Submitted:
29 July 2023
Posted:
31 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
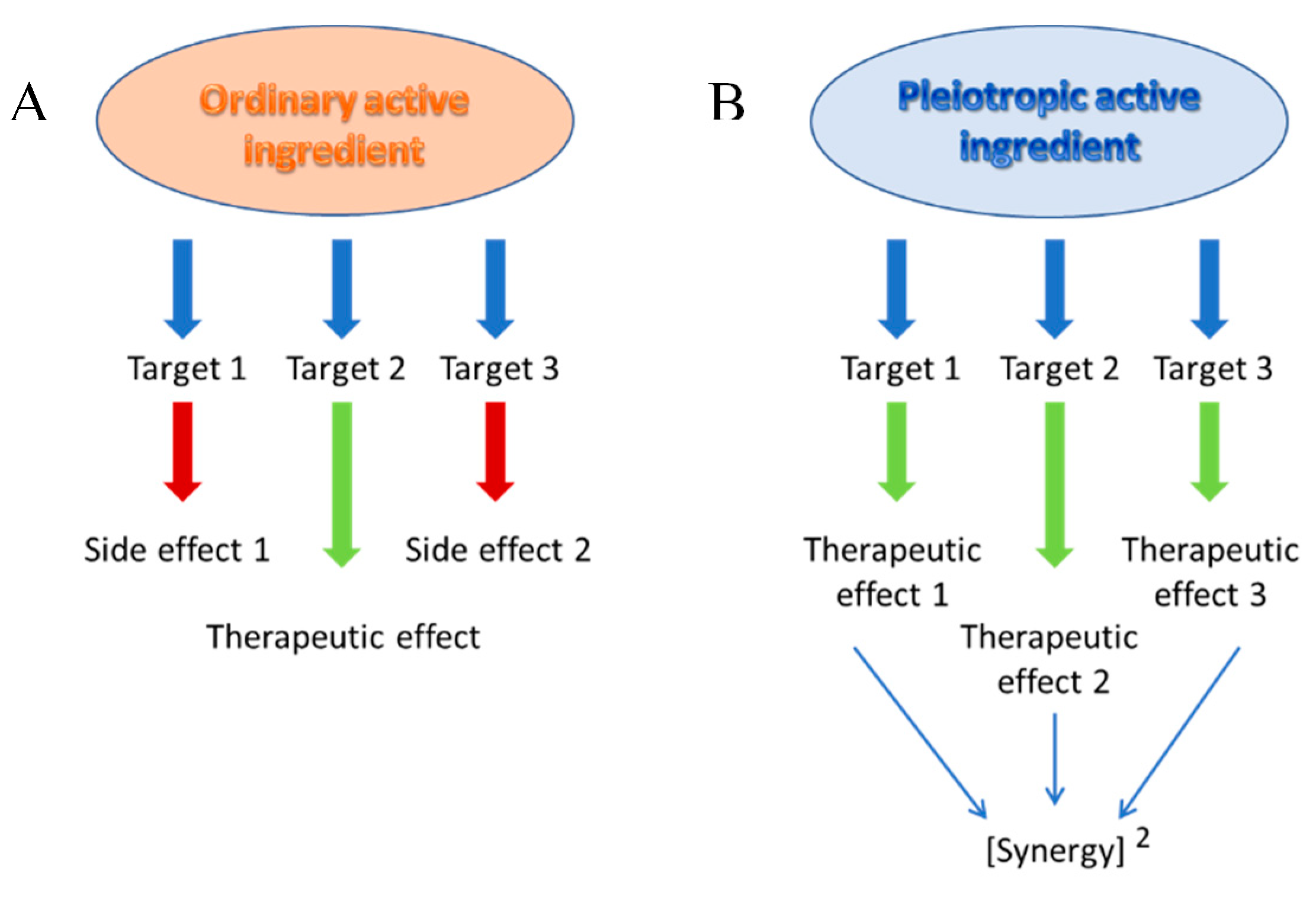
1. The concept of pleiotropic active drugs
2. The application of the concept of pleiotropic active compounds to the therapeutic management of Alzheimer’s disease
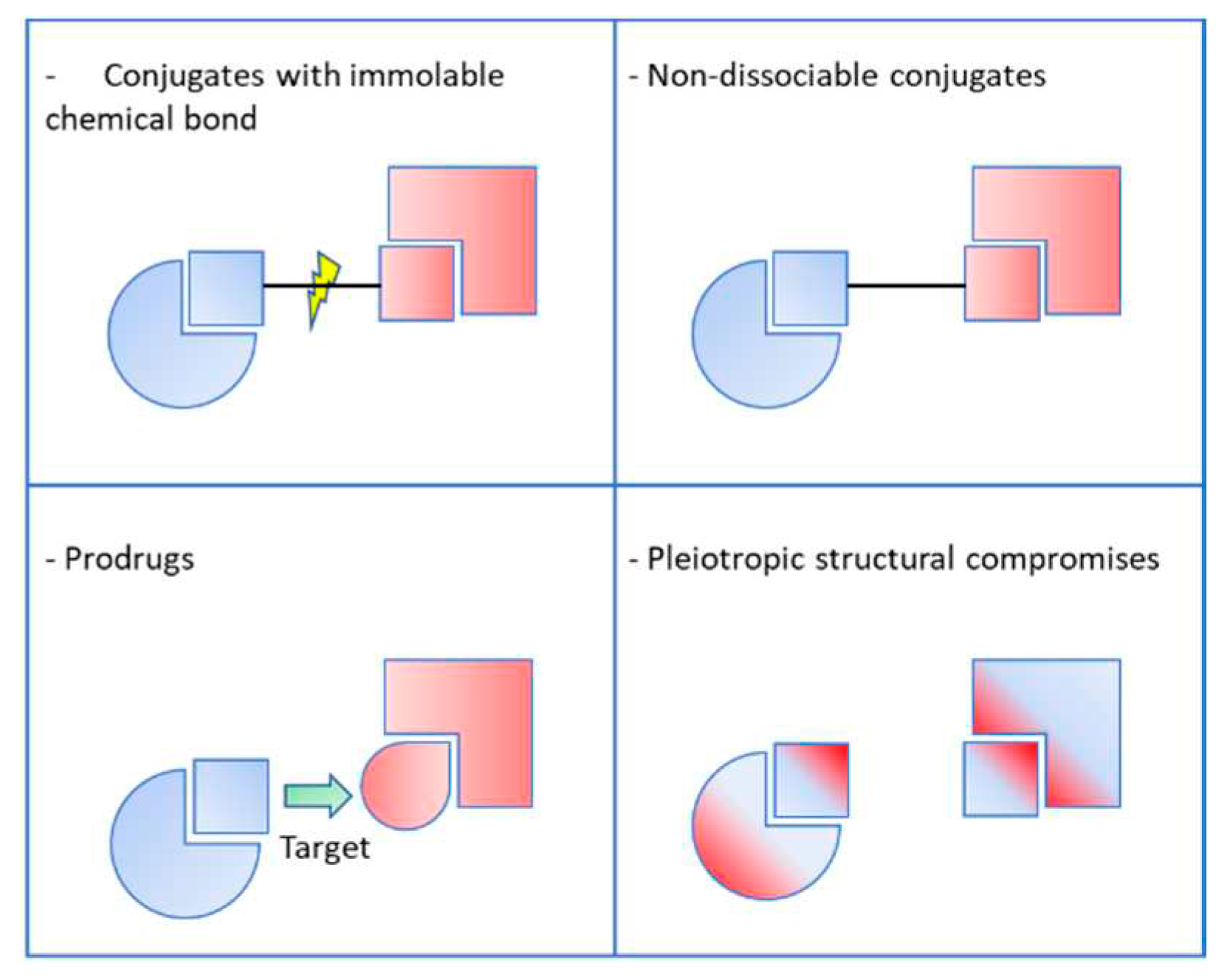
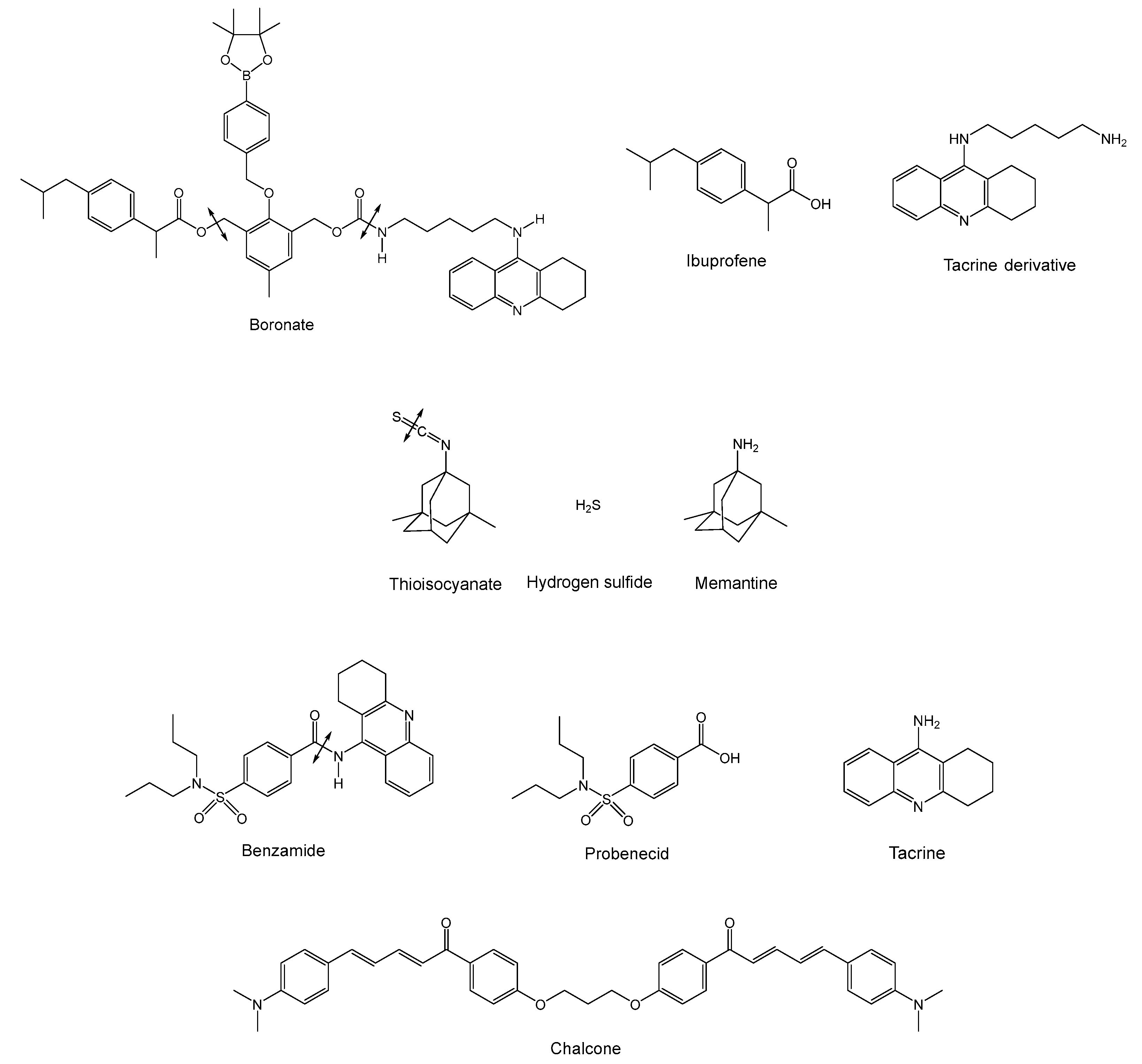
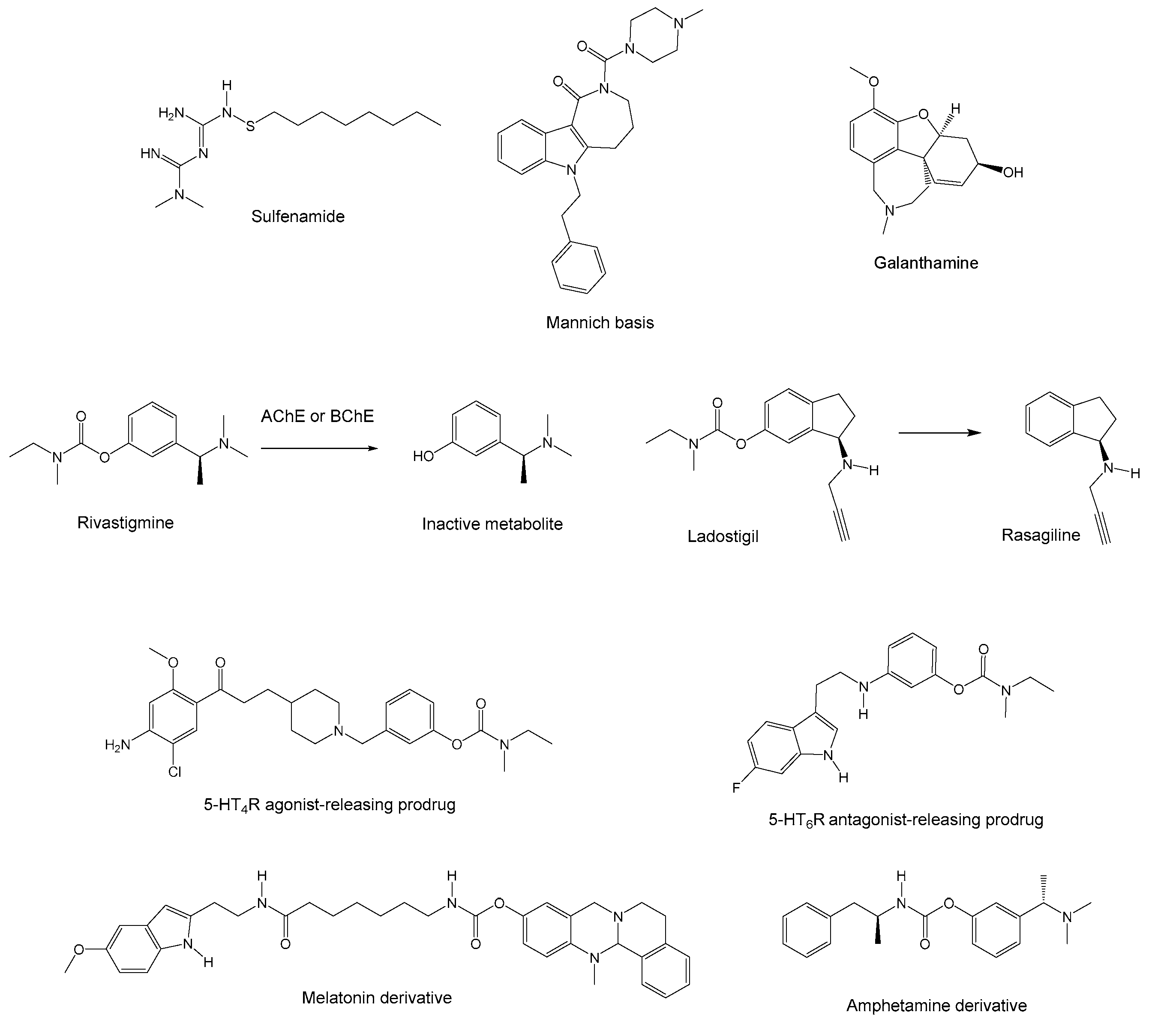
2.1. Conjugates with immolable chemical bond
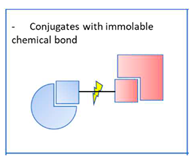
2.2. Non-dissociable conjugates
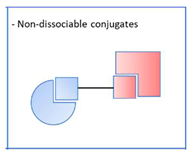
2.3. Pleiotropic prodrugs
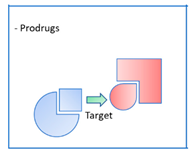
2.4. Pleiotropic structural compromises
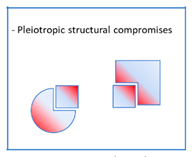
3. Conclusion
Funding
Declaration of Interest Statement
References
- Ehrlich P. Experimental researches on specific therapy. Pergamon Press Ltd, Ed. The collected papers of Paul Ehrlich. London: Himmelweit; 1960: 106–117.
- Lalut J., Rochais C., Dallemagne P. Multiple ligands in neurodegenerative diseases. Wiley-VCH Verlag GmbH & Co. Drug selectivity: An evolving concept in medicinal chemistry. Hoboken: Handler and Bushmann; 2017: 477-508.
- Cavalli A., Bolognesi M.L., Minarini A., et al. Multi-Target Directed Ligands to combat neurodegenerative diseases. J. Med. Chem. 2008; 51(3): 347-372. [CrossRef]
- Parvin N., Jozwiak K. Effects of linkers and substitutions on Multi-Target Directed Ligands for Alzheimer’s diseases: Emerging paradigms and strategies. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2022;23: 6085.
- De Simone A., Tumiatti V., Andrisano V., et al. Glycogen Synthase Kinase 3β: A New Gold Rush in Anti-Alzheimer’s Disease Multitarget Drug Discovery? J. Med. Chem. 2021;64: 26−41.
- Kumar N., Kumar V., Anand P., et al. Advancements in the development of multi-target directed ligands for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Med. Chem. 2022;61: 116742. [CrossRef]
- Travers--Lesage V., Mignani S., Dallemagne P., Rochais C. Advances in prodrug design for Alzheimer’s disease: the state of the art. Expert. Opin. Drug. Discov. 2022;17(4): 325-41. [CrossRef]
- Liu Z., Zhang B., Xia S., et al. ROS-responsive and multifunctional anti-alzheimer prodrugs: tacrine-ibuprofen hybrids via a phenylboronate linker. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021;212: 112997.
- Sestito S., Daniele S., Pietrobono D., et al. Memantine prodrug as a new agent for Alzheimer’s disease. Sci. Rep. 2019;9(1): 4612. [CrossRef]
- Gong T., Huang Y., Zhang Z-R., et al. Synthesis and characterization of 9-[P-(N,N-dipropylsulfamide)] benzoylamino-1,2,3,4-4H-acridine- A potential prodrug for the CNS delivery of tacrine. J. Drug. Target. 2004;12(3): 177-182.
- Liargkova T., Hadjipavlou-Litina D.J., Koukoulitsa C., et al. Simple chalcones and bis-chalcones ethers as possible pleiotropic agents. J. Enzyme Inhib. Med. Chem. 2016;31(2): 302-301. [CrossRef]
- Gody J., Zareba P., Lazewska D., et al. Cyanobiphenyls: Novel H3 receptor ligands with cholinesterase and MAO B inhibitory activity as multitarget compounds for potential treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2021;114: 105129. [CrossRef]
- George N., Akhtar M.J., Al Balushi K.A., et al. Rational drug design strategies for the development of promising multi-target directed indole hybrids as Anti-Alzheimer agents. Bioorg. Chem. 2022;127: 105941. [CrossRef]
- Rossi M., Freschi M., de Camargo Nascente L., et al. Sustainable drug discovery of multi-target-directed ligands for Alzheimer’s disease. J. Med. Chem. 2021;64: 4972−4990. [CrossRef]
- Ismaili L., Monnin J., Etievant A., et al. (±)-BIGI-3h: Pentatarget-directed ligand combining cholinesterase, monoamine oxidase, and glycogen synthase kinase 3β inhibition with calcium channel antagonism and antiaggregating properties for Alzheimer’s disease. ACS. Chem. Neurosci. 2021;12: 1328-1342.
- Javed M.A., Ashraf N., Jan M.S., et al. Structural modification, in vitro, in vivo, ex vivo, and in silico exploration of pyrimidine and pyrrolidine cores for targeting enzymes associated with neuroinflammation and cholinergic deficit in Alzheimer’s disease. ACS. Chem. Neurosci. 2021;12: 4123−4143.
- Nozal V., Garcia-Rubia A., Cuevas E.P., et al. From kinase inhibitors to multitarget ligands as powerful drug leads for Alzheimer’s disease using protein-templated synthesis. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. 2021;60: 19344–19354. [CrossRef]
- Mazej T., Knez D., Meden A., et al. 4-Phenethyl-1-propargylpiperidine-derived dual inhibitors of butyrylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase B. Molecules 2021;26: 4118. [CrossRef]
- Zhang P., Wang Z., Mou C., et al. Design and synthesis of novel tacrine-dipicolylamine dimers that are multiple-target-directed ligands with potential to treat Alzheimer’s disease. Bioorg. Chem. 2021;116: 105387.
- Markowicz-Piasecka M., Sikora J., Mateusiak L., et al. Metformin and its sulfenamide prodrugs inhibit human cholinesterase activity. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2017;2017: 1–11. [CrossRef]
- Purgatorio R., Candia M., Catto M., et al. Evaluation of water-soluble Mannich base prodrugs of 2,3,4,5-tetrahydroazepino[4,3-b]indol-1(6H)-one as multitarget-directed agents for Alzheimer’s disease. ChemMedChem. 2021;16(3): 589–598.
- Weinstock M., Goren T., Youdim M.B.H. Development of a novel neuroprotective drug (TV3326) for the treatment of Alzheimer’s disease, with cholinesterase and monoamine oxidase inhibitory activities. Drug. Dev. Res. 2000;50(3–4): 216–222.
- Youdim M.B., Weinstock M. Molecular basis of neuroprotective activities of rasagiline and the anti-Alzheimer drug TV3326 [(N-propargyl-(3R)aminoindan-5-yl)-ethyl methyl carbamate]. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2001;21(6): 555–573. [CrossRef]
- Zheng H., Youdim M.B.H., Fridkin M. Site-activated chelators targeting acetylcholinesterase and monoamine oxidase for Alzheimer’s therapy. ACS. Chem. Biol. 2010;5(6): 603–610. [CrossRef]
- Huang W., Liang M., Li Q., et al. Development of the “hidden” multifunctional agents for Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019;177: 247–258.
- Zheng H., Youdim M.B.H., Fridkin M. Site-activated multifunctional chelator with acetylcholinesterase and neuroprotective−neurorestorative moieties for Alzheimer’s therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2009;52(14): 4095–4098. [CrossRef]
- Toublet F-X., Lecoutey C., Lalut J., et al. Inhibiting acetylcholinesterase to activate pleiotropic prodrugs with therapeutic interest in Alzheimer’s disease. Molecules. 2019;24(15): 2786. [CrossRef]
- Toublet F-X., Lalut J., Hatat B., et al. Pleiotropic prodrugs: Design of a dual butyrylcholinesterase inhibitor and 5-HT6 receptor antagonist with therapeutic interest in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021;210: 113059. [CrossRef]
- Scheiner M., Hoffmann M., He F., et al. Selective pseudo-irreversible butyrylcholinesterase inhibitors transferring antioxidant moieties to the enzyme show pronounced neuroprotective efficacy in vitro and in vivo in an Alzheimer’s disease mouse model. J. Med. Chem. 2021;64(13): 9302–9320. [CrossRef]
- Verheijen J.C., Wiig K.A., Du S., et al. Novel carbamate cholinesterase inhibitors that release biologically active amines following enzyme inhibition. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2009;19(12): 3243–3246.
- Iancu G., Serban D., Badiu C.D., et al. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors in breast cancer. Exp. Ther. Med. 2022; 23(2): 114. [CrossRef]
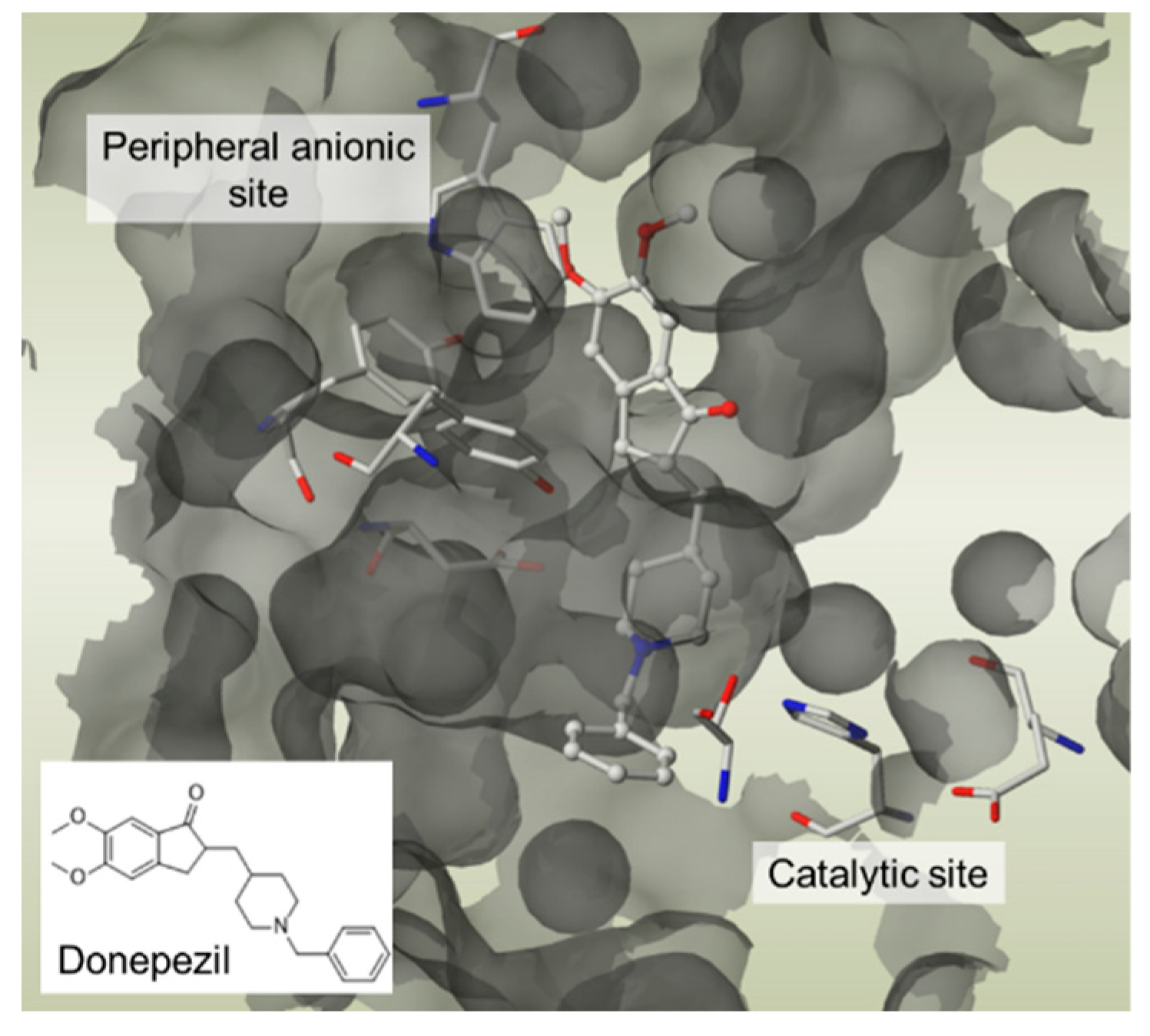
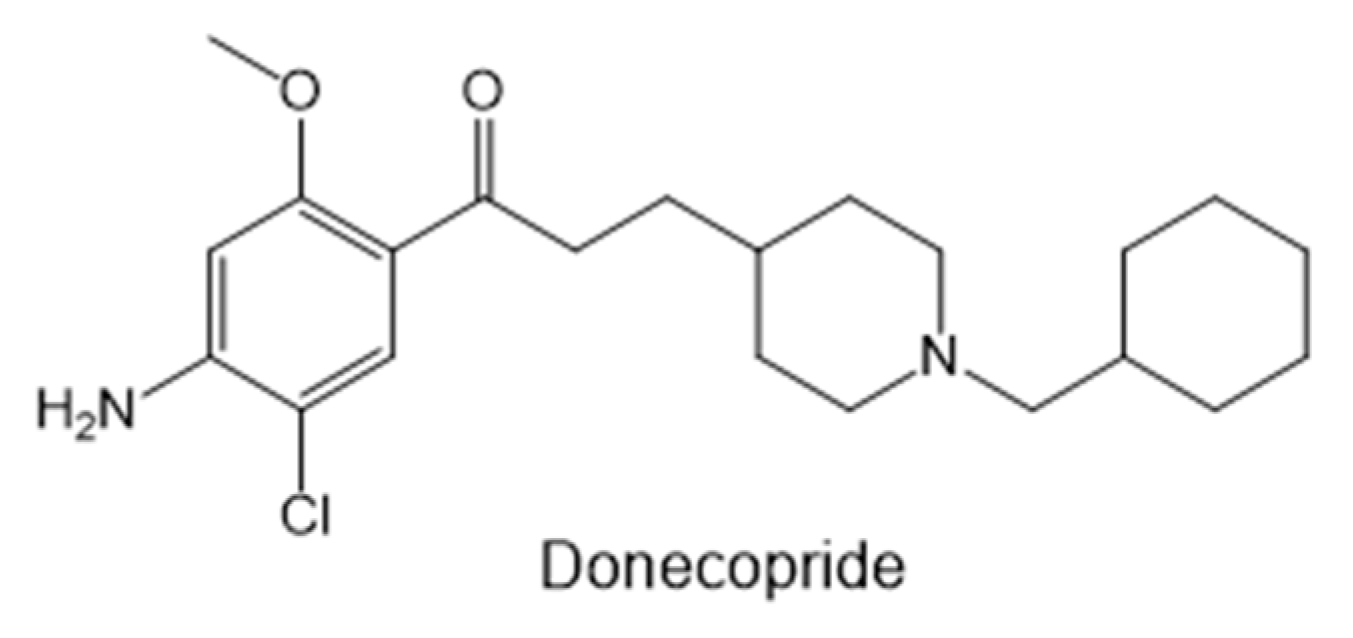
- Lecoutey C., Hedou D., Freret T., et al. Design of Donecopride, a Dual Serotonin Subtype 4 Receptor Agonist/Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitor with Potential Interest for Alzheimer’s Disease Treatment. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2014;111(36): E3825–E3830. [CrossRef]
- Giannoni P., Gaven F., de Bundel D., et al. Early administration of RS 67333, a specific 5-HT4 receptor agonist, prevents amyloidogenesis and behavioral deficits in the 5XFAD mouse model of Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging. Neurosci. 2013; 5:96.
- Baranger K., Giannoni P., Girard S.D., et al. Chronic treatments with a 5-HT4 receptor agonist decrease amyloid pathology in the entorhinal cortex and learning and memory deficits in the 5xFAD mouse model of Alzheimer's disease. Neuropharmacol. 2017;126: 128-141.
- Rochais C., Lecoutey C., Gaven F., et al. Novel Multitarget-Directed Ligands (MTDLs) with acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitory and serotonergic subtype 4 receptor (5-HT4R) agonist activities as potential agents against Alzheimer’s disease: The design of Donecopride. J. Med. Chem. 2015; 58(7): 3172–3187. [CrossRef]
- Rochais C., Lecoutey C., Hamidouche K., et al. Donecopride, a Swiss army knife with potential against Alzheimer’s disease. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2020; 177(9): 1988–2005.
- Lalut J., Santoni G., Karila D., et al. Novel Multitarget-Directed Ligands targeting Acetylcholinesterase and σ1 receptors as lead compounds for treatment of Alzheimer’s disease: Synthesis, evaluation, and structural characterization of their complexes with acetylcholinesterase. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2018;162 : 234–248.
- Guieu B., Lecoutey C., Legay R., et al. First Synthesis of Racemic Trans Propargylamino-Donepezil, a Pleiotrope Agent Able to Both Inhibit AChE and MAO-B, with Potential Interest against Alzheimer’s Disease. Molecules. 2021;26(1): 80.
- Hatat B., Yahiaoui S., Lecoutey C., et al. A novel in vivo anti-amnesic agent, specially designed to express both acetylcholinesterase (AChE) inhibitory, serotonergic subtype 4 receptor (5-HT4R) agonist and serotonergic subtype 6 receptor (5-HT6R) inverse agonist activities, with a potential interest against Alzheimer’s disease. Front. Aging. Neurosci. 2019;11: 148. [CrossRef]
- Lecoutey C., Legay R., Davis A., et al. Development of novel potential pleiotropic compounds of interest in Alzheimer ’s disease treatment through rigidification strategy. Molecules. 2021;26: 2536. [CrossRef]
- Jourdan J-P., Since M., El Kihel L., et al. Novel benzylidenephenylpyrrolizinones with pleiotropic activities potentially useful in Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016;114: 365–379. [CrossRef]
- Yahiaoui S., Hamidouche K., Ballandonne C., et al. Design, synthesis, and pharmacological evaluation of Multitarget-Directed Ligands with both serotonergic subtype 4 receptor (5-HT4R) partial agonist and 5-HT6R antagonist activities, as potential treatment of Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2016;121: 283–293. [CrossRef]
- Lalut J., Karila D., Dallemagne P., et al. Modulating 5-HT4 and 5-HT6 receptors in Alzheimer’s disease treatment. Future Med. Chem. 2017;9(8): 781–795.
- Jourdan J-P., Since M.; El Kihel L., et al. Benzylphenylpyrrolizinones with anti-amyloid and radical scavenging effects, potentially useful in Alzheimer’s disease treatment. ChemMedChem. 2017;12(12): 913–916. [CrossRef]
- Lanthier C., Payan H., Liparulo I., et al. Novel Multi Target-Directed Ligands targeting 5-HT4 Receptors with in cellulo antioxidant properties as promising leads in Alzheimer’s disease. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019;182: 111596. [CrossRef]
- Sergeant N., Vingtdeux V., Eddarkaoui S., et al. New piperazine multi-effect drugs prevent neurofibrillary degeneration and amyloid deposition, and preserve memory in animal models of Alzheimer’s disease. Neurobiol. Dis. 2019;129: 217–233. [CrossRef]
- Freret T., Bouet V., Quiedeville A., et al. Synergistic effect of acetylcholinesterase inhibition (Donepezil) and 5-HT4 receptor activation (RS67333) on object recognition in mice. Behav. Brain. Res. 2012;230(1): 304–308. [CrossRef]
- Sopkova-de Oliveira Santos J., Lesnard A., Agondanou J.H., et al. Virtual screening discovery of new acetylcholinesterase inhibitors issued from CERMN chemical library. J. Chem. Inf. Model. 2010;50(3): 422–428. [CrossRef]
- Lecoutey C., Rochais C., Genest D., et al. Synthesis of dual AChE/5-HT4 receptors Multi-Target Directed Ligands. MedChemCom. 2012;3: 627–634. [CrossRef]
- Dallemagne P., Rochais C.. Facing the Complexity of Alzheimer’s Disease. Future Med. Chem. 2020;12(3): 175–177. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




