Submitted:
25 July 2023
Posted:
27 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
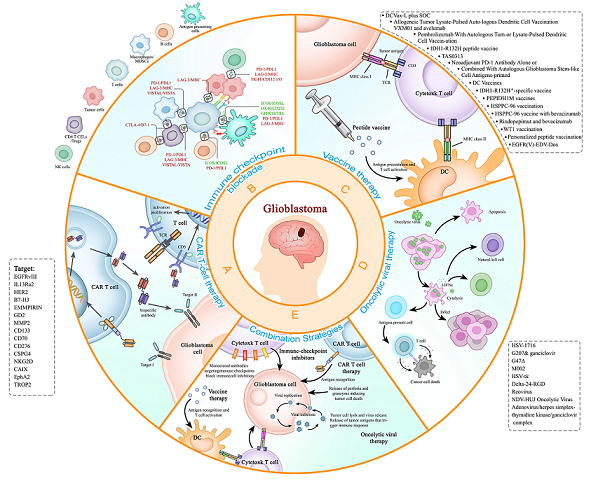
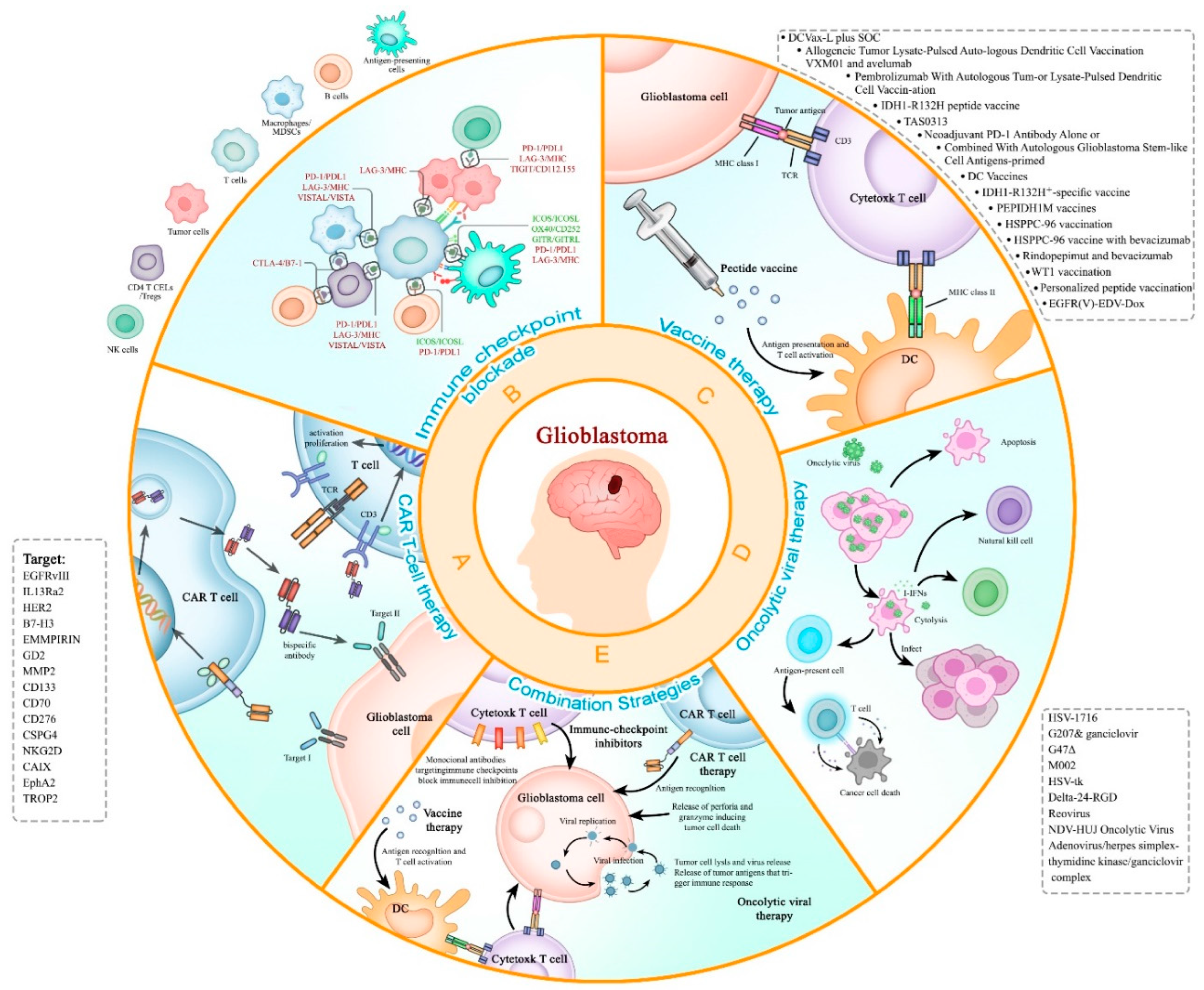
2. Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Recurrent Glioblastoma
2.1. CAR-T therapy
2.1.1. The background of CAR-T therapy
2.1.2. The latest development of CAR-T therapy
2.1.3. The limitation of CAR-T therapy
2.1.4. The prospective of CAR-T therapy
2.2. Immune checkpoint inhibitor
2.2.1. CTLA-4 inhibitors
2.2.2. PD1/PDL1
2.2.3. Negative immune regulation
2.2.5. Challenges and future directions of ICB in rGBM
2.3. Cancer vaccination therapy for rGBM
2.3.1. The background of cancer vaccination therapy for rGBM
2.3.2. Peptide vaccines
2.3.3. Cell-based vaccines
Dendritic cell (DC) vaccines
B cell vaccines
2.3.4. Nucleic acid vaccines
2.5. Oncolytic viral therapy in recurrent GBM (rGBM).
| Agents | Year | Study design | Subjects | Experiment time | Registration Number |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Herpes simplex virus (HSV-1716) |
2000 | Phrase Ⅰ trial | Patients had biopsy proven high grade glioma | 24 months | PMID10845724[134] |
| G207 | 2009 | Phrase Ⅰ b trial | Patients had an initial histologically confirmed diagnosis of glioblastoma multiforme | 19 months | F05041106[135] |
| G207 | 2014 | Phrase Ⅰ trial | Patients had pathologically confirmed residual/recurrent glioblastoma multiforme, gliosarcoma, or astrocytoma | 11-51 months | NCT00157703[136] |
| G207 | 2015 | Case report | A 52-year-old Caucasian female had a GBM with an infltrative glial tumor | More than 5.5 years | NCT00028158[137] |
| G207 | 2022 | Cross-sectional study (a Gene Expression Analyses) | Patients are from the phase Ib G207 clinical trial (NCT00028158) | / | /[138] |
| G47Δ | 2022 | Phrase Ⅱ trial | Patients who had a pathologically confirmed diagnosis of glioblastoma with a persistent or recurrent tumor | 2-5 years | UMIN000015995[139] |
| Herpes simplex virus Expressing Interleukin-12 (M002) | 2012 | Animal experiment | Specific-pathogen-free female SCID and B6D2F1 mice | More than 80 days | /[140] |
| Herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase suicide gene therapy (HSV1-tk) | 1998 | Phrase Ⅰ/Ⅱ trial | Patients had a recurrence of primary glioblastoma | 830 days | /[141] |
| Herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene (HSV-tk) | 1999 | Phrase Ⅱ trial | Patients with relapsed GBM | More than 15 months | /[142] |
| Adenovirus mediated HSV-tk gene therapy (AdvHSV-tk) | 2004 | RCT | All patients with operable primary or recurrent highgrade glioma | More than 200 weeks | /[143] |
| Delta-24-RGD | 2018 | Phrase Ⅰ trial | Patients with recurrent malignant glioma | More than 3 years | NCT00805376[144] |
| Delta-24-RGD | 2022 | Animal experiment | 95 mice | More than 100 days | /[145] |
| Reovirus | 2008 | Phrase Ⅰ trial | Patients had a diagnosis of GBM | More than 234 weeks | /[146] |
| Reovirus | 2014 | Phrase Ⅰ trial | Patients had either first, second, or third occurrence of a supratentorial tumor with a histologic diagnosis consistent with glioblastoma multiforme | More than 989 days | /[147] |
| NDV-HUJ Oncolytic Virus | 2005 | Phase I/II Trial | Patients had been diagnosed with GBM based on histology and gadolinium-enhanced (Gd+) MRI, and all had a recurrence of GBM | More than 66 weeks | /[148] |
| G207& ganciclovir | 2000 | Animal experiment | Six-week-old female A/J mice | More than 30 days | /[149] |
| Adenovirus/herpes simplex-thymidine kinase/ganciclovir complex | 2003 | Phase I Trial | Patients had histologically confirmed malignant glioma, defined as GBM | More than 248 weeks | /[150] |
2.5.1. Herpes simplex virus-1 based (HSV-1-based)
HSV1716
G207
G47Δ
Genetically Engineered Herpes Simplex Virus Expressing Interleukin-12 (M002)
2.5.2. Adenovirus-Based
Delta-24-RGD (DNX⁃2401)
2.5.3. Reovirus-Based
2.5.4. Newcastle Disease Virus Based
2.5.5. The future directions of Oncolytic viral therapy in (rGBM)
2.6. Combination Strategies for GBM
2.6.1. Chemotherapy and radiotherapy
2.6.2. Molecularly targeted drugs
2.6.3. Tumor Treatment Fields (TTFields)
| Clinical Trails | Phase | Interventions | Arms | Combined Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00684567 | Ⅱ | Drug: TMZ Radiation: RT |
Single arm:TMZ + RT | Chemotherapy and radiotherapy |
| NCT01730950 | Ⅱ |
Biological: BVZ Radiation: RT |
Arm 1: BVZ Arm 2: BVZ + RT |
Radiation therapy with bevacizumab for the rGBM |
| NCT01894061 | Ⅱ | Biological: BVZ Device: NovoTTF-l00A Other: Quality of Life Assessment |
Arm 1: BVZ + NovoTTF-100A | NovoTTF-100A With Bevacizumab (Avastin) for the rGBM |
| NCT01849146 | Ⅰ | Drug: Adavosertib, TMZ Radiation: RT |
Arm 1: Adavosertib + TMZ + RT Arm 2: adavosertib + TMZ |
Adavosertib, RT, and TMZfor the Newly Diagnosed GBM or rGBM |
| NCT00650923 | Ⅰ |
Drug: Ziv-aflibercept, TMZ, Procedure: RT, pharmacological study, laboratory biomarker analysis |
Arm 1: ziv-aflibercept + RT + TMZ |
Aflibercept, RT, and TMZ for the Newly Diagnosed GBM or rGBM |
2.6.4. Combination Strategies of immunotherapy
2.6.5. Virus-based Combination Strategies
2.6.6. The current situation and prospect of combination strategies for GBM
3. Conclusion and future perspective of immunotherapy to recurrent GBM
Author Contributions
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Board, W.C.o.T.E. Central Nervous System Tumours.
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Price, M.; Neff, C.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.A.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2015-2019. Neuro-Oncology 2022, 24, v1-v95. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alifieris, C.; Trafalis, D.T. Glioblastoma multiforme: Pathogenesis and treatment. Pharmacology & Therapeutics 2015, 152, 63-82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- R, S.; Wp, M.; Mj, v.d.B.; M, W.; B, F.; Mj, T.; K, B.; Aa, B.; C, M.; U, B.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. The New England journal of medicine 2005, 352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, P.Y.; Reardon, D.A. Neuro-oncology in 2015: Progress in glioma diagnosis, classification and treatment. Nature Reviews. Neurology 2016, 12, 69–70. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.-C.; Gorlia, T.; Hamou, M.-F.; de Tribolet, N.; Weller, M.; Kros, J.M.; Hainfellner, J.A.; Mason, W.; Mariani, L.; et al. MGMT gene silencing and benefit from temozolomide in glioblastoma. The New England Journal of Medicine 2005, 352, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van Linde, M.E.; Brahm, C.G.; de Witt Hamer, P.C.; Reijneveld, J.C.; Bruynzeel, A.M.E.; Vandertop, W.P.; van de Ven, P.M.; Wagemakers, M.; van der Weide, H.L.; Enting, R.H.; et al. Treatment outcome of patients with recurrent glioblastoma multiforme: a retrospective multicenter analysis. Journal of Neuro-Oncology 2017, 135, 183-192. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Le Rhun, E.; Preusser, M.; Tonn, J.-C.; Roth, P. How we treat glioblastoma. ESMO Open 2019, 4, e000520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cohen, M.H.; Shen, Y.L.; Keegan, P.; Pazdur, R. FDA Drug Approval Summary: Bevacizumab (Avastin®) as Treatment of Recurrent Glioblastoma Multiforme. The Oncologist 2012, 17, 1482. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gilbert, M.R.; Dignam, J.J.; Armstrong, T.S.; Wefel, J.S.; Blumenthal, D.T.; Vogelbaum, M.A.; Colman, H.; Chakravarti, A.; Pugh, S.; Won, M.; et al. A Randomized Trial of Bevacizumab for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2014, 370, 699–708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chinot, O.L.; Wick, W.; Mason, W.; Henriksson, R.; Saran, F.; Nishikawa, R.; Carpentier, A.F.; Hoang-Xuan, K.; Kavan, P.; Cernea, D.; et al. Bevacizumab plus Radiotherapy–Temozolomide for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2014, 370, 709–722. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- EORTC 26101 phase III trial exploring the combination of bevacizumab and lomustine in patients with first progression of a glioblastoma. Journal of Clinical Oncology.
- Mooney, J.; Bernstock, J.D.; Ilyas, A.; Ibrahim, A.; Yamashita, D.; Markert, J.M.; Nakano, I. Current Approaches and Challenges in the Molecular Therapeutic Targeting of Glioblastoma. World Neurosurgery 2019, 129, 90–100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, M.; Cloughesy, T.; Perry, J.R.; Wick, W. Standards of care for treatment of recurrent glioblastoma--are we there yet? Neuro-Oncology 2013, 15, 4-27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, J.H.; Singh Achrol, A.; Aghi, M.K.; Bankiewiecz, K.; Bexon, M.; Brem, S.; Brenner, A.; Chandhasin, C.; Chowdhary, S.; Coello, M.; et al. Targeting the IL4 Receptor with MDNA55 in Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma: Results of a Phase 2b Trial. Neuro-Oncology 2023, noac285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmad, G.; Amiji, M.M. Cancer stem cell-targeted therapeutics and delivery strategies. Expert Opinion on Drug Delivery 2017, 14, 997–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magrath, J.W.; Kim, Y. Salinomycin's potential to eliminate glioblastoma stem cells and treat glioblastoma multiforme (Review). International Journal of Oncology 2017, 51, 753–759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Yuan, X.; Zeng, Z.; Tunici, P.; Ng, H.; Abdulkadir, I.R.; Lu, L.; Irvin, D.; Black, K.L.; Yu, J.S. Analysis of gene expression and chemoresistance of CD133+ cancer stem cells in glioblastoma. Molecular Cancer 2006, 5, 67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bao, S.; Wu, Q.; McLendon, R.E.; Hao, Y.; Shi, Q.; Hjelmeland, A.B.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Bigner, D.D.; Rich, J.N. Glioma stem cells promote radioresistance by preferential activation of the DNA damage response. Nature 2006, 444, 756–760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kumar, S.; Bar-Lev, L.; Sharife, H.; Grunewald, M.; Mogilevsky, M.; Licht, T.; Goveia, J.; Taverna, F.; Paldor, I.; Carmeliet, P.; et al. Identification of vascular cues contributing to cancer cell stemness and function. Angiogenesis 2022, 25, 355–371. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galli, R.; Binda, E.; Orfanelli, U.; Cipelletti, B.; Gritti, A.; De Vitis, S.; Fiocco, R.; Foroni, C.; Dimeco, F.; Vescovi, A. Isolation and characterization of tumorigenic, stem-like neural precursors from human glioblastoma. Cancer Research 2004, 64, 7011–7021. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bischof, J.; Westhoff, M.-A.; Wagner, J.E.; Halatsch, M.-E.; Trentmann, S.; Knippschild, U.; Wirtz, C.R.; Burster, T. Cancer stem cells: The potential role of autophagy, proteolysis, and cathepsins in glioblastoma stem cells. Tumour Biology: The Journal of the International Society for Oncodevelopmental Biology and Medicine 2017, 39, 1010428317692227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Campos, B.; Gal, Z.; Baader, A.; Schneider, T.; Sliwinski, C.; Gassel, K.; Bageritz, J.; Grabe, N.; von Deimling, A.; Beckhove, P.; et al. Aberrant self-renewal and quiescence contribute to the aggressiveness of glioblastoma. The Journal of Pathology 2014, 234, 23–33. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, C.M.; Lim, M.; Drake, C.G. Immunotherapy for brain cancer: recent progress and future promise. Clinical Cancer Research: An Official Journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2014, 20, 3651-3659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Biollaz, G.; Bernasconi, L.; Cretton, C.; Püntener, U.; Frei, K.; Fontana, A.; Suter, T. Site-specific anti-tumor immunity: differences in DC function, TGF-beta production and numbers of intratumoral Foxp3+ Treg. European Journal of Immunology 2009, 39, 1323–1333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nduom, E.K.; Weller, M.; Heimberger, A.B. Immunosuppressive mechanisms in glioblastoma. Neuro-Oncology 2015, 7 Suppl 7, vii9-vii14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fu, W.; Wang, W.; Li, H.; Jiao, Y.; Huo, R.; Yan, Z.; Wang, J.; Wang, S.; Wang, J.; Chen, D.; et al. Single-Cell Atlas Reveals Complexity of the Immunosuppressive Microenvironment of Initial and Recurrent Glioblastoma. Frontiers in Immunology 2020, 11, 835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Network, C.G.A.R. Comprehensive genomic characterization defines human glioblastoma genes and core pathways. Nature 2008, 455, 1061–1068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, W.-k.; Shao, C.; Qi, Z.-y.; Yang, C.; Wang, Z. The role of Gliadel wafers in the treatment of newly diagnosed GBM: a meta-analysis. Drug Design, Development and Therapy 2015, 9, 3341-3348. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McNutt, M. Cancer immunotherapy. Science (New York, N.Y. Science (New York, N.Y.) 2013, 342, 1417. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mellman, I.; Coukos, G.; Dranoff, G. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Nature 2011, 480, 480–489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Weiner, G.J.; Pardoll, D.M. Cancer immunotherapy comes of age. Journal of Clinical Oncology: Official Journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2011, 29, 4828-4836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Topalian, S.L.; Drake, C.G.; Pardoll, D.M. Immune checkpoint blockade: a common denominator approach to cancer therapy. Cancer Cell 2015, 27, 450–461. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seyfrid, M.; Maich, W.T.; Shaikh, M.V.; Tatari, N.; Upreti, D.; Piyasena, D.; Subapanditha, M.; Savage, N.; McKenna, D.; Mikolajewicz, N.; et al. CD70 as an actionable immunotherapeutic target in recurrent glioblastoma and its microenvironment. Journal for ImmunoTherapy of Cancer 2022, 10, e003289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, P.; Venugopal, C.; Salim, S.K.; Tatari, N.; Bakhshinyan, D.; Singh, M.; Seyfrid, M.; Upreti, D.; Rentas, S.; Wong, N.; et al. The Rational Development of CD133-Targeting Immunotherapies for Glioblastoma. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 832-844. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thomas, A.A.; Brennan, C.W.; DeAngelis, L.M.; Omuro, A.M. Emerging therapies for glioblastoma. JAMA neurology 2014, 71, 1437–1444. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R.A.; Johnson, L.A.; Davis, J.L.; Zheng, Z.; Woolard, K.D.; Reap, E.A.; Feldman, S.A.; Chinnasamy, N.; Kuan, C.-T.; Song, H.; et al. Recognition of glioma stem cells by genetically modified T cells targeting EGFRvIII and development of adoptive cell therapy for glioma. Human Gene Therapy 2012, 23, 1043–1053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rong, L.; Li, N.; Zhang, Z. Emerging therapies for glioblastoma: current state and future directions. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 2022, 41, 142. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- News, N. Searching for a Cure for Deadly Brain Tumors. Neuroscience News 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Maude, S.L.; Frey, N.; Shaw, P.A.; Aplenc, R.; Barrett, D.M.; Bunin, N.J.; Chew, A.; Gonzalez, V.E.; Zheng, Z.; Lacey, S.F.; et al. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells for sustained remissions in leukemia. N Engl J Med 2014, 371, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hong, M.; Clubb, J.D.; Chen, Y.Y. Engineering CAR-T Cells for Next-Generation Cancer Therapy. Cancer Cell 2020, 38, 473–488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Labanieh, L.; Majzner, R.G.; Mackall, C.L. Programming CAR-T cells to kill cancer. Nat Biomed Eng 2018, 2, 377–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galea, I.; Bechmann, I.; Perry, V.H. What is immune privilege (not)? Trends Immunol 2007, 28, 12–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salinas, S.; Schiavo, G.; Kremer, E.J. A hitchhiker's guide to the nervous system: the complex journey of viruses and toxins. Nat Rev Microbiol 2010, 8, 645–655. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arima, Y.; Harada, M.; Kamimura, D.; Park, J.H.; Kawano, F.; Yull, F.E.; Kawamoto, T.; Iwakura, Y.; Betz, U.A.; Marquez, G.; et al. Regional neural activation defines a gateway for autoreactive T cells to cross the blood-brain barrier. Cell 2012, 148, 447–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maggs, L.; Cattaneo, G.; Dal, A.E.; Moghaddam, A.S.; Ferrone, S. CAR T Cell-Based Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Glioblastoma. Front Neurosci 2021, 15, 662064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woroniecka, K.I.; Rhodin, K.E.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Keith, K.A.; Fecci, P.E. T-cell Dysfunction in Glioblastoma: Applying a New Framework. Clin Cancer Res 2018, 24, 3792–3802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kahlon, K.S.; Brown, C.; Cooper, L.J.; Raubitschek, A.; Forman, S.J.; Jensen, M.C. Specific recognition and killing of glioblastoma multiforme by interleukin 13-zetakine redirected cytolytic T cells. Cancer Res 2004, 64, 9160–9166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.E.; Warden, C.D.; Starr, R.; Deng, X.; Badie, B.; Yuan, Y.C.; Forman, S.J.; Barish, M.E. Glioma IL13Ralpha2 is associated with mesenchymal signature gene expression and poor patient prognosis. PLoS One 2013, 8, e77769. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.E.; Badie, B.; Barish, M.E.; Weng, L.; Ostberg, J.R.; Chang, W.C.; Naranjo, A.; Starr, R.; Wagner, J.; Wright, C.; et al. Bioactivity and Safety of IL13Ralpha2-Redirected Chimeric Antigen Receptor CD8+ T Cells in Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 2015, 21, 4062–4072. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.E.; Rodriguez, A.; Palmer, J.; Ostberg, J.R.; Naranjo, A.; Wagner, J.R.; Aguilar, B.; Starr, R.; Weng, L.; Synold, T.W.; et al. Off-the-shelf, steroid-resistant, IL13Ralpha2-specific CAR T cells for treatment of glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 2022, 24, 1318–1330. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gan, H.K.; Cvrljevic, A.N.; Johns, T.G. The epidermal growth factor receptor variant III (EGFRvIII): where wild things are altered. FEBS J 2013, 280, 5350–5370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ekstrand, A.J.; Sugawa, N.; James, C.D.; Collins, V.P. Amplified and rearranged epidermal growth factor receptor genes in human glioblastomas reveal deletions of sequences encoding portions of the N- and/or C-terminal tails. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A 1992, 89, 4309–4313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bullain, S.S.; Sahin, A.; Szentirmai, O.; Sanchez, C.; Lin, N.; Baratta, E.; Waterman, P.; Weissleder, R.; Mulligan, R.C.; Carter, B.S. Genetically engineered T cells to target EGFRvIII expressing glioblastoma. J Neurooncol 2009, 94, 373–382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Rourke, D.M.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Desai, A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Mansfield, K.; Morrissette, J.J.D.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Brem, S.; Maloney, E.; Shen, A.; et al. A single dose of peripherally infused EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci Transl Med 2017, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durgin, J.S.; Henderson, F., Jr.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Mohan, S.; Wang, S.; Lacey, S.F.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Desai, A.S.; Lee, J.Y.K.; Maus, M.V.; et al. Case Report: Prolonged Survival Following EGFRvIII CAR T Cell Treatment for Recurrent Glioblastoma. Front Oncol 2021, 11, 669071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmed, N.; Salsman, V.S.; Kew, Y.; Shaffer, D.; Powell, S.; Zhang, Y.J.; Grossman, R.G.; Heslop, H.E.; Gottschalk, S. HER2-specific T cells target primary glioblastoma stem cells and induce regression of autologous experimental tumors. Clin Cancer Res 2010, 16, 474–485. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, N.; Brawley, V.; Hegde, M.; Bielamowicz, K.; Kalra, M.; Landi, D.; Robertson, C.; Gray, T.L.; Diouf, O.; Wakefield, A.; et al. HER2-Specific Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Modified Virus-Specific T Cells for Progressive Glioblastoma: A Phase 1 Dose-Escalation Trial. JAMA Oncol 2017, 3, 1094–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vora, P.; Venugopal, C.; Salim, S.K.; Tatari, N.; Bakhshinyan, D.; Singh, M.; Seyfrid, M.; Upreti, D.; Rentas, S.; Wong, N.; et al. The Rational Development of CD133-Targeting Immunotherapies for Glioblastoma. Cell Stem Cell 2020, 26, 832-844 e836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goff, S.L.; Morgan, R.A.; Yang, J.C.; Sherry, R.M.; Robbins, P.F.; Restifo, N.P.; Feldman, S.A.; Lu, Y.C.; Lu, L.; Zheng, Z.; et al. Pilot Trial of Adoptive Transfer of Chimeric Antigen Receptor-transduced T Cells Targeting EGFRvIII in Patients With Glioblastoma. J Immunother 2019, 42, 126–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morgan, R.A.; Yang, J.C.; Kitano, M.; Dudley, M.E.; Laurencot, C.M.; Rosenberg, S.A. Case report of a serious adverse event following the administration of T cells transduced with a chimeric antigen receptor recognizing ERBB2. Mol Ther 2010, 18, 843–851. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krenciute, G.; Prinzing, B.L.; Yi, Z.; Wu, M.F.; Liu, H.; Dotti, G.; Balyasnikova, I.V.; Gottschalk, S. Transgenic Expression of IL15 Improves Antiglioma Activity of IL13Ralpha2-CAR T Cells but Results in Antigen Loss Variants. Cancer Immunol Res 2017, 5, 571–581. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lechpammer, M.; Rao, R.; Shah, S.; Mirheydari, M.; Bhattacharya, D.; Koehler, A.; Toukam, D.K.; Haworth, K.J.; Pomeranz Krummel, D.; Sengupta, S. Advances in Immunotherapy for the Treatment of Adult Glioblastoma: Overcoming Chemical and Physical Barriers. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.E.; Aguilar, B.; Starr, R.; Yang, X.; Chang, W.C.; Weng, L.; Chang, B.; Sarkissian, A.; Brito, A.; Sanchez, J.F.; et al. Optimization of IL13Ralpha2-Targeted Chimeric Antigen Receptor T Cells for Improved Anti-tumor Efficacy against Glioblastoma. Mol Ther 2018, 26, 31–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, B.D.; Yu, X.; Castano, A.P.; Bouffard, A.A.; Schmidts, A.; Larson, R.C.; Bailey, S.R.; Boroughs, A.C.; Frigault, M.J.; Leick, M.B.; et al. CAR-T cells secreting BiTEs circumvent antigen escape without detectable toxicity. Nat Biotechnol 2019, 37, 1049–1058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muhammad, N.; Wang, R.; Li, W.; Zhang, Z.; Chang, Y.; Hu, Y.; Zhao, J.; Zheng, X.; Mao, Q.; Xia, H. A novel TanCAR targeting IL13Ralpha2 and EphA2 for enhanced glioblastoma therapy. Mol Ther Oncolytics 2022, 24, 729–741. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lugade, A.A.; Sorensen, E.W.; Gerber, S.A.; Moran, J.P.; Frelinger, J.G.; Lord, E.M. Radiation-induced IFN-gamma production within the tumor microenvironment influences antitumor immunity. J Immunol 2008, 180, 3132–3139. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Portella, L.; Scala, S. Ionizing radiation effects on the tumor microenvironment. Semin Oncol 2019, 46, 254–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, L.; Ge, H.; Long, Y.; Yang, C.; Chang, Y.E.; Mu, L.; Sayour, E.J.; De Leon, G.; Wang, Q.J.; Yang, J.C.; et al. CD70, a novel target of CAR T-cell therapy for gliomas. Neuro Oncol 2018, 20, 55–65. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- DeSelm, C.; Palomba, M.L.; Yahalom, J.; Hamieh, M.; Eyquem, J.; Rajasekhar, V.K.; Sadelain, M. Low-Dose Radiation Conditioning Enables CAR T Cells to Mitigate Antigen Escape. Mol Ther 2018, 26, 2542–2552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Zeng, G. Cancer and innate immune system interactions: translational potentials for cancer immunotherapy. J Immunother 2012, 35, 299–308. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fong, B.; Jin, R.; Wang, X.; Safaee, M.; Lisiero, D.N.; Yang, I.; Li, G.; Liau, L.M.; Prins, R.M. Monitoring of regulatory T cell frequencies and expression of CTLA-4 on T cells, before and after DC vaccination, can predict survival in GBM patients. PLoS One 2012, 7, e32614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, F.; Huang, J.; Liu, X.; Cheng, Q.; Luo, C.; Liu, Z. CTLA-4 correlates with immune and clinical characteristics of glioma. Cancer Cell Int 2020, 20, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fecci, P.E.; Ochiai, H.; Mitchell, D.A.; Grossi, P.M.; Sweeney, A.E.; Archer, G.E.; Cummings, T.; Allison, J.P.; Bigner, D.D.; Sampson, J.H. Systemic CTLA-4 blockade ameliorates glioma-induced changes to the CD4+ T cell compartment without affecting regulatory T-cell function. Clin Cancer Res 2007, 13, 2158–2167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Galstyan, A.; Markman, J.L.; Shatalova, E.S.; Chiechi, A.; Korman, A.J.; Patil, R.; Klymyshyn, D.; Tourtellotte, W.G.; Israel, L.L.; Braubach, O.; et al. Blood-brain barrier permeable nano immunoconjugates induce local immune responses for glioma therapy. Nat Commun 2019, 10, 3850. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reardon, D.A.; Gokhale, P.C.; Klein, S.R.; Ligon, K.L.; Rodig, S.J.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; Jones, K.L.; Conway, A.S.; Liao, X.; Zhou, J.; et al. Glioblastoma Eradication Following Immune Checkpoint Blockade in an Orthotopic, Immunocompetent Model. Cancer Immunol Res 2016, 4, 124–135. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Tang, L.; Li, X.; Fan, F.; Liu, Z. Immunotherapy for glioma: Current management and future application. Cancer Lett 2020, 476, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghouzlani, A.; Kandoussi, S.; Tall, M.; Reddy, K.P.; Rafii, S.; Badou, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Human Glioma Microenvironment. Front Immunol 2021, 12, 679425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Malley, D.M.; Randall, L.M.; Jackson, C.G.; Coleman, R.L.; Hays, J.L.; Moore, K.N.; Naumann, R.W.; Rocconi, R.P.; Slomovitz, B.M.; Tewari, K.S.; et al. RaPiDS (GOG-3028): randomized Phase II study of balstilimab alone or in combination with zalifrelimab in cervical cancer. Future Oncol 2021, 17, 3433–3443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Perets, R.; Bar, J.; Rasco, D.W.; Ahn, M.J.; Yoh, K.; Kim, D.W.; Nagrial, A.; Satouchi, M.; Lee, D.H.; Spigel, D.R.; et al. Safety and efficacy of quavonlimab, a novel anti-CTLA-4 antibody (MK-1308), in combination with pembrolizumab in first-line advanced non-small-cell lung cancer. Ann Oncol 2021, 32, 395–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodges, T.R.; Ott, M.; Xiu, J.; Gatalica, Z.; Swensen, J.; Zhou, S.; Huse, J.T.; de Groot, J.; Li, S.; Overwijk, W.W.; et al. Mutational burden, immune checkpoint expression, and mismatch repair in glioma: implications for immune checkpoint immunotherapy. Neuro Oncol 2017, 19, 1047–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omuro, A.; Vlahovic, G.; Lim, M.; Sahebjam, S.; Baehring, J.; Cloughesy, T.; Voloschin, A.; Ramkissoon, S.H.; Ligon, K.L.; Latek, R.; et al. Nivolumab with or without ipilimumab in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: results from exploratory phase I cohorts of CheckMate 143. Neuro Oncol 2018, 20, 674–686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Carter, T.; Shaw, H.; Cohn-Brown, D.; Chester, K.; Mulholland, P. Ipilimumab and Bevacizumab in Glioblastoma. Clin Oncol (R Coll Radiol) 2016, 28, 622-626. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Youssef, G.; Dietrich, J. Ipilimumab: an investigational immunotherapy for glioblastoma. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2020, 29, 1187–1193. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fathi, M.; Razavi, S.M.; Sojoodi, M.; Ahmadi, A.; Ebrahimi, F.; Namdar, A.; Hojjat-Farsangi, M.; Gholamin, S.; Jadidi-Niaragh, F. Targeting the CTLA-4/B7 axes in glioblastoma: preclinical evidence and clinical interventions. Expert Opin Ther Targets 2022, 26, 949–961. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamid, O.; Robert, C.; Daud, A.; Hodi, F.S.; Hwu, W.J.; Kefford, R.; Wolchok, J.D.; Hersey, P.; Joseph, R.W.; Weber, J.S.; et al. Safety and tumor responses with lambrolizumab (anti-PD-1) in melanoma. N Engl J Med 2013, 369, 134–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reck, M.; Rodriguez-Abreu, D.; Robinson, A.G.; Hui, R.; Csoszi, T.; Fulop, A.; Gottfried, M.; Peled, N.; Tafreshi, A.; Cuffe, S.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus Chemotherapy for PD-L1-Positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. N Engl J Med 2016, 375, 1823–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Berghoff, A.S.; Kiesel, B.; Widhalm, G.; Rajky, O.; Ricken, G.; Wohrer, A.; Dieckmann, K.; Filipits, M.; Brandstetter, A.; Weller, M.; et al. Programmed death ligand 1 expression and tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes in glioblastoma. Neuro Oncol 2015, 17, 1064–1075. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Awada, G.; Ben Salama, L.; De Cremer, J.; Schwarze, J.K.; Fischbuch, L.; Seynaeve, L.; Du Four, S.; Vanbinst, A.M.; Michotte, A.; Everaert, H.; et al. Axitinib plus avelumab in the treatment of recurrent glioblastoma: a stratified, open-label, single-center phase 2 clinical trial (GliAvAx). J Immunother Cancer 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reardon, D.A.; Brandes, A.A.; Omuro, A.; Mulholland, P.; Lim, M.; Wick, A.; Baehring, J.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Roth, P.; Bahr, O.; et al. Effect of Nivolumab vs Bevacizumab in Patients With Recurrent Glioblastoma: The CheckMate 143 Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol 2020, 6, 1003–1010. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nayak, L.; Molinaro, A.M.; Peters, K.; Clarke, J.L.; Jordan, J.T.; de Groot, J.; Nghiemphu, L.; Kaley, T.; Colman, H.; McCluskey, C.; et al. Randomized Phase II and Biomarker Study of Pembrolizumab plus Bevacizumab versus Pembrolizumab Alone for Patients with Recurrent Glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 2021, 27, 1048–1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bouffet, E.; Larouche, V.; Campbell, B.B.; Merico, D.; de Borja, R.; Aronson, M.; Durno, C.; Krueger, J.; Cabric, V.; Ramaswamy, V.; et al. Immune Checkpoint Inhibition for Hypermutant Glioblastoma Multiforme Resulting From Germline Biallelic Mismatch Repair Deficiency. J Clin Oncol 2016, 34, 2206–2211. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rizvi, N.A.; Hellmann, M.D.; Snyder, A.; Kvistborg, P.; Makarov, V.; Havel, J.J.; Lee, W.; Yuan, J.; Wong, P.; Ho, T.S.; et al. Cancer immunology. Mutational landscape determines sensitivity to PD-1 blockade in non-small cell lung cancer. Science 2015, 348, 124-128. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Le, D.T.; Uram, J.N.; Wang, H.; Bartlett, B.R.; Kemberling, H.; Eyring, A.D.; Skora, A.D.; Luber, B.S.; Azad, N.S.; Laheru, D.; et al. PD-1 Blockade in Tumors with Mismatch-Repair Deficiency. N Engl J Med 2015, 372, 2509–2520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Touat, M.; Li, Y.Y.; Boynton, A.N.; Spurr, L.F.; Iorgulescu, J.B.; Bohrson, C.L.; Cortes-Ciriano, I.; Birzu, C.; Geduldig, J.E.; Pelton, K.; et al. Mechanisms and therapeutic implications of hypermutation in gliomas. Nature 2020, 580, 517–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Blake, S.J.; Yong, M.C.; Harjunpaa, H.; Ngiow, S.F.; Takeda, K.; Young, A.; O'Donnell, J.S.; Allen, S.; Smyth, M.J.; et al. Improved Efficacy of Neoadjuvant Compared to Adjuvant Immunotherapy to Eradicate Metastatic Disease. Cancer Discov 2016, 6, 1382–1399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloughesy, T.F.; Mochizuki, A.Y.; Orpilla, J.R.; Hugo, W.; Lee, A.H.; Davidson, T.B.; Wang, A.C.; Ellingson, B.M.; Rytlewski, J.A.; Sanders, C.M.; et al. Neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 immunotherapy promotes a survival benefit with intratumoral and systemic immune responses in recurrent glioblastoma. Nat Med 2019, 25, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalper, K.A.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Diez-Valle, R.; Lopez-Janeiro, A.; Porciuncula, A.; Idoate, M.A.; Inoges, S.; de Andrea, C.; Lopez-Diaz de Cerio, A.; Tejada, S.; et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab modifies the tumor immune microenvironment in resectable glioblastoma. Nat Med 2019, 25, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, J.; Chen, A.X.; Gartrell, R.D.; Silverman, A.M.; Aparicio, L.; Chu, T.; Bordbar, D.; Shan, D.; Samanamud, J.; Mahajan, A.; et al. Author Correction: Immune and genomic correlates of response to anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in glioblastoma. Nat Med 2019, 25, 1022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arrieta, V.A.; Chen, A.X.; Kane, J.R.; Kang, S.J.; Kassab, C.; Dmello, C.; Zhao, J.; Burdett, K.B.; Upadhyayula, P.S.; Lee-Chang, C.; et al. ERK1/2 phosphorylation predicts survival following anti-PD-1 immunotherapy in recurrent glioblastoma. Nat Cancer 2021, 2, 1372–1386. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, S.; Akbay, E.A.; Li, Y.Y.; Herter-Sprie, G.S.; Buczkowski, K.A.; Richards, W.G.; Gandhi, L.; Redig, A.J.; Rodig, S.J.; Asahina, H.; et al. Adaptive resistance to therapeutic PD-1 blockade is associated with upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints. Nat Commun 2016, 7, 10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Woroniecka, K.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Rhodin, K.; Kemeny, H.; Dechant, C.; Farber, S.H.; Elsamadicy, A.A.; Cui, X.; Koyama, S.; Jackson, C.; et al. T-Cell Exhaustion Signatures Vary with Tumor Type and Are Severe in Glioblastoma. Clin Cancer Res 2018, 24, 4175–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yano, H.; Andrews, L.P.; Workman, C.J.; Vignali, D.A.A. Intratumoral regulatory T cells: markers, subsets and their impact on anti-tumor immunity. Immunology 2019, 157, 232–247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shen, R.; Postow, M.A.; Adamow, M.; Arora, A.; Hannum, M.; Maher, C.; Wong, P.; Curran, M.A.; Hollmann, T.J.; Jia, L.; et al. LAG-3 expression on peripheral blood cells identifies patients with poorer outcomes after immune checkpoint blockade. Sci Transl Med 2021, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ascierto, P.A.; Melero, I.; Bhatia, S.; Bono, P.; Sanborn, R.E.; Lipson, E.J.; Callahan, M.K.; Gajewski, T.; Gomez-Roca, C.A.; Hodi, F.S.; et al. Initial efficacy of anti-lymphocyte activation gene-3 (anti-LAG-3; BMS-986016) in combination with nivolumab (nivo) in pts with melanoma (MEL) previously treated with anti-PD-1/PD-L1 therapy. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2017, 35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kraman, M.; Faroudi, M.; Allen, N.L.; Kmiecik, K.; Gliddon, D.; Seal, C.; Koers, A.; Wydro, M.M.; Batey, S.; Winnewisser, J.; et al. FS118, a Bispecific Antibody Targeting LAG-3 and PD-L1, Enhances T-Cell Activation Resulting in Potent Antitumor Activity. Clin Cancer Res 2020, 26, 3333–3344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anderson, A.C. Tim-3: an emerging target in the cancer immunotherapy landscape. Cancer Immunol Res 2014, 2, 393–398. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Zhang, X.; Yu, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhu, S.; Zhang, Y.H.; Lin, X.P.; Mou, Y.; Zhang, J. Correlation of Tim-3 expression with chemokine levels for predicting the prognosis of patients with glioblastoma. J Neuroimmunol 2021, 355, 577575. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenzadegan, M.; Nowroozi, M.R.; Fotovvat, A.; Bavandpour Baghshahi, P.; Bokaie, S.; Inanloo, S.H.; Sharifi, L. The prospect of targeting T cell immunoglobulin and mucin-domain containing-3 in renal cell carcinoma immunotherapy. Scand J Immunol 2022, 96, e13197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohsenzadegan, M.; Bavandpour, P.; Nowroozi, M.R.; Amini, E.; Kourosh-Arami, M.; Momeni, S.A.; Bokaie, S.; Sharifi, L. The Potential of T Cell Immunoglobulin and Mucin-Domain Containing-3 (Tim-3) in Designing Novel Immunotherapy for Bladder Cancer. Endocr Metab Immune Disord Drug Targets 2021, 21, 2131–2146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morad, G.; Helmink, B.A.; Sharma, P.; Wargo, J.A. Hallmarks of response, resistance, and toxicity to immune checkpoint blockade. Cell 2021, 184, 5309–5337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stone, E.L.; Pepper, M.; Katayama, C.D.; Kerdiles, Y.M.; Lai, C.Y.; Emslie, E.; Lin, Y.C.; Yang, E.; Goldrath, A.W.; Li, M.O.; et al. ICOS coreceptor signaling inactivates the transcription factor FOXO1 to promote Tfh cell differentiation. Immunity 2015, 42, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wikenheiser, D.J.; Stumhofer, J.S. ICOS Co-Stimulation: Friend or Foe? Front Immunol 2016, 7, 304. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herman, S.; Zurgil, N.; Langevitz, P.; Ehrenfeld, M.; Deutsch, M. The immunosuppressive effect of methotrexate in active rheumatoid arthritis patients vs. its stimulatory effect in nonactive patients, as indicated by cytometric measurements of CD4+T cell subpopulations. Immunological Investigations 2004, 33, 351-362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Shi, F.; Shan, A. Transcriptome profile and clinical characterization of ICOS expression in gliomas. Front Oncol 2022, 12, 946967. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, Y.; Ma, W.; Fan, W.; Ren, C.; Xu, J.; Zeng, F.; Bao, Z.; Jiang, T.; Zhao, Z. Comprehensive transcriptomic characterization reveals core genes and module associated with immunological changes via 1619 samples of brain glioma. Cell Death Dis 2021, 12, 1140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Le, K.S.; Thibult, M.L.; Just-Landi, S.; Pastor, S.; Gondois-Rey, F.; Granjeaud, S.; Broussais, F.; Bouabdallah, R.; Colisson, R.; Caux, C.; et al. Follicular B Lymphomas Generate Regulatory T Cells via the ICOS/ICOSL Pathway and Are Susceptible to Treatment by Anti-ICOS/ICOSL Therapy. Cancer Res 2016, 76, 4648–4660. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mo, L.J.; Chen, Q.M.; Zhang, X.J.; Shi, X.J.; Wei, L.L.; Zheng, D.P.; Li, H.W.; Gao, J.M.; Li, J.L.; Hu, Z.M. Depletion of regulatory T cells by anti-ICOS antibody enhances anti-tumor immunity of tumor cell vaccine in prostate cancer. Vaccine 2017, 35, 5932–5938. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, J.H.; Gunn, M.D.; Fecci, P.E.; Ashley, D.M. Brain immunology and immunotherapy in brain tumours. Nat Rev Cancer 2020, 20, 12–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kostine, M.; Mauric, E.; Tison, A.; Barnetche, T.; Barre, A.; Nikolski, M.; Rouxel, L.; Dutriaux, C.; Dousset, L.; Prey, S.; et al. Baseline co-medications may alter the anti-tumoural effect of checkpoint inhibitors as well as the risk of immune-related adverse events. Eur J Cancer 2021, 157, 474–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duerinck, J.; Schwarze, J.K.; Awada, G.; Tijtgat, J.; Vaeyens, F.; Bertels, C.; Geens, W.; Klein, S.; Seynaeve, L.; Cras, L.; et al. Intracerebral administration of CTLA-4 and PD-1 immune checkpoint blocking monoclonal antibodies in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: a phase I clinical trial. J Immunother Cancer 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villarroel-Espindola, F.; Yu, X.; Datar, I.; Mani, N.; Sanmamed, M.; Velcheti, V.; Syrigos, K.; Toki, M.; Zhao, H.; Chen, L.; et al. Spatially Resolved and Quantitative Analysis of VISTA/PD-1H as a Novel Immunotherapy Target in Human Non-Small Cell Lung Cancer. Clin Cancer Res 2018, 24, 1562–1573. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Sun, J.; Liu, L.N.; Flies, D.B.; Nie, X.; Toki, M.; Zhang, J.; Song, C.; Zarr, M.; Zhou, X.; et al. Siglec-15 as an immune suppressor and potential target for normalization cancer immunotherapy. Nat Med 2019, 25, 656–666. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wei, Y.; Ren, X.; Galbo, P.M., Jr.; Moerdler, S.; Wang, H.; Sica, R.A.; Etemad-Gilbertson, B.; Shi, L.; Zhu, L.; Tang, X.; et al. KIR3DL3-HHLA2 is a human immunosuppressive pathway and a therapeutic target. Sci Immunol 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide for glioblastoma. N Engl J Med 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Akira, S.; Takeda, K. Toll-like receptor signalling. Nat Rev Immunol 2004, 4, 499–511. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barber, G.N. Cytoplasmic DNA innate immune pathways. Immunol Rev 2011, 243, 99–108. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hengel, H.; Koszinowski, U.H.; Conzelmann, K.K. Viruses know it all: new insights into IFN networks. Trends Immunol 2005, 26, 396–401. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- O'Neill, L.A.; Bowie, A.G. Sensing and signaling in antiviral innate immunity. Curr Biol 2010, 20, R328–333. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, B.S.; Rautela, J.; Hertzog, P.J. Antitumour actions of interferons: implications for cancer therapy. Nat Rev Cancer 2016, 16, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schroder, K.; Hertzog, P.J.; Ravasi, T.; Hume, D.A. Interferon-gamma: an overview of signals, mechanisms and functions. J Leukoc Biol 2004, 75, 163–189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takeuchi, O.; Akira, S. Pattern recognition receptors and inflammation. Cell 2010, 140, 805–820. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rampling, R.; Cruickshank, G.; Papanastassiou, V.; Nicoll, J.; Hadley, D.; Brennan, D.; Petty, R.; MacLean, A.; Harland, J.; McKie, E.; et al. Toxicity evaluation of replication-competent herpes simplex virus (ICP 34. 5 null mutant 1716) in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. Gene therapy 2000, 7, 859–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Markert, J.M.; Liechty, P.G.; Wang, W.; Gaston, S.; Braz, E.; Karrasch, M.; Nabors, L.B.; Markiewicz, M.; Lakeman, A.D.; Palmer, C.A.; et al. Phase Ib trial of mutant herpes simplex virus G207 inoculated pre-and post-tumor resection for recurrent GBM. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2009, 17, 199-207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markert, J.M.; Razdan, S.N.; Kuo, H.C.; Cantor, A.; Knoll, A.; Karrasch, M.; Nabors, L.B.; Markiewicz, M.; Agee, B.S.; Coleman, J.M.; et al. A phase 1 trial of oncolytic HSV-1, G207, given in combination with radiation for recurrent GBM demonstrates safety and radiographic responses. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2014, 22, 1048-1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Whisenhunt, T.R., Jr.; Rajneesh, K.F.; Hackney, J.R.; Markert, J.M. Extended disease-free interval of 6 years in a recurrent glioblastoma multiforme patient treated with G207 oncolytic viral therapy. Oncolytic virotherapy 2015, 4, 33–38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Miller, K.E.; Cassady, K.A.; Roth, J.C.; Clements, J.; Schieffer, K.M.; Leraas, K.; Miller, A.R.; Prasad, N.; Leavenworth, J.W.; Aban, I.B.; et al. Immune Activity and Response Differences of Oncolytic Viral Therapy in Recurrent Glioblastoma: Gene Expression Analyses of a Phase IB Study. Clinical cancer research : an official journal of the American Association for Cancer Research 2022, 28, 498-506. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todo, T.; Ito, H.; Ino, Y.; Ohtsu, H.; Ota, Y.; Shibahara, J.; Tanaka, M. Intratumoral oncolytic herpes virus G47∆ for residual or recurrent glioblastoma: a phase 2 trial. Nature medicine 2022, 28, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Markert, J.M.; Cody, J.J.; Parker, J.N.; Coleman, J.M.; Price, K.H.; Kern, E.R.; Quenelle, D.C.; Lakeman, A.D.; Schoeb, T.R.; Palmer, C.A.; et al. Preclinical evaluation of a genetically engineered herpes simplex virus expressing interleukin-12. Journal of virology 2012, 86, 5304–5313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatzmann, D.; Valery, C.A.; Bensimon, G.; Marro, B.; Boyer, O.; Mokhtari, K.; Diquet, B.; Salzmann, J.L.; Philippon, J. A phase I/II study of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase "suicide" gene therapy for recurrent glioblastoma. Study Group on Gene Therapy for Glioblastoma. Human gene therapy 1998, 9, 2595–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shand, N.; Weber, F.; Mariani, L.; Bernstein, M.; Gianella-Borradori, A.; Long, Z.; Sorensen, A.G.; Barbier, N. A phase 1-2 clinical trial of gene therapy for recurrent glioblastoma multiforme by tumor transduction with the herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene followed by ganciclovir. GLI328 European-Canadian Study Group. Human gene therapy 1999, 10, 2325-2335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Immonen, A.; Vapalahti, M.; Tyynela, K.; Hurskainen, H.; Sandmair, A.; Vanninen, R.; Langford, G.; Murray, N.; Yla-Herttuala, S. AdvHSV-tk gene therapy with intravenous ganciclovir improves survival in human malignant glioma: a randomised, controlled study. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2004, 10, 967-972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lang, F.F.; Conrad, C.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Yung, W.K.A.; Sawaya, R.; Weinberg, J.S.; Prabhu, S.S.; Rao, G.; Fuller, G.N.; Aldape, K.D.; et al. Phase I Study of DNX-2401 (Delta-24-RGD) Oncolytic Adenovirus: Replication and Immunotherapeutic Effects in Recurrent Malignant Glioma. Journal of clinical oncology : official journal of the American Society of Clinical Oncology 2018, 36, 1419-1427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shimizu, Y.; Gumin, J.; Gao, F.; Hossain, A.; Shpall, E.J.; Kondo, A.; Parker Kerrigan, B.C.; Yang, J.; Ledbetter, D.; Fueyo, J.; et al. Characterization of patient-derived bone marrow human mesenchymal stem cells as oncolytic virus carriers for the treatment of glioblastoma. Journal of neurosurgery 2022, 136, 757–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forsyth, P.; Roldan, G.; George, D.; Wallace, C.; Palmer, C.A.; Morris, D.; Cairncross, G.; Matthews, M.V.; Markert, J.; Gillespie, Y.; et al. A phase I trial of intratumoral administration of reovirus in patients with histologically confirmed recurrent malignant gliomas. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2008, 16, 627-632. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kicielinski, K.P.; Chiocca, E.A.; Yu, J.S.; Gill, G.M.; Coffey, M.; Markert, J.M. Phase 1 clinical trial of intratumoral reovirus infusion for the treatment of recurrent malignant gliomas in adults. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2014, 22, 1056-1062. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freeman, A.I.; Zakay-Rones, Z.; Gomori, J.M.; Linetsky, E.; Rasooly, L.; Greenbaum, E.; Rozenman-Yair, S.; Panet, A.; Libson, E.; Irving, C.S.; et al. Phase I/II trial of intravenous NDV-HUJ oncolytic virus in recurrent glioblastoma multiforme. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2006, 13, 221-228. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todo, T.; Rabkin, S.D.; Martuza, R.L. Evaluation of ganciclovir-mediated enhancement of the antitumoral effect in oncolytic, multimutated herpes simplex virus type 1 (G207) therapy of brain tumors. Cancer gene therapy 2000, 7, 939–946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Germano, I.M.; Fable, J.; Gultekin, S.H.; Silvers, A. Adenovirus/herpes simplex-thymidine kinase/ganciclovir complex: preliminary results of a phase I trial in patients with recurrent malignant gliomas. Journal of neuro-oncology 2003, 65, 279-289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollmann, G.; Ozduman, K.; van den Pol, A.N. Oncolytic virus therapy for glioblastoma multiforme: concepts and candidates. Cancer J 2012, 18, 69–81. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parker, J.N.; Bauer, D.F.; Cody, J.J.; Markert, J.M. Oncolytic viral therapy of malignant glioma. Neurotherapeutics 2009, 6, 558–569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patel, D.M.; Foreman, P.M.; Nabors, L.B.; Riley, K.O.; Gillespie, G.Y.; Markert, J.M. Design of a Phase I Clinical Trial to Evaluate M032, a Genetically Engineered HSV-1 Expressing IL-12, in Patients with Recurrent/Progressive Glioblastoma Multiforme, Anaplastic Astrocytoma, or Gliosarcoma. Hum Gene Ther Clin Dev 2016, 27, 69–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- McKie, E.A.; MacLean, A.R.; Lewis, A.D.; Cruickshank, G.; Rampling, R.; Barnett, S.C.; Kennedy, P.G.; Brown, S.M. Selective in vitro replication of herpes simplex virus type 1 (HSV-1) ICP34.5 null mutants in primary human CNS tumours--evaluation of a potentially effective clinical therapy. Br J Cancer 1996, 74, 745-752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hunter, W.D.; Martuza, R.L.; Feigenbaum, F.; Todo, T.; Mineta, T.; Yazaki, T.; Toda, M.; Newsome, J.T.; Platenberg, R.C.; Manz, H.J.; et al. Attenuated, replication-competent herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant G207: safety evaluation of intracerebral injection in nonhuman primates. Journal of virology 1999, 73, 6319–6326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mineta, T.; Rabkin, S.D.; Yazaki, T.; Hunter, W.D.; Martuza, R.L. Attenuated multi-mutated herpes simplex virus-1 for the treatment of malignant gliomas. Nature medicine 1995, 1, 938–943. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sundaresan, P.; Hunter, W.D.; Martuza, R.L.; Rabkin, S.D. Attenuated, replication-competent herpes simplex virus type 1 mutant G207: safety evaluation in mice. Journal of virology 2000, 74, 3832–3841. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, F.F.; Conrad, C.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Tufaro, F.; Yung, W.K.A.; Sawaya, R.; Weinberg, J.; Prabhu, S.; Fuller, G.; Aldape, K.; et al. First-in-Human Phase I Clinical Trial of Oncolytic Delta-24-Rgd (Dnx-2401) with Biological Endpoints: Implications for Viro- Immunotherapy. Neuro Oncol. 2014, 16 (Suppl 3), iii39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Klatzmann, D.; Valéry, C.A.; Bensimon, G.; Marro, B.; Boyer, O.; Mokhtari, K.; Diquet, B.; Salzmann, J.L.; Philippon, J. A phase I/II study of herpes simplex virus type 1 thymidine kinase "suicide" gene therapy for recurrent glioblastoma. Study Group on Gene Therapy for Glioblastoma. Human gene therapy 1998, 9, 2595–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smitt, P.S.; Driesse, M.; Wolbers, J.; Kros, M.; Avezaat, C. Treatment of relapsed malignant glioma with an adenoviral vector containing the herpes simplex thymidine kinase gene followed by ganciclovir. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2003, 7, 851-858. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Immonen, A.; Vapalahti, M.; Tyynelä, K.; Hurskainen, H.; Sandmair, A.; Vanninen, R.; Langford, G.; Murray, N.; Ylä-Herttuala, S. AdvHSV-tk gene therapy with intravenous ganciclovir improves survival in human malignant glioma: a randomised, controlled study. Molecular therapy : the journal of the American Society of Gene Therapy 2004, 10, 967-972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fueyo, J.; Gomez-Manzano, C.; Alemany, R.; Lee, P.S.; McDonnell, T.J.; Mitlianga, P.; Shi, Y.X.; Levin, V.A.; Yung, W.K.; Kyritsis, A.P. A mutant oncolytic adenovirus targeting the Rb pathway produces anti-glioma effect in vivo. Oncogene 2000, 19, 2–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whyte, P.; Williamson, N.M.; Harlow, E. Cellular targets for transformation by the adenovirus E1A proteins. Cell 1989, 56, 67–75. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hochberg, F.H.; Linggood, R.; Wolfson, L.; Baker, W.H.; Kornblith, P. Quality and Duration of Survival in Glioblastoma Multiforme: Combined Surgical, Radiation, and Lomustine Therapy. JAMA 1979, 241, 1016–1018. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stupp, R.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Weller, M.; Fisher, B.; Taphoorn, M.J.B.; Belanger, K.; Brandes, A.A.; Marosi, C.; Bogdahn, U.; et al. Radiotherapy plus Concomitant and Adjuvant Temozolomide for Glioblastoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2005, 352, 987–996. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Perry, J.R.; Laperriere, N.; O'Callaghan, C.J.; Brandes, A.A.; Menten, J.; Phillips, C.; Fay, M.; Nishikawa, R.; Cairncross, J.G.; Roa, W.; et al. Short-course radiation plus temozolomide in elderly patients with glioblastoma. New England Journal of Medicine 2017, 376, 1027–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Malmström, A.; Grønberg, B.H.; Marosi, C.; Stupp, R.; Frappaz, D.; Schultz, H.; Abacioglu, U.; Tavelin, B.; Lhermitte, B.; Hegi, M.E.; et al. Temozolomide versus standard 6-week radiotherapy versus hypofractionated radiotherapy in patients older than 60 years with glioblastoma: the Nordic randomised, phase 3 trial. The Lancet Oncology 2012, 13, 916–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gzell, C.; Wheeler, H.; Guo, L.; Kastelan, M.; Back, M. Elderly patients aged 65–75 years with glioblastoma multiforme may benefit from long course radiation therapy with temozolomide. Journal of Neuro-Oncology 2014, 119, 187-196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegi, M.E.; Diserens, A.-C.; Godard, S.; Dietrich, P.-Y.; Regli, L.; Ostermann, S.; Otten, P.; Van Melle, G.; de Tribolet, N.; Stupp, R. Clinical Trial Substantiates the Predictive Value of O-6-Methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase Promoter Methylation in Glioblastoma Patients Treated with Temozolomide. Clinical Cancer Research 2004, 10, 1871–1874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mir, T.; Pond, G.; Greenspoon, J.N. Outcomes in Elderly Patients with Glioblastoma Multiforme Treated with Short-Course Radiation Alone Compared to Short-Course Radiation and Concurrent and Adjuvant Temozolomide Based on Performance Status and Extent of Resection. Current Oncology 2021, 28, 2399–2408. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stupp, R.; Dietrich, P.-Y.; Kraljevic, S.O.; Pica, A.; Maillard, I.; Maeder, P.; Meuli, R.; Janzer, R.; Pizzolato, G.; Miralbell, R.; et al. Promising Survival for Patients With Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma Multiforme Treated With Concomitant Radiation Plus Temozolomide Followed by Adjuvant Temozolomide. Journal of Clinical Oncology 2002, 20, 1375–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, W.; Zhang, L.; Wei, Q.; Shao, A. O6-Methylguanine-DNA Methyltransferase (MGMT): Challenges and New Opportunities in Glioma Chemotherapy. Frontiers in Oncology 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, M.M.; Umemura, Y.; Leung, D. Bevacizumab and Glioblastoma: Past, Present, and Future Directions. The Cancer Journal 2018, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gramatzki, D.; Roth, P.; Rushing, E.J.; Weller, J.; Andratschke, N.; Hofer, S.; Korol, D.; Regli, L.; Pangalu, A.; Pless, M.; et al. Bevacizumab may improve quality of life, but not overall survival in glioblastoma: an epidemiological study. Annals of Oncology 2018, 29, 1431–1436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Swanson, K.D.; Lok, E.; Wong, E.T. An Overview of Alternating Electric Fields Therapy (NovoTTF Therapy) for the Treatment of Malignant Glioma. Current Neurology and Neuroscience Reports 2016, 16, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bokstein, F.; Blumenthal, D.; Limon, D.; Harosh, C.B.; Ram, Z.; Grossman, R. Concurrent Tumor Treating Fields (TTFields) and Radiation Therapy for Newly Diagnosed Glioblastoma: A Prospective Safety and Feasibility Study. Frontiers in Oncology 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lazaridis, L.; Schäfer, N.; Teuber-Hanselmann, S.; Blau, T.; Schmidt, T.; Oster, C.; Weller, J.; Tzaridis, T.; Pierscianek, D.; Keyvani, K.; et al. Tumour Treating Fields (TTFields) in combination with lomustine and temozolomide in patients with newly diagnosed glioblastoma. Journal of Cancer Research and Clinical Oncology 2020, 146, 787–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, P.A.; Gaal, J.T.; Strebe, J.K.; Pasch, C.A.; Deming, D.A.; Kuo, J.S.; Robins, H.I. The effects of tumor treating fields and temozolomide in MGMT expressing and non-expressing patient-derived glioblastoma cells. J Clin Neurosci 2017, 36, 120–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stachelek, G.C.; Grimm, J.; Moore, J.; Huang, E.; Spoleti, N.; Redmond, K.J.; Lim, M.; Bettegowda, C.; Kleinberg, L. Tumor-Treating Field Arrays Do Not Reduce Target Volume Coverage for Glioblastoma Radiation Therapy. Adv Radiat Oncol 2020, 5, 62–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verhaak, R.G.; Hoadley, K.A.; Purdom, E.; Wang, V.; Qi, Y.; Wilkerson, M.D.; Miller, C.R.; Ding, L.; Golub, T.; Mesirov, J.P. Integrated genomic analysis identifies clinically relevant subtypes of glioblastoma characterized by abnormalities in PDGFRA, IDH1, EGFR, and NF1. Cancer cell 2010, 17, 98–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zeng, J.; See, A.P.; Phallen, J.; Jackson, C.M.; Belcaid, Z.; Ruzevick, J.; Durham, N.; Meyer, C.; Harris, T.J.; Albesiano, E. Anti-PD-1 blockade and stereotactic radiation produce long-term survival in mice with intracranial gliomas. International Journal of Radiation Oncology* Biology* Physics 2013, 86, 343-349. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.Y.; Zhan, Y.P.; Zong, W.J.; Yu, C.J.; Li, J.F.; Qu, Y.M.; Han, S. The PD-1/B7-H1 pathway modulates the natural killer cells versus mouse glioma stem cells. PloS one 2015, 10, e0134715. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gordon, S.; Martinez, F.O. Alternative activation of macrophages: mechanism and functions. Immunity 2010, 32, 593–604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saha, D.; Martuza, R.L.; Rabkin, S.D. Macrophage polarization contributes to glioblastoma eradication by combination immunovirotherapy and immune checkpoint blockade. Cancer cell 2017, 32, 253-267. e255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Filley, A.C.; Henriquez, M.; Dey, M. Recurrent glioma clinical trial, CheckMate-143: the game is not over yet. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 91779. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloughesy, T.F.; Mochizuki, A.Y.; Orpilla, J.R.; Hugo, W.; Lee, A.H.; Davidson, T.B.; Wang, A.C.; Ellingson, B.M.; Rytlewski, J.A.; Sanders, C.M. Neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 immunotherapy promotes a survival benefit with intratumoral and systemic immune responses in recurrent glioblastoma. Nature medicine 2019, 25, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sakuishi, K.; Apetoh, L.; Sullivan, J.M.; Blazar, B.R.; Kuchroo, V.K.; Anderson, A.C. Targeting Tim-3 and PD-1 pathways to reverse T cell exhaustion and restore anti-tumor immunity. Journal of Experimental Medicine 2010, 207, 2187–2194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Koyama, S.; Akbay, E.A.; Li, Y.Y.; Herter-Sprie, G.S.; Buczkowski, K.A.; Richards, W.G.; Gandhi, L.; Redig, A.J.; Rodig, S.J.; Asahina, H. Adaptive resistance to therapeutic PD-1 blockade is associated with upregulation of alternative immune checkpoints. Nature communications 2016, 7, 10501. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Woroniecka, K.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Rhodin, K.; Kemeny, H.; Dechant, C.; Farber, S.H.; Elsamadicy, A.A.; Cui, X.; Koyama, S.; Jackson, C. T-Cell Exhaustion Signatures Vary with Tumor Type and Are Severe in GlioblastomaT-Cell Exhaustion Signatures in Glioblastoma. Clinical Cancer Research 2018, 24, 4175–4186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bagley, S.J.; Desai, A.S.; Linette, G.P.; June, C.H.; O’Rourke, D.M. CAR T-cell therapy for glioblastoma: recent clinical advances and future challenges . Neuro-oncology 2018, 20, 1429-1438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Porter, D.L.; Levine, B.L.; Kalos, M.; Bagg, A.; June, C.H. Chimeric antigen receptor–modified T cells in chronic lymphoid leukemia. N engl j Med 2011, 365, 725–733. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maude, S.L.; Frey, N.; Shaw, P.A.; Aplenc, R.; Barrett, D.M.; Bunin, N.J.; Chew, A.; Gonzalez, V.E.; Zheng, Z.; Lacey, S.F. Chimeric antigen receptor T cells for sustained remissions in leukemia. New England Journal of Medicine 2014, 371, 1507–1517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grupp, S.A.; Kalos, M.; Barrett, D.; Aplenc, R.; Porter, D.L.; Rheingold, S.R.; Teachey, D.T.; Chew, A.; Hauck, B.; Wright, J.F. Chimeric antigen receptor–modified T cells for acute lymphoid leukemia. New England Journal of Medicine 2013, 368, 1509–1518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- !!! INVALID CITATION !!! [15,16].
- Saikali, S.; Avril, T.; Collet, B.; Hamlat, A.; Bansard, J.-Y.; Drenou, B.; Guegan, Y.; Quillien, V. Expression of nine tumour antigens in a series of human glioblastoma multiforme: interest of EGFRvIII, IL-13Rα2, gp100 and TRP-2 for immunotherapy. Journal of neuro-oncology 2007, 81, 139-148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sampson, J.H.; Archer, G.E.; Mitchell, D.A.; Heimberger, A.B.; Bigner, D.D. Tumor-specific immunotherapy targeting the EGFRvIII mutation in patients with malignant glioma. In Proceedings of the Seminars in immunology; 2008; pp. 267–275. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, X.; Prasad, S.; Gaedicke, S.; Hettich, M.; Firat, E.; Niedermann, G. Patient-derived glioblastoma stem cells are killed by CD133-specific CAR T cells but induce the T cell aging marker CD57. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Heimberger, A.B.; Sun, W.; Hussain, S.F.; Dey, M.; Crutcher, L.; Aldape, K.; Gilbert, M.; Hassenbusch, S.J.; Sawaya, R.; Schmittling, B. Immunological responses in a patient with glioblastoma multiforme treated with sequential courses of temozolomide and immunotherapy: case study. Neuro-oncology 2008, 10, 98-103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhowmik, A.; Khan, R.; Ghosh, M.K. Blood brain barrier: a challenge for effectual therapy of brain tumors. BioMed research international 2015. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Okada, H.; Kalinski, P.; Ueda, R.; Hoji, A.; Kohanbash, G.; Donegan, T.E.; Mintz, A.H.; Engh, J.A.; Bartlett, D.L.; Brown, C.K. Induction of CD8+ T-cell responses against novel glioma–associated antigen peptides and clinical activity by vaccinations with α-type 1 polarized dendritic cells and polyinosinic-polycytidylic acid stabilized by lysine and carboxymethylcellulose in patients with recurrent malignant glioma. Journal of clinical oncology 2011, 29, 330. [Google Scholar]
- Yang, T.; Kong, Z.; Ma, W. PD-1/PD-L1 immune checkpoint inhibitors in glioblastoma: Clinical studies, challenges and potential. Human Vaccines & Immunotherapeutics 2021, 17, 546-553. [Google Scholar]
- O’Rourke, D.M.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Desai, A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Mansfield, K.; Morrissette, J.J.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Brem, S.; Maloney, E.; Shen, A. A single dose of peripherally infused EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Science translational medicine 2017, 9, eaaa0984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, E.A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Lacey, S.F.; Ambrose, D.E.; Gonzalez, V.; Levine, B.L.; June, C.H.; Schuster, S.J. PD-1 blockade modulates chimeric antigen receptor (CAR)–modified T cells: refueling the CAR. Blood, The Journal of the American Society of Hematology 2017, 129, 1039-1041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maes, W.; Van Gool, S.W. Experimental immunotherapy for malignant glioma: lessons from two decades of research in the GL261 model. Cancer immunology, immunotherapy 2011, 60, 153-160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Han, S.; Feng, S.; Xu, L.; Shi, W.; Wang, X.; Wang, H.; Yu, C.; Dong, T.; Xu, M.; Liang, G. Tim-3 on peripheral CD4+ and CD8+ T cells is involved in the development of glioma. DNA and cell biology 2014, 33, 245–250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, G.; Wang, Z.; Zhang, C.; Liu, X.; Cai, J.; Wang, Z.; Hu, H.; Wu, F.; Bao, Z.; Liu, Y. Molecular and clinical characterization of TIM-3 in glioma through 1,024 samples. Oncoimmunology 2017, 6, e1328339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Granier, C.; De Guillebon, E.; Blanc, C.; Roussel, H.; Badoual, C.; Colin, E.; Saldmann, A.; Gey, A.; Oudard, S.; Tartour, E. Mechanisms of action and rationale for the use of checkpoint inhibitors in cancer. ESMO open 2017, 2, e000213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Harris-Bookman, S.; Mathios, D.; Martin, A.M.; Xia, Y.; Kim, E.; Xu, H.; Belcaid, Z.; Polanczyk, M.; Barberi, T.; Theodros, D. Expression of LAG-3 and efficacy of combination treatment with anti-LAG-3 and anti-PD-1 monoclonal antibodies in glioblastoma. International journal of cancer 2018, 143, 3201–3208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rutledge, W.C.; Kong, J.; Gao, J.; Gutman, D.A.; Cooper, L.A.; Appin, C.; Park, Y.; Scarpace, L.; Mikkelsen, T.; Cohen, M.L. Tumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Glioblastoma Are Associated with Specific Genomic Alterations and Related to Transcriptional ClassTumor-Infiltrating Lymphocytes in Glioblastoma. Clinical Cancer Research 2013, 19, 4951–4960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Guo, G.; Guan, H.; Yu, Y.; Lu, J.; Yu, J. Challenges and potential of PD-1/PD-L1 checkpoint blockade immunotherapy for glioblastoma. 2019, 38, 1-13. Journal of Experimental & Clinical Cancer Research 2019, 38, 1–13. [Google Scholar]
- Shindo, Y.; Yoshimura, K.; Kuramasu, A.; Watanabe, Y.; Ito, H.; Kondo, T.; Oga, A.; Ito, H.; Yoshino, S.; Hazama, S. Combination immunotherapy with 4-1BB activation and PD-1 blockade enhances antitumor efficacy in a mouse model of subcutaneous tumor. Anticancer research 2015, 35, 129–136. [Google Scholar]
- Croft, M.; So, T.; Duan, W.; Soroosh, P. The significance of OX40 and OX40L to T-cell biology and immune disease. Immunological reviews 2009, 229, 173–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Munks, M.W.; Mourich, D.V.; Mittler, R.S.; Weinberg, A.D.; Hill, A.B. 4-1BB and OX40 stimulation enhance CD8 and CD4 T-cell responses to a DNA prime, poxvirus boost vaccine. Immunology 2004, 112, 559–566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Messenheimer, D.J.; Jensen, S.M.; Afentoulis, M.E.; Wegmann, K.W.; Feng, Z.; Friedman, D.J.; Gough, M.J.; Urba, W.J.; Fox, B.A. Timing of PD-1 Blockade Is Critical to Effective Combination Immunotherapy with Anti-OX40Timing Is Critical for OX40 plus PD-1 Combination. Clinical Cancer Research 2017, 23, 6165–6177. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shrimali, R.K.; Ahmad, S.; Verma, V.; Zeng, P.; Ananth, S.; Gaur, P.; Gittelman, R.M.; Yusko, E.; Sanders, C.; Robins, H. Concurrent PD-1 blockade negates the effects of OX40 agonist antibody in combination immunotherapy through inducing T-cell apoptosis. Cancer immunology research 2017, 5, 755–766. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wheeler, C.J.; Das, A.; Liu, G.; Yu, J.S.; Black, K.L. Clinical responsiveness of glioblastoma multiforme to chemotherapy after vaccination. Clinical Cancer Research 2004, 10, 5316–5326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nabors, L.B.; Portnow, J.; Ammirati, M.; Baehring, J.; Brem, H.; Butowski, N.; Fenstermaker, R.A.; Forsyth, P.; Hattangadi-Gluth, J.; Holdhoff, M. NCCN guidelines insights: central nervous system cancers, version 1. 2017. Journal of the National Comprehensive Cancer Network 2017, 15, 1331–1345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghfuri, E.; Faramarzi, M.A.; Nikfar, S.; Abdollahi, M. Nivolumab and pembrolizumab as immune-modulating monoclonal antibodies targeting the PD-1 receptor to treat melanoma. Expert review of anticancer therapy 2015, 15, 981–993. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Formenti, S.C.; Demaria, S. Combining radiotherapy and cancer immunotherapy: a paradigm shift. JNCI: Journal of the National Cancer Institute 2013, 105, 256-265. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Teng, F.; Kong, L.; Meng, X.; Yang, J.; Yu, J. Radiotherapy combined with immune checkpoint blockade immunotherapy: achievements and challenges. Cancer letters 2015, 365, 23–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fisher, J.P.; Adamson, D.C. Current FDA-Approved Therapies for High-Grade Malignant Gliomas. Biomedicines 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Burgman, B.; Wu, E.; Huang, J.H.; Sahni, N.; Yi, S.S. i-Modern: Integrated multi-omics network model identifies potential therapeutic targets in glioma by deep learning with interpretability. Computational and Structural Biotechnology Journal 2022, 20, 3511–3521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, X.; Burgman, B.; Sahni, N.; Yi, S.S. Deep learning based on multi-omics integration identifies potential therapeutic targets in breast cancer. bioRxiv 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, B.; Liu, Y.; Pan, X.; Li, M.; Yang, S.; Li, S.C. DNA methylation markers for pan-cancer prediction by deep learning. Genes 2019, 10, 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, F.; Kovács, I.A.; Barabási, A.-L. Network-based prediction of drug combinations. Nature communications 2019, 10, 1197. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ianevski, A.; Giri, A.K.; Gautam, P.; Kononov, A.; Potdar, S.; Saarela, J.; Wennerberg, K.; Aittokallio, T. Prediction of drug combination effects with a minimal set of experiments. Nature machine intelligence 2019, 1, 568–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
| Project name | Target | Clinic Phase |
Start Date | Estimated or Actual Completion Date |
Estimated or actual Enrollment |
Status |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT00730613 | IL-13Rα2 | Phase 1 | Feb-02, 2002 | Aug-11, 2011 | 3 participants | done |
| NCT01082926 | IL-13Rα2 | Phase 1 | May-10, 2010 | Sep-1, 2013 | 6 participants | done |
| NCT02208362 | IL-13Rα2 | Phase 1 | May-15, 2015 | Jun-18, 2023 | 82 participants | going |
| NCT04003649 | IL-13Rα2 | Phase 1 | Dec-19, 2019 | Dec-31, 2023 | 60 participants | going |
| NCT02209376 | EGFRvIII | Phase 1 | Nov-14, 2014 | Apr-1, 2018 | 11 participants | done |
| NCT01454596 | EGFRvIII | Phase 1 | May-12, 2012 | May-1, 2012 | 18 participants | done |
| NCT03726515 | EGFRvIII | Phase 1 | Mar-11, 2019 | Feb-27, 2021 | 7 participants | done |
| NCT05024175 | EGFRvIII and EGFR | Phase 1 | Dec-1, 2021 | Aug-1, 2039 | 18 participants | going |
| NCT05168423 | EGFR and IL13Rα2 | Phase 1 | Mar-19, 2023 | Dec-19, 2029 | 18 participants | going |
| NCT01109095 | HER2 | Phase 1 | Oct-1, 2010 | Mar-1, 2018 | 16 participants | done |
| NCT03389230 | HER2 | Phase 1 | Aug-14, 2018 | Dec-15, 2023 | 42 participants | going |
| NCT03383978 | HER2 | Phase 1 | Dec-1, 2017 | Dec-31, 2023 | 42 participants | going |
| NCT04045847 | CD147 | Phase 1 | Oct-30, 2020 | May-30, 2022 | 31 participants | Unknown |
| NCT05627323 | MMP2 | Phase 1 | Feb-1, 2023 | Jan-1, 2041 | 42 participants | going |
| NCT04214392 | MMP2 | Phase 1 | Feb-26, 2020 | Feb-26, 2020 | 36 participants | going |
| NCT04385173 | B7-H3 | Phase 1 | Dec-1, 2022 | May-1, 2024 | 12 participants | going |
| NCT05241392 | B7-H3 | Phase 1 | Jan-27, 2022 | Dec-31, 2024 | 30 participants | going |
| NCT04077866 | B7-H3 | Phase 1/2 | Jun-1, 2023 | Aug-1, 2025 | 40 participants | going |
| NCT05366179 | B7-H3 | Phase 1 | Sep-2, 2022 | May, 2030 | 36 participants | going |
| NCT05474378 | B7-H3 | Phase 1 | Jul-12, 2022 | Aug-1, 2025 | 39 participants | |
| NCT05353530 | CD70 | Phase 1 | Oct-1, 2022 | Dec, 2040 | 18 participants | going |
| NCT04717999 | NKG2D | Unknown | Sep-1, 2021 | Dec-21, 2023 | 20 participants | going |
| Clinical Trail | Phase | Interventions | Arms | Combined Therapy |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| NCT05700955 | I | Drug: pembrolizumab and TMZ | Single arm: neoadjuvant pembrolizumab + TMZ | Neoadjuvant chemotherapy |
| NCT03661723 | II | Drug: pembrolizumab, bevacizumab Radiation: re-RT |
Arm 1: pembrolizumab + RT (lead-in) Arm 2: pembrolizumab + bevacizumab + RT (lead-in) Arm 3: pembrolizumab + RT Arm 4: pembrolizumab + bevacizumab + RT |
Adjusted RT, VEGFA inhibitor |
| NCT03743662 | II | Drug: pembrolizumab, bevacizumab Radiation: re-RT Procedure: re-resection |
Arm 1: re-RT + bevacizumab + Nivolumab Arm 2: re-RT + bevacizumab + Nivolumab + re-resection |
re-RT, bevacizumab, re-resection |
| NCT04977375 | I/II | Drug: pembrolizumab radiation: stereotactic RT |
Single arm: pembrolizumab + stereotactic RT + surgical resection | Stereotactic RT |
| NCT02866747 | I/II | Drug: durvalumab Radiation: HFSRT |
Arm 1: RT alone Arm 2: RT + durvalumab |
HFSRT |
| NCT02829931 | I | Radiation: HFSRT Drug: nivolumab, bevacizumab, ipilimumab |
Single arm: HFSRT + ipilimumab + nivolumab + bevacizumab | VEGFA, CTLA-4 inhibitors, HFSRT |
| NCT03722342 | I | Drug: TTAC-0001, pembrolizumab | Arm 1: TTAC-0001 12 mg/kg on D1, D8 and D15 + pembrolizumab 200 mg on D1 Arm 2: TTAC-0001 16 mg/kg on D1, D8 and D15 + pembrolizumab 200 mg on D1 Arm 3: TTAC-0001 8 mg/kg on D1, D8 and D15 + pembrolizumab 200 mg on D1 |
VEGFR2 inhibitor |
| NCT02311582 | I/II | Drug: pembrolizumab Procedure: LITT |
Arm 1: pembrolizumab + LITT Arm 2: pembrolizumab only |
Thermotherapy |
| NCT03277638 | I/II | Drug: pembrolizumab Procedure: LITT |
Single arm: pembrolizumab + LITT | Thermotherapy |
| NCT03341806 | I | Drug: avelumab Procedure: LITT |
Arm 1: avelumab Arm 2: avelumab + LITT |
Thermotherapy |
| NCT03430791 | I/II | Drug: nivolumab, ipilimumab Device: TTF |
Arm 1: nivolumab + TTF Arm 2: nivolumab + ipilimumab +TTF |
CTLA-4 inhibitor, tumor treating fields |
| NCT03532295 | II | Drug: epacadostat, retifanlimab, bevacizumab Radiation: RT |
Arm 1: retifanlimab + RT + bevacizumab Arm 2: retifanlimab + RT + bevacizumab + epacadostat |
RT, VEGFA, and IDO1 inhibitor |
| NCT02794883 | II | Drug: durvalumab, tremelimumab | Arm 1: durvalumab Arm 2: durvalumab + tremelimumab Arm 3: tremelimumab |
CTLA-4 inhibitor |
| NCT03493932 | I | Drug: BMS-986016, nivolumab | Single arm: BMS-986016 + nivolumab | LAG-3 inhibitor |
| NCT02658981 | I | Drug: BMS-986016, urelumab, nivolumab | Arm 1: BMS-986016 Arm 2: BMS-986016 + nivolumab Arm 3: urelumab + nivolumab |
LAG-3, CD137 inhibitors |
| NCT05465954 | II | Drug: efineptakin alfa, pembrolizumab | Single arm: efineptakin alfa + pembrolizumab, before and after surgery | Neoadjuvant IL7 |
| NCT04201873 | I | Biological: DC tumor cell lysate vaccine Drug: pembrolizumab, poly ICLC |
Arm 1: pembrolizumab + ATL-DC + poly ICLC Arm 2: placebo + ATL-DC + poly ICLC |
DC vaccine |
| NCT04013672 | II | Drug: pembrolizumab, surVaxM, sargramostim, montanide ISA 51 | Arm 1: have not received immunotherapy Arm 2: have failed prior anti-PD1 therapy |
Peptide-based vaccine |
| NCT03665545 | I/II | Drug: IMA950/Poly-ICLC and pembrolizumab | Arm 1: IMA950/Poly-ICLC Arm 2: IMA950/Poly-ICLC + pembrolizumab |
Peptide-based vaccine |
| NCT05084430 | I/II | Drug: M032, pembrolizumab | Single arm: pembrolizumab + M032 | Oncolytic herpes simplex virus |
| NCT04479241 | II | Drug: lerapolturev, pembrolizumab | Single arm: lerapolturev + pembrolizumab | Oncolytic poliovirus |
| NCT02798406 | II | Biological: DNX-2401 Drug: pembrolizumab |
Single arm: DNX-2401 + pembrolizumab | Oncolytic adenovirus |
| NCT05463848 | II | Drug: pembrolizumab, olaparib, TMZ | Arm 1: pembrolizumab + olaparib + TMZ Arm 2: pembrolizumab monotherapy |
PARP inhibitor, chemotherapy |
| NCT02430363 | I/II | Drug: pembrolizumab Biological: suppressor of the PI3K/Akt pathways |
Single arm: pembrolizumab + suppressors of the PI3K/Akt pathways | PI3K/Akt suppressors |
| NCT05053880 | I/II | Drug: ACT001, pembrolizumab | Arm 1: pembrolizumab Arm 2: pembrolizumab+ACT001 |
PAI-1 inhibitor |
| type | Last reported | Therapy | phase | Registration number |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| DC vaccines | 2023 | Allogeneic Tumor Lysate-Pulsed Autologous Dendritic Cell Vaccination | Early Phase I | NCT03360708 |
| Peptide vaccines | 2023 | Allogeneic tumor lysate vaccine | Phase I | NCT04642937 |
| Nucleic acid vaccines | 2022 | VXM01 (DNA plasmid vaccine for VEGFR-2) and avelumab (anti-PD-L1) | Phase I/II | NCT03750071 |
| DC vaccines | 2022 | DCVax-L plus SOC | Phase III | NCT00045968 |
| DC vaccines | 2022 | Pembrolizumab With Autologous Tumor Lysate-Pulsed Dendritic Cell Vaccination | Phase I | NCT04201873 |
| DC vaccines | 2022 | mRNA tumor antigen-pulsed autologous DCs | Phase I | NCT02808364 |
| Peptide vaccines | 2022 | TAS0313 | Phase II | JapicCTI-183824 |
| Peptide vaccines | 2022 | VBI-1901 (targeting CMV antigen gB and pp65) | Phase I/II | NCT03382977 |
| DC vaccines | 2021 | Neoadjuvant PD-1 Antibody Alone or Combined With Autologous Glioblastoma Stem-like Cell Antigens-primed DC Vaccines | Phase II | NCT04888611 |
| DC vaccines | 2021 | allogeneic glioblastoma stem-like cell line-pulsed DC cell | Phase I | NCT02010606 |
| Peptide vaccines | 2021 | PEPIDH1M vaccines | Phase I | NCT02193347 |
| Peptide vaccines | 2021 | HSPPC-96 vaccine | Phase II | NCT00293423 |
| Peptide vaccines | 2021 | HSPPC-96 vaccine with bevacizumab | Phase II | NCT01814813 |
| Peptide vaccines | 2020 | Rindopepimut and bevacizumab | Phase II | NCT01498328 |
| Peptide vaccines | 2020 | HSPPC-96 vaccine | Phase I | NCT02722512 |
| DC vaccines | 2020 | Autologous tumor cell-pulsed DCs (ADCTA) | Phase III | NCT04277221 |
| Peptide vaccines | 2019 | Personalized peptide vaccination | Phase III | AMED number: 16ck0106086h0003 |
| Nucleic acid vaccines | 2019 | EGFR(V)-EDV-Dox | Phase I | NCT02766699 |
| DC vaccines | 2019 | Autologous tumor lysate-loaded DCs | Phase I | NCT04002804 |
| DC vaccines | 2019 | Tumor lysate-pulsed DCs | Phase II | NCT00576537 |
| DC vaccines | 2019 | GSC (Glioma Stem Cells) -Loaded Dendritic Cells | Phase I | NCT02820584 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





