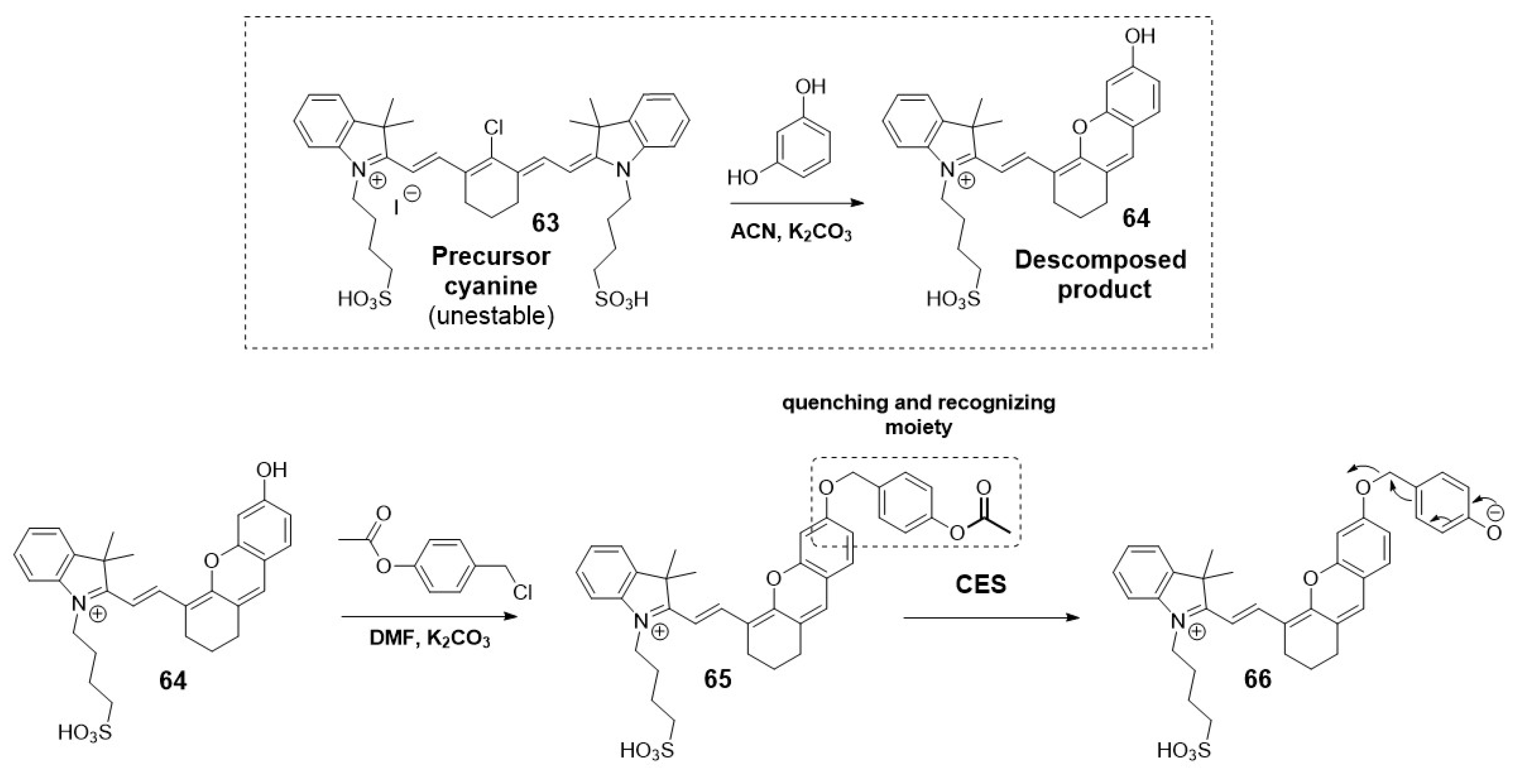
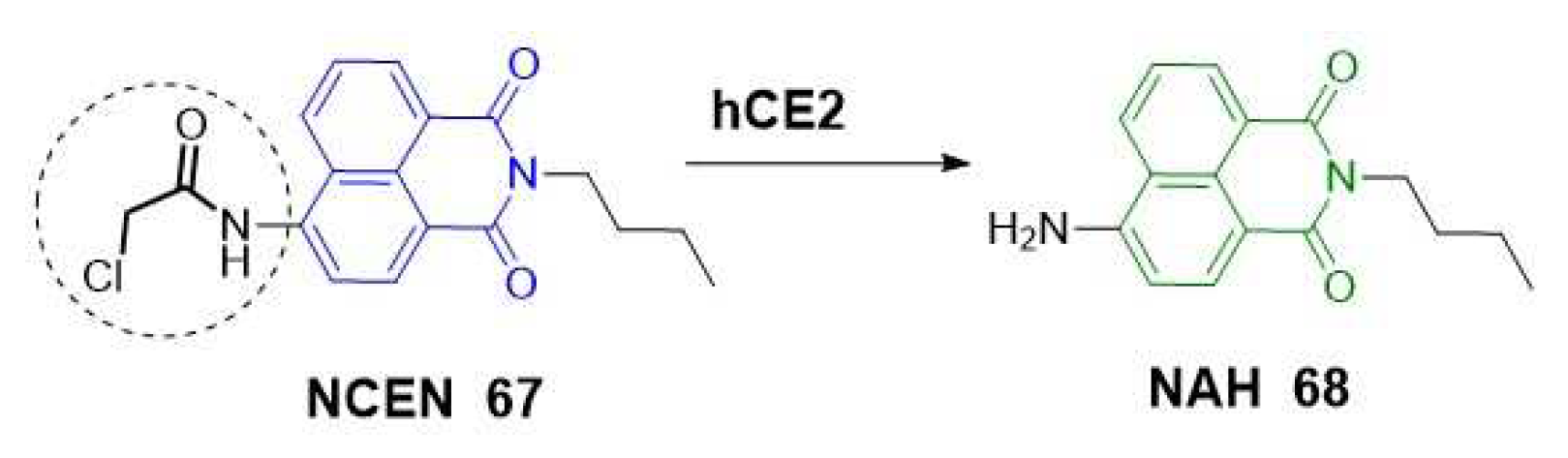
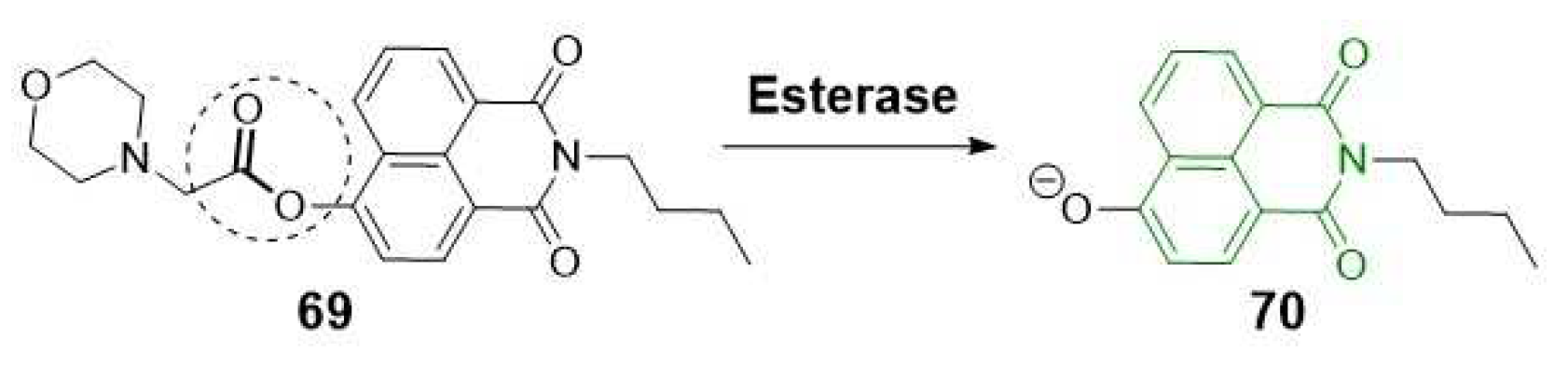
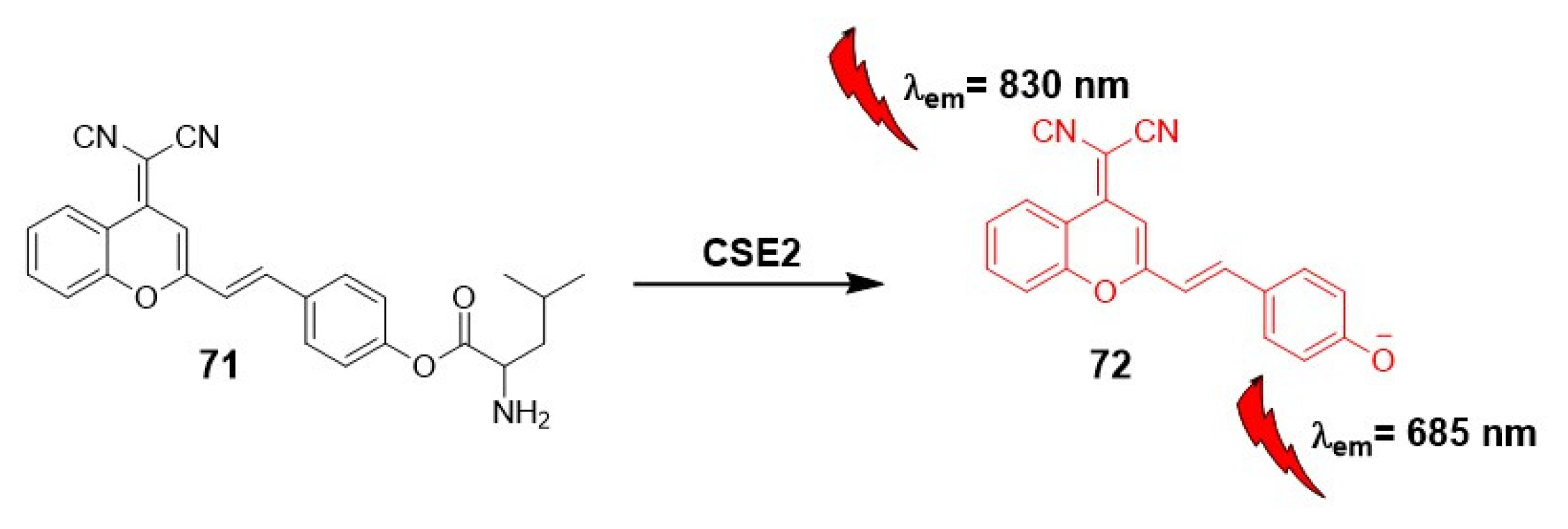
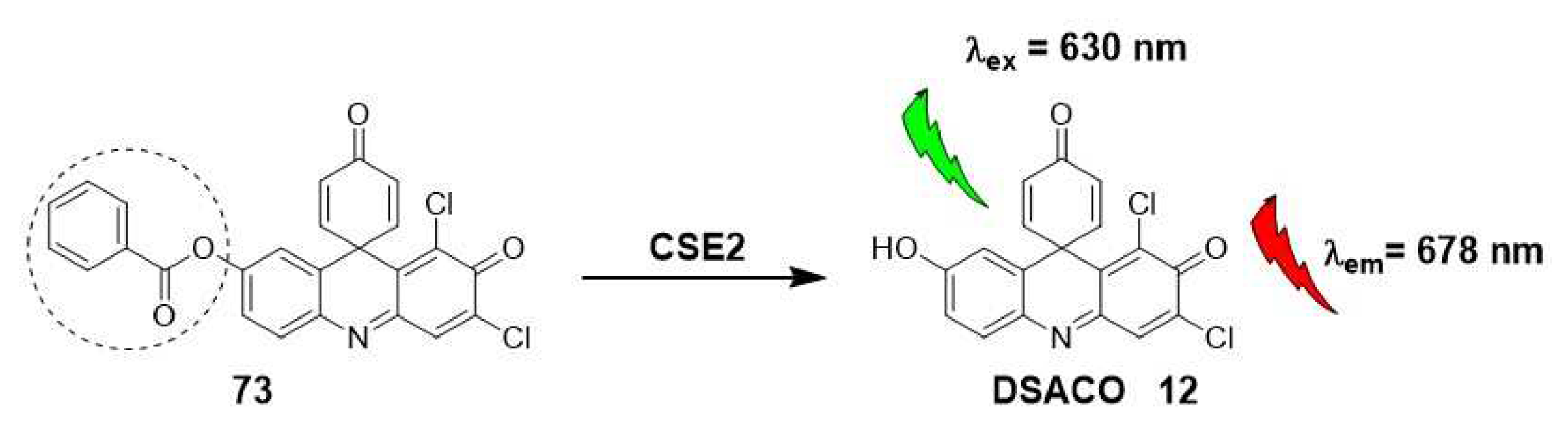
2.1.4. Carboxylesterases
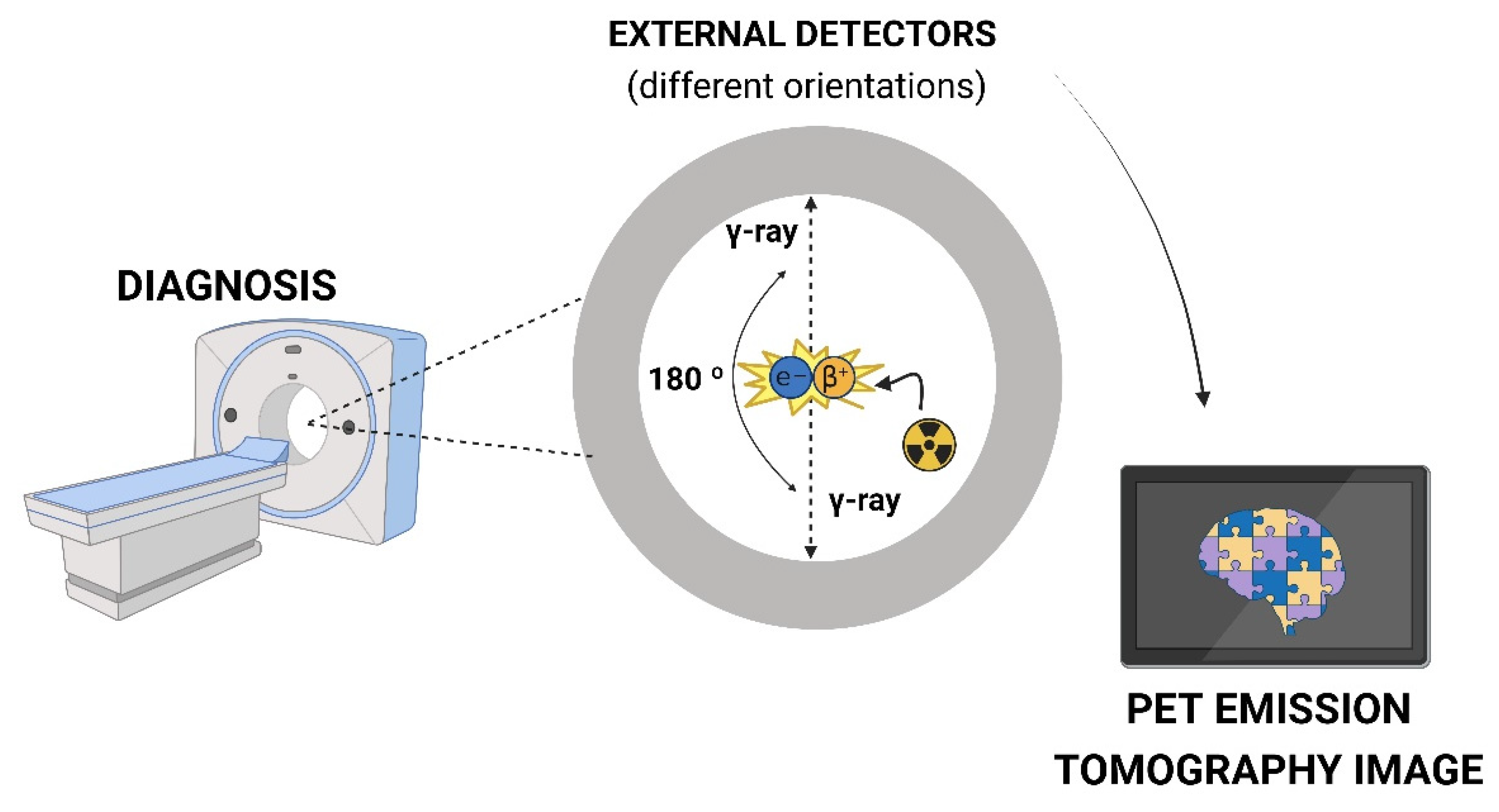
3. PET technique and PET probes
3.1. Non-invasive nuclear molecular imaging on neurological disorders
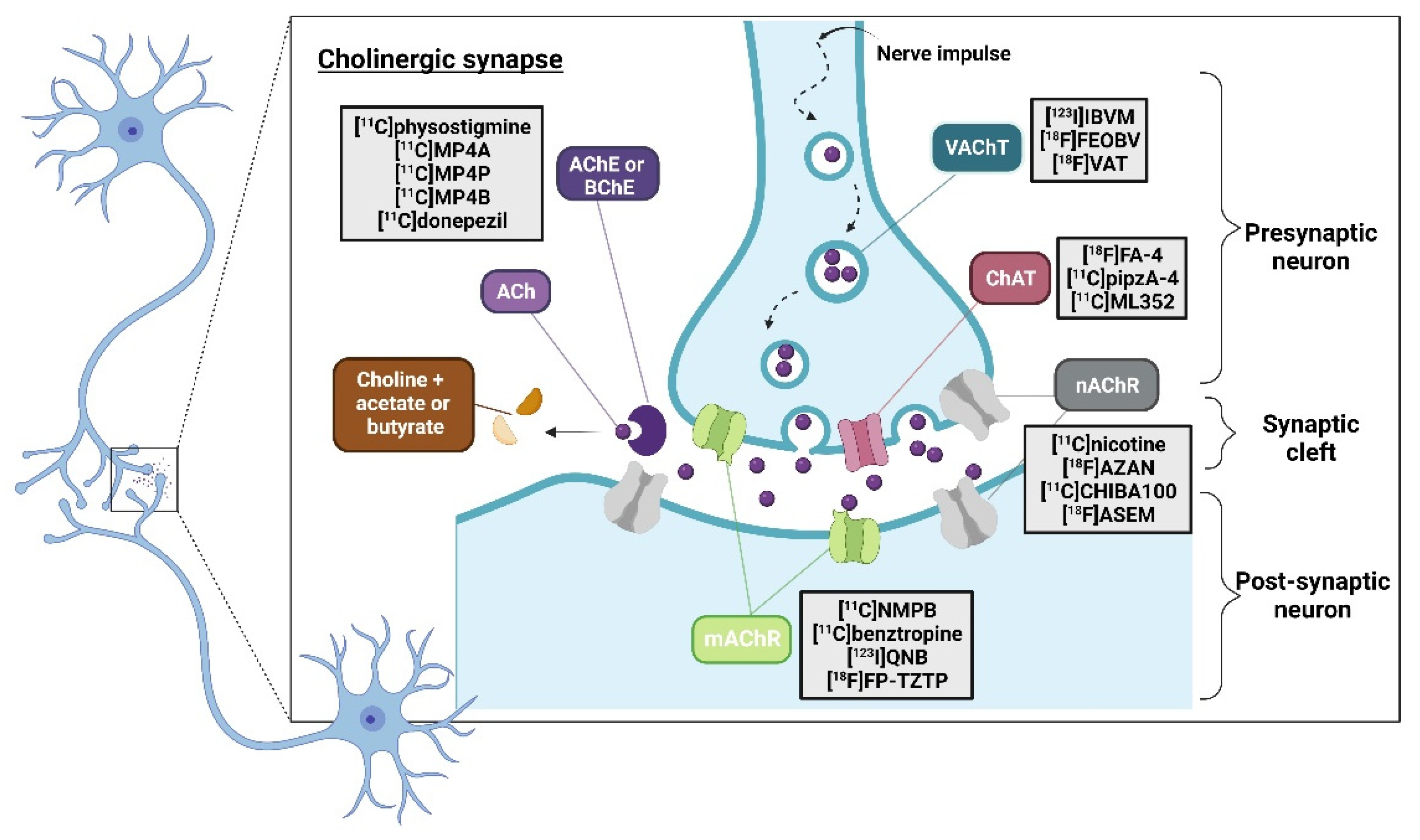
3.1.1. PET probes for imaging AChE and BChE in dementia disorders
First class of AChE´s PET probes (labeled AChEIs)
Second class of AChE´s PET probes (analogues of ACh)
4. Materials and Methods
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Wu, X.F.; Shi, W.; Li, X.H.; Ma, H.M. Recognition Moieties of Small Molecular Fluorescent Probes for Bioimaging of Enzymes. Accounts of Chemical Research 2019, 52, 1892-1904. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.M.; Teng, Z.D.; Zhang, L.; Yang, Y.X.; Qian, J.; Cao, T.; Cao, Y.P.; Qin, W.W.; Liu, Y.; Guo, H.C. Multifunctional Near-Infrared Fluorescent Probes with Different Ring-Structure Trigger Groups for Cell Health Monitoring and In Vivo Esterase Activity Detection. Acs Sensors 2020, 5, 3264-3273. [CrossRef]
- Fukami, T.; Yokoi, T. The Emerging Role of Human Esterases. Drug Metabolism and Pharmacokinetics 2012, 27, 466-477. [CrossRef]
- Dai, J.A.; Hou, Y.D.; Wu, J.C.; Shen, B.X. A Minireview of Recent Reported Carboxylesterase Fluorescent Probes: Design and Biological Applications. Chemistryselect 2020, 5, 11185-11196. [CrossRef]
- Kong, Q.; Wang, J.; Chen, Y.H.; Zheng, S.Y.; Chen, X.Q.; Wang, Y.H.; Wang, F. The visualized fluorescent probes based on benzothiazole used to detect esterase. Dyes and Pigments 2021, 191, 109349. [CrossRef]
- Yin, Y.G.; Kong, X.Q.; Li, M.; Wang, J.C.; Dai, X.Y.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Lin, W.Y. Development of an esterase fluorescent probe based on naphthalimide-benzothiazole conjugation and its applications for qualitative detection of esterase in orlistat-treated biosamples. Analytica Chimica Acta 2022, 1190, 339248. [CrossRef]
- Guo, B.P.; Shen, T.J.; Liu, Y.F.; Jing, J.; Shao, C.X.; Zhang, X.L. An endoplasmic reticulum-specific ratiometric fluorescent probe for imaging esterase in living cells. Spectrochimica Acta Part a-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2023, 291, 122389. [CrossRef]
- Sidhu, J.S.; Rajendran, K.; Mathew, A.B.; Iqbal, T.; Saini, D.K.; Das, D. Acetylcholine Structure-Based Small Activatable Fluorogenic Probe for Specific Detection of Acetylcholinesterase. Analytical Chemistry 2023, 95, 7594-7602. [CrossRef]
- Li, J.X.; Cao, J.R.; Wu, W.; Xu, L.L.; Zhang, S.Q.; Ma, P.Y.; Wu, Q.; Song, D.Q. A molecular imaging tool for monitoring carboxylesterase 2 during early diagnosis of liver-related diseases. Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical 2023, 377, 133122. [CrossRef]
- Chu, B.B.; Chen, Z.M.; Shi, H.L.; Wu, X.F.; Wang, H.Y.; Dong, F.L.; He, Y. Fluorescence, ultrasonic and photoacoustic imaging for analysis and diagnosis of diseases. Chemical Communications 2023, 59, 2399-2412. [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Yu, F.B.; Lv, C.J.; Choo, J.; Chen, L.X. Fluorescent chemical probes for accurate tumor diagnosis and targeting therapy. Chemical Society Reviews 2017, 46, 2237-2271. [CrossRef]
- Tiepolt, S.; Meyer, P.M.; Patt, M.; Deuther-Conrad, W.; Hesse, S.; Barthel, H.; Sabri, O. PET Imaging of Cholinergic Neurotransmission in Neurodegenerative Disorders. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 2022, 63, 33S-44S. [CrossRef]
- Smith, B.A.; Smith, B.D. Biomarkers and Molecular Probes for Cell Death Imaging and Targeted Therapeutics. Bioconjugate Chemistry 2012, 23, 1989-2006. [CrossRef]
- Pimlott, S.L.; Sutherland, A. Molecular tracers for the PET and SPECT imaging of disease. Chemical Society Reviews 2011, 40, 149-162. [CrossRef]
- Fu, Y.H.; Finney, N.S. Small-molecule fluorescent probes and their design. Rsc Advances 2018, 8, 29051-29061. [CrossRef]
- Wiederschain, G.Y. The Molecular Probes Handbook. A Guide to Fluorescent Probes and Labeling Technologies. Biochemistry (Moscow) 2011, 76, 1276. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.J.; Chai, X.Z.; He, X.P.; Kim, H.J.; Yoon, J.; Tian, H. Fluorogenic probes for disease-relevant enzymes. Chemical Society Reviews 2019, 48, 683-722. [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.; Dodani, S.C.; Chang, C.J. Reaction-based small-molecule fluorescent probes for chemoselective bioimaging. Nature Chemistry 2012, 4, 973-984. [CrossRef]
- Li, X.Y.; Pan, C.; Cao, J.; Liu, Z.X.; Zhu, Z.R.; Yan, C.X.; Zhao, W.J.; Zhu, W.H.; Wang, Q. An AIE-active probe for monitoring calcium-rich biological environment with high signal-to-noise and long-term retention in situ. Biomaterials 2022, 289, 121778. [CrossRef]
- Dong, B.L.; Song, W.H.; Lu, Y.R.; Tian, M.G.; Kong, X.Q.; Mehmood, A.H.; Lin, W.Y. Live cell-specific fluorescent probe for the detection of labile Fe(II) and the evaluation of esterase activity in live animals. Sensors and Actuators B-Chemical 2020, 305, 127470. [CrossRef]
- Tian, X.; Murfin, L.C.; Wu, L.L.; Lewis, S.E.; James, T.D. Fluorescent small organic probes for biosensing. Chemical Science 2021, 12, 3406-3426. [CrossRef]
- Lee, M.H.; Kim, J.S.; Sessler, J.L. Small molecule-based ratiometric fluorescence probes for cations, anions, and biomolecules. Chemical Society Reviews 2015, 44, 4185-4191. [CrossRef]
- Reja, S.I.; Minoshima, M.; Hori, Y.; Kikuchi, K. Near-infrared fluorescent probes: a next-generation tool for protein-labeling applications. Chemical Science 2021, 12, 3437-3447. [CrossRef]
- Grimm, J.B.; Heckman, L.M.; Lavis, L.D. The Chemistry of Small-Molecule Fluorogenic Probes. Fluorescence-Based Biosensors: from Concepts to Applications 2013, 113, 1-34. [CrossRef]
- Tallman, K.R.; Beatty, K.E. Far-Red Fluorogenic Probes for Esterase and Lipase Detection. Chembiochem 2015, 16, 70-75. [CrossRef]
- Mao, Y.Y.; Ma, M.M.; Wei, P.; Zhang, P.; Liu, L.; Guan, T.T.; Zhang, X.J.; Yi, T. A sensitive and rapid "off-on" fluorescent probe for the detection of esterase and its application in evaluating cell status and discrimination of living cells and dead cells. Analyst 2020, 145, 1408-1413. [CrossRef]
- Levine, S.R.; Beatty, K.E. Synthesis of a far-red fluorophore and its use as an esterase probe in living cells. Chemical Communications 2016, 52, 1835-1838. [CrossRef]
- Tallman, K.R.; Levine, S.R.; Beatty, K.E. Profiling Esterases in Mycobacterium tuberculosis Using Far-Red Fluorogenic Substrates. Acs Chemical Biology 2016, 11, 1810-1815. [CrossRef]
- Nakamura, N.; Uchinomiya, S.; Inoue, K.; Ojida, A. Trimethyl-Substituted Carbamate as a Versatile Self-Immolative Linker for Fluorescence Detection of Enzyme Reactions. Molecules 2020, 25, 2153. [CrossRef]
- Okada, K.; Yamaguchi, T.; Dodo, K.; Sodeoka, M.; Obika, S. Detection of esterase activity by chromogenic and fluorogenic probe based on an O-nitrobenzoxadiazole (O-NBD) unit. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 2019, 27, 1444-1448. [CrossRef]
- Oe, M.; Miki, K.; Ohe, K. An enzyme-triggered turn-on fluorescent probe based on carboxylate-induced detachment of a fluorescence quencher. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 2020, 18, 8620-8624. [CrossRef]
- Fujioka, H.; Uno, S.; Kamiya, M.; Kojima, R.; Johnsson, K.; Urano, Y. Activatable fluorescent probes for hydrolase enzymes based on coumarin-hemicyanine hybrid fluorophores with large Stokes shifts. Chemical Communications 2020, 56, 5617-5620. [CrossRef]
- Yang, Y.Z.; Xu, Z.Y.; Li, N.B.; Luo, H.Q. Ultrasensitive fluorescent probe for visual biosensing of esterase activity in living cells and its imaging application. Spectrochimica Acta Part a-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2021, 262, 120094,. [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.G.; Ma, Y.Y.; Lin, W.Y. Fluorescent Probes for the Visualization of Cell Viability. Accounts of Chemical Research 2019, 52, 2147-2157. [CrossRef]
- Tian, M.G.; Sun, J.; Tang, Y.H.; Dong, B.L.; Lin, W.Y. Discriminating Live and Dead Cells in Dual-Color Mode with a Two-Photon Fluorescent Probe Based on ESIPT Mechanism. Analytical Chemistry 2018, 90, 998-1005. [CrossRef]
- Lu, Y.R.; Dong, B.L.; Song, W.H.; Sun, Y.R.; Mehmood, A.H.; Lin, W.Y. An ESIPT-based ratiometric fluorescent probe for the discrimination of live and dead cells. Spectrochimica Acta Part a-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2020, 240, 118588,. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Xu, W.B.; Yang, Z.C.; Yan, Y.C.; Xie, X.X.; Qu, N.; Wang, Y.; Wang, C.Y.; Hua, J.L. New Diketopyrrolopyrrole-Based Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Intracellular Esterase Detection and Discrimination of Live and Dead Cells in Different Fluorescence Channels. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces 2018, 10, 31088-31095. [CrossRef]
- Shen, T.J.; Zang, S.P.; Shu, W.; Nie, L.X.; Jing, J.; Zhang, X.L. A ratiometric fluorescent probe for mitochondrial esterase specific detection in living cells. Dyes and Pigments 2020, 178, 108345. [CrossRef]
- Gao, M.; Hu, Q.L.; Feng, G.X.; Tang, B.Z.; Liu, B. A fluorescent light-up probe with "AIE plus ESIPT" characteristics for specific detection of lysosomal esterase. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2014, 2, 3438-3442. [CrossRef]
- Xiang, C.B.; Xiang, J.J.; Yang, X.; Zhu, B.D.; Mo, Q.Y.; Zhou, L.H.; Gong, P. An easily available endoplasmic reticulum targeting near-infrared fluorescent probe for esterase imaging in vitro and in vivo. Analyst 2022, 147, 789-793. [CrossRef]
- Lai, Y.B.; Zhang, T.T.; Song, W.H.; Li, Z.H.; Lin, W.Y. Evaluation of Cell Viability with a Single Fluorescent Probe Based on Two Kinds of Fluorescence Signal Modes. Analytical Chemistry 2021, 93, 12487-12493. [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.H.; Zhang, Y.W.; Wang, X.D.; Zan, Q.; Yu, X.; Fan, L. An esterase-sensitive AIEgen probe targeting mitochondria and lipid droplets for assessing cell viability. Spectrochimica Acta Part a-Molecular and Biomolecular Spectroscopy 2023, 287, 122122. [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.P.; Huang, J.; Ren, T.B.; Yuan, L.; Zhang, X.B. De Novo Design of Activatable Photoacoustic/Fluorescent Probes for Imaging Acute Lung Injury In Vivo. Analytical Chemistry 2023, 95, 1566-1573. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J.; Cheng, K.; Wu, Q.; Ding, D.S.; Li, C.G.; Li, Z. A dual fluorogenic and F-19 NMR probe for the detection of esterase activity. Materials Chemistry Frontiers 2018, 2, 1201-1206. [CrossRef]
- Hetrick, K.J.; Ramos, M.A.A.; Raines, R.T. Terbium(III) Luminescence-Based Assay for Esterase Activity. Analytical Chemistry 2019, 91, 8615-8621. [CrossRef]
- Schena, A.; Johnsson, K. Sensing Acetylcholine and Anticholinesterase Compounds. Angewandte Chemie-International Edition 2014, 53, 1302-1305. [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Shen, Y.M.; Yin, P.; Li, L.D.; Liu, M.L.; Zhang, Y.Y.; Li, H.T.; Yao, S.Z. Sensitive detection of acetylcholine based on a novel boronate intramolecular charge transfer fluorescence probe. Analytical Biochemistry 2014, 465, 172-178. [CrossRef]
- Wu, S.J.; Li, Y.G.; Deng, T.; Wang, X.J.; Hu, S.Y.; Peng, G.Y.; Huang, X.A.; Ling, Y.W.; Liu, F. A new fluorescent probe for sensing of biothiols and screening of acetylcholinesterase inhibitors. Organic & Biomolecular Chemistry 2020, 18, 2468-2474. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.Y.; Liu, T.T.; Liang, J.H.; Tian, X.G.; Zhang, B.J.; Huang, H.L.; Ma, X.C.; Feng, L.; Sun, C.P. A highly selective near infrared fluorescent probe for carboxylesterase 2 and its biological applications. Journal of Materials Chemistry B 2021, 9, 2457-2461. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kang, J.S.; Kim, I.Y.; Choi, K.S.; Kim, H.M. Carboxylesterase-2-Selective Two-Photon Ratiometric Probe Reveals Decreased Carboxylesterase-2 Activity in Breast Cancer Cells. Analytical Chemistry 2018, 90, 9465-9471. [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Yu, F.F.; Luo, X.Z.; Li, M.S.; Zhao, L.L.; Yu, F.B. Visualization of carboxylesterase 2 with a near-infrared two-photon fluorescent probe and potential evaluation of its anticancer drug effects in an orthotopic colon carcinoma mice model. Chemical Communications 2020, 56, 4412-4415. [CrossRef]
- Park, S.J.; Lee, H.W.; Kim, H.R.; Kang, C.; Kim, H.M. A carboxylesterase-selective ratiometric fluorescent two-photon probe and its application to hepatocytes and liver tissues. Chemical Science 2016, 7, 3703-3709. [CrossRef]
- Li, M.Y.; Zhai, C.; Wang, S.Y.; Huang, W.X.; Liu, Y.G.; Li, Z. Detection of carboxylesterase by a novel hydrosoluble near-infrared fluorescence probe. Rsc Advances 2019, 9, 40689-40693. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Q.; Feng, L.; Wang, D.D.; Dai, Z.R.; Wang, P.; Zou, L.W.; Liu, Z.H.; Wang, J.Y.; Yu, Y.; Ge, G.B.; et al. A Two-Photon Ratiometric Fluorescent Probe for Imaging Carboxylesterase 2 in Living Cells and Tissues. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces 2015, 7, 28474-28481. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, M.M.; Li, P.; Hai, F.; Jia, Y. Determination of carboxylesterase 2 by fluorescence probe to guide pancreatic adenocarcinoma profiling. Chemical Physics Letters 2021, 785, 139143. [CrossRef]
- Davis, K.M.; Ryan, J.L.; Aaron, V.D.; Sims, J.B. PET and SPECT Imaging of the Brain: History, Technical Considerations, Applications, and Radiotracers. Seminars in Ultrasound Ct and Mri 2020, 41, 521-529. [CrossRef]
- Crisan, G.; Moldovean-Cioroianu, N.S.; Timaru, D.G.; Andries, G.; Cainap, C.; Chis, V. Radiopharmaceuticals for PET and SPECT Imaging: A Literature Review over the Last Decade. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2022, 23, 5023. [CrossRef]
- Gawne, P.J.; Man, F.; Blower, P.J.; de Rosales, R.T.M. Direct Cell Radiolabeling for in Vivo Cell Tracking with PET and SPECT Imaging. Chemical Reviews 2022, 122, 10266-10318. [CrossRef]
- Kijewski, M.F. Positron Emission Tomography (PET) and Single-Photon Emission Computed Tomography (SPECT) Physics. Handbook of Neuro-Oncology Neuroimaging, 2nd Edition 2016, 353-358. [CrossRef]
- Linden, D.E.J. The Challenges and Promise of Neuroimaging in Psychiatry. Neuron 2012, 73, 8-22. [CrossRef]
- Zimmer, L.; Luxen, A. PET radiotracers for molecular imaging in the brain: Past, present and future. Neuroimage 2012, 61, 363-370. [CrossRef]
- Sala, A.; Lizarraga, A.; Caminiti, S.P.; Calhoun, V.D.; Eickhoff, S.B.; Habeck, C.; Jamadar, S.D.; Perani, D.; Pereira, J.B.; Veronese, M.; et al. Brain connectomics: time for a molecular imaging perspective? Trends in Cognitive Sciences 2023, 27, 353-366. [CrossRef]
- Reichel, A. The role of blood-brain barrier studies in the pharmaceutical industry. Current Drug Metabolism 2006, 7, 183-203. [CrossRef]
- Josserand, V.; Pelerin, H.; de Bruin, B.; Jego, B.; Kuhnast, B.; Hinnen, F.; Duconge, F.; Boisgard, R.; Beuvon, F.; Chassoux, F.; et al. Evaluation of drug penetration into the brain: A double study by in vivo Imaging with positron emission tomography and using an in vitro model of the human blood-brain barrier. Journal of Pharmacology and Experimental Therapeutics 2006, 316, 79-86. [CrossRef]
- Reshma, S.; Megha, K.B.; Amir, S.; Rukhiya, S.; Mohanan, P.V. Blood brain barrier-on-a-chip to model neurological diseases. Journal of Drug Delivery Science and Technology 2023, 80, 104174. [CrossRef]
- Ferrando, R.; Damian, A. Brain SPECT as a Biomarker of Neurodegeneration in Dementia in the Era of Molecular Imaging: Still a Valid Option? Frontiers in Neurology 2021, 12, 629442. [CrossRef]
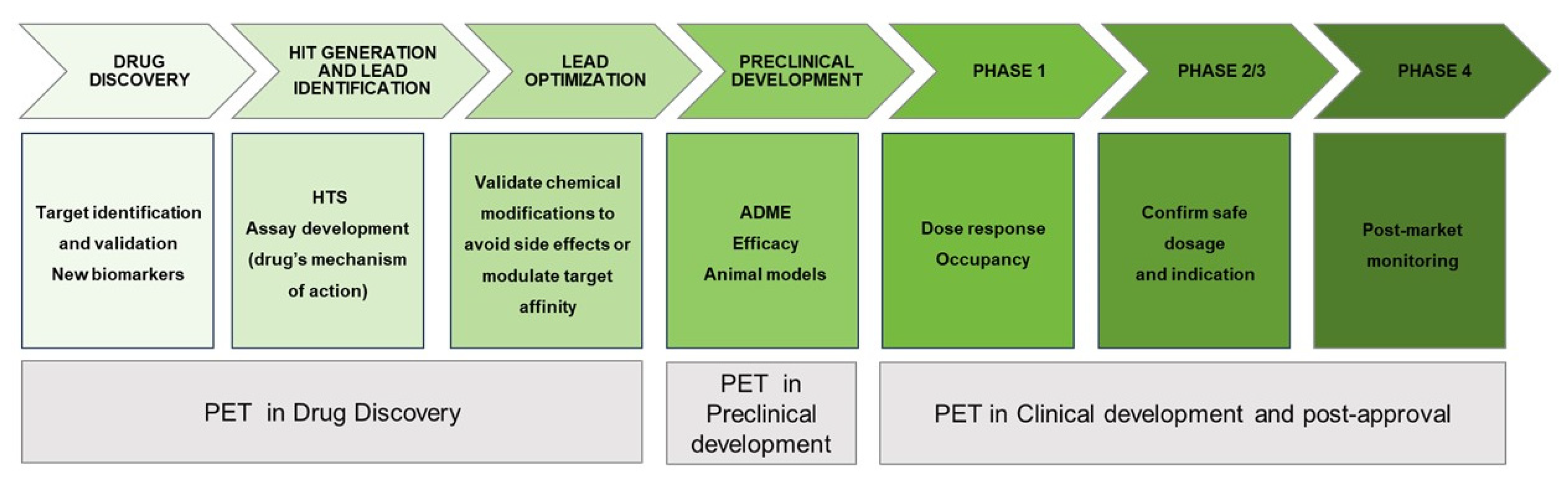
- Mercier, J.; Provins, L.; Hannestad, J. Progress and Challenges in the Development of PET Ligands to Aid CNS Drug Discovery. Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry Iii, Vol 7: Cns, Pain, Metabolic Syndrome, Cardiovascular, Tissue Fibrosis and Urinary Incontinence 2017, 20-64. [CrossRef]
- Rempel, B.P.; Price, E.W.; Phenix, C.P. Molecular Imaging of Hydrolytic Enzymes Using PET and SPECT. Molecular Imaging 2017, 16, 1-30. [CrossRef]
- Farde, L. The advantage of using positron emission tomography in drug research. Trends in Neurosciences 1996, 19, 211-214. [CrossRef]
- Lee, C.M.; Farde, L. Using positron emission tomography to facilitate CNS drug development. Trends in Pharmacological Sciences 2006, 27, 310-316. [CrossRef]
- Wagner, C.C.; Langer, O. Approaches using molecular imaging technology - use of PET in clinical microdose studies. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews 2011, 63, 539-546. [CrossRef]
- Volkow, N.D.; Ding, Y.S.; Fowler, J.S.; Gatley, S.J. Imaging brain cholinergic activity with positron emission tomography: Its role in the evaluation of cholinergic treatments in Alzheimer's dementia. Biological Psychiatry 2001, 49, 211-220. [CrossRef]
- Morgan, P.; Van der Graaf, P.H.; Arrowsmith, J.; Feltner, D.E.; Drummond, K.S.; Wegner, C.D.; Street, S.D.A. Can the flow of medicines be improved? Fundamental pharmacokinetic and pharmacological principles toward improving Phase II survival. Drug Discovery Today 2012, 17, 419-424. [CrossRef]
- Goud, N.S.; Bhattacharya, A.; Joshi, R.K.; Nagaraj, C.; Bharath, R.D.; Kumar, P. Carbon-11: Radiochemistry and Target-Based PET Molecular Imaging Applications in Oncology, Cardiology, and Neurology. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2021, 64, 1223-1259. [CrossRef]
- Goud, N.S.; Joshi, R.K.; Bharath, R.D.; Kumar, P. Fluorine-18: A radionuclide with diverse range of radiochemistry and synthesis strategies for target based PET diagnosis. European Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2020, 187, 111979. [CrossRef]
- Dumond, A.R.S.; Gross, H.K.; Bohnen, N.I.; Kanel, P.; Muller, M.; Koeppe, R.A.; Kilbourn, M.R.; Scott, P.J.H. Classics in Neuroimaging: Imaging the Cholinergic System with Positron Emission Tomography. Acs Chemical Neuroscience 2021, 12, 1472-1479. [CrossRef]
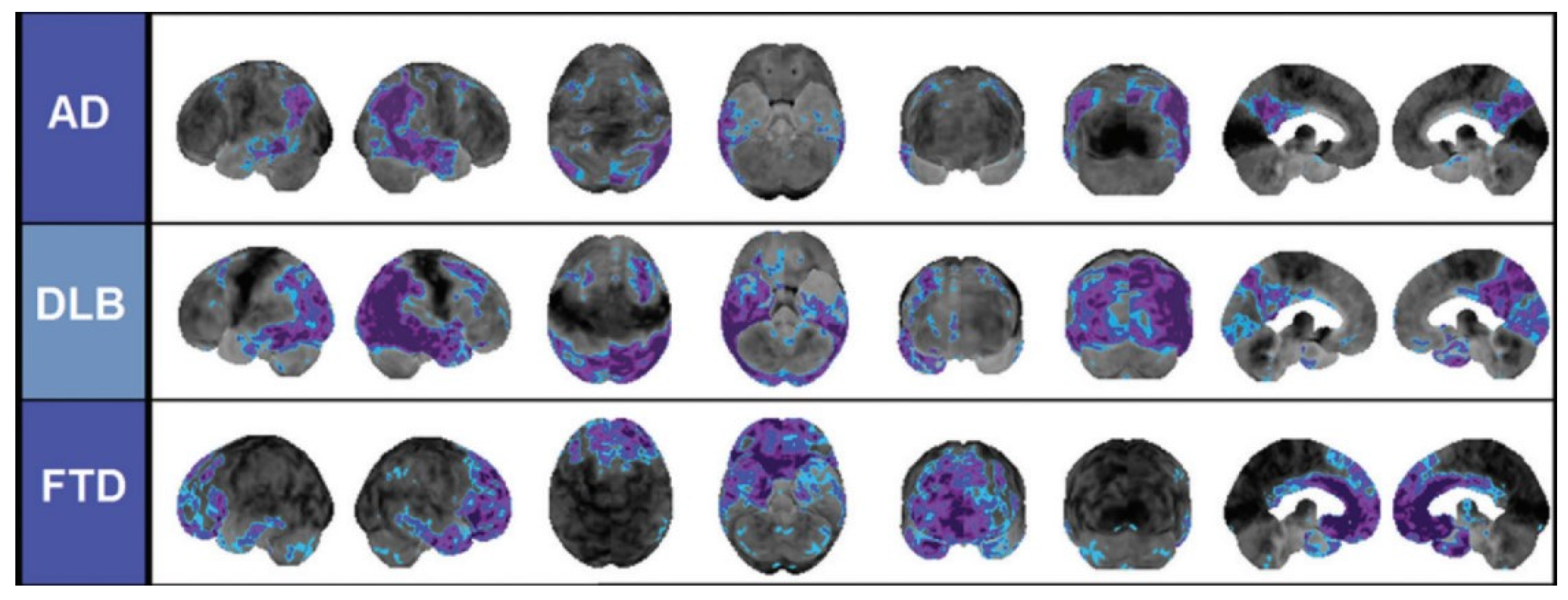
- Roy, R.; Niccolini, F.; Pagano, G.; Politis, M. Cholinergic imaging in dementia spectrum disorders. European Journal of Nuclear Medicine and Molecular Imaging 2016, 43, 1376-1386. [CrossRef]
- https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/what-is-dementia. Available online: (accessed on 21 st july 2023).
- Bohnen, N.I.; Frey, K.A. Imaging of cholinergic and monoaminergic neurochemical changes in neurodegenerative disorders. Molecular Imaging and Biology 2007, 9, 243-257. [CrossRef]
- Pohanka, M. Cholinesterase, a target of pharmacology and toxicology. Biomedical Papers-Olomouc 2011, 155, 219-229. [CrossRef]
- Contestabile, A. The history of the cholinergic hypothesis. Behavioural Brain Research 2011, 221, 334-340. [CrossRef]
- Jana, A.; Bhattacharjee, A.; Das, S.S.; Srivastava, A.; Choudhury, A.; Bhattacharjee, R.; De, S.; Perveen, A.; Iqbal, D.; Gupta, P.K.; et al. Molecular Insights into Therapeutic Potentials of Hybrid Compounds Targeting Alzheimer's Disease. Molecular Neurobiology 2022, 59, 3512-3528. [CrossRef]
- van Waarde, A.; Marcolini, S.; de Deyn, P.P.; Dierckx, R. PET Agents in Dementia: An Overview. Seminars in Nuclear Medicine 2021, 51, 196-229. [CrossRef]
- Gentzsch, C.; Hoffmann, M.; Ohshima, Y.; Nose, N.; Chen, X.Y.; Higuchi, T.; Decker, M. Synthesis and Initial Characterization of a Selective, Pseudo-irreversible Inhibitor of Human Butyrylcholinesterase as PET Tracer. Chemmedchem 2021, 16, 1427-1437. [CrossRef]
- Fernandez, S.; Giglio, J.; Reyes, A.L.; Damian, A.; Perez, C.; Perez, D.I.; Gonzalez, M.; Oliver, P.; Rey, A.; Engler, H.; et al. 3-(Benzyloxy)-1-(5- F-18 fluoropentyl)-5-nitro-1H-indazole: a PET radiotracer to measure acetylcholinesterase in brain. Future Medicinal Chemistry 2017, 9, 983-994. [CrossRef]
- https://www.alz.org/alzheimers-dementia/treatments/medications-for-memory? Available online: (accessed on 21st july 2023).
- Brown, R.K.J.; Bohnen, N.I.; Wong, K.K.; Minoshima, S.; Frey, K.A. Brain PET in Suspected Dementia: Patterns of Altered FDG Metabolism. Radiographics 2014, 34, 684-701. [CrossRef]
- Kikuchi, T.; Okamura, T.; Zhang, M.R.; Irie, T. PET probes for imaging brain acetylcholinesterase. Journal of Labelled Compounds & Radiopharmaceuticals 2013, 56, 172-179. [CrossRef]
- Pappata, S.; Tavitian, B.; Traykov, L.; Jobert, A.; Dalger, A.; Mangin, J.F.; Crouzel, C.; DiGiamberardino, L. In vivo imaging of human cerebral acetylcholinesterase. Journal of Neurochemistry 1996, 67, 876-879. [CrossRef]
- Bonnotlours, S.; Crouzel, C.; Prenant, C.; Hinnen, F. C-11 Labeling of an inhibitor of acetylcholinesterase 11C-physostigmine. Journal of Labelled Compounds & Radiopharmaceuticals 1993, 33, 277-284. [CrossRef]
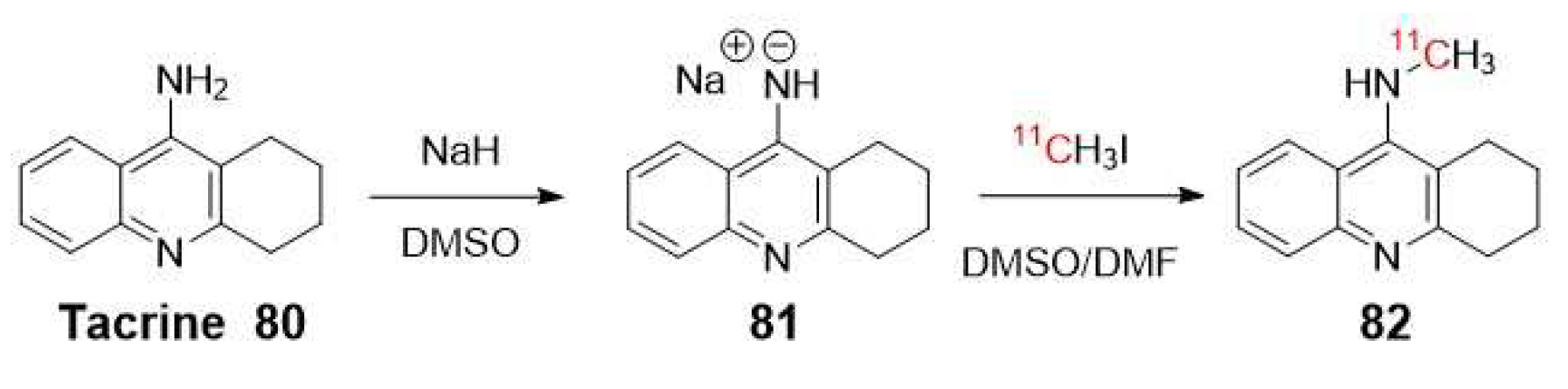
- Bonnot, S.; Prenant, C.; Crouzel, C. Synthesis of 9-11C-methylamino-1,2,3,4-tetrahydroacridine, a potent acetylcholine esterase inhibitor. Applied Radiation and Isotopes 1991, 42, 690-691. [CrossRef]
- Tavitian, B.; Pappata, S.; Bonnotlours, S.; Prenant, C.; Jobert, A.; Crouzel, C.; Digiamberardino, L. Positron emission tomography study of 11C methyl-tetrahydroaminoacridine (methyl-tacrine) in baboon brain. European Journal of Pharmacology 1993, 236, 229-238. [CrossRef]
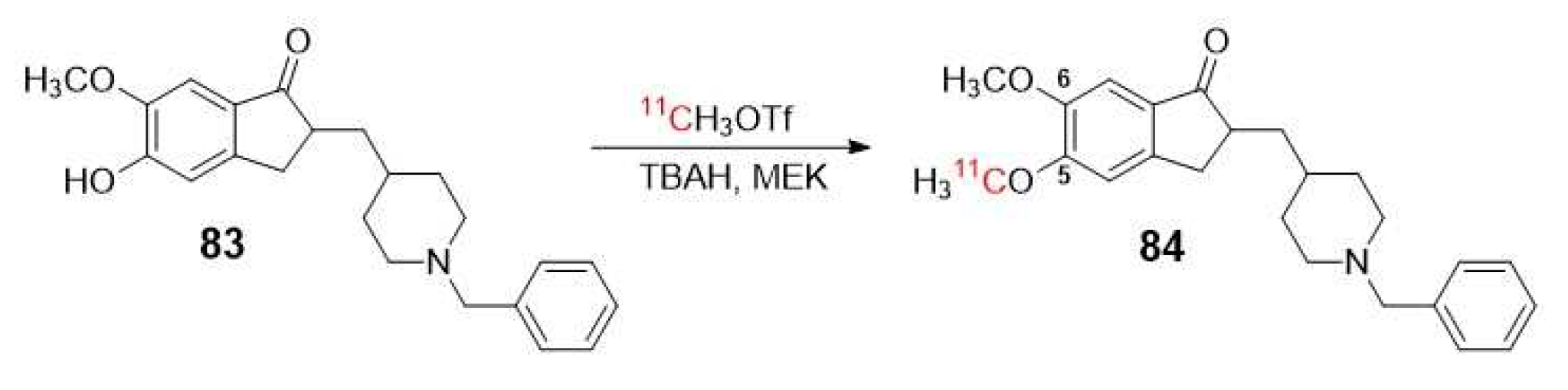
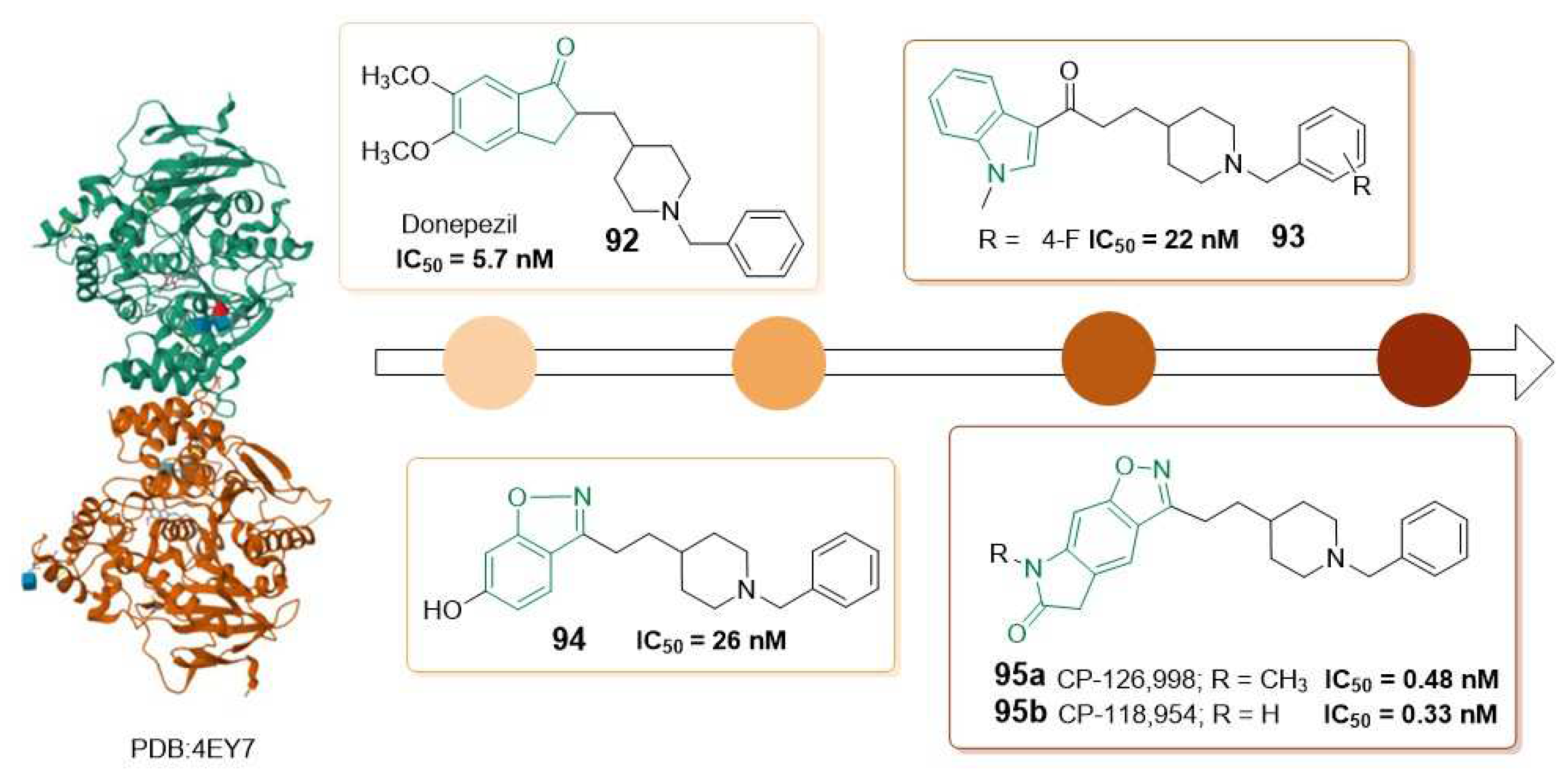
- Funaki, Y.; Kato, M.; Iwata, R.; Sakurai, E.; Tashiro, M.; Ido, T.; Yanai, K. Evaluation of the binding characteristics of 5-C-11-methoxy Donepezil in the rat brain for in vivo visualization of acetylcholinesterase. Journal of Pharmacological Sciences 2003, 91, 105-112. [CrossRef]
- Okamura, N.; Funaki, Y.; Tashiro, M.; Kato, M.; Ishikawa, Y.; Maruyama, M.; Ishikawa, H.; Meguro, K.; Iwata, R.; Yanai, K. In vivo visualization of donepezil binding in the brain of patients with Alzheimer's disease. British Journal of Clinical Pharmacology 2008, 65, 472-479. [CrossRef]
- De Vos, F.; Santens, P.; Vermeirsch, H.; Dewolf, I.; Dumont, F.; Slegers, G.; Dierckx, R.A.; De Reuck, J. Pharmacological evaluation of C-11 conepezil as tracer for visualization of acetylcholinesterase by PET. Nuclear Medicine and Biology 2000, 27, 745-747. [CrossRef]
- Conti, M.; Eriksson, L. Physics of pure and non-pure positron emitters for PET: a review and a discussion. Ejnmmi Physics 2016, 3, 8. [CrossRef]
- Wuest, F. Fluorine-18 labeling of small molecules: The use of F-18-labeled aryl fluorides derived from no-carrier-added F-18 fluoride as labeling precursors. Pet Chemistry: the Driving Force in Molecular Imaging 2007, 62, 51-78. [CrossRef]
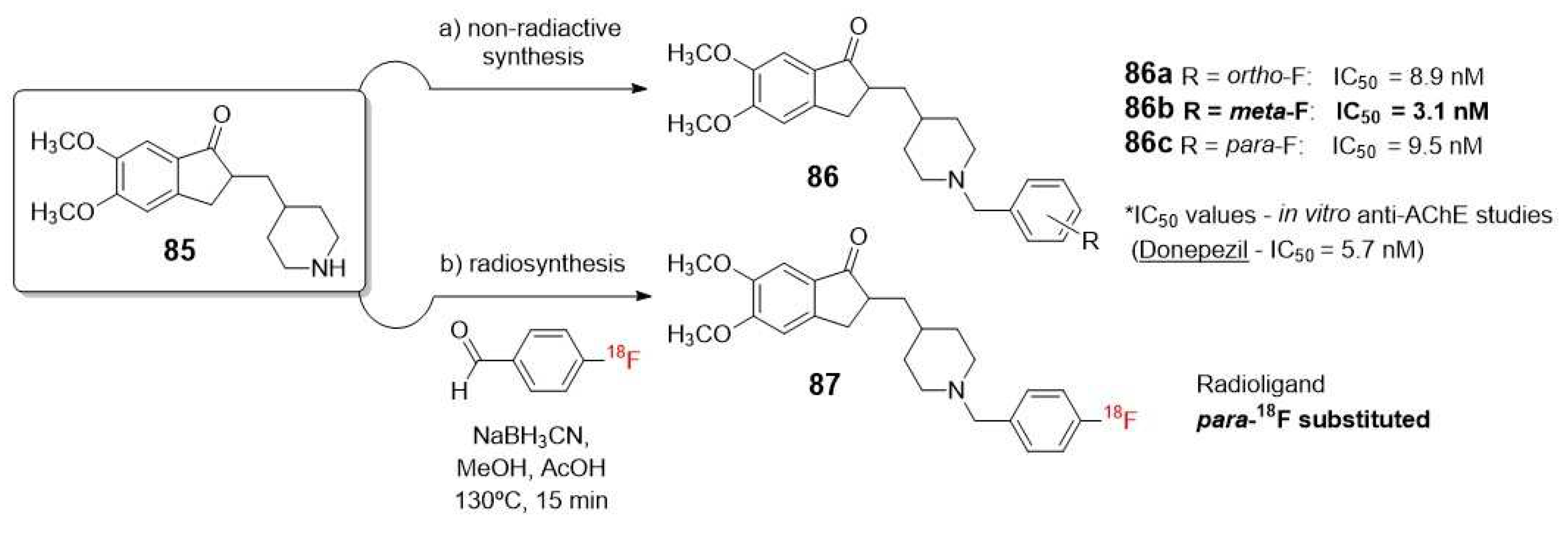
- Lee, S.Y.; Choe, Y.S.; Sugimoto, H.; Kim, S.E.; Hwang, S.H.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, Y.; Lee, J.; Kim, B.T. Synthesis and biological evaluation of 1-(4- F-18 fluorobenzyl)-4- (5,6-dimethoxy-1-oxoindan-1-yl) methyl piperidine for in vivo studies of acetylcholinesterase. Nuclear Medicine and Biology 2000, 27, 741-744. [CrossRef]
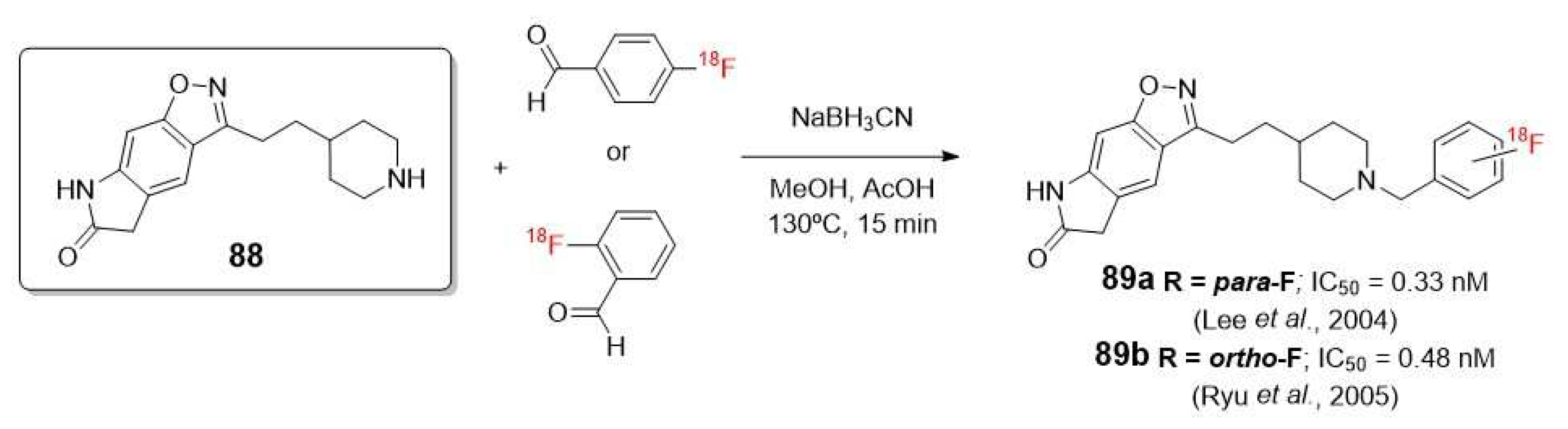
- Lee, S.Y.; Choe, Y.S.; Kim, Y.R.; Paik, J.Y.; Choi, B.W.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, B.T. Synthesis and evaluation of 5,7-dihydro-3- 2- 1-(4- F-18 fluorobenzyl)-4-piperidinyl ethyl -6H-pyrrolo 3,2-f 1,2-benzisoxazol-6-o ne for in vivo mapping of acetylcholinesterase. Nuclear Medicine Communications 2004, 25, 591-596. [CrossRef]
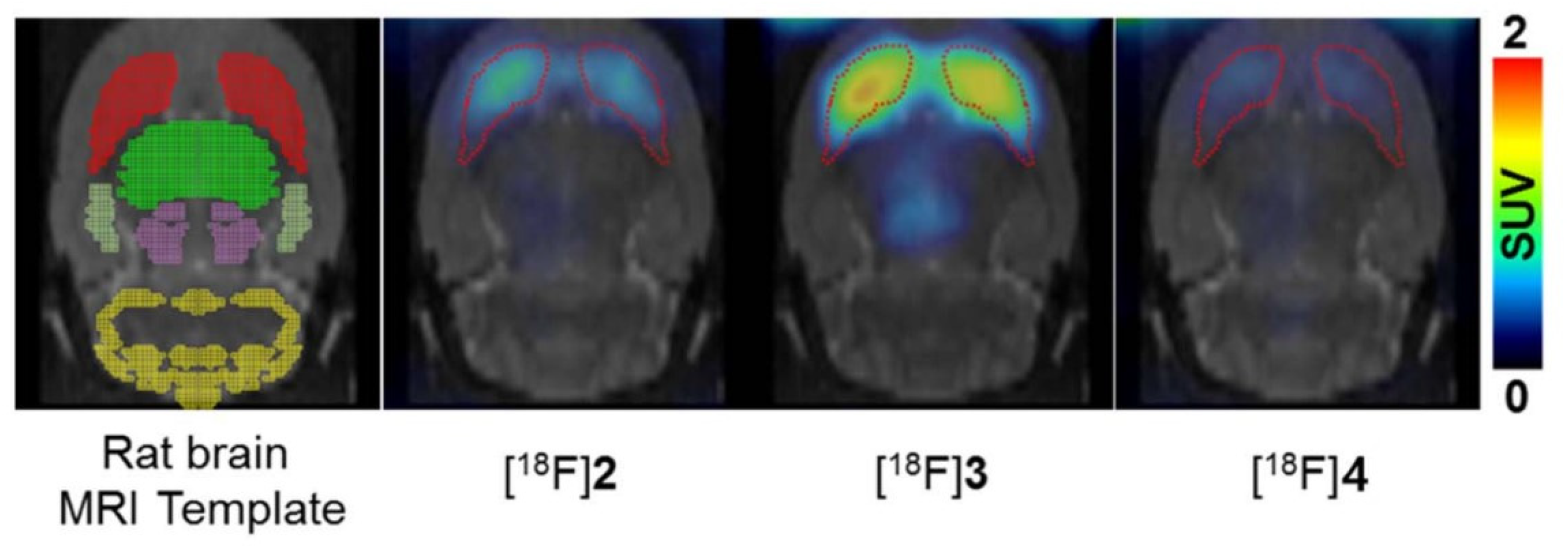
- Ryu, E.K.; Choe, Y.S.; Park, E.Y.; Paik, J.P.; Kim, Y.R.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, S.E.; Kim, B.T. Synthesis and evaluation of 2- F-18 fluoro-CP-118,954 for the in vivo mapping of acetylcholinesterase. Nuclear Medicine and Biology 2005, 32, 185-191. [CrossRef]
- Lee, B.C.; Moon, B.S.; Park, H.S.; Jung, J.H.; Park, D.D.; de Candia, M.; Denora, N.; Altomare, C.D.; Kim, S.E. The position of fluorine in CP-118,954 affects AChE inhibition potency and PET imaging quantification for AChE expression in the rat brain. European Journal of Pharmaceutical Sciences 2017, 109, 209-216. [CrossRef]
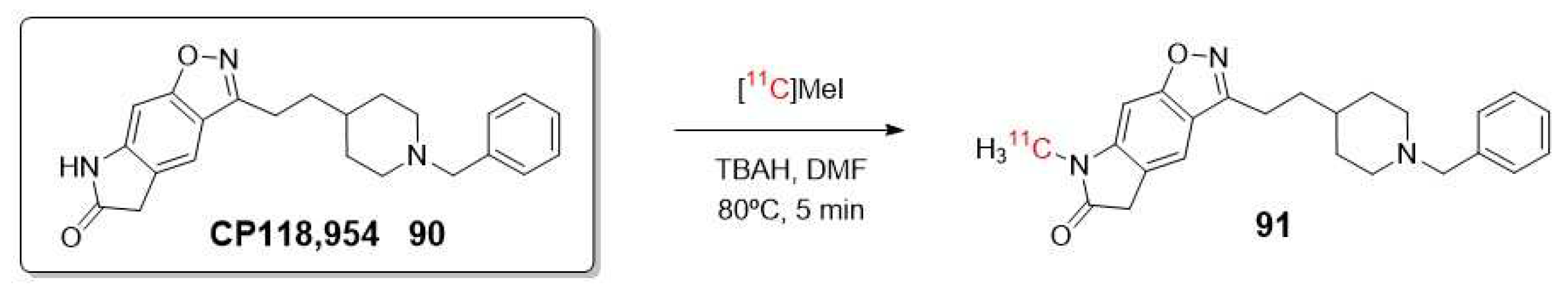
- Musachio, J.L.; Flesher, J.E.; Scheffel, U.A.; Rauseo, P.; Hilton, J.; Mathews, W.B.; Ravert, H.T.; Dannals, R.F.; Frost, J.J. Radiosynthesis and mouse brain distribution studies of C-11 CP-126,998: a PET ligand for in vivo study of acetylcholinesterase. Nuclear Medicine and Biology 2002, 29, 547-552. [CrossRef]
- Bencherif, B.; Endres, C.; Musachio, J.L.; Villalobos, A.; Hilton, J.; Scheffel, U.; Dannals, R.F.; Williams, S.; Frost, J. PET imaging of brain acetylcholinesterase using C-11 CP-126,998, a brain selective enzyme inhibitor. Synapse 2002, 45, 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Brown-Proctor, C.; Snyder, S.E.; Sherman, P.S.; Kilbourn, M.R. Synthesis and evaluation of 6- C-11 methoxy-3- 2- l-(phenylmethyl)-4-piperidinyl ethyl -1,2-benzisox azole as an in vivo radioligand for acetylcholinesterase. Nuclear Medicine and Biology 1999, 26, 99-103. [CrossRef]
- Choe, Y.S.; Oh, S.J.; Shim, I.; Naruto, S.; Chi, D.Y.; Kim, S.E.; Lee, K.H.; Choi, Y.; Kim, B.T. Syntheses and biological evaluation of F-18-labeled 3-(1-benzyl-piperidin-4-yl)-1-(1-methyl-1H-indol-3-yl) propan-1-ones for in vivo mapping of acetylcholinesterase. Nuclear Medicine and Biology 2000, 27, 263-267. [CrossRef]
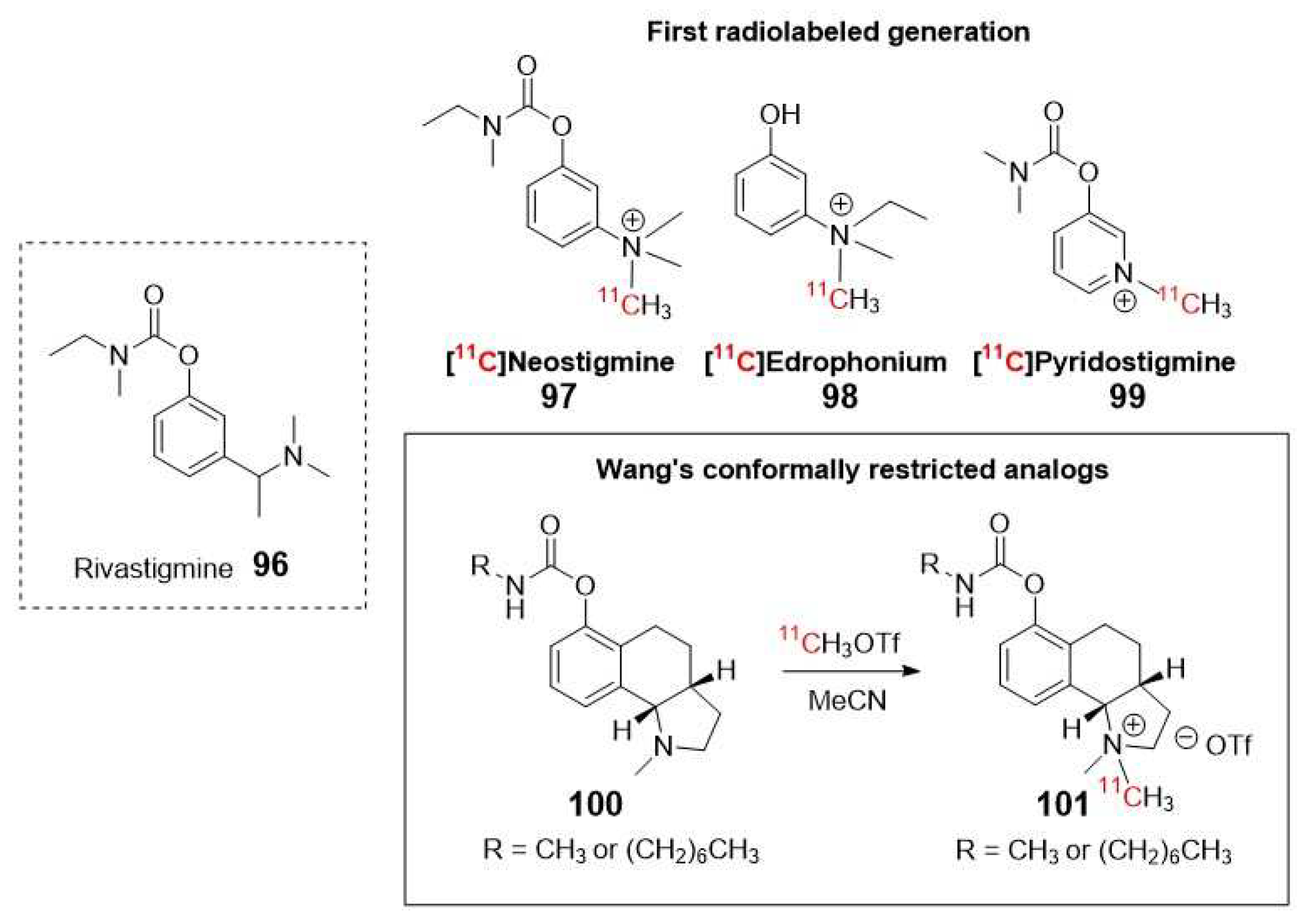
- Wang, M.; Wang, J.Q.; Gao, M.Z.; Zheng, Q.H. Facile synthesis of new carbon-11 labeled conformationally restricted rivastigmine analogues as potential PET agents for imaging AChE and BChE enzymes. Applied Radiation and Isotopes 2008, 66, 506-512. [CrossRef]
- https://go.drugbank.com/drugs/DB00674. Available online: (accessed on 21st july 2023).
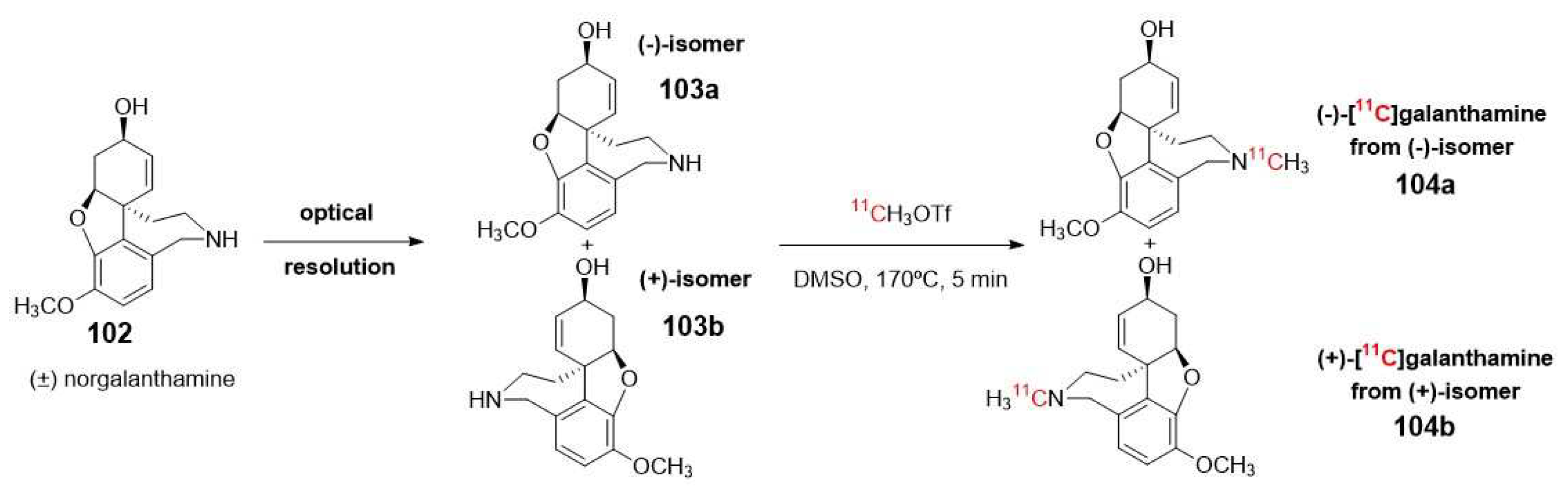
- Kimura, H.; Kawai, T.; Hamashima, Y.; Kawashima, H.; Miura, K.; Nakaya, Y.; Hirasawa, M.; Arimitsu, K.; Kajimoto, T.; Ohmomo, Y.; et al. Synthesis and evaluation of (-)- and (+)- C-11 galanthamine as PET tracers for cerebral acetylcholinesterase imaging. Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry 2014, 22, 285-291. [CrossRef]
- Giacobini, E. Selective inhibitors of butyrylcholinesterase - A valid alternative for therapy of Alzheimer's disease? Drugs & Aging 2001, 18, 891-898. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.; Lin, H.Z.; Yang, H.Y.; Tan, R.X.; Bian, Y.Y.; Fu, T.M.; Li, W.; Wu, L.; Pei, Y.Q.; Sun, H.P. Discovery of new acetylcholinesterase and butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors through structure-based virtual screening. Rsc Advances 2017, 7, 3429-3438. [CrossRef]
- Hoffmann, M.; Stiller, C.; Endres, E.; Scheiner, M.; Gunesch, S.; Sotriffer, C.; Maurice, T.; Decker, M. Highly Selective Butyrylcholinesterase Inhibitors with Tunable Duration of Action by Chemical Modification of Transferable Carbamate Units Exhibit Pronounced Neuroprotective Effect in an Alzheimer's Disease Mouse Model. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry 2019, 62, 9116-9140. [CrossRef]
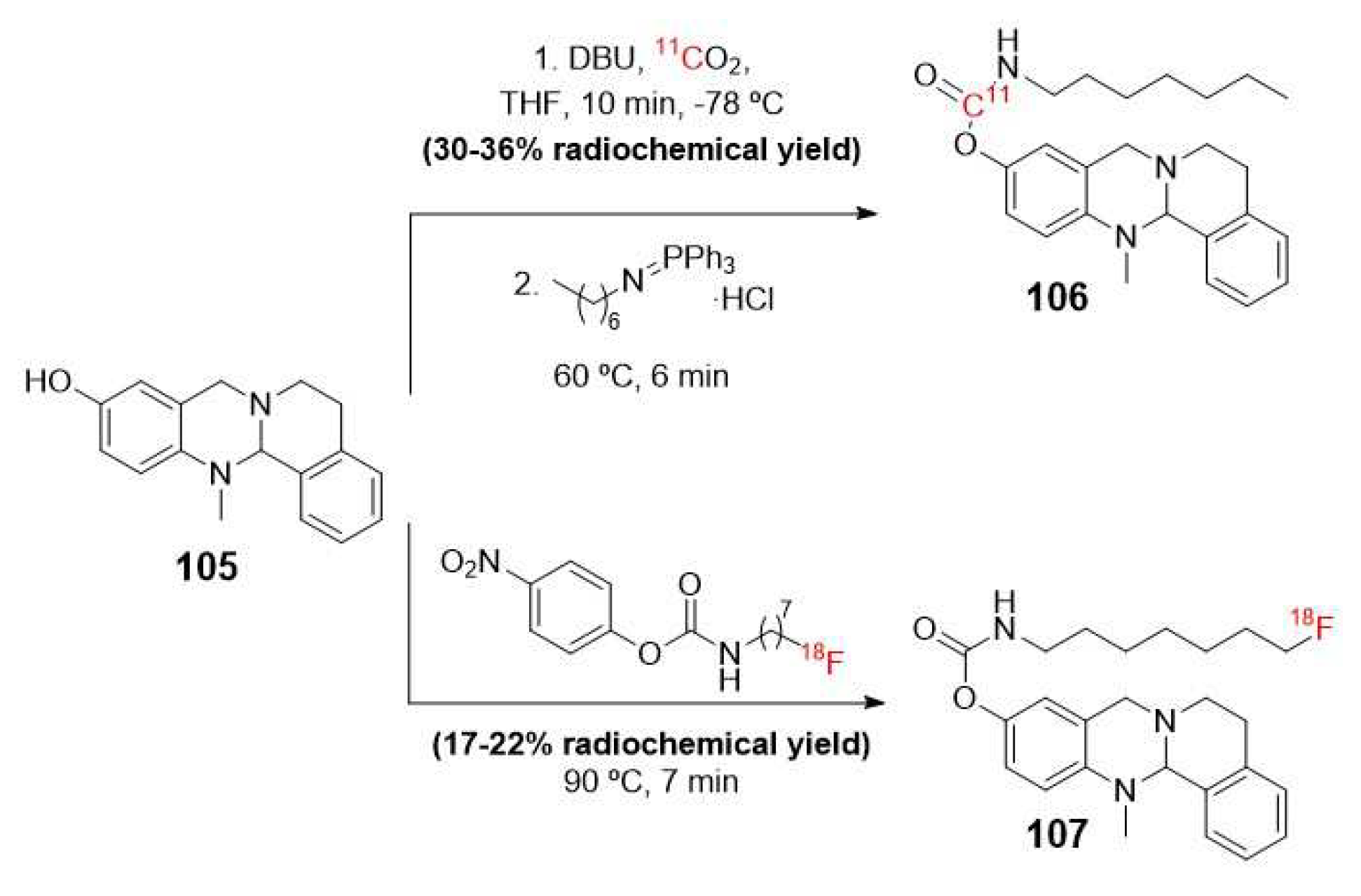
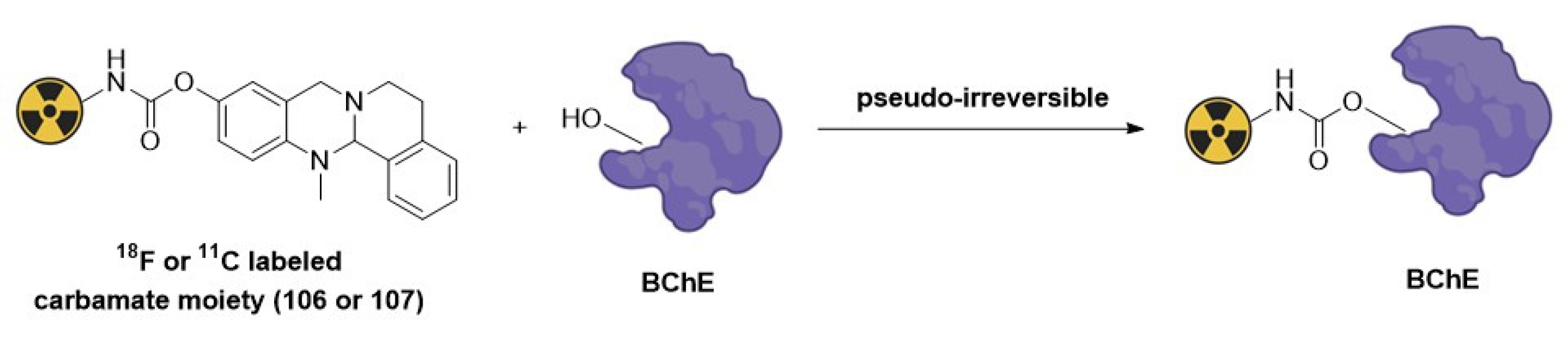
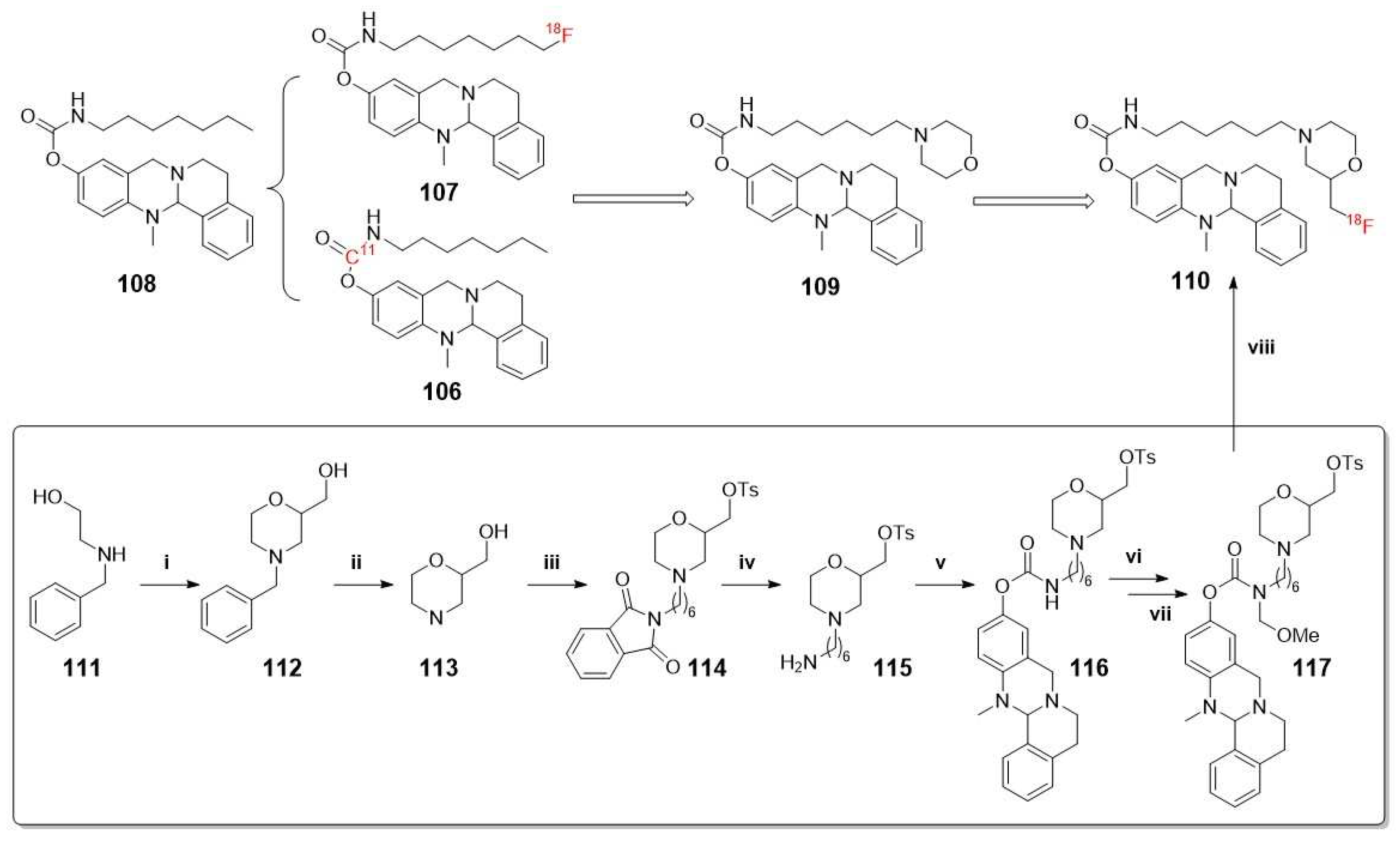
- Sawatzky, E.; Al-Momani, E.; Kobayashi, R.; Higuchi, T.; Samnick, S.; Decker, M. A Novel Way To Radiolabel Human Butyrylcholinesterase for Positron Emission Tomography through Irreversible Transfer of the Radiolabeled Moiety. Chemmedchem 2016, 11, 1540-1550. [CrossRef]
- Roivainen, A.; Rinne, J.; Virta, J.; Jarvenpaa, T.; Salomaki, S.; Yu, M.X.; Nagren, K. Biodistribution and blood metabolism of 1-(11)G methyl-4-piperidinyl n-butyrate in humans: An imaging agent for in vivo assessment of butyrylcholinesterase activity with PET. Journal of Nuclear Medicine 2004, 45, 2032-2039.
- Shinotoh, H.; Hirano, S.S., Hitoshi. PET Imaging of Acetylcholinesterase. In PET and SPECT of Neurobiological Systems; Springer, Cham: Switzerland AG, 2021.
- Kadir, A.; Darreh-Shori, T.; Almkvist, O.; Wall, A.; Grut, M.; Strandberg, B.; Ringheim, A.; Eriksson, B.; Blomquist, G.; Langstrom, B.; et al. PET imaging of the in vivo brain acetylcholinesterase activity and nicotine binding in galantamine-treated patients with AD. Neurobiology of Aging 2008, 29, 1204-1217. [CrossRef]
- Namba, H.; Fukushi, K.; Nagatsuka, S.; Iyo, M.; Shinotoh, H.; Tanada, S.; Irie, T. Positron emission tomography: quantitative measurement of brain acetylcholinesterase activity using radiolabeled substrates. Methods 2002, 27, 242-250. [CrossRef]
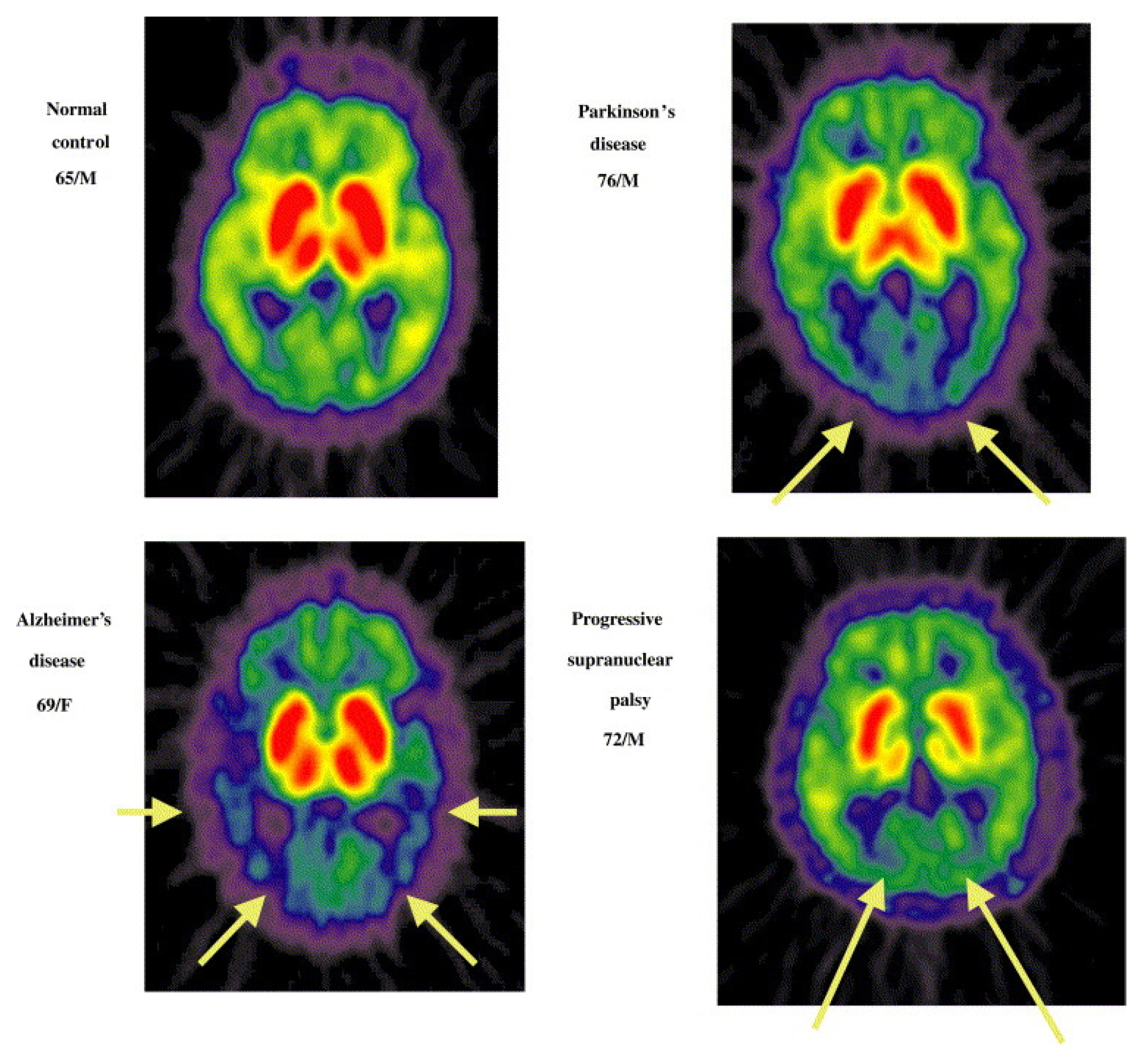
- Shinotoh, H.; Namba, H.; Yamaguchi, M.; Fukushi, K.; Nagatsuka, S.; Iyo, M.; Asahina, M.; Hattori, T.; Tanada, S.; Irie, T. Positron emission tomographic measurement of acetylcholinesterase activity reveals differential loss of ascending cholinergic systems in Parkinson's disease and progressive supranuclear palsy. Annals of Neurology 1999, 46, 62-69. [CrossRef]
- Shinotoh, H.; Fukushi, K.; Nagatsuka, S.; Irie, T. Acetylcholinesterase imaging: Its use in therapy evaluation and drug design. Current Pharmaceutical Design 2004, 10, 1505-1517. [CrossRef]








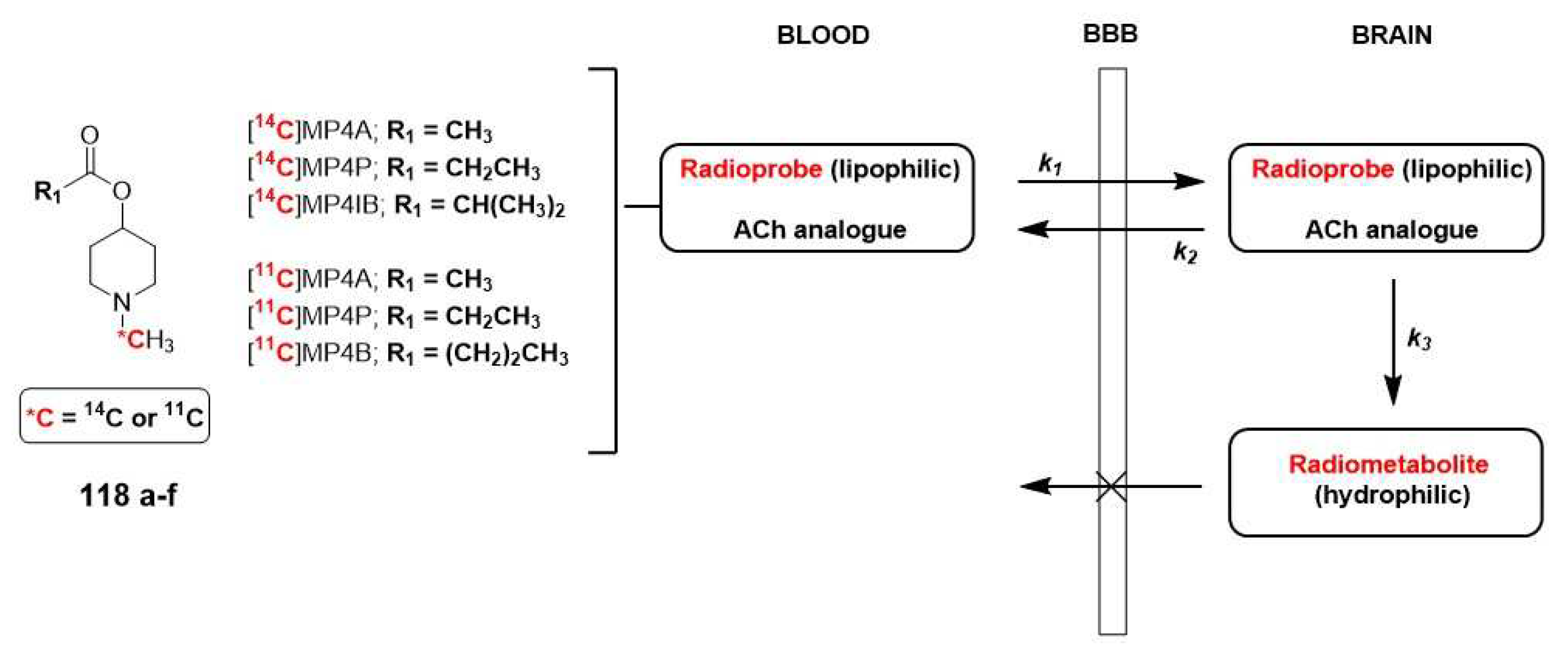
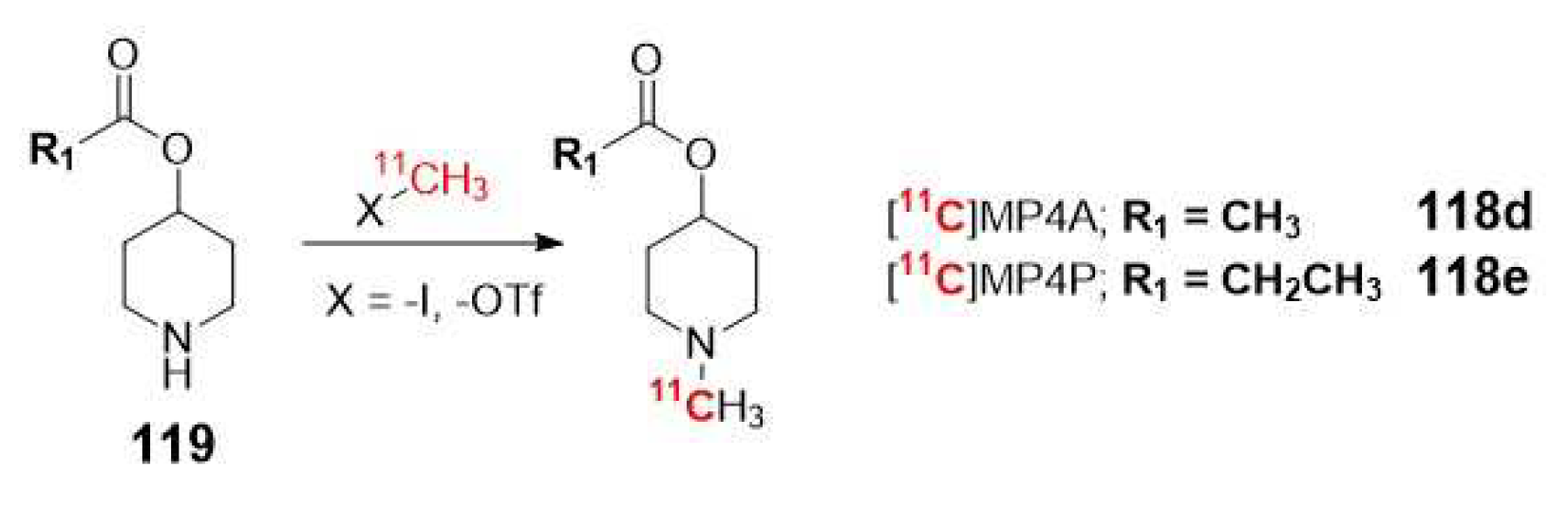
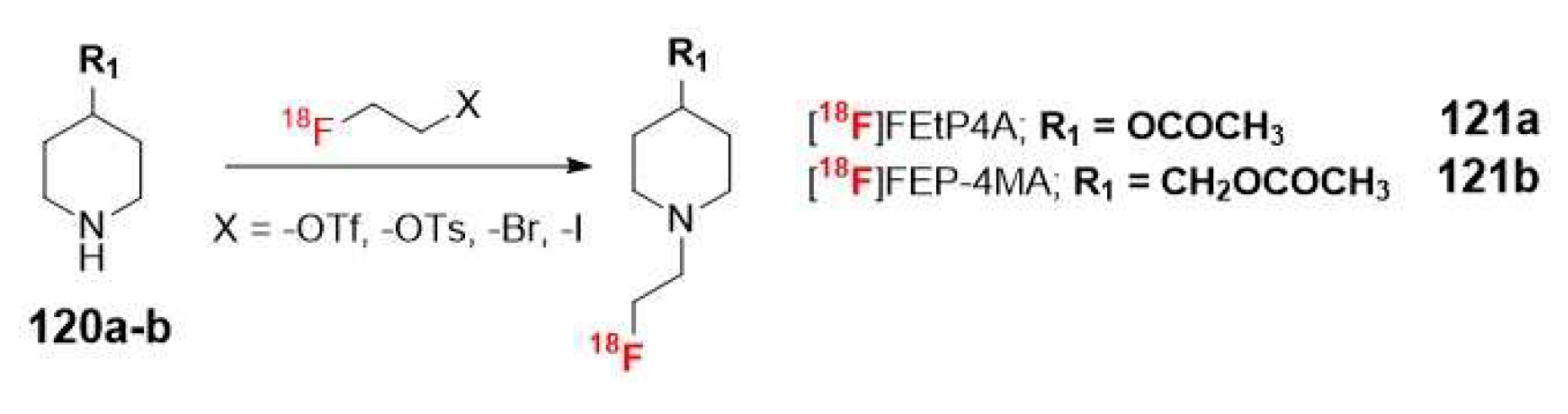
| Selectivity for AChE | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Radiotracer | Human cerebral cortex (Irie et al. 1996) | PET scan time | Optimum brain regions for measurement in humans |
| [11C]MP4A | 94% | 40-60 min | Cerebral cortex, thalamus |
| [11C]MP4P | 86% | 60-80 min | Cerebral cortex, thalamus, and cerebellar cortex (striatum) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





