Submitted:
25 July 2023
Posted:
26 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Part 1: Introduction
1.1. Introduction to Educational Data Mining and Machine Learning
1.2. Comparison of Classical Statistical Analysis and Machine Learning Models:
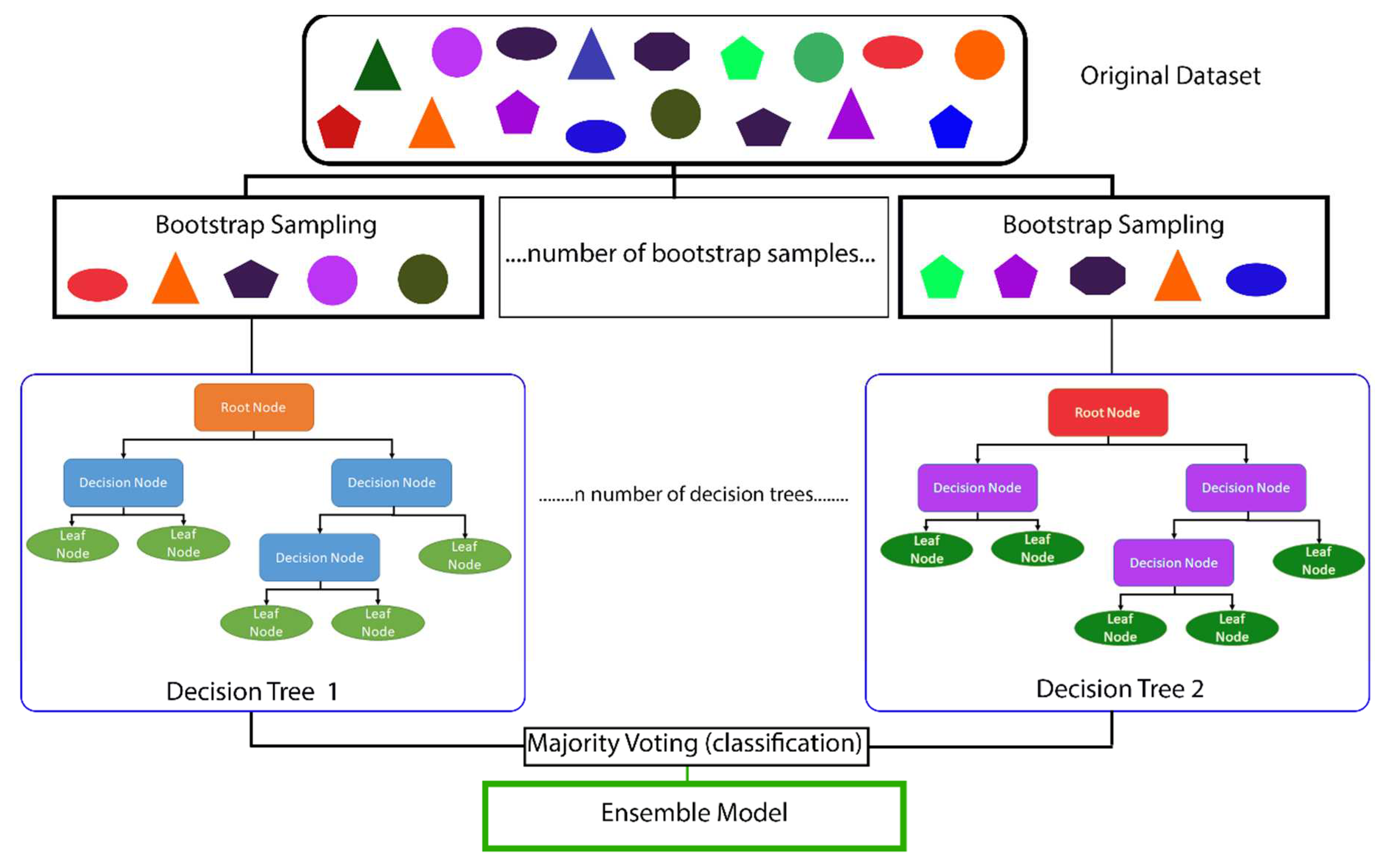
1.3. Overview of the Main Types of Machine Learning Algorithms and Random Forest Machine Learning Models:
1.4. Programming Languages and Tools:
2. Part 2: Simulation of Dataset and Creation of a Random Forest Machine Learning Model
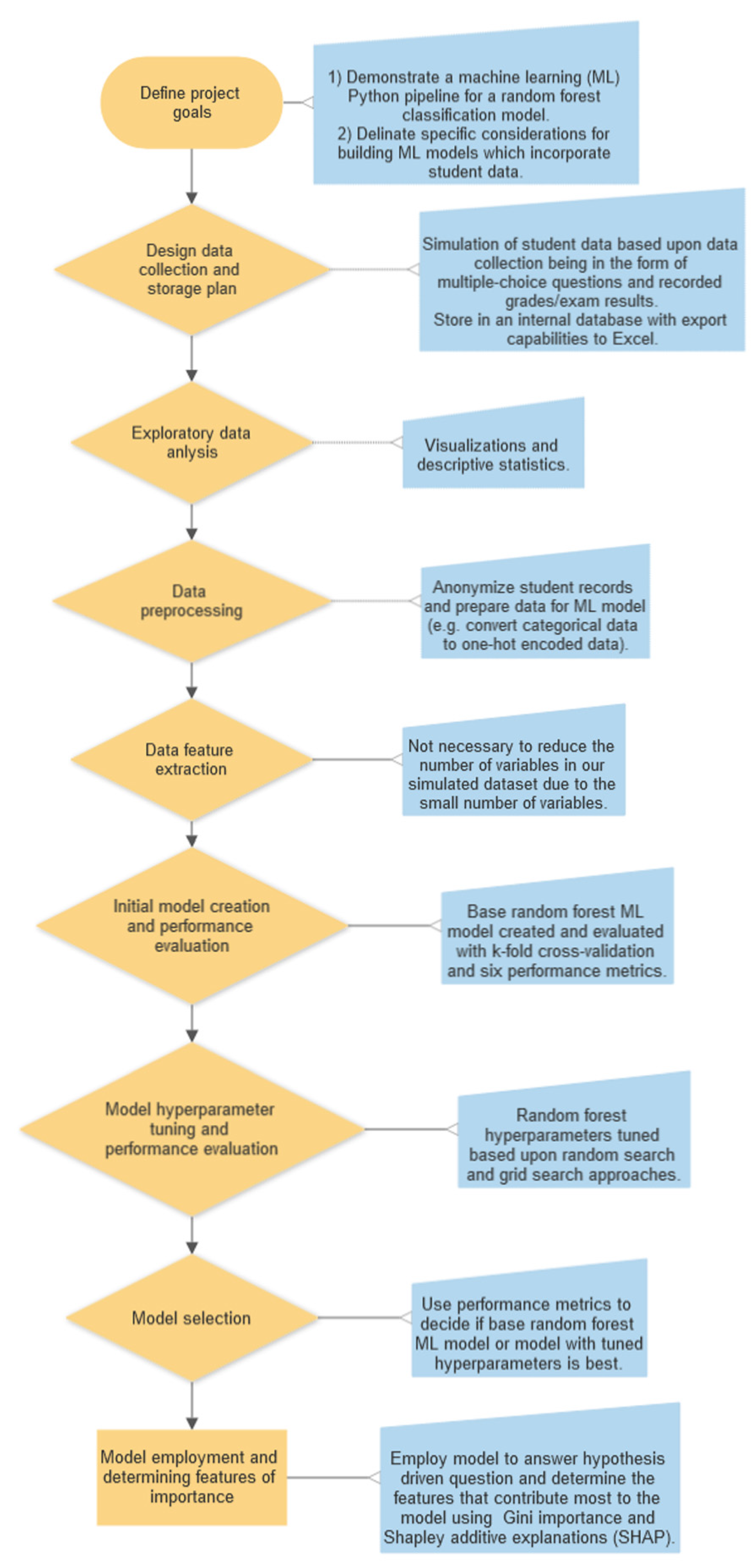
2.1. Defining the Project Goals:
2.2. Data Collection and Storage Plan
2.2.1. Simulated Data Collection and Storage:
2.2.2. Importing the Dataset:
2.3. Exploratory Data Analysis:
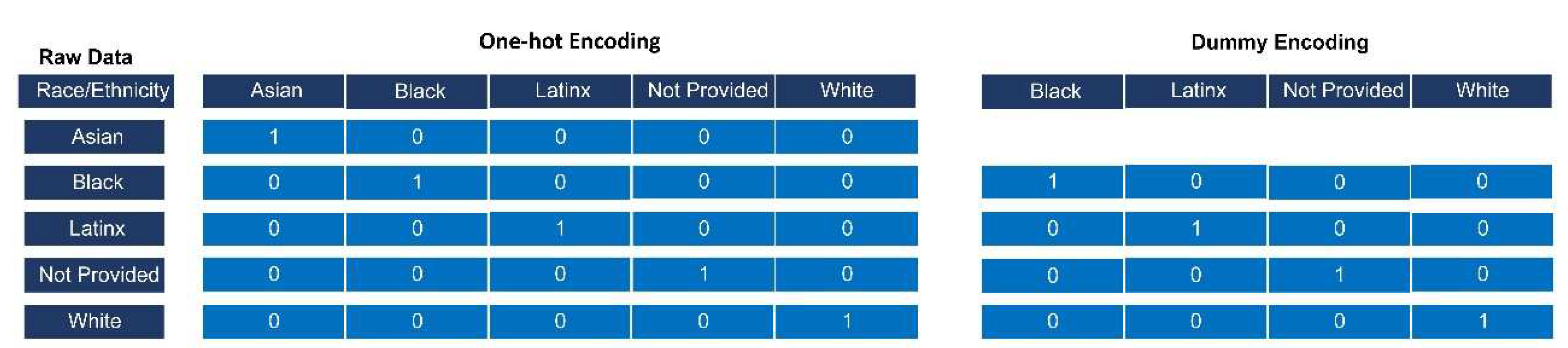
2.4. Data Preprocessing:
2.5. Data Feature Extraction:
2.6. Model Creation and Performance Evaluation:
2.6.1. Generation of Base Random Forest Model:
2.6.2. Evaluation of The Base Random Forest Model:
2.6.3. Tuning of the Random Forest Model:
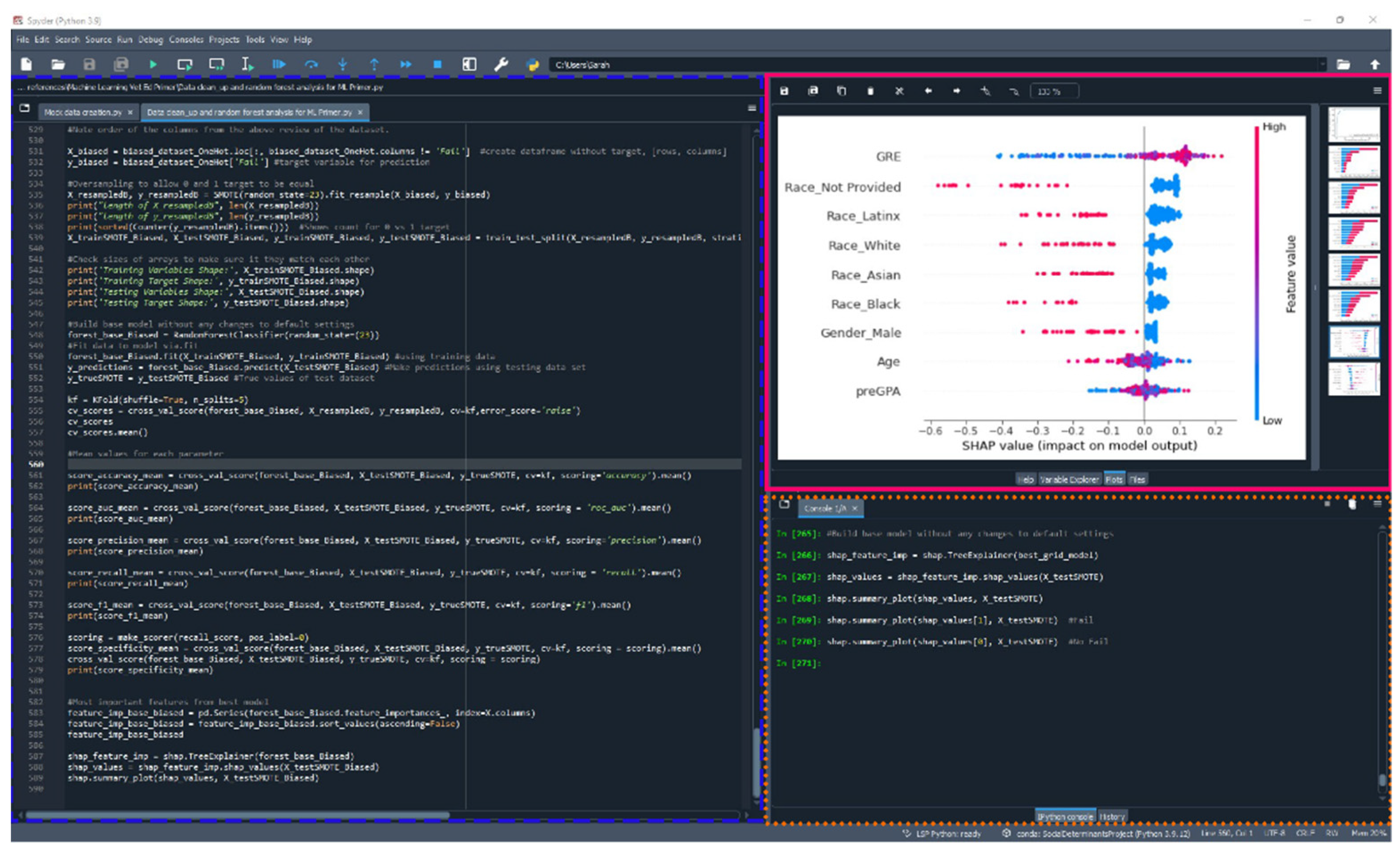
2.6.3. Determining the Most Important Features of the Random Forest Model:
3. Part 2: Results
4. Part 2: Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Basran, P.S.; Appleby, R.B. The unmet potential of artificial intelligence in veterinary medicine. American Journal of Veterinary Research 2022, 83, 385–392. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hennessey, E.; DiFazio, M.; Hennessey, R.; Cassel, N. Artificial intelligence in veterinary diagnostic imaging: A literature review. Veterinary Radiology & Ultrasound 2022, 63, 851–870. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calvet Liñán, L.; Juan Pérez, Á.A. Educational Data Mining and Learning Analytics: differences, similarities, and time evolution. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education 2015, 12, 98–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Algarni, A. Data mining in education. International Journal of Advanced Computer Science and Applications 2016, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alyahyan, E.; Düştegör, D. Predicting academic success in higher education: literature review and best practices. International Journal of Educational Technology in Higher Education 2020, 17, 1–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samuel, A.L. Some studies in machine learning using the game of checkers. IBM Journal of research and development 1959, 3, 210–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bi, Q.; Goodman, K.E.; Kaminsky, J.; Lessler, J. What is Machine Learning? A Primer for the Epidemiologist. American Journal of Epidemiology 2019, 188, 2222–2239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Von Davier, A.A.; Mislevy, R.J.; Hao, J. Introduction to Computational Psychometrics: Towards a Principled Integration of Data Science and Machine Learning Techniques into Psychometrics . In Computational Psychometrics: New Methodologies for a New Generation of Digital Learning and Assessment: With Examples in R and Python; von Davier, A.A., Mislevy, R.J., Hao, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Khamisy-Farah, R.; Gilbey, P.; Furstenau, L.B.; Sott, M.K.; Farah, R.; Viviani, M.; Bisogni, M.; Kong, J.D.; Ciliberti, R.; Bragazzi, N.L. Big Data for Biomedical Education with a Focus on the COVID-19 Era: An Integrative Review of the Literature. Int J Environ Res Public Health 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peers, I. Statistical analysis for education and psychology researchers: Tools for researchers in education and psychology; Routledge, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Nie, R.; Guo, Q.; Morin, M. Machine Learning Literacy for Measurement Professionals: A Practical Tutorial. Educational Measurement: Issues and Practice 2023, 42, 9–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Van Vertloo, L.R.; Burzette, R.G.; Danielson, J.A. Predicting Academic Difficulty in Veterinary Medicine: A Case-Control Study. J Vet Med Educ 2022, 49, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stoltzfus, J.C. Logistic Regression: A Brief Primer. Academic Emergency Medicine 2011, 18, 1099–1104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, S.; Mo, B.; Zhao, J. Theory-based residual neural networks: A synergy of discrete choice models and deep neural networks. Transportation Research Part B: Methodological 2021, 146, 333–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dass, S.; Gary, K.; Cunningham, J. Predicting Student Dropout in Self-Paced MOOC Course Using Random Forest Model. Information 2021, 12, 476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, L.; Levine, R.A.; Fan, J.; Beemer, J.; Stronach, J. Random forest as a predictive analytics alternative to regression in institutional research. Practical Assessment, Research and Evaluation 2018, 23, 1–16. [Google Scholar]
- Sarker, I.H. Machine Learning: Algorithms, Real-World Applications and Research Directions. SN Computer Science 2021, 2, 160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romero, C.; Ventura, S. Educational Data Mining: A Review of the State of the Art. IEEE Transactions on Systems, Man, and Cybernetics, Part C (Applications and Reviews) 2010, 40, 601–618. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louppe, G. Understanding random forests: From theory to practice. arXiv preprint arXiv:1407.7502 2014.
- Spoon, K.; Beemer, J.; Whitmer, J.C.; Fan, J.; Frazee, J.P.; Stronach, J.; Bohonak, A.J.; Levine, R.A. Random Forests for Evaluating Pedagogy and Informing Personalized Learning. Journal of Educational Data Mining 2016, 8, 20–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choudhary, R.; Gianey, H.K. Comprehensive Review On Supervised Machine Learning Algorithms. In Proceedings of the 2017 International Conference on Machine Learning and Data Science (MLDS), 14-15 Dec. 2017; pp. 37–43. [Google Scholar]
- Kumar, N. Advantages and Disadvantages of Random Forest Algorithm in Machine Learning. Available online: http://theprofessionalspoint.blogspot.com/2019/02/advantages-and-disadvantages-of-random.html (accessed on 11/2/2022).
- Altman, N.; Krzywinski, M. Ensemble methods: bagging and random forests. Nature Methods 2017, 14, 933–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dietterich, T.G. Ensemble Learning. In The Handbook of Brain Theory and Neural Networks: Second Edition second edition Arbib, M.A., Ed.; MIT Press: Cambridge, MA, 2002. [Google Scholar]
- Anaconda Software Distribution. v22.9.0., Oct. 2022. Available online: https://www.anaconda.com/download.
- Wang, Y.; Wen, M.; Liu, Y.; Wang, Y.; Li, Z.; Wang, C.; Yu, H.; Cheung, S.-C.; Xu, C.; Zhu, Z. Watchman: Monitoring dependency conflicts for python library ecosystem. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the ACM/IEEE 42nd International Conference on Software Engineering, 2020; pp. 125–135.
- Gudivada, V.; Apon, A.; Ding, J. Data quality considerations for big data and machine learning: Going beyond data cleaning and transformations. International Journal on Advances in Software 2017, 10, 1–20. [Google Scholar]
- Hao, J.; Mislevy, R.J. A Data Science Perspective on Computational Psychometrics. In Computational Psychometrics: New Methodologies for a New Generation of Digital Learning and Assessment: With Examples in R and Python; von Davier, A.A., Mislevy, R.J., Hao, J., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; pp. 133–158. [Google Scholar]
- Adtalem Global Education. OutReach IQ. 2022.
- McKinney, W. Data structures for statistical computing in python. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 9th Python in Science Conference, 2010; pp. 51–56.
- Pedregosa, F.; Varoquaux, G.; Gramfort, A.; Michel, V.; Thirion, B.; Grisel, O.; Blondel, M.; Prettenhofer, P.; Weiss, R.; Dubourg, V. Scikit-learn: Machine learning in Python. the Journal of machine Learning research 2011, 12, 2825–2830. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, A.; Cutler, D.R.; Stevens, J.R. Random Forests. In Ensemble Machine Learning: Methods and Applications, Zhang, C., Ma, Y., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, 2012; pp. 157–175. [Google Scholar]
- Horning, N. Random Forests: An algorithm for image classification and generation of continuous fields data sets. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the International Conference on Geoinformatics for Spatial Infrastructure Development in Earth and Allied Sciences, Osaka, Japan, 2010; pp. 1–6. [Google Scholar]
- Sullivan, L.M.; Velez, A.A.; Longe, N.; Larese, A.M.; Galea, S. Removing the Graduate Record Examination as an Admissions Requirement Does Not Impact Student Success. Public Health Reviews 2022, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Langin, K. A wave of graduate programs drops the GRE application requirement. Available online: https://www.science.org/content/article/wave-graduate-programs-drop-gre-application-requirement (accessed on.
- Peng, J.; Harwell, M.; Liou, S.M.; Ehman, L.H. Advances in missing data methods and implications for educational research. Real Data Analysis 2006, 31–78. [Google Scholar]
- Pigott, T.D. A Review of Methods for Missing Data. Educational Research and Evaluation 2001, 7, 353–383. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khalid, S.; Khalil, T.; Nasreen, S. A survey of feature selection and feature extraction techniques in machine learning. In Proceedings of the 2014 science and information conference; 2014; pp. 372–378. [Google Scholar]
- Chizi, B.; Maimon, O. Dimension Reduction and Feature Selection. In Data Mining and Knowledge Discovery Handbook, Maimon, O., Rokach, L., Eds.; Springer US: Boston, MA, 2010; pp. 83–100. [Google Scholar]
- Brownlee, J. Data preparation for machine learning: data cleaning, feature selection, and data transforms in Python; Machine Learning Mastery, 2020. [Google Scholar]
- Jabbar, H.; Khan, R.Z. Methods to avoid over-fitting and under-fitting in supervised machine learning (comparative study). Computer Science, Communication and Instrumentation Devices 2015, 70, 163–172. [Google Scholar]
- Gu, J.; Oelke, D. Understanding bias in machine learning. arXiv preprint 2019, arXiv:1909.01866 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Ashfaq, U.; Poolan Marikannan, B.; Raheem, M. Managing Student Performance: A Predictive Analytics using Imbalanced Data. International Journal of Recent Technology and Engineering 2020, 8, 2277–2283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flores, V.; Heras, S.; Julian, V. Comparison of Predictive Models with Balanced Classes Using the SMOTE Method for the Forecast of Student Dropout in Higher Education. Electronics 2022, 11, 457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revathy, M.; Kamalakkannan, S.; Kavitha, P. Machine Learning based Prediction of Dropout Students from the Education University using SMOTE. In Proceedings of the 2022 4th International Conference on Smart Systems and Inventive Technology (ICSSIT), 20-22 Jan. 2022; pp. 1750–1758. [Google Scholar]
- Berrar, D. Cross-Validation. 2018.
- Hanley, J.A.; McNeil, B.J. The meaning and use of the area under a receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curve. Radiology 1982, 143, 29–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jin, H.; Ling, C.X. Using AUC and accuracy in evaluating learning algorithms. IEEE Transactions on Knowledge and Data Engineering 2005, 17, 299–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bergstra, J.; Bengio, Y. Random search for hyper-parameter optimization. Journal of machine learning research 2012, 13. [Google Scholar]
- Belete, D.M.; Huchaiah, M.D. Grid search in hyperparameter optimization of machine learning models for prediction of HIV/AIDS test results. International Journal of Computers and Applications 2022, 44, 875–886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feature importance evaluation. Available online: https://scikit-learn.org/stable/modules/ensemble.html (accessed on August 1, 2022).
- Lundberg, S.M.; Erion, G.; Chen, H.; DeGrave, A.; Prutkin, J.M.; Nair, B.; Katz, R.; Himmelfarb, J.; Bansal, N.; Lee, S.-I. From local explanations to global understanding with explainable AI for trees. Nature Machine Intelligence 2020, 2, 56–67. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aljuaid, T.; Sasi, S. Proper imputation techniques for missing values in data sets. In Proceedings of the 2016 International Conference on Data Science and Engineering (ICDSE), 23-25 Aug. 2016; pp. 1–5. [Google Scholar]
- Newgard, C.D.; Lewis, R.J. Missing Data: How to Best Account for What Is Not Known. JAMA 2015, 314, 940–941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sawilowsky, S.S. Real Data Analysis; Information Age Pub., 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Baudeu, R.; Wright, M.N.; Loecher, M. Are SHAP Values Biased Towards High-Entropy Features? Cham, 2023; pp. 418–433.
- Seger, C. An investigation of categorical variable encoding techniques in machine learning: binary versus one-hot and feature hashing. Student thesis, 2018.
- Cerda, P.; Varoquaux, G.; Kégl, B. Similarity encoding for learning with dirty categorical variables. Machine Learning 2018, 107, 1477–1494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, J.; Galal, G.; Etemadi, M.; Vaidyanathan, M. Evaluation and Mitigation of Racial Bias in Clinical Machine Learning Models: Scoping Review. JMIR Med Inform 2022, 10, e36388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Afrose, S.; Song, W.; Nemeroff, C.B.; Lu, C.; Yao, D. Subpopulation-specific machine learning prognosis for underrepresented patients with double prioritized bias correction. Communications Medicine 2022, 2, 111. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- American Assocation of Veterinary Medical Colleges. Annual Data Report 2022-2023; Washington, DC, 2023; pp. 1–67. [Google Scholar]

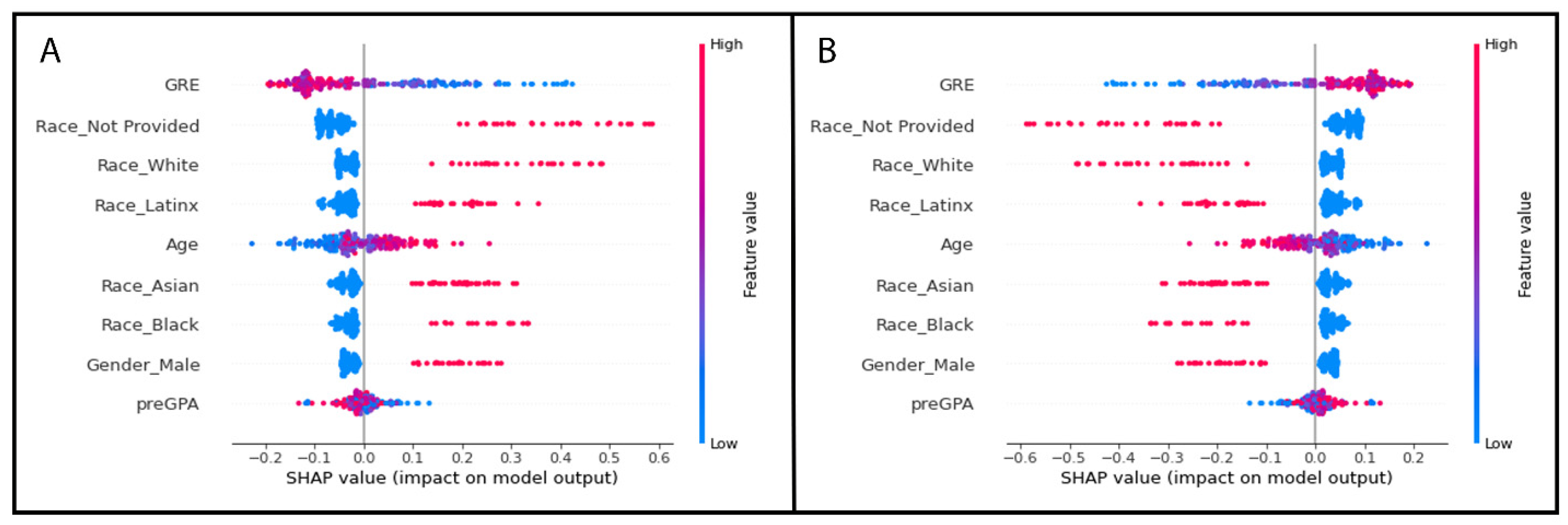
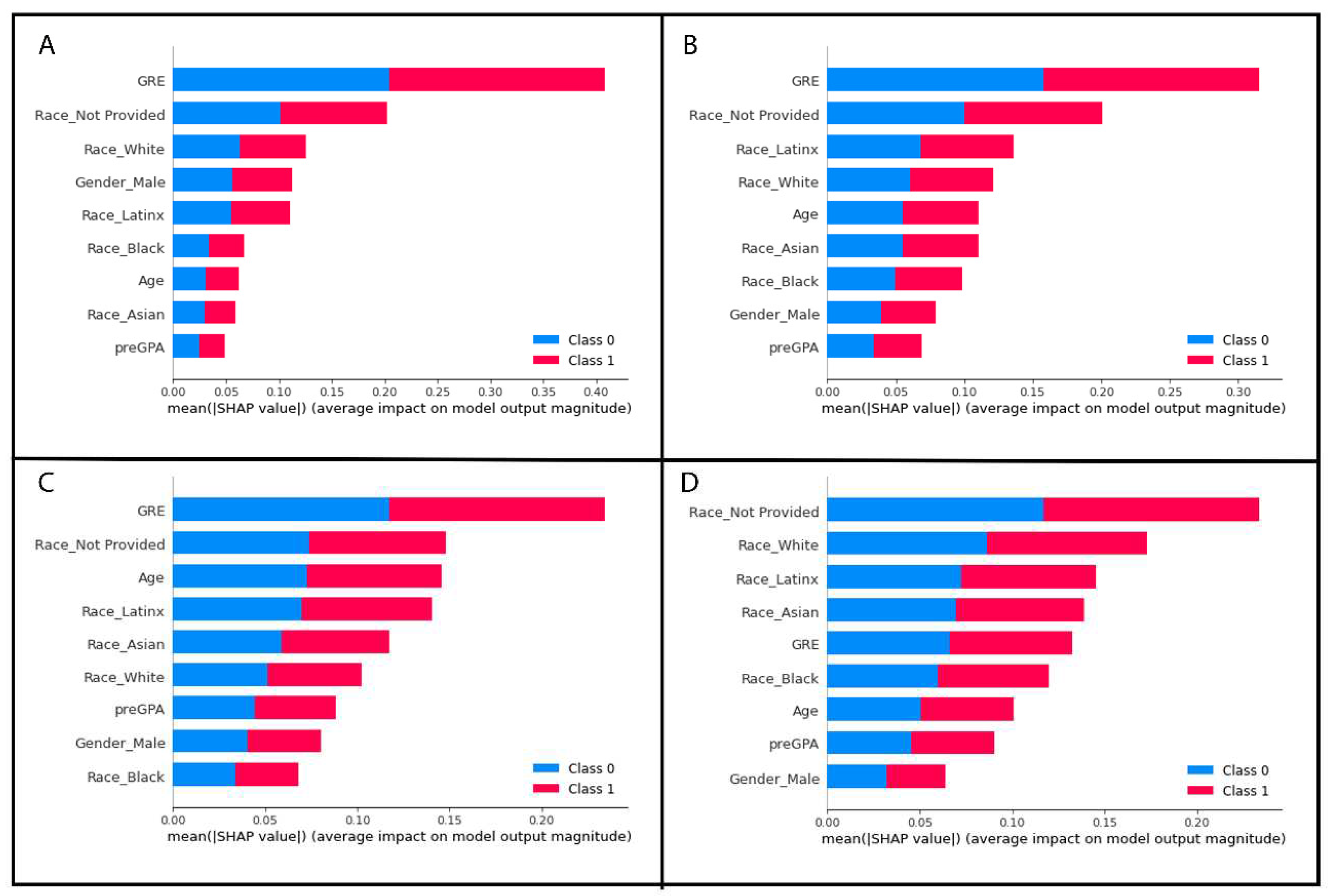
| Variable Name | Range of Values | Type of Data |
|---|---|---|
| Full Name | 400 randomly generated female and male names | Categorical |
| Gender | Male or Female | Categorical |
| Race/Ethnicity | Asian, Black, Latinx, Not Provided, White | Categorical |
| Age | 20 – 40 years | Numeric |
| Pre-Vet School GPA | 3.00 – 4.00 | Numeric |
| GRE | 260 – 330 | Numeric |
| Fail | 0-1 | Numeric |
| Actual negative Class: 0, student who did not fail |
Actual positive Class: 1, student who did fail |
|
|---|---|---|
| Predicted negative Class: 0, student who did not fail |
True negative (TN) | False negative (FN) |
| Predicted positive Class: 1, student who did fail |
False positive (FP) | True positive (TP) |
| Performance Metric | Random Forest Base Model | Radom Forest Tuned Model |
|---|---|---|
| Accuracy | 87.07% | 86.61% |
| Recall/Sensitivity/TPR | 89.61% | 89.77% |
| Specificity/TNR | 87.15% | 88.11% |
| Precision | 86.46% | 86.21% |
| F1-Score | 86.24% | 88.40% |
| ROC curve AUC | 87.15% | 88.11% |
| All GRE records | Feature Importance Score | Missing Low GRE values removed | Feature Importance Score | Missing Low GRE Values Replaced with Mean | Feature Importance Score | Random Missing GRE values removed | Feature Importance Score | Random Missing GRE values Replaced with Mean | Feature Importance Score |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GRE | 0.241850 | GRE | 0.370290 | GRE | 0.357720 | GRE | 0.291419 | preGPA | 0.218575 |
| Age | 0.150457 | Race_Not Provided | 0.131981 | preGPA | 0.152793 | preGPA | 0.199777 | GRE | 0.181400 |
| Race_Not Provided | 0.146913 | preGPA | 0.106498 | Age | 0.146683 | Age | 0.163021 | Age | 0.180350 |
| preGPA | 0.130455 | Age | 0.100696 | Race_Not Provided | 0.096973 | Race_Not Provided | 0.071514 | Race_Not Provided | 0.117902 |
| Race_White | 0.078924 | Race_White | 0.093832 | Race_Latinx | 0.062529 | Race_Asian | 0.062693 | Race_White | 0.073569 |
| Race_Latinx | 0.067359 | Gender_Male | 0.082514 | Race_White | 0.057276 | Race_White | 0.059140 | Race_Black | 0.071190 |
| Gender_Male | 0.063287 | Race_Latinx | 0.047706 | Race_Asian | 0.044694 | Race_Black | 0.051953 | Race_Asian | 0.062513 |
| Race_Black | 0.063043 | Race_Black | 0.041844 | Gender_Male | 0.042020 | Gender_Male | 0.050608 | Race_Latinx | 0.060454 |
| Race_Asian | 0.057713 | Race_Asian | 0.024639 | Race_Black | 0.039311 | Race_Latinx | 0.049876 | Gender_male | 0.034048 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





