1. Introduction
According to the FAO, approximately one-third of the World's food production is lost or wasted over the various stages of the food-supply chain. The extent of this loss varies greatly depending on the region and type of food. For fruit and vegetables, losses throughout the entire supply chain can be as high as 50%. This issue stands firmly in the field of one of the United Nations’ Sustainable Development Objectives (OSD), which aims to reduce food waste by approximately 50% by 2050. [
1]
This ambitious goal can be pursued using the Circular Economy concept, identified as a key principle for sustainable innovation, with an emphasis on creating a "zero waste" society and economy that aim to reduce waste and promote the efficient use of resources. In particular, (food)waste valorization refers to the process of utilizing this waste as a resource to create new products, rather than simply discarding it. Thus, it is necessary to emphasize that food waste, besides its applications in the energy, agronomy and animal feed sectors, can be a valuable feedstock for the recovery of bioactive compounds, including antioxidants and dietary fiber. [
2,
3,
4,
5] Extracting these compounds from food waste not only provides a sustainable approach to waste management but also generates value-added products that can be utilized in various applications, including as functional foods, nutraceuticals and cosmetics. [
6,
7] Furthermore, the residues generated after food-waste extraction for the recovery of valuable compounds can be further converted into new products, such as fermentation substrates, [
8] bioplastics, [
9] fine chemicals [
10] or used as a source of energy through aerobic digestion. [
11,
12]
However, the extraction and conversion processes must be optimized to ensure that high-quality bioactive compounds are recovered while green chemistry principles are fulfilled. The importance of green chemistry in influencing future industrial processes cannot be denied. However, a significant number of procedures that involve extractions and chemical processes still rely on conventional reactors and methods. [
13] The fundamental principles of green extraction focus not only on minimizing waste, but also on optimizing process efficiency while mitigating, at the same time, risks to human health and the environment. [
14] This approach to so-called “process intensification” can be mainly achieved using enabling technologies (such as microwaves, ultrasound, pulsed electric fields, supercritical fluid extraction, ohmic heating, etc.) that aim to maximize process heat and mass transfer, leading to increased yield/conversion rates and, thus, savings in time and energy. [
15] In this context, water-based extractions play a pivotal role, with water being considered “green” by definition as it is an easily usable and non-hazardous solvent. [
16] Water, with its high polarity, possesses the ability to dissolve a wide range of polar compounds. However, although certain molecules (
i.e. polyphenols) exhibit limited polarity, using water under subcritical conditions is still a viable option. Significant physico-chemical changes occur under these conditions, and selecting the appropriate temperature can lead to the recovery of several classes of target compounds. [
17]
Green metrics are key tools in assessing the environmental impact of chemical processes. They provide quantitative measures that evaluate the efficiency and sustainability of chemical reactions and processes. Reaction Mass Efficiency (RME), the E-factor and Process Mass Intensity (PMI) are three crucial and commonly used green metrics. [
18]
RME is a metric that quantifies the use of reactants in a chemical reaction. It represents the proportion of the total mass of reactants that is converted into desired products (see Equation (1)).
Higher reaction mass efficiency indicates a more efficient use of raw materials and reduced waste generation. This parameter, typical in organic synthesis, can be adapted for extraction procedures (with lower values being expected, naturally). [
19]
The E-factor, or environmental factor, is a measure of the waste generated during a process. It is calculated by dividing the total mass of waste generated by the mass of the desired product (see Equation (2)). A lower E-factor signifies a more sustainable process with minimal waste generation. [
20]
Process mass intensity (PMI) is a metric that evaluates the efficiency of a chemical process by considering the overall mass of all materials, including reactants, solvents, catalysts and products, per unit of desired product (see Equation (3)). Lower process mass intensity indicates a more resource-efficient process, as this indicates reduced material usage and waste generation. Another way to express PMI is the Process Mass Efficiency (PME), which is expressed as a percentage and is directly proportional to the overall process sustainability (see Equation (4)). [
21]
These green metrics play a crucial role in guiding sustainable-process design and optimization. Using green metrics, the chemical industry can strive for more sustainable practices, minimize waste, conserve resources and reduce the overall environmental footprint of chemical processes.
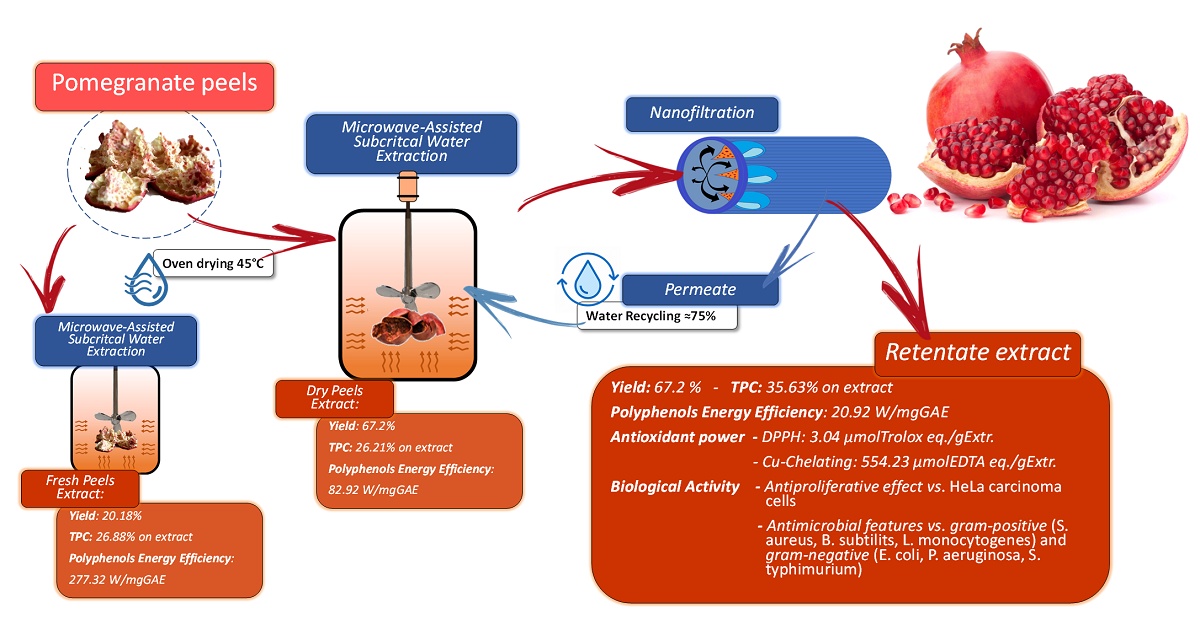
This present study, the investigation of a new sustainable approach for the valorization of Pomegranate peels (PP) as a food residue using microwave-assisted extraction (MAE) with water as the solvent medium, fits well into this context.
Pomegranate (
Punica granatum L.) is one of the world’s oldest known fruits, is deeply embedded in the cultures of the Mediterranean region and widely cultivated in many countries due to its numerous health benefits. [
22] Its production is estimated to be about 8.1 million tons worldwide, with Turkey being the fourth-largest producer after India, China and Iran. [
23] The fruit contains bioactive compounds such as polyphenols, flavonoids, and tannins, which have been shown to exhibit a range of biological activity including antioxidant, anticancer and anti-inflammatory effects. [
24,
25] However, the majority of these bioactive compounds are found in the peel and seeds, which are usually discarded during the processing of pomegranate fruit, leading to significant waste and environmental concerns. PP are generated during the processing of fruits, which involves the removal of the outer skin and the separation of the seeds and juice. The generated quantity depends on the processing method and the source of the fruit, but typically ranges from 30% to 50% of the total fruit weight. [
26] We can therefore estimate, considering the abovementioned global production of the fruit, that around 3.6 million tons of waste are produced per year. This enormous amount of residue presents environmental and health risks, as it contributes to environmental pollution and disposal issues, particularly if not managed properly. Finding appropriate methods for the extraction of bioactive compounds from pomegranate residues and their transformation into added-value products is essential.
In recent years, there has been increasing interest in the recovery of bioactive compounds from PP using non-conventional technologies including MAE, ultrasound-assisted extraction (UAE), Supercritical Fluid Extraction (SFE) and Enzymatic assisted extraction (EAE), among others. [
27] These innovative extraction technologies have shown great potential in improving the efficiency of the recovery of bioactives from biomass waste while reducing solvent usage and processing times. A recent review by Cano-Lamadrid
et al., (2022) has focused on the valorization of pomegranate by-products and outlined several sustainable approaches to PP extraction, of which microwaves emerge as being particularly promising. [
27] However, the reviewers concluded that: “although there are relevant and promising results, they are non-unanimous and scarce. Therefore, more research on MAE and comparison with other green techniques is required”. Our present paper therefore aims to contribute to the development of more sustainable and efficient methods for the MW-assisted recovery of bioactives from PP, with potential applications in the food, pharmaceutical and nutraceutical industries. To further support the produced results, the optimized samples were also evaluated in terms of energy consumption and biological activity.
In particular, MW-assisted water extraction has been exploited for the recovery of bioactives from PP waste, with both temperatures and extraction times being optimized. The antioxidant activity of the MAE extracts has been evaluated in terms of DPPH· scavenging activity (2,2-diphenyl-1-picrylhydrazyl assay) and the results have been compared with those of the extracts obtained from the conventional protocol. Moreover, the total phenolic, anthocyanin, flavonoid and tannin contents of the recovered PP extracts have been determined. Finally, the biological activity of the PP extracts, in terms of antibacterial activity toward Gram-positive and Gram-negative bacteria, has been investigated as has its antiproliferative activity in a HeLa cell line.
In addition, in order ensure that the protocol is in line with the requisites of sustainable and eco-friendly protocols, a preliminary evaluation of the potential water recycling from the aqueous PP extracts, using membrane filtration via a nanofiltration protocol, has been performed on the optimized MAE. This downstream strategy may not only enable water reuse for further extraction cycles, but can also concentrate the extracted antioxidants, dramatically reducing process times and energy consumption. Moreover, the main green metrics, RME, E-Factor and PMI (PME), have been exploited to evaluate the proposed MAE approach for PP valorization.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Pomegranate Peels and Chemicals
The PP utilized in this study were sourced fresh from Tropical Food Machinery (Parma, Italy), stored under frozen conditions at -20 °C and protected from light. A series of tests were conducted on the fresh peels, while a separate fraction was subjected to drying at 45 °C for a duration of 12 hours in a ventilated laboratory oven (FALC Instruments, Treviglio, Italy). In order to determine the moisture content and the proportions of the organic and inorganic fractions, a thermogravimetric investigation was carried out using a muffle furnace (Nabertherm GmbH, Lilienthal, Germany). The experimental protocol involved dehydration at 100 °C for 12 hours, followed by calcination at 650 °C for 4 hours (see
Table 1). All solvents and reagents utilized in this study were purchased from Sigma-Aldrich (St. Louis, MO, USA).
2.2. MW-Assisted Extraction (MAE) of Pomegranate Peels in Water
The MAE experiments were conducted using an MW multimodal reactor (SynthWAVE, Milestone, Bergamo, Italy) equipped with external inert gas feeding capability (N2). The optimization of the extraction protocol was performed using 1g of either fresh pomegranate peels (F-PP) or dried pomegranate peels (D-PP) with a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:30. The screening explored three different extraction temperatures (100 °C, 125 °C and 150 °C) with a MW power of 1500 W and three different time intervals (10, 20 and 30 minutes). Agitation was provided by a magnetic stirrer working at ca. 650 rpm.
In order to minimize oxidative stress in the biomass, each test was preceded by three N2 purges to eliminate atmospheric oxygen. Subsequently, the reaction chamber was pressurized with an appropriate amount of N2 to prevent water ebullition (5–10 bars). Following the optimized protocol, a scaled-up experiment was conducted using 20 grams of biomass and 600 mL of solvent in a 1 L Teflon vessel, mixed using a mechanical stirrer at 650 rpm. The extraction process was performed at 100 °C for 10 minutes, utilizing both fresh and dried peels. Furthermore, the same conditions were employed for the extraction of D-PP, utilizing the permeate recycled from membrane nanofiltration.
After extraction, the resulting solutions were subjected to vacuum filtration after centrifugation at 4200 rpm to separate the solid particles. The dry extracts were subsequently recovered via freeze-drying (LyoQuest-85, Telstar, Madrid, Spain), weighed and stored at 4 °C for further analysis.
2.3. Hydroalcoholic Extraction of Pomegranate Peels
A conventional hydroalcoholic extraction was chosen as the benchmark protocol for pomegranate peels, for use as a comparison with the principal results achieved by means of MAE. The method involved reflux conditions using a hydroalcoholic solvent composition of 70% ethanol and 30% distilled water. 5g of dry peels were subjected to extraction with 150 mL of the hydroalcoholic solution, resulting in a solid-to-liquid ratio of 1:30. The extraction was carried out for 1 hour. Reflux conditions were achieved by employing an oil bath equipped with a magnetic stirrer (650 rpm). After extraction, the resulting solution was subjected to centrifugation at 4200 rpm, to separate the solid particles, and was then filtered under vacuum. The ethanolic fraction was removed using a rotavapor system operating at 40 °C and 175 mbar. The residual water fraction was removed under freeze-drying using a LyoQuest-85 freeze dryer (Telstar, Madrid, Spain). The dried extracts were weighed and stored at 4 °C for further analysis.
2.4. Membrane Nanofiltration (NF) for Bioactives Concentration and Water Recovery
Membrane nanofiltration (NF) was conducted on a 2 L solution of the D-PP extract that was produced under the optimized conditions (solid/liquid ratio of 1:30, 100 °C, 10 min). During this study, a pilot membrane filtration skid was used (PB100, Hydro Air Research Srl, Lodi, Italy). The system was equipped with a DKU 1812 NF membrane (filtering area: 0.38 m2, molecular weight cut-off range: 150–300 Da). During the process, the retentate was recirculated within the system, while the permeate was continuously separated and collected, working under appropriate counter-pressure (5 bars). The separation was performed for approximately 25 minutes. As a result, 500 mL of retentate and 1500 mL of permeate, which were freeze-dried, weighed and stored at 4 °C for future analysis, were obtained from the 2 L solution. Part of the permeate was used “as obtained” for PP MAE, to evaluate its recyclability in the process.
2.5. Colorimetric Tests on Pomegranate Peel Extracts: Quali-Quantitative Characterization
2.5.1. Total Phenolic Content (TPC)
The determination of the Total Phenolic Content (TPC) followed a modified version of the
Folin–Ciocalteu procedure described by Hillis and Swain. [
28] For each extract, an aliquot of 0.25 mL was combined with 0.5 mL of a 10 %
w/v Na
2CO
3 solution, followed by the addition of 0.25 mL of
Folin–Ciocalteu reagent. The resulting solution was immediately diluted to a final volume of 5 mL using distilled water and thoroughly mixed. After allowing the solution to stand for 25 minutes, absorbance was measured at 725 nm using a Cary 60 UV–vis spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). A calibration curve was prepared using gallic acid solutions ranging from 0.01 to 0.45 mg/mL. TPC is expressed as mg/g of Gallic Acid Equivalents (GAE) over the extract (referred to as TPC selectivity) and over the matrix (referred as TPC Yield).
2.5.2. Total Anthocyanin Content (TAC)
The Total Anthocyanin Content (TAC) was determined using the pH differential method. [
29] The dried extract was dissolved in deionized water to achieve a concentration of approximately 1.5 mg/mL. Two solutions were prepared by mixing 1 mL of the sample with 5 mL of potassium chloride buffer (0.025 M KCl, pH 1 with HCl) and sodium acetate buffer (0.4 M CH
3COONa, pH 4.5 with HCl). After allowing the solutions to equilibrate for 5 minutes, absorbance was measured at 510 nm and 700 nm using a Cary 60 UV–vis spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). Deionized water was used as a blank. The resulting sample absorbance was calculated using Equations (5) and (6):
where MW is the molecular weight and ε is the molar absorptivity of the anthocyanin pigment in an acidic aqueous solvent. The values used in this formula correspond to Cyanidin-3-Glucoside (Cy3G, MW = 449.2 and ε = 26,900), meaning that the TAC results are expressed as Cy3G equivalents.
2.5.3. Total Tannin Content (TTC)
The determination of Total Tannin Content (TTC) was performed using the Peri and Pompei protocol [
30] with some adjustments, as reported by Aimone et al. [
31] In this analysis, 600 µL of hemisulfate cinchonine solution (0.5% w/v) was added to 600 µL of the extract solution in a 1.5 mL Eppendorf tube. The resulting mixture was shaken and then left overnight at 4 °C to promote the precipitation of tannate cinchonine. The sample was then centrifuged at 26,000 rpm for 2 min at 10 °C (Allegra 64R, Beckman Coulter Srl, Italy), and the supernatant, which contains a polyphenol-rich solution, was separated and analyzed using the
Folin–Ciocalteu test (see
Section 2.5.1). The total tannin content was calculated by determining the difference between the TPC of the fresh sample and the TPC obtained after tannin precipitation, and was expressed as Gallic Acid Equivalents (GAE).
2.5.4. Total Flavonoid Content (TFC)
The quantification of the Total Flavonoid Content (TFC) was performed using the colorimetric method described by Saikan Set
et al., with modifications. [
32] A 0.5 mL aliquot of the sample (water solution) with a concentration of 1 mg/mL was mixed with 0.1 mL of 10% aluminum nitrate, 0.1 mL of 1M potassium acetate and 4.3 mL of 80% ethanol. The mixture was thoroughly mixed and allowed to stand at room temperature for 40 minutes. The absorbance of the supernatant was measured at 415 nm (Cary 60 UV–vis spectrophotometer, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA) to determine the presence of flavonoids based on the development of a yellow color. The results were expressed as Quercetin equivalents in milligrams per gram (mgQE/g) of dry extract, using a standardized calibration curve.
2.5.5. Total Sugar Content (TSC)
The quantification of Total Carbohydrate Content (TSC) was conducted using the anthrone method, with modifications. [
33] A calibration curve was prepared using a glucose-water solution, with dilutions ranging from 10 to 200 µg/mL, to serve as a reference for determining the sugar content in the samples. An aliquot of the sample solution, consisting of 1 mL with concentrations ranging from 0.01 to 0.5 mg/mL in deionized water, was mixed with 5 mL of anthrone reagent (0.2 g anthrone in 100 mL of concentrated 96% sulfuric acid). The solution was then heated at 100 °C for 20 minutes and absorbance was measured at 620 nm (Cary 60 UV–vis spectrophotometer, Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The increase in color intensity, from yellow to green/blue, was directly proportional to the carbohydrate concentration in the sample. The obtained data were analyzed using the glucose standard calibration curve and expressed as Glucose equivalents in milligrams per gram (mgGluE/g) of dry extract.
2.5.6. Antioxidant Activity: DPPH· Inhibition
The antioxidant activity of the extracts was assessed using the method described by Brand-Williams et al. [
34] The antioxidant activity of the extracts was determined by measuring the inhibition of DPPH· radicals, which indicates their scavenging ability. The EC50 value, which represents the concentration of the extract required to inhibit 50% of the DPPH· radical, was determined as the parameter for scavenging activity. A Trolox methanolic solution served as the standard reference. The sample EC50 values were then compared to the EC50 values obtained from the standard to express the results as Trolox equivalents (μmolTE/mL). Various dry-extract concentrations were prepared via sequential dilution, and absorbance was measured at 515 nm using a Cary 60 UV-vis spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The obtained absorbance data were processed using Bobo Least Squares software with Probit regression analysis. [
35] Blank samples containing only water and methanol were used for instrument zeroing, while blank samples with the dry extract, but without the DPPH· radical, were used to account for matrix effects. A reference sample containing water and the DPPH· radical was utilized to normalize the results and verify absorbance due to natural inhibition.
2.5.7. Cu-chelating Activity of PP Extracts
The chelating ability of the sample was evaluated using the pyrocatechol violet (PV) assay, following the method described by Santos et al. [
36] PV forms a dark red complex with Cu
2+ ions not bound by polyphenols in a slightly acidic medium, and the rate of color reduction indicates chelating activity. A solution containing the extract was mixed with sodium acetate buffer and a copper sulfate solution, and the PV solution was then added. After specific reaction times, absorbance was measured at 632 nm using a Cary 60 UV-Vis spectrophotometer (Agilent Technologies, Santa Clara, CA, USA). The inhibition of PV-Cu
2+ complex formation was expressed as the percentage of inhibition compared to a reference solution prepared without the extract. Percentage inhibition was calculated using different sample concentrations, and the EC50 value was determined using probit regression and Bobo Least Squares software. [
35] The sample EC50 values were then compared to the EC50 values obtained from an EDTA solution to express the results as EDTA equivalents (μmolEDTA/mL).
2.6. Biological Activity
2.6.1. Antibacterial Activity Test
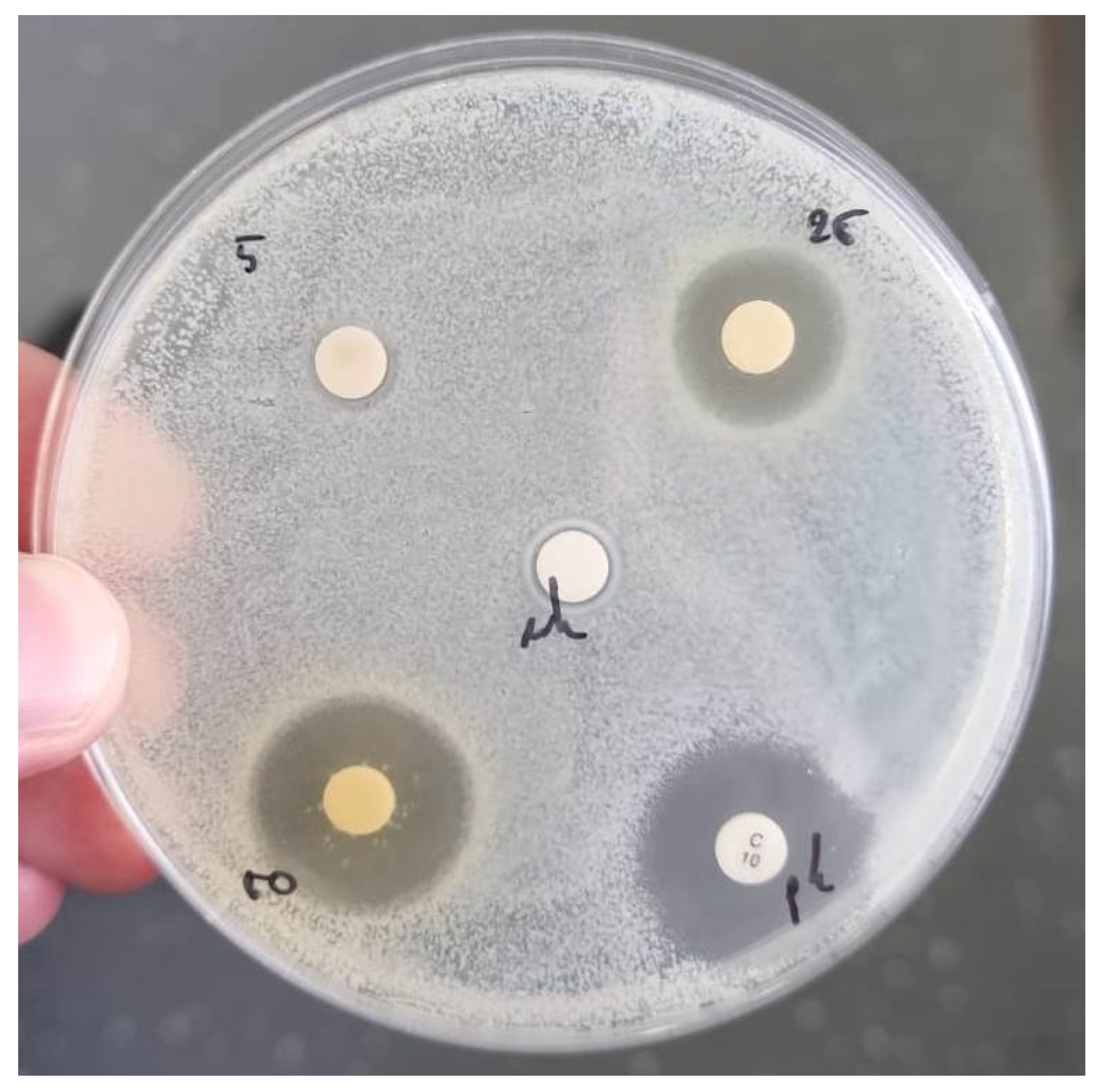
Gram-negative bacterial strains of Escherichia coli 3014, Pseudomonas aeruginosa 3024, Salmonella typhimurium 3064 and Gram-positive bacterial strains of Staphylococcus aureus 3048, Bacillus subtilits 3045 and Listeria monocytogenes 3112 were obtained from the Collection of Microorganisms at the Laboratory of General Microbiology and Food Microbiology, Faculty of Food Technology and Biotechnology, University of Zagreb (Zagreb, Croatia). All cultures were stored at -70 °C in nutrition broth (Biolife, Milano, Italy) with 30 % glycerol (by volume). To perform antibacterial activity test, microorganisms were firstly activated via incubation at 37 °C in the corresponding broths. The antibacterial activity of the PP extracts (F-PP, D-PP, D-PP/NF scaled-ups and hydroalcoholic benchmark) was tested on selected bacterial cultures in disc diffusion assays. Bacterial cultures were prepared and the CFUs of all the used suspensions were determined, and amounted to 107 – 108 CFU mL−1. To perform the test, 100 µL of the bacterial suspensions was smeared, using a Drigalski rod, onto the nutrient agar plate and left to dry. After 30 minutes, sterile filter discs (6 mm) (Macherey-Nagel GmbH, Düren, Germany) were immersed into 50, 250 and 500 µg/mL of the PP extracts and placed on the surface of inoculated nutrient agar. After incubation, for 24 hours at 37 °C, inhibition was detected as clear halo diameter (mm). Discs with chloramphenicol (10 µg per disc) (Liofilchem, Roseto, Italy) were used as positive controls, while discs immersed in sterile water that was used to make the water solutions of the PP extracts acted as negative controls for all tested microorganisms. All assays were performed in triplicate.
2.6.2. Antiproliferation Assay on Human Cell Line
The antiproliferative activity of PP extracts (F-PP, D-PP, D-PP/NF scaled-ups and hydroalcoholic benchmark) was evaluated in vitro against an adherent human tumor cell line using the CellTiter AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay (Promega). HeLa (ATCC No. CCL-2) cells were cultured in Dulbecco’s modified Eagle’s medium (DMEM) (Sigma, USA) supplemented with 5% (v/v) heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum (FBS) (Gibco Invitrogen Corporation, U.K.) and maintained in BioLite Petri dishes (Thermo Fisher Scientific) in an incubator with a humidified atmosphere and 5% CO2 at 37 °C. Experiments were performed three times with four parallels for each concentration of extract tested in BioLite 96-well plates (Thermo Fisher Scientific) that were seeded with exponentially growing cells at the indicated concentration (∼3 × 104 cells per well in 100 μL of medium) and incubated for 24 h. Lyophilized extracts were dissolved in 10 mg/mL of water and further diluted in DMEM to the final tested concentration (50 μg/mL,100 μg/mL, 250 μg/mL, 500 μg/mL) before being applied to the cells. The control cells were untreated cells. After treatment, the cells were incubated for an additional 72 h, after which the CellTiter AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay was performed according to the manufacturer’s instructions, with minor modifications. In brief, 10 μL of the CellTiter AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Reagent was added to each well and the cells were incubated for an additional 3 h, after which the absorbance was measured at 490 nm using a microplate reader (Tecan, Switzerland). Cell viability was expressed as the percentage of treated cells over control cells. Experiments were performed three times with four parallels for each concentration of tested compounds and data are expressed as mean ± S.D.
2.6.3. Clonogenic Analysis
The clonogenic assays began by seeding pre-cultured HeLa cells in 6-well plates at an initial concentration of 200 cells in 2 mL of culture medium per well. The cells were incubated under optimal conditions and treated with the scaled-up extract of F-PP, D-PP, D-PP/NF and the hydroalcoholic benchmark at a concentration of 500 mg/mL after 24 h. Untreated control cells were also analyzed. Three days after the cells were treated, the growth medium containing the tested extracts was removed and replaced with fresh growth medium, after which, the plate with the HeLa cells was returned to the incubator for further cultivation. After treatment, the surviving cells required about 1–3 weeks to form colonies. In this work, the produced colonies were visible 19 days after the initial seeding of the cells. Staining the grown colonies with crystal-violet was begun by removing the growth medium and washing the cells with 1 mL of PBS buffer. 2.5 mL of methanol was then added to fix the cells, but was removed after 10 min. The plates were then allowed to air dry completely. A 0.5 % solution of crystal-violet was then added and incubated for 10 min. In the final step, the dye was removed and the colonies in the wells were rinsed with 1 mL of PBS buffer and deionized water. The number of colonies grown was then counted and the plating efficiency (PE) and survival fraction (SF) were calculated according to the equations in the protocol of Franken et al. [
37] PE is the ratio of the number of colonies to the number of seeded cells, while SF is the number of colonies formed after the treatment of the cells, expressed as PE.
5. Conclusions
The “zero-waste economy” concept, which aims to reduce waste and promote the efficient use of resources, perfectly meets the urgency of (food)waste-valorization strategies via the design of protocols that can exploit those residues as a resource for new products, rather than simply discarding it. Furthermore, it is necessary to emphasize that food waste can be an outstanding source of bioactive compounds, including antioxidants and phenols. Pomegranate (Punica granatum L.) production is estimated to be about 8.1 million t/y, with related peel generation being of approx. 3.6 million tons, making it a huge environmental problem and economic loss. In this work, an MAE protocol has been optimized by evaluating the recovery of several components, such as polyphenols, anthocyanins, flavonoids, tannins and sugars, and their antioxidant and copper-chelating activity.
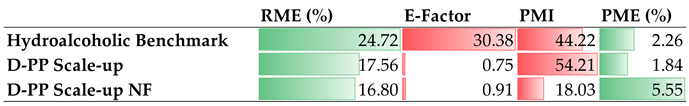
During the screening, matrix nature was explored, in addition to time and temperature variations, as we investigated how product quality and yield are affected by fresh and dried peels, as the latter was found to be the most promising feedstock. The study also involved the evaluation of potential water recycling, performed by means of a nanofiltration approach, which led to overall water reuse of approx. 75%. An evaluation of energy consumption (20.92W/mgGAE) and common green metrics gave encouraging results in terms of the sustainability of the non-conventional valorization strategy vs. the conventional approach (PME: 5.55% and 2.26%, respectively).
The screening also involved a preliminary transposition from lab-scale to a scaled-up protocol, from 1 to 20 grams, as a feasibility test, paving the way for further piloting considerations in view of the enormous amount of waste produced yearly.
The product furnished by the tuned extraction protocol can boast of the following contents per gram of PP extract: TPC: 356.35 mgGAE; TAC: 303.97 µgCy3G; TFC: 37.28 mgQE; TTC: 56.48 mgGAE; and, TSC: 615.41 mgGLU. In addition, Cu-chelation was 529.81 µmolEDTA and antioxidant activity was 1.43 µmolTE (according to the adopted reference). The biological activity of the recovered PP extracts has also been studied. The samples possess antimicrobial activity in laboratory studies, but further research is needed to determine their effectiveness for potential applications in the food, cosmetics and even pharmaceutical industries. While findings on the extracts’ antiproliferative activity, i.e. the anti-cancer activity of PP extracts, are also promising, it is important to note that research on the anti-cancer activity of pomegranate extracts is still evolving, and more studies, including clinical trials, are needed to determine its efficacy, optimal dosage and potential interactions with other cancer therapies. Nevertheless, pomegranate peel is a valuable by-product whose extracts, especially those achieved using green extraction, deserve further investigation due to numerous benefits of the approach.
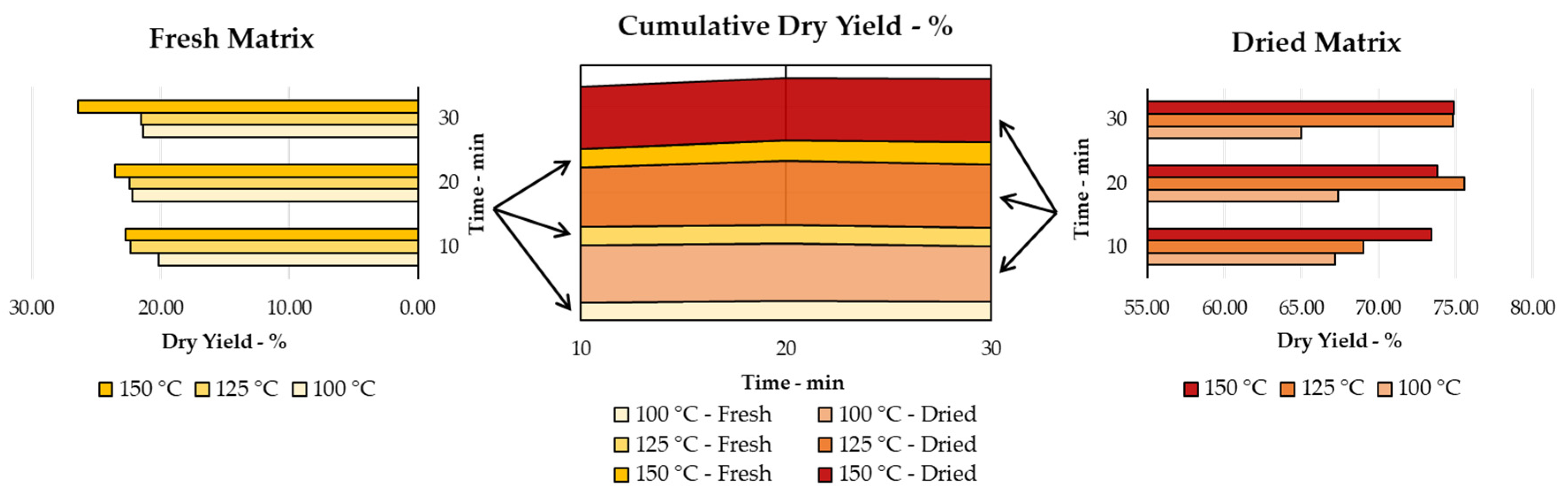
Figure 1.
Dry extraction yields for MAE of F-PP and D-PP: time and temperature screening; cumulative Dry Yield reports stacked percentage, for comparison.
Figure 1.
Dry extraction yields for MAE of F-PP and D-PP: time and temperature screening; cumulative Dry Yield reports stacked percentage, for comparison.
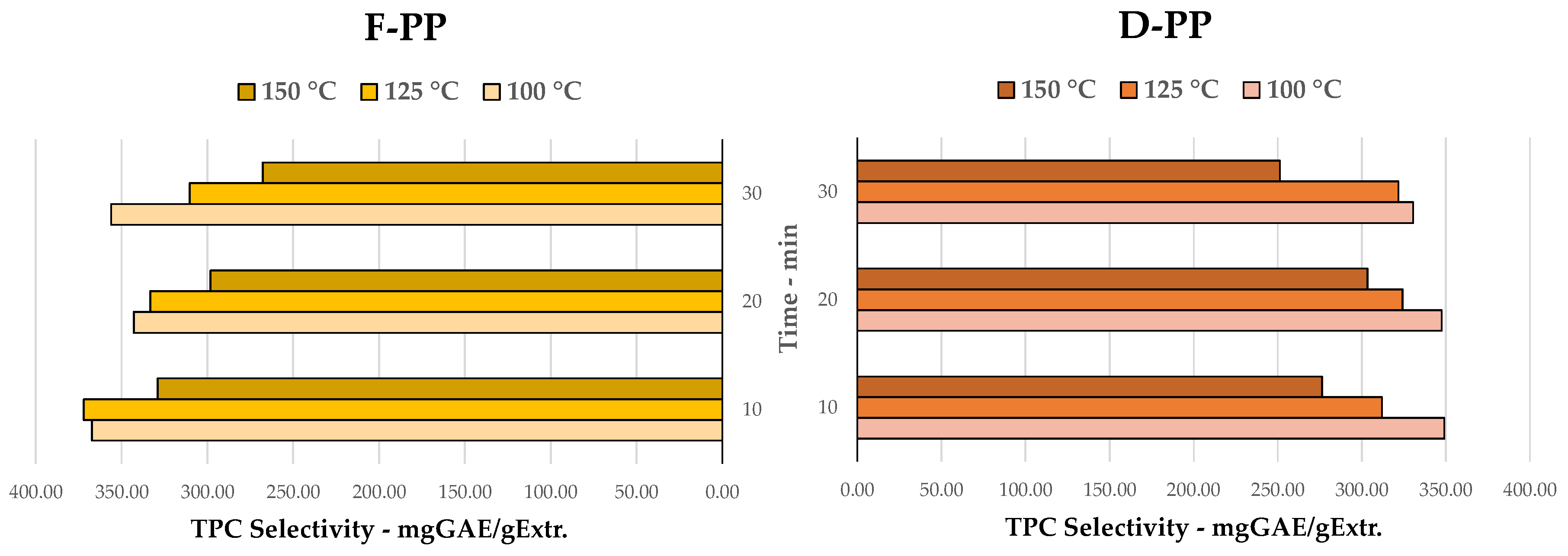
Figure 2.
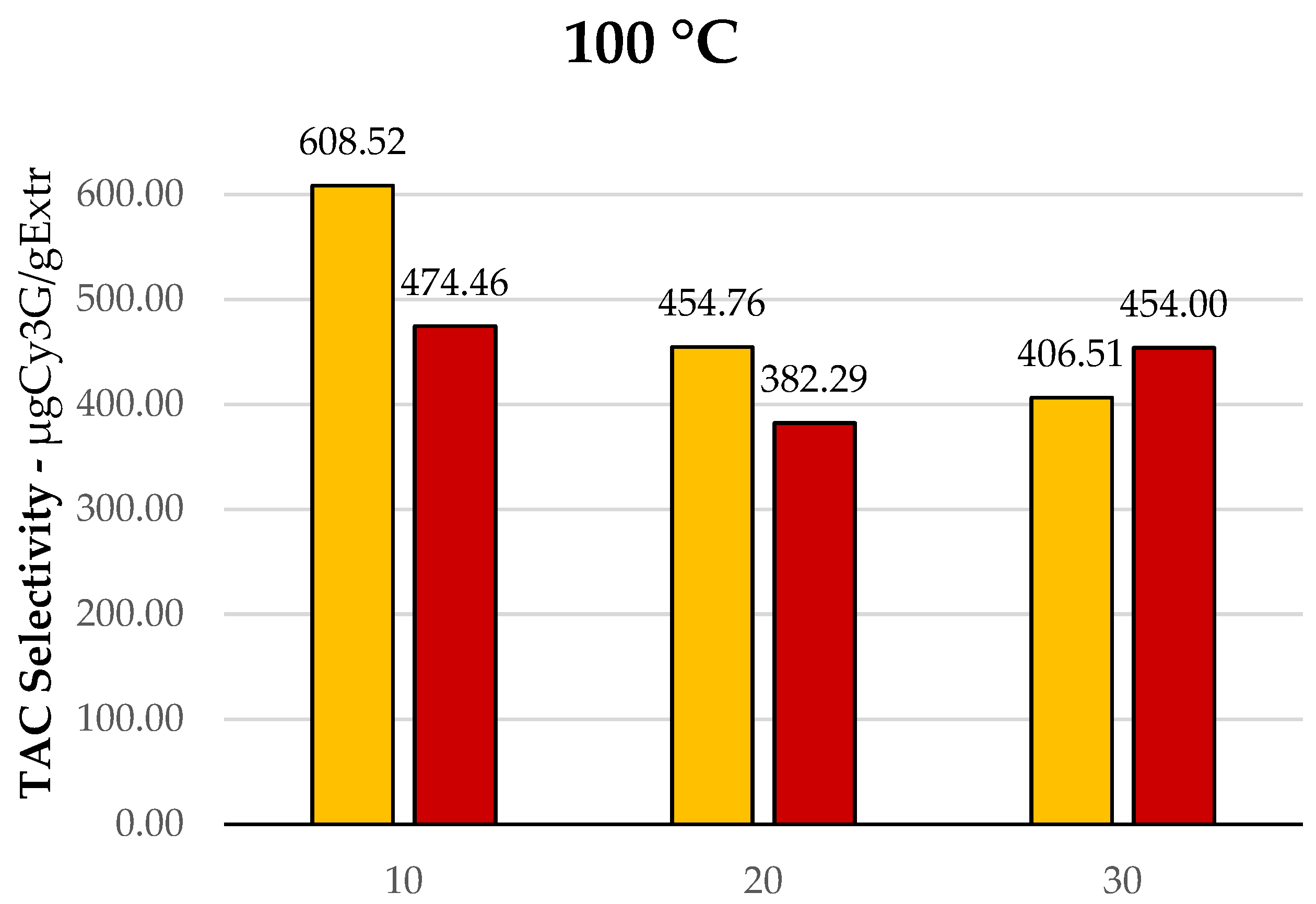
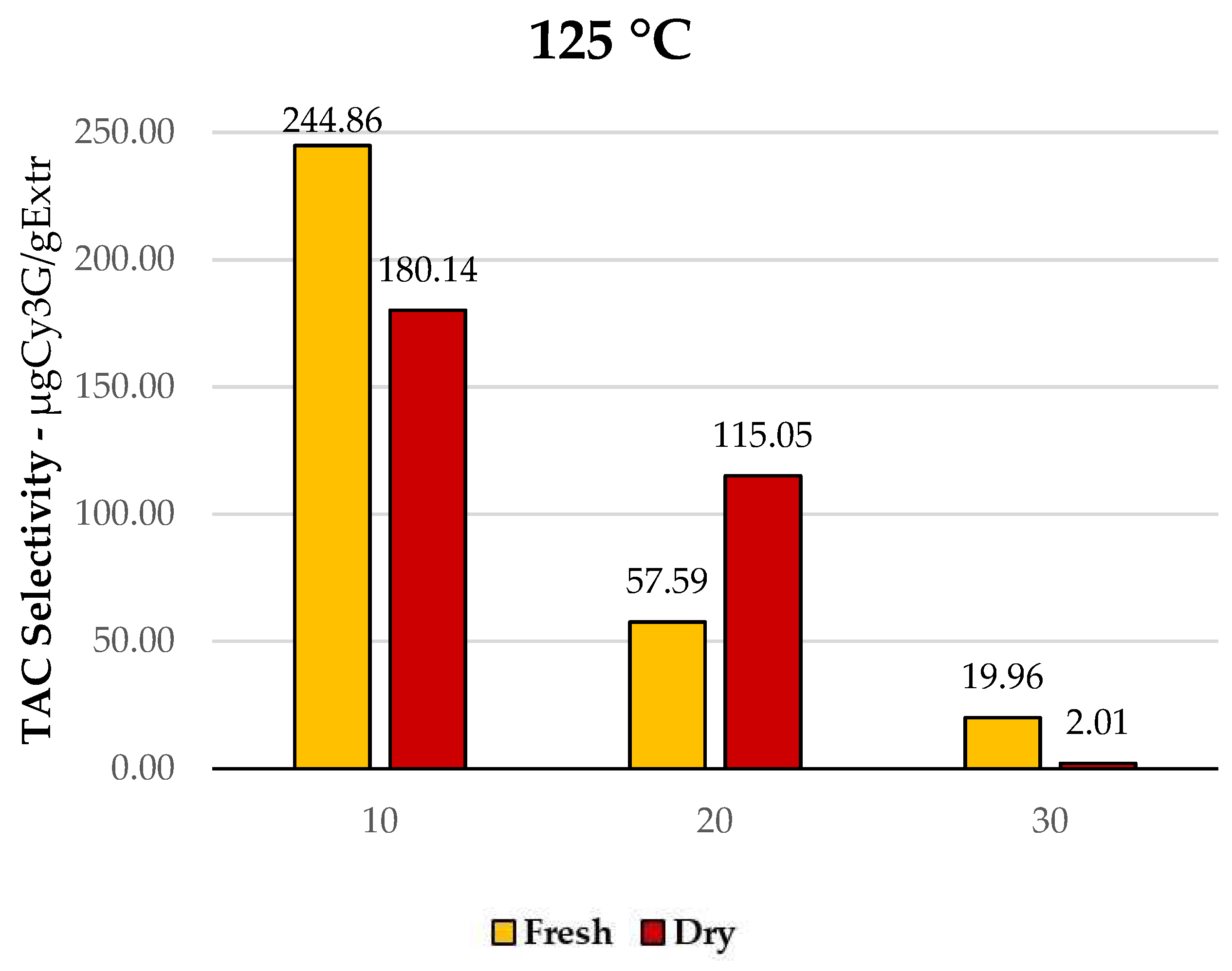
TPC selectivity for MAE of F-PP and D-PP, time and temperature screening.
Figure 2.
TPC selectivity for MAE of F-PP and D-PP, time and temperature screening.
Figure 3.
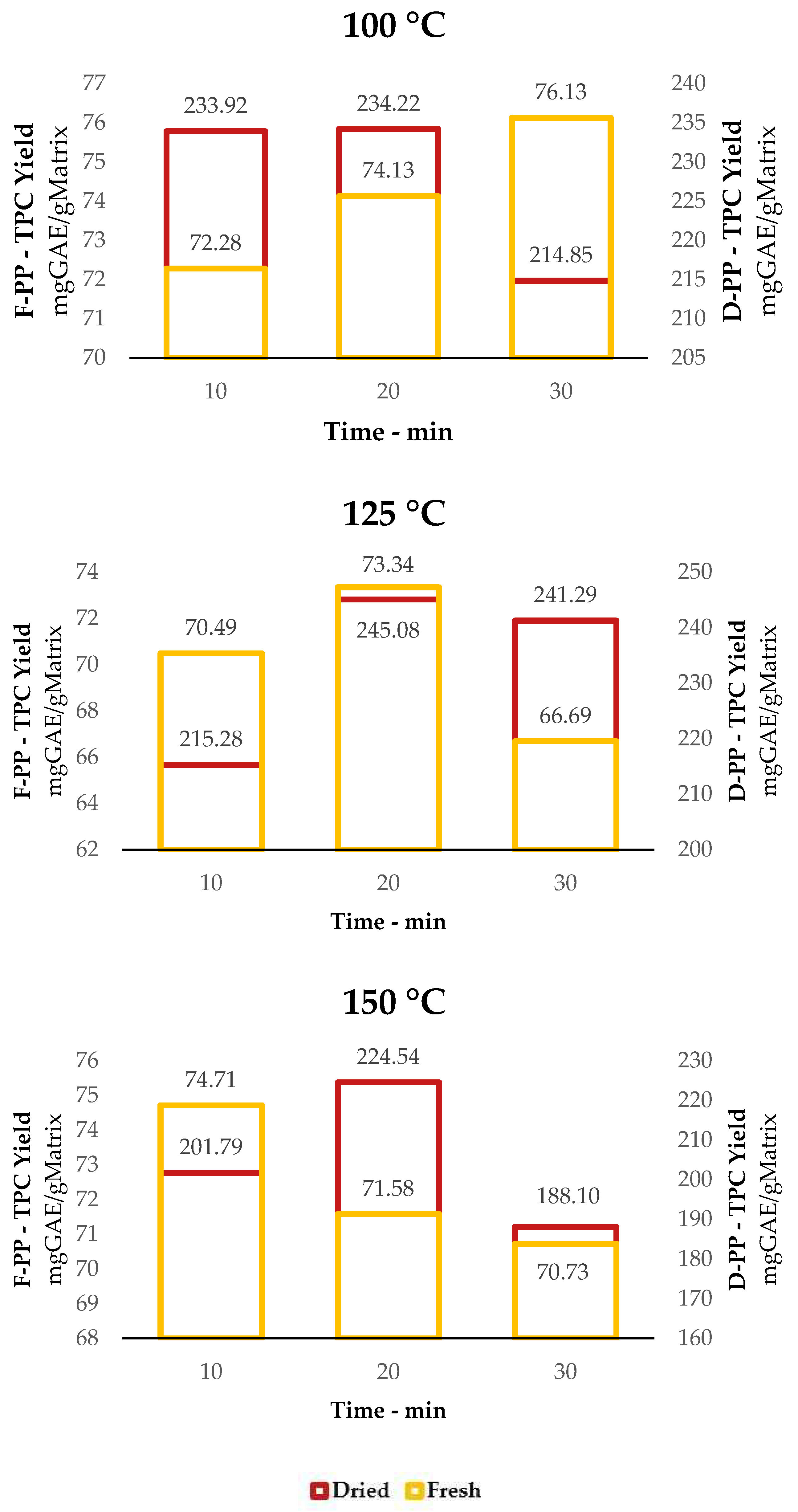
TPC yield for MAE of F-PP and D-PP at different temperatures: 100 °C, 125 °C and 150 °C.
Figure 3.
TPC yield for MAE of F-PP and D-PP at different temperatures: 100 °C, 125 °C and 150 °C.
Figure 4.
Extraction TAC for MAE of F-PP and D-PP, time and temperature dependence: 100 °C and 125 °C. 150 °C not reported due to absence of signal.
Figure 4.
Extraction TAC for MAE of F-PP and D-PP, time and temperature dependence: 100 °C and 125 °C. 150 °C not reported due to absence of signal.
Figure 5.
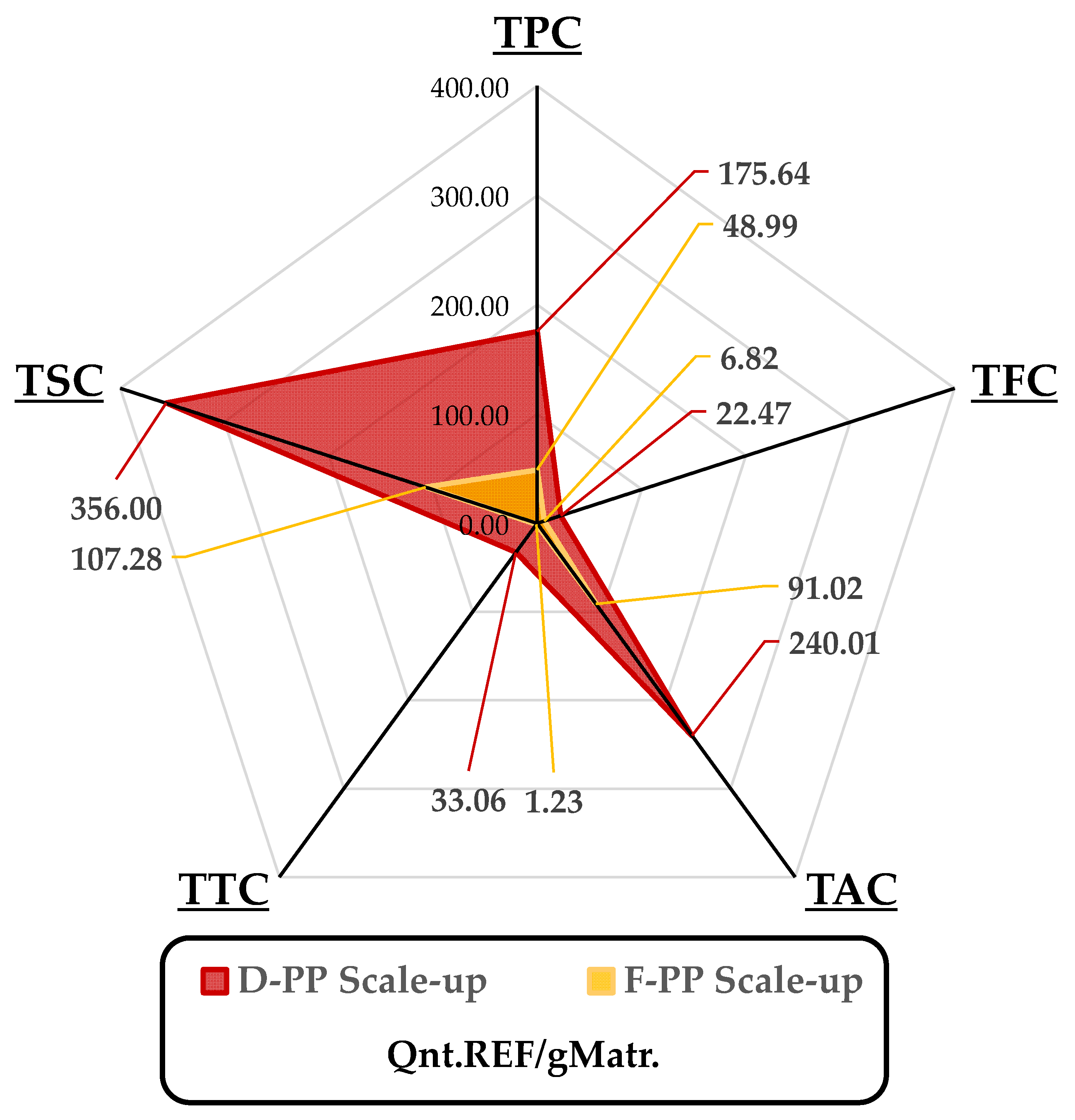
The main components of the quali-quantitative analysis for MAE scale-up for F-PP and D-PP. Yields are reported per gram of extracted matrix, reporting total weight of polyphenols, flavonoids, anthocyanins, tannins and sugars according to the adopted reference. In detail, TPC: mgGAE; TFC: mgQE; TAC: µgCy3G; TTC: mgGAE; TSC mgGLU.
Figure 5.
The main components of the quali-quantitative analysis for MAE scale-up for F-PP and D-PP. Yields are reported per gram of extracted matrix, reporting total weight of polyphenols, flavonoids, anthocyanins, tannins and sugars according to the adopted reference. In detail, TPC: mgGAE; TFC: mgQE; TAC: µgCy3G; TTC: mgGAE; TSC mgGLU.
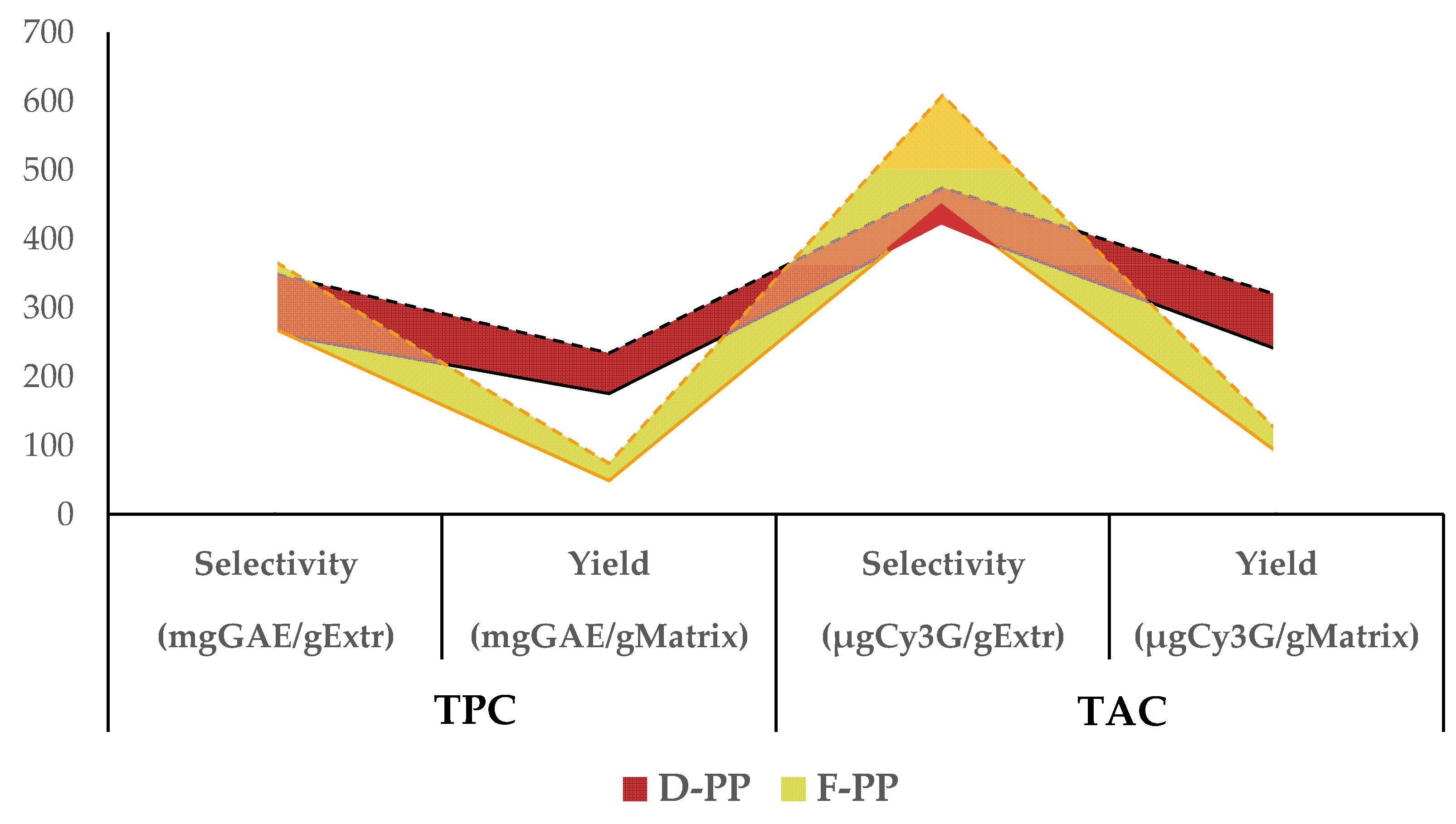
Figure 6.
Comparison of TPC and TAC variation in scale-up transposition. Selectivity and yields are reported for D-PP and F-PP. Dashed lines: Lab-scale; Solid lines: Scaled-up.
Figure 6.
Comparison of TPC and TAC variation in scale-up transposition. Selectivity and yields are reported for D-PP and F-PP. Dashed lines: Lab-scale; Solid lines: Scaled-up.
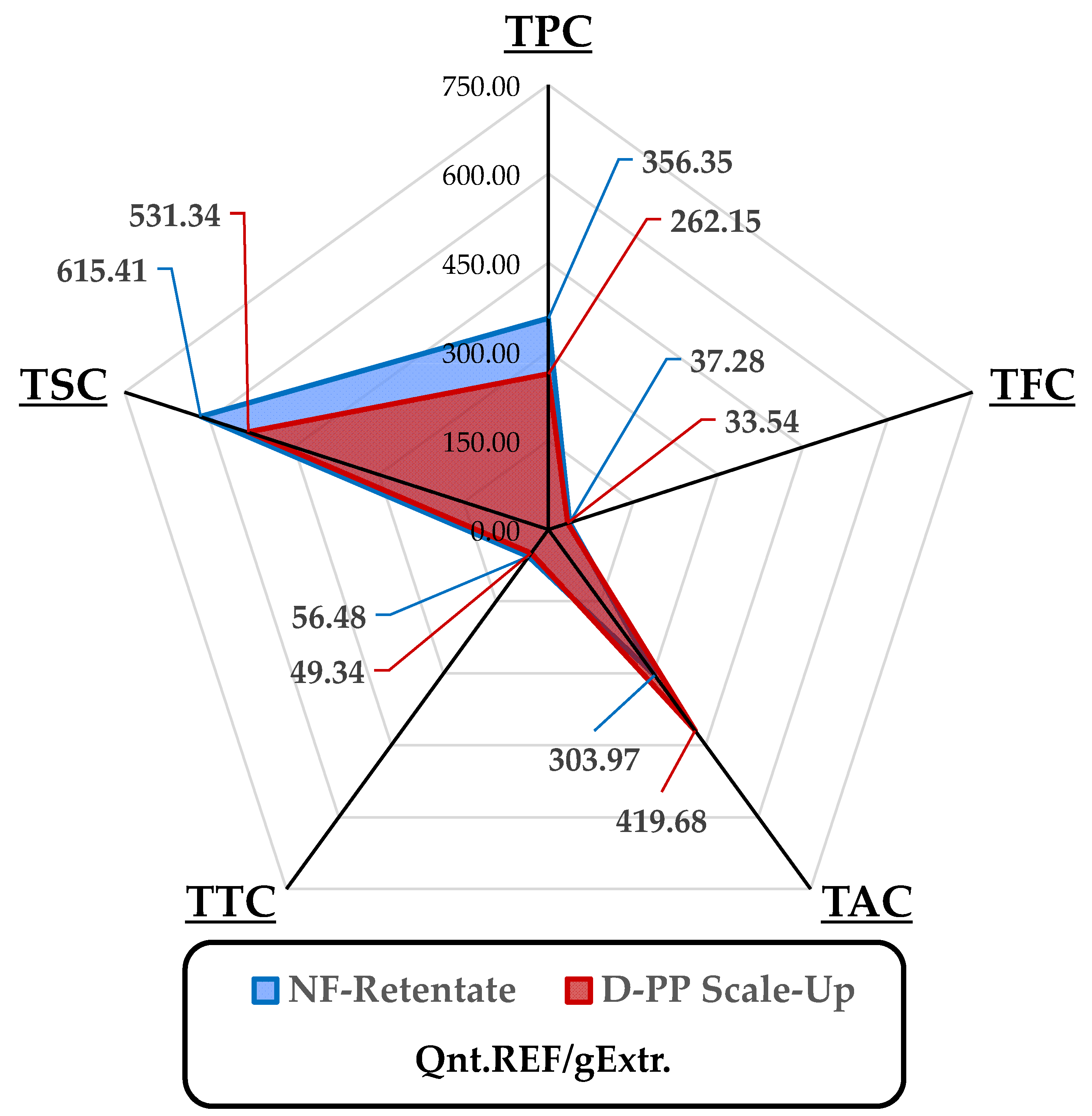
Figure 7.
Main components of quali-quantitative analysis for MAE scale-up of D-PP and its NF-retentate. Selectivity is reported per gram of extract, reporting total weight of polyphenols, flavonoids, anthocyanins, tannins and sugars according to the adopted reference. In detail, TPC: mgGAE; TFC: mgQE; TAC: µgCy3G; TTC: mgGAE; TSC mgGLU.
Figure 7.
Main components of quali-quantitative analysis for MAE scale-up of D-PP and its NF-retentate. Selectivity is reported per gram of extract, reporting total weight of polyphenols, flavonoids, anthocyanins, tannins and sugars according to the adopted reference. In detail, TPC: mgGAE; TFC: mgQE; TAC: µgCy3G; TTC: mgGAE; TSC mgGLU.
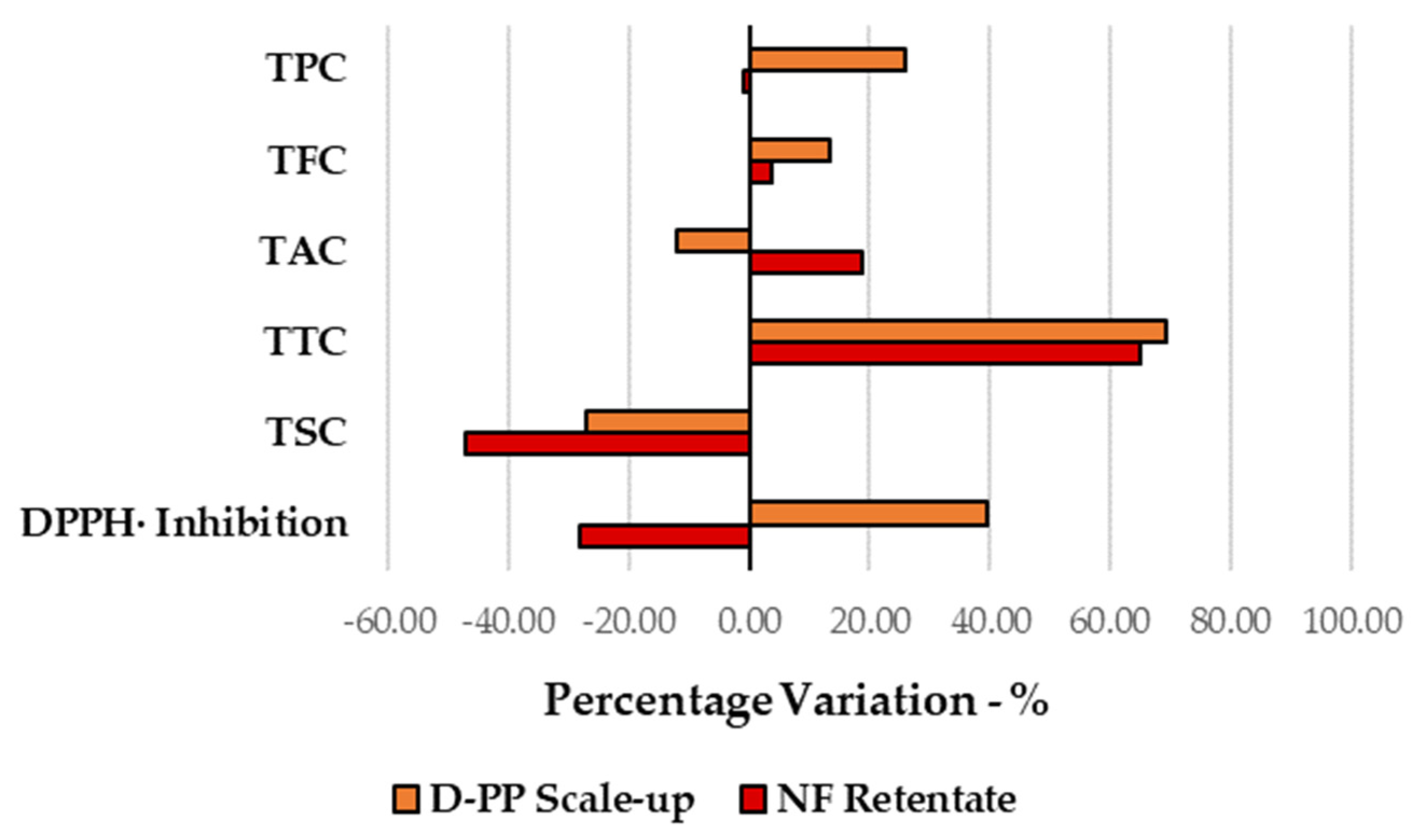
Figure 8.
Comparison with hydroalcoholic benchmark extraction for D-PP scaled-up extraction and the related NF retentate. Percentage variations are calculated using conventional benchmark as the reference (y-axis).
Figure 8.
Comparison with hydroalcoholic benchmark extraction for D-PP scaled-up extraction and the related NF retentate. Percentage variations are calculated using conventional benchmark as the reference (y-axis).
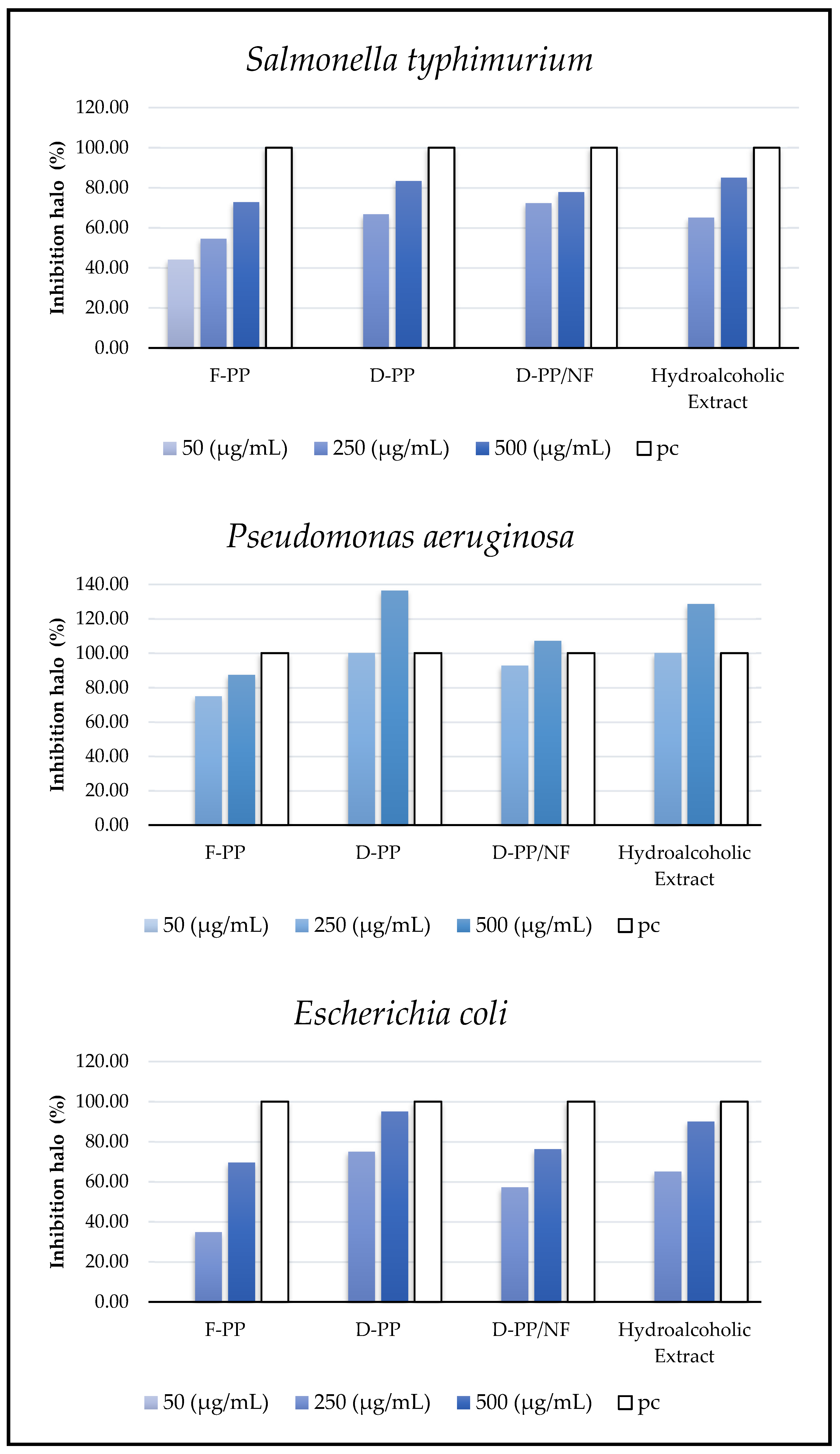
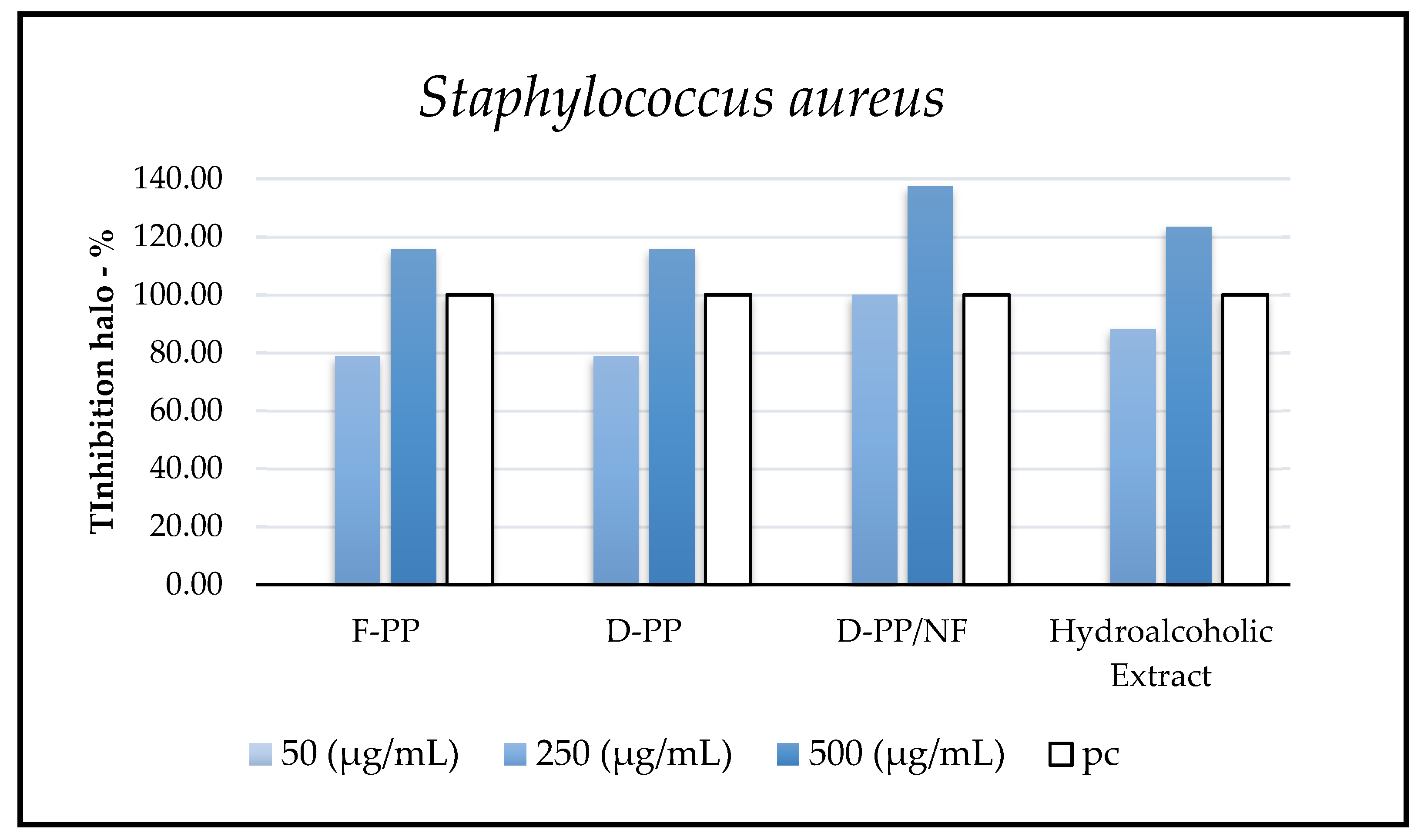
Figure 9.
Antimicrobial activity of PP extracts against pathogens (mm). pc = positive control. Reported data are normalized on pc.
Figure 9.
Antimicrobial activity of PP extracts against pathogens (mm). pc = positive control. Reported data are normalized on pc.
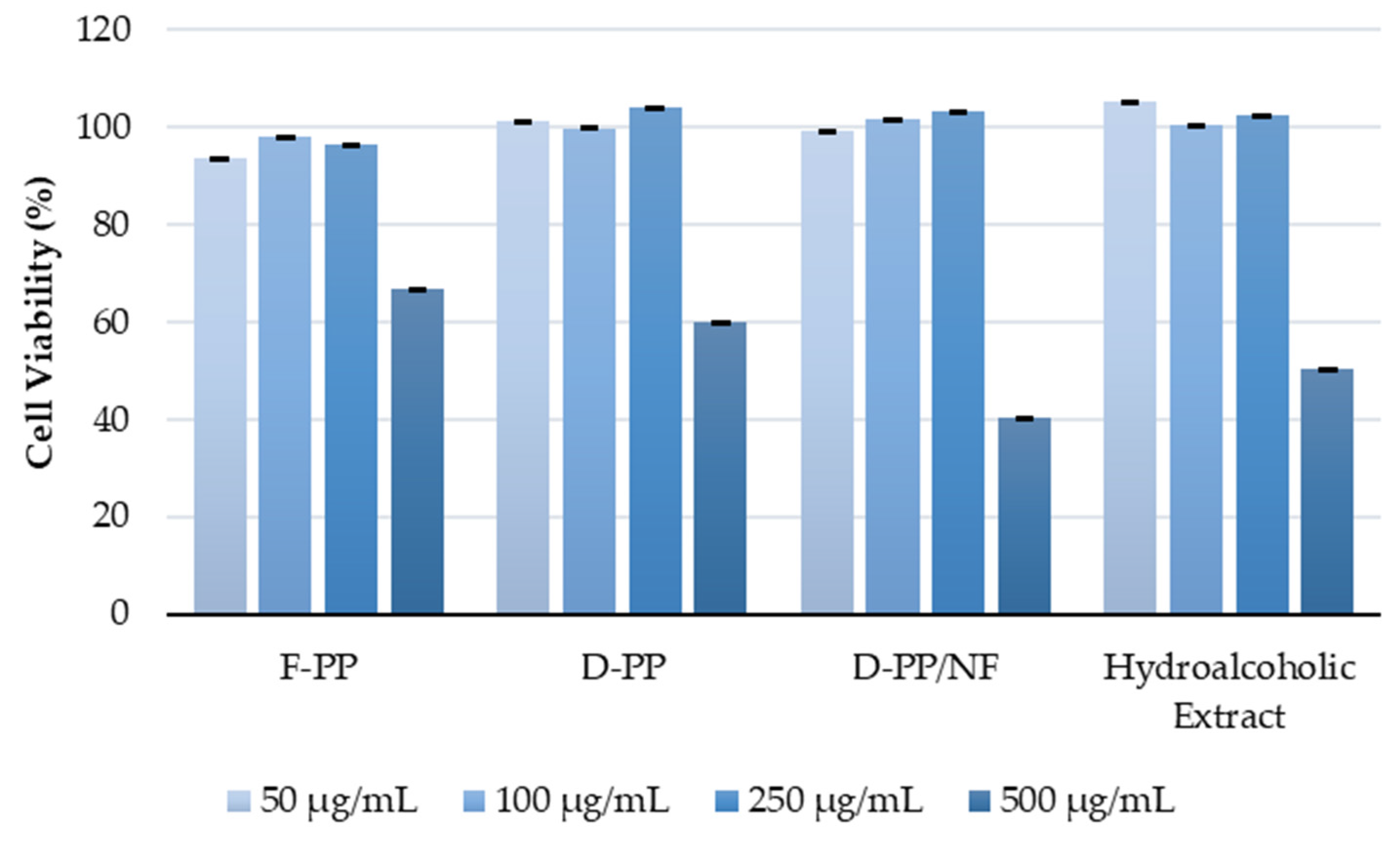
Figure 10.
Viability of HeLa cells treated with four PP extracts for 72 h in the range of concentration from 50 μg/mL to 500 μg/mL assessed using the CellTiter AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay. Cell viability (%) is expressed as percentage of treated cells versus control cells.
Figure 10.
Viability of HeLa cells treated with four PP extracts for 72 h in the range of concentration from 50 μg/mL to 500 μg/mL assessed using the CellTiter AQueous One Solution Cell Proliferation Assay. Cell viability (%) is expressed as percentage of treated cells versus control cells.
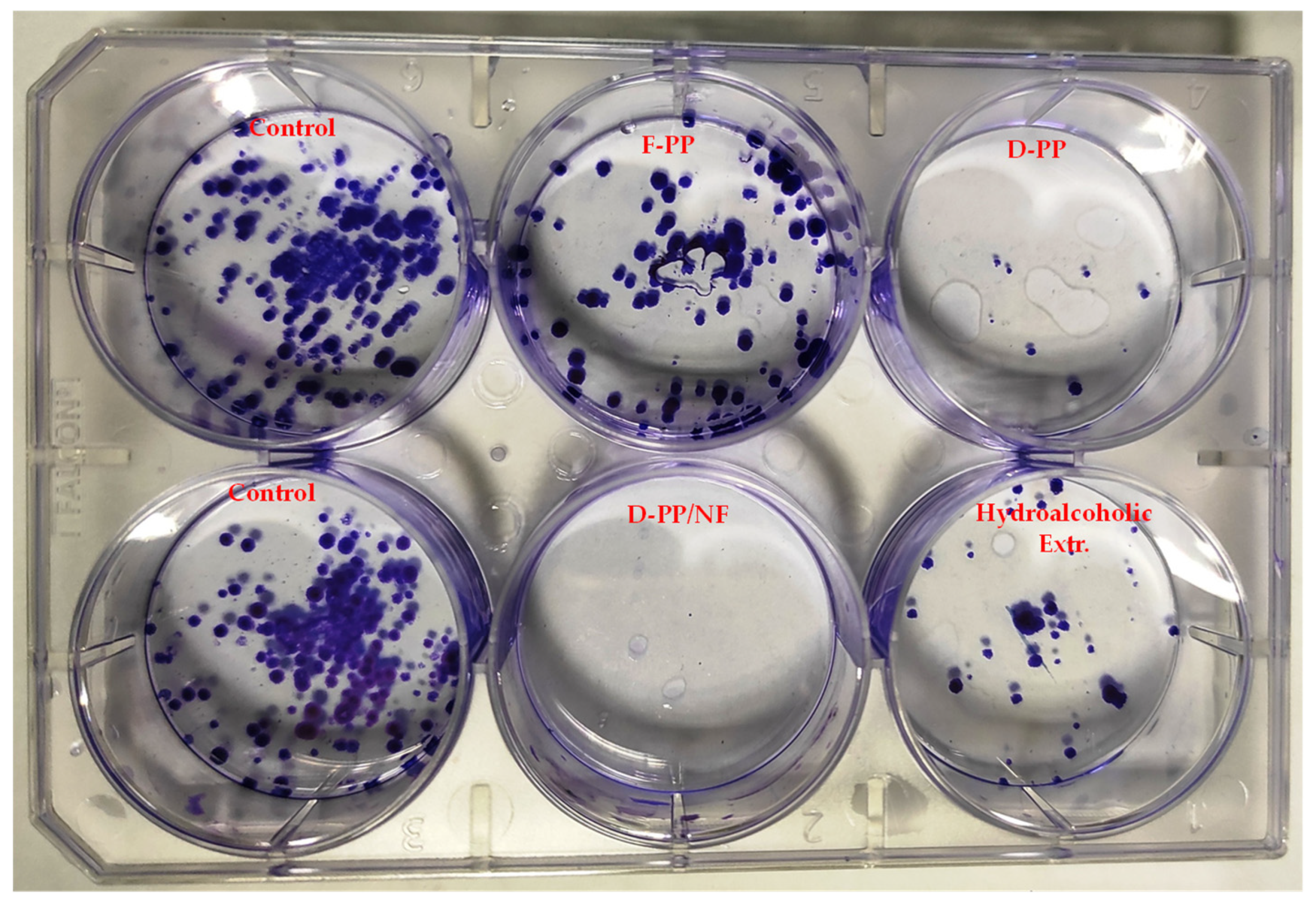
Figure 11.
Result of clonogenic analysis after treatment with PP extracts at a concentration of 500 µg/mL.
Figure 11.
Result of clonogenic analysis after treatment with PP extracts at a concentration of 500 µg/mL.
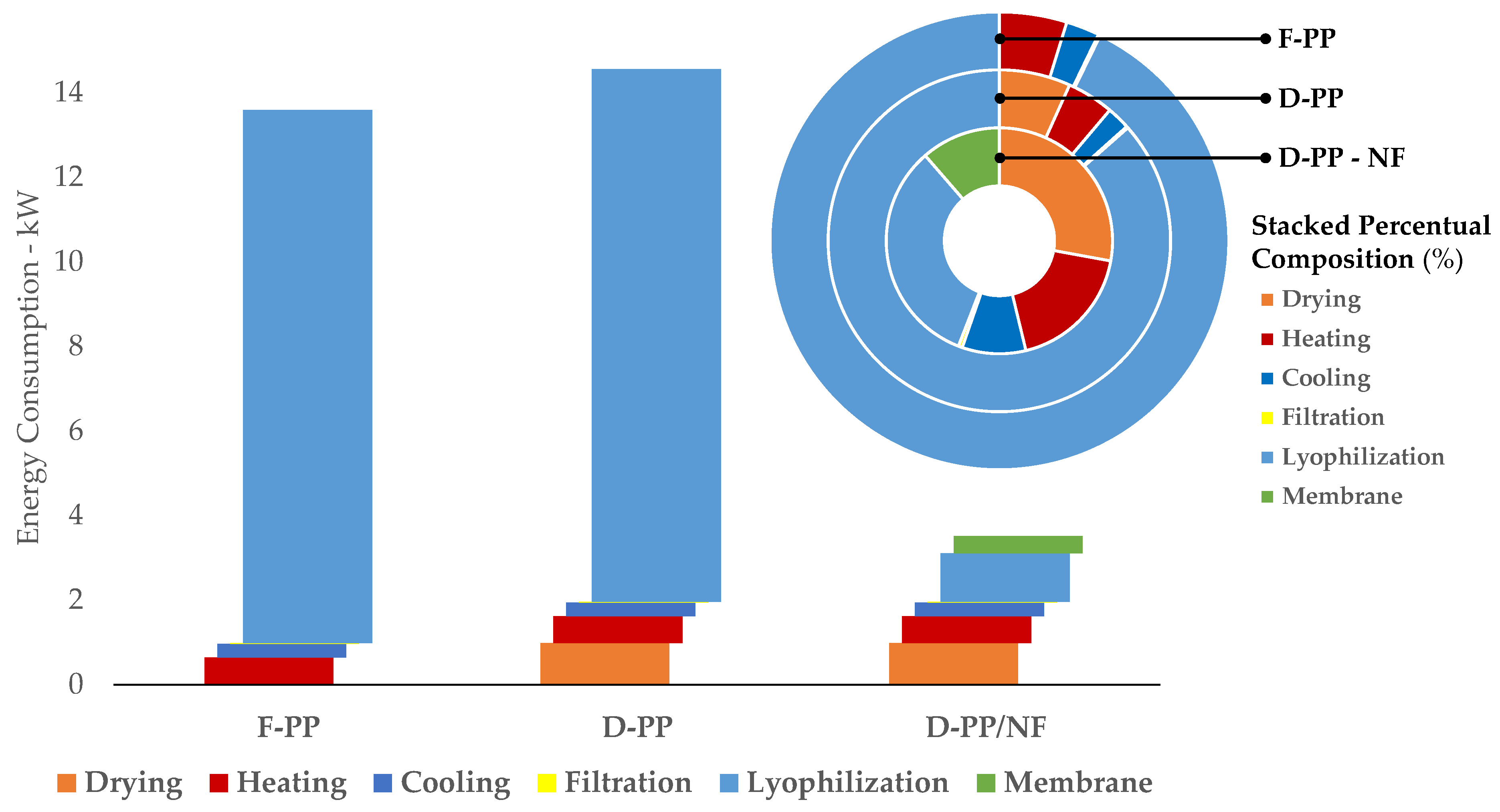
Figure 12.
Energy Consumption and relative distribution. All data refer to scaled-up extractions.
Figure 12.
Energy Consumption and relative distribution. All data refer to scaled-up extractions.
Table 1.
Thermogravimetric analysis of F-PP and D-PP.
Table 1.
Thermogravimetric analysis of F-PP and D-PP.
| Fraction |
Percentage Composition (%) |
| Fresh Matrix |
Dried Matrix |
| Water |
75.52 |
3.50 |
| Organic |
23.86 |
94.06 |
| Inorganic |
0.62 |
2.44 |
Table 2.
Antioxidant activity expressed as DPPH· radical inhibition and Cu-chelation, with relative EC50, Trolox eq. and EDTA eq. values. Samples produced at 100 °C, 10 min.
Table 2.
Antioxidant activity expressed as DPPH· radical inhibition and Cu-chelation, with relative EC50, Trolox eq. and EDTA eq. values. Samples produced at 100 °C, 10 min.
| |
DPPH· Inhibition |
|
Cu-Chelating Activity |
| Matrix |
EC50 |
Trolox eq. |
|
EC50 |
EDTA eq. |
| (µg/mL) |
(µmolTE/gext) |
|
(µg/mL) |
(µmolEDTA/gext) |
| F-PP |
2.30 |
3.30 |
|
88.60 |
513.66 |
| D-PP |
5.30 |
1.43 |
|
85.90 |
529.81 |
Table 3.
Scaled-up MAE (100 °C, 10 min) of F-PP and D-PP: Polyphenol Energy Efficiency calculation as a function of yields and energy consumption.
Table 3.
Scaled-up MAE (100 °C, 10 min) of F-PP and D-PP: Polyphenol Energy Efficiency calculation as a function of yields and energy consumption.
| |
D-PP |
F-PP |
| Dry yield (%)
|
67.20 |
20.18 |
| TPC Yield (mgGAE/gMatrix)
|
175.64 |
48.99 |
| Energy Consumption (kW)*
|
1.94** |
0.97 |
| Polyphenols Energy Efficiency (W/mgGAE)
|
11.07 |
19.72 |
Table 4.
Surviving fraction (SF) for HeLa cells treated with PP extracts (500 µg/mL).
Table 4.
Surviving fraction (SF) for HeLa cells treated with PP extracts (500 µg/mL).
| |
F-PP |
D-PP |
D-PP/NF |
Hydroalcoholic Extr. |
| SF |
0.646 |
0.074 |
0 |
0.274 |
Table 5.
Green metrics for MAE of D-PP; comparison of hydroalcoholic benchmark, D-PP scale-up and its relative NF. Green bars: metrics considered directly proportional to sustainability; red bars: metrics considered inversely proportional to sustainability.
Table 5.
Green metrics for MAE of D-PP; comparison of hydroalcoholic benchmark, D-PP scale-up and its relative NF. Green bars: metrics considered directly proportional to sustainability; red bars: metrics considered inversely proportional to sustainability.