Submitted:
23 July 2023
Posted:
25 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
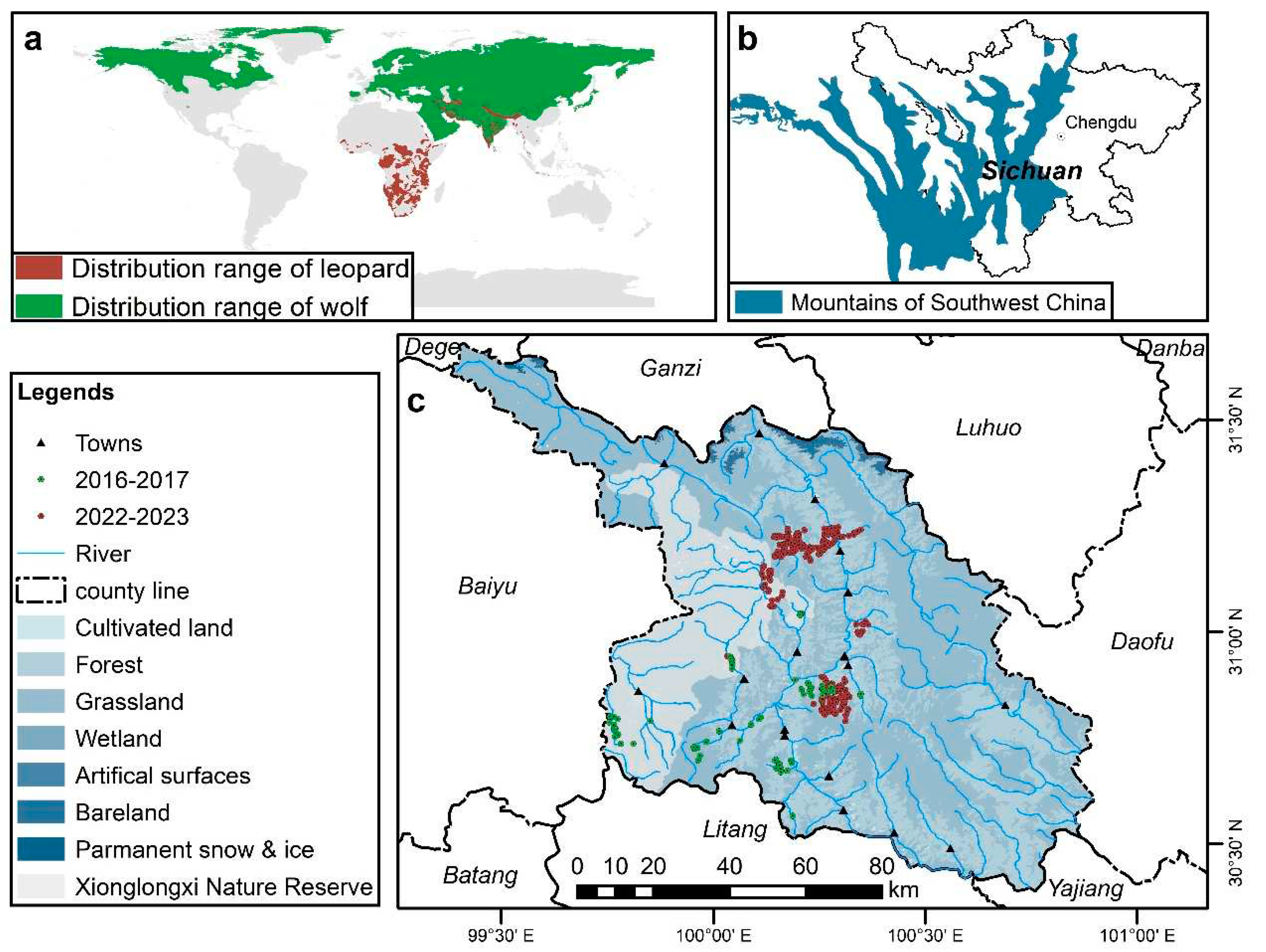
2.1. study area
2.2. Data collection
2.2.1. Camera trapping surveys
2.2.2. Environment variables
2.3. Data analysis
2.3.1. Ensemble model
2.3.2. Assessment of habitat suitability
2.3.3. Assessment of suitable habitat landscapes
3. Results
3.1. Ensemble model accuracy assessment
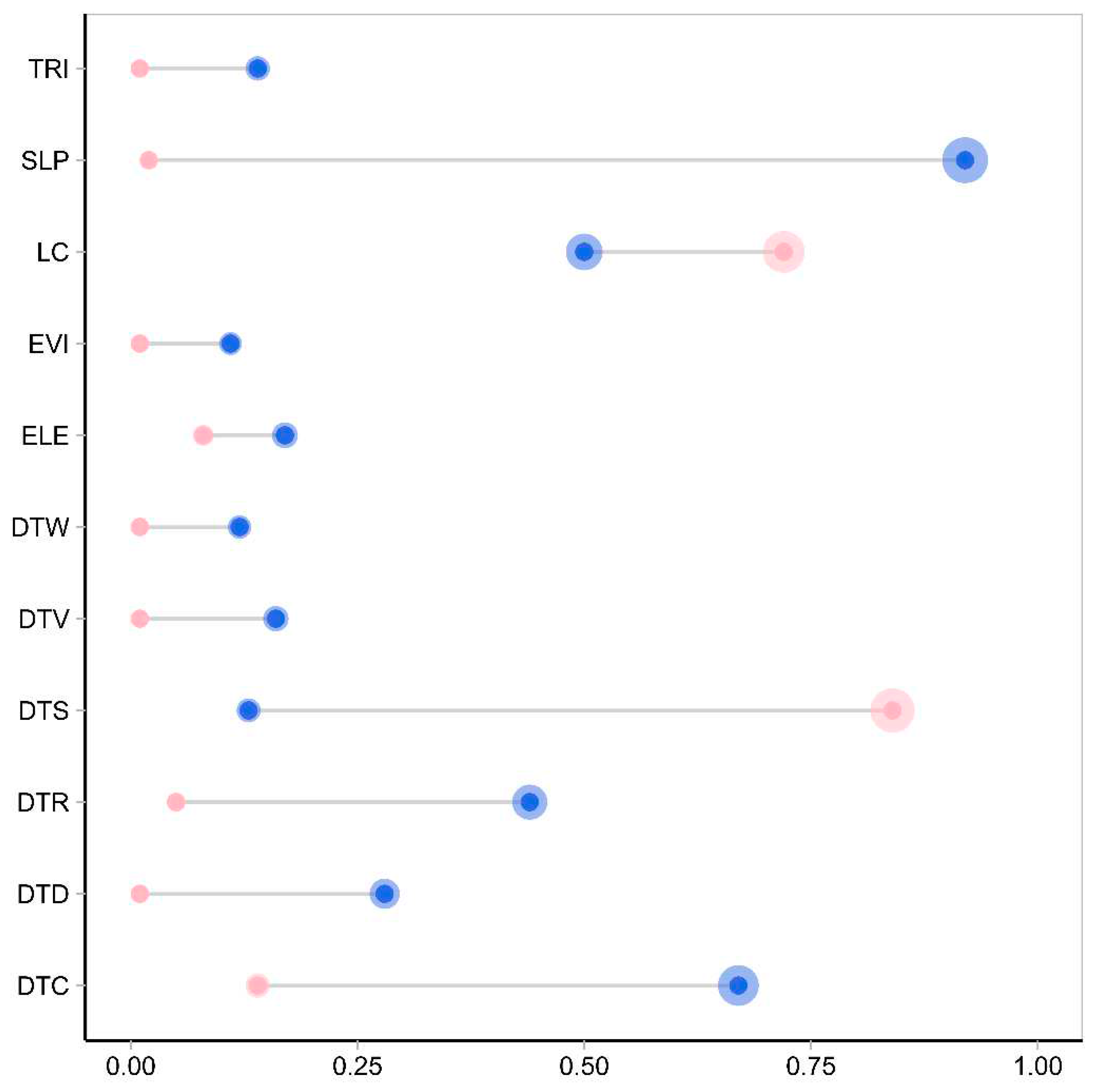
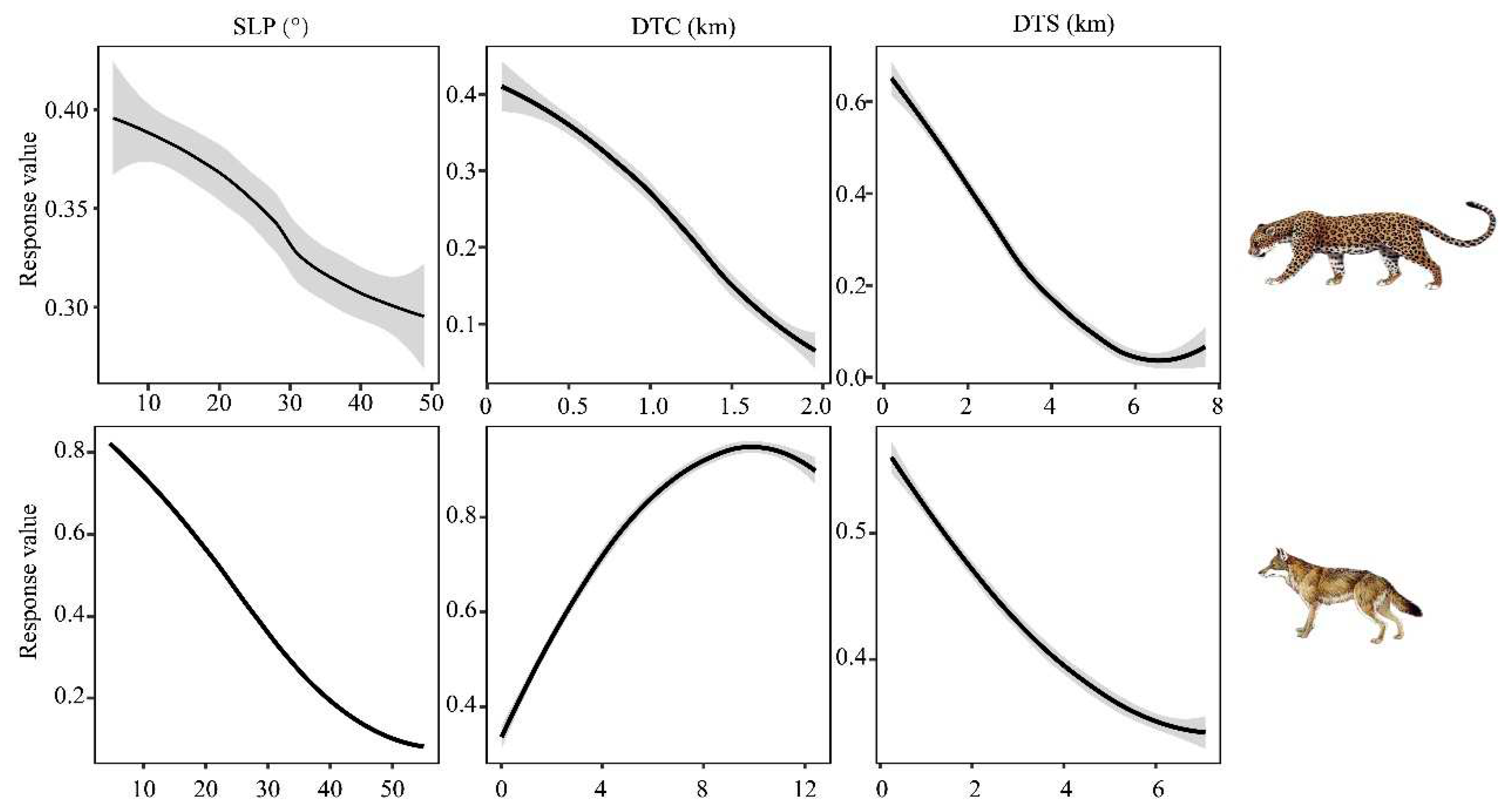
3.2. Environmental variable importance analysis
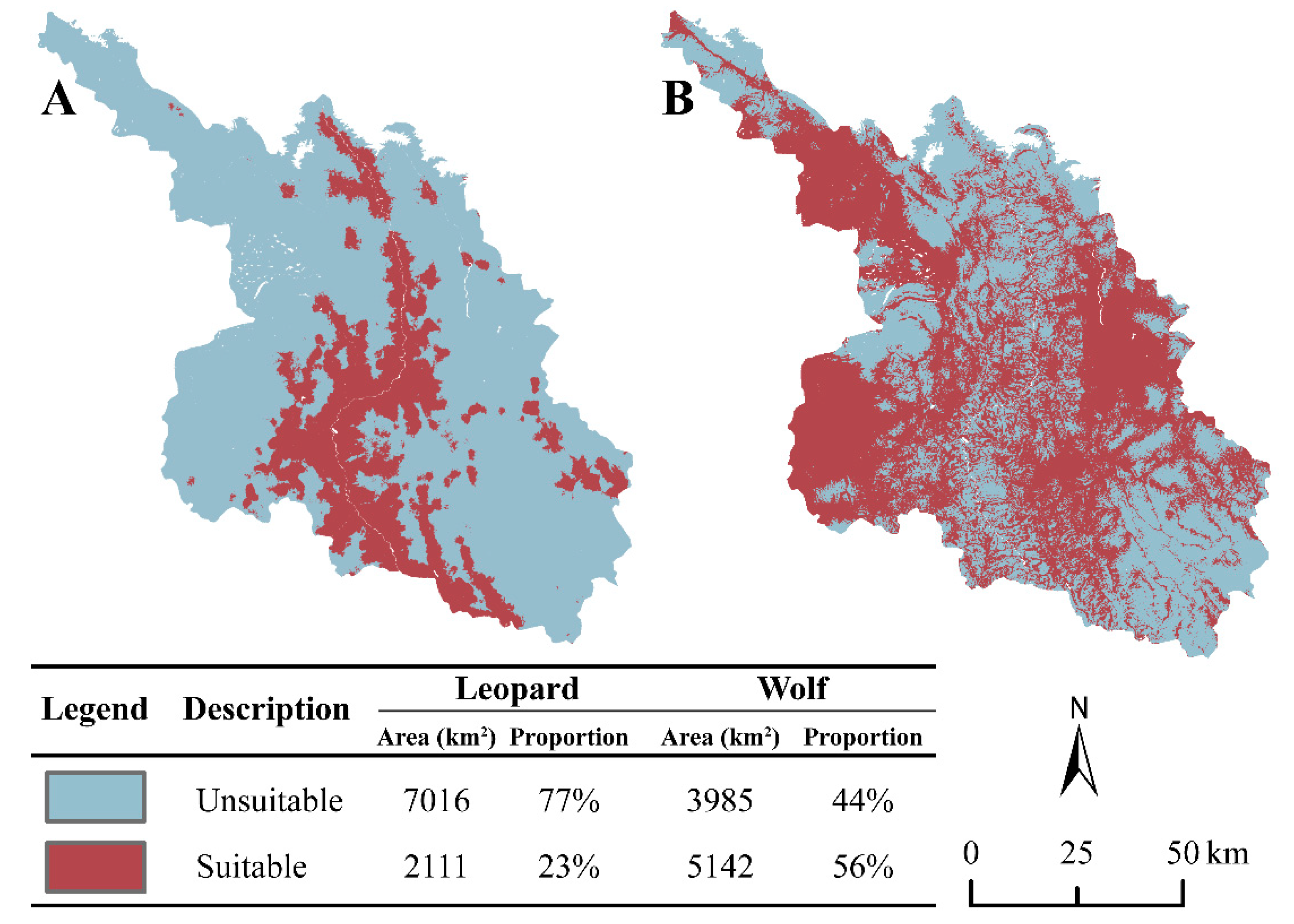
3.3. Habitat suitability evaluation
3.4. Habitat suitability landscape evaluation
4. Discussion
4.1. Divergent suitable habitats selection
4.2. Divergence in main environmental factors
4.3. Habitats fragmentation of wolf's near settlements
4.4. Future work
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix 1
| Index type | Exponential type | Meaning |
|---|---|---|
| Area index | Percentage of landscape (PLAND) | is the percentage (%) of the total area of a certain patch type in the entire landscape area. |
| Shape index | Landscape Shape Index(LSI) | The LSI value calculated the deviation degree of patch edge shape from a circle or square in the landscape. The closer the value was to 1, the closer the patch shape was to a circle or square. |
| Edge Density(ED) | Reflects the degree of landscape fragmentation, the larger the value, the greater the degree of fragmentation. | |
| Perimeter-Area Fractal Dimension(PAFRAC) | Reflecting the complexity of the landscape shape, 1≤PAFRAC≤2, the closer it tends to 1, the simpler the landscape shape is, and it may be less disturbed by humans. | |
| Connectivity index | Connectance index(CONNECT) | Reflecting the connectivity between patch types, the higher the value, the higher the landscape connectivity. |
| Aggregation index(AI) | Reflects the aggregation between patches of the same type, the smaller the value, the more discrete the landscape. | |
| Breakage index | Patch Density(PD) | Indicates the number of patches per unit area, reflecting the fragmentation of the landscape. |
| Variable | Code | Description | Variable types |
|---|---|---|---|
| Vegetation factor | EVI | Enhanced vegetation index | Continuous |
| Topographic factor | ELE | Elevation | Continuous |
| SLP | Slope | Continuous | |
| DTW | Distance to water | Continuous | |
| TRI | Terrain roughness index | Continuous | |
| DTC | Distance to cliffs | Continuous | |
| DTV | Distance to valleys | Continuous | |
| DTR | Distance to ridges | Continuous | |
| Disturbance factor | DTD | Distance to roads | Continuous |
| DTS | Distance to settlements | Continuous | |
| Other variables | LC | Land Cover | Categorical |
References
- Ripple, W.J.; Estes, J.A.; Beschta, R.L.; Wilmers, C.C.; Ritchie, E.G.; Hebblewhite, M.; Berger, J.; Elmhagen, B.; Letnic, M.; Nelson, M.P.; et al. Status and Ecological Effects of the World’s Largest Carnivores. Science 2014, 343, 1241484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Duo, L.; Li, S.; Wang, T. Competition and coexistence among terrestrial mammalian carnivores. Biodivers. Sci. 2021, 29, 81–97. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hardin, G. The Competitive Exclusion Principle: An Idea That Took a Century to Be Born Has Implications in Ecology, Economics, and Genetics. Science 1960, 131, 1292–1297. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Odden, M.; Wegge, P.; Fredriksen, T. Do Tigers Displace Leopards? If so Why? Ecol Res. Ecol. Res. 2010, 25, 875–881. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fennell, J.G.; Talas, L.; Baddeley, R.J.; Cuthill, I.C.; Scott-Samuel, N.E. Optimizing Colour for Camouflage and Visibility Using Deep Learning: The Effects of the Environment and the Observer’s Visual System. J. R. Soc. Interface. 2019, 16, 20190183. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahsavarzadeh, R.; Hemami, M.-R.; Farhadinia, M.S.; Fakheran, S.; Ahmadi, M. Spatially Heterogeneous Habitat Use across Distinct Biogeographic Regions in a Wide-Ranging Predator, the Persian Leopard. Biodivers. Conserv. 2023, 32, 2037–2053. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ngoprasert, D.; Lynam, A.J.; Gale, G.A. Human Disturbance Affects Habitat Use and Behaviour of Asiatic Leopard Panthera Pardus in Kaeng Krachan National Park, Thailand. Oryx 2007, 41, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haddad, N.M.; Brudvig, L.A.; Clobert, J.; Davies, K.F.; Gonzalez, A.; Holt, R.D.; Lovejoy, T.E.; Sexton, J.O.; Austin, M.P.; Collins, C.D.; et al. Habitat Fragmentation and Its Lasting Impact on Earth’s Ecosystems. Sci. Adv. 2015, 1, e1500052. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Lima Filho, J.A.; Vieira, R.J.A.G.; De Souza, C.A.M.; Ferreira, F.F.; De Oliveira, V.M. Effects of Habitat Fragmentation on Biodiversity Patterns of Ecosystems with Resource Competition. Physica. A. 2021, 564, 125497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ahmadi, M.; Balouchi, B.N.; Jowkar, H.; Hemami, M.-R.; Fadakar, D.; Malakouti-Khah, S.; Ostrowski, S. Combining Landscape Suitability and Habitat Connectivity to Conserve the Last Surviving Population of Cheetah in Asia. Divers. Distrib. 2017, 23, 592–603. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, X. Overlapping dietary and food ecological niches of three species of canids in eastern Inner Mongolia. Master thesis, Qufu Normal University, China, 2009. [Google Scholar]
- Zafar-ul Islam, M.; Volmer, R.; Al Boug, A.; Shehri, A.A.; Gavashelishvili, A. Modelling the Effect of Competition for Prey and Poaching on the Population of the Arabian Leopard, Panthera Pardus Nimr, in Saudi Arabia (Mammalia: Felidae). Zool. Middle East 2020, 66, 95–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, Y.; Wang, B.; Gu, X.; Song, D.; Yang, B. Camera Trapping Reveals Area of Conservation Significance for Large and Medium-Sized Mammals on the Eastern Tibetan Plateau. Oryx 2022, 56, 137–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J. Distribution and behavior of leopard (Panthera pardus), snow leopard (Panthera unica) and gray wolf (Canis lupus) in Gongga Mountain, Sichuan Province. Master thesis, Sichuan Agricultural University, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Kamino, L.H.Y.; Stehmann, J.R.; Amaral, S.; De Marco, P.; Rangel, T.F.; de Siqueira, M.F.; De Giovanni, R.; Hortal, J. Challenges and Perspectives for Species Distribution Modelling in the Neotropics. Biol. Letters 2011, 8, 324–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Gao, H.; Teng, L.; Su, Y.; Wang, X.; Kong, Y. Habitat suitability assessment of blue sheep in Helan Mountain based on MAXENT modeling. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2013, 33, 7243–7249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Xu, W.; Xiong, X.; Ou, Y.; Zheng, H.; Gan, D. Assessment of potential habitat for Ursus thibetanus in the Qinling Mountains. Biodivers. Sci. 2011, 19, 343–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, B.; Zhang, Q.; Wang, B.; Gong, X.; Duan, C.; Zhang, Y. The habitat suitability evaluation of Salweenia bouffordiana based on MaxEnt model. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2020, 40, 6077–6085. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, J.C.; Crespo, E.G.; Paulo, O.S. Modelling Wildlife Distributions: Logistic Multiple Regression vs Overlap Analysis. Ecography 1999, 22, 251–260. [Google Scholar]
- Swets, J. Measuring the Accuracy of Diagnostic Systems. Science 1988, 240, 1285–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Interspecific Killing among Mammalian Carnivores. [CrossRef]
- Linnell, J.D.C.; Strand, O. Interference Interactions, Co-Existence and Conservation of Mammalian Carnivores. Divers. Distrib. 2000, 6, 169–176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Snider, M.H.; Athreya, V.R.; Balme, G.A.; Bidner, L.R.; Farhadinia, M.S.; Fattebert, J.; Gompper, M.E.; Gubbi, S.; Hunter, L.T.B.; Isbell, L.A.; et al. Home Range Variation in Leopards Living across the Human Density Gradient. J. Mammal. 2021, 102, 1138–1148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gwynn, V.; Symeonakis, E. Rule-Based Habitat Suitability Modelling for the Reintroduction of the Grey Wolf (Canis lupus) in Scotland. PLoS ONE 2022, 17, e0265293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mondal, K.; Bhattacharjee, S.; Gupta, S.; Sankar, K.; Qureshi, Q. Home Range and Resource Selection of “problem” Leopards Trans-Located to Forested Habitat. Curr. Sci. India. 2013, 105, 338–345. [Google Scholar]
- Nams, V.O.; Parker, D.M.; Weise, F.J.; Patterson, B.D.; Buij, R.; Radloff, F.G.T.; Vanak, A.T.; Tumenta, P.N.; Hayward, M.W.; Swanepoel, L.H.; et al. Spatial Patterns of Large African Cats: A Large-scale Study on Density, Home Range Size, and Home Range Overlap of Lions Panthera Leo and Leopards Panthera Pardus. Mammal Rev. 2023, 53, 49–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryce, C.M.; Dunford, C.E.; Pagano, A.M.; Wang, Y.; Borg, B.L.; Arthur, S.M.; Williams, T.M. Environmental Correlates of Activity and Energetics in a Wide-Ranging Social Carnivore. Anim. Biotelem. 2022, 10, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z. Periodic habitat utilization and its driving factors of North China Leopard. Master thesis, Northeast Forestry University, China, 2022. [Google Scholar]
- Lovari, S.; Ventimiglia, M.; Minder, I. Food Habits of Two Leopard Species, Competition, Climate Change and Upper Treeline: A Way to the Decrease of an Endangered Species? Ethol. Ecol. Evol. 2013, 25, 305–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wei, W. The suitability evaluation of Amur Tiger ( Panthera tigris altaica) and Amur Leopard( Panthera pardus orientalis) habitat based on remote sensing and GIS. Master thesis, JinLin University, China, 2019. [Google Scholar]
- Han, L. Habitat selectivities and seasonal variations of wolves(Canis lupus) in Mount Kalamaili Ungulate Nature Reserve, Xinjiang,China. Master thesis, Xinjiang University, China, 2015. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, Y. Habitats selection during wintering of the steppe wolf (Canis lupus) in eastern Inner Mongolia. Master thesis, Qufu Normal University, China, 2007. [Google Scholar]
- Zhang, H.; Zhou, Y.; Dou, H.; Liu, X.; Zhang, C.; Liu, S. Prelimnary analysis on the habitat selection of wolf (Canis lupus) in Dalai Lake Natural Reserve in Inner Mongolia. Acta Ecol. Sin. 2010, 30, 3637–3644. [Google Scholar]
- Xinning, S.; Dazhao, S.; Qiaowen, H.; Sheng, L.; Meng, Y. Fast Surveys and Molecular Diet Analysis of Carnivores Based on Fecal DNA and Metabarcoding. Biodivers. Sci. 2019, 27, 543. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allen, W.L.; Cuthill, I.C.; Scott-Samuel, N.E.; Baddeley, R. Why the Leopard Got Its Spots: Relating Pattern Development to Ecology in Felids. P. Roy. Soc. B-Biol. Sci. 2010, 278, 1373–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bannasch, D.L.; Kaelin, C.B.; Letko, A.; Loechel, R.; Hug, P.; Jagannathan, V.; Henkel, J.; Roosje, P.; Hytonen, M.K.; Lohi, H.; et al. Dog Colour Patterns Explained by Modular Promoters of Ancient Canid Origin. Nat. Ecol. Evol. 2021, 5, 1415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Botts, R.T.; Eppert, A.A.; Wiegman, T.J.; Blankenship, S.R.; Rodriguez, A.; Wagner, A.P.; Ullrich, S.E.; Allen, G.R.; Garley, W.M.; Asselin, E.M.; et al. Does Moonlight Increase Predation Risk for Elusive Mammals in Costa Rica? Trop. Conserv. Sci. 2020, 13, 194008292095240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Z.; Wang, T.; Smith, J.L.D.; Feng, R.; Feng, L.; Mou, P.; Ge, J. Coexistence of Two Sympatric Flagship Carnivores in the Human-Dominated Forest Landscapes of Northeast Asia. Landscape Ecol. 2019, 34, 291–305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Seasonal differences in prey abundance and food composition of the North China leopard (Panthera pardus fontanierii) in Tieqiaoshan Nature Reserve, Shanxi. Master thesis, Northeast Forestry University, China, 2020. [Google Scholar]
| Species | GLM | MaxEnt | Ensemble model |
|---|---|---|---|
| Leopard | 0.84 | 0.76 | 0.81 |
| Wolf | 0.86 | 0.73 | 0.82 |
| Species | PLAND | PD | ED | LSI | AI | CONNECT | PAFRAC |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Leopard | 13.76 | 0.35 | 5.78 | 41.17 | 96.60 | 0.99 | 1.35 |
| Wolf | 64.83 | 1.17 | 41.35 | 126.82 | 95.09 | 0.06 | 1.44 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





