Submitted:
27 July 2023
Posted:
31 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Methods
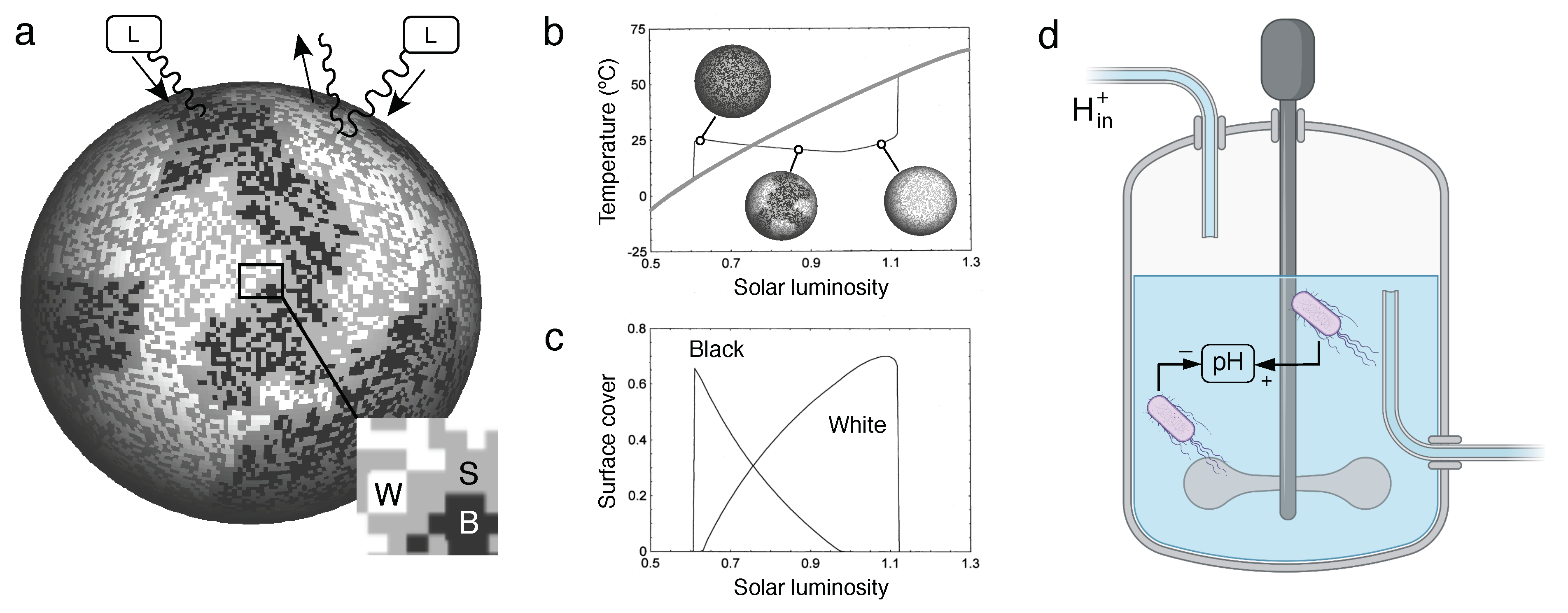
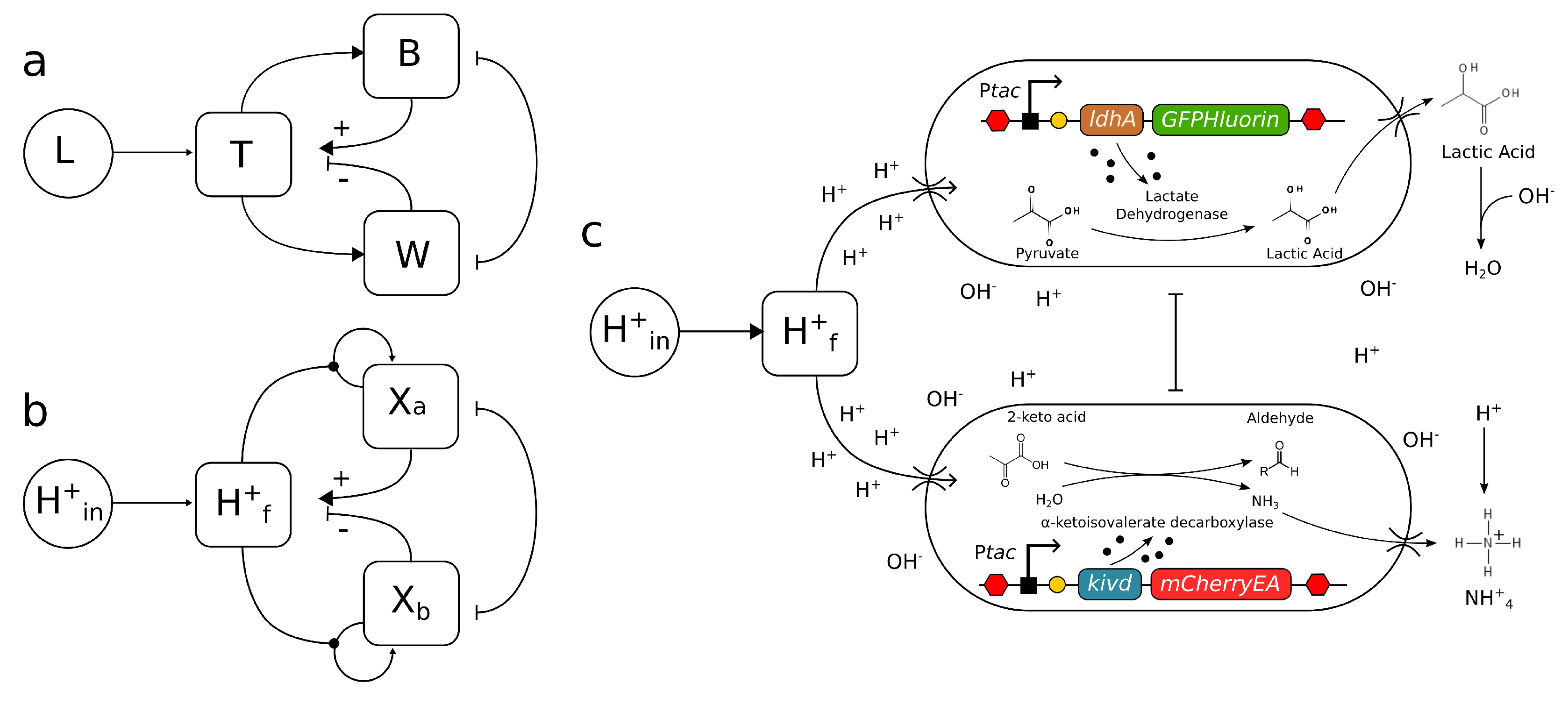
2.1. Microbial Daisy World: synthetic circuits
2.2. Microbial Daisy World: two-species model
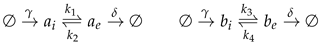
3. Results
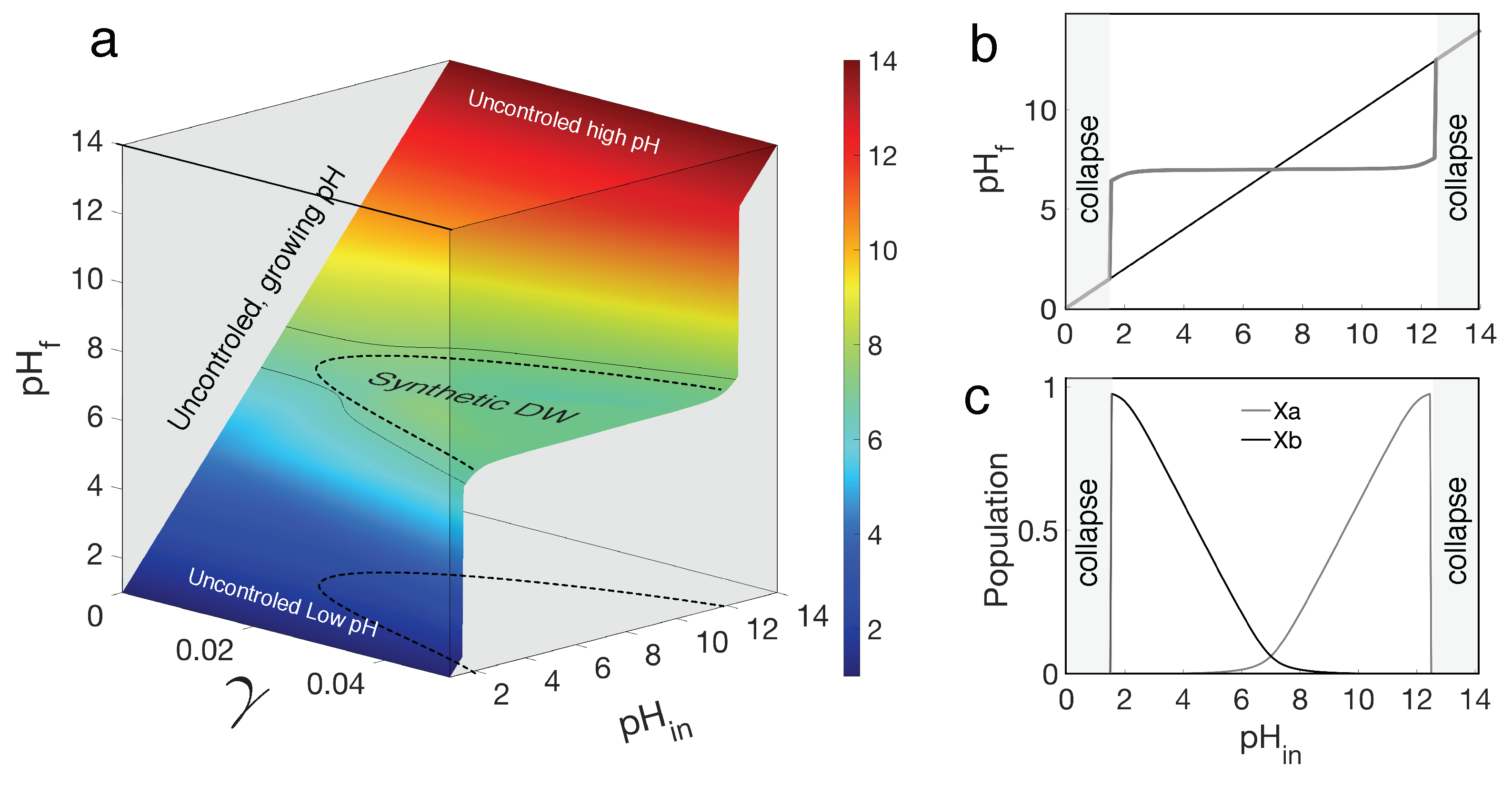
3.1. Two-species consortium
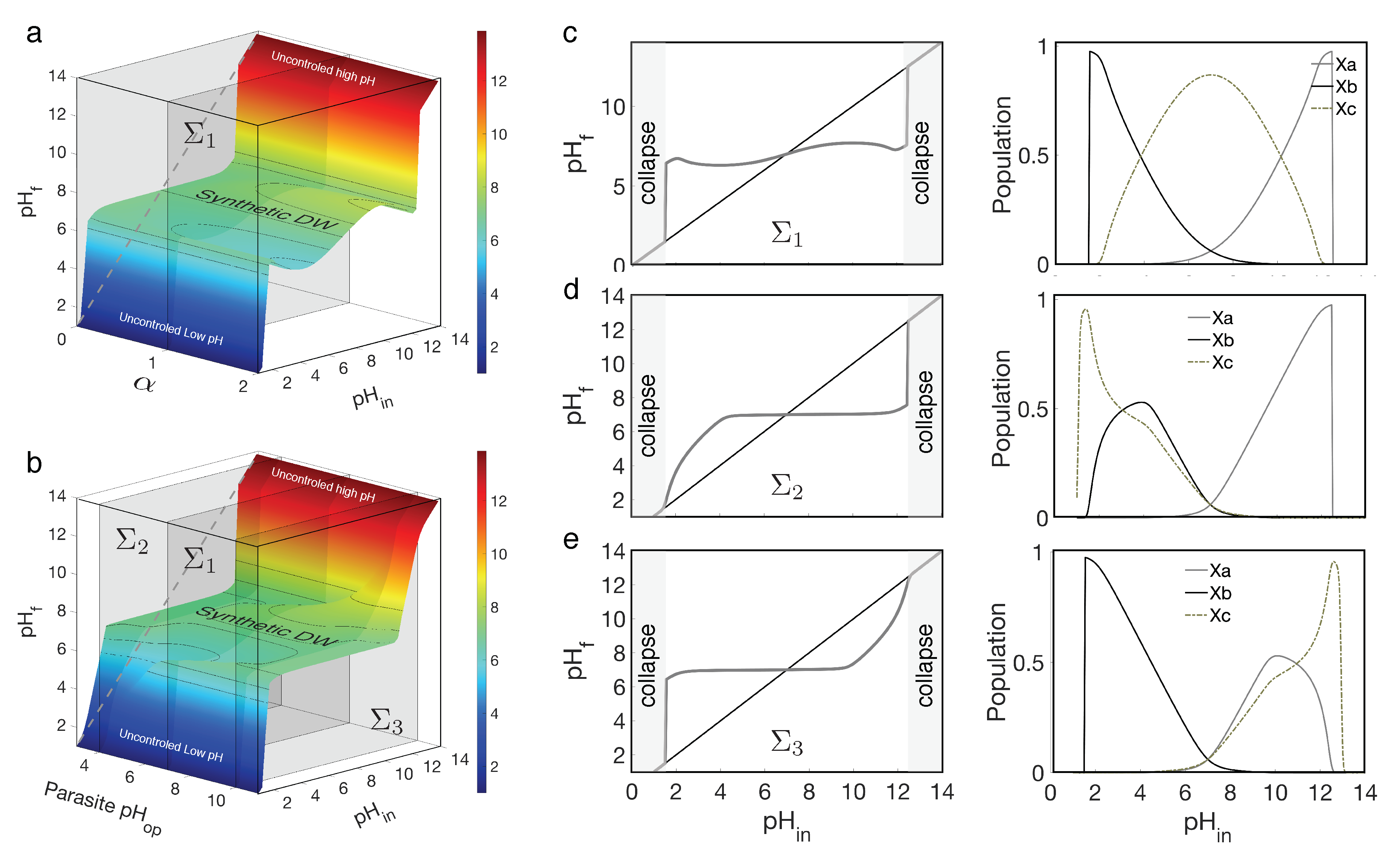
3.2. Two-species plus parasites
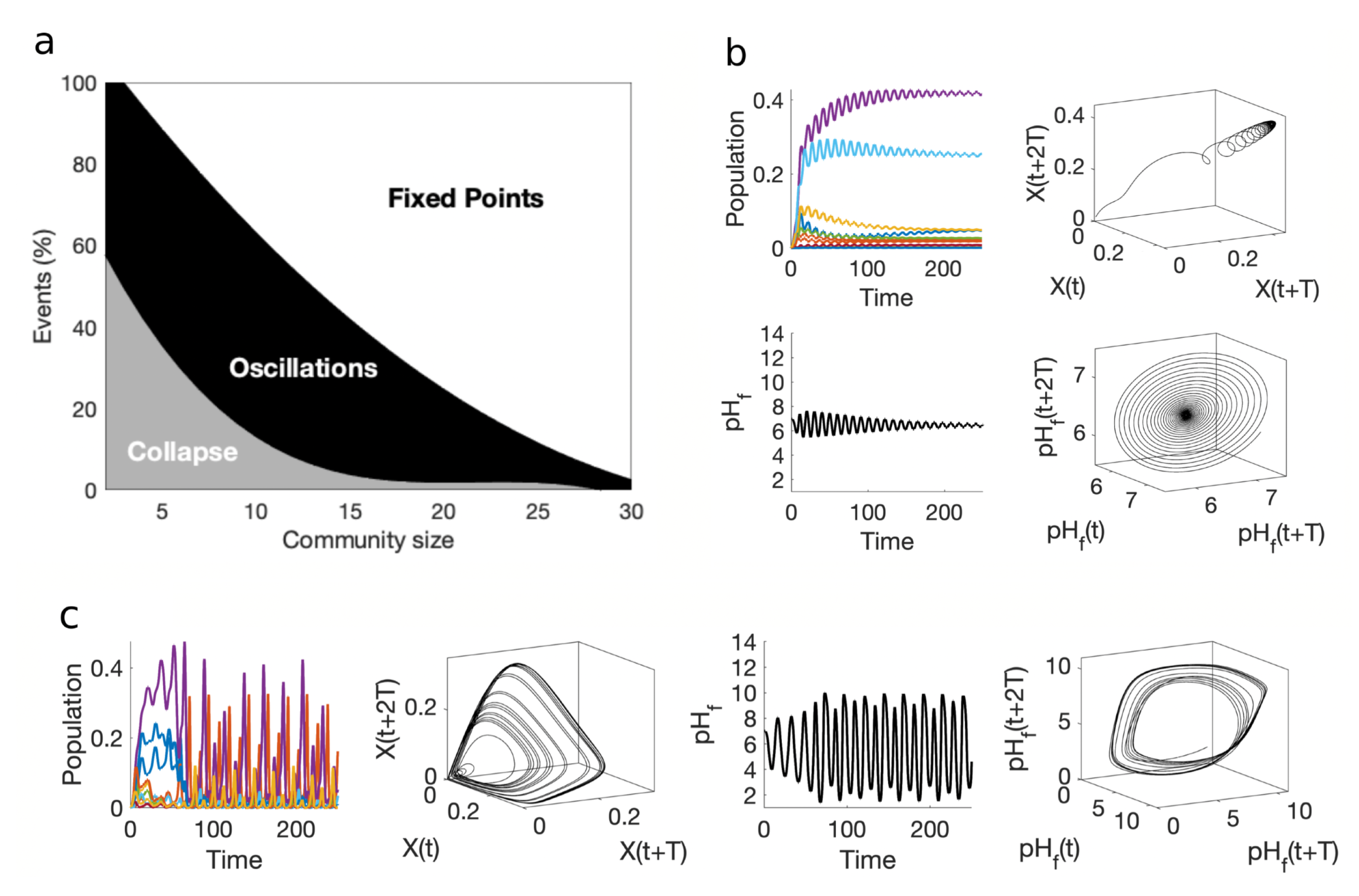
3.3. Multispecies SDW: order and chaos
4. Discussion
Acknowledgments
References
- Alberti, T. , Lepreti, F., Vecchio, A. and Carbone, V., 2018. On the stability of a climate model for an Earth-like planet with land-ocean coverage. Journal of Physics Communications 2, 065018. [CrossRef]
- Knoll, A.H. , 2015. Life on a young planet, Princeton University Press.
- Knoll, A.H. and Nowak, M.A., 2017. The timetable of evolution. Science advances 3, e1603076.
- Lenton, T. and Watson, A., 2013. Revolutions that made the Earth, OUP Oxford.
- Vernadsky, V.I. , 1998. The biosphere, Springer Science, New York.
- Lovelock, J. E. , 1972. Gaia as seen through the atmosphere. Atmos. Environ. 6, 579-580.
- Lovelock, J.E. and Margulis, L., 1974. Atmospheric homeostasis by and for the biosphere: the Gaia hypothesis. Tellus 26, 2-10. [CrossRef]
- Margulis, L. and Lovelock, J.E., 1974. Biological modulation of the Earth’s atmosphere. Icarus 21, 471-489. [CrossRef]
- Lovelock, J. , 2016. Gaia: A new look at life on earth, Oxford University Press.
- Adams, B. , Carr, J., Lenton, T.M. and White, A., 2003. One-dimensional daisyworld: spatial interactions and pattern formation. Journal of theoretical biology 223, 505-513. [CrossRef]
- Ackland, G. J. , Clark, M. A. and Lenton, T. M., 2003. Catastrophic desert formation in Daisyworld. Journal of theoretical biology 223, 39-44. [CrossRef]
- Ackland, G.J. and Wood, A.J., 2010. Emergent patterns in space and time from daisyworld: a simple evolving coupled biosphere?climate model. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A 368, 161-179. [CrossRef]
- Punithan, D. , Kim, D.K. and McKay, R.B., 2012. Spatio-temporal dynamics and quantification of daisyworld in two-dimensional coupled map lattices. Ecological complexity 12, 43-57. [CrossRef]
- Mackwell, S.J. , Simon-Miller, A.A., Harder, J.W. and Bullock, M.A. eds., 2014. Comparative climatology of terrestrial planets, University of Arizona Press.
- Murante, G. , Provenzale, A., Vladilo, G. et al, 2020. Climate bistability of Earth-like exoplanets. Monthly Notices of the Royal Astronomical Society 492, 2638-2650. [CrossRef]
- Shou, W. , Ram, S. and Vilar, J.M., 2007. Synthetic cooperation in engineered yeast populations. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 104 1877–1882. [CrossRef]
- Amor, D.R. , Montanez, R., Duran-Nebreda, S. and Solé, R., 2017. Spatial dynamics of synthetic microbial mutualists and their parasites. PLOS Computational Biology 13, e1005689. [CrossRef]
- Balagadde, F.K. , Song, H., Ozaki, J., Collins, C.H., Barnet, M., Arnold, F.H., Quake, S.R. and You, L., 2008. A synthetic Escherichia coli predator?prey ecosystem. Molecular systems biology 4, 87. [CrossRef]
- Mee, M.T. and Wang, H.H., 2012. Engineering ecosystems and synthetic ecologies. Molecular BioSystems 8, 2470-2483. [CrossRef]
- Johns, N.I. , Blazejewski, T., Gomes, A.L. and Wang, H.H., 2016. Principles for designing synthetic microbial communities. Current Opinion in Microbiology 31, 146-153. [CrossRef]
- Hu, J. , Amor, D.R., Barbier, M., Bunin, G. and Gore, J., 2022. Emergent phases of ecological diversity and dynamics mapped in microcosms. Science 378, 85-89. [CrossRef]
- Watson, A.J. and Lovelock, J.E., 1983. Biological homeostasis of the global environment: the parable of Daisyworld. Tellus B 35, 284-289. [CrossRef]
- Lenton, T.M. and Lovelock, J.E., 2001. Daisyworld revisited: quantifying biological effects on planetary self?regulation. Tellus B 53, 288-305. [CrossRef]
- Lenton, T.M. , Daines, S.J., Dyke, J.G., Nicholson, A.E., Wilkinson, D.M. and Williams, H.T., 2018. Selection for Gaia across multiple scales. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 33, 633-645. [CrossRef]
- Lovelock, J.E. and Watson, A.J., 1982. The regulation of carbon dioxide and climate: Gaia or geochemistry. Planetary and Space Science 30, 795-802. [CrossRef]
- Steffen, W. , Richardson, K., Rockstrm, J., Schellnhuber, H.J., Dube, O.P., Dutreuil, S., Lenton, T.M. and Lubchenco, J., 2020. The emergence and evolution of Earth System Science. Nature Reviews Earth Environment 1, 54-63. [CrossRef]
- Wilkinson, D.M. , 2003. Catastrophes on daisyworld. Trends in Ecology and Evolution 18, 266-268. [CrossRef]
- Wood, A.J. , Ackland, G.J., Dyke, J.G., Williams, H.T. and Lenton, T.M., 2008. Daisyworld: A review. Reviews of Geophysics, 46(1). [CrossRef]
- Li, C. , Gao, X., Peng, X. et al. 2020. Intelligent microbial cell factory with genetic pH shooting (GPS) for cell self-responsive base/acid regulation. Microbial Cell Factories, 19, 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.J. , 2011. A new model for the effect of pH on microbial growth: an extension of the Gamma hypothesis. Journal of applied microbiology 110, 61-68. [CrossRef]
- Presser, K.A. , Ratkowsky, D.A. and Ross, T., 1997. Modelling the growth rate of Escherichia coli as a function of pH and lactic acid concentration. Applied and environmental microbiology 63, 2355-2360. [CrossRef]
- Lambert, R.J.W. and Pearson, J., 2000. Susceptibility testing: accurate and reproducible minimum inhibitory concentration (MIC) and non-inhibitory concentration (NIC) values. Journal of applied microbiology 88, 784-790. [CrossRef]
- Lv, X. , Hueso-Gil, A., Bi, X., Wu, Y., Liu, Y., Liu, L. and Ledesma-Amaro, R., 2022. New synthetic biology tools for metabolic control. Current Opinion in Biotechnology 76, 102724. [CrossRef]
- Kambale, S.D. , George, S. and Zope, R.G., 2015. Controllers used in pH neutralization process: a review. IRJET, 2, 354-61.
- Mikami, Y. , Yoneda, H., Aoki, W. and Ueda, M., 2017. Ammonia production from amino acid-based biomass-like sources by engineered Escherichia coli. AMB Expr, 7-83. [CrossRef]
- Núñez, M.F. , Kwon, O., Wilson, T.H., Aguilar, J., Baldoma, L. and Lin, E.C.C., 2017. Transport of L-Lactate, D-Lactate, and Glycolate by the LldP and GlcA Membrane Carriers of Escherichia coli. Biochemical and Biophysical Research Communications 290, 824-829. [CrossRef]
- de la Plaza, M. , Peláez, C. and Requena, T., 2009. Regulation of α-Ketoisovalerate Decarboxylase Expression in Lactococcus lactis IFPL730. J Mol Microbiol Biotechnol 17:96-100. [CrossRef]
- Reifenrath, M. and Boles, E., 2018. A superfolder variant of pH-sensitive pHluorin for in vivo pH measurements in the endoplasmic reticulum. Scientific Reports 8:11985. [CrossRef]
- Hartmann, F.S.F. , Weiss, T., Shen, J., Smahajcsik, D., Savickas, S. and Seibold, G.M., 2022. Visualizing the pH in Escherichia coli colonies via the sensor protein mCherryEA allows high-throughput screening of mutant libraries. Msystems 7, e00219-22. [CrossRef]
- Smith J., M. 1979. Hypercycles and the origin of life. Nature, 280, 445-446.
- Boerlijst M., C. and Hogeweg P. 1991. Spiral wave structure in pre-biotic evolution: hypercycles stable against parasites. Physica D 48, 17-28. [CrossRef]
- Sardanyes, J. and Solé R. (2007). Spatio-temporal dynamics in simple asymmetric hypercycles under weak parasitic coupling. Physica D 231, 116-129. [CrossRef]
- Sneppen, K. , 2014. Models of life, Cambridge University Press.
- Munch, S.B. , Rogers, T.L., Johnson, B.J., Bhat, U. and Tsai, C.H., 2022. Rethinking the prevalence and relevance of chaos in ecology. Annual Review of Ecology, Evolution, and Systematics, 53, pp.227-249. [CrossRef]
- Ratzke, C. and Gore, J., 2018. Modifying and reacting to the environmental pH can drive bacterial interactions. PLoS biology, 16(3), p.e2004248. [CrossRef]
- Maull, V. and Solé, R., 2022. Network-level containment of single-species bioengineering. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B, 377(1857), p.20210396. [CrossRef]
- NH Packard, JP Crutchfield, JD Farmer, RS Shaw (1980) Geometry from a time series. Physical Review Letters 45, 712. [CrossRef]
- Schaffer, W.M. , 1985. Order and chaos in ecological systems. Ecology, 66(1), pp.93-106. [CrossRef]
- Williams, H.T. and Lenton, T.M., 2007. The Flask model: emergence of nutrient?recycling microbial ecosystems and their disruption by environment?altering OrebelOorganisms. Oikos, 116(7), pp.1087-1105. [CrossRef]
- Ratzke, C. , Denk, J. and Gore, J., 2018. Ecological suicide in microbes. Nature ecology and evolution, 2(5), pp.867-872. [CrossRef]
- Conde-Pueyo, N. , Vidiella, B., Sardanyés, J., Berdugo, M., Maestre, F.T., De Lorenzo, V. and Solé, R., 2020. Synthetic biology for terraformation lessons from mars, earth, and the microbiome. life, 10(2), p.14. [CrossRef]
- Saunders, P.T. , Koeslag, J.H. and Wessels, J.A., 1998. Integral rein control in physiology. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 194(2), pp.163-173. [CrossRef]
- Saunders, P.T. ., Koeslag, J.H. and Wessels, J.A., 2000. Integral rein control in physiology II: a general model. Journal of Theoretical Biology, 206(2), pp.211-220. [CrossRef]
- Lenton, T.M. , 1998. Gaia and natural selection. Nature 394, 439-447. [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




