Submitted:
29 July 2023
Posted:
31 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results and Discussion
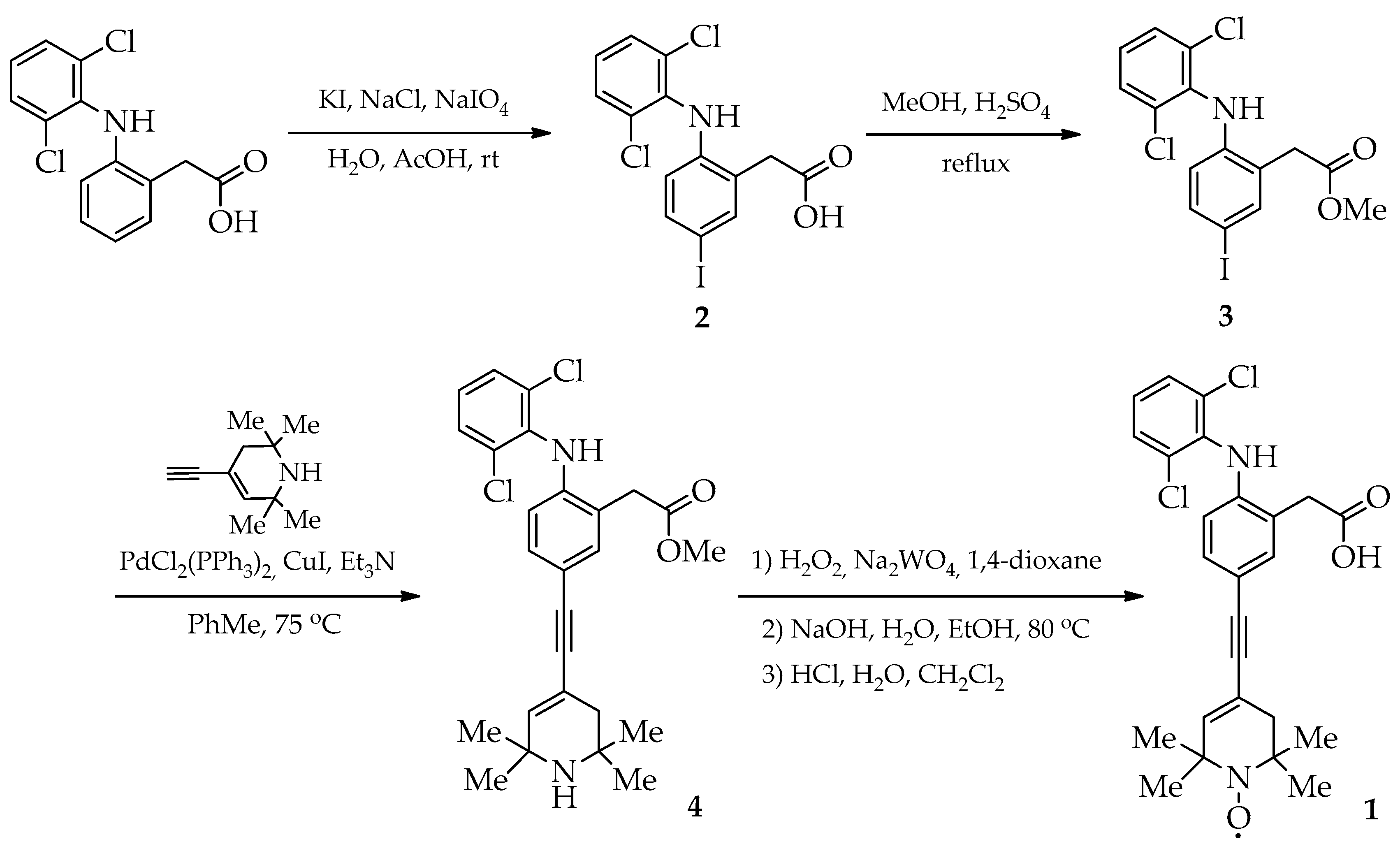
2.1. Synthesis
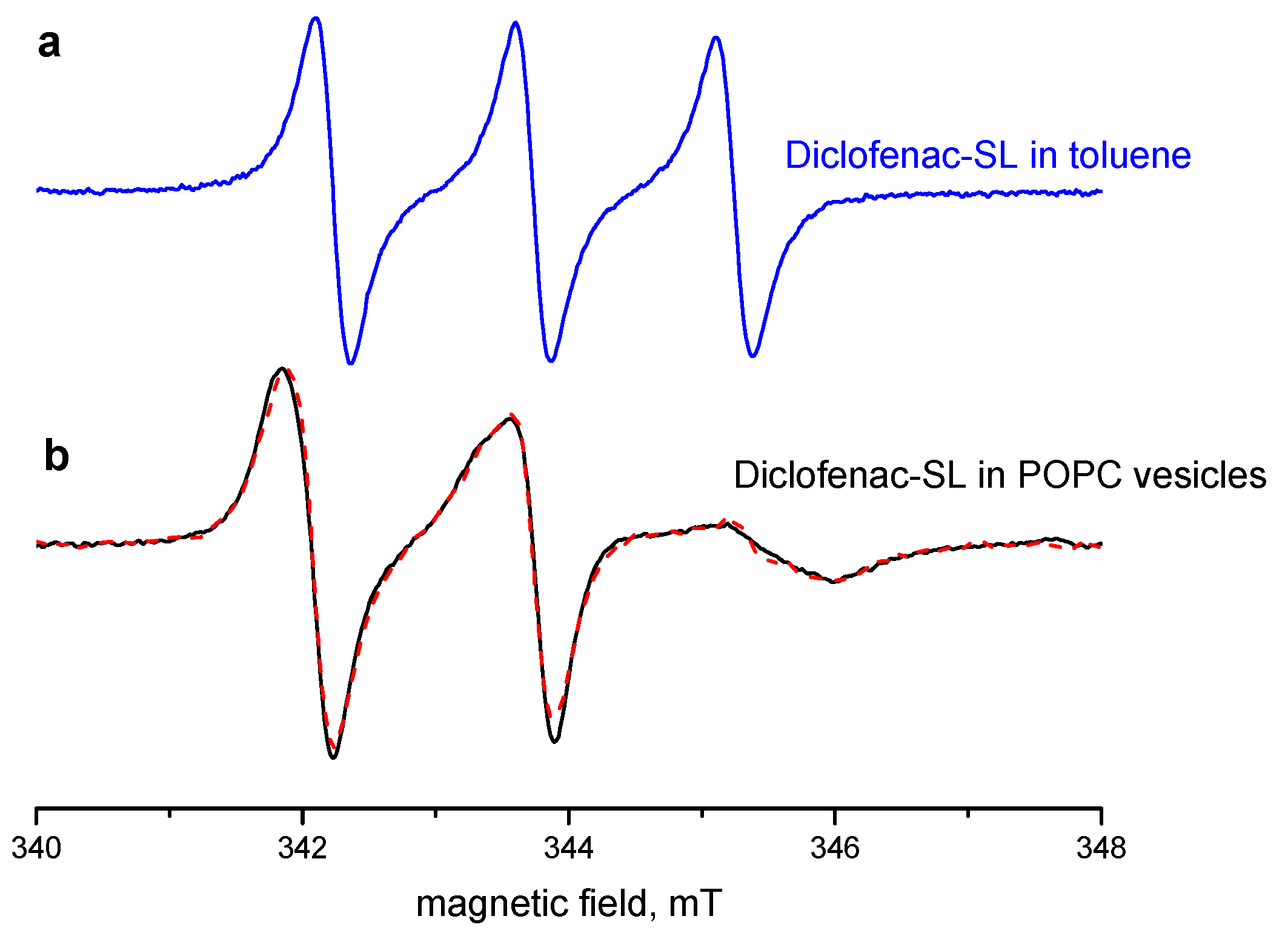
2.2. EPR Spectra: Interaction with the POPC Membrane
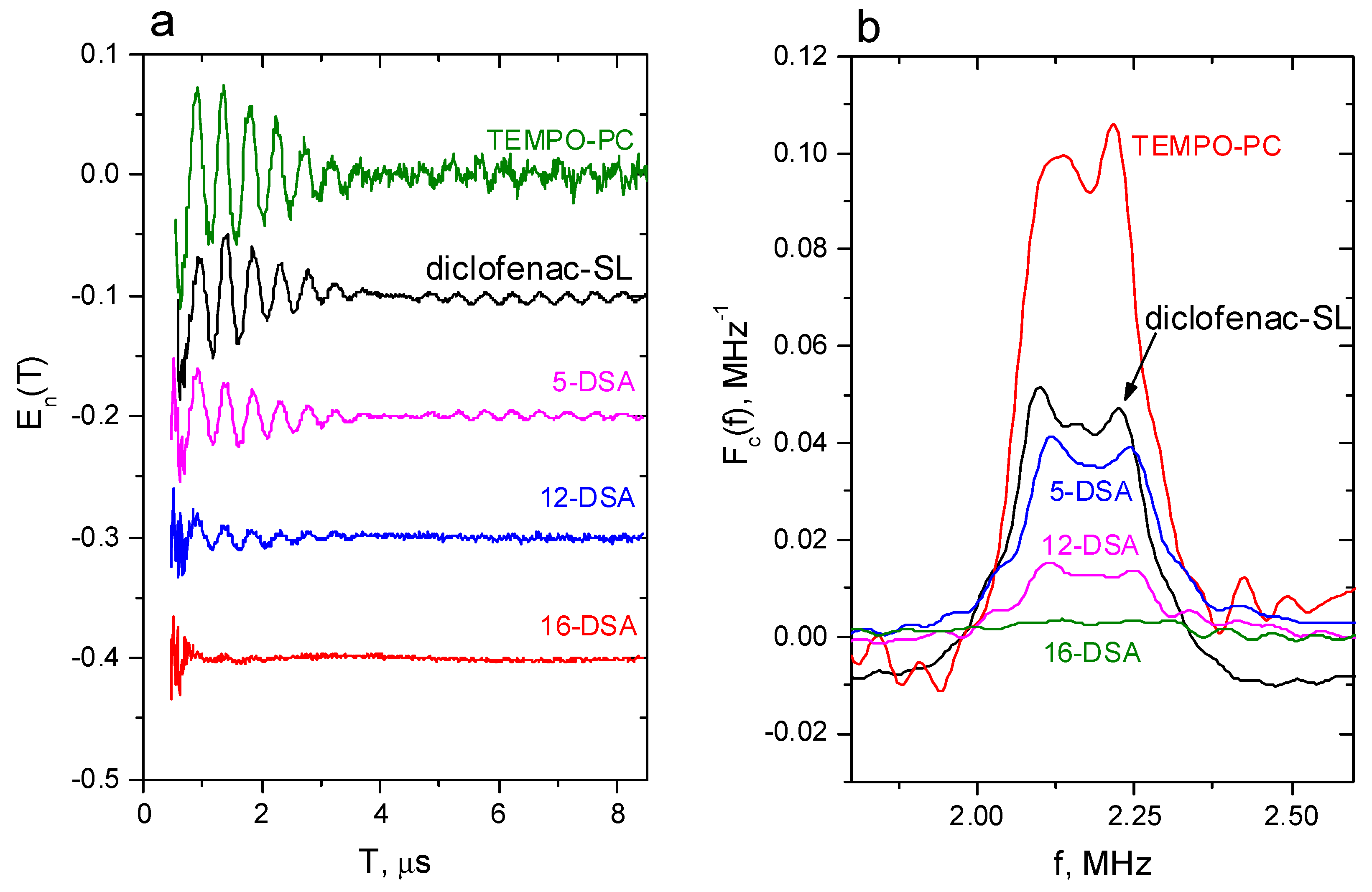
2.3. Pulsed EPR: Location in the POPC Membrane
3. Materials and Methods
3.1. Chemical Analysis
3.2. Synthesis and Characterization
3.3. Sample Preparations for EPR Investigation
3.4. EPR Measurements
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Sample Availability
References
- Manrique-Moreno, M.; Heinbockel, L.; Suwalsky, M.; Garidel, P.; Brandenburg, K. Biophysical study of the non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAID) ibuprofen, naproxen and diclofenac with phosphatidylserine bilayer membranes. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2016, 1858, 2123–2131. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ulrich, C.M.; Bigler, J.; Potter, J.D. Non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs for cancer prevention: promise, perils and pharmacogenetics. Nature Reviews Cancer. 2006, 6, 130–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crofford, L.J. Use of NSAIDs in treating patients with arthritis. Arthritis Res. Ther. 2013, 15, S2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- González-Gay, M.A.; González-Juanatey. C. NSAIDs and cardiovascular risk in arthritis. Nat. Rev. Cardiol. 2017, 14, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lleo, A.; Galea, E.; Sastre, M. Molecular targets of non-steroidal anti-inflammatory drugs in neurodegenerative diseases. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2007, 64, 1403–1418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreno, M.M.; Garidel, P.; Suwalsky, M.; Howe, J.; Brandenburg, K. The membrane-activity of ibuprofen, diclofenac, and naproxen: a physico-chemical study with lecithin phospholipids. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2009, 1788, 1296–1303. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Madikizela, L.M.; Chimuka, L. Determination of ibuprofen, naproxen and diclofenac in aqueous samples using a multi-template molecularly imprinted polymer as selective adsorbent for solid-phase extraction. J. Pharm. Biomed. Analysis 2016, 128, 210–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Warner, T.D.; Giuliano, F.; Vojnovic, I.; Bukasa, A.; Mitchell, J.A.; Vane, J.R. Nonsteroid drug selectivities for cyclo-oxygenase-1 rather than cyclo-oxygenase-2 are associated with human gastrointestinal toxicity: a full in vitro analysis. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1999, 96, 7563–7568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Leite, C.P.; Nunes, C.; Reis, S. Interaction of nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs with membranes: in vitro assessment and relevance for their biological actions. Prog. Lipid Res. 2013, 52, 571–584. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Y.; Plowman, S.J.; Lichtenberger, L.M.; Hancock, J.F. The anti-inflammatory drug indomethacin alters Nanoclustering in synthetic and cell plasma membranes. J. Biol. Chem. 2010, 285, 35188–35195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seddon, A.M.; Casey, D.; Law, R.V.; Gee, A.; Templer, R.H.; Ces, O. Drug interactions with lipid membranes. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2009, 38, 2509–2519. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wallace, J.L. Prostaglandins, NSAIDs, and gastric mucosal protection: why doesn’t the stomach digest itself? Physiol Rev. 2008, 88, 1547–1565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fernandes, E.; Soares, T.B.; Gonçalves, H.; Bernstorff, S.; Real Oliveira, M.E.C.D.; Lopes, С.M. , Lúcio, M. A Molecular Biophysical Approach to Diclofenac Topical Gastrointestinal Damage. Int J Mol Sci. 2018, 19, 3411. [Google Scholar]
- Lichtenberger, L.M.; Zhou, Y.; Dial, E.J. , Raphael, R.M. NSAID injury to the gastrointestinal tract: evidence that NSAIDs interact with phospholipids to weaken the hydrophobic surface barrier and induce the formation of unstable pores in membranes. J Pharm Pharmacol. 2006, 58, 1421–1428. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alsop, R.J.; Armstrong, C.L.; Maqbool, A.; Toppozini, L.; Dies, H.; Rheinstädter, M.C. Cholesterol expels ibuprofen from the hydrophobic membrane core and stabilizes lamellar phases in lipid membranes containing ibuprofen. Soft Matter 2015, 11, 4756–4767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sreij, R.; Prévost, S.; Dargel, C.; Dattani, R.; Hertle, Y.; Wrede, O.; Hellweg, T. Interaction of the Saponin Aescin with Ibuprofen in DMPC Model Membranes. Mol. Pharm. 2018, 15, 4446–4461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, V.K.; Mamontov, E.; Tyagi, M. Effects of NSAIDs on the nanoscopic dynamics of lipid membrane. Biochim. Biophys. Acta Biomembr. 2020, 1862, 183100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yefimova, S.L.; Tkacheva, T.N.; Kasian, N.A. Study of the Combined Effect of Ibuprofen and Cholesterol on the Microviscosityand Ordering of Model Lipid Membranes by Timeresolved Measurement of Fluorescence Anisotropy Decay. J. Appl. Spectrosc. 2017, 84, 284–290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadurai, S.; Sarangi, N.K.; Maher, S.; Macconnell, N.; Bond, A.M.; McDaid, D.; Flynn, D.; Keyes, T.E. Microcavity-Supported Lipid Bilayers; Evaluation of Drug-Lipid Membrane Interactions by Electrochemical Impedance and Fluorescence Correlation Spectroscopy. Langmuir 2019, 35, 8095–8109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wood, M.; Morales, M.; Miller, E.; Braziel, S.; Giancaspro, J.; Scollan, P.; Rosario, J.; Gayapa, A.; Krmic, M.; Lee, S. Ibuprofen and the Phosphatidylcholine Bilayer: MembraneWater Permeability in the Presence and Absence of Cholesterol. Langmuir 2021, 37, 4468–4480. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, S.; Sendecki, A.M.; Pullanchery, S.; Huang, D.; Yang, T.; Cremer, P.S. Multistep Interactions between Ibuprofen and Lipid Membranes. Langmuir 2018, 34, 10782–10792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kremkow, J.; Luck, M.; Huster, D.; Müller, P.; Scheidt, H.A. Membrane interaction of ibuprofen with cholesterol-containing lipid membranes. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 1384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aloi, E.; Rizzuti, B.; Guzzi, R.; Bartucci, R. Association of ibuprofen at the polar/apolar interface of lipid membranes. Arch. Biochem. Biophys. 2018, 654, 77–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranov, D.S.; Smorygina, A.S.; Dzuba, S.A. Synthesis of Spin-Labeled Ibuprofen and Its Interaction with Lipid Membranes. Molecules 2022, 27, 4127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozak, K.R.; Prusakiewicz, J.J.; Rowlinson, S.W.; Marnett, L.J. Enantiospecific, Selective Cyclooxygenase-2 Inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2002, 12, 1315–1318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jilani, J.; Idkaidek, N.; Alzoubi, K. Synthesis, In Vitro and In Vivo Evaluation of the N-Ethoxycarbonylmorpholine Ester of Diclofenac as a Prodrug. Pharm. 2014, 7, 453–463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tammara, V.K.; Narurkar, M.M.; Crider, A.M.; Khan, M.A. Synthesis and Evaluation of Morpholinoalkyl Ester Prodrugs of Indomethacin and Naproxen. Pharm. Res. 1993, 10, 1191–1199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, K.; Kaub, C.J.; Carey, K.N.; Casillas, E.G.; Selinsky, B.S.; Loll, P.J. Manipulation of Kinetic Profiles in 2-Aryl Propionic Acid Cyclooxygenase Inhibitors. Bioorganic Med. Chem. Lett. 2004, 14, 667–671. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akdogan, Y.; Emrullahoglu, M.; Tatlidil, D.; Ucuncu, M.; Cakan-Akdogan, G. EPR Studies of Intermolecular Interactions and Competitive Binding of Drugs in a Drug–BSA Binding Model. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics. 2016, 18, 22531–22539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Ito, T.; Fujii, H.G.; Sato, S. Synthesis and Reduction Kinetics of Five Ibuprofen–Nitroxides for Ascorbic Acid and Methyl Radicals. Chem. Pharm. Bull. 2016, 64, 1509–1513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores-Santana, W.; Moody, T.; Chen, W.; Gorczynski, M.J.; Shoman, M.E.; Velázquez, C.; Thetford, A.; Mitchell, J.B.; Cherukuri, M.K.; King, S.B.; Wink, D.A. Nitroxide Derivatives of Non-Steroidal Anti-Inflammatory Drugs Exert Anti-Inflammatory and Superoxide Dismutase Scavenging Properties in A459 Cells. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2012, 165, 1058–1067. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Golubeva, E.N.; Chumakova, N.A.; Kuzin, S.V.; Grigoriev, I.A.; Kalai, T.; Korotkevich, A.A.; Bogorodsky, S.E.; Krotova, L.I.; Popov, V.K.; Lunin, V.V. Paramagnetic Bioactives Encapsulated in Poly(D,L-Lactide) Microparticules: Spatial Distribution and in Vitro Release Kinetics. J. Supercrit. Fluids. 2020, 158, 104748. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chumakova, N.A.; Golubeva, E.N.; Kuzin, S.V.; Ivanova, T.A.; Grigoriev, I.A.; Kostjuk, S.V.; Melnikov, M.Y. New Insight into the Mechanism of Drug Release from Poly(d,l-Lactide) Film by Electron Paramagnetic Resonance. Polym. J. 2020, 12, 3046. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rainsford, K.D. Ibuprofen: Discovery, Development and Therapeutics; Rainsford, K.D., Ed.; Wiley, 2015. [CrossRef]
- Galati, G.; Tafazoli, S.; Sabzevari, O.; Chan, T.S.; O’Brien, P.J. Idiosyncratic NSAID Drug Induced Oxidative Stress. Chem. Biol. Interact. 2002, 142, 25–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boelsterli, U. Diclofenac-Induced Liver Injury: A Paradigm of Idiosyncratic Drug Toxicity. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2003, 192, 307–322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marsh, D. Spin-Label Electron Paramagnetic Resonance Spectroscopy; CRC Press: Boca Raton, FL, USA, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Erilov, D.A.; Bartucci, R.; Guzzi, R.; Shubin, A.A.; Maryasov, A.G.; Marsh, D.; Dzuba, S.A.; Sportelli, L. Water concentration profiles in membranes measured by ESEEM of spin-labeled lipids. J. Phys. Chem. B 2005, 109, 12003–12013. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milov, A.D.; Samoilova, R.I.; Shubin, A.A.; Grishin, Y.A.; Dzuba, S.A. ESEEM measurements of local water concentration in D2O-containing spin-labeled systems. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2008, 35, 73–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dzuba, S.A.; Marsh, D. ESEEM of Spin Labels to Study Intermolecular Interactions, Molecular Assembly and Conformation. In A Specialist Periodic Report, Electron Paramagnetic Resonance; Gilbert, C., Chechik, V., Murphy, D.M., Eds.; RSC Publishing: Cambridge, UK, 2015; Volume 24, pp. 102–121. [Google Scholar]
- Konov, K.B.; Isaev, N.P.; Dzuba, S.A. Glycerol penetration profile in phospholipid bilayers measured by ESEEM of spin-labelled lipids, Mol. Phys. 2013, 111, 2882–28863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shapiro, A.B.; Skripnichenko, L.N.; Pavlikov, V.V.; Rozantsev, E.G. Synthesis of Nitroxyl Radicals Based on 4-Ethynyl-4-Hydroxy-2,2,6,6-Tetramethylpiperidine. Russ. Chem. Bull. 1979, 28, 140–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tanwar, L.; Börgel, J.; Lehmann, J.; Ritter, T. Selective C-H Iodination of (Hetero)Arenes. Org. Lett. 2021, 23, 5024–5027. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dalai, P.G.; Palit, K.; Panda, N. Generation of Dimethyl Sulfoxide Coordinated Thermally Stable Halogen Cation Pools for C−H Halogenation. Adv. Synth. Catal. 2022, 364, 1031–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smorygina, A.S.; Golysheva, E.A.; Dzuba, S.A. Clustering of Stearic Acids in Model Phospholipid Membranes Revealed by Double Electron−Electron Resonance. Langmuir 2021, 37, 13909–13916. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Unguryan, V.V.; Golysheva, E.A.; Dzuba, S.A. Double electron-electron resonance of spin-labeled cholestane in model membranes: evidence for substructures inside the lipid rafts. J. Phys. Chem. B 2021, 125, 33–9557. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashnik, A.S.; Baranov, D.S.; Dzuba, S.A. Ibuprofen in a lipid bilayer: nanoscale spatial arrangement. Membranes 2022, 12, 1077. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashnik, A.S.; Syryamina, V.N.; Biondi, B.; Peggion, C.; Formaggio, F.; Dzuba, S.A. DEER/PELDOR Study of the Effect of Extremely Low Concentrations of the Antimicrobial Peptide Chalciporin A on the Membrane Lipid Organization. Appl. Magn. Reson. 2023, 54, 401–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




