Submitted:
27 July 2023
Posted:
31 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
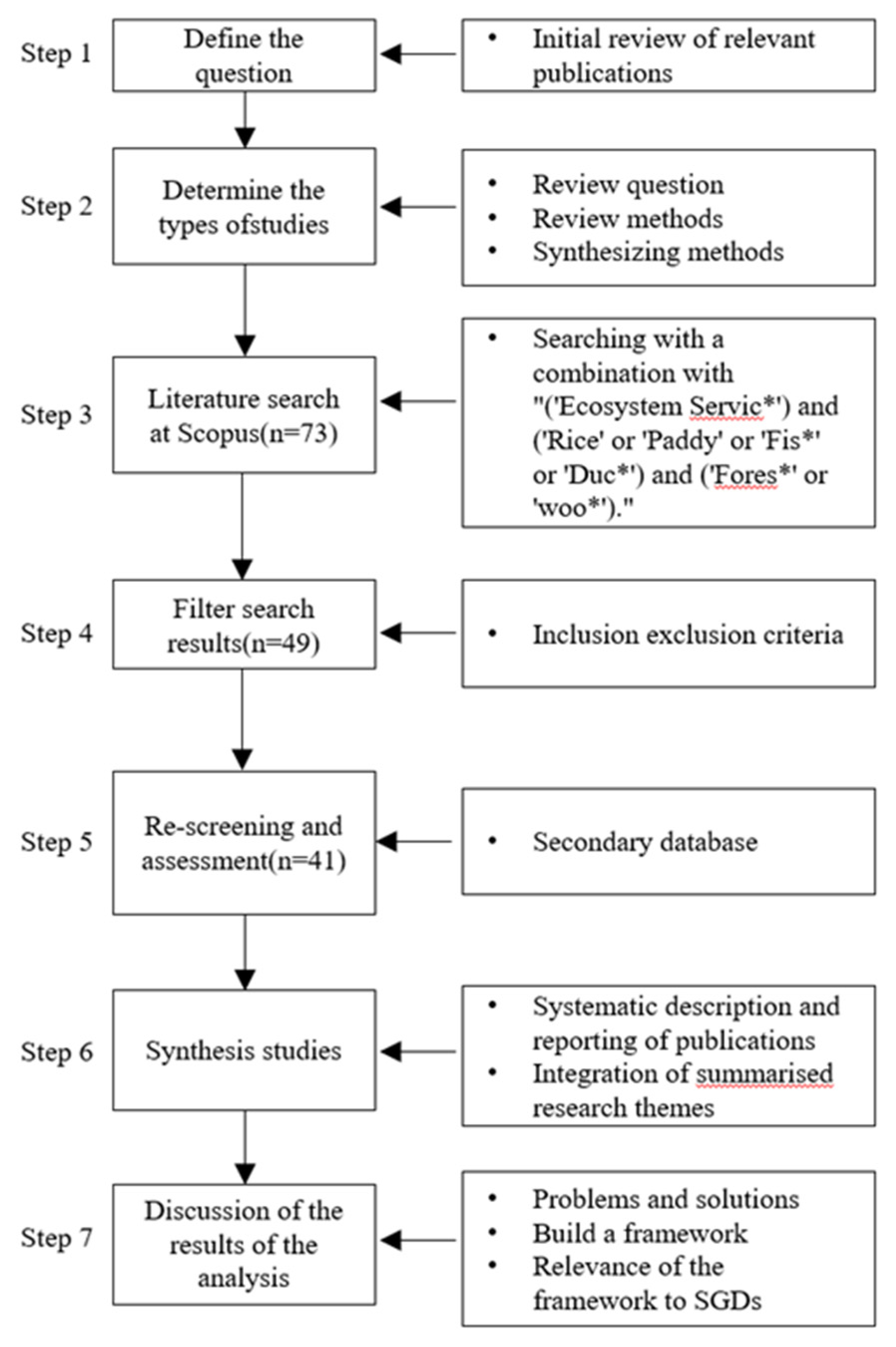
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Search and Appraisal
2.2. Synthesis
2.3. Report
3. Results
3.1. Descriptive analysis
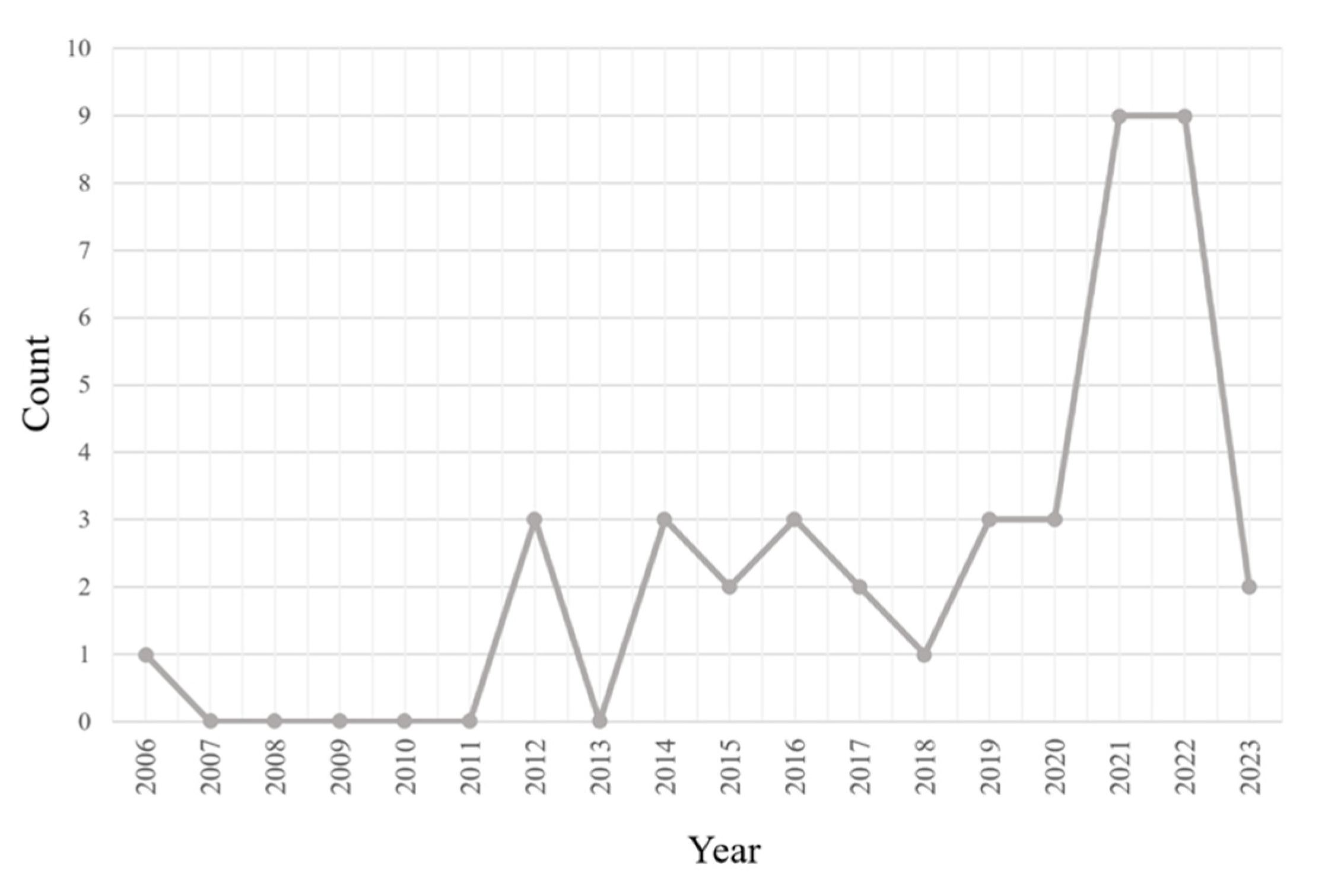
3.1.1. Year of publication
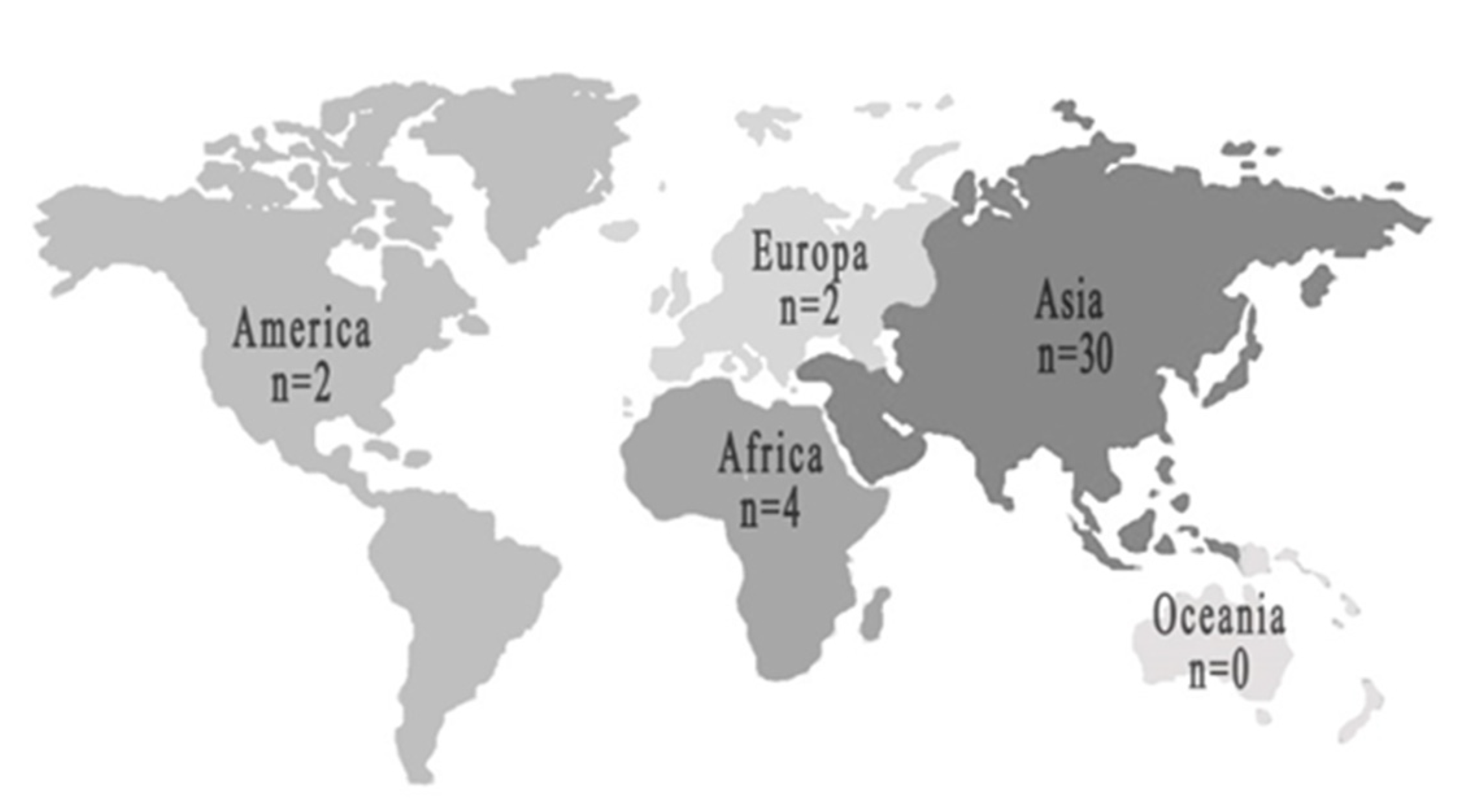
3.1.2. Geographical distribution of analysed publications
3.1.3. Areas covered
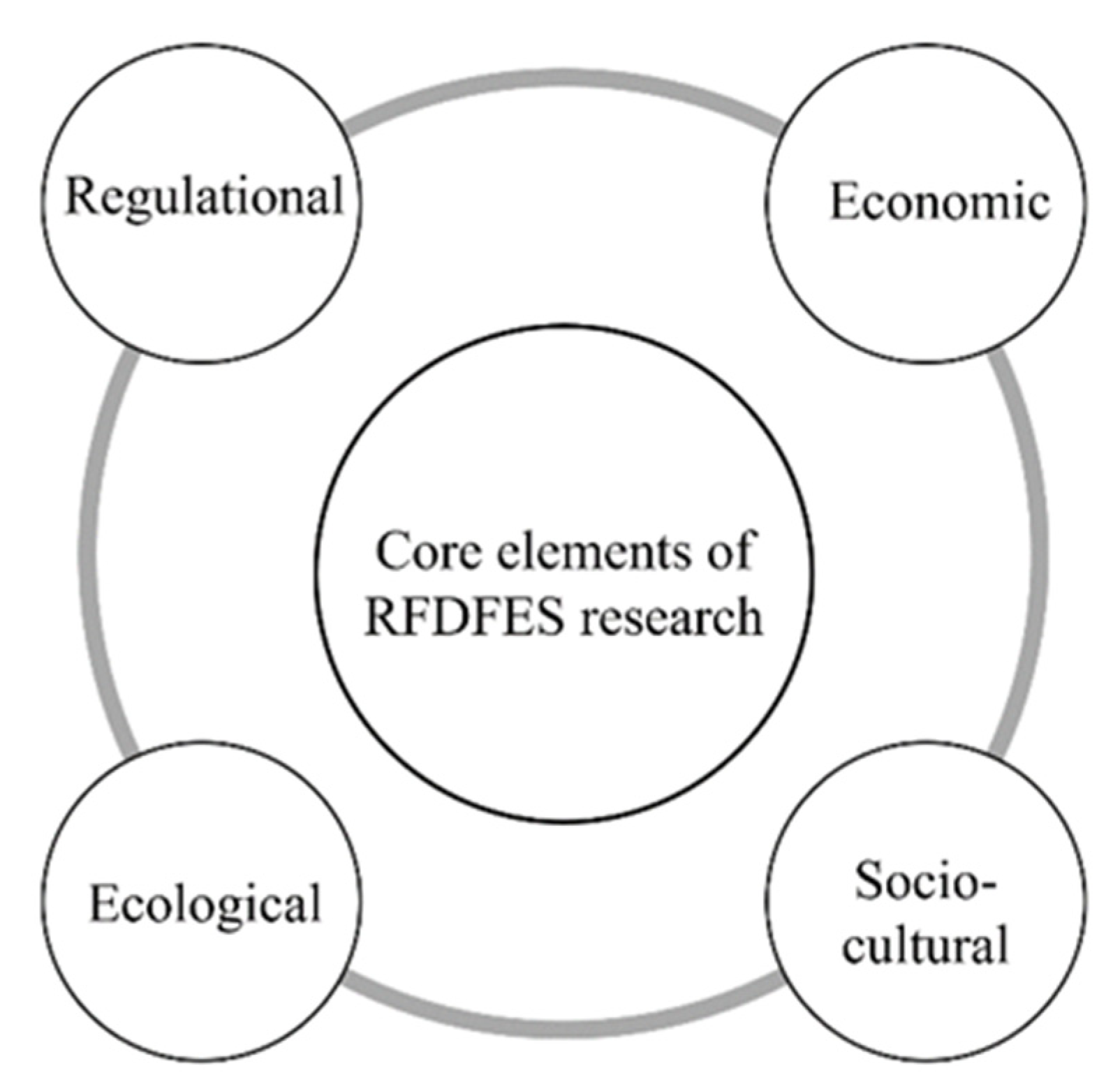
3.2. Core elements of RFDFES in publications
3.2.1. Socio-cultural
3.2.2. Ecological
3.2.3. Regulational
3.2.4. Economic
4. Discussion
4.1. Current gaps in literature
4.1.1. Deforested forests with multifunctionality
4.1.2. Marginalized socio-cultural aspects
4.1.3. Low-participation communities
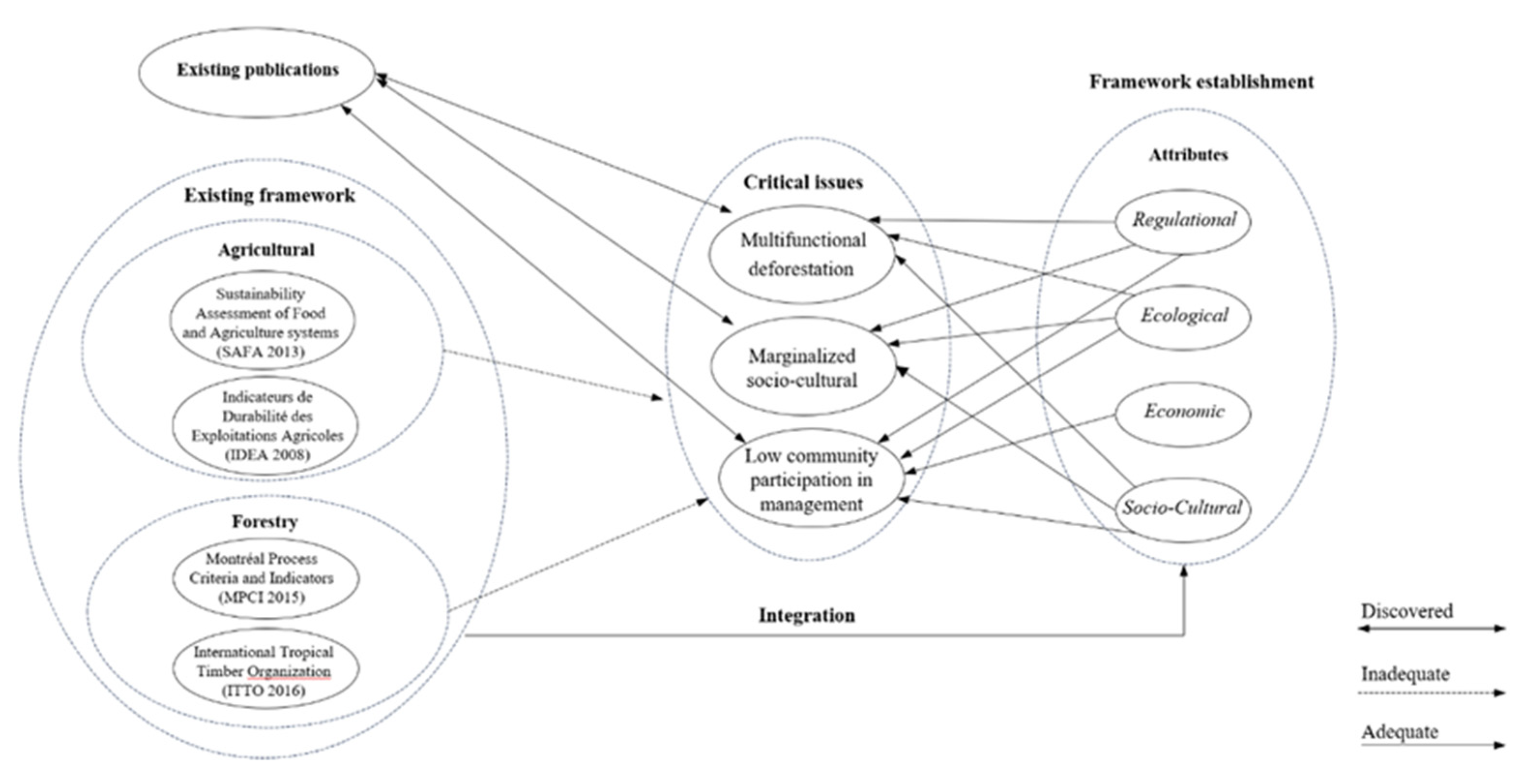
4.2. RFDFES framework Establishment
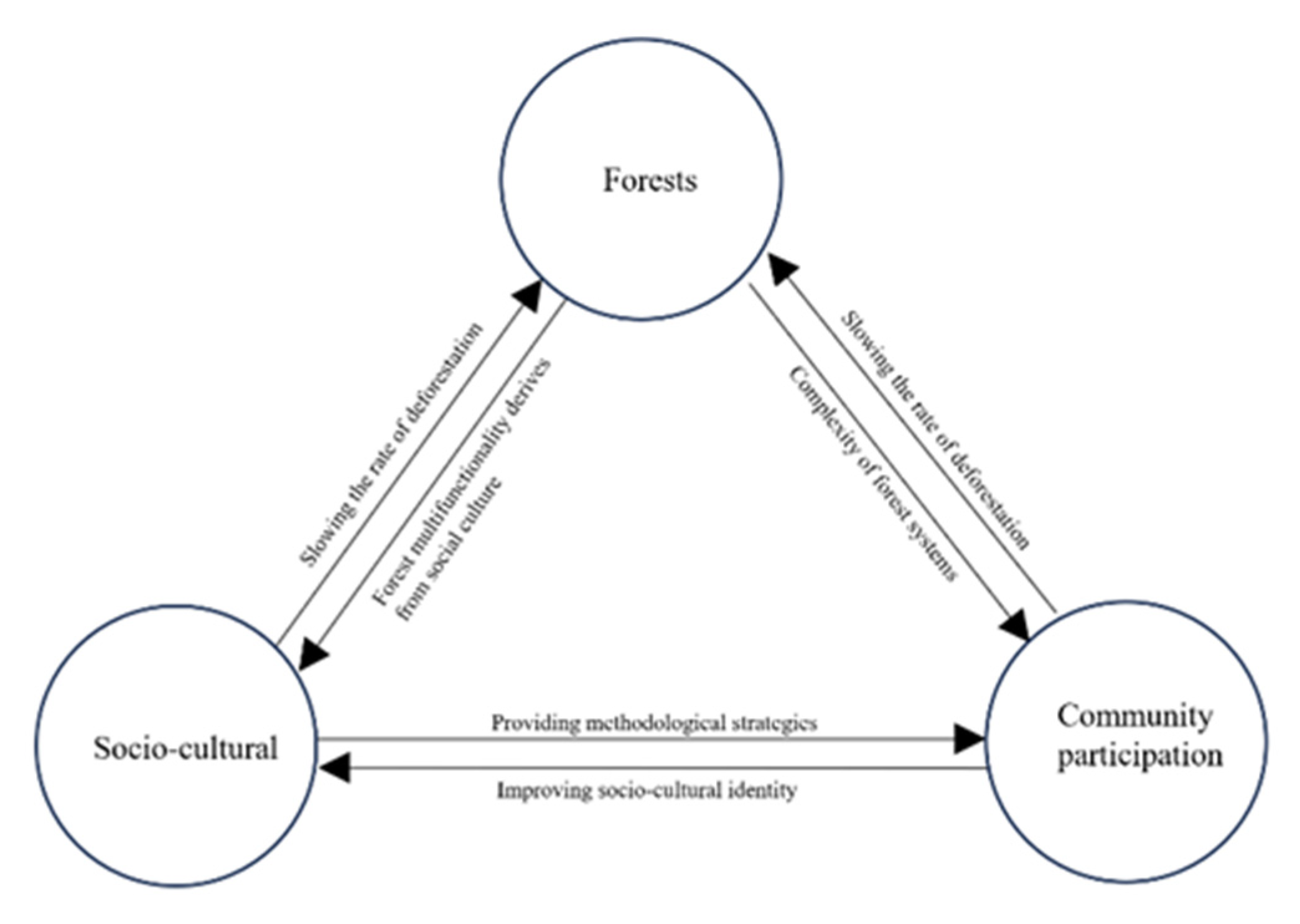
4.2.1. Correlation between forests, socio-cultural and community participation in management
4.2.2. Gaps in existing frameworks
4.2.3. RFDFES Sustainable Management Framework
4.3. RFDFES Sustainable Management Framework and SDGs
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| RFDFES Sustainable Development Framework | Sources | Problems | ||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Themes | Sub-Themes | Indicators | ITTO (2016) | SAFA (2013) | MPCI (2015) | IDEA (2008) | Publications | Deforestation | Marginalised socio-cultural | Low-Participation Communities |
| Regulational | 1.1Rule of Law: governments and locals | 1.1.1policies、laws、regulations | × | × | × | × | ||||
| 1.1.2Decentralisation management | × | × | × | |||||||
| 1.2Recommendations:NGOs and experts | 1.2.1Applying modern knowledge and skills | × | × | |||||||
| 1.2.2Assisting governments and communities | × | × | × | × | ||||||
| 1.3Communities and indigenous | 1.3.1Village Rules | × | × | × | × | |||||
| 1.3.2Indigenous Knowledge Management | × | × | × | × | × | × | ||||
| Ecological | 2.1Ecological environment | 2.1.1Different land uses | × | × | × | × | × | × | ||
| 2.1.2Soil use and protection | × | × | × | × | × | × | ||||
| 2.1.3Water use and protection | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | |||
| 2.1.4Forests use and conservation | × | × | × | × | × | × | ||||
| 2.1.5Climate regulation | × | × | × | × | ||||||
| 2.2Biodiversity | 2.2.1Landscape/habitat conservation plans | × | × | × | × | |||||
| 2.2.2Species diversit (Rice varieties, fish varieties, plant diversity) | × | × | × | × | × | × | × | |||
| Economic | 3.1Economic investments | 3.1.1Material investments (Money, equipment farming tools, buildings, production materials, water and energy) | × | × | × | |||||
| 3.1.2Non-material investments (manpower, time, and,Operation & Management) | × | × | ||||||||
| 3.2Economic benefits | 3.2.1Crop yield and production | × | × | × | × | × | ||||
| 3.2.2Production subsidies | × | |||||||||
| 3.2.3Participant's investment (Suppliers) | × | |||||||||
| 3.2.4Production added value (Tourism, education, cultural activities) | × | × | × | × | × | |||||
| Socio-cultural | 4.1Quality of life | 4.1.1Working conditions (Environment, farm equipment, time) | × | × | ||||||
| 4.1.2Public Health and Health Safety | × | × | × | × | × | |||||
| 4.1.3Provide employment | × | × | × | × | × | |||||
| 4.1.4Food Security and Livelihood Protection | × | × | × | × | × | × | ||||
| 4.2Cultural diversities | 4.2.1Indigenous knowledge | × | × | × | × | × | × | |||
| 4.2.2History and Culture | × | × | × | × | × | |||||
| 4.2.3Religious beliefs | × | × | × | × | × | |||||
| 4.2.4Cultural activities | × | × | × | × | ||||||
| 4.3Conflict resolution among stakeholders | 4.3.1Resource management rights | × | × | × | × | |||||
| 4.3.2Recognition of indigenous knowledge and skills | × | × | × | |||||||
Appendix B
| RFDFES Sustainable Development Framework | Sustainable Development Goals (SDGs) | |||||||||||||||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Themes | Sub-Themes | Indicators | SDG 1 | SDG 2 | SDG 3 | SDG 4 | SDG 5 | SDG 6 | SDG 7 | SDG 8 | SDG 9 | SDG 10 | SDG 11 | SDG 12 | SDG 13 | SDG 14 | SDG 15 | SDG 16 | SDG 17 | Count |
| Regulational | 1.1Rule of Law: Governments and Locals | 1.1.1policies, laws, regulations | × | × | × | × | 4 | |||||||||||||
| 1.1.2Decentralisation management | × | × | × | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| 1.2Recommendations: NGOs and e×perts | 1.2.1Applying modern knowledge and skills | × | × | × | 3 | |||||||||||||||
| 1.2.2Assisting governments and communities | × | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 1.3Communities and Indigenous | 1.3.1Village Rules | × | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| 1.3.2Indigenous Knowledge Management | × | × | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| Ecological | 2.1Ecological environment | 2.1.1Different land uses | × | 1 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2.1.2Soil use and protection | × | × | × | × | 3 | |||||||||||||||
| 2.1.3Water use and protection | × | × | × | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 2.1.4Forests use and conservation | × | × | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2.1.5Climate regulation | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 2.2 Biodiversity | 2.2.1Landscape/habitat conservation plans | × | 1 | |||||||||||||||||
| 2.2.2Species diversity (Rice varieties, fish varieties, plant diversity) | × | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| Economic | 3.1Economic investments | 3.1.1Material investments (Money, equipment farming tools, buildings, production materials, water and energy) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||
| 3.1.2Non-material investments (manpower, time, and,Operation & Management) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 3.2Economic benefits | 3.2.1Crop yield and production | × | × | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| 3.2.2Production subsidies | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 3.2.3Participant's investment (Suppliers) | 0 | |||||||||||||||||||
| 3.2.4Production added value (Tourism, education, cultural activities) | × | × | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| Socio-Cultural | 4.1Quality of life | 4.1.1Working conditions (Environment, farm equipment, time) | × | × | 2 | |||||||||||||||
| 4.1.2Public Health and Health Safety | × | × | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| 4.1.3Provide employment | × | × | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| 4.1.4Food Security and Livelihood Protection | × | × | 2 | |||||||||||||||||
| 4.2Cultural diversities | 4.2.1Indigenous knowledge | × | × | 2 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4.2.2History and Culture | × | × | × | × | 4 | |||||||||||||||
| 4.2.3Religious beliefs | × | 1 | ||||||||||||||||||
| 4.2.4Cultural activities | × | × | × | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| 4.3Conflict resolution among stakeholders | 4.3.1Resource management rights | × | × | × | 3 | |||||||||||||||
| 4.3.2Recognition of indigenous knowledge and skills | × | × | × | 3 | ||||||||||||||||
| Count | 1 | 8 | 2 | 5 | 0 | 4 | 3 | 5 | 1 | 0 | 5 | 7 | 1 | 0 | 8 | 0 | 2 | |||
References
- Palomo-Campesino, S.; González, J.A.; García-Llorente, M. Exploring the Connections between Agroecological Practices and Ecosystem Services: A Systematic Literature Review. Sustainability 2018, 10, 4339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Agricultural Land (% of Land Area) | Data. Available online: https://data.worldbank.org/indicator/AG.LND.AGRI.ZS (accessed on 22 July 2023).
- Renting, H.; Rossing, W.A.H.; Groot, J.C.J.; Van Der Ploeg, J.D.; Laurent, C.; Perraud, D.; Stobbelaar, D.J.; Van Ittersum, M.K. Exploring Multifunctional Agriculture. A Review of Conceptual Approaches and Prospects for an Integrative Transitional Framework. J. Environ. Manage. 2009, 90, S112–S123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Van Huylenbroeck, G.; Vandermeulen, V.; Mettepenningen, E.; Verspecht, A. Multifunctionality of Agriculture: A Review of Definitions, Evidence and Instruments. Living Rev. Landsc. Res. 2007, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kumar, S.; Singh, S.P.; Meena, R.S.; Lalotra, S.; Parihar, R.K.; Mitra, B. Reduction of Energy Consumption in Agriculture for Sustainable Green Future. In Input Use Efficiency for Food and Environmental Security; Bhatt, R., Meena, R.S., Hossain, A., Eds.; Springer Nature: Singapore, 2021; pp. 199–239 ISBN 9789811651991.
- Takahashi, K.; Otsuka, K. The Role of Extension in the Green Revolution. In Rice Green Revolution in Sub-Saharan Africa; Otsuka, K., Mano, Y., Takahashi, K., Eds.; Natural Resource Management and Policy; Springer Nature Singapore: Singapore, 2023; Vol. 56, pp. 27–44 ISBN 978-981-19804-5-9.
- Shahbaz, M.U.; Arshad, M.; Mukhtar, K.; Nabi, B.G.; Goksen, G.; Starowicz, M.; Nawaz, A.; Ahmad, I.; Walayat, N.; Manzoor, M.F.; et al. Natural Plant Extracts: An Update about Novel Spraying as an Alternative of Chemical Pesticides to Extend the Postharvest Shelf Life of Fruits and Vegetables. Molecules 2022, 27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nair, P.K.R.; Kumar, B.M.; Nair, V.D. Historical Developments: The Coming of Age of Agroforestry. In An Introduction to Agroforestry: Four Decades of Scientific Developments; Nair, P.K.R., Kumar, B.M., Nair, V.D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; ISBN 978-3-030-75358-0. [Google Scholar]
- Davis, K.F.; Chhatre, A.; Rao, N.D.; Singh, D.; Ghosh-Jerath, S.; Mridul, A.; Poblete-Cazenave, M.; Pradhan, N.; DeFries, R. Assessing the Sustainability of Post-Green Revolution Cereals in India. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2019, 116, 25034–25041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choudhary, S.; Raheja, N.; Yadav, S.; Sharma, A.; Yamini, N.; Raheja, S.; Yadav, M.; Kamboj, A. ; Sharma A Review: Pesticide Residue: Cause of Many Animal Health Problems. J. Entomol. Zool. Stud. 2018, 6. [Google Scholar]
- Harwood, J. Could the Adverse Consequences of the Green Revolution Have Been Foreseen? How Experts Responded to Unwelcome Evidence. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2020, 44, 509–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- John, D.A.; Babu, G.R. Lessons From the Aftermaths of Green Revolution on Food System and Health. Front. Sustain. Food Syst. 2021, 5, 644559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prasad, S.C. Innovating at the Margins: The System of Rice Intensification in India and Transformative Social Innovation. Ecol. Soc. 2016, 21, art7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benbi, D.K. Carbon Footprint and Agricultural Sustainability Nexus in an Intensively Cultivated Region of Indo-Gangetic Plains. Sci. Total Environ. 2018, 644, 611–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Domené-Painenao, O.; Herrera, F.F. Situated Agroecology: Massification and Reclaiming University Programs in Venezuela. Agroecol. Sustain. Food Syst. 2019, 43, 936–953. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- INTENSIVE FARMING VERSUS-AGRICULTURE ENVIRONMENTALLY SUSTAINABLE - ProQuest. Available online: https://www.proquest.com/openview/9f39b58337b8f3a40db65c733452c3bd/1?pq-origsite=gscholar&cbl=1046413 (accessed on 22 July 2023).
- Kerr, R.B. Lessons from the Old Green Revolution for the New: Social, Environmental and Nutritional Issues for Agricultural Change in Africa. Prog. Dev. Stud. 2012, 12, 213–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tscharntke, T.; Clough, Y.; Wanger, T.C.; Jackson, L.; Motzke, I.; Perfecto, I.; Vandermeer, J.; Whitbread, A. Global Food Security, Biodiversity Conservation and the Future of Agricultural Intensification. Biol. Conserv. 2012, 151, 53–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basit, A.; Shah, S.T.; Ullah, I.; Muntha, S.T.; Mohamed, H.I. Microbe-Assisted Phytoremediation of Environmental Pollutants and Energy Recycling in Sustainable Agriculture. Arch. Microbiol. 2021, 203, 5859–5885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jeanneret, Ph.; Aviron, S.; Alignier, A.; Lavigne, C.; Helfenstein, J.; Herzog, F.; Kay, S.; Petit, S. Agroecology Landscapes. Landsc. Ecol. 2021, 36, 2235–2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cassman, K.G.; Grassini, P. A Global Perspective on Sustainable Intensification Research. Nat. Sustain. 2020, 3, 262–268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Searchinger, T.; Waite, R.; Hanson, C.; Ranganathan, J.; Dumas, P.; Matthews, E. World Resources Report: Creating a Sustainable Food Future; 2018;
- Martin, D.A.; Andrianisaina, F.; Fulgence, T.R.; Osen, K.; Rakotomalala, A.A.N.A.; Raveloaritiana, E.; Soazafy, M.R.; Wurz, A.; Andriafanomezantsoa, R.; Andriamaniraka, H.; et al. Land-Use Trajectories for Sustainable Land System Transformations: Identifying Leverage Points in a Global Biodiversity Hotspot. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2022, 119, e2107747119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosati, A.; Borek, R.; Canali, S. Agroforestry and Organic Agriculture. Agrofor. Syst. 2021, 95, 805–821. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nair, P.K.R.; Kumar, B.M.; Nair, V.D. Definition and Concepts of Agroforestry. In An Introduction to Agroforestry: Four Decades of Scientific Developments; Nair, P.K.R., Kumar, B.M., Nair, V.D., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; pp. 21–28 ISBN 978-3-030-75358-0.
- Hernández Ordoñez, J.O.; Gutiérrez Castorena, M. del C.; Ortiz Solorio, C.A.; Sánchez Guzmán, P.; Ángeles Cervantes, E.; Hernández Ordoñez, J.O.; Gutiérrez Castorena, M. del C.; Ortiz Solorio, C.A.; Sánchez Guzmán, P.; Ángeles Cervantes, E. Calidad de Andosols en sistemas forestal, agroforestal y agrícola con diferentes manejos en Zacatlán, Puebla. Terra Latinoam. 2017, 35, 179–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reid, W.V.; Mooney, H.A.; Cropper, A.; Capistrano, D.; Carpenter, S.R.; Chopra, K.; Dasgupta, P.; Dietz, T.; Duraiappah, A.K.; Hassan, R.; et al. Ecosystems and Human Well-Being - Synthesis: A Report of the Millennium Ecosystem Assessment; Island Press: Washington D.C, 2005; ISBN 978-1-59726-040-4. [Google Scholar]
- FAO Global forest resources assessment, 2010 :: main report; Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations, 2010; ISBN 978-92-5-106654-6.
- Moreno, G.; Aviron, S.; Berg, S.; Crous-Duran, J.; Franca, A.; de Jalón, S.G.; Hartel, T.; Mirck, J.; Pantera, A.; Palma, J.H.N.; et al. Agroforestry Systems of High Nature and Cultural Value in Europe: Provision of Commercial Goods and Other Ecosystem Services. Agrofor. Syst. 2018, 92, 877–891. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torralba, M.; Fagerholm, N.; Burgess, P.J.; Moreno, G.; Plieninger, T. Do European Agroforestry Systems Enhance Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services? A Meta-Analysis. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2016, 230, 150–161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngaji, A.U.K.; Baiquni, M.; Suryatmojo, H.; Haryono, E. Assessing the Sustainability of Traditional Agroforestry Practices: A Case of Mamar Agroforestry in Kupang-Indonesia. For. Soc. 2021, 5, 438–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kindler, E. A Comparison of the Concepts: Ecosystem Services and Forest Functions to Improve Interdisciplinary Exchange. For. Policy Econ. 2016, 67, 52–59. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieterich, V. Forstwirtschaftliche Futurologie. Forstwiss. Cent. 1969, 88, 321–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Waldfunktionen Im Land Brandenburg. Eberswalder Forstliche Schriftenreihe Band XXXIV - PDF Kostenfreier Download. Available online: https://docplayer.org/29172939-Waldfunktionen-im-land-brandenburg-eberswalder-forstliche-schriftenreihe-band-xxxiv.html (accessed on 22 July 2023).
- Persha, L.; Fischer, H.; Chhatre, A.; Agrawal, A.; Benson, C. Biodiversity Conservation and Livelihoods in Human-Dominated Landscapes: Forest Commons in South Asia. Biol. Conserv. 2010, 143, 2918–2925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kosaka, Y.; Takeda, S.; Prixar, S.; Sithirajvongsa, S.; Xaydala, K. Species Composition, Distribution and Management of Trees in Rice Paddy Fields in Central Lao, PDR. Agrofor. Syst. 2006, 67, 1–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Thevs, N.; Aliev, K.; Lleshi, R. Water Productivity of Tree Wind Break Agroforestry Systems in Irrigated Agriculture – An Example from Ferghana Valley, Kyrgyzstan. Trees For. People 2021, 4, 100085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brockerhoff, E.G.; Barbaro, L.; Castagneyrol, B.; Forrester, D.I.; Gardiner, B.; González-Olabarria, J.R.; Lyver, P.O.; Meurisse, N.; Oxbrough, A.; Taki, H.; et al. Forest Biodiversity, Ecosystem Functioning and the Provision of Ecosystem Services. Biodivers. Conserv. 2017, 26, 3005–3035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foli, S.; Reed, J.; Clendenning, J.; Petrokofsky, G.; Padoch, C.; Sunderland, T. To What Extent Does the Presence of Forests and Trees Contribute to Food Production in Humid and Dry Forest Landscapes?: A Systematic Review Protocol. Environ. Evid. 2014, 3, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ntawuruhunga, D.; Ngowi, E.E.; Mangi, H.O.; Salanga, R.J.; Shikuku, K.M. Climate-Smart Agroforestry Systems and Practices: A Systematic Review of What Works, What Doesn’t Work, and Why. For. Policy Econ. 2023, 150, 102937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, S.; Lee, Y. Food Security and Agroforestry from the Perspective of the SDGs: A Case Study of the Democratic People’s Republic of Korea. Int. For. Rev. 2022, 23, 437–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ofori Acheampong, J.; Morgan Attua, E.; Mensah, M.; Fosu-Mensah, B.Y.; Akuka Apambilla, R.; Kofi Doe, E. Livelihood, Carbon and Spatiotemporal Land-Use Land-Cover Change in the Yenku Forest Reserve of Ghana, 2000–2020. Int. J. Appl. Earth Obs. Geoinformation 2022, 112, 102938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.; Venturi, M.; Bertani, R.; Agnoletti, M. A Review of the Role of Forests and Agroforestry Systems in the FAO Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS) Programme. Forests 2020, 11, 860. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Guan, C.; Li, Z.; Luo, J.; Ren, B.; Chen, C.; Xu, Y.; Ding, J.; Huang, H. Review of Rice–Fish–Duck Symbiosis System in China—One of the Globally Important Ingenious Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS). Sustainability 2023, 15, 1910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Min, Q.; Li, H.; He, L.; Zhang, C.; Yang, L. A Conservation Approach of Globally Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (GIAHS): Improving Traditional Agricultural Patterns and Promoting Scale-Production. Sustainability 2017, 9, 295. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nan, M.; Lun, Y.; Qingwen, M.; Keyu, B.; Wenhua, L. The Significance of Traditional Culture for Agricultural Biodiversity—Experiences from GIAHS. J. Resour. Ecol. 2021, 12, 453–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miyata, S.; Kosugi, K.; Gomi, T.; Mizuyama, T. Effects of Forest Floor Coverage on Overland Flow and Soil Erosion on Hillslopes in Japanese Cypress Plantation Forests. Water Resour. Res. 2009, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, Y.; Xu, G.; Shen, N.; Nie, Z.; Li, H.; Zhang, L.; Gong, Y.; He, Y.; Ma, X.; Zhang, H.; et al. Valuation of Ecosystem Services for the Sustainable Development of Hani Terraces: A Rice–Fish–Duck Integrated Farming Model. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2022, 19, 8549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, M.; Li, Y.; Luo, G.; Yu, L.; Chen, M. Agroecosystem Composition and Landscape Ecological Risk Evolution of Rice Terraces in the Southern Mountains, China. Ecol. Indic. 2022, 145, 109625. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Evangelista de Oliveira, R.; Carvalhaes, M. Agroforestry as a Tool for Restoration in Atlantic Forest: Can We Find Multi-Purpose Species? Oecologia Aust. 2016, 20, 425–435. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z. Landscape Pattern Optimization Approach to Protect Rice Terrace Agroecosystem: Case of GIAHS Site Jiache Valley, Guizhou, Southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petticrew, M.; Roberts, H. Systematic Reviews in the Social Sciences: A Practical Guide; Systematic reviews in the social sciences: A practical guide; Blackwell Publishing: Malden, 2006; pp. xv, 336; ISBN 978-1-4051-2110-1.
- Gough, D.; Elbourne, D. Systematic Research Synthesis to Inform Policy, Practice and Democratic Debate. Soc. Policy Soc. 2002, 1, 225–236. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dai, T.; Zheng, X.; Yang, J. A Systematic Review of Studies at the Intersection of Urban Climate and Historical Urban Landscape. Environ. Impact Assess. Rev. 2022, 97, 106894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arunrat, N.; Sereenonchai, S. Assessing Ecosystem Services of Rice–Fish Co-Culture and Rice Monoculture in Thailand. Agronomy 2022, 12, 1241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, P.K.; Nayak, A.K.; Panda, B.B.; Lal, B.; Gautam, P.; Poonam, A.; Shahid, M.; Tripathi, R.; Kumar, U.; Mohapatra, S.D.; et al. Ecological Mechanism and Diversity in Rice Based Integrated Farming System. Ecol. Indic. 2018, 91, 359–375. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Li, J.; Zhou, Z. Landscape Pattern Optimization Approach to Protect Rice Terrace Agroecosystem: Case of GIAHS Site Jiache Valley, Guizhou, Southwest China. Ecol. Indic. 2021, 129, 107958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quevedo-Cascante, M.; Mogensen, L.; Kongsted, A.G.; Knudsen, M.T. How Does Life Cycle Assessment Capture the Environmental Impacts of Agroforestry? A Systematic Review. Sci. Total Environ. 2023, 890, 164094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, P.; Choudhary, B.B.; Dwivedi, R.P.; Arunachalam, A.; Kumar, S.; Dev, I. Agroforestry Improves Food Security and Reduces Income Variability in Semi-Arid Tropics of Central India. Agrofor. Syst. 2023, 97, 509–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Milheiras, S.G.; Sallu, S.M.; Marshall, A.R.; Shirima, D.D.; Kioko, E.N.; Loveridge, R.; Moore, E.; Olivier, P.; Teh, Y.A.; Rushton, S.; et al. A Framework to Assess Forest-Agricultural Landscape Management for Socioecological Well-Being Outcomes. Front. For. Glob. Change 2022, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jose, S. Agroforestry for Ecosystem Services and Environmental Benefits: An Overview. Agrofor. Syst. 2009, 76, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mariel, J.; Penot, E.; Labeyrie, V.; Herimandimby, H.; Danthu, P. From Shifting Rice Cultivation (Tavy) to Agroforestry Systems: A Century of Changing Land Use on the East Coast of Madagascar. Agrofor. Syst. 2023, 97, 415–431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wotlolan, D.L.; Lowry, J.H.; Wales, N.A.; Glencross, K. Land Suitability Evaluation for Multiple Crop Agroforestry Planning Using GIS and Multi-Criteria Decision Analysis: A Case Study in Fiji. Agrofor. Syst. 2021, 95, 1519–1532. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tyagi, D.K. , Santosh K. Arya, Deepti Srivastava, Md Shamim, L.J. Desai, Manjusha Impact of Major Rice Bacterial Diseases on Agriculture and Food Security. In Bacterial Diseases of Rice and Their Management; Apple Academic Press, 2023 ISBN 978-1-00-333162-9.
- Troell, M.; Costa-Pierce, B.; Stead, S.; Cottrell, R.S.; Brugere, C.; Farmery, A.K.; Little, D.C.; Strand, Å.; Pullin, R.; Soto, D.; et al. Perspectives on Aquaculture’s Contribution to the Sustainable Development Goals for Improved Human and Planetary Health. J. World Aquac. Soc. 2023, 54, 251–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampantamit, T.; Ho, L.; Van Echelpoel, W.; Lachat, C.; Goethals, P. Links and Trade-Offs between Fisheries and Environmental Protection in Relation to the Sustainable Development Goals in Thailand. Water 2020, 12, 399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mabhaudhi, T.; Nhamo, L.; Mpandeli, S.; Nhemachena, C.; Senzanje, A.; Sobratee, N.; Chivenge, P.P.; Slotow, R.; Naidoo, D.; Liphadzi, S.; et al. The Water–Energy–Food Nexus as a Tool to Transform Rural Livelihoods and Well-Being in Southern Africa. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public. Health 2019, 16, 2970. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Piras, F.; Fiore, B.; Santoro, A. Small Cultural Forests: Landscape Role and Ecosystem Services in a Japanese Cultural Landscape. Land 2022, 11, 1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paing, J.N.; van Bussel, L.G.J.; Gomez, R.A.; Hein, L.G. Ecosystem Services through the Lens of Indigenous People in the Highlands of Cordillera Region, Northern Philippines. J. Environ. Manage. 2022, 308, 114597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lambers, H.; Cong, W.-F. CHALLENGES PROVIDING MULTIPLE ECOSYSTEM BENEFITS FOR SUSTAINABLE MANAGED SYSTEMS. Front. Agric. Sci. Eng. 2022, 9, 170–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baba, Y.G.; Osawa, T.; Kusumoto, Y.; Tanaka, K. Multi-Spatial-Scale Factors Determining the Abundance of Frogs in Rice Paddy Fields and Their Potential as Biological Control Agents. Wetlands 2023, 43, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Helseth, E.V.; Vedeld, P.; Framstad, E.; Gómez-Baggethun, E. Forest Ecosystem Services in Norway: Trends, Condition, and Drivers of Change (1950–2020). Ecosyst. Serv. 2022, 58, 101491. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hayat, M.; TianShan, Z.; Nizami, S.M.; Gulzar, S.; Khan, A.; Iqbal, S.; Khan, M.S. Productive Role of Agroforestry System in Context of Ecosystem Services in District Dir Lower, Pakistan. Pak. J. Bot. 2020, 52, 1411–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bin, W.; Yehong, S.; Wenjun, J. Ecological Benefit Evaluation of Agricultural Heritage System Conservation—A Case Study of the Qingtian Rice-Fish Culture System. J. Resour. Ecol. 2021, 12, 489–497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siminski, A.; Santos, K.L.; Wendt, J.G.N. Rescuing Agroforestry as Strategy for Agriculture in Southern Brazil. J. For. Res. 2016, 4, 739–746. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H. Regional Assessment of Ecological Risk Caused by Human Activities on Wetlands in the Muleng-Xingkai Plain of China Using a Pressure–Capital–Vulnerability–Response Model. Wetl. Ecol. Manag. 2022, 30, 111–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suwarno, A.; Hein, L.; Sumarga, E. Who Benefits from Ecosystem Services? A Case Study for Central Kalimantan, Indonesia. Environ. Manage. 2016, 57, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, W.-Y.; Chuang, Y.-L. Assessing the Incentives and Financial Compensation of Agroforestry Considering the Uncertainty of Price and Yield. Ecol. Indic. 2023, 146, 109753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xie, J.; Wu, X.; Tang, J.; Zhang, J.; Luo, S.; Chen, X. Conservation of Traditional Rice Varieties in a Globally Important Agricultural Heritage System (GIAHS): Rice-Fish Co-Culture. Agric. Sci. China 2011, 10, 754–761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berg, H.; Tam, N. Decreased Use of Pesticides for Increased Yields of Rice and Fish-Options for Sustainable Food Production in the Mekong Delta. Sci. Total Environ. 2017; 619–620, 319–327. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amano, T.; Kusumoto, Y.; Tokuoka, Y.; Yamada, S.; Kim, E.-Y.; Yamamoto, S. Spatial and Temporal Variations in the Use of Rice-Paddy Dominated Landscapes by Birds in Japan. Biol. Conserv. 2008, 141, 1704–1716. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Zhang, J.; Ren, W.; Guo, L.; Cheng, Y.; Li, J.; Li, K.; Zhu, Z.; Zhang, J.; Luo, S.; et al. Can the Co-Cultivation of Rice and Fish Help Sustain Rice Production? Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 28728. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, L.; Weizheng, R.; Tang, J.; Li, N.; Zhang, J.; Chen, X. The Productivity of Traditional Rice–Fish Co-Culture Can Be Increased without Increasing Nitrogen Loss to the Environment. Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2013, 177, 28–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Benton, T.G. Ecology. Managing Farming’s Footprint on Biodiversity. Science 2007, 315, 341–342. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, R.E.; Cornell, S.J.; Scharlemann, J.P.W.; Balmford, A. Farming and the Fate of Wild Nature. Science 2005, 307, 550–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Swift, M.J.; Izac, A.-M.N.; van Noordwijk, M. Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services in Agricultural Landscapes—Are We Asking the Right Questions? Agric. Ecosyst. Environ. 2004, 104, 113–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kalaba, F.K.; Quinn, C.H.; Dougill, A.J. Contribution of Forest Provisioning Ecosystem Services to Rural Livelihoods in the Miombo Woodlands of Zambia. Popul. Environ. 2013, 35, 159–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Muhamad, D.; Okubo, S.; Harashina, K.; Parikesit; Gunawan, B. ; Takeuchi, K. Living Close to Forests Enhances People׳s Perception of Ecosystem Services in a Forest–Agricultural Landscape of West Java, Indonesia. Ecosyst. Serv. 2014, 8, 197–206. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Ding, Y.; Zha, Z.; Okuro, T. Crises of Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services in Satoyama Landscape of Japan: A Review on the Role of Management. Sustainability 2019, 11, 454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodenburg, J.; Zwart, S.J.; Kiepe, P.; Narteh, L.T.; Dogbe, W.; Wopereis, M.C.S. Sustainable Rice Production in African Inland Valleys: Seizing Regional Potentials through Local Approaches. Agric. Syst. 2014, 123, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiao, Y.; Li, X.; Liang, L.; Takeuchi, K.; Okuro, T.; Zhang, D.; Sun, L. Indigenous Ecological Knowledge and Natural Resource Management in the Cultural Landscape of China’s Hani Terraces. Ecol. Res. 2012, 27, 247–263. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heyao, L.I.; Siyuan, H.E.; Lubin, D.; Nan, M.A.; Qingwen, M.I.N. Conceptual Framework for Key Element Identification in Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (IAHS): Case of Honghe Hani Rice Terraces System in China. J. Resour. Ecol. 2021, 12, 522. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, G.Y.; Darachanthara, S.; Soukkhamthat, T. Economic Valuation of Land Uses in Oudomxay Province, Lao PDR: Can REDD+ Be Effective in Maintaining Forests? Land 2014, 3, 1059–1074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li Zhaokeng, Ecological Planning Principles of the Surrounding Mountains of Lianhe Terraces in Youxi. . FUJIANLINYE 2018, 45–48.
- BERKES, F. Rethinking Community-Based Conservation. Conserv. Biol. 2004, 18, 621–630. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiu, Z.; Chen, B.; Takemoto, K. Conservation of Terraced Paddy Fields Engaged with Multiple Stakeholders: The Case of the Noto GIAHS Site in Japan. Paddy Water Environ. 2013, 12, 275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Groot, R.; Brander, L.; van der Ploeg, S.; Costanza, R.; Bernard, F.; Braat, L.; Christie, M.; Crossman, N.; Ghermandi, A.; Hein, L.; et al. Global Estimates of the Value of Ecosystems and Their Services in Monetary Units. Ecosyst. Serv. 2012, 1, 50–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Joshi, G.; Negi, G.C.S. Quantification and Valuation of Forest Ecosystem Services in the Western Himalayan Region of India. Int. J. Biodivers. Sci. Ecosyst. Serv. Manag. 2011, 7, 2–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wan, N.-F.; Li, S.-X.; Li, T.; Cavalieri, A.; Weiner, J.; Zheng, X.-Q.; Ji, X.-Y.; Zhang, J.-Q.; Zhang, H.-L.; Zhang, H.; et al. Ecological Intensification of Rice Production through Rice-Fish Co-Culture. J. Clean. Prod. 2019, 234, 1002–1012. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasaki, K.; Hotes, S.; Ichinose, T.; Doko, T.; Wolters, V. Hotspots of Agricultural Ecosystem Services and Farmland Biodiversity Overlap with Areas at Risk of Land Abandonment in Japan. Land 2021, 10, 1031. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Tang, R.; Xie, J.; Tian, J.; Shi, R.; Zhang, K. Valuation of Ecosystem Services of Rice–Fish Coculture Systems in Ruyuan County, China. Ecosyst. Serv. 2020, 41, 101054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youn, Y.-C. Use of Forest Resources, Traditional Forest-Related Knowledge and Livelihood of Forest Dependent Communities: Cases in South Korea. For. Ecol. Manag. 2009, 257, 2027–2034. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramakrishnan, P.S. Traditional Forest Knowledge and Sustainable Forestry: A North-East India Perspective. For. Ecol. Manag. 2007, 249, 91–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramírez, O.A.; Somarriba, E.; Ludewigs, T.; Ferreira, P. Financial Returns, Stability and Risk of Cacao-Plantain-Timber Agroforestry Systems in Central America. Agrofor. Syst. 2001, 51, 141–154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, J.; Li, F.; Zhou, X.; Xu, C.; Fang, F. Nutrient Removal Ability and Economical Benefit of a Rice-Fish Co-Culture System in Aquaculture Pond. Ecol. Eng. 2016, 94, 315–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vromant, N.; Duong, L.T.; Ollevier, F. Effect of Fish on the Yield and Yield Components of Rice in Integrated Concurrent Rice–Fish Systems. J. Agric. Sci. 2002, 138, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sumarga, E.; Hein, L. Benefits and Costs of Oil Palm Expansion in Central Kalimantan, Indonesia, under Different Policy Scenarios. Reg. Environ. Change 2016, 16, 1011–1021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kohsaka, R.; Ito, K.; Miyake, Y.; Uchiyama, Y. Cultural Ecosystem Services from the Afforestation of Rice Terraces and Farmland: Emerging Services as an Alternative to Monoculturalization. For. Ecol. Manag. 2021, 497, 119481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zaehringer, J.G.; Schwilch, G.; Andriamihaja, O.R.; Ramamonjisoa, B.; Messerli, P. Remote Sensing Combined with Social-Ecological Data: The Importance of Diverse Land Uses for Ecosystem Service Provision in North-Eastern Madagascar. Ecosyst. Serv. 2017, 25, 140–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Babu, S.; Singh, R.; Avasthe, R.K.; Yadav, G.S.; Mohapatra, K.P.; Selvan, T.; Das, A.; Singh, V.K.; Valente, D.; Petrosillo, I. Soil Carbon Dynamics in Indian Himalayan Intensified Organic Rice-Based Cropping Sequences. Ecol. Indic. 2020, 114, 106292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Drewes, A.D.; Silbernagel, J. Uncovering the Spatial Dynamics of Wild Rice Lakes, Harvesters and Management across Great Lakes Landscapes for Shared Regional Conservation. Ecol. Model. 2012, 229, 97–107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- IMPACT: The Effects of Tourism on Culture and the Environment in Asia and the Pacific: Sustainable Tourism and the Preservation of the World Heritage Site of the Ifugao Rice Terraces, Philippines - UNESCO Digital Library. Available online: https://unesdoc.unesco.org/ark:/48223/pf0000182647 (accessed on 23 July 2023).
- Zhu, G.; Li, X.; Zhang, Y. Multi-Stakeholder Involvement Mechanism in Tourism Management for Maintaining Terraced Landscape in Important Agricultural Heritage Systems (IAHS) Sites: A Case Study of Dazhai Village in Longji Terraces, China. Land 2021, 10, 1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Min, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Jiao, W.; Sun, X. Responding to Common Questions on the Conservation of Agricultural Heritage Systems in China. J. Geogr. Sci. 2016, 26, 969–982. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, N.; Fang, M.; Beauchamp, M.; Jia, Z.; Zhou, Z. An Indigenous Knowledge-Based Sustainable Landscape for Mountain Villages: The Jiabang Rice Terraces of Guizhou, China. Habitat Int. 2021, 111, 102360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Step | Publications | Process |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 73 | Publications that were retrieved |
| 2 | 66 | Publications not in the Environmental Sciences, Agricultural and Biological Sciences, Social Sciences are excluded(n=7) |
| 3 | 50 | Publications that are not articles, reviews are excluded(n=6) |
| 4 | 44 | Publications with keyword frequencies below 4 were excluded(n=6) |
| 5 | 49 | Publications that are not in English are excluded(n=5) |
| 6 | 41 | Publications not related to the topic of this review(n=8) |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




