Submitted:
27 July 2023
Posted:
27 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
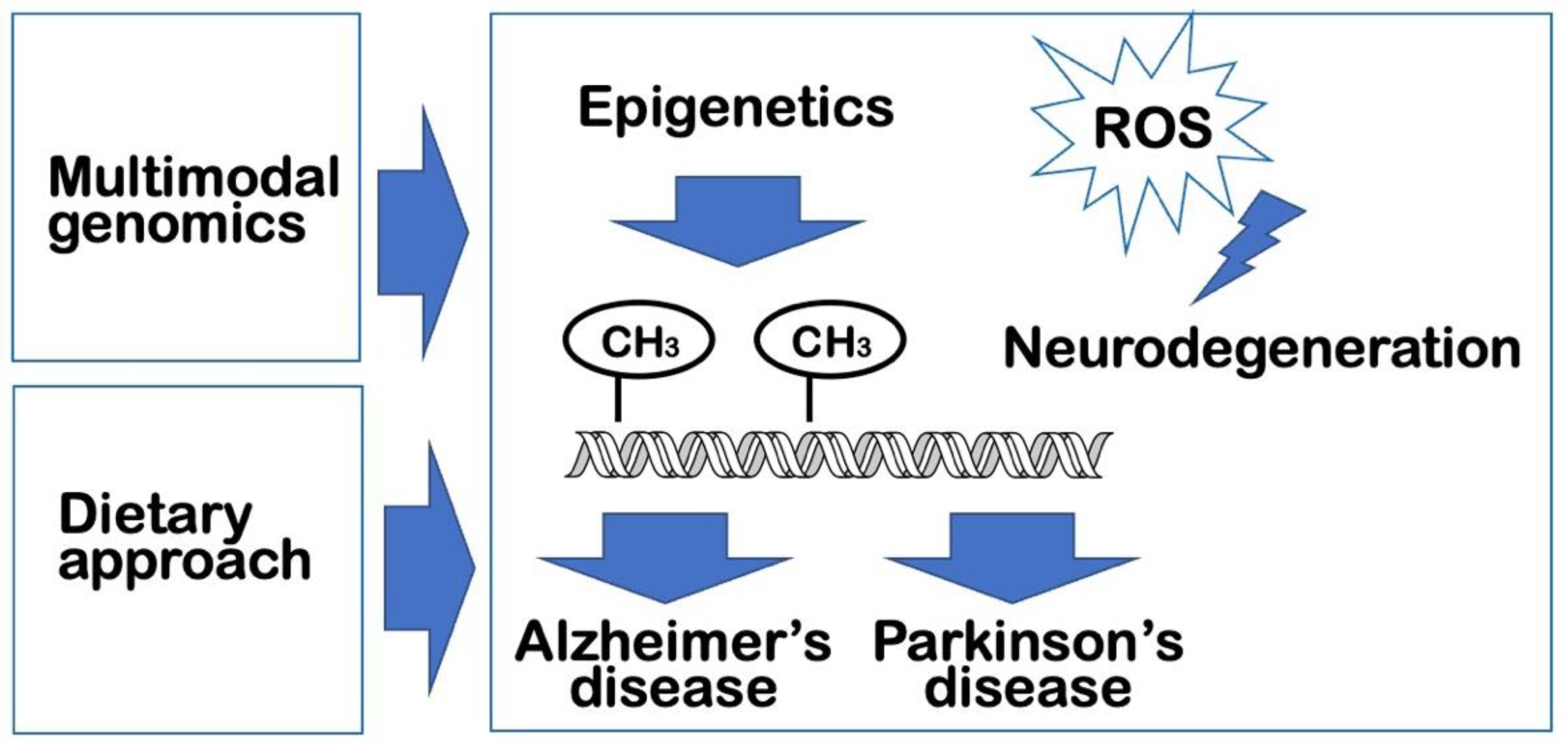
1. Introduction
2. Epigenetics and Alzheimer’s disease
3. Epigenetics and Parkinson’s disease
4. Multimodal genomic studies on neurodegenerative diseases
5. Dietary approaches to impede neurodegeneration
6. Conclusions and future directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Abbreviations
| Aβ | amyloid-β |
| AD | Alzheimer’s disease |
| AI | artificial intelligence |
| ATAC-seq | Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin sequencing |
| CITE-seq | Cellular Indexing of Transcriptomes and Epitopes by sequencing |
| CSF | erebrospinal fluid |
| lncRNA | long non-coding RNA |
| miRNA | microRNA |
| ncRNA | non-coding RNA |
| PD | Parkinson’s disease |
| REAP-seq | RNA Expression And Protein sequencing |
| ROS | reactive oxygen species |
| scRNA-seq | single-cell RNA sequencing |
| scATAC-seq | Single-Cell Assay for Transposase-Accessible Chromatin sequencing |
| SN | substantia nigra |
| t-SNE | t-stochastic neighbor embedding |
| UTR | untranslated region |
References
- Bossy-Wetzel, E.; Schwarzenbacher, R.; Lipton, SA. Molecular pathways to neurodegeneration. Nat. Med. 2004, 10, S2–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hou, Y.; Dan, X.; Babbar, M.; Wei, Y.; Hasselbalch, S.G.; Croteau, D.L.; Bohr, V.A. Ageing as a risk factor for neurodegenerative disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 565–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hansson, O. Biomarkers for neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Med. 2021, 27, 954–963. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Teunissen, C.E.; Verberk, I.M.W.; Thijssen, E.H.; Vermunt, L.; Hansson, O.; Zetterberg, H.; van der Flier, W.M.; Mielke, M.M.; Del Campo, M. Blood-based biomarkers for Alzheimer’s disease: towards clinical implementation. Lancet Neurol. 2022, 21, 66–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, B.; Villain, N.; Frisoni, G.B.; Rabinovici, G.D.; Sabbagh, M.; Cappa, S.; Bejanin, A.; Bombois, S.; Epelbaum, S.; Teichmann, M.; Habert, M.O.; Nordberg, A.; Blennow, K.; Galasko, D.; Stern, Y.; Rowe, C.C.; Salloway, S.; Schneider, L.S.; Cummings, J.L.; Feldman, H.H. Clinical diagnosis of Alzheimer’s disease: recommendations of the International Working Group. Lancet Neurol. 2021, 20, 484–496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Berger, S.L.; Kouzarides, T.; Shiekhattar, R.; Shilatifard, A. An operational definition of epigenetics. Genes Dev. 2009, 23, 781–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sen, P.; Shah, P.P.; Nativio, R.; Berger, S.L. Epigenetic mechanisms of longevity and aging. Cell 2016, 166, 822–839. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilson, D.M. 3rd; Cookson, M.R.; Van Den Bosch, L.; Zetterberg, H.; Holtzman, D.M.; Dewachter, I. 3rd; Cookson, M.R.; Van Den Bosch, L.; Zetterberg, H.; Holtzman, D.M.; Dewachter, I. Hallmarks of neurodegenerative diseases. Cell 2023, 186, 693–714. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Otín, C.; Blasco, M.A.; Partridge, L.; Serrano, M.; Kroemer, G. The hallmarks of aging. Cell 2013, 153, 1194–217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Migliore, L.; Coppedè, F. Gene-environment interactions in Alzheimer disease: the emerging role of epigenetics. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2022, 18, 643–660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spillantini, M.G.; Goedert, M. Tau pathology and neurodegeneration. Lancet Neurol. 2013, 12, 609–622. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Leng, F.; Edison, P. Neuroinflammation and microglial activation in Alzheimer disease: where do we go from here? Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2021, 17, 157–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Matsuda, S.; Nakagawa, Y.; Tsuji, A.; Kitagishi, Y.; Nakanishi, A.; Murai, T. Implications of PI3K/AKT/PTEN signaling on superoxide dismutases expression and in the pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s disease. Diseases 2018, 6, E28. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Murai, T.; Matsuda, S. Therapeutic implications of probiotics in the gut microbe-modulated neuroinflammation and progression of Alzheimer’s disease. Life 2023, 13, 1466. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Halliwell, B. Oxidative stress and neurodegeneration: where are we now? J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 1634–1658. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contestabile, A. Oxidative stress in neurodegeneration: mechanisms and therapeutic perspectives. Curr. Top. Med. Chem. 2001, 1, 553–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T.; Matsuda, S. Pleiotropic signaling by reactive oxygen species concerted with dietary phytochemicals and microbial-derived metabolites as potent therapeutic regulators of the tumor microenvironment. Antioxidants 2023, 12, 1056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ischiropoulos, H.; Beckman, J.S. Oxidative stress and nitration in neurodegeneration: cause, effect, or association? J. Clin. Invest. 2003, 111, 163–169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baker, D.J.; Petersen, R.C. Cellular senescence in brain aging and neurodegenerative diseases: evidence and perspectives. J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 128, 1208–1216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zawia, N.H.; Lahiri, D.K.; Cardozo-Pelaez, F. Epigenetics, oxidative stress, and Alzheimer disease. Free Radic. Biol. Med. 2009, 46, 1241–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dauer, W.; Przedborski, S. Parkinson’s disease: mechanisms and models. Neuron 2003, 39, 889–909. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Borsche, M.; Pereira, S.L.; Klein, C.; Grünewald, A. Mitochondria and Parkinson’s disease: Clinical, molecular, and translational aspects. J. Parkinsons Dis. 2021, 11, 45–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Qian, H.; Kang, X.; Hu, J.; Zhang, D.; Liang, Z.; Meng, F.; Zhang, X.; Xue, Y.; Maimon, R.; Dowdy, S.F.; Devaraj, N.K.; Zhou, Z.; Mobley, W.C.; Cleveland, D.W.; Fu, X.D. Reversing a model of Parkinson’s disease with in situ converted nigral neurons. Nature 2020, 582, 550–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, N.; Matsuda, S.; Ichimura, M.; Minami, A.; Ogino, M.; Murai, T.; Kitagishi, Y. PI3K/AKT signaling mediated by G,protein-coupled receptors is involved in neurodegenerative Parkinson’s disease. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2017, 39, 253–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Elkouzi, A.; Vedam-Mai, V.; Eisinger, R.S.; Okun, M.S. Emerging therapies in Parkinson disease - repurposed drugs and new approaches. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2019, 15, 204–223. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labbé, C.; Lorenzo-Betancor, O.; Ross, O.A. Epigenetic regulation in Parkinson’s disease. Acta Neuropathol. 2016, 132, 515–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pavlou, M.A.S.; Outeiro, T.F. Epigenetics in Parkinson’s Disease. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2017, 978, 363–390. [Google Scholar]
- Masliah, E.; Dumaop, W.; Galasko, D.; Desplats, P. Distinctive patterns of DNA methylation associated with Parkinson disease: identification of concordant epigenetic changes in brain and peripheral blood leukocytes. Epigenetics 2013, 8, 1030–1038. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Espay, A.J.; Brundin, P.; Lang, A.E. Precision medicine for disease modification in Parkinson disease. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2017, 13, 119–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schraivogel, D.; Kuhn, T.M.; Rauscher, B.; Rodríguez-Martínez, M.; Paulsen, M.; Owsley, K.; Middlebrook, A.; Tischer, C.; Ramasz, B.; Ordoñez-Rueda, D.; Dees, M.; Cuylen-Haering, S.; Diebold, E.; Steinmetz, L.M. High-speed fluorescence image-enabled cell sorting. Science 2022, 375, 315–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filby, A.; Carpenter, A.E. A new image for cell sorting. N. Engl. J. Med. 2022, 386, 1755–1758. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- LaBelle, C.A.; Massaro, A.; Cortés-Llanos. B.; Sims, C.E.; Allbritton, N,L. Image-based live cell sorting. Trends Biotechnol. 2021, 39, 613–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Z.; Sun, Z.; Yin, H.; Liu, X.; Wang, J.; Zhao, H.; Pang, C.H.; Wu, T.; Li, S.; Yin, Z.; Yu, X.F. Data-driven materials innovation and applications. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, e2104113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Steponaitis, G.; Stakaitis, R.; Valiulyte, I.; Krusnauskas, R.; Dragunaite, R.; Urbanavičiūtė, R.; Tamasauskas, A.; Skiriute, D. Transcriptome-wide analysis of glioma stem cell specific m6A modifications in long-non-coding RNAs. Sci. Rep. 2022, 12, 5431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buenrostro, J.D.; Wu, B.; Litzenburger, U.M.; Ruff, D.; Gonzales, M.L.; Snyder, M.P.; Chang, H.Y.; Greenleaf, W.J. Single-cell chromatin accessibility reveals principles of regulatory variation. Nature 2015, 523, 486–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanan, H.; Dingfelder, F.; Butté, A.; Lorenzen, N.; Sokolov, M.; Arosio, P. Machine learning for biologics: opportunities for protein engineering, developability, and formulation. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2021, 42, 151–165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoeckius, M.; Hafemeister, C.; Stephenson, W.; Houck-Loomis, B.; Chattopadhyay, P.K.; Swerdlow, H.; Satija, R.; Smibert, P. Simultaneous epitope and transcriptome measurement in single cells. Nat. Methods 2017, 14, 865–868. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peterson, V.M.; Zhang, K.X.; Kumar, N.; Wong, J.; Li, L.; Wilson, D.C.; Moore, R.; McClanahan, T.K.; Sadekova, S.; Klappenbach, J.A. Multiplexed quantification of proteins and transcripts in single cells. Nat. Biotechnol. 2017, 35, 936–939. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McIntyre, D.; Lashkaripour, A.; Fordyce, P.; Densmore, D. Machine learning for microfluidic design and control. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 2925–2937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hudson, W.H.; Wieland, A. Technology meets TILs: deciphering T cell function in the -omics era. Cancer Cell 2023, 41, 41–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmad, A.; Sala, F.; Paiè, P.; Candeo, A.; D’Annunzio, S.; Zippo, A.; Frindel, C.; Osellame, R.; Bragheri, F.; Bassi, A.; Rousseau, D. On the robustness of machine learning algorithms toward microfluidic distortions for cell classification via on-chip fluorescence microscopy. Lab Chip 2022, 22, 3453–3463. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Myszczynska, M.A.; Ojamies, P.N.; Lacoste, A.M.B.; Neil, D.; Saffari, A.; Mead, R.; Hautbergue, G.M.; Holbrook, J.D.; Ferraiuolo, L. Applications of machine learning to diagnosis and treatment of neurodegenerative diseases. Nat. Rev. Neurol. 2020, 16, 440–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- van der Maaten, L.J.P.; Hinton, G.E. Visualizing high-dimensional data using t-SNE. J. Machine Learning Res. 2008, 9, 2579–2605. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, K.; Grayson, J.M.; Khuri, N. Multi-objective genetic algorithm for cluster analysis of single-cell transcriptomes. J. Pers. Med. 2023, 13, 183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ganesh, G.; Kolusu, A.S.; Prasad, K.; Samudrala, P.K.; Nemmani, K.V.S. Advancing health care via artificial intelligence: from concept to clinic. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2022, 934, 175320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Efremova, M.; Teichmann, SA. Computational methods for single-cell omics across modalities. Nat. Methods 2020, 17, 14–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zare Harofte, S.; Soltani, M.; Siavashy, S.; Raahemifar, K. Recent advances of utilizing artificial intelligence in lab on a chip for diagnosis and treatment. Small 2022, 18, e2203169. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pratapa, A.; Doron, M.; Caicedo, J.C. Image-based cell phenotyping with deep learning. Curr. Opin. Chem. Biol. 2021, 65, 9–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T.; Matsuda, S. The chemopreventive effects of chlorogenic acids, phenolic compounds in coffee, against inflammation, cancer, and neurological diseases. Molecules 2023, 28, 2381. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Murai, T.; Matsuda, S. Fatty acid metabolites and the tumor microenvironment as potent regulators of cancer stem cell signaling. Metabolites 2023, 13, 709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
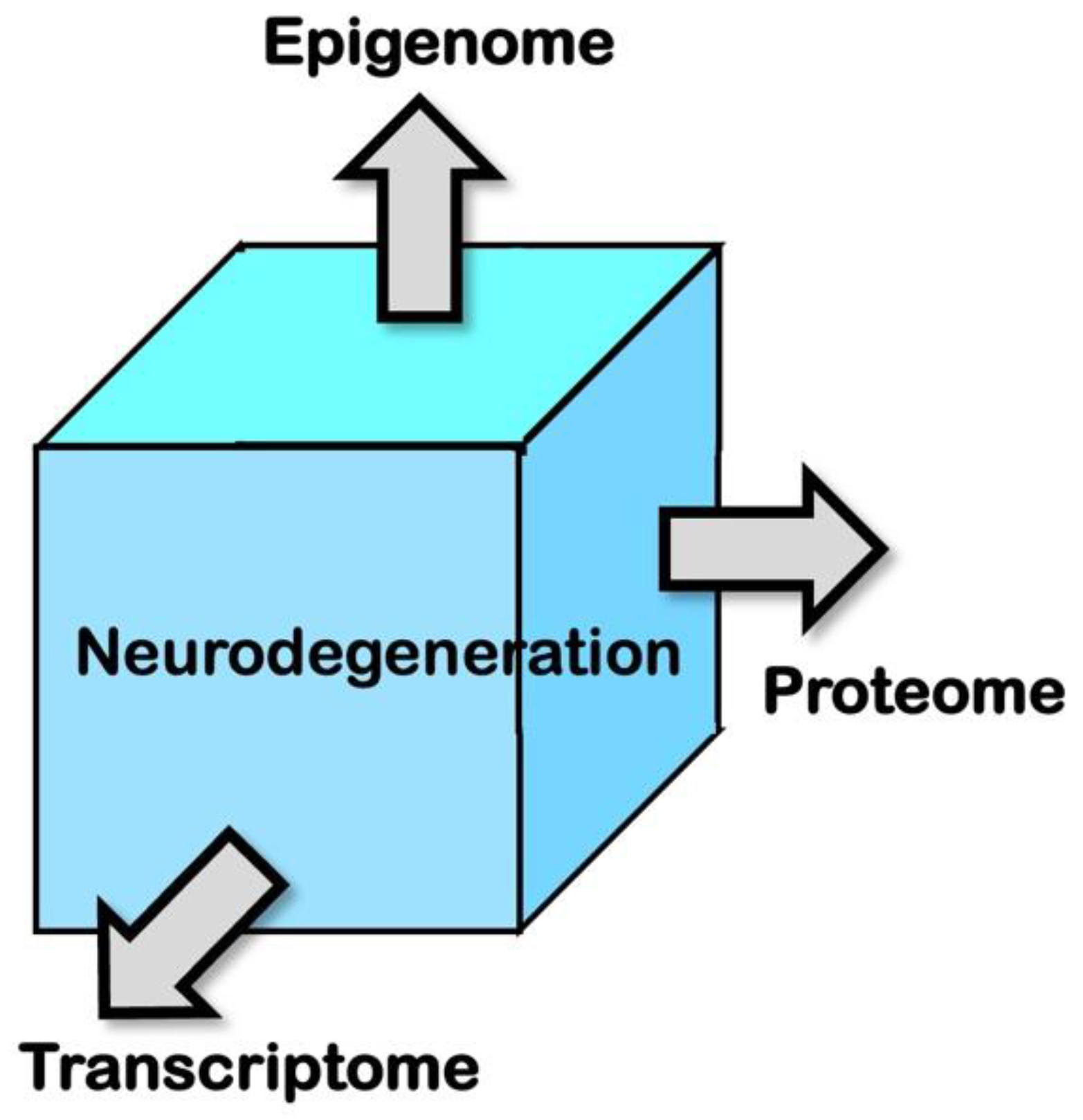
| Methods | Targets | References |
|---|---|---|
| scATAC-seq1 | Epigenome | 35 |
| CITE-seq2 | Transcriptome and proteome | 37 |
| REAP-seq3 | Transcriptome and proteome | 38 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





