1. Introduction
The sudden water pollution accident frequently occurred nowadays, posing a serious threat to water ecology, water environment and water safety in a changing world [
1,
2]. Conceptually, it refers to a rapid deterioration of water quality due to the large amount of pollutant discharges in a short period caused by human activities, natural disasters and some emergency [
3,
4]. Since the type, quantity, leaking mode and environmental damage capacity of discharge pollutants are difficult to determine, the sudden water pollution accidents are unpredictable and uncertain in variable hydrological and meteorological conditions [
5,
6]. Furthermore, water pollution caused by oil spills, explosions, traffic accidents, and other abnormal discharge of large amounts of sewage poses a serious threat to socio-economic development and human health [
4,
7]. Notably, the proportion of dangerous goods transportation is increasing year by year due to the rapid development of industrialization and quick expansion of urbanization, leading to the sudden water pollution accidents more frequent [
8,
9,
10,
11]. Specifically, the construction of cross-tributary bridges has significantly increased in river network areas, making the dangerous goods transportation accidents happening more frequently [
12,
13,
14]. Therefore, it is necessary to evaluate the risk of sudden water pollution accidents associated with dangerous goods transportation, which can provide basis for the corresponding emergency prevention and control [
15,
16].
Research on the risk assessment of dangerous goods transportation started early and achieved many research advancements [
17,
18,
19]. The American Chemical Company proposed an evaluation index method for fire explosions in 1964 [
20]. In the late 1980s, many studies have focused on the accident rates and casualties of dangerous goods transportation by simulating different accident scenarios [
21]. Recently, the path optimization of dangerous goods transportation has generated considerable research interest with the increasing application of modern information technology. A risk analysis framework was proposed by Verter and Kara [
22] who considered population, weather condition, surrounding environment and other geographic factors, thus obtaining the spatial distribution of dangerous goods transportation risks. Kara, et al. [
23] modified the traditional shortest path algorithm and connection labeling algorithm to evaluate the risk of dangerous goods transportation. Generally, the accuracy and practicability of risk assessment for the dangerous goods transportation need to be further improved. Bayesian network, also known as belief network, is the product of the combination of artificial intelligence, probability theory, graph theory and decision-making analysis. It has been widely applied to describe the uncertainty and probability, which can intuitively express the interaction between various factors and get a inference from incomplete or uncertain information [
24]. Bayesian network has significant advantages for small sample events by using prior knowledge of probability calculations [
25]. For example, Guo, et al. [
26] built a risk assessment model for the high-speed railway bridges in mountainous areas based on fuzzy Bayesian networks.
Baiyangdian Lake is an important part of Xiongan New Area in China, playing a significant role in ecological and environmental protection [
27]. With the improvement of urbanization and industrialization, the polluting enterprises are densely distributed around the lake and the surrounding tributaries; and many sewage treatment stations with dense drainage pipe are distributed in the area [
28]. Furthermore, there are many cross-tributary bridges between the nine rivers entering the lake and the roads, and the ships are transported frequently. Thus, the risk of sudden water pollution in the Baiyangdian Lake is high due to rollover, leakage and ship accidents. The frequent occurrence of water pollution accidents in Baiyangdian area poses serious threats to the safety and reliability of water supply [
29]. However, the risk assessment of sudden water pollution accidents in the Baiyang Lake has not been reported yet. Therefore, the Baiyang Lake was chosen as the study area to conduct risk assessment of sudden water pollution accidents associated with dangerous goods transportation on the cross-tributary bridges.
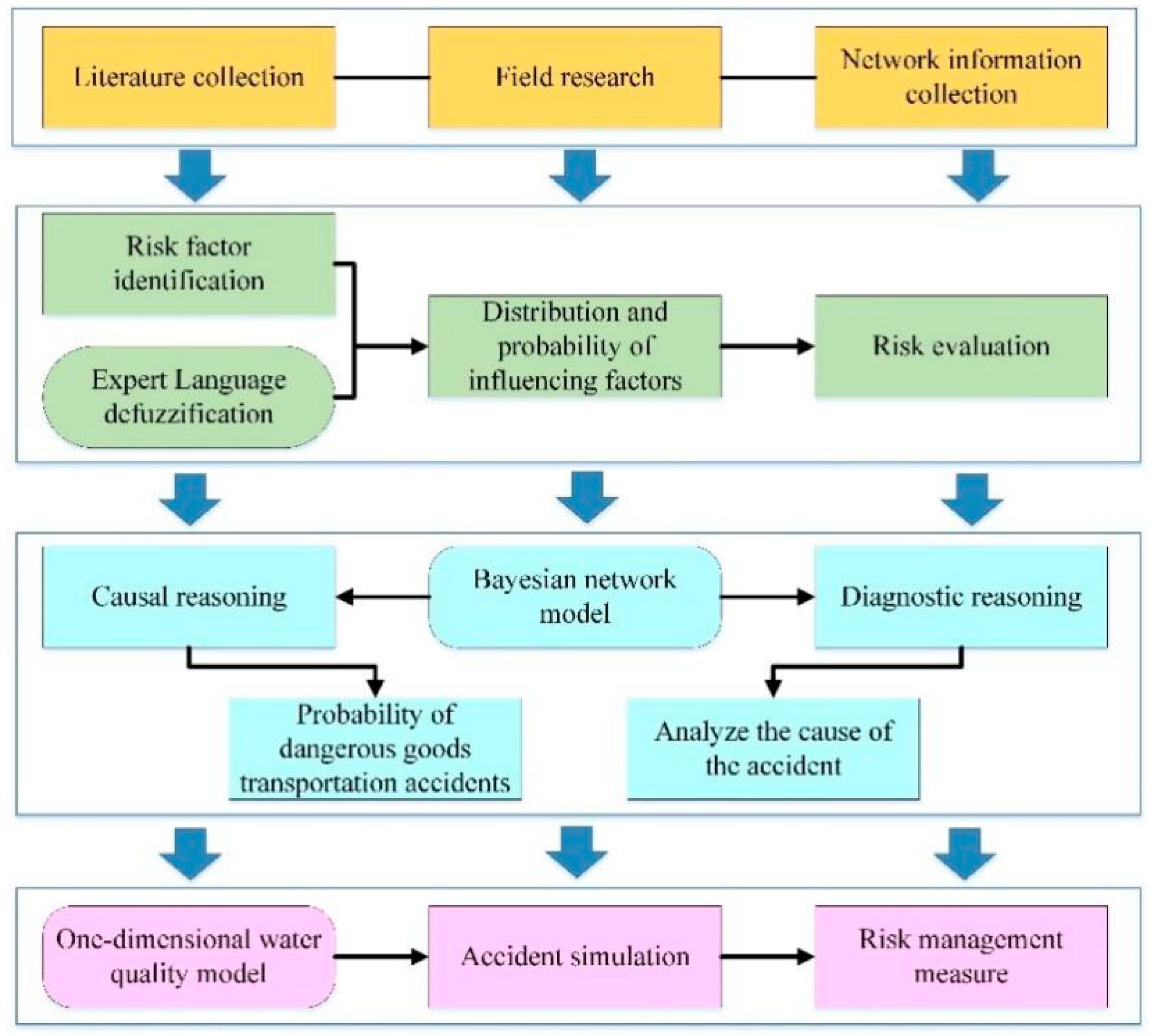
Overall, the aim of this study was to: (i) identify and determine the risk factors of dangerous goods transportation accidents on cross-tributary bridges around Baiyangdian Lake by field investigation and expert evaluation fuzzy language method; (ii) establish the Bayesian network; that is, the probability of dangerous goods transportation accident is calculated by causal reasoning, and the cause of the accident is analyzed by diagnostic reasoning; (iii) simulate the sudden water pollution accidents on Baiyangdian Lake by using the one-dimensional water quality model, and the corresponding emergency prevention and control measures are put forward
Figure 1 shows the schematic diagram of this paper.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Study area
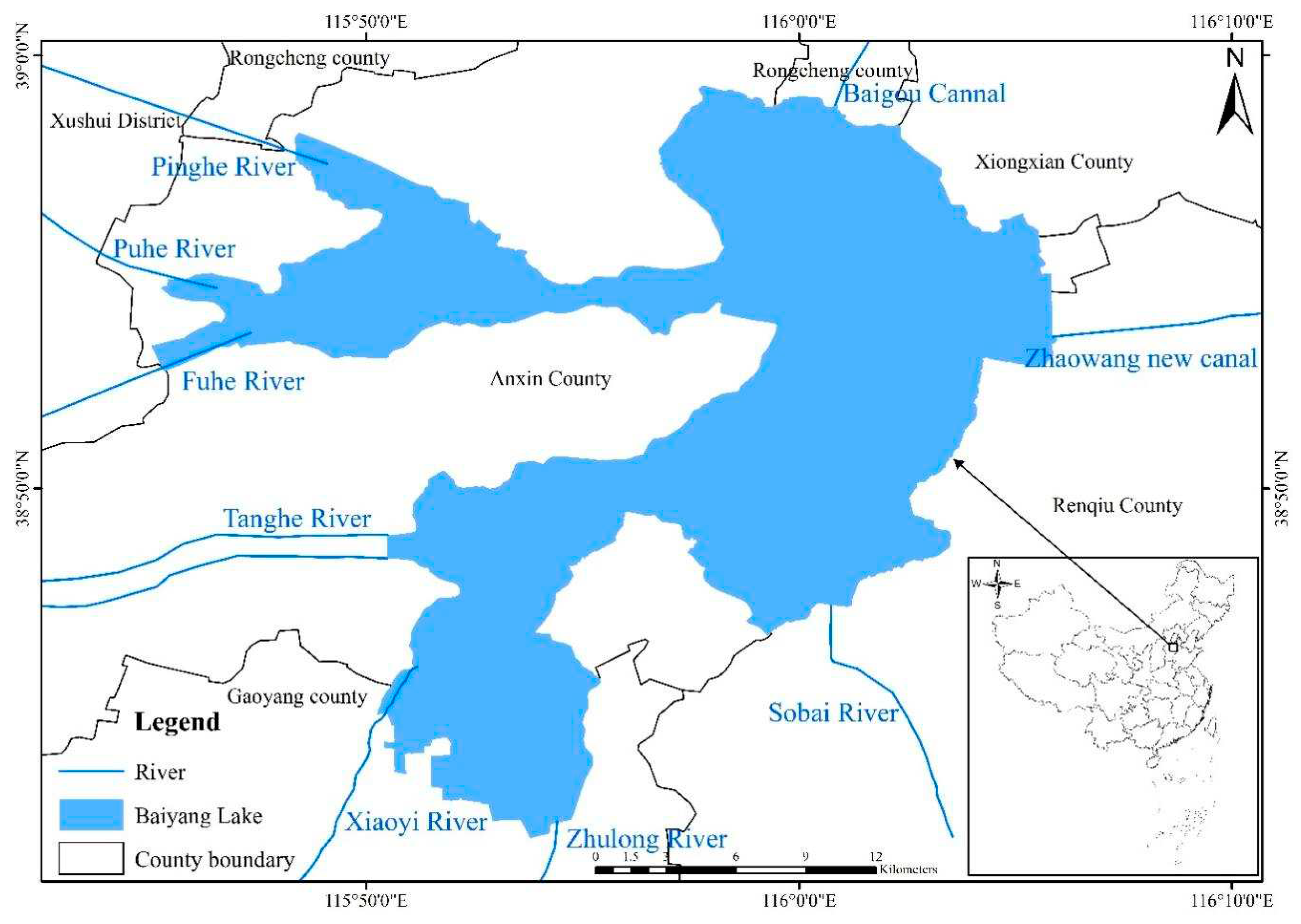
The Baiyangdian Lake is the largest freshwater shallow lake in North China (113°400′~116°480′E, 38°100 ~40°30′N), as shown in
Figure 2. It plays an important role in flood mitigation, drought prevention, regional microclimate improvement, and biodiversity protection [
27]. Furthermore, it supports water resources for hundreds of thousands of people which is famous for Pearl of North China and End of the Nine Rivers in China. The climate belongs to continental monsoon, with mean annual precipitation of 554 mm and temperature of 7~12 ℃. Besides, over 60% of the rainfall is concentrated during shorter periods between June and August. Wetlands, arable cropland (e.g., paddy fields and dry lands), forestland, grassland, residential and industrial land are the main land-use types in this basin. The Baiyangdian lake receives water from nine rivers, including Baigouyin River, Bao River, Cao River, Fu River, Zhulong River, Ping River, Qingshui River, Tang River, and Xiaoyi River. Moreover, the basin is also replenished by the Yellow River diversion project and the middle route of the South-to-North Water Diversion Project, thereby increasing the water resources and improving the water quality. Baiyangdian Lake Basin rapidly develops as it has been included in Xiongan New Area of China sine 2017. As a result, there exists numerous cross-tributary bridges due to the dense river networks, abundant water compensation project and high-intensity human activities. Therefore, there is a high occurrence frequency of the sudden water pollution accidents associated with dangerous goods transportation on the cross-tributary bridges of Baiyangdian lake [
30,
31,
32].
2.2. Bayesian network model
Bayesian Networks, alternatively referred to as causal probability networks or causal networks [
33], is acyclic directed graph models that depict the probabilistic interdependence among random variables. It served as network structure diagrams commonly employed for reasoning and analysis purposes [
34]. Once the probabilities of certain variables (typically input variables) are established, Bayesian network reasoning can be accomplished by employing basic probability operations and Bayesian theory to calculate the probabilities of all or specific nodes. In the absence of empirical evidence to establish the occurrence of event A, the utilization of a Bayesian network model enables the analysis and estimation of the probability of event
A based on the interrelation between event
B and event
A[
35].
2.2.1. Bayesian network composition
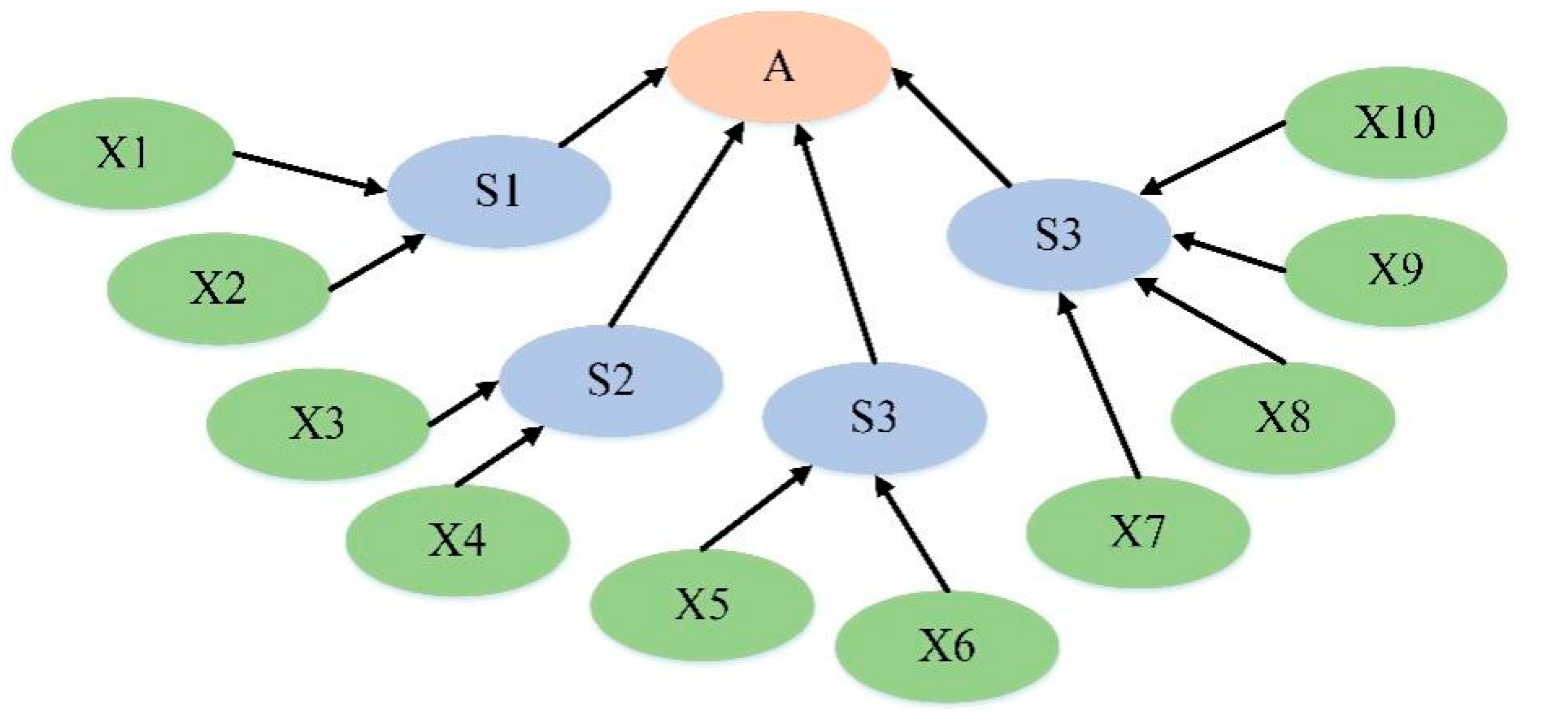
(1)The Bayesian network structure
The Bayesian network comprises three primary node categories (
Figure 3): (i) The target node, which represents the risk level of sudden water pollution accidents and serves as the ultimate outcome of the Bayesian network in this study, offering guidance for subsequent decision-making. (ii) The evidence node, also known as the parent node, plays a crucial role in providing supporting information for the Bayesian network analysis. (iii) The intermediate node plays a linking role between target nodes and evidence nodes. In this study, the fundamental unit of a Bayesian network consists of identified risk factors for sudden water pollution accidents. The connecting lines with directivity between each node indicate the relationships between them [
36].
The structure and reasoning process of a Bayesian network exhibit characteristics that are suitable for risk assessment modeling and analysis [
37]. The structure of a Bayesian network allows for the expression of uncertainty relationships and polymorphism characteristics among variables. The causal reasoning of the system can be utilized to compute the joint probability of system risk occurrence under different fault conditions for the purpose of risk assessment. Additionally, the diagnostic reasoning of the system involves calculating the conditional probability of each component state when the system risk occurs, facilitating system diagnosis and targeted risk management [
27].
(2) The Bayesian network parameter
The Bayesian network parameter pertains to the conditional probability table, which encompasses the conditional probability of each node. A single conditional probability within this table signifies the impact of one node variable on another node variable [
38]. Each node within the system possesses a distinct state, and the initial likelihood of evidence nodes is typically established based on empirical knowledge and monitoring data [
39]. In this study, the notation
P(
A) is employed to denote the evidence node, signifying the probability of event
A transpiring without accounting for the pertinent factors associated with event
B. Conversely, intermediate and target nodes are typically expressed in terms of conditional probability, denoting the posterior probability that elucidates the relationship between two nodes interconnected by a directed edge[
40]. In this study, the notation
P(A|B) is utilized to represent this conditional probability, indicating the probability of event
A transpiring given the occurrence of event
B.
2.2.2. Causal reasoning
The causal reasoning involves the process of reasoning from the evidence node to the target node. In the analysis of inference using Bayesian networks, an initial subjective probability estimation is conducted for the prior probability of the evidence node. Subsequently, the estimated probability values are inserted into the formula to compute the posterior probability of the final target event. Scientific decisions are then made based on this output, which is theoretically derived from the well-known Bayesian formula[
41]:
The risk frequency interval division standards established by the International Tunnel Association (ITA) are presented in
Table 1[
42]. The natural probability
PN of the occurrence of a risk event obtained by Bayesian network inference is related to the log probability
P as :
2.2.3. Diagnostic reasoning
The diagnostic reasoning function of a Bayesian network is employed to analyze the primary factors and combinations of factors that contribute to accidents. Specifically, the probability of each risk factor is assessed assuming a 100% probability for node
A being “1”, and the extent of change is compared to the impact of each risk factor on accidents [
43].
The Bayesian network risk assessment model must address numerous instances of incomplete and inaccurate data and information during inference, necessitating the execution of inference processes in various states. In order to enhance the precision of logical deductions, it is imperative to employ Netica, a specialized tool for graphical decision theory[
44], which facilitates the graphical representation of node states. This graphical depiction enhances the intuitiveness and accuracy of the reasoning process. Consequently, this study primarily utilized Netica to reason about risks associated with social security incidents.
2.3. Conditional probability calculation
2.3.1. The evaluation level establishment
Describing risk factors pertaining to accidents in the transportation of hazardous materials is a significant challenge, prompting the introduction of language evaluation levels to effectively characterize variables [
42,
45].
Table 2 shows seven natural language variables to express the risk levels, as well as their corresponding triangular fuzzy numbers and probability range.
2.3.2. Fuzzy language acquisition
Due to the limited availability of data and clear guidelines for classifying and assessing various risk factors, the direct and accurate determination of conditional probability for each evidence node is also a challenge [
46,
47]. Consequently, this study employed the Delphi method as a means to compensate for the lack of data [
48], thus establishing the probabilities of evidence nodes. Through an anonymous questionnaire survey, experts were invited to evaluate and predict the evidence nodes until a consensus was reached[
49]. Given that expert judgment relied on personal knowledge and experience and the results were expressed in vague language, it was imperative to employ defuzzification techniques to enhance the clarity of expert language.
2.3.3. Expert language defuzzification
The commonly used defuzzification methods are trapezoidal fuzzy numbers[
50], triangular fuzzy numbers[
51], and LR-type fuzzy numbers[
52]. Considering the attributes and suitability of these methods, the triangular fuzzy number was chosen as the membership function for defuzzifying expert language, which was proposed by Vanlaarhoven and Pedrycz [
53] for fuzzy judgment..
Fuzzy numbers typically encompass upper and lower limits, as well as intermediate potential values. Assuming the risk assessment membership set is denoted as
A, the triangular fuzzy number’s upper and lower limits are represented by
a and
b, respectively. When the membership degree of set
A is 1 and the value is m, the triangular fuzzy number
A is denoted as
with the membership function expressed as follows:
where a and b signify the degree of fuzziness (a≤m≤b). The greater the difference between b and a, the higher the degree of fuzziness.
2.3.4. Calculation of the conditional probability
After obtaining expert opinions and transforming them into triangular fuzzy numbers, the quantized triangular fuzzy numbers must undergo processing to compute the probability information for each evidence node. The processing procedure primarily involves averaging, defuzzification, and normalization [
54]. The expert opinions are calculated and averaged based on the number of invited experts, thereby eliminating outliers and enhancing the rationality of the fuzzy probability value in the judgment. The formula is as follows:
The defuzzification of the average triangular fuzzy number is conducted by utilizing the mean area method, resulting in the conversion into the precise probability
P’ of the node [
55]. This formula is expressed as follows:
Ultimately, the probability information of each node was normalized, thereby achieving a sum of probability values equal to 1 across various risk levels. Consequently, the obtained probability value was used for subsequent inference calculations, as follows:
The Bayesian network was established to assign values to each node, and the calculated probability value was then substituted into the Bayesian network. The Netica data analysis software was utilized for reasoning calculations[
56]. On the node definition screen, State 0 represented non-occurrence, while State 1 signified occurrence.
2.4. Simulation of sudden water pollution accidents
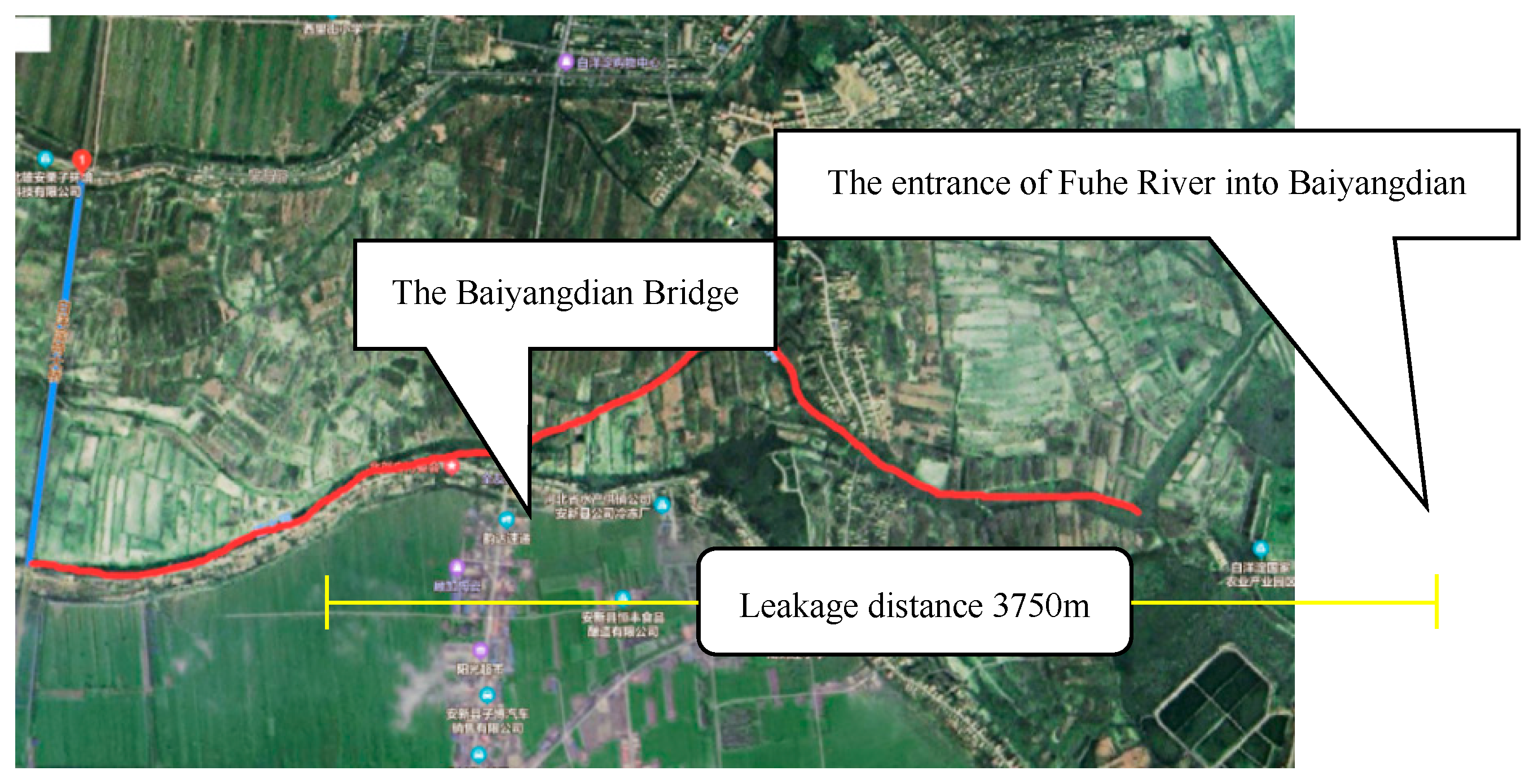
The Fuhe River flows into the Baiyangdian lake located in the north of Jianchang Village, Anxin County, passing through Baoding City and Qingyuan County. It has a total length of 30.83 km, a drainage area of 643.2km2, and an average water depth ranging from 1.5 to 3m. The distance between the Baiyangdian Lake Bridge and Shaochedian along the Fuhe River measured 3750 m. Situated within the Baiyangdian Lake Baojing Line, the region were susceptible to sudden water pollution incidents. The bridge spanned a total length of 1203.88 m and possesses a width of 19.5 m, as depicted in
Figure 4.
The oil vehicle overturning on the Fuhe River Bridge would cause the oil leakage into the river directly. Therefore, a one-dimensional water quality model was employed to simulate the longitudinal dispersion of pollutants along the river [
57]. It can be calculated as follows:
where
C(
x) represents the measured pollutant concentration of the control section (kg/L),
C0 represents the measured pollutant concentration of the initial section (kg/L),
k is the comprehensive self-purification coefficient of pollutants (1/d), and
x is the river section distance downstream of the sewage outlet (km). The
k of pollutants can be assumed as 0.0213 [
58]. The scenario settings and fundamental parameters for the oil transportation accidents simulation on the cross-tributary bridges of Baiyangdian lake are presented in
Table 3.
2.5. The proposed emergency indicator system
A emergency prevention index system for sudden water pollution accidents was proposed, including the following treatment stages: (1) reporting phase, (2) detection phase, (3) forecasting phase, and (4) processing phase. According to these four stages, targeted emergency prevention and control measures should be implemented to provide decision support for mitigating the hazards of accidents [
59]. This recommendation is in accordance with the guidelines outlined in the National Emergency Plan for Public Emergencies (2006.1.8), the Dangerous Chemicals Safety Management Regulations, the General Technical Requirements for Transport and Packaging of Dangerous Goods (GB12463), and the Signs of Vehicles for Road Transport of Dangerous Goods (GB13392). The Ministry of Communications has developed risk prevention management measures and emergency plans for dangerous goods transportation accidents on bridges across tributaries in accordance with the Road Dangerous Goods Transportation Management Regulations, Automotive Dangerous Goods Transportation Regulations (JT3130), and other relevant regulations. [
60,
61]. All of them was taken into consideration in this study.
3. Results and discussion
3.1. Risk factors identification
The present study employed a comprehensive approach, including literature analysis, field investigation, and the Delphi method, to gather data on water pollution incidents caused by the transportation of hazardous materials on the cross-tributary bridges of Baiyangdian lake between 2000 and 2020[
62,
63,
64,
65,
66]. Consequently, the factors influencing these accidents were identified and summarized in
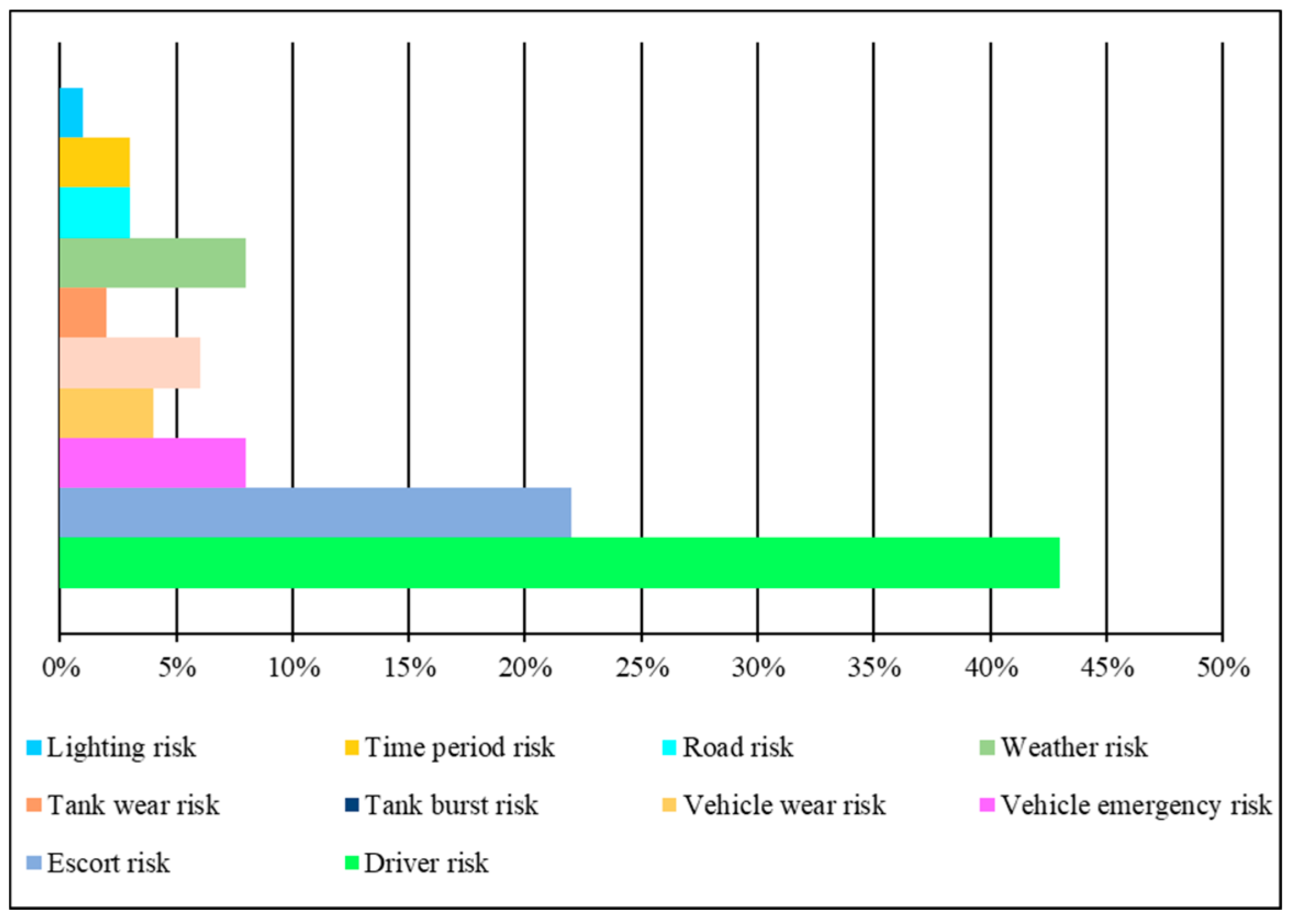
Figure 5.
It was found that driver risk and escort risk factors constituted the largest proportion of these accidents, accounting for a total of 65%. Additionally, tank risk factors accounted for 20% of the accidents on the cross-tributary bridges, surpassing the average level of road transportation accidents involving hazardous materials, which stands at 18% [
67].
The weather risk, road risk, time risk and lighting risk belonged to unpredictable force majeure factors, thereby it was necessary to consider these accidental factors in the transportation distance and time arrangement, so as to reduce the possibility of sudden water pollution accidents [
68]. Unforeseeable force majeure elements encompassed the hazards of weather, road conditions, time, and lighting. Therefore, it was imperative to account for these incidental factors when planning transportation distance and time, in order to minimize the likelihood of unexpected water pollution incidents. Additionally, after analyzing the factors that contribute to sudden water pollution accidents during the transportation of hazardous materials on the cross-tributary bridges of Baiyangdian lake, four types of risk factors were identified: personnel, vehicle, tank risks and environmental risk. Overall, 4 first grade indices and 10 second grade indices were shown in
Table 4.
3.2. Conditional probability
Based on the risk factors system and assessment standards, a panel of seven experts was assembled to assess the occurrence probability of each evidence node in the Bayesian network. The evaluation outcomes are presented in
Table 5.
By utilizing the relationship between the evaluation level and the triangular fuzzy number, the statistical analysis of the experts’ ratings of the triangular fuzzy number was conducted, as demonstrated in
Table 6.
Subsequently, the expert opinion results were subjected to arithmetic averaging in order to eliminate any anomalous values, thereby rendering the fuzzy probability value of the judgment more rational. The defuzzification process involved applying the averaging calculation formula. For instance, in the case of the evidence node, the following calculation outcomes were obtained:
The occurrence probability of the evidence nodes was determined using the arithmetical average method, resulting in triangular fuzzy numbers. These average triangular fuzzy numbers were subsequently employed in the mean area method for defuzzification. The normalization of the conditional probability for each node was conducted, and the corresponding results are presented in
Table 7.
For instance, the calculation of the conditional probability for node X1 was performed as follows:
Based on the outcomes of the conditional probability calculation, it can be inferred that the likelihood of driver factor, vehicle emergency factor, tank emergency factor, road factor, and lighting situation occurring is high. Consequently, driver, vehicle, tank, road, and lighting are deemed essential components in the transportation of hazardous materials.
Once these factors are present, adverse conditions can easily lead to accidents during the transportation process, resulting in incidents of water pollution.
Machado, et al. [
69] conducted a monitoring and counting study on the 050 highway in Brazil, revealing that 14 accidents occurred. The distribution of these accidents was as follows: 35.71% in the morning, 28.57% in the afternoon, 21.43% at night, and 14.29% in the early morning. Furthermore, the probability of accidents during the rainy season (64.29%) was higher compared to periods with little or no rain (35.71%) occurring five times. Notably, a significant proportion (28.57%) of the accidents took place on sections of the road with steep slopes, specifically between km 77 and km 83.
This study did not incorporate the temporal duration of the accident, specifically the seasonal and regional aspects. It is observed that adverse weather conditions during the rainy season contribute to an elevated risk of road-related factors, while the presence of steep slopes further exacerbates road conditions, thereby increasing the probability of risk during the transportation of hazardous materials. These findings align with the outcomes of the present study. Notably, the lighting factors examined in this research solely pertain to the nighttime period. No analysis of the accident in different periods was conducted due to the significantly lower transportation intensity of the bridge entering Baiyangdian compared to the 050 expressway in Brazil.
3.3. Risk assessment based on Bayesian network model
Consequently, the study employed the Bayesian network model with a two-way reasoning function to establish the occurrence probability, main causes, and their combinations of dangerous goods transportation accidents on the cross-tributary bridges of Baiyangdian Lake. Specifically, the study employed causal reasoning and diagnostic reasoning [
70].
3.3.1. Causal reasoning results
According to the Bayesian network structure and probability table, the probability of “Yes” at node
A (
PA) was determined to be 0.115, as depicted in
Figure 6. Additionally, by considering the relationship between natural probability, logarithmic probability, and risk level from
Table 1, the value of
P was calculated to be 4.061. This value indicates a high risk level for the transportation of dangerous goods, suggesting a probable occurrence with a high probability.
3.3.2. Diagnostic reasoning results
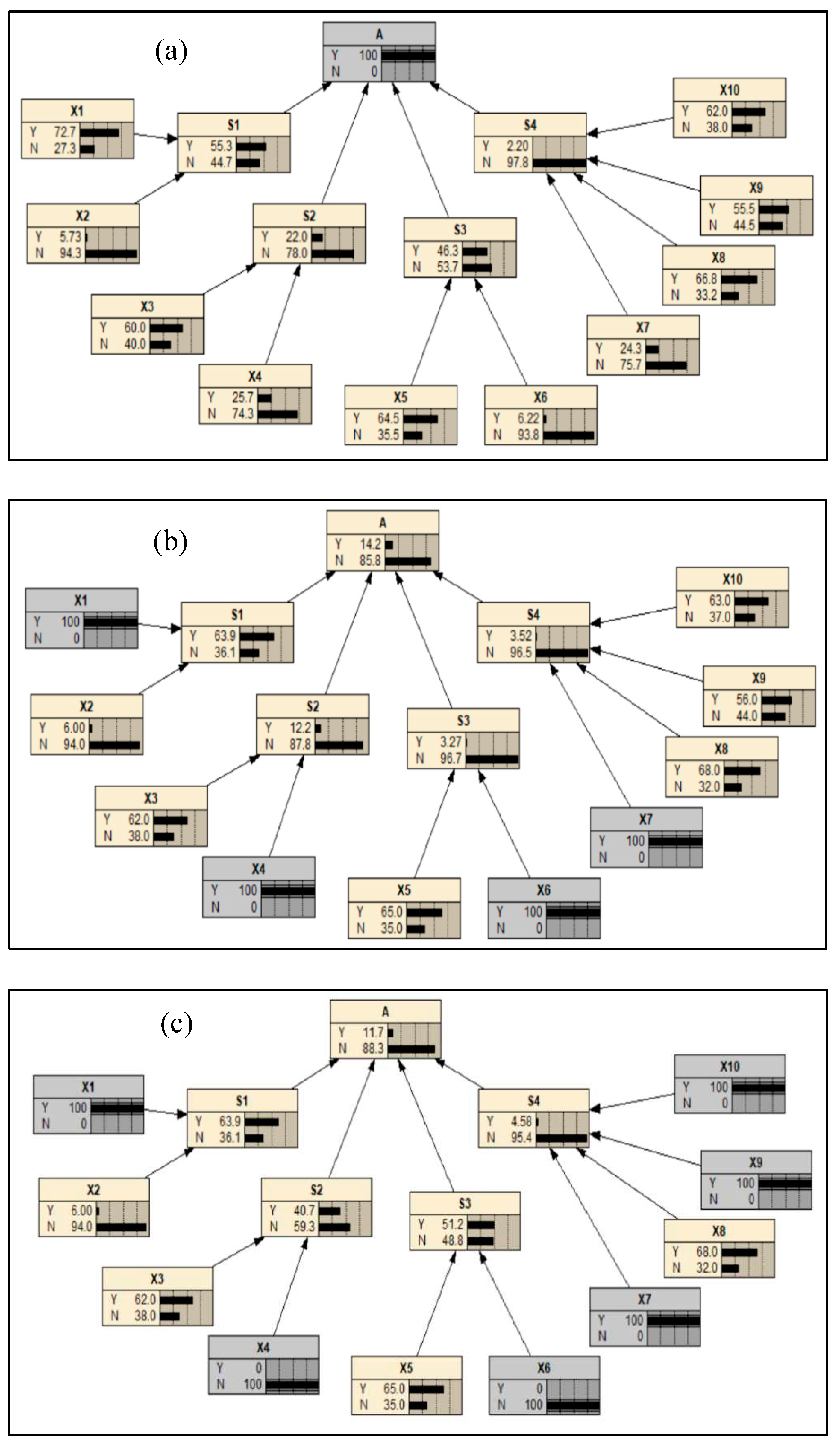
According to the Bayesian diagnostic reasoning, the probability of each risk factor was illustrated in
Figure 7a, assuming an occurrence probability of 1 for the target node A.
The variations of X3, X4, and X7 exhibited a significantly greater magnitude compared to other factors, suggesting that the vehicle emergent factor, vehicle wear factor, and weather factor exerted a more substantial influence on the occurrence of accidents. The combination of X1, X4, X6, and X7 was identified as the most probable state combination leading to accidents, with an occurrence probability of 0.142, as depicted in
Figure 7b. This finding indicates that hazardous goods transportation accidents are most likely to transpire on cross-tributary bridges when the driver is in a compromised state, the vehicle and tank exhibit signs of wear, and the weather conditions are unfavorable.
Based on the assumption of the vehicles and tanks being in optimal condition, the accident is most likely to occur due to a combination of states X1, X7, X9, and X10. Specifically, the accident has the highest probability of occurrence on the cross-tributary bridges, where drivers have poor status, weather conditions are unfavorable, and there are no street lights at night, with a value of 0.117 (
Figure 7c). Consequently, implementing risk prevention measures prior to accidents can effectively decrease the likelihood of such incidents.
Hua, et al. [
10] conducted a systematic analysis of the causes of dangerous goods explosion accidents at Tianjin Port using the FTA method. This findings indicated that management factors and human factors held a prominent position within the overall causal framework of such accidents, while environmental factors, goods, and facilities also exerted a discernible influence on their occurrence. The study conducted by Khan, et al. [
71] utilized Bayesian networks to analyze 348 accident reports spanning from 1990 to 2018, revealing the intricate nature of causes contributing to dangerous goods explosion accidents in ports. The findings indicate that, in typical conditions, there is a 59.8% likelihood of major accidents occurring, with human factors and management factors being the primary contributors to such incidents. Moreover, in the context of environmental and pollution accidents, the probability of management factors exacerbating the occurrence of accidents increases by 7.06%.
Within the scope of this investigation, driver factors, vehicle factors, tank factors and lighting factors are classified as human factors and management factors, respectively, and they significantly contribute to water pollution accidents during the transportation of hazardous materials on Baiyangdian bridge, aligning with the aforementioned conclusion.
Overall, the identification and evaluation of sudden water pollution risk in the Baiyangdian lake are subject to numerous uncertain factors. Further research is required to address the following aspects: (1) Enhancing the selection of factors in the construction of the Bayesian network model. The development of a comprehensive Bayesian network structure necessitates iterative discussions and collaborative decision-making involving experts. The determination of the probability associated with each factor within the Bayesian network serves as the foundation for quantitative accident analysis. This article employs the expert consultation method to ascertain the likelihood of each parameter. Subsequent research should integrate historical traffic accident data to consistently revise and update the network.
3.4. Accident simulation results, emergency prevention and control measures
3.4.1. Accident simulation
The selection of the Nanliuzhuang section as a simulation case was based on its significant role in the entry of the Fuhe River into Baiyangdian Lake. The average concentration of pollutants at this section was determined through various setting scenarios, as presented in
Table 8. To exemplify the transportation of dangerous goods across the tributary bridges of Baiyangdian Lake, an oil leakage accident was chosen as a case study.
The results indicate that without proper prevention and control measures, the oil concentration at the Nanliuzhuang section reached extremely high levels. The absence of additional treatment would result in a direct discharge into Baiyangdian lake, thereby significantly compromising its water quality. Consequently, efforts were made to specifically address the issue of oil leakage into the river. In order to simulate potential accident scenarios and mitigate associated risks, appropriate preventive management measures must be implemented.
3.4.2. Risk emergency prevention and control
The risk management approach for transportation accidents involving hazardous materials on the cross-tributary bridges of Baiyangdian lake should prioritize prevention. To facilitate emergency preparedness for sudden water pollution incidents, a comprehensive index system was developed and presented in
Table 9. More details can seen from our previous study [
72].
The primary risk mitigation measures for emergency prevention and control encompass the following seven aspects [
73,
74,
75]: (1) it is recommended to enforce an inspection system for vehicles involved in the transportation of hazardous materials; (2)the velocity of hazardous materials transportation by vehicles should be restricted on cross-tributary bridges; (3) engineering protective measures, such as reinforcing and elevating guardrails, can be implemented on both sides of the bridges; (4) the installation of pollutant discharge collection devices in the vicinity of the bridges is advisable; (5) implement real-time monitoring systems for transportation vehicles, hazardous materials, and transportation routes; (6) develop an auxiliary decision-making system to facilitate emergency response procedures; (7) enhance and refine legislation pertaining to water environment risk management. It is crucial to promptly report the occurrence time and location, pollutant type and source, potential consequences, and other preliminary information regarding sudden water pollution incidents in order to devise targeted measures for risk prevention and control [
76].
Based on the categorization of abrupt water pollution incidents, as well as the geographical, topographical, and meteorological factors, the extent and velocity of pollutant migration and dispersion are established. Subsequently, the identification and assessment of pollution sources and their consequential impacts are continuously monitored [
77]. During the forecasting stage, the utilization of a water quality early warning model becomes imperative in predicting the likelihood of accidents, the concentration, dynamics, and extent of pollutants, as well as potential hazards. During the processing phase, it is imperative for all pertinent departments to adhere strictly to the emergency division of labor, promptly investigate the extent of impact and level of harm, evaluate the resulting losses, report to higher authorities, and disclose the findings [
78].
This study has certain limitations that should be acknowledged. Firstly, the categorization of the role of each node in accident causality does not include various states such as negligible, low, medium, high, and severe. Incorporating these states could enhance the comprehension of accident causality aspects and factor levels. Additionally, the lack of data and knowledge hinders the further subdivision of environmental pollution risks based on type and severity. Nevertheless, the findings of this study hold significant implications for enhancing the comprehension of risk assessment pertaining to sudden water pollution incidents, as well as the corresponding measures for prevention and control.
With the ongoing advancements in geographic information system (GIS) technology, future studies can utilize the GIS visualization operating system to develop a GIS system for emergency planning in response to sudden water pollution incidents in Baiyangdian Lake. This system can serve as a valuable resource for enhancing the management of water pollution emergencies and facilitating the development of space-assisted decision-making support in the context of Baiyangdian Lake.
4. Conclusion
This study explored the potential risk of sudden water pollution accidents associated with dangerous goods transportation on the cross-tributary bridges of Baiyangdian Lake. Specifically, the risk factors were identified, and their conditional probabilities were determined using the expert evaluation method employing fuzzy language. Then, a Bayesian network model was then established for the risk assessment. The simulation of oil leakage accident was conducted to predict potential risks, and the emergency prevention and control measures were proposed. The conclusions are as follows:
(1) The dangerous goods transportation accidents on the cross-tributary bridges of Baiyangdian Lake was a possible event, with node A (PA) value of 0.115 and logarithmic probability P value of 4.061. The risk level was relatively high, indicating the accidents posed a potential threat to water environment and human health. (2) Vehicle emergent factors, vehicle wear factors, and weather factors had a greater impact on the occurrence of accidents, with the decreasing order of X4>X3>X7. (3) The combination of X1, X4, X6 and X7 contributed to an accident most. That showed that the highest probability (0.142) of an accident occurred on the region where the driver was not in good condition, the vehicle and tank were worn, and the weather was bad. (4) When the vehicle and the tank were in good condition, the most likely combination of conditions leading to the accident is : X1, X7, X9, X10. This indicated that the probability of an accident reached the highest (0.117) on the cross-tributary bridges with poor driver status, bad weather conditions, and no street lighting at night. (5) The emergency prevention and control measure was an effective approach to mitigating the risk of sudden water pollution accidents.
Data Availability Statement
All data included in this study are available upon request by contactingthe corresponding author.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Joint Funds of the National Natural Science Foundation of China ( U2243236) and National Science Fund for Distinguished Young Scholars (52025092).
Declaration of Competing Interest
The authors declare that they do not have any competing interests that could have appeared to influence the work reported in this paper.
References
- LI D Y, WEI Y M, DONG Z C, et al. Quantitative study on the early warning indexes of conventional sudden water pollution in a plain river network. J Clean Prod, 2021, 303. [CrossRef]
- YAN B, LIU Y T, GAO Z W, et al. Simulation of Sudden Water Pollution Accidents in Hunhe River Basin Upstream of Dahuofang Reservoir. Water-Sui, 2022, 14(6). [CrossRef]
- HOU D B, GE X F, HUANG P J, et al. A real-time, dynamic early-warning model based on uncertainty analysis and risk assessment for sudden water pollution accidents. Environ Sci Pollut R, 2014, 21(14): 8878-92. [CrossRef]
- ZHAO Y, PAN Y L, WANG W S, et al. A Brain-Inspired Dynamic Environmental Emergency Response Framework for Sudden Water Pollution Accidents. Water-Sui, 2021, 13(21). [CrossRef]
- TANG C H, YI Y J, YANG Z F, et al. Water pollution risk simulation and prediction in the main canal of the South-to-North Water Transfer Project. J Hydrol, 2014, 519: 2111-20. [CrossRef]
- YIN H L, LIN Y Y, ZHANG H J, et al. Identification of pollution sources in rivers using a hydrodynamic diffusion wave model and improved Bayesian-Markov chain Monte Carlo algorithm. Front Env Sci Eng, 2023, 17(7). [CrossRef]
- LI D Y, DONG Z C, SHI L Y, et al. Risk Probability Assessment of Sudden Water Pollution in the Plain River Network Based on Random Discharge from Multiple Risk Sources. Water Resour Manag, 2019, 33(12): 4051-65. [CrossRef]
- YANG J, LI F Y, ZHOU J B, et al. A survey on hazardous materials accidents during road transport in China from 2000 to 2008. J Hazard Mater, 2010, 184(1-3): 647-53. [CrossRef]
- XIA Q, WEI Q P. Analysis on the Necessity and Reasonableness of Project Management of Dangerous Cargo Declaration. Aebmr Adv Econ, 2017, 26: 547-51. [CrossRef]
- HUA W Y, CHEN J H, QIN Q D, et al. Causation analysis and governance strategy for hazardous cargo accidents at ports: Case study of Tianjin Port’s hazardous cargo explosion accident. Mar Pollut Bull, 2021, 173. [CrossRef]
- YANG Y L, LEI X H, LONG Y, et al. A novel comprehensive risk assessment method for sudden water accidents in the Middle Route of the South-North Water Transfer Project (China). Sci Total Environ, 2020, 698. [CrossRef]
- BLASCO J, DURAN-GRADOS V, HAMPEL M, et al. Towards an integrated environmental risk assessment of emissions from ships’ propulsion systems. Environ Int, 2014, 66: 44-7. [CrossRef]
- CHEN L, HABIBOVIC A, ENGLUND C, et al. Coordinating dangerous goods vehicles: C-ITS applications for safe road tunnels. Ieee Int Veh Sym, 2015: 156-61. [CrossRef]
- GALIERIKOVA A, SOSEDOVA J. Inland Waterway Transportation of Dangerous Goods: Risk Assessment and Decision-Making Strategies. Globalization and Its Socio-Economic Consequences, 2018: 517-23.
- LI D Y, DONG Z C, WANG C H, et al. Calculation Method for the Early Warning Index of Sudden Water Pollution Based on the Linear Variation Assumption of the Substance Concentration in the River Network. Water Resour Manag, 2020, 34(9): 2821-35. [CrossRef]
- WU W, REN J C, ZHOU X D, et al. Identification of source information for sudden water pollution incidents in rivers and lakes based on variable-fidelity surrogate-DREAM optimization. Environ Modell Softw, 2020, 133. [CrossRef]
- COZZANI V, BONVICINI S, SPADOLLI G, et al. Hazmat transport: A methodological framework for the risk analysis of marshalling yards. J Hazard Mater, 2007, 147(1-2): 412-23. [CrossRef]
- BRETON T, SANCHEZ-GHENO J C, ALAMILLA J L, et al. Identification of failure type in corroded pipelines: A Bayesian probabilistic approach. J Hazard Mater, 2010, 179(1-3): 628-34. [CrossRef]
- KHAN R U, YIN J B, MUSTAFA F S, et al. Risk assessment for berthing of hazardous cargo vessels using Bayesian networks. Ocean Coast Manage, 2021, 210. [CrossRef]
- AKHAVAN M, SEBT M V, AMELI M. Risk assessment modeling for knowledge based and startup projects based on feasibility studies: A Bayesian network approach. Knowl-Based Syst, 2021, 222. [CrossRef]
- FAM M L, KONOVESSIS D, HE X H, et al. Data learning and expert judgment in a Bayesian belief network for aiding human reliability assessment in offshore decommissioning risk assessment. J Ocean Eng Sci, 2021, 6(2): 170-84. [CrossRef]
- VERTER V, KARA B Y. A GIS-based framework for hazardous materials transport risk assessment. Risk Anal, 2001, 21(6): 1109-20. [CrossRef]
- KARA B Y, ERKUT E, VERTER V. Accurate calculation of hazardous materials transport risks. Oper Res Lett, 2003, 31(4): 285-92. [CrossRef]
- LIU J, LIU R Z, YANG Z F, et al. Quantifying and predicting ecological and human health risks for binary heavy metal pollution accidents at the watershed scale using Bayesian Networks. Environ Pollut, 2021, 269. [CrossRef]
- HOU W T, DING M F, LI X H, et al. Comparative evaluation of cardiovascular risks among nine FDA-approved VEGFR-TKIs in patients with solid tumors: a Bayesian network analysis of randomized controlled trials. J Cancer Res Clin, 2021, 147(8): 2407-20. [CrossRef]
- GUO X X, JI J, KHAN F, et al. Fuzzy Bayesian network based on an improved similarity aggregation method for risk assessment of storage tank accident. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 149: 817-30. [CrossRef]
- WANG G W, LV C C, GU C K, et al. Pollutants Source Assessment and Load Calculation in Baiyangdian Lake Using Multi-Model Statistical Analysis. Water-Sui, 2022, 14(21). [CrossRef]
- YAO X, WANG Z, LIU W, et al. Pollution in river tributaries restricts the water quality of ecological water replenishment in the Baiyangdian watershed, China. Environ Sci Pollut R, 2023. [CrossRef]
- GUAN X Y, REN X Q, TAO Y, et al. Study of the Water Environment Risk Assessment of the Upper Reaches of the Baiyangdian Lake, China. Water-Sui, 2022, 14(16). [CrossRef]
- ZYWIEC W J, MAZZUCHI T A, SARKANI S. Analysis of process criticality accident risk using a metamodel-driven Bayesian network. Reliab Eng Syst Safe, 2021, 207. [CrossRef]
- YIN B T, LI B Y, LIU G, et al. Quantitative risk analysis of offshore well blowout using bayesian network. Safety Sci, 2021, 135. [CrossRef]
- HUANG S Q, WANG H M, XU Y J, et al. Key Disaster-Causing Factors Chains on Urban Flood Risk Based on Bayesian Network. Land-Basel, 2021, 10(2). [CrossRef]
- ZHU S M, LI J, ZHAO X Y. Comparative risk of new-onset hyperkalemia for antihypertensive drugs in patients with diabetic nephropathy: A Bayesian network meta-analysis. Int J Clin Pract, 2021, 75(8). [CrossRef]
- ROOSTAEI J, COLLEY S, MULHERN R, et al. Predicting the risk of GenX contamination in private well water using a machine-learned Bayesian network model. J Hazard Mater, 2021, 411. [CrossRef]
- LIU M, LIU Z Z, CHU F, et al. A new robust dynamic Bayesian network approach for disruption risk assessment under the supply chain ripple effect. Int J Prod Res, 2021, 59(1): 265-85. [CrossRef]
- LIU Z K, MA Q, CAI B P, et al. Risk assessment on deepwater drilling well control based on dynamic Bayesian network. Process Safety and Environmental Protection, 2021, 149: 643-54. [CrossRef]
- SIU N O, KELLY D L. Bayesian parameter estimation in probabilistic risk assessment. Reliab Eng Syst Safe, 1998, 62(1-2): 89-116. [CrossRef]
- LIEDLOFF A C, WOODWARD E L, HARRINGTON G A, et al. Integrating indigenous ecological and scientific hydro-geological knowledge using a Bayesian Network in the context of water resource development. J Hydrol, 2013, 499: 177-87. [CrossRef]
- TANG C H, YI Y J, YANG Z F, et al. Risk forecasting of pollution accidents based on an integrated Bayesian Network and water quality model for the South to NorthWater Transfer Project. Ecol Eng, 2016, 96: 109-16. [CrossRef]
- QAZI A, SIMSEKLER M C E. Assessment of humanitarian crises and disaster risk exposure using data-driven Bayesian Networks. Int J Disast Risk Re, 2021, 52. [CrossRef]
- HECKERMAN D, GEIGER D, CHICKERING D M. Learning Bayesian Networks - the Combination of Knowledge and Statistical-Data. Mach Learn, 1995, 20(3): 197-243. [CrossRef]
- YUNANA D, MACLAINE S, TNG K H, et al. Developing Bayesian networks in managing the risk of Legionella colonisation of groundwater aeration systems. Water Res, 2021, 193. [CrossRef]
- KAIKKONEN L, PARVIAINEN T, RAHIKAINEN M, et al. Bayesian Networks in Environmental Risk Assessment: A Review. Integr Environ Asses, 2021, 17(1): 62-78. [CrossRef]
- MITCHELL C J, LAWRENCE E, CHU V R, et al. Integrating Metapopulation Dynamics into a Bayesian Network Relative Risk Model: Assessing Risk of Pesticides to Chinook Salmon (Oncorhynchus tshawytscha) in an Ecological Context. Integr Environ Asses, 2021, 17(1): 95-109. [CrossRef]
- XIE X L, ZUO J X, XIE B Q, et al. Bayesian network reasoning and machine learning with multiple data features: air pollution risk monitoring and early warning. Nat Hazards, 2021, 107(3): 2555-72. [CrossRef]
- CARRIGER J F, PARKER R A. Conceptual Bayesian networks for contaminated site ecological risk assessment and remediation support. J Environ Manage, 2021, 278. [CrossRef]
- PARVIAINEN T, GOERLANDT F, HELLE I, et al. Implementing Bayesian networks for ISO 31000:2018-based maritime oil spill risk management: State-of-art, implementation benefits and challenges, and future research directions. J Environ Manage, 2021, 278. [CrossRef]
- MICHIE S, RICHARDSON M, JOHNSTON M, et al. The Behavior Change Technique Taxonomy (v1) of 93 Hierarchically Clustered Techniques: Building an International Consensus for the Reporting of Behavior Change Interventions. Ann Behav Med, 2013, 46(1): 81-95. [CrossRef]
- DALKEY N, HELMER O. An Experimental Application of the Delphi Method to the Use of Experts. Manage Sci, 1963, 9(3): 458-67. [CrossRef]
- CHEN C T, LIN C T, HUANG S F. A fuzzy approach for supplier evaluation and selection in supply chain management. Int J Prod Econ, 2006, 102(2): 289-301. [CrossRef]
- CHANG D Y. Applications of the extent analysis method on fuzzy AHP. Eur J Oper Res, 1996, 95(3): 649-55. [CrossRef]
- YANG M S, KO C H. On a class of fuzzy c-numbers clustering procedures for fuzzy data. Fuzzy Set Syst, 1996, 84(1): 49-60. [CrossRef]
- VANLAARHOVEN P J M, PEDRYCZ W. A Fuzzy Extension of Saatys Priority Theory. Fuzzy Set Syst, 1983, 11(3): 229-41. [CrossRef]
- WANG Y M, LUO Y, HUA Z. On the extent analysis method for fuzzy AHP and its applications. Eur J Oper Res, 2008, 186(2): 735-47. [CrossRef]
- HSIEH H F, SHANNON S E. Three approaches to qualitative content analysis. Qual Health Res, 2005, 15(9): 1277-88. [CrossRef]
- DLAMINI W M. A Bayesian belief network analysis of factors influencing wildfire occurrence in Swaziland. Environ Modell Softw, 2010, 25(2): 199-208. [CrossRef]
- HAMILTON D P, SCHLADOW S G. Prediction of water quality in lakes and reservoirs .1. Model description. Ecol Model, 1997, 96(1-3): 91-110. [CrossRef]
- LANDIS W G. The Origin, Development, Application, Lessons Learned, and Future Regarding the Bayesian Network Relative Risk Model for Ecological Risk Assessment. Integr Environ Asses, 2021, 17(1): 79-94. [CrossRef]
- PIFFADY J, CARLUER N, GOUY V, et al. ARPEGES: A Bayesian Belief Network to Assess the Risk of Pesticide Contamination for the River Network of France. Integr Environ Asses, 2021, 17(1): 188-201. [CrossRef]
- MOE S J, CARRIGER J F, GLENDELL M. Increased Use of Bayesian Network Models Has Improved Environmental Risk Assessments. Integr Environ Asses, 2021, 17(1): 53-61. [CrossRef]
- SAHLIN U, HELLE I, PEREPOLKIN D. “This Is What We Don’t Know”: Treating Epistemic Uncertainty in Bayesian Networks for Risk Assessment. Integr Environ Asses, 2021, 17(1): 221-32. [CrossRef]
- LIU K F, YANG L Z, LI M. Application of Cloud Model and Bayesian Network to Piracy Risk Assessment. Math Probl Eng, 2021, 2021. [CrossRef]
- BORGHEIPOUR H, TEHRANI G M, ESKANDARI T, et al. Dynamic risk analysis of hydrogen gas leakage using Bow-tie technique and Bayesian network. International Journal of Environmental Science and Technology, 2021, 18(11): 3613-24. [CrossRef]
- SONG Y C, KOU S Y, WANG C. Modeling crash severity by considering risk indicators of driver and roadway: A Bayesian network approach. J Safety Res, 2021, 76: 64-72. [CrossRef]
- ZENG R, JIANG Y T, CHEN T W, et al. Longitudinal associations of sleep duration and sleep quality with coronary heart disease risk among adult population: classical meta-analysis and Bayesian network meta-analysis. Sleep Biol Rhythms, 2021, 19(3): 265-76. [CrossRef]
- SANUY M, JIMENEZ J A. Probabilistic characterisation of coastal storm-induced risks using Bayesian networks. Nat Hazard Earth Sys, 2021, 21(1): 219-38. [CrossRef]
- YANG L, LI K P, SONG G Z, et al. Dynamic Railway Derailment Risk Analysis with Text-Data-Based Bayesian Network. Appl Sci-Basel, 2021, 11(3). [CrossRef]
- LI Z, HU S P, GAO G P, et al. Risk Reasoning from Factor Correlation of Maritime Traffic under Arctic Sea Ice Status Association with a Bayesian Belief Network. Sustainability-Basel, 2021, 13(1). [CrossRef]
- MACHADO E R, DO VALLE R F, PISSARRA T C T, et al. Diagnosis on Transport Risk Based on a Combined Assessment of Road Accidents and Watershed Vulnerability to Spills of Hazardous Substances. Int J Env Res Pub He, 2018, 15(9). [CrossRef]
- XU B, HU J, HU T, et al. Quantitative assessment of seismic risk in hydraulic fracturing areas based on rough set and Bayesian network: A case analysis of Changning shale gas development block in Yibin City, Sichuan Province, China. J Petrol Sci Eng, 2021, 200. [CrossRef]
- KHAN R U, YIN J B, MUSTAFA F S. Accident and pollution risk assessment for hazardous cargo in a port environment. Plos One, 2021, 16(6). [CrossRef]
- LI C H, TIAN Y T, ZHAO Y W, et al. Research progress on risk assessment and emergency countermeasures of sudden water pollution[J].Journal of Agro-Environment Science,2020,39(6):1161-1167.
- ZHAO Y B, ZHANG K, XU X T, et al. Substantial Changes in Nitrogen Dioxide and Ozone after Excluding Meteorological Impacts during the COVID-19 Outbreak in Mainland China. Environ Sci Tech Let, 2020, 7(6): 402-8. [CrossRef]
- LINARES C, DIAZ J, NEGEV M, et al. Impacts of climate change on the public health of the Mediterranean Basin population - Current situation, projections, preparedness and adaptation. Environ Res, 2020, 182. [CrossRef]
- DING L, CHEN K L, LIU T, et al. Spatial-Temporal Hotspot Pattern Analysis of Provincial Environmental Pollution Incidents and Related Regional Sustainable Management in China in the Period 1995-2012. Sustainability-Basel, 2015, 7(10): 14385-407. [CrossRef]
- YANG H D, SHAO D G, LU B Y. A New Traceability Method for Sudden Water Pollution Accidents. Environmental Protection and Resources Exploitation, Pts 1-3, 2013, 807-809: 1570-+. [CrossRef]
- WANG H T, JIA X B, LIU D M, et al. Emergency treatment measures for sudden pollution incidents in source water with some contaminants: A review. Advances in Chemical Engineering Iii, Pts 1-4, 2013, 781-784: 1950-+. [CrossRef]
- PAN F H, WANG Y B, ZHANG X X. Emergency measure of soft isolation controlling pollution diffusion response to sudden water pollution accidents. Water Sci Technol, 2019, 80(7): 1238-48. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).