Submitted:
26 July 2023
Posted:
27 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
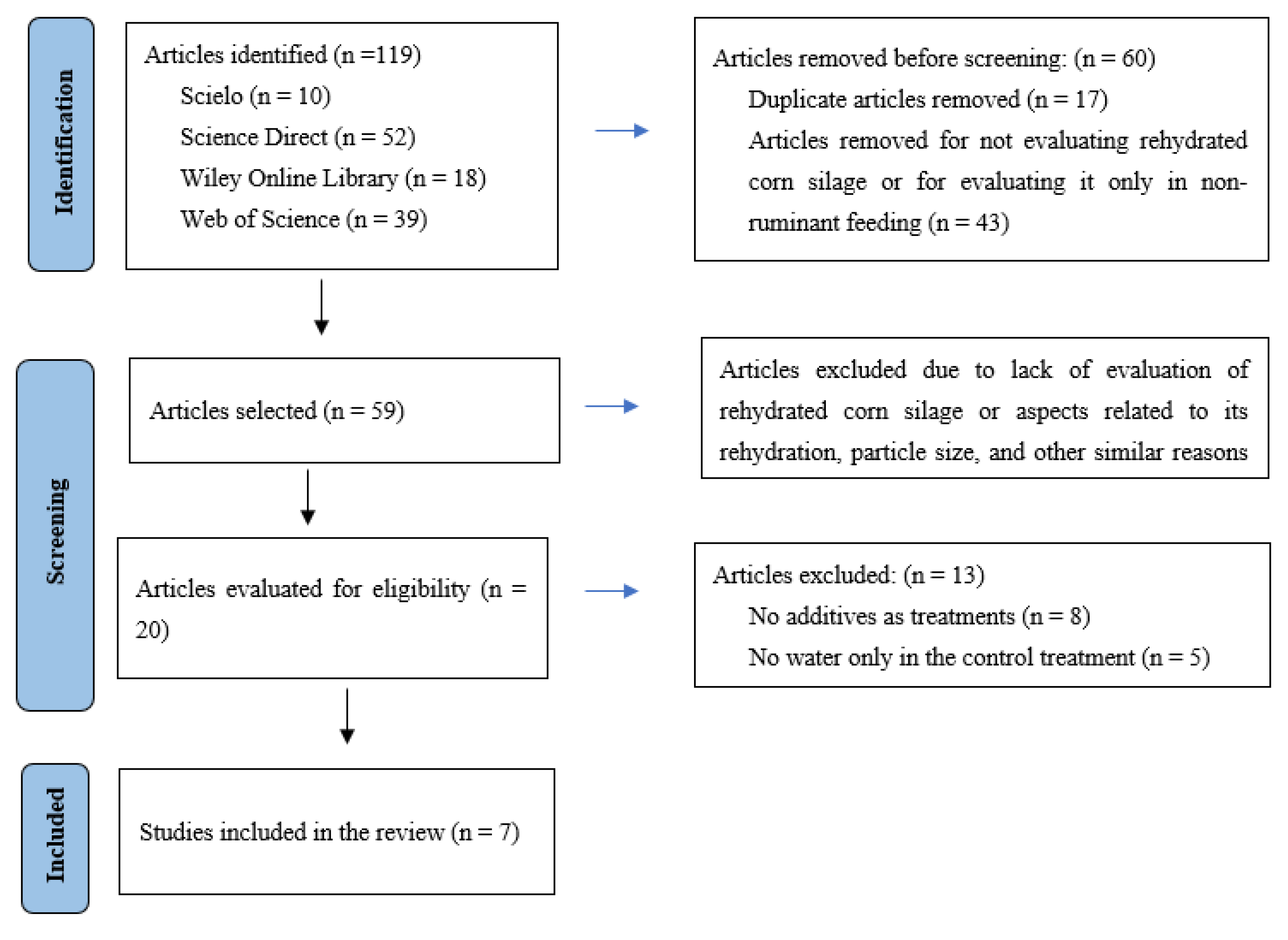
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Dataset
2.2. Data Mining
2.3. Statistical Analysis
3. Results
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Firkins, J.L.; Eastridge, M.L.; St-Pierre, N.R.; Noftsger, S.M. Effects of grain variability and processing on starch utilization by lactating dairy cattle. J. Anim. Sci., 2001, 79, E218. [CrossRef]
- Ferraretto, L.F.; Fredin, S.M.; Shaver, R.D. Influence of ensiling, exogenous protease addition, and bacterial inoculation on fermentation profile, nitrogen fractions, and ruminal in vitro starch digestibility in rehydrated and high-moisture corn. J. dairy Sci.,2015, 98, 7318-7327. [CrossRef]
- Morais, G.; Daniel, C.; Kleinshmitt, Carvalho, P.A.; Fernandes, J.; Nussio, L.G. Additives for grain silages: A review. Slov. J. Anim. Sci.,2017,50, 42-54. https://office.sjas-journal.org/index.php/sjas/article/view/137.
- Daniel, J.L.P.; Bernardes, T.F.; Jobim, C.C.; Schmidt, P.; Nussio, L.G. Production and utilization of silages in tropical areas with focus on Brazil. Grass forage Sci. 2019, 74, 188-200. [CrossRef]
- Jacovaci, F.A.; Salvo, P.A.R.; Jobim, C.C.; Daniel, J.L.P. Effect of ensiling on the feeding value of flint corn grain for feedlot beef cattle: A meta-analysis. Rev. Bras. de Zootec, 2021, 50. [CrossRef]
- Correa, C.E.S.; Shaver, R.D.; Pereira, M.N.; Lauer, J.G.; Kohn, K. Relationship Between Corn Vitreousness and Ruminal In Situ Starch Degradability. J. Dairy Sci., 2002,85, 3008-3012. [CrossRef]
- Santos, W.P.; Salvati, G.G.S.; Arthur, B.A.V.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Nussio, L.G. The effect of sodium benzoate on the nutritive value of rehydrated sorghum grain silage for dairy cows. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol., 2019, 256, 114267. [CrossRef]
- Benton, J.R.; Klopfenstein, T.J.; Erickson, G.E. Effects of Corn Moisture and Length of Ensiling on Dry Matter Digestibility and Rumen Degradable Protein. Nebras. Beef Catt. Reports. 2005. https://digitalcommons.unl.edu/animalscinbcr/151.
- Silva, N.C.; Nascimento, C.F.; Nascimento, F.A.; Resende, F.D.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Siqueira, G.R. Fermentation and aerobic stability of rehydrated corn grain silage treated with different doses of Lactobacillus buchneri or a combination of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus acidilactici. J. dairy sci.,2018, 101, 4158-4167. [CrossRef]
- McDonald, P.; Henderson, A. R.; and Heron, S. J. E. Bioch. Silag., 1991,2nd ed. Chalcombe Publications, Kingston, UK.
- Kleinschmit, D.H.; Schmidt, R.J.; Kung, L. The Effects of Various Antifungal Additives on the Fermentation and Aerobic Stability of Corn Silage. J. dairy sci., 2005, 88, 2130-2139. [CrossRef]
- Moher, D.; Liberati, A.; Tetzlaff, J.; Altman, D.G. Preferred reporting items for systematic reviews and meta-analyses: the PRISMA statement. Ann. Intern. Med.,2009, 151, 264-269. https://www.acpjournals.org/doi/full/10.7326/0003-4819-151-4-200908180-00135.
- McGowan, J.; Sampson, M.; Salzwedel, D.M.; Cogo, E.; Foerster, V.; Lefebvre, C. PRESS Peer Review of Electronic Search Strategies: 2015 Guideline Statement. J. clin. Epidemiol., 2016, 75, 40-46. [CrossRef]
- Salvati, G.G.S.; Santos, W.P.; Silveira, J.M.; Gritti, V.C.; Arthur, B.A.V.; Salvo, P.A.R.; Fachin, L.; Ribeiro, A.P.; Morais Júnior, N.N.; Ferraretto, L.F.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Beauchemin, K.A.; Santos, F.A.P.; Nussio, L.G. Effect of kernel processing and particle size of whole-plant corn silage with vitreous endosperm on dairy cow performance. J. Dairy Sci.,2021, 104, 1794-1810. [CrossRef]
- Ferraretto, L.F.; Shaver, R.D.; Luck, B.D. Silage review: Recent advances and future technologies for whole-plant and fractionated corn silage harvesting. J. dairy sci., 2018 101, 3937-3951. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, P.A.; Bigaton, A.D.; Fernandes, J.; Santos, M.C.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Duarte, A.P.; Nussio, L.G. 2015. Shifts on bacterial population of high moisture corn silages and its correlation with fermentation end-products. In Proceedings. Piracicaba: ESALQ. http://www.isc2015brazil.com/pictures/Proceedings-of-the-XVII-International-Silage-Conference-Brazil%202015.pdf.
- Hu, W.; Schmidt, R.J.; McDonell, E.E.; Klingerman, C.M.; Kung, L. The effect of Lactobacillus buchneri 40788 or Lactobacillus plantarum MTD-1 on the fermentation and aerobic stability of corn silages ensiled at two dry matter contents. J. dairy sci., 2009, 92, 3907-3914. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, P.C.; Esser, N.M.; Shaver, R.D.; Coblentz, W.K.; Scott, M.P.; Bodnar, A.L.; Schmidt, R.J.; Charley, R.C. Influence of ensiling time and inoculation on alteration of the starch-protein matrix in high-moisture corn. J. dairy sci.,2011,94, 2465-2474. [CrossRef]
- Junges, D.; Morais, G.; Spoto, M.H.F.; Santos, P.S.; Adesogan, A.T.; Nussio, L.G.; Daniel, J.L.P. Short communication: Influence of various proteolytic sources during fermentation of reconstituted corn grain silages. J. Dairy Sci., 2017, 100, 9048-9051. [CrossRef]
- Silva, N.C.; Nascimento, C.F.; Campos, V.M.A.; Alves, M.A.P.; Resende, F.D.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Siqueira, G.R. Influence of storage length and inoculation with Lactobacillus buchneri on the fermentation, aerobic stability, and ruminal degradability of high-moisture corn and rehydrated corn grain silage. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol.,2019, 251, 124-133. [CrossRef]
- Morrison, I.M. Changes in the cell wall components of laboratory silages and the effect of various additives on these changes. J. Agric. Sci.,1979,93(3), 581-586. [CrossRef]
- Rezende, A.V.; Rabelo, C.H.; Veiga, R.M.; Andrade, L.P.; Härter, C.J.; Rabelo, F.H.; Basso, F.C.; Reis, R.A. Rehydration of corn grain with acid whey improves the silage quality. Anim. Feed Sci. Technol., 2014,197, 213-221. [CrossRef]
- Souza, W.L.; Cidrini, I.A.; Neiva Júnior, A.P.; Silva, M.D.; Gervásio, J.R.S.; Abreu, M.J.I.; Nascimento, D.C. Effect of rehydration with whey and inoculation with Lactobacillus plantarum and Propionibacterium acidipropionici on the chemical composition, microbiological dynamics, and fermentative losses of corn grain silage. Semina: Ciênc. Agrár., 2020,41, 3351-3363. [CrossRef]
- Cruz, F.N.F.; Moncao, F.P.; Rocha, V.R.; Alencar, A.M.S.; Rigueira, J.P.S.; Silva, A.F.; Miorin, R.L.; Soares, A.C.M.; Carvalho, C.C.S.; Albuquerque, C.J.B. Fermentative losses and chemical composition and in vitro digestibility of corn grain silage rehydrated with water or acid whey combined with bacterial-enzymatic inoculant. Semina Ciênc. Agrár. 2021, 42, 3497-3513. [CrossRef]
- Kung, L.; Shaver, R.D.; Grant, R.J.; Schmidt, R.J. Silage review: Interpretation of chemical, microbial, and organoleptic components of silages. J. dairy Sci., 2018, 101, 4020-4033. [CrossRef]
- Woolford, M.K.; Pahlow, G. The silage fermentation. In Wood, B.J.B. (eds) Microbiology of Fermented Foods. Springer, Boston, MA.1998. [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Lv, H.; Chen, N.; Wang, C.; Zhou, W.; Chen, X.; Zhang, Q. Improving fermentation, protein preservation and antioxidant activity of Moringa oleifera leaves silage with gallic acid and tannin acid. Bioresour. technol,2020,297, 122390. [CrossRef]
- Ávila, C.L.S.; Carvalho, B.F. Silage fermentation updates focusing on the performance of micro-organisms. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2019,128, 966-984. [CrossRef]
- Pahlow, G. Role of microflora in forage conservation. Page 26–36 in Forage Conservation Towards 2000. G. Pahlow and H. Honig, ed. Institute of Grassland Forage Research, Braunschweig, Germany.1991.
- Bueno, A.V.I.; Jobim, C.C.; Daniel, J.L.P.; Gierus, M. Fermentation profile and hygienic quality of rehydrated corn grains treated with condensed tannins from quebracho plant extract. Anim. Sci. Technol. 2020,267,114559. [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, B.F.; Ávila, C.L.S.; Bernardes, T.F.; Pereira, M.N.; Santos, C.; Schwan, R.F. Fermentation profile and identification of lactic acid bacteria and yeasts of rehydrated corn kernel silage. J. Appl. Microbiol. 2017,122, 589-600. [CrossRef]
- Menezes, G.L.; Oliveira, A.F.; Lana, Â.M.Q.; Pires, F.P.A. de A.; de Menezes, R.A.; Sousa, P.G.; Oliveira, E.C.; Monteiro, R.G.A.; Martins, G.G.; Souza, R.C.; Gonçalves, L.C.; Jayme, D.G. Effects of different moist orange pulp inclusions in the corn grain rehydration for silage production on chemical composition, fermentation, aerobic stability, microbiological profile, and losses. Anim. Sci. J., 2022, 93, e13701. [CrossRef]
| ID | Reference | Title | Evaluated parameters |
|---|---|---|---|
| 1 | Menezes et al.[32] | Effects of different moist orange pulp inclusions in the corn grain rehydration for silage production on chemical composition, fermentation, aerobic stability, microbiological profile, and losses | Chemical composition, fermentation parameters, aerobic stability and DM in vitro digestibility |
| 2 | Ferraretto et al.[15] | Effect of ensiling time on fermentation profile and ruminal in vitro starch digestibility in rehydrated corn with or without varied concentrations of wet brewers grains | Chemical composition |
| 3 | Rezende et al.[22]. | Rehydration of corn grain with acid whey improves the silage quality | Chemical composition, fermentation parameters, and aerobic stability |
| 4 | Souza et al.[23] | Effect of rehydration with whey and inoculation with Lactobacillus plantarum and Propionibacterium acidipropionici on the chemical composition, microbiological dynamics, and fermentative losses of corn grain silage | Chemical composition and fermentation parameters |
| 5 | Cruz et al.[24] | Fermentative losses and chemical composition and in vitro digestibility of corn grain silage rehydrated with water or acid whey combined with bacterial-enzymatic inoculant | Chemical composition, fermentation parameters and DM in vitro digestibility |
| 6 | Silva et al.[9] | Fermentation and aerobic stability of rehydrated corn grain silage treated with different doses of Lactobacillus buchneri or a combination of Lactobacillus plantarum and Pediococcus acidilactici | Chemical composition, fermentation parameters, and aerobic stability |
| 7 | Jungues et al.[19] | Short communication: Influence of various proteolytic sources during fermentation of reconstituted corn grain silages | Chemical composition and fermentation parameters |
| Category | Additives | Classification1 |
|---|---|---|
| By-product | Wet orange pulp | Fermentation stimulants / nutrients |
| Wet brewery waste | Nutrients | |
| By-product | Milk whey | Fermentation stimulants / nutrients |
| Bacterial inoculant | Lactobacillus plantarum | Fermentation stimulants |
| Pediococcus | Fermentation stimulants | |
| Lactobacillus buchneri | Fermentation stimulants / Aerobic spoilage inhibitors | |
| Enterococcus faecium | Fermentation stimulants | |
| Pediococcus acidilactici | Fermentation stimulants | |
| Propionibacteriu acidipropionici | Fermentation stimulants | |
| Enzymatic Inoculant | Cellulase and hemi-cellulase | Fermentation stimulants |
| Antimycotic agent | Natamycin | Fermentation inhibitors |
| Irradiation | Gama irradiation | Fermentation inhibitors |
| Chemical compound | Lactic acid | Fermentation stimulants |
| Acetic acid | Fermentation inhibitors / Aerobic spoilage inhibitors | |
| Ethanol | Fermentation inhibitors |
| Item | Rehydrated corn grain silage | n1 | SEM2 | P-value3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without additive | With additive | |||||
| Chemical composition (g kg-1 DM) | ||||||
| Dry matter | Mean | 658 | 644 | 39 | 8.91 | 0.27 |
| Minimum | 586 | 564 | ||||
| Maximum | 700 | 695 | ||||
| Crude protein | Mean | 90.3 | 93.0 | 39 | 3.67 | 0.48 |
| Minimum | 70.0 | 74.7 | ||||
| Maximum | 101 | 118 | ||||
| Neutral detergent fiber | Mean | 120 | 130 | 28 | 19.8 | 0.66 |
| Minimum | 61.2 | 56.9 | ||||
| Maximum | 214 | 232 | ||||
| Acid detergent fiber | Mean | 27.2 | 28.3 | 20 | 4.81 | 0.88 |
| Minimum | 11.4 | 5.4 | ||||
| Maximum | 38.2 | 62.2 | ||||
| Item | Rehydrated corn grain silage | n1 | SEM2 | P-value3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without additive | With additive | |||||
| pH | Mean | 4.09 | 4.25 | 28 | 0.20 | 0.42 |
| Minimum | 3.74 | 3.67 | ||||
| Maximum | 4.94 | 5.66 | ||||
| Organic acids and ethanol (g kg-1 DM) | ||||||
| Lactic acid | Mean | 15.4 | 15.54 | 27 | 2.21 | 0.99 |
| Minimum | 9.07 | 0.90 | ||||
| Maximum | 27.6 | 28.1 | ||||
| Acetic acid | Mean | 2.27 | 4.47 | 27 | 1.74 | 0.26 |
| Minimum | 1.49 | 1.10 | ||||
| Maximum | 3.60 | 16.2 | ||||
| Propionic acid | Mean | 0.54 | 0.68 | 23 | 0.38 | 0.62 |
| Minimum | 0.03 | 0.01 | ||||
| Maximum | 1.10 | 1.51 | ||||
| Butyric acid | Mean | 0.47 | 0.01 | 15 | 0.16 | 0.074 |
| Minimum | 0.01 | 0.00 | ||||
| Maximum | 1.71 | 0.14 | ||||
| Ethanol | Mean | 6.53 | 5.57 | 15 | 2.08 | 0.66 |
| Minimum | 5.25 | 0.30 | ||||
| Maximum | 7.16 | 12.5 | ||||
| Microbial population (log cfu g-1) | ||||||
| Lactic acid bacteria (LAB) | Mean | 5.03 | 4.74 | 12 | 0.95 | 0.50 |
| Minimum | 3.70 | 2.00 | ||||
| Maximum | 6.10 | 6.28 | ||||
| Yeasts | Mean | 3.49 | 2.47 | 8 | 0.40 | 0.13 |
| Minimum | 4.02 | 2.00 | ||||
| Maximum | 4.23 | 3.37 | ||||
| Molds | Mean | 3.54 | 3.23 | 12 | 0.67 | 0.65 |
| Minimum | 2.39 | 2.00 | ||||
| Maximum | 4.51 | 4.85 | ||||
| Item | Rehydrated corn grain silage | n1 | SEM2 | P-value3 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Without additive | With additive | |||||
| Effluent losses (kg/t4) | Mean | 2.36 | 3.05 | 8 | 1.07 | 0.55 |
| Minimum | 2.12 | 1.23 | ||||
| Maximum | 2.33 | 5.70 | ||||
| Gas losses (%) | Mean | 4.84 | 5.13 | 15 | 3.70 | 0.93 |
| Minimum | 1.11 | 1.31 | ||||
| Maximum | 12.3 | 21.2 | ||||
| Dry matter recovery (g kg-1) | Mean | 965 | 976 | 24 | 7.48 | 0.14 |
| Minimum | 941 | 936 | ||||
| Maximum | 987 | 999 | ||||
| Aerobic stability (hours) | Mean | 96.2 | 98.9 | 23 | 42.7 | 0.95 |
| Minimum | 36.0 | 25.5 | ||||
| Maximum | 213 | 288 | ||||
| DM in vitro digestibility (g kg-1 DM) |
Mean | 875 | 839 | 8 | 48.1 | 0.77 |
| Minimum | 805 | 786 | ||||
| Maximum | 911 | 909 | ||||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





