Submitted:
27 July 2023
Posted:
27 July 2023
Read the latest preprint version here
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and methods
2.1. Plant materials
2.2. Experimental design
2.3. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Analysis of variance and heritability of parents and controls
3.2. Genetic and phenotypic correlations
| 100 seed weight (g) | Preference | Consumption (g) | Consumption (%) | |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100 seed weight (g) | 0.06 | 0.15* | 0.06 | |
| Preference | 0.30 | 0.20* | 0.20* | |
| Consumption (g) | 0.45 | 2.9 | 0.99* | |
| Consumption (%) | 0.12 | 2.7 | 0.94* |
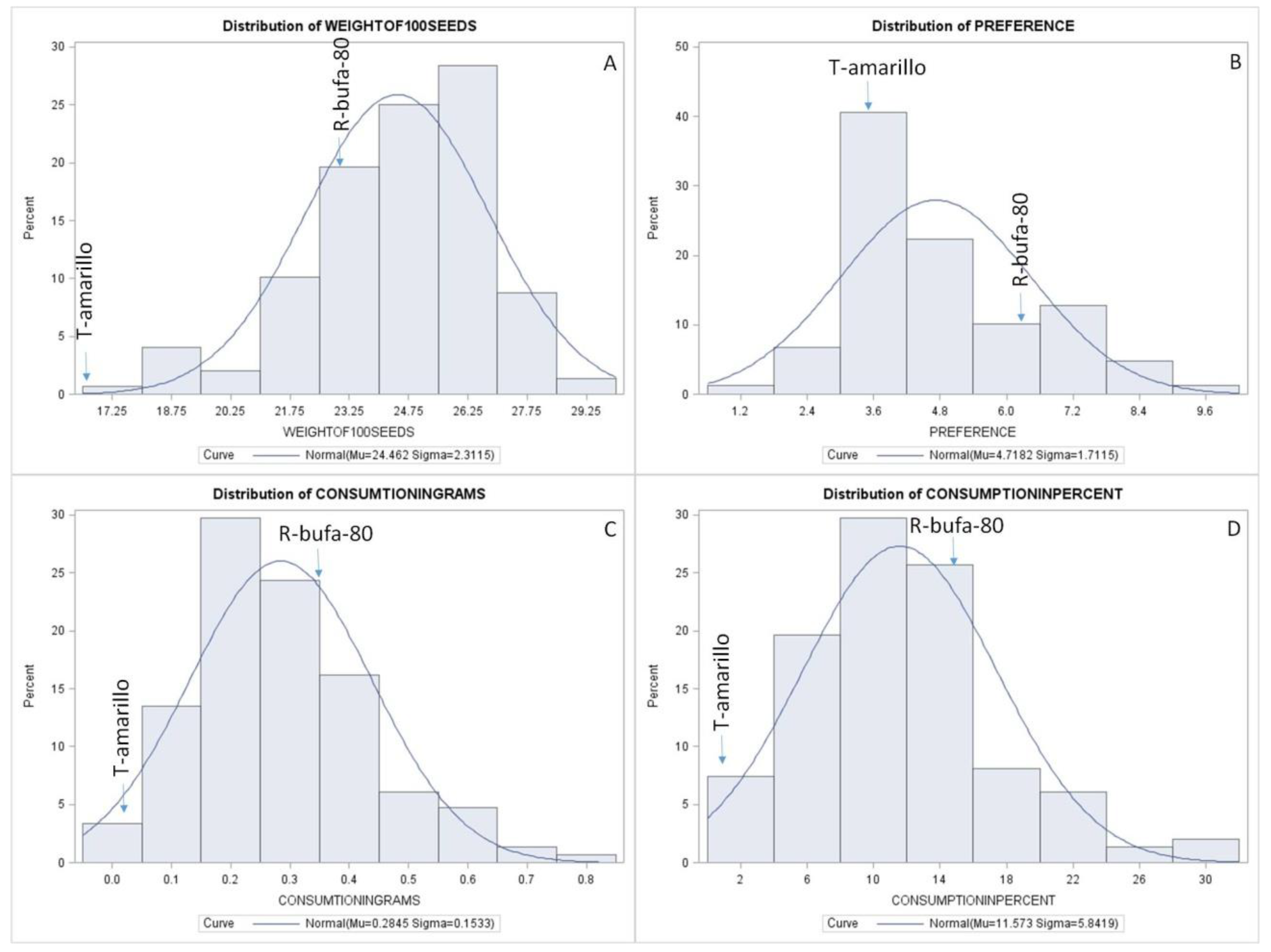
3.3. Normality analysis
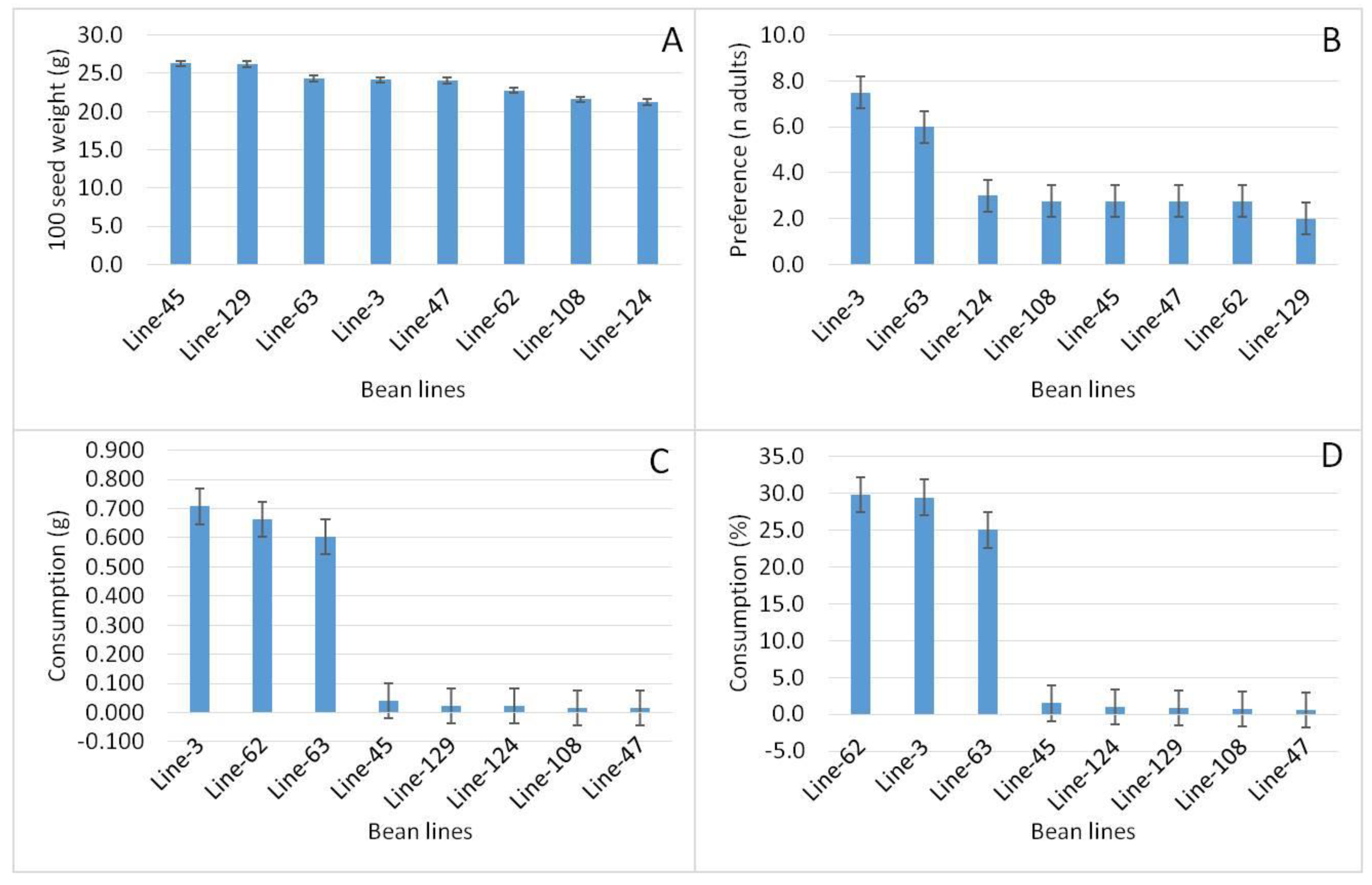
3.4. Analysis of variance for 5 best and 3 most inferior lines for resistance to A. obtectus
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Mbow, C., et al., Food security. 2019.
- Roser, M. and L. Rodés-Guirao, Future population growth. Our world in data, 2013.
- Ziegler, V., R.T. Paraginski, and C.D. Ferreira, Grain storage systems and effects of moisture, temperature and time on grain quality-A review. Journal of Stored Products Research, 2021. 91: p. 101770. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, C.D., et al., Quality of black beans as a function of long-term storage and moldy development: Chemical and functional properties of flour and isolated protein. Food Chemistry, 2018. 246: p. 473-480. [CrossRef]
- Uebersax, M.A., et al., Dry beans (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) as a vital component of sustainable agriculture and food security—A review. Legume Science, 2023. 5(1): p. e155. [CrossRef]
- Broughton, W.J., et al., Beans (Phaseolus spp.)–model food legumes. Plant and soil, 2003. 252: p. 55-128. [CrossRef]
- Ayvaz, A., et al., Insecticidal activity of the essential oils from different plants against three stored-product insects. Journal of insect science, 2010. 10(1): p. 21. [CrossRef]
- Baldin, E.L.L. and F.M. Lara, Resistance of stored bean varieties to Acanthoscelides obtectus (Coleoptera : Bruchidae). Insect Science, 2008. 15(4): p. 317-326. [CrossRef]
- Ogendo, J.O., et al., Plant-Based Products as Control Agents of Stored-Product Insect Pests in the Tropics. Progress in Food Preservation, 2012: p. 581-601. [CrossRef]
- Aidoo, K., Post-harvest storage and preservation of tropical crops. International Biodeterioration & Biodegradation, 1993. 32(1-3): p. 161-173. [CrossRef]
- Jiménez, J.C., et al., Resistance categories to Acanthoscelides obtectus (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius), new sources of resistance for dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) breeding. Crop Protection, 2017. 98: p. 255-266. [CrossRef]
- Baldin, E.L., et al., Characterization of resistance to the bean weevil Acanthoscelides obtectus Say, 1831 (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in common bean genotypes. Arthropod-Plant Interactions, 2017. 11: p. 861-870. [CrossRef]
- Mbogo, K., J. Davis, and J. Myers, Transfer of the arcelin-phytohaemagglutinin-α amylase inhibitor seed protein locus from tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius A. Gray) to common bean (P. vulgaris L.). Biotechnology, 2009. 8(3): p. 285-295. [CrossRef]
- Ebinu, J., et al., Susceptibility to bruchids among common beans in Uganda. African Crop Science Journal, 2016. 24(3): p. 289-303. [CrossRef]
- Kusolwa, P.M., Breeding for bruchid resistance in common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.): interspecific introgression of lectin-like seed proteins from tepary bean (P. acutifolius A. Gray), genetic control and bruchid resistance characterization. 2007.
- Mallqui, K.S.V., E.E. Oliveira, and R.N.C. Guedes, Competition between the bean weevils Acanthoscelides obtectus and Zabrotes subfasciatus in common beans. Journal of Stored Products Research, 2013. 55: p. 32-35. [CrossRef]
- Hernandez-Lambraño, R., et al., Essential oils from plants of the genus Cymbopogon as natural insecticides to control stored product pests. Journal of Stored Products Research, 2015. 62: p. 81-83. [CrossRef]
- Askey, J., et al., Oxygen demand of bean bruchids (Acanthoscelides obtectus Say). Journal of Stored Products and Postharvest Research, 2020. 11(2): p. 8-14.
- Li, X., et al., QTL mapping and identification of genes associated with the resistance to Acanthoscelides obtectus (Say) in cultivated common bean using a high-density genetic linkage map. 2022.
- Oliveira, M.R.C., et al., Mesoamerican origin and pre-and post-Columbian expansions of the ranges of Acanthoscelides obtectus Say, a cosmopolitan insect pest of the common bean. PloS one, 2013. 8(7): p. e70039. [CrossRef]
- Kaplin, V., Distribution and Biology of Invasive Species of Bean Bruchid Acanthoscelides obtectus (Insecta, Coleoptera, Bruchidae). Russian Journal of Biological Invasions, 2022. 13(1): p. 41-57. [CrossRef]
- Iturralde-García, R.D., et al., Biological control of Acanthoscelides obtectus and Zabrotes subfasciatus in stored dried beans. BioControl, 2020. 65(6): p. 693-701. [CrossRef]
- Kornegay, J.L. and C. Cardona, Inheritance of resistance to Acanthoscelides obtectus in a wild common bean accession crossed to commercial bean cultivars. Euphytica, 1991. 52(2): p. 103-111. [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Galindo, J.C., et al., Inheritance and metabolomics of the resistance of two F 2 populations of Phaseolus spp. to Acanthoscelides obtectus. Arthropod-Plant Interactions, 2020. 14(5): p. 641-651. [CrossRef]
- Ishimoto, M., et al., Bruchid resistance of transgenic azuki bean expressing seed alpha-amylase inhibitor of common bean. Entomologia Experimentalis Et Applicata, 1996. 79(3): p. 309-315. [CrossRef]
- Jimenez-Galindo, J.C., et al., Screening for Drought Tolerance in Tepary and Common Bean Based on Osmotic Potential Assays. Plant, 2018. 6(2): p. 24. [CrossRef]
- Jiménez Galindo, J.C. and J.A. Acosta Gallegos, Caracterización de genotipos criollos de frijol Tepari (Phaseolus acutifolius A. Gray) y común (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) bajo temporal. Revista mexicana de ciencias agrícolas, 2012. 3(8): p. 1565-1577. [CrossRef]
- Cilia García, M., et al., Effects of water restriction on carbohydrates concentration, starch granules size and amylolytic activity in seeds of Phaseolus vulgaris L. and P. acutifolius A. Gray. Botanical Sciences, 2021. 99(2): p. 364-376. [CrossRef]
- Cayetano-Marcial, M., et al., Humidity restriction, high night temperature and their combination, during post flowering on common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.) canopy and pod senescence. Legume Research-An International Journal, 2021. 44(6): p. 634-640. [CrossRef]
- Kamfwa, K., et al., QTL Mapping of Resistance to Bean Weevil in Common Bean. Crop Sci, 2018. 58: p. 1-9. [CrossRef]
- Jiménez-Galindo, J.C., et al., Fine analysis of a genomic region involved in resistance to Mediterranean corn borer. BMC plant biology, 2018. 18(1): p. 1-13. [CrossRef]
- Tuinstra, M.R., G. Ejeta, and P.B. Goldsbrough, Heterogeneous inbred family (HIF) analysis: a method for developing near-isogenic lines that differ at quantitative trait loci. Theoretical and Applied Genetics, 1997. 95(5-6): p. 1005-1011. [CrossRef]
- Singh, S.P., A key for identification of different growth habits of Phaseolus vulgaris L. 1981.
- Holland, J.B., W.E. Nyquist, and C.T. Cervantes-Martinez, Estimating and interpreting heritability for plant breeding: An update. Plant Breeding Reviews, Vol 22, 2002. 22: p. 9-112. [CrossRef]
- Holland, J.B., Estimating genotypic correlations and their standard errors using multivariate restricted maximum likelihood estimation with SAS Proc MIXED. Crop Science, 2006. 46(2): p. 642-654. [CrossRef]
- Minney, B.H., Breeding phaseolus vulgaris (common bean) for resistance to the major pest bruchids Zabrotes subfasciatus and Acanthoscelides obtectus. Biochemical bases for seed resistance in wild lines. 1990, Durham University.
- Rendón-Huerta, J.A., et al., Insecticide effect of wild plant powders on bean weevil (Zabrotes subfasciatus Boheman; Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in vitro. African Journal of Agricultural Research, 2013. 8(11): p. 971-977.
- Thakur, D., Taxonomy, distribution and pest status of Indian biotypes of Acanthoscelides obtectus (Coleoptera: Chrysomelidae: Bruchinae)-A new record. Pakistan Journal of Zoology, 2012. 44(1).
- Duan, C., et al., Genetic diversity and differentiation of A canthoscelides obtectus S ay (C oleoptera: B ruchidae) populations in C hina. Agricultural and Forest Entomology, 2017. 19(2): p. 113-121.
- Mhlaba, Z.B., et al., Variance components and heritability of yield and yield-related traits in tepary bean (Phaseolus acutifolius). South African Journal of Plant and Soil, 2019. 36(2): p. 117-128. [CrossRef]
- White, J.W., et al., Inheritance of seed yield, maturity and seed weight of common bean (Phaseolus vulgaris) under semi-arid rainfed conditions. The Journal of Agricultural Science, 1994. 122(2): p. 265-273.
- Galwey, N. and A.M. Evans, The inheritance of resistance to Empoasca kraemeri R oss & M oore in the common bean, Phaseolus vulgaris L. Euphytica, 1982. 31(3): p. 933-952.
- Kornegay, J.L. and S.R. Temple, Inheritance and Combining Ability of Leafhopper Defense Mechanisms in Common Bean 1. Crop science, 1986. 26(6): p. 1153-1158. [CrossRef]
- Gonzales, J.W., D.P. Coyne, and D.T. Lindgren, Inheritance and heritability of leafhopper resistance in common beans (Phaseolus vulgaris). ANNUAL REPORT-BEAN IMPROVEMENT COOPERATIVE, 2002. 45: p. 80-81.
- Kornegay, J., et al., Breeding for insect resistance in beans. A. Schoonhoven & O. van and Voysest (Eds.), Common Beans: Research for Crop Improvement, 1991: p. 619-648.
- Schoonhoven, A.v., C.v. Cardona, and J. Valor, Resistance to the bean weevil and the Mexican bean weevil (Coleoptera: Bruchidae) in noncultivated common bean accessions. Journal of Economic Entomology, 1983. 76(6): p. 1255-1259. [CrossRef]
- Soares, M.A., et al., Effect of temperature on the development and feeding behavior of Acanthoscelides obtectus (Chrysomelidae: Bruchinae) on dry bean (Phaseolus vulgaris L.). Journal of Stored Products Research, 2015. 61: p. 90-96.
- FAOSTAT. Statistical Database. In Food and Agriculture Organization of the United Nations; FAO: Rome, Italy, 2022. Available online: http://faostat.fao.org/(accessed on 20 May 2023).
- SAS Institute. Base SAS 9.4 Procedures Guide: Statistical Procedures. Version 9.4; SAS Institute: Cary, NC, USA, 2016.
- Hernández C. A., Mayra C. S. C., María A. F. C., Juan L. J. C., Rafael A. P. Q., and José Cruz J. G. 2021. Resistencia a Acanthoscelides obtectus en una población F2:3 de frijol P-saltillo × T-amarillo. Tesis de Licenciatura. Universidad Autónoma de Chihuahua, México.
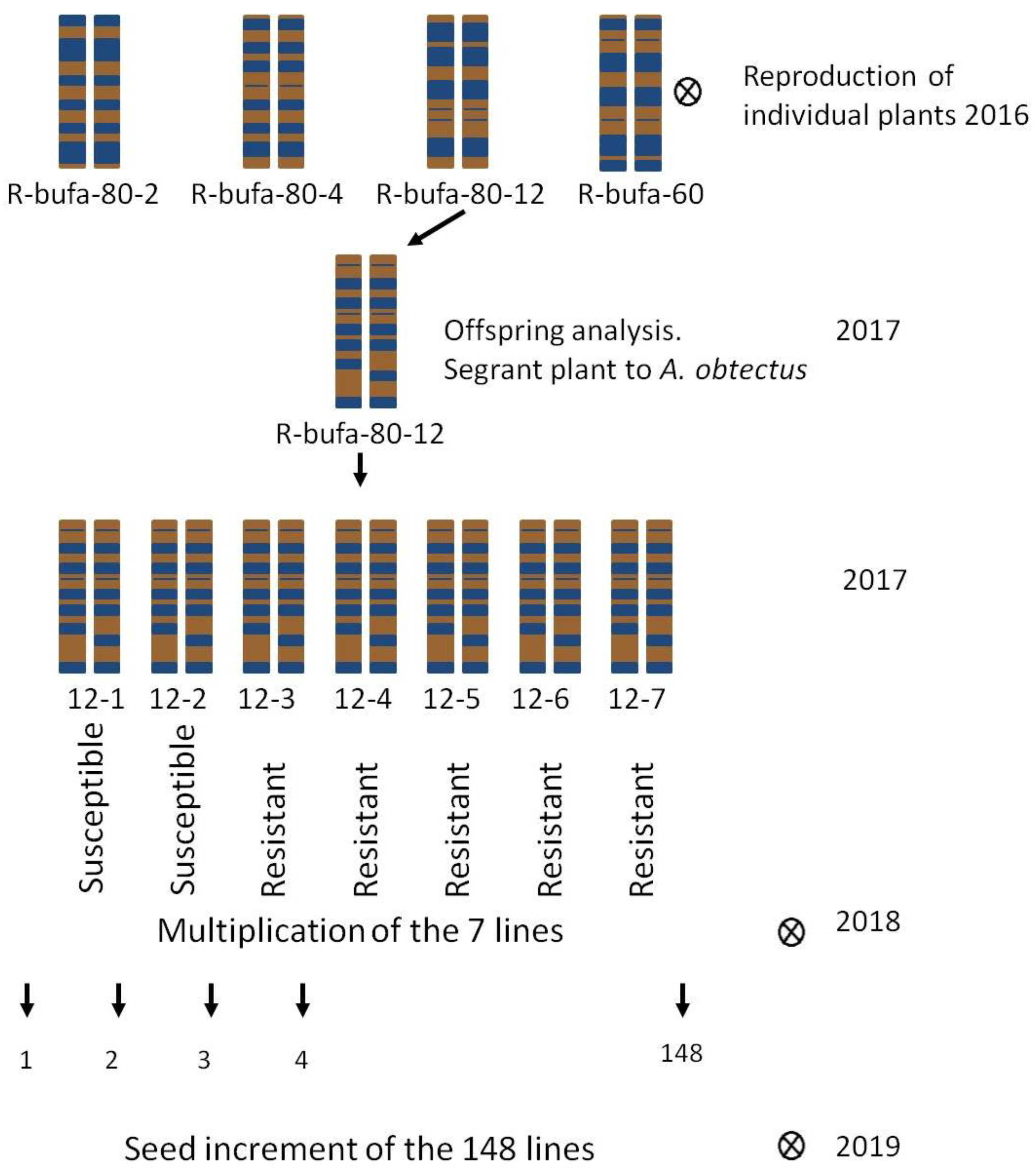
| Genotype | Species | Growth habit | Resistance level1 |
|---|---|---|---|
| R-bufa-80 | P. vulgaris | II | Susceptible |
| R-bufa-80-12 | P. vulgaris | II | Segregant |
| T-amarillo | P. acutifolius | III | Resistant |
| Seed trait | Resistance traits | |||||
| 100 seed weight | Consumption (g) | Consumption (%) | Adult preference (n) | |||
| 148 NILs | ||||||
| Media | 24.5 | 0.284 | 11.5 | 4.5 | ||
| ± SE | 0.11 | 0.01 | 0.46 | 0.21 | ||
| Rank | 17.2–29.2 | 0.0–0.8 | 2–30 | 1.2–9.6 | ||
| h2 | 0.90 | 0.19 | 0.18 | 0.08 | ||
| Parent and control | ||||||
| R-bufa-80 | 22.05 a | 0.356 a | 15.0 a | 6.37 a | ||
| T-amarillo | 13.98 b | 0.021 b | 1.47 b | 3.50 a | ||
| LSD | 1.8 | 0.273 | 11.3 | 4.3 | ||
| ± SE | 1.23 | 0.09 | 3.16 | 1.27 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





