1. Introduction
The liver serves as a primary target for the innate immune response due to its continuous exposure to microorganisms and products originating from the gut [
1,
2]. Within the liver, monocytes/macrophages, along with granulocytes and dendritic cells, act as key effector cells of the innate immune system. Hepatic macrophages are primarily composed of two distinct types: resident macrophages known as Kupffer cells (KCs), which originate from erythromyeloid progenitors derived from the yolk sac, and monocyte-derived macrophages (MDM). In the context of inflammation, monocytes migrate from the peripheral circulation to the liver, where they differentiate into tissue macrophages. These macrophages play crucial roles in functions such as phagocytosis of foreign particles and cellular debris, antigen presentation to lymphocytes, secretion of cytokines, modulation of immune responses, and the restoration of a normal tissue environment [
3,
4].
Macrophages possess remarkable plasticity, allowing them to adapt their phenotypes and functions in response to environmental cues.
In vitro studies have revealed that macrophages can be broadly categorized into two major populations based on their distinct phenotypes: classically activated proinflammatory M1 macrophages and alternatively activated anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages [
5,
6]. However, it is worth noting that certain macrophages, such as tumor-associated macrophages, may exhibit characteristics that overlap between these two groups [
7]. The prototypical signals triggering M1 proinflammatory activation include interferon gamma (IFN-gamma), lipopolysaccharide (LPS), and tumor necrosis factor alpha (TNFα), while interleukin 4 (IL4) serves as a key signal for anti-inflammatory M2 activation. Although the M1/M2 classification may oversimplify the intricate biological response of macrophages
in vivo, numerous studies have substantiated that macrophage differentiation into distinct pro-inflammatory or anti-inflammatory phenotypes significantly influences host defense and the pathogenesis of various liver diseases [
8,
9,
10]. Therefore, the identification of heterogeneous macrophage populations and a comprehensive understanding of the molecular mechanisms governing macrophage heterogeneity are crucial for assessing disease progression, evaluating treatment outcomes, and developing targeted therapeutics that specifically modulate macrophage function [
11,
12,
13,
14,
15].
Our study aimed to investigate the involvement of small heterodimer partner (Nr0b2,
Homo sapiens SHP;
Mus musculus Shp) in macrophage differentiation during the innate immune response. SHP is a nuclear receptor lacking DNA binding domain and known endogenous ligands [
16]. It functions as a negative regulator of gene transcription and plays a crucial role in the regulation of bile acid, glucose, and energy metabolism through its interactions with other nuclear receptors and transcription factors [
16,
17,
18,
19,
20]. Recent studies have shed light on a novel function of SHP in inflammation, where it acts as a negative regulator of immune response [
21]. Mice lacking SHP are more susceptible to endotoxin-induced sepsis and concanavalin A-induced hepatitis [
16,
22,
23,
24] while inducing SHP expression has been found to ameliorate systemic inflammatory responses [
25]. Moreover, we have recently discovered an anti-inflammatory role of SHP during the development of non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH), where the loss of SHP in hepatocytes triggers nuclear factor kappa B (NF-κB) activation and the release of chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2 (CCL2), exacerbating liver inflammation and fibrosis [
26,
27].
While the role of SHP in repressing innate immune activation has been well-documented, its involvement in macrophage differentiation during the innate immune response remains unclear. To address this gap in knowledge, we utilized a cell type-specific knockout mouse model to examine the role of SHP in macrophage differentiation. We found that Shp mRNA was down-regulated in pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages, but up-regulated in anti-inflammatory M2 macrophages. Deletion of Shp promoted M1 macrophage differentiation while interfering with M2 macrophage polarization. Conversely, overexpression of SHP resulted in increased expression of peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma (Pparg) with decreased M1 differentiation. Consistently, in Shp myeloid cell specific knockout (Shp-MKO) mouse model, we observed increased hepatic infiltration of monocytes and M1 macrophage differentiation following LPS challenge, accompanied by augmented activation of the mitogen-activated protein kinase (MAPK) and NF-κB pathways resulting from the loss of macrophage SHP in Shp-MKO. In summary, our study sheds light on the crucial role of SHP in modulating hepatic macrophage differentiation, contributing to the regulation of the inflammatory response and immune balance in the liver.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Cell lines, chemicals, plasmids, and antibodies
Mouse macrophage RAW 264.7 cells (ATCC TIB-71) were cultured in Dulbecco's Modified Eagle's Medium supplemented with 100 units/ml penicillin G-streptomycin sulfate and 10% heat-inactivated fetal bovine serum. To achieve overexpression of FLAG-SHP, a lentiviral vector pMSCV-puro was employed, and stable overexpression cells were selected using puromycin (Fisher, A1113802). The cells were treated with 100 ng/ml lipopolysaccharide (LPS, Sigma, L2654) for various time intervals (0, 5, 10, 30, and 60 minutes) for subsequent western blot analysis. For western blotting, immunohistochemistry staining, and immunoprecipitation, the following antibodies were utilized: β-actin (Sigma, A-1978), phospho-JNK (Thr-183/Tyr-185) (Cell Signaling Technology, 4668), JNK (Cell Signaling Technology, 9252), phospho-c-Jun (Ser-63) (Cell Signaling Technology, 2361), α-tubulin (Sigma, T6074), histone H3 (Cell Signaling Technology, 14269), phosphor-TAK1 (Ser-412) (Cell Signaling Technology, 9339), TAK1 (Cell Signaling Technology, 4505), phospho-SEK1/MKK4 (Ser257) (Cell Signaling Technology, 4514), SEK1/MKK4 (Cell Signaling Technology, 9152), phospho-IKKα (Ser176)/IKKβ (Ser177) (Cell Signaling Technology, 2078), IKKβ (Cell Signaling Technology, 8943), phospho-IκBα (Ser32/36) (Cell Signaling Technology, 9246), IκBα (Cell Signaling Technology, 4814), NF-κB p65 (Cell Signaling Technology, 8242), and F4/80 (Cell Signaling Technology, 70076).
2.2. Animal studies
C57BL/6J mice (stock no. 000664) were procured from the Jackson Laboratory.
Shpflox/flox mice, generously provided by Drs. Johan Auwerx and Kristina Schoonjans at the Ecole Polytechnique de Lausanne were backcrossed into the C57BL/6J background for 10 generations.
Shpflox/flox mice were crossed with LysM-Cre mice (Jackson Laboratory, Stock No: 004781) to generate heterozygous mice. Subsequently, the heterozygous mice were bred to obtain
Shp myeloid cell specific knockout (
Shp-MKO represents
Shp flox/flox; LysMcre positive) and their littermate wild-type controls (WT represents
Shp flox/flox; LysMcre negative). Mice were housed in a virus-free facility with a 12-h light/dark cycle (lights on from 6 a.m. to 6 p.m.) and maintained at a temperature of 25 °C, with ad libitum access to food and water. Male mice aged 8-10 weeks were used for the experiments, unless otherwise stated (n = 5/group). In the LPS injection experiment, both WT and
Shp-MKO mice received intraperitoneal injection of LPS at 1 mg/kg body weight. Samples were collected at 0-, 3-, and 7-hour post-injection. For the bone marrow-derived macrophage polarization experiment, a published protocol was followed [
28]. In brief, the femur and tibia were collected from the mice, and bone marrow cells were differentiated into macrophages using mouse macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF, R&D Systems™, 416ML010) at 10 ng/ml for 7 days. On the 7
th day, the differentiated macrophages were cultured with IFN-gamma (100 ng/mL) or IL4 (50 ng/ml) for 24 hours to induce M1 or M2 macrophage polarization, respectively. All experiments were conducted in compliance with relevant guidelines and regulations approved by the Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (ICAUC) at the University of Kansas Medical Center.
2.3. Hepatic cell isolation and flow cytometry analysis
Hepatic cell isolation and purification were conducted at the Kansas University Medical Center Cell Isolation Core, following a previously described method [
29] with slight modifications. In brief, mouse livers were perfused with 25 ml of solution I (9.5 g/liter Hanks’ balanced salt solution, 0.5 mmol/liter EGTA, pH 7.2), followed by 50 ml of solution II (9.5 g/liter Hanks’ balanced salt solution, 0.14 g/liter collagenase IV, and 40 mg/liter trypsin inhibitor, pH 7.5). After digestion, a single-cell suspension was obtained and filtered through a 100-μm Falcon cell strainer (Fisher Scientific, 08-771-19). The cells were centrifuged at 50 × g for 5 min at 4 °C to pellet hepatocytes. The supernatant containing nonparenchymal cells (NPCs) was then centrifuged at 300 × g for 10 min at 4 °C to enrich NPCs. In hepatic macrophage polarization experiment, macrophages were captured from NPCs by CD11b MicroBeads (Miltenyi Biotec Inc. 130-049-601) and differentiated into M1 or M2 macrophages using DMEM media supplemented with IFN-gamma (100 ng/mL) or IL4 (50 ng/ml) for 24 hours, respectively. In flow cytometry experiment, approximately 1 × 10
6 NPCs were incubated with anti-mouse CD16/CD32 (TruStain FcX, BioLegend, USA, cat. 101319) diluted in FACS buffer (2 mM EDTA, 10% FBS in PBS) for 15 minutes on ice to block non-specific antibody binding. Subsequently, the cells were incubated with the Brilliant Violet 605™ CD45 (BioLegend, USA, 103139), Brilliant Violet 421™ CD11b (BioLegend, USA, 101235), PE/Cyanine7 Ly-6C (BioLegend, USA, 128017) anti-mouse antibodies, and the fixable viability dye (Zombie Aqua, BioLegend, 423101) for 30 minutes on ice. After centrifugation (300 × g) for 5 minutes, the cells were washed twice with 1 ml of PBS for 5 minutes and finally resuspended in 300 µl of FACS buffer. The cells were then analyzed using a FACS Calibur instrument (BD, Franklin Lakes, New Jersey). FlowJo-V10 software was used for data analysis.
2.4. Liver histology and immunohistochemistry
Fresh liver tissues were fixed with 10% formalin (Fisher, SF100) to preserve their structural integrity. Paraffin sections of 5 μm thickness were prepared and subjected to staining with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) for general tissue examination, as well as immunohistochemical staining. For the immunohistochemistry staining of F4/80, the paraffin sections were rehydrated and treated with 0.3% hydrogen peroxide in PBS for 15 minutes to block endogenous peroxidase activity. Antigen retrieval was achieved by boiling the sections in sodium citrate buffer (pH 6.0) for 5 minutes using a pressure cooker. Subsequently, the slides were treated with 5% normal serum for 30 minutes to block non-specific binding, followed by overnight incubation with rabbit anti-mouse F4/80 antibody at 4 °C. For the final detection, an ImmPRESS peroxidase polymer detection kit (Vector Laboratories, MP-7444) and ImmPACT 3,3'-diaminobenzidine peroxidase substrate (Vector Laboratories, SK-4105) were utilized. After thorough washing, the sections were counterstained with hematoxylin, dehydrated, cleared, and mounted. Microscopic images were captured using a BX60 microscope, and the area of positive staining for DAB (3,3'-diaminobenzidine) was quantified using ImageJ software.
2.5. Real-time quantitative PCR
The real-time quantitative PCR (qPCR) analysis was performed using the SYBR Green PCR master mix (Applied Biosystems), following the previously described protocols [
26,
27,
30]. The specific primer sequences utilized for the qPCR are provided in Table S1. The hsa-miR-34a-5p LNA™ PCR primer set (Exiqon, 204486) has been used to measure the expression level of miR-34a. The abundance of PCR products was quantified using threshold cycle (Ct) values, and the relative ratio of specific genes to the housekeeping gene actin was determined. The resulting values were then presented as the fold change in the tested group compared to the control group.
2.6. Western blotting and immunoprecipitation
Mouse liver tissues were prepared for protein analysis using the following procedures. First, the tissues were homogenized using a PowerGen 700 homogenizer (Fisher Scientific) in lysis buffer containing protease inhibitors (Fisher Scientific, protease inhibitor mixture PI78410). The lysis buffer consisted of 50 mM Tris (pH 7.5), 1% Nonidet P-40, 150 mM NaCl, 0.5% sodium deoxycholate, and 0.1% SDS, ensuring efficient extraction of whole protein lysates. For the extraction of nuclear and cytoplasmic proteins, a commercial kit (Fisher, PI78833) was utilized according to the manufacturer's instructions. Next, protein lysates (60 μg) were separated by SDS-PAGE and transferred to nitrocellulose membranes. The membranes were then blocked and incubated with primary antibodies specific to the target proteins. Subsequently, horseradish peroxidase-conjugated secondary antibodies were applied, allowing for the detection of antibody binding. The visualization of antibody-bound proteins was achieved using either SuperSignal West Pico Plus Chemiluminescent Substrate (Fisher, PI34580) or SuperSignal West Femto Chemiluminescent Substrate (Fisher, PI34094). Images were captured using a LI-COR imaging system. To ensure equal protein loading, loading controls such as β-actin, α-tubulin, and histone H3 were included and verified. Quantitative analysis of band intensity was performed using Image Studio Lite software, and the relative expression levels were normalized to the loading controls. For the immunoprecipitation experiment, 1000 μg of whole protein lysates from control PMSCV cells and PMSCV-SHP cells overexpressing FLAG-SHP were incubated with 2 μg of anti-FLAG M2 magnetic beads (Sigma, M8823). The immune complexes were captured using a magnetic stand, and subsequent elution was performed using 2× SDS loading buffer. The pulldown of p65 and FLAG-SHP was detected by Western blotting. A TrueBlot® anti-rabbit IgG HRP (Rockland, RL18-8816-33) was used as a secondary antibody as this antibody does not interfere with the immunoprecipitation of immunoglobulin heavy and light chains, ensuring accurate detection.
2.7. Statistical analysis
GraphPad Prism 8.0 (GraphPad Software, La Jolla, CA, USA) was used for data analysis. The quantitative data are presented as the mean ± SEM. Statistical analysis was performed using Student's t-test to determine the significant difference between two groups. For comparisons among multiple groups, one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) was conducted, followed by Duncan's test. Statistical significance was considered at a 95% confidence level.
4. Discussion
Hepatic macrophages are key players in innate immunity and vital components of the liver. These macrophages display remarkable heterogeneity and plasticity, allowing them to respond to diverse stimuli in different physiological and pathological conditions [
39,
40,
41,
42]. Traditionally, macrophages have been classified into two extreme groups: M1 classically activated proinflammatory macrophages and M2 alternatively activated anti-inflammatory macrophages. However, emerging research employing single-cell RNA sequencing has unveiled the intricate nature of macrophage differentiation, showcasing a multitude of activation states that surpass the conventional M1/M2 classification. Nevertheless, despite this newfound complexity, the M1/M2 classification continues to serve as a valuable framework for understanding macrophage function and gene roles, offering a useful overview in the study of macrophage biology. SHP is an atypical nuclear receptor that plays a critical role in various pathophysiological processes, including inflammation, metabolism, and energy homeostasis [
17,
19,
23]. Our previous research has highlighted the anti-inflammatory role of hepatic SHP in a mouse model of nonalcoholic steatohepatitis [
26,
27]. Building upon these findings, our current study aimed to investigate the role of myeloid SHP in macrophage polarization during acute innate immune response. We discovered that SHP regulates macrophage polarization, and its influence on M1 and M2 differentiation is an important mechanism through which SHP inhibits inflammation. Mechanistically, we made the novel discovery that myeloid SHP modulates macrophage differentiation by regulating Pparg, MAPK, and NF-κB pathways.
An intriguing finding of our study is the alteration of SHP expression during macrophage polarization. Specifically, anti-inflammatory M2 macrophage differentiation led to an increase in
Shp mRNA expression, while pro-inflammatory M1 macrophage differentiation resulted in its decrease. Although the precise mechanisms underlying this regulation are unknown and beyond the scope of our current study, previous studies have demonstrated that several nuclear receptors and transcription factors bind to the
Shp gene promoter and influence its expression [
16]. For instance, PPARg can bind to the PPAR response element on the
Shp gene promoter and induce
Shp mRNA expression [
43]. Macrophage-stimulating factor (MSP) increases
Shp mRNA expression through the activation of AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) pathway [
44,
45]. Considering that PPARg and AMPK pathways are upregulated during M2 macrophage differentiation [
46,
47], it is tempting to speculate that the increase in
Shp mRNA in M2 macrophages may be attributed to the activation of these pathways. Conversely, JNK activation suppresses
Shp transcription in hepatocytes [
26] and JNK activation is required for M1 macrophage polarization [
48]. Hence, it is possible that JNK activation in M1 macrophages leads to the decreased
Shp mRNA expression. Further investigations are warranted to explore whether manipulating PPARg, AMPK, or JNK in macrophages can alter SHP expression during macrophage differentiation.
Motivated by the differential SHP expression observed in M1 and M2 macrophages, we sought to determine whether SHP plays a functional role in macrophage polarization. To this end, we generated a genetic mouse model lacking
Shp specifically in myeloid cells using LysM-Cre-mediated knockout. We isolated BMDMs from both
Shp-MKO and WT controls and found that
Shp loss inhibited the polarization of BMDMs toward an M2 phenotype while promoting polarization toward an M1 state. Moreover, overexpression of SHP in the macrophage cell line RAW cells increased
Pparg mRNA expression and inhibited macrophage polarization toward a M1 phenotype. Encouraged by these
in vitro results, we conducted
in vivo studies by injecting a low dose of LPS into
Shp-MKO and WT controls. We observed a sustained increase in liver macrophage numbers in
Shp-MKO mice following LPS challenge. Notably, flow cytometry revealed a higher population of CD11b
High F4/80
Intermediate monocyte-derived macrophages in
Shp-MKO livers compared to WT controls after LPS challenge, suggesting that the loss of SHP in myeloid cells enhances monocyte infiltration into the liver, replenishing hepatic macrophage populations. Monocyte recruitment to the liver is finely regulated by chemokines, among which CCL2 plays a crucial role. Inhibition of CCL2 or genetic knockout of
Ccl2 specifically in myeloid cells has been shown to reduce monocyte infiltration into the liver during both acute and chronic hepatic injury [
49,
50,
51]. In our previous study, we found that the loss of
Shp in hepatocytes triggers the production of CCL2, leading to the initiation of monocyte recruitment [
26]. Hence, we postulated that the increased monocyte infiltration observed in
Shp-MKO livers after LPS challenge might be due to elevated CCL2 levels following SHP loss in myeloid cells. Our observations confirmed this speculation, as we noted a significant increase in hepatic
Ccl2 mRNA expression and elevated serum CCL2 levels in
Shp-MKO mice. These results suggest that SHP universally regulates CCL2 expression in various cell types, contributing to the enhanced monocyte infiltration observed in
Shp-MKO livers during the response to LPS challenge.
Our flow cytometry analysis yielded a significant discovery, revealing increased populations of F4/80
+Ly6C
High and CD11b
+Ly6C
High cells in
Shp-MKO livers compared to WT controls. Ly6C, a member of the lymphocyte antigen-6 (Ly6)/urokinase-type plasminogen activator receptor protein superfamily, is closely associated with infiltrating monocytes and is involved in the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines and chemokines, such as interleukin 1 (IL-1), interleukin 18 (IL-18), and Ccl2 [
52]. Ly6C
High monocytes are recognized as a pro-inflammatory subset contributing to tissue inflammation and T-cell activation [
53]. Notably, Ly6C
High monocytes infiltration and their subsequent differentiation into pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages are considered crucial early steps in liver inflammation [
51]. In our study, flow cytometry analysis demonstrated a notable increase in pro-inflammatory CD11b
+Ly6C
High monocytes and F4/80
+Ly6C
High M1-like macrophages in
Shp-MKO livers compared to WT controls, both under basal condition and after LPS challenge. These findings suggest that the loss of
Shp in myeloid cells promotes the infiltration of pro-inflammatory monocytes into the liver and enhances their differentiation into pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages. The precise mechanisms by which SHP regulates the expression of Ly6C remain unclear. Additional studies are needed to unravel the molecular pathways and signaling events through which SHP modulates Ly6C expression in myeloid cells.
Pparg, MAPK, and NF-κB are critical players in the regulation of macrophage activation and differentiation [
37,
54]. In our study, we observed that mice lacking myeloid
Shp exhibited a pronounced activation of the MAPK and NF-κB pathways in the liver following LPS challenge. In contrast, when SHP was overexpressed in macrophages, it resulted in increased
Pparg expression and inhibited the activation of MAPK and NF-κB signaling. Additionally, we made an interesting discovery of a protein-protein interaction between SHP and p65. While previous research has established that SHP interacts with p65 and TRAF6, leading to the inhibition of NF-κB signaling [
23], our study provides the first evidence of SHP’s regulatory role in modulating Pparg expression and impeding MKK4 and JNK activation. These findings further underscore the significance of SHP in shaping macrophage differentiation during the innate immune response.
One limitation of our study is the use of the LyzCre system, which achieves high level gene knockout in myeloid cells, including monocytes and macrophages [
55]. However, the LyzCre knock-out strategy also affects a subset of neutrophils [
56]. Therefore, some of the pro-inflammatory phenotypes observed in the
Shp-MKO mice, such as increased cytokine and chemokine production, may also be attributed to
Shp loss in neutrophils. Future studies employing alternative conditional macrophage-specific gene knockout models will be necessary to confirm our results obtained from the LyzCre system.
Abbreviations
SHP: small heterodimer partner; Pparg, peroxisome proliferator activated receptor gamma; LPS, lipopolysaccharide; MDM, monocyte-derived macrophages; BMDM, bone marrow-derived macrophages; Shp-MKO, Shp myeloid cell specific knockout; Tnfa, tumor necrosis factor alpha; Ccl2, chemokine (C-C motif) ligand 2; MAPK, mitogen-activated protein kinase; NF-κB, nuclear factor kappa B; KC, Kupffer cells; IFN-gamma, interferon gamma; IL4, interleukin 4; NASH, non-alcoholic steatohepatitis; Nos2, nitric oxide synthase 2; Arg1, arginase 1; Cd163, CD163 antigen; Mrc1, mannose receptor C type 1; 3’UTR, 3’-untranslated region; Emr1 or F4/80, adhesion G protein-coupled receptor E1; NPCs, non-parenchymal cells; PTPRC or CD45, protein tyrosine phosphatase receptor type C; Itgam or CD11b, monocyte marker integrin alpha M; Ly6C, Ly6-C antigen; FSC, forward scatter; SSC, side scatter; Co-IP, co-immunoprecipitation; MSP, Macrophage-stimulating factor; AMPK, AMP-activated protein kinase; IL-1, interleukin 1; IL-18, interleukin 18.
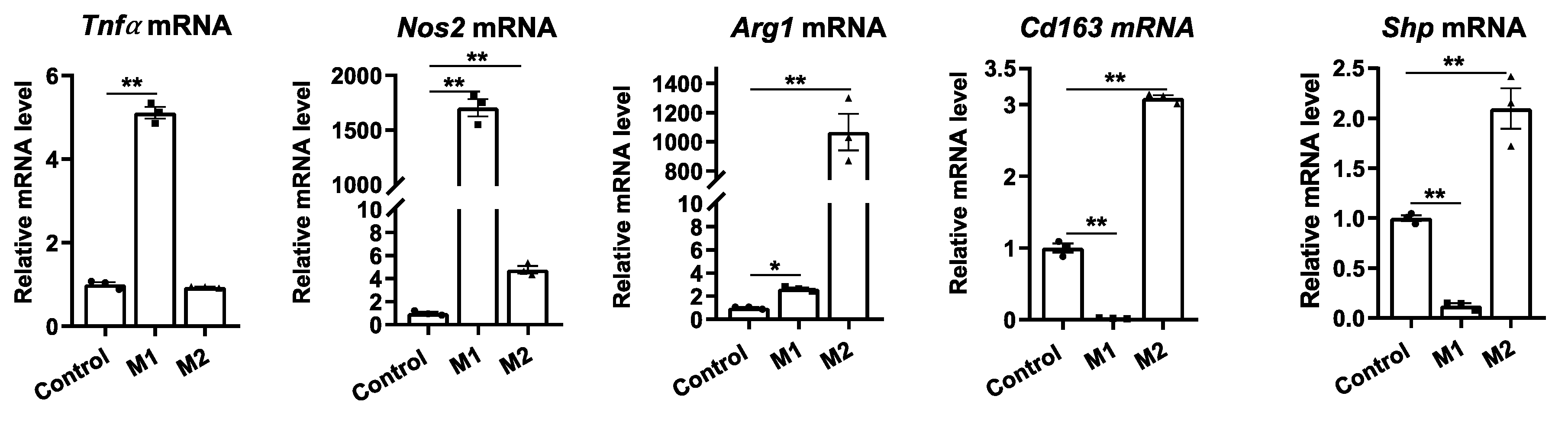
Figure 1.
Macrophage differentiation alters Shp mRNA expression. The livers of C57BL/6 mice were perfused and digested to harvest nonparenchymal cells (NPCs). Hepatic macrophages were then isolated from NPCs by CD11b MicroBeads and differentiated into M1 or M2 macrophages using DMEM media supplemented with IFN-gamma (100 ng/mL) or IL4 (50 ng/ml) for 24 hours, respectively. The relative mRNA levels of M1 markers (Tnfa and Nos2), M2 markers (Arg1 and Cd163), and Shp were determined using quantitative PCR (qPCR). Data are presented as mean ± SEM for 3 samples/group. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 between the indicated groups.
Figure 1.
Macrophage differentiation alters Shp mRNA expression. The livers of C57BL/6 mice were perfused and digested to harvest nonparenchymal cells (NPCs). Hepatic macrophages were then isolated from NPCs by CD11b MicroBeads and differentiated into M1 or M2 macrophages using DMEM media supplemented with IFN-gamma (100 ng/mL) or IL4 (50 ng/ml) for 24 hours, respectively. The relative mRNA levels of M1 markers (Tnfa and Nos2), M2 markers (Arg1 and Cd163), and Shp were determined using quantitative PCR (qPCR). Data are presented as mean ± SEM for 3 samples/group. *p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 between the indicated groups.
Figure 2.
Shp deletion in macrophages enhances M1 polarization but impairs M2 differentiation. (A) Peritoneal macrophages were isolated from WT and Shp-MKO mice, and the relative mRNA levels of Shp were determined by qPCR. (B) Bone marrow cells were isolated from WT and Shp-MKO mice and differentiated into macrophages using M-CSF (10 ng/ml) for 7 days. On the 7th day, the differentiated macrophages were cultured with IFN-gamma (100 ng/mL) or IL4 (50 ng/ml) for 24 hours to induce M1 or M2 macrophage polarization, respectively. The mRNA expression of Tnfa, Nos2, and Cd206 was determined using qPCR. (C) Left, western blot confirmed the overexpression of Flag-SHP in mouse macrophage RAW cells. Right, the expression of miR-34a and Pparg was determined by qPCR. (D) RAW cells with or without SHP overexpression were treated with IFN-gamma (100 ng/mL) for 24 hours. qPCR was employed to measure mRNA levels of Nos2 and Pparg. The data are presented as mean ± SEM for 3 samples/group. * p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 between the indicated groups.
Figure 2.
Shp deletion in macrophages enhances M1 polarization but impairs M2 differentiation. (A) Peritoneal macrophages were isolated from WT and Shp-MKO mice, and the relative mRNA levels of Shp were determined by qPCR. (B) Bone marrow cells were isolated from WT and Shp-MKO mice and differentiated into macrophages using M-CSF (10 ng/ml) for 7 days. On the 7th day, the differentiated macrophages were cultured with IFN-gamma (100 ng/mL) or IL4 (50 ng/ml) for 24 hours to induce M1 or M2 macrophage polarization, respectively. The mRNA expression of Tnfa, Nos2, and Cd206 was determined using qPCR. (C) Left, western blot confirmed the overexpression of Flag-SHP in mouse macrophage RAW cells. Right, the expression of miR-34a and Pparg was determined by qPCR. (D) RAW cells with or without SHP overexpression were treated with IFN-gamma (100 ng/mL) for 24 hours. qPCR was employed to measure mRNA levels of Nos2 and Pparg. The data are presented as mean ± SEM for 3 samples/group. * p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 between the indicated groups.
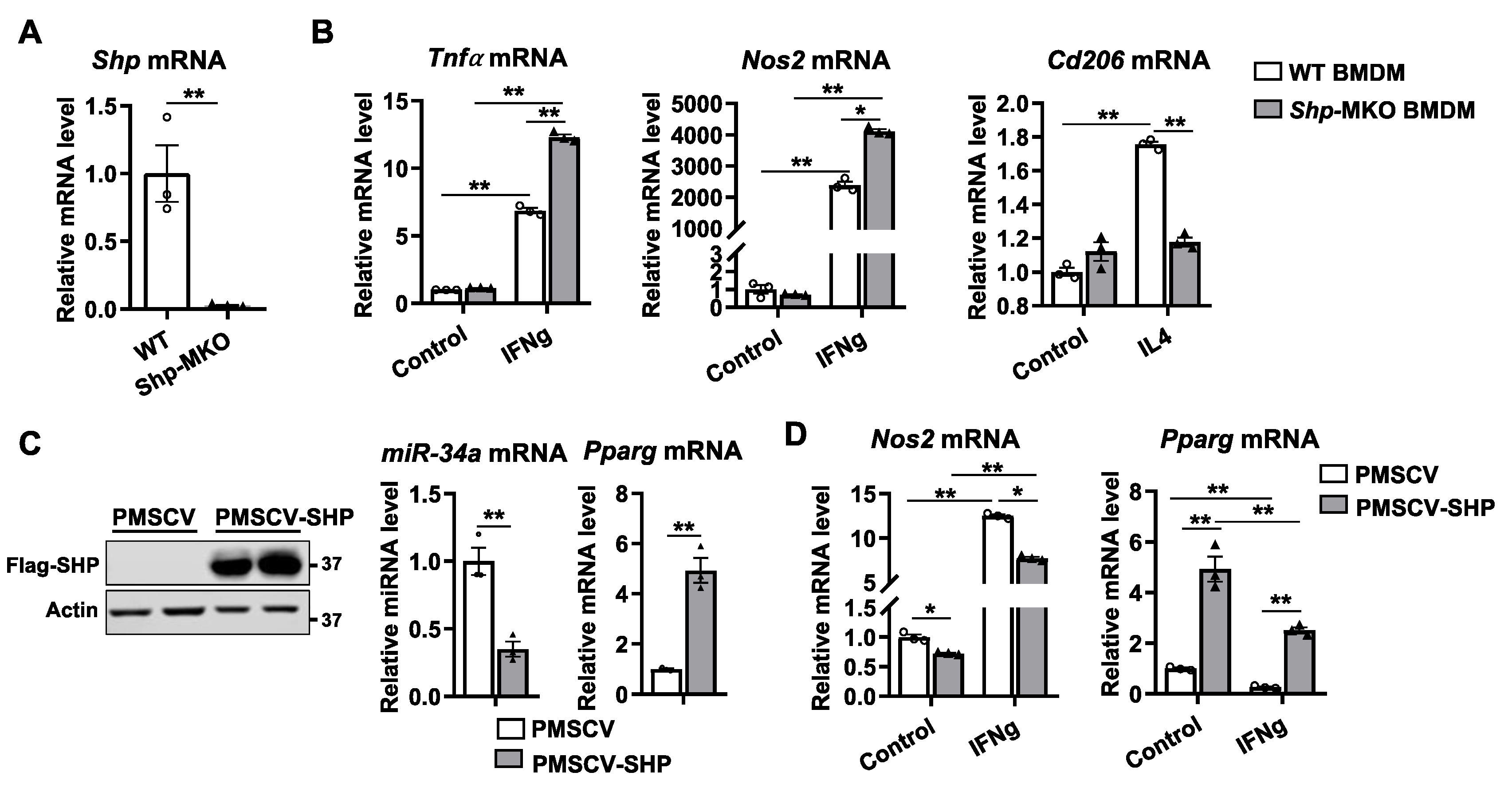
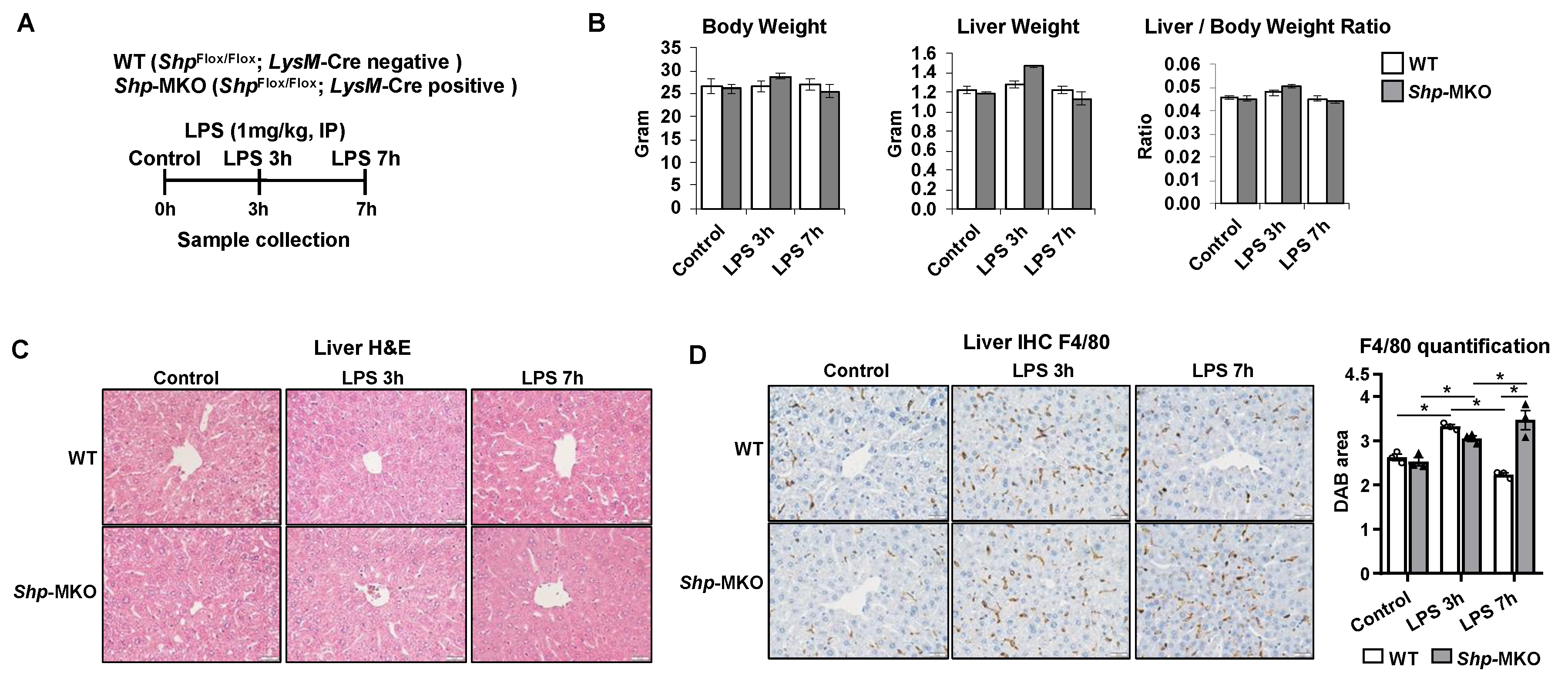
Figure 3.
Shp knockout results in a persistent hepatic accumulation of macrophages following LPS challenge. (A) Shp myeloid cell specific knockout (Shp-MKO) was generated by breeding Shpflox/flox with LysM-Cre mice. Both WT and Shp-MKO mice were subjected to intraperitoneal LPS (1 mg/kg body weight) injection, and samples were collected at 0-, 3-, and 7-hour post injection. (B) Mouse body weight, liver weight, and liver-to-body weight ratio. (C) Liver sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) to examine the histological changes in the liver. (D) Left, representative images of liver sections stained with macrophage marker F4/80. Original magnification, X40. Right, quantification of the DAB-positive staining area. n=3/group. The data are presented as mean ± SEM for 3 samples/group. * p < 0.05 between the indicated groups.
Figure 3.
Shp knockout results in a persistent hepatic accumulation of macrophages following LPS challenge. (A) Shp myeloid cell specific knockout (Shp-MKO) was generated by breeding Shpflox/flox with LysM-Cre mice. Both WT and Shp-MKO mice were subjected to intraperitoneal LPS (1 mg/kg body weight) injection, and samples were collected at 0-, 3-, and 7-hour post injection. (B) Mouse body weight, liver weight, and liver-to-body weight ratio. (C) Liver sections were stained with hematoxylin and eosin (H&E) to examine the histological changes in the liver. (D) Left, representative images of liver sections stained with macrophage marker F4/80. Original magnification, X40. Right, quantification of the DAB-positive staining area. n=3/group. The data are presented as mean ± SEM for 3 samples/group. * p < 0.05 between the indicated groups.
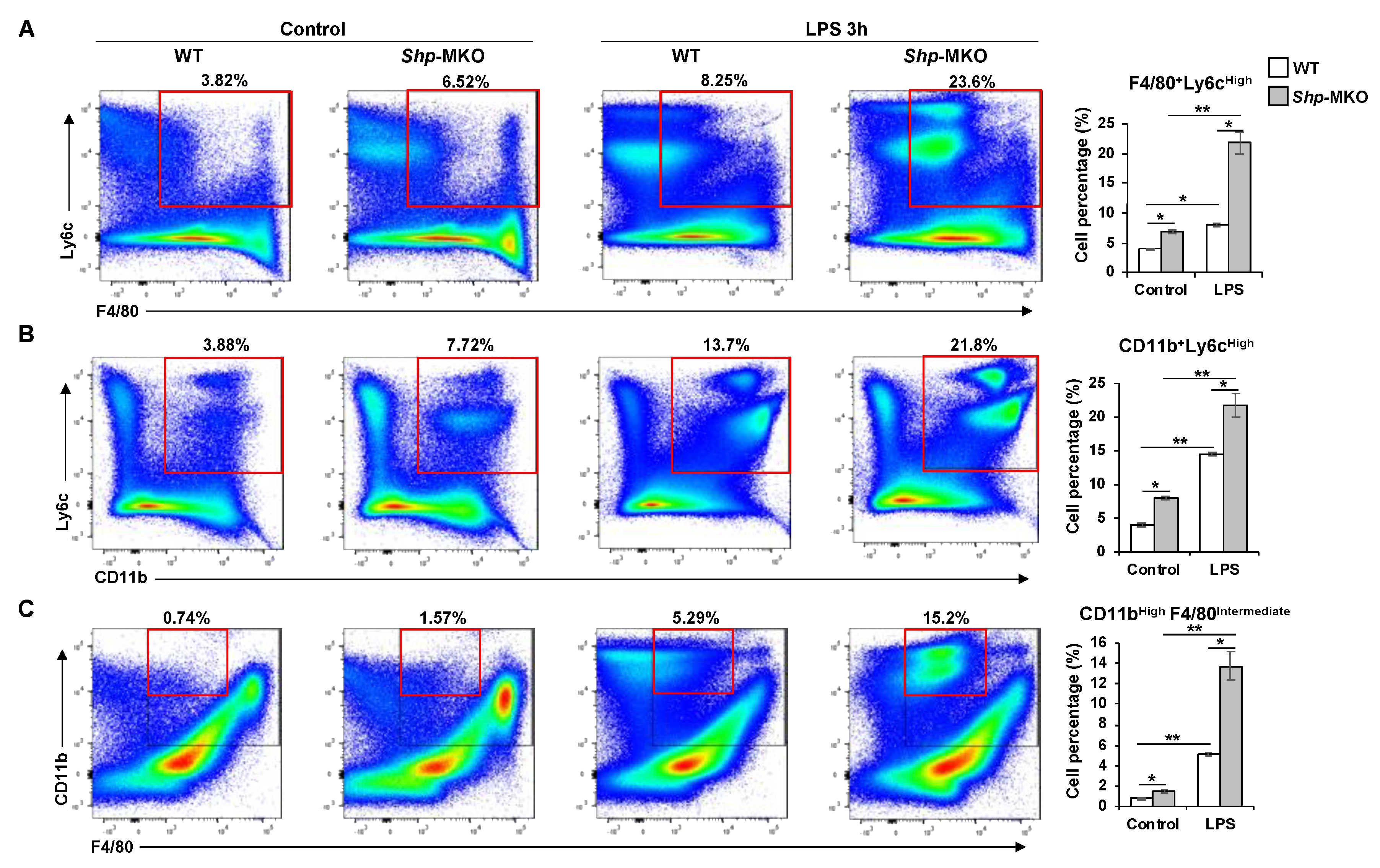
Figure 4.
Flow cytometry analysis of composition of hepatic macrophages and monocytes following LPS challenge. WT and Shp-MKO mice were intraperitoneally injected with or without LPS (1 mg/kg body weight). After 3 hours, mouse livers were perfused and digested to isolate nonparenchymal cells (NPCs). Approximately 1 × 106 NPCs were labeled with specific antibodies and prepared for flow cytometry analysis. Single cells were gated based on FSC-A and FSC-H to exclude doublets. Dead cells stained with Zombie Aqua were excluded from the analysis. Live cells positive for CD45 expression were gated, and the populations of interest were calculated, including F4/80+Ly6CHigh pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages (A), CD11b+Ly6CHigh pro-inflammatory monocytes (B), and CD11bHighF4/80Intermediate monocyte-derived macrophages (C). The data are presented as mean ± SEM for 3 samples/group. * p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 between the indicated groups.
Figure 4.
Flow cytometry analysis of composition of hepatic macrophages and monocytes following LPS challenge. WT and Shp-MKO mice were intraperitoneally injected with or without LPS (1 mg/kg body weight). After 3 hours, mouse livers were perfused and digested to isolate nonparenchymal cells (NPCs). Approximately 1 × 106 NPCs were labeled with specific antibodies and prepared for flow cytometry analysis. Single cells were gated based on FSC-A and FSC-H to exclude doublets. Dead cells stained with Zombie Aqua were excluded from the analysis. Live cells positive for CD45 expression were gated, and the populations of interest were calculated, including F4/80+Ly6CHigh pro-inflammatory M1 macrophages (A), CD11b+Ly6CHigh pro-inflammatory monocytes (B), and CD11bHighF4/80Intermediate monocyte-derived macrophages (C). The data are presented as mean ± SEM for 3 samples/group. * p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 between the indicated groups.
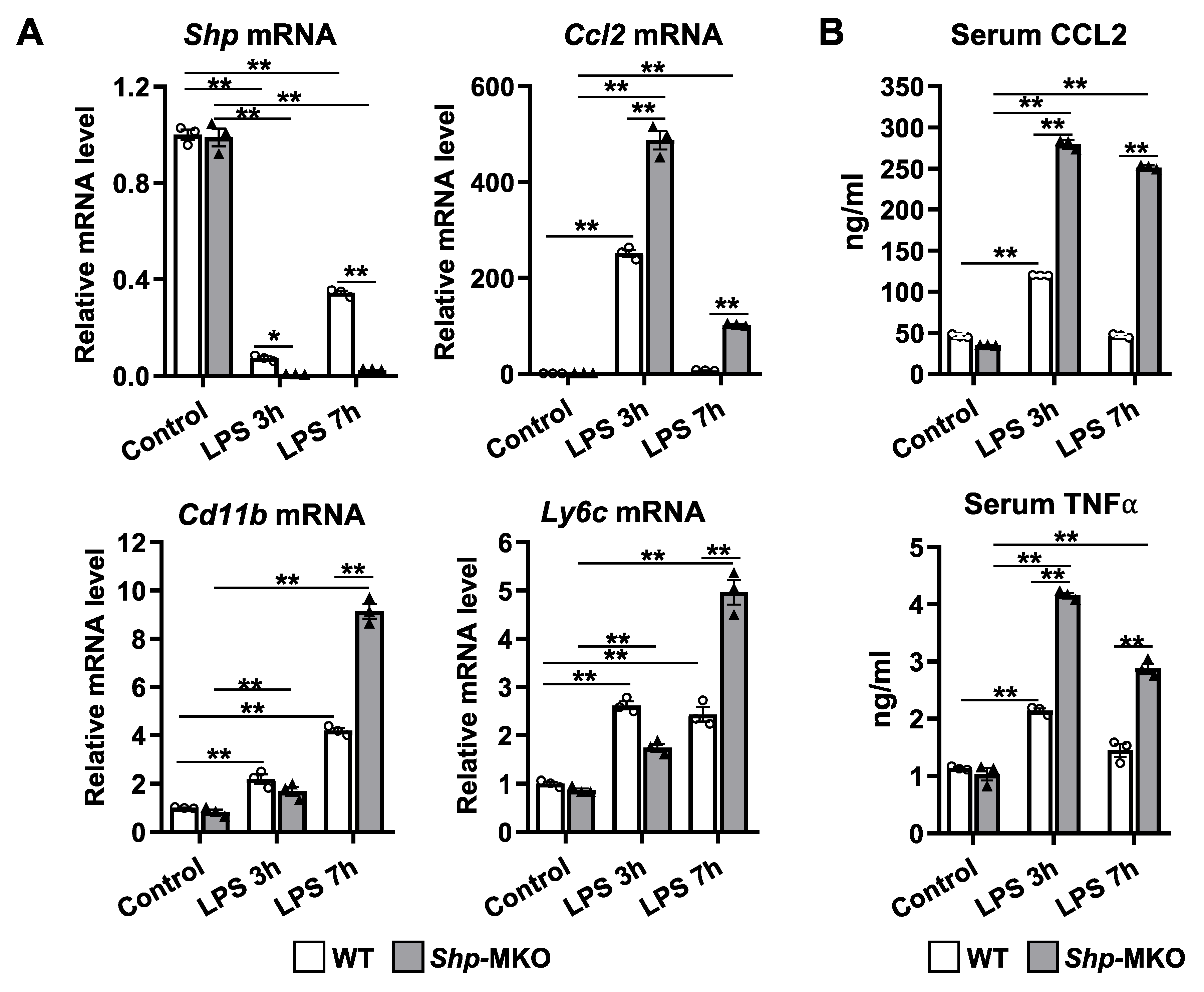
Figure 5.
Myeloid cell specific deletion of Shp leads to enhanced chemokines production in response to LPS challenge. WT and Shp-MKO mice were intraperitoneally injected with LPS (1 mg/kg body weight), and samples were collected at 0-, 3-, and 7-hour post-injection. (A) The mRNA levels of Shp, Ccl2, Cd11b, and Ly6c in liver tissues were quantified using qPCR. (B) The serum levels of CCL2 and TNFα were measured using ELISA to evaluate the circulating levels of these chemokines. The data are presented as mean ± SEM for 3 samples/group. * p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 between the indicated groups.
Figure 5.
Myeloid cell specific deletion of Shp leads to enhanced chemokines production in response to LPS challenge. WT and Shp-MKO mice were intraperitoneally injected with LPS (1 mg/kg body weight), and samples were collected at 0-, 3-, and 7-hour post-injection. (A) The mRNA levels of Shp, Ccl2, Cd11b, and Ly6c in liver tissues were quantified using qPCR. (B) The serum levels of CCL2 and TNFα were measured using ELISA to evaluate the circulating levels of these chemokines. The data are presented as mean ± SEM for 3 samples/group. * p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 between the indicated groups.
Figure 6.
Myeloid cell specific deletion of Shp results in hyperactivation of MAPK and NF-κB pathways in response to LPS challenge. WT and Shp-MKO mice were intraperitoneally injected with LPS (1 mg/kg body weight), and samples were collected at 0-, 3-, and 7-hour post-injection. (A) Left, Western blot analysis of whole protein lysates from liver tissues revealed the expression and phosphorylation levels of proteins involved in MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Right, the protein band density was quantified using Image Studio software, and the relative expression levels were normalized to the loading control β-actin. (B) Left, Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions demonstrated the expression and phosphorylation levels of proteins involved in NF-κB signaling. Right, the protein band density was quantified using Image Studio software, and the relative levels of proteins were normalized to the nuclear loading control Histone H3 and the cytoplasmic loading control α-tubulin, respectively. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. Western blots were repeated for 3 times and one represented image was included in the figure. * p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 between the indicated groups.
Figure 6.
Myeloid cell specific deletion of Shp results in hyperactivation of MAPK and NF-κB pathways in response to LPS challenge. WT and Shp-MKO mice were intraperitoneally injected with LPS (1 mg/kg body weight), and samples were collected at 0-, 3-, and 7-hour post-injection. (A) Left, Western blot analysis of whole protein lysates from liver tissues revealed the expression and phosphorylation levels of proteins involved in MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Right, the protein band density was quantified using Image Studio software, and the relative expression levels were normalized to the loading control β-actin. (B) Left, Western blot analysis of cytoplasmic and nuclear fractions demonstrated the expression and phosphorylation levels of proteins involved in NF-κB signaling. Right, the protein band density was quantified using Image Studio software, and the relative levels of proteins were normalized to the nuclear loading control Histone H3 and the cytoplasmic loading control α-tubulin, respectively. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. Western blots were repeated for 3 times and one represented image was included in the figure. * p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 between the indicated groups.
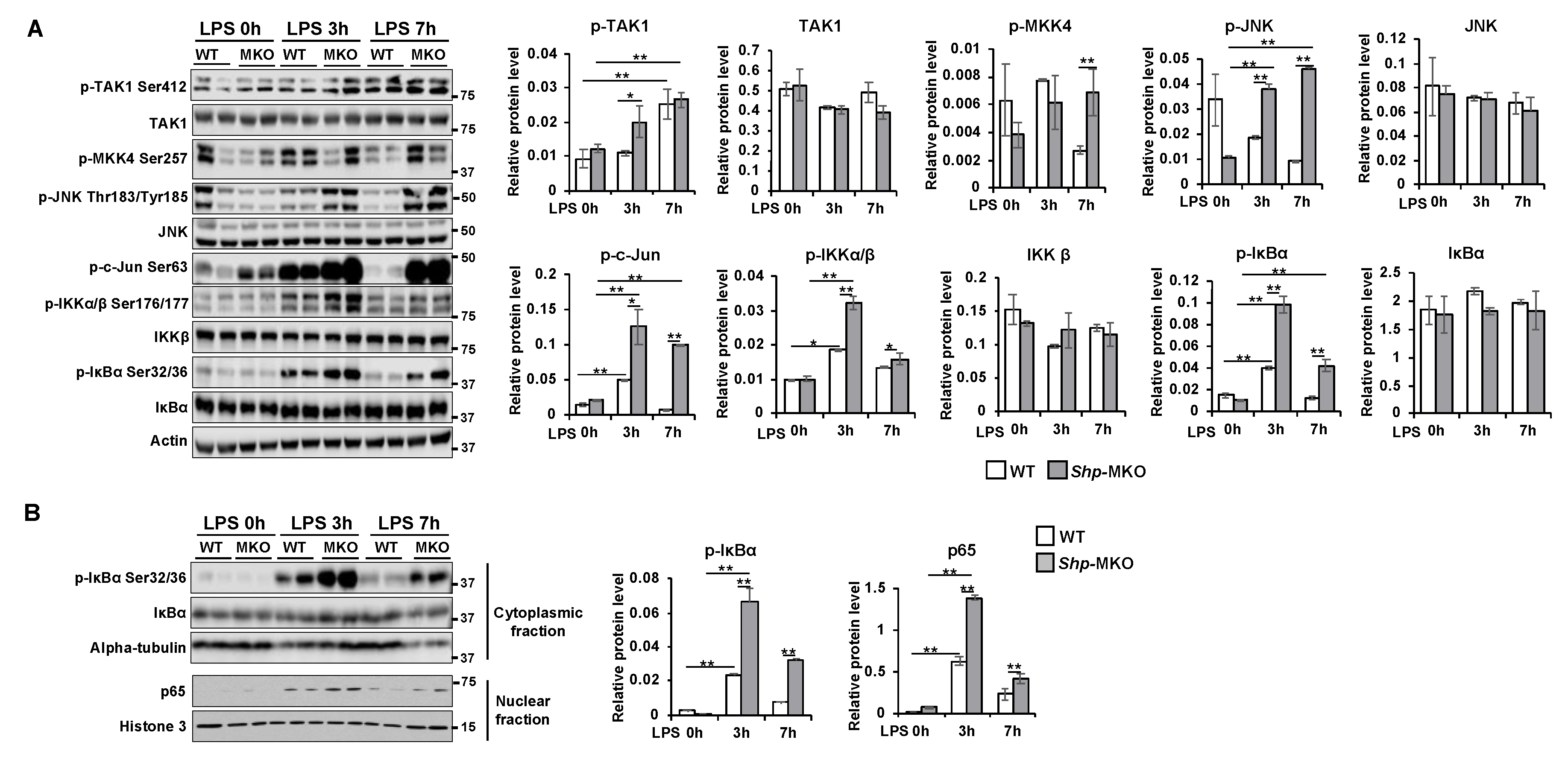
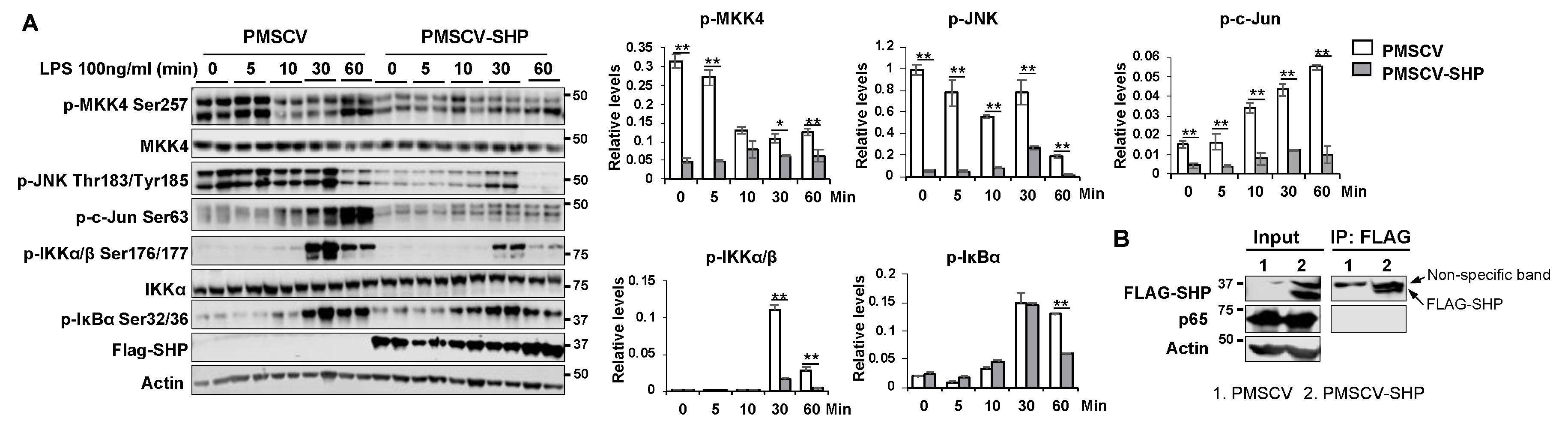
Figure 7.
SHP overexpression hinders the activation of MAPK and NF-κB pathways in response to LPS challenge. (A) Left, mouse macrophage RAW cells with or without SHP overexpression were treated with 100 ng/ml LPS for different durations (0, 5, 10, 30, and 60 minutes). Whole cell lysates were collected and subjected to western blot analysis to assess the expression and phosphorylation levels of proteins involved in MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Right, the protein band density was quantified using Image Studio software, and the relative expression levels were normalized to the loading control β-actin. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation experiments were conducted using whole protein lysates from RAW cells with or without FLAG-SHP overexpression. The protein-protein interaction of SHP with p65 was detected by western blot analysis. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. Western blots were repeated for 3 times and one represented image was included in the figure. * p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 between the indicated groups.
Figure 7.
SHP overexpression hinders the activation of MAPK and NF-κB pathways in response to LPS challenge. (A) Left, mouse macrophage RAW cells with or without SHP overexpression were treated with 100 ng/ml LPS for different durations (0, 5, 10, 30, and 60 minutes). Whole cell lysates were collected and subjected to western blot analysis to assess the expression and phosphorylation levels of proteins involved in MAPK and NF-κB signaling pathways. Right, the protein band density was quantified using Image Studio software, and the relative expression levels were normalized to the loading control β-actin. (B) Co-immunoprecipitation experiments were conducted using whole protein lysates from RAW cells with or without FLAG-SHP overexpression. The protein-protein interaction of SHP with p65 was detected by western blot analysis. The data are presented as mean ± SEM. Western blots were repeated for 3 times and one represented image was included in the figure. * p < 0.05 and **p < 0.01 between the indicated groups.