Submitted:
25 July 2023
Posted:
26 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Results
2.1. Features of Pregnancy Course and Outcomes with COVID-19 Infection
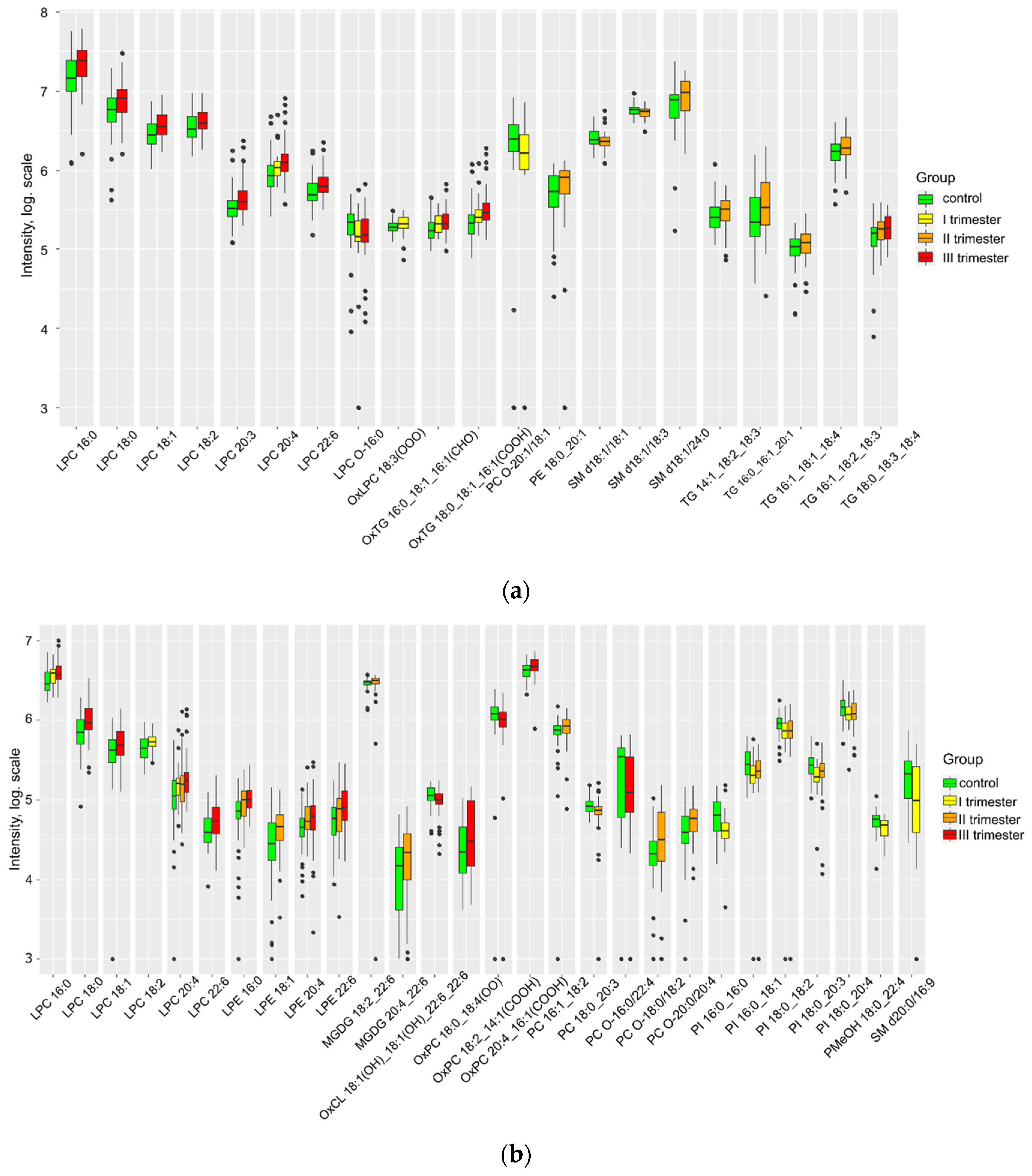
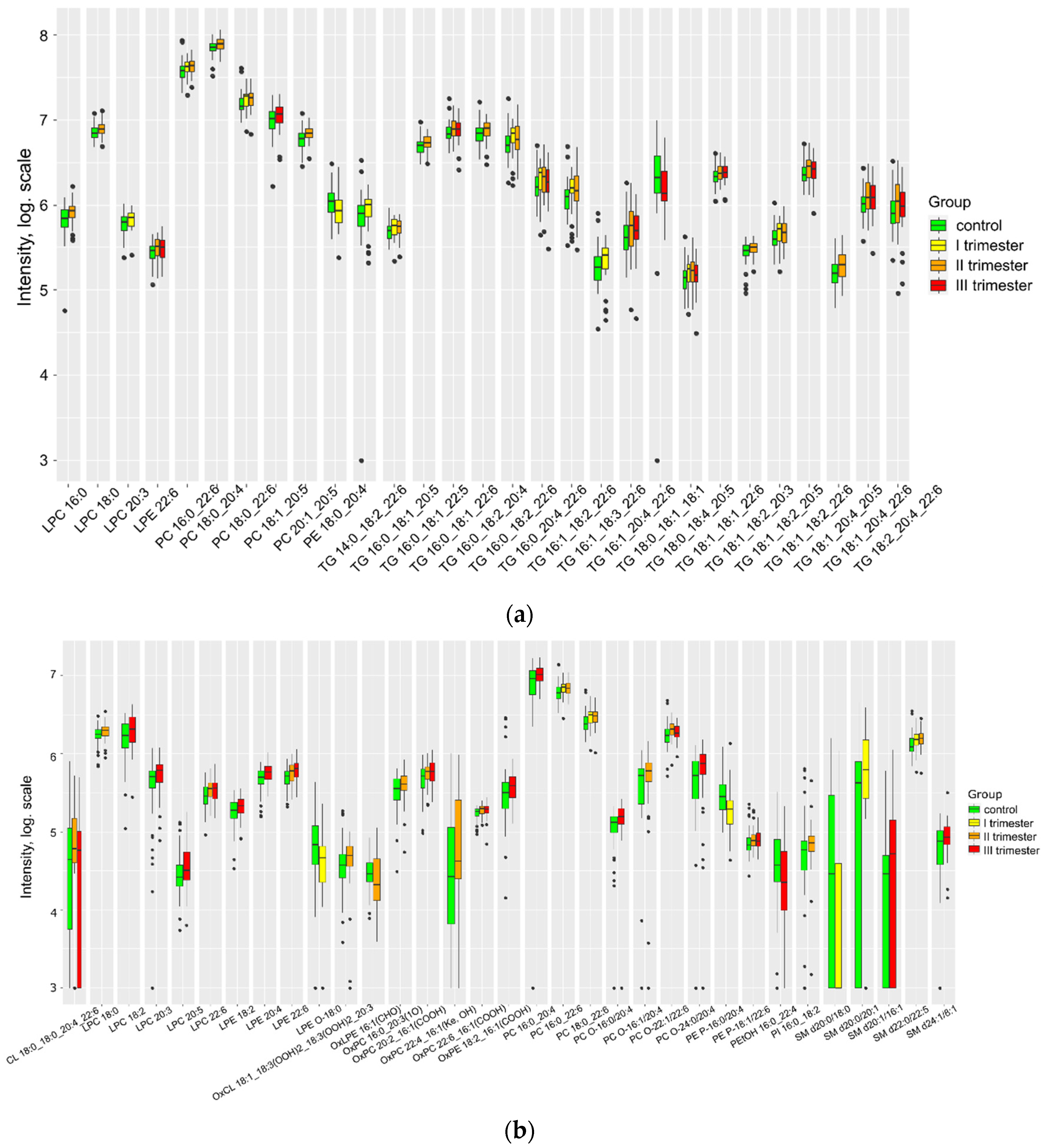
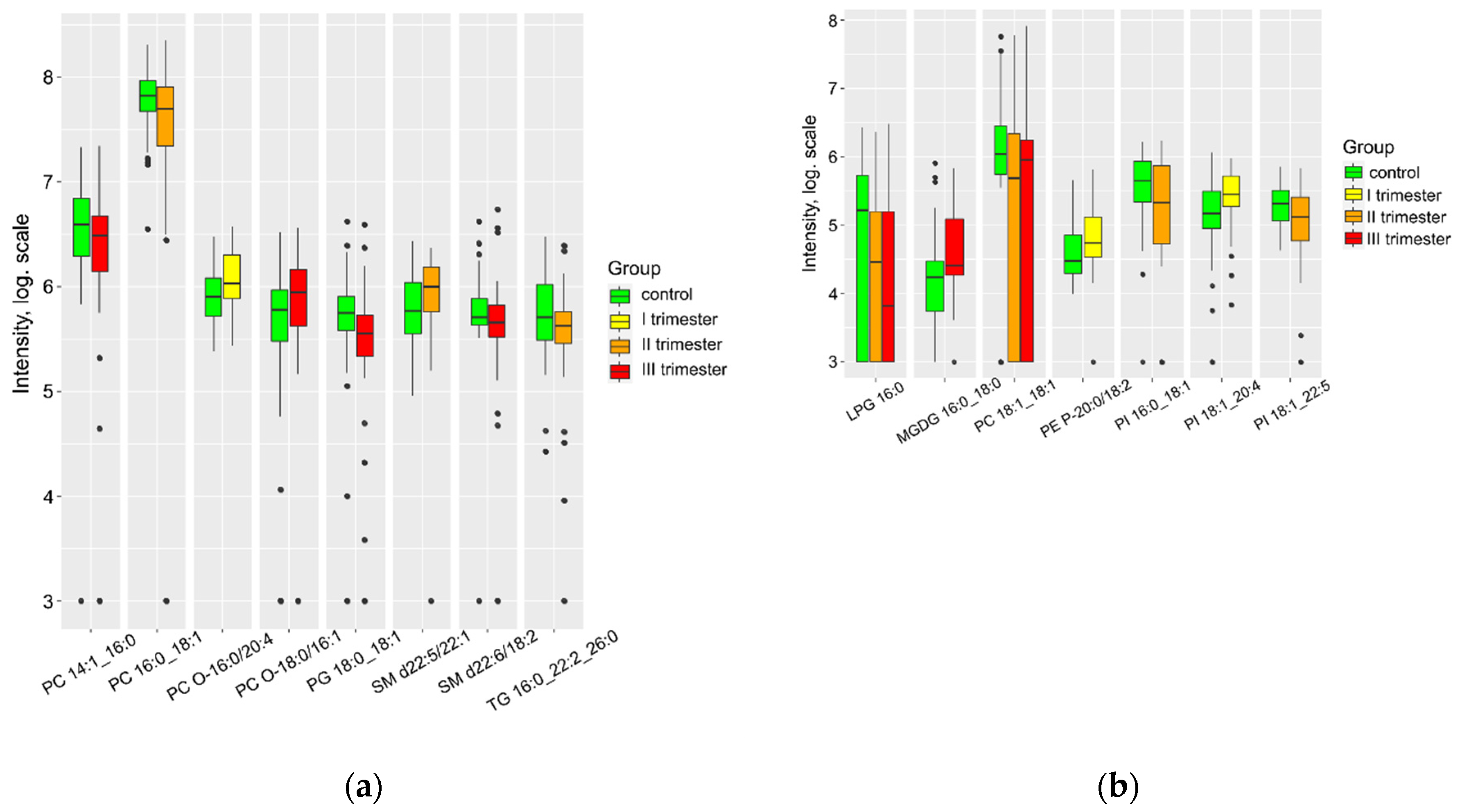
2.2. COVID-19 Related Changes in Maternal Plasma, Cord Blood and Amniotic Fluid Lipidome
3. Discussion
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Study Design
4.2 Sample Collection
4.3. Sample Preparation and Lipidomic Analysis (HPLC-MS/MS)
4.4. Statistical Analysis
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Collier, S.A.; Rasmussen, S.A.; Feldkamp, M.L.; Honein, M.A. Prevalence of self-reported infection during pregnancy among control mothers in the national birth defects prevention study. Birth Defects Res. Part A - Clin. Mol. Teratol. 2009, 85, 193–201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, Y.; Teng, H.; Xiao, Y.; Yao, M.; Yin, J.; Sun, G. Impact of SARS-CoV-2 Infection During Pregnancy on Infant Neurobehavioral Development: A Case-Control Study. Front. Pediatr. 2021, 9, 1–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivanti, A.J.; Vauloup-Fellous, C.; Prevot, S.; Zupan, V.; Suffee, C.; Do Cao, J.; Benachi, A.; De Luca, D. Transplacental transmission of SARS-CoV-2 infection. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sukhikh, G.; Petrova, U.; Prikhodko, A.; Starodubtseva, N.; Chingin, K.; Chen, H.; Bugrova, A.; Kononikhin, A.; Bourmenskaya, O.; Brzhozovskiy, A.; et al. Vertical transmission of SARS-CoV-2 in second trimester associated with severe neonatal pathology. Viruses 2021, 13, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yuan, J.; Qian, H.; Cao, S.; Dong, B.; Yan, X.; Luo, S.; Zhou, M.; Zhou, S.; Ning, B.; Zhao, L. Is there possibility of vertical transmission of COVID-19: A systematic review. Transl. Pediatr. 2021, 10, 423–434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liang, H.; Acharya, G. Novel corona virus disease (COVID-19) in pregnancy: What clinical recommendations to follow? Acta Obstet. Gynecol. Scand. 2020, 99, 439–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gootjes, D. V.; Posthumus, A.G.; Wols, D.F.; de Rijke, Y.B.; Roeters Van Lennep, J.E.; Steegers, E.A.P. Maternal lipid profile in pregnancy and embryonic size: a population-based prospective cohort study. BMC Pregnancy Childbirth 2022, 22, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- San Martín-González, N.; Castro-Quintas, Á.; Marques-Feixa, L.; Ayesa-Arriola, R.; López, M.; Fañanás, L. Maternal respiratory viral infections during pregnancy and offspring’s neurodevelopmental outcomes: A systematic review. Neurosci. Biobehav. Rev. 2023, 149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Yuan, D.; Chen, D.G.; Ng, R.H.; Wang, K.; Choi, J.; Li, S.; Hong, S.; Zhang, R.; Xie, J.; et al. Multiple early factors anticipate post-acute COVID-19 sequelae. Cell 2022, 185, 881–895.e20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Szczuko, M.; Kikut, J.; Komorniak, N.; Bilicki, J.; Celewicz, Z.; Ziętek, M. The role of arachidonic and linoleic acid derivatives in pathological pregnancies and the human reproduction process. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 1–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nicotra, M.; Muttinelli, C.; Sbracia, M.; Rolfi, G.; Passi, S. Blood levels of lipids, lipoperoxides, vitamin E and glutathione peroxidase in women with habitual abortion. Gynecol. Obstet. Invest. 1994, 38, 223–226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Newman, J.W.; Stok, J.E.; Vidal, J.D.; Corbin, C.J.; Huang, Q.; Hammock, B.D.; Conley, A.J. Cytochrome P450-dependent lipid metabolism in preovulatory follicles. Endocrinology 2004, 145, 5097–5105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X. Lysophospholipid signaling in the function and pathology of the reproductive system. Hum. Reprod. Update 2008, 14, 519–536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ye, X.; Chun, J. Lysophosphatidic Acid (LPA) Signaling in Vertebrate Reproduction. Trends Endocrinol. Metab. 2010, 21, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsalouhidou, S.; Argyrou, C.; Theofilidis, G.; Karaoglanidis, D.; Orfanidou, E.; Nikolaidis, M.G.; Petridou, A.; Mougios, V. Mitochondrial phospholipids of rat skeletal muscle are less polyunsaturated than whole tissue phospholipids: Implications for protection against oxidative stress. J. Anim. Sci. 2006, 84, 2818–2825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Veyrat-Durebex, C.; Bocca, C.; Chupin, S.; Kouassi Nzoughet, J.; Simard, G.; Lenaers, G.; Reynier, P.; Blasco, H. Metabolomics and Lipidomics Profiling of a Combined Mitochondrial Plus Endoplasmic Reticulum Fraction of Human Fibroblasts: A Robust Tool for Clinical Studies. J. Proteome Res. 2018, 17, 745–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pecks, U.; Brieger, M.; Schiessl, B.; Bauerschlag, D.O.; Piroth, D.; Bruno, B.; Fitzner, C.; Orlikowsky, T.; Maass, N.; Rath, W. Maternal and fetal cord blood lipids in intrauterine growth restriction. J. Perinat. Med. 2012, 40, 287–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adank, M.C.; Benschop, L.; Kors, A.W.; Peterbroers, K.R.; Smak Gregoor, A.M.; Mulder, M.T.; Schalekamp-Timmermans, S.; Roeters Van Lennep, J.E.; Steegers, E.A.P. Maternal lipid profile in early pregnancy is associated with foetal growth and the risk of a child born large-for-gestational age: A population-based prospective cohort study. BMC Med. 2020, 18, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quinn, J.F.; Raman, R.; Thomas, R.G.; Yurko-Mauro, K.; Nelson, E.B.; Van Dyck, C.; Galvin, J.E.; Emond, J.; Jack, C.R.; Weiner, M.; et al. Docosahexaenoic acid supplementation and cognitive decline in Alzheimer disease: A randomized trial. Jama 2010, 304, 1903–1911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.-R.; Xu, Z.-Z.; Strichartz, G.; Serhan, C.N. Emerging Roles of Resolvins in the Resolution of Inflammation and pain. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 599–609. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matesanz, N.; Park, G.; Mcallister, H.; Leahey, W.; Devine, A.; Mcveigh, G.E.; Gardiner, T.A.; Mcdonald, D.M. Docosahexaenoic Acid Improves the Nitroso-Redox Balance and Reduces VEGF-Mediated Angiogenic Signaling in Microvascular Endothelial Cells AND. Invest. Ophthalmol. Vis. Sci. 2010, 51, 6815–6825. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Basak, S.; Mallick, R. Maternal Docosahexaenoic Acid Status during Pregnancy and Its Impact on Infant Neurodevelopment. Nutrients 2020, 12, 3615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Williams, N.C.; Neill, L.A.J.O.; Munder, M.; Gutenberg-universität, J. A Role for the Krebs Cycle Intermediate Citrate in Metabolic Reprogramming in Innate Immunity and Inflammation. Front. Immunol. 2018, 9, 141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Martínez-reyes, I.; Chandel, N.S. Mitochondrial TCA cycle metabolites control. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sa, F.J.; Ange, C.; Rodr, M. The Role of Tricarboxylic Acid Cycle Metabolites in Viral Infections. Front. Cell. Infect. Microbiol. 2021, 11, 725043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bertolaccini, M.L.; Amengual, O.; Atsumi, T.; Binder, W.L.; De Laat, B.; Forastiero, R.; Kutteh, W.H.; Lambert, M.; Matsubayashi, H.; Murthy, V.; et al. “Non-criteria” aPL tests: Report of a task force and preconference workshop at the 13th International Congress on Antiphospholipid Antibodies, Galveston, TX, USA, April 2010. Lupus 2011, 20, 191–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsuragawa, H.; Kanzaki, H.; Inoue, T.; Hirano, T.; Mori, T.; Rote, N.S. Monoclonal Antibody against Phosphatidylserine Inhibits In Vitro Human Trophoblastic Hormone Production and Invasion ’. Biol. Reprod. 1997, 56, 50–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cervera, R.; Balasch, J. Autoimmunity and Recurrent Pregnancy Losses. Clin. Rev. Allergy Immunol. 2010, 39, 148–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sastry, S.; Cuomo, F.; Muthusamy, J. COVID-19 and thrombosis: The role of hemodynamics. Thromb. Res. J. 2020, 212, 51–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abusukhun, M.; Winkler, M.S.; Pöhlmann, S.; Moerer, O.; Meissner, K.; Tampe, B.; Hofmann-Winkler, H.; Bauer, M.; Gräler, M.H.; Claus, R.A. Activation of Sphingomyelinase-Ceramide-Pathway in COVID-19 Purposes Its Inhibition for Therapeutic Strategies. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hallman, M.; Gluck, L. Phosphatidylglycerol in lung surfactant. III. Possible modifier of surfactant function. J. Lipid Res. 1976, 17, 257–262. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kornhuber, J. The acid sphingomyelinase / ceramide system in COVID-19. Mol. Psychiatry 2022, 27, 307–314. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fakhr, Y.; Brindley, D.N.; Hemmings, D.G. Physiological and pathological functions of sphingolipids in pregnancy. Cell. Signal. 2021, 85, 110041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lomova, N.; Dolgushina, N.; Tokareva, A.; Chagovets, V.; Starodubtseva, N. Past COVID-19 : The Impact on IVF Outcomes Based on Follicular Fluid Lipid Profile. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iurova, M. V.; Chagovets, V. V.; Pavlovich, S. V.; Starodubtseva, N.L.; Khabas, G.N.; Chingin, K.S.; Tokareva, A.O.; Sukhikh, G.T.; Frankevich, V.E. Lipid Alterations in Early-Stage High-Grade Serous Ovarian Cancer. Front. Mol. Biosci. 2022, 9, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tonoyan, N.M.; Chagovets, V. V.; Starodubtseva, N.L.; Tokareva, A.O.; Chingin, K.; Kozachenko, I.F.; Adamyan, L. V.; Frankevich, V.E. Alterations in lipid profile upon uterine fibroids and its recurrence. Sci. Rep. 2021, 11, 11447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Starodubtseva, N.L.; Tokareva, A.O.; Rodionov, V. V; Brzhozovskiy, A.G.; Bugrova, A.E.; Chagovets, V. V; Kometova, V. V; Kukaev, E.N.; Soares, N.C.; Kovalev, G.I.; et al. Integrating Proteomics and Lipidomics for Evaluating the Risk of Breast Cancer Progression : A Pilot Study. Biomedicines 2023, 11, 1786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koelmel, J.P.; Kroeger, N.M.; Ulmer, C.Z.; Bowden, J.A.; Patterson, R.E.; Cochran, J.A.; Beecher, C.W.W.; Garrett, T.J.; Yost, R.A. LipidMatch: An automated workflow for rule-based lipid identification using untargeted high-resolution tandem mass spectrometry data. BMC Bioinformatics 2017, 18, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tokareva, A.O.; Chagovets, V. V.; Kononikhin, A.S.; Starodubtseva, N.L.; Nikolaev, E.N.; Frankevich, V.E. Normalization methods for reducing interbatch effect without quality control samples in liquid chromatography-mass spectrometry-based studies. Anal. Bioanal. Chem. 2021, 413, 3479–3486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Group Ia (n = 41) | Group Ib (n = 67) | Group Ic (n = 67) | Control (n = 59) | P | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Anthropometric data and age | |||||
| Age, years | 32.0(28.0;36.0) | 32.0(28.0;34.0) | 31.0(28.3;25.0) | 33.0(29.0;36.0) | 0.54 |
| Height, cm | 165(160;171) | 165(162;170) | 165(163;170) | 168(163;170) | 0.50 |
| Weight, kg | 74.0(66.3;82.0) | 72.0(67.0;83.5) | 73.0(66.5;78.3) | 72.0(66.0;81.0) | 0.88 |
| BMI, kg/m2 | 27.0(25.0;30.5) | 26.0(24.0;29.0) | 27.0(24.3;29.0) | 26.0(24.0;29.0) | 0.66 |
| Lipid metabolism disorders, n (%) | 26 (63.4) | 39 (58.2) | 39 (58.2) | 34 (25.1) | 0.94 |
| Reproductive history | |||||
| Number of pregnancies | 2.0 (1.0; 3.0) |
2.0 (1.0; 3.0) |
2.0 (1.0; 3.0) |
2.0 (1.0; 2.5) |
0.95 |
| Medical abortion | 4 (9.8) | 10(14.9) | 12(17.9) | 4 (6.8) | 0.25 |
| Non-developing pregnancy | 6 (14.6) | 14 (20.9) | 16 (23.9) | 6 (10.2) | 0.19 |
| The course of the first trimester of pregnancy | |||||
| Chorion previa n(%) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.5) | 2(3.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.41 |
| Toxicosis n(%) | 6 (14.6) | 18(26.9) | 17(25.3) | 10(16.9) | 0.32 |
| Anemia before 12 weeks n (%) | 4 (9.8) | 0(0.0) | 0(0.0) | 2 (3.4) | 0.007 |
| Exacerbation of chronic diseases before 12 weeks n (%) | 0(0.0) | 2(3.0) | 1(1.5) | 2(3.4) | 0.64 |
| Hormonal support up to 12 weeks n(%) | 9 (20.0) | 10(14.9) | 16(23.9) | 6 (10.1) | 0.18 |
| Gestational diabetes up to 12 weeks n(%) | 2 (4.9) | 1(1.5) | 1(1.5) | 1 (1.7) | 0.62 |
| Antibacterial therapy up to 12 weeks n (%) | 5(12.1) | 3(4.5) | 3(4.5) | 2 (3.4) | 0.22 |
| Threatened miscarriage before 12 weeks n(%) | 8(19.5) | 12(17.9) | 14(20.9) | 6 (10.9) | 0.41 |
| The course of the second trimester of pregnancy | |||||
| Isthmic-cervical insufficiency n(%) | 3 (7.3) | 4 (6.0) | 4(6.0) | 0 (0.0) | 0.26 |
| Surgical correction n(%) | 2 (4.9) | 3(4.5) | 2(3.1) | 0 (0.0) | 0.41 |
| Obstetric pessary n(%) | 1 (2.4) | 1(1.5) | 3(4.5) | 0 (0.0) | 0.37 |
| Threatened miscarriage or preterm birth from 13 to 27 weeks n(%) | 2 (4.9) | 7(10.4) | 7(10.4) | 1 (1.7) | 0.17 |
| Anemia from 13 to 27 weeks n(%) | 4(9.7) | 9(13.4) | 6(9.0) | 8 (13.6) | 0.79 |
| Antibacterial therapy from 13 to 27 weeks n(%) | 3(7.3) | 13(19.4) | 2(3.0) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| Gestational diabetes from 13 to 27 weeks n(%) | 3 (7.3) | 7(10.4) | 5(7.5) | 1 (1.7) | 0.27 |
| The course of the third trimester of pregnancy | |||||
| Risk of preterm birth after 28 weeks n(%) | 5(12.2) | 3(4.5) | 5(7.5) | 4(6.7) | 0.53 |
| Anemia after 28 weeks n(%) | 12(29.3) | 17(25.8) | 13(19.4) | 21(35.6) | 0.23 |
| Edema of pregnancy n(%) | 1(2.1) | 5(7.8) | 2(3.0) | 1(1.7) | 0.31 |
| Antibacterial therapy after 28 weeks n(%) | 0(0.0) | 0(0.0) | 6(9.0) | 0(0.0) | 0.002 |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus after 28 weeks n(%) | 1(2.1) | 4(6.1) | 0(0.0) | 1(1.7) | 0.16 |
| Terms and methods of delivery | |||||
| Delivery time, weeks | 39.2 (38.3;40.1) |
39.6 (38.4;40.4) |
39.4 (38.5;40.1) |
39.5 (39.0;40.2) |
0.26 |
| Type of delivery n(%) Natural birth | 29(70.7) | 50(74.6) | 44(65.7) | 39 (66.1) | 0.19 |
| Type of delivery n(%) Cesarean section | 12(29.3) | 17(25.4) | 23(34.3) | 20(33.9) | |
| Planned caesarean section, n(%) | 5(41.7) | 5 (29.4) | 10 (50.0) | 15 (75.0) | 0.04 |
| Emergency caesarean section, n(%) | 7 (58.3) | 12 (70.6) | 10 (50.0) | 5 (25.0) | |
| Newborn Data | |||||
| Weight, kg | 3.4(2.9;3.6) | 3.4(3.0;3.8) | 3.4(3.1;3.8) | 3.5(3.2;3.7) | 0.50 |
| Length cm | 53(51;54) | 52(50;54) | 52(51;54) | 53(51;54) | 0.55 |
| Presence of deviations n(%) | 30 (73.2) | 38 (56.7) | 41 (61.1) | 19 (32.2) | <0.001 |
| Apgar-1 n(%) 8 | 37 (90.2) | 60 (89.6) | 63 (94.0) | 54 (91.5) | 0.52 |
| 7 | 4 (9.7) | 3 (4.5) | 4 (6.0) | 4 (6.8) | |
| 6 | 0 (0.0) | 2 (3.0) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.7) | |
| 5 | 0 (0.0) | 2(3.0) | 0(0.0) | 0 (0.0) | |
| Apgar-5 n(%) 9 | 26 (63.4) | 53 (79.1) | 56 (83.6) | 53 (89.8) | 0.007 |
| 8 | 14 (34.1) | 9 (13.4) | 11 (16.4) | 5 (8.5) | |
| 7 | 1 (2.4) | 5 (7.5) | 0 (0.0) | 1 (1.7) | |
| Additional chord of the ventricle, n(%) | 3 (7.3) | 13 (19.4) | 4(5.9) | 0 (0.0) | <0.001 |
| Interatrial communication n(%) | 17 (41.5) | 22 (32.8) | 25 (37.3) | 8(13.6) | 0.007 |
| Group Ia (n=41) | Group Ib (n=67) | Group Ic (n=67) | P | |||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Treatment | Outpatient | 36 (87.8) | 54 (80.6) | 56 (83.6) | 0.60 | |||||
| Hospital | 5 (12.2) | 13 (19.4) | 11 (16.4) | |||||||
| The course of the disease | Asymptomatic | 11 (26.8) | 20(29.9) | 18(26.9) | 0.86 | 0.55 | ||||
| Symptoms | temperature | 30(73.2) | 22(53.7) | 47 (70.1) | 38 (56.7) | 49(73.1) | 33(49.3) | |||
| cough | 14 (34.1) | 20 (29.9) | 23 (34.3) | 0.94 | ||||||
| anosmia | 14 (34.1) | 32(47.8) | 28 (41.8) | 0.11 | ||||||
| pneumonia | 3 (7.3) | 11 (16.4) | 4 (6.0) | 0.06 | ||||||
| Parameter | Control (n=59) | Group I (n=175) | P |
|---|---|---|---|
| I trimester of pregnancy | |||
| Delivery time | Timely—54 (91.5%) Premature—1 (1.7%) Belated—4 (6.8%) |
Timely—34 (82.9%) Premature—6 (14.6%) Belated—1 (2.4%) |
0.03 |
| Apgar-5 minutes | 9–53 (89.8%) 8–5 (8.4%) 7–1 (1.7%) |
9–26 (65.0%) 8–13 (33.5%) 7–1 (2.5%) |
0.009 |
| Baby is healthy | No—19 (32.2%) Yes—40 (67.7%) |
No–30 (75.0%) Yes–10 (30.0%) |
<0.001 |
| II trimester of pregnancy | |||
| Delivery time | Timely–54 (91.5%) Premature–1 (1.7%) Belated–4 (6.8%) |
Timely—58 (86.6%) Premature—8 (11.9%) Belated—1 (1.5%) |
0.03 |
| Type of delivery | Emergency caesarean section—5 (8.6%) Natural childbirth—38 (64.4%) Planned caesarean section—15 (25.4%) |
Emergency caesarean section – 12 (18.2%) Natural childbirth—49 (72.0%) Planned caesarean section – 5 (6.5%) |
0.01 |
| Gestational diabetes mellitus | No—56 (94.9%) Yes. diet—2 (3.4%) Yes. insulin—1 (1.7%) |
No—54 (80.6%) Yes. diet—13 (19.4%) Yes. insulin—0 (0.0%) |
0.01 |
| Baby is healthy | No—19 (32.2%) Yes—40 (67.8%) |
No—38 (56.7%) Yes—29 (43.3%) |
0.01 |
| Additional chord | Yes—0 (0.0%) No—59 (100%) |
Yes—13 (19.7%) No—53 (80.3%) |
<0.001 |
| CHDs (Congenital Heart Defects) | No—51 (86.4%) Yes—8 (13.4%) |
No—44 (66.6%) Yes—22 (33.4%) |
0.02 |
| III trimester of pregnancy | |||
| Baby is healthy | No—19 (32.2%) Yes—40 (67.8%) |
No—41 (61.2%) Yes—26 (38.8%) |
0.002 |
| Model | Sensitivity | Specificity | Cutoff threshold |
AUC ROC | Variables |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Control | 0.94 | 0.89 | 0.63 | 0.93 | PC 16:0_16:0 *TG 14:0_16:1_18:2, OxLPC 18:4(OOO) * PC 16:0_18:2, PC P-16:0/18:2 * TG 16:0_16:0_18:1, PC 16:0_20:5 * OxPC 18:2_16:1(COOH) |
| COVID-19 at the I trimester |
0.89 | 0.86 | 0.31 | 0.87 | PC 16:1_18:0 * LPC 16:1 |
| COVID-19 at the II trimester |
0.75 | 0.92 | 0.37 | 0.88 | PC 16:0_20:1 * TG 16:0_16:1_18:0, SM d18:0/22:0 * TG 18:1_22:5_8:0, MGDG 16:0_20:0 * SM d18:0/22:0, PC 18:1_18:3 * OxPC 18:2_16:1(COOH) |
| COVID-19 at the III trimester |
0.88 | 0.89 | 0.28 | 0.89 | SM d18:1/24:1 * PC 18:1_20:1, PC 16:0_22:6 * PC O-16:0/20:4, PC 16:1_22:6 *PC 16:0_22:6, LPC 16:0 * PC P-20:1/18:1 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





