1. Introduction
Glioma is the most prevalent and aggressive tumor of the central nervous system. According to cellular sources, gliomas may be divided into oligodendroglioma, astrocytoma, mixed gliomas (oligo-astrocytomas), and ependymomas [
1]. The World Health Organization (WHO) has separated gliomas into four grade subtypes. Grades I and II are classically investigated as low-grade gliomas, whereas grade III and IV tumor types are perceived as high-grade glioma types. Glioblastoma multiform (GBM, grade IV astrocytoma) is a competitive and fast-growing tumor, with an average survival time of 12-14 months after preliminary diagnosis [
2]. Thus the discovery of an impressive therapeutic approach is essential in this disease [
2].
The high development potential and diminished apoptosis potential of the glioma cells are chiefly reliant upon hereditary intensifications or transformations and changes in pro-apoptotic and oncogenic genes expression [
3]. The idea of molecular treatment for GBM tumors is dependent on probable pharmacological or genetic changes in the main molecular signaling pathways such as the Notch pathway to reduce GBM proliferation and angiogenesis [
4]. Notch signaling is complicated in different cellular processes related to normal growth and cellular hemostasis; however, its role in many features is also associated with cancer, for example: variation types, proliferation, the transition of epithelial-mesenchymal, stemness, or angiogenesis [
5].
Abnormal Notch molecular signaling in GBM stem cells increases tumor reappearance and invasion [
6]. It is vital to regulate the underlying processes in GBM tumorigenesis to understand the molecular mechanism involved in this progress to find more efficient therapeutic approaches. More importantly, several recent studies have reported the significance of the interaction between Notch signaling and non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) such as microRNAs (miRNAs), long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and circular RNAs in the various aspects of GBM pathogenesis. This review discusses the potential role of ncRNAs in regulating notch signaling in GBM.
2. ncRNAs Functions in GBM
Despite the fact that the majority of the human genome (80%) is transcribed into RNA, only ~2% of RNA is translated into proteins [
7]. Therefore, ncRNAs make up the large majority of cellular RNAs and have substantial functions in the regulation of physiological, biological, and pathological events [
8]. The last decades have witnessed robust interests in studying the involvement of two important categories of ncRNAs including miRNAs and lncRNAs in the regulation of various human malignancies [
9]. miRNAs are a class related to minor 20–22 nucleotide-ncRNAs that control important cellular events via targeting the 3’ untranslated region (UTR) of mRNAs of target genes [
10,
11]. lncRNAs are much preserved non-coding RNAs that are more than 200 nucleotides in length with no protein-coding ability [
12,
13,
14,
15]. They were originally believed to be ‘transcriptional sounds’ leading to short RNA polymerase loyalty [
16,
17,
18,
19].
Previous studies have demonstrated an abnormal expression pattern of miRNAs and lncRNAs in GBM [
9]. According to these studies, 95 miRNAs have been reported to be downregulated in GBM and 256 miRNAs upregulated in GBM tissues compared to normal brain tissues [
20]. miR-21, which is overexpressed in human glioma cells and tissues, showed a significant link of this miRNA with the malignant transformation of GBM [
21]. One of the most frequently overexpressed miRNAs in GBM is miR-221/222. MiR-181 family, miR-26a, miR-34a, miR-148a, and miR-10b are other important miRNAs with aberrant expression levels in GBM cells and tissues. miRNAs play a number of crucial roles in the cell proliferation, viability, and stemness, migration and invasion, angiogenesis immune evasion, and drug resistance of GBM cells [
22]. In this regard, miRNAs represent promising therapeutic agents or targets for GBM.
In addition to miRNAs, lncRNAs are another group of ncRNAs with increasing importance in the numerous aspects of GBM [
23]. Deregulation of lncRNAs might influence signaling pathways and establish a cellular proliferation benefit, leading to unrestrained growth of tumors [
24]. Previous studies have indicated that lncRNAs have a pivotal function in glioma development by controlling multiple tumorigenic processes such as cellular proliferation and apoptosis [
25,
26]. Differential expression of specific lncRNAs might correlate with disease progression and cancer malignancy and thus could potentially be used as therapeutic targets and biomarkers for prognosis [
26,
27]. The latest confirmations propose that lncRNAs act as important factors in various biological progressions, such as X chromosome deactivation, regulating gene expression and post-transcriptional changes , as well as controlling translation [
28,
29,
30]. LncRNAs can also act as tumor suppressors or oncogenes in GBM and can be used as prognostic or diagnostic valuable biomarkers for this tumor [
31,
32,
33].
3. Notch Signaling Pathway in the Pathogenesis of GBM
The Notch pathway has been demonstrated to have major functions in a broad range of developmental and cellular events, from cell fate decision and stem cell maintenance, to cell growth and apoptosis, and tissue homeostasis [
34,
35]. The Notch family is a cytoplasmic receptor and Notch1, Notch2, Notch3, and Notch4 are four well-known homologous of this family, which act through bridging two major ligands families including Delta-like (Dll1-3 and -4) and Jagged (Jagged1 and -2) [
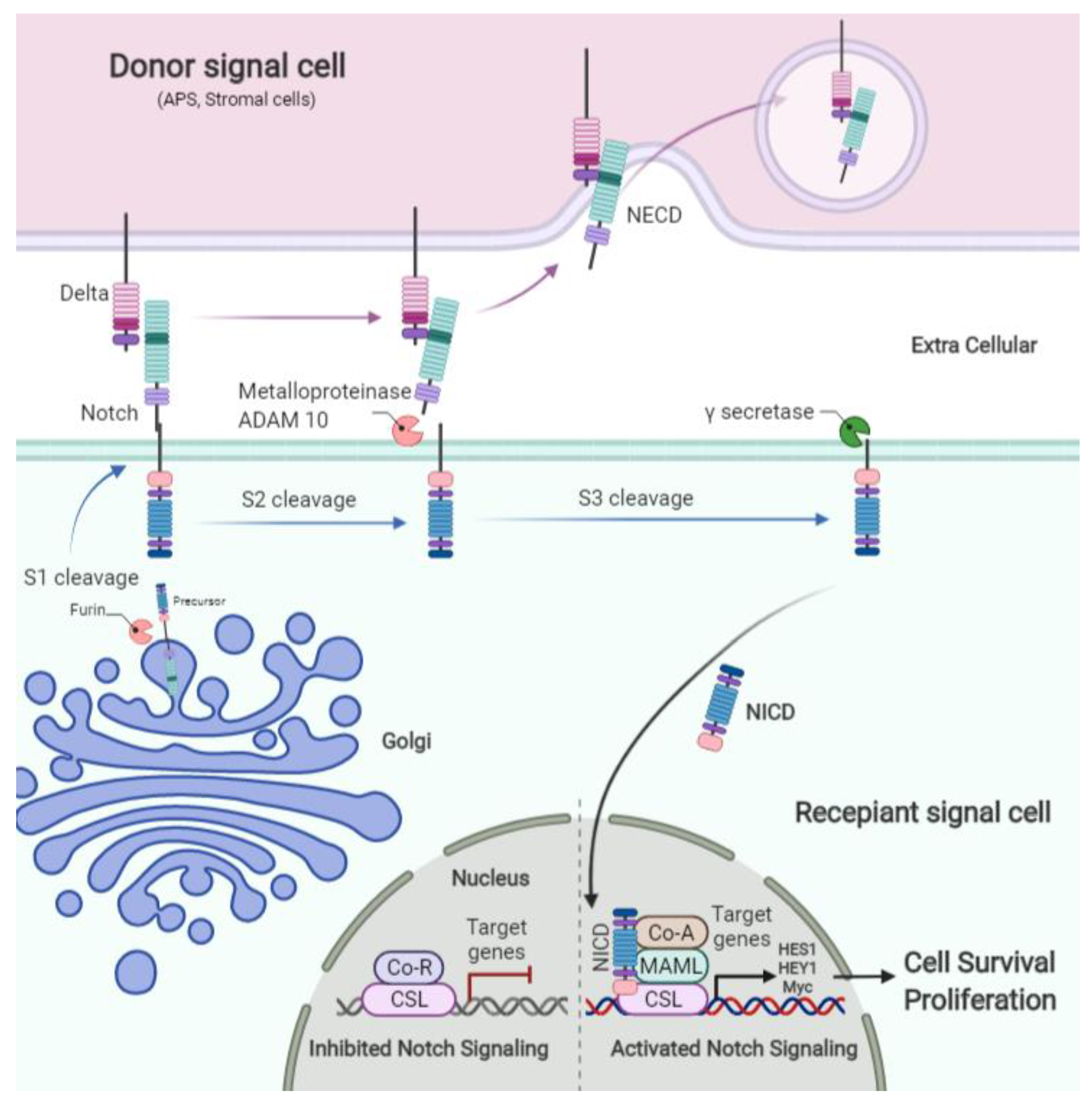
36]. Interaction between Notch receptors and ligands results in the receptor cleavage via member A Disintegrin and Metalloprotease (ADAM) (S2 cleavage) and following intracellular cleavage by γ-secretase (S3 cleavage) leads to the release of the Notch intracellular domain (NICD). NICD then translocates to the nucleus and interacts with members of the Suppressor of Hairless, Lag 1 (Longevity Assurance Gene) (CSL) family, C-Promoter binding factor (CBF1) [
37].
At the nucleus, Notch targets and activates the transcription of various genes, such as members of the Hey (hairy and enhancer of split related with XRPW motif) and basic Hes (helix-loop-helix family) [
38] (
Figure 1). Due to the importance of this signaling pathway in the various cellular processes, an accumulating number of studies have reported aberrant expression patterns of key components of Notch signaling in numerous human malignancies including GBM. Notch2 overexpression has been frequently observed in GBM [
39,
40]. Notch1 was demonstrated to control the expression levels of epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR), which is upregulated in GBM [
41]. In addition, one of the most common genetic alterations in GBM is the genomic amplification of EGFR. On the other hand, EGF is considered as one of the significant proliferation pathways in GBM, which is mediated by activation of the PI3K-AKT-mTOR and RAS-RAF-MEK-ERK cascades [
42,
43,
44]. Therefore, targeting the Notch signaling pathway has been considered as a promising therapeutic strategy for combating GBM.
Before transfer to the surface of signal recipient cell Notch receptor is cleaved by Furin (S1 cleavage) and then located on the surface of the plasma membrane. Notch signaling is activated by binding the Notch receptor to its ligand on the signal donor cells, which causes metalloproteinase (ADAM 10) to cleave the extracellular (S2 cleavage). Then the intracellular part of the Notch receptor is cleaved by ϒ secretase enzyme (S3 cleavage) and the NICD translocates from cytoplasm to nucleus, removes the repressing effect of CSL from the promotor, and activates Notch target gene expression such as HES 1 family, HEY1, and Myc (
Figure 1).
4. Cancer Stem Cells, Cancer Stem-like Cells, and Notch Pathway in Glioblastoma
The resistance of GBM to radiation and chemotherapy is related to the presence of an infrequent division of cancer stem cells (CSCs) that have been recognized in the tumor central part [
4]. Cancer stem-like cells (CSLCs) are probable aims for curing GBM because of their important task in reappearance and tumorigenesis. Notch signaling blocks arsenic trioxide (As2O3) in GBM cell lines, reducing the levels of CSLCs, which are necessary for in vivo tumor creation; consequently, As2O3 represses tumorigenesis of cell lines of GBM [
45,
46].
GBM also includes a collection of stem cells with multipotent characters. These cells crosstalk in neurovascular positions with endothelial cells. The stimulation of the Notch1 pathway by the expression of the NICD in these cells has been established to decrease their migration and proliferation, which is supplemented by the severe diminution in the expression of transcription factors of neural stem cells (Oligodendrocyte transcription factor (OLIG2), sex-determining region Y)-box 2 (SOX2), and Achaete-scute homolog 1(ASCL1)), while Snail family transcriptional repressor 2 (SNAI2), Kruppel-like transcription factor 9 (KLF9), and Hairy/enhancer-of-split related with YRPW motif protein (HEY)1/2 transcription factors will be up-regulated. The expression of NICD stimulates the expression of markers of pericytes (PDGFRb and NG2) in glioma stem cells. This is paralleled with the stimulation of many angiogenesis-associated agents, most remarkably cytokines (IL8 and Heparin-binding epidermal growth factor), adhesion molecule types (such as Vascular cell adhesion molecule 1), and matrix metalloproteinases especially type 9. Thus, these discoveries show the importance of the Notch1 signaling in regulating angiogenic and plasticity potencies of stem cells of GBM [
47,
48,
49,
50].
The investigation of the influence of the Hes1-aimed shRNA (shHes1), a Notch1 gene goal, particularly on the refractory of GBM CSCs to γ-secretase inhibitor-X (GSI-X), has shown that reduction of Hes1 stimulates alterations in cells growth, morphology, and rate and also in the aggressive potency of shHes1-CSCs in reply to growth factors [
51]. These effects are associated with suppression of EGFR and regulation of Stat3 phosphorylation. Stat3/5 inhibitors prompt the apoptosis process of both control and shHes1-CSC cells. Taken together, Hes1 appears to be a promising target, but is not adequate to aim glioma effectively. Thus a prospective pharmacological interference should be designed for GBM therapy based on anti-Stat3/5 agents either unaccompanied or as combined treatments [
4,
51,
52,
53].
Protein Kinase C iota (PKCi) is a vital applicant gene for the survival of GBM stem-like cells (GSCs). PKCi has been established as a therapeutic beneficial aim in non-small cell lung cancer, leading to the detection of an inhibitor titled aurothiomalate (ATM), which interrupts the PKCi/ERK signaling. It has been revealed that, although GSCs have sensitivity to inhibition by drugs through a pseudosubstrate inhibitor, they are much less delicate to ATM, suggesting that PKCi goes along a various pathway axis in GSCs. Profiling gene expression of PKCI-quieted GSCs has discovered a new character of the Notch signaling in PKCi intermediated GSC survival. A ligation assessment has exhibited that PKCi and Notch1 are very close in GSCs. Directing PKCi in the Notch signaling context can be an efficient approach to attacking the GSCs position in GBM [
54].
5. Notch Pathway-Related Channels and Glioblastoma
Hypoxia has been shown to direct glioma in the direction of a more aggressive position. Transient receptor potential 6 (TRPC6) is essential for the expansion of the destructive phenotype, and TRPC6 knockdown inhibits GBM proliferation, angiogenesis, and invasion. TRPC6 creates a continued increase of calcium in the cells that are connected to the stimulation of the activity of the pathway of the calcineurin-nuclear factor of activated T-cell (NFAT). The inhibition of the calcineurin-NFAT pathway by drugs considerably decreases the expansion of the aggressive GBM under hypoxia conditions. Clinically, the expression of TRPC6 is increased in GBM samples in comparison with typical tissues. Collectively, studies indicate that TRPC6 is a basic mediator of the proliferation of GBM in vitro and in vivo and that TRPC6 may be a favorable therapeutic goal in GBM treatment [
55].
Transient receptor potential cation channel, subfamily M, member 7 (TRPM7), is ubiquitous, and forms a constitutively active Mg2+ and Ca2+ penetrable ion channel that is singular in being both a serine/threonine kinase and an ion channel [
56]. TRPM7 is single in the sense that it codes an α kinase domain merged to the moiety of ion channel, the channel area and kinase can be commonly controlled, but the existence of the domain related to a kinase is not essential for TRPM7 channel function, even though it helps relatively to the changes of the sensitivity of the channel to cAMP [
57,
58] and Mg2+ [
59]. TRPM7 knockdown reduced the Notch1 and STAT3 pathways in GBM cells grown in monolayer culture. Moreover, markers of CSC (CD133 and ALDH1), Notch1 target genes, and phospho-STAT3 are considerably greater in spheroid GBM CSCs when compared to monolayer cultures. Consequently, phosphorylated STAT3 binds to the ALDH1 promoter in GBM cells. In addition, TRMP7-stimulated high regulation of expression of ALDH1 is related to enhance in ALDH1 function in stem-like cells once enlarge as spheroid type CSCs [
56].
6. Notch Signaling Interacting Molecules, Proteins, Markers, and Related Drug Effects in Glioblastoma
Neural stem cells (NSCs) develop into the central nervous system and are located in special parts of the mature brain for replacing injured cells. The loss of the balance between NSC differentiation and self-renewal can result in tumor progression. Recent studies have exhibited that mRNA expressions of insulin-like growth factor binding protein 2 (IGFBP2) are extortionate during fetal brain growth, and are reduced during the brain maturation to adults. IGFBP2 is also often expressed highly in GBM, which is associated with tumor reappearance and reduced survival, and subsequently causes GBM development. IGFBP2 is also overexpressed in NSCs and induces their proliferation but prevents their changes in astrocytes and neurons. The IGFBP2 knockdown in NSCs strongly affects the gene expression associated with Notch signaling and the cell cycle [
60].
Inhibition of Notch signaling through the mastermind-like 1 (DN-MAML1), or the remedy of a GSI, leads to a noteworthy decrease in glioma cells proliferation in vivo and in vitro. The specific Notch receptors knockdown revealed that Notch1 and Notch2 receptors diversely help GBM cells proliferation, although Notch2 performs the main function. Moreover, Notch pathway blocking hinders the glioma-derived neurospheres proliferation in vivo and in vitro [
61]. These findings show that the Notch signaling pathway helps to ideal GBM proliferation, and strongly support that this could be a promising therapeutic target for GBM.
Current Notch signaling inhibitors block the crucial enzymes involved in these pathways, including metalloproteinases (10 and 17) and γ-secretase enzyme, which is essential for the Notch signal activation. Notch S2 and S3 cleavage inhibitors strongly reduce GBM growth. Furthermore, it has been shown α-secretase is a substitute to g type for inhibiting Notch in GBM [
62].
The effect of leptin and its receptors has been revealed in glioma cells. The expression of leptin and related receptors is much higher in GBM cells (T98G and U-87MG) than the normal glial cell line (SVG p12), which indicates that inducing leptin prompts proliferation in human GBM cells. Treatment with leptin enhances neurosphere generation by increasing the self-renewal property and inducing the expression rate of SOX2. Mechanistically, a leptin facilitates upregulating Notch1 receptors and activates its effectors and target factors. The crosstalk between Notch and leptin emphasizes leptin/ Notch interaction as a possible new therapeutic aim for curing GBM. [
63].
Herbal drugs having antitumor characteristics have been applied in adjuvant treatment that are harmless and inexpensive in comparison to chemotherapy. Bacopa monnieri has been applied for the growth of brain cells due to its neuroprotective properties. Antitumor compositions of Bacopa monnieri have been revealed to be favorable in the treatment of cancer. Monnieri Bacoside A - a dynamic and plentiful factor of Bacopa Monnieri - has displayed significant cytotoxicity in human GBM in vitro through cell cycle arrest and apoptosis via decreasing the expression of Notch1 [
64]. Temozolomide (TMZ) is the typical chemotherapy drug for human GBM. Nonetheless, resistance to TMZ is a key problem for this remedy. Genomics assay has verified that EGF-containing fibulin-like extracellular matrix protein 1(EFEMP1), a matrix protein of extracellular, is related to TMZ-resistance [
65]. Suppressing EFEMP1 in GBM cells leads to reduced cell survival after TMZ therapy, while its high expression creates resistance to TMZ. EFEMP1's performances operate in different ways, particularly γ-secretase-facilitated stimulation of the Notch signaling. γ-Secretase inhibition via RO4929097 has been revealed to create the limited sensitivity of GBM cells to TMZ in vivo and in vitro [
65,
66]. These results demonstrated the promising role of EFEMP1 in reducing resistance to TMZ in human GBM [
66,
67].
The elastin-like polypeptide (ELP) is a reactive polypeptide in terms of temperature that can be dynamically aimed at the tumor location by hyperthermia restricted application. Conjugation of the ELP with a Notch inhibitory peptide Dominant-negative Mastermind-like (dnMAML) and a penetrating peptide Synthetic Battlefield (SynB1) improved cellular acceptance and blood-brain barrier diffusion, and increased GBM, cytotoxicity, apoptosis, and cell cycle arrest by inhibition of the Notch target genes. Briefly, hyperthermia inhibits proliferation via cell cycle arrest, and promotes apoptosis in U251 and D54 cells. Subsequently, hyperthermia enhances the general delivery of the polypeptide by cells, causes the anti-notch activity of dnMAML in receiving cells, and decreases the Notch target genes including Hey-L and Hes-1 [
68].
Collapsin response mediator protein 5 (CRMP5) is highly expressed in the developing brain. This protein was first defined as cancer-induced by autoimmunity and results in neurodegenerative disorders including paraneoplastic syndromes or neurologic pathologies. Moutal
et al. revealed the two distinct CRMP5 expression patterns seen in human glioblastoma (GBM) biopsies which stimulate expression of Notch receptor and activation of Akt protein in human GBM stem cells [
69]. They demonstrated that increasing CRMP5 mechanistically hijack Notch receptors from Itch-dependent lysosomal degradation and increase stemness in GBM cells [
70].
Sec61 is a fundamental constituent of the translocation apparatus of protein in the membrane of the endoplasmic reticulum [
71], which is involved in protein folding, translocation, modification, and unfolded protein response to nutrient deprivation and hypoxia in tumor microenvironments [
72,
73]. Sec61 includes three different subunits, and the gamma subunit of Sec61 (Sec61G) is highly expressed in most GBM patients and associated with reduced prognosis. It was reported that overexpression of SEC61G decreased the sensitivity of TMZ in patients with GBM [
74]. There is a significant association between the expression of SEC61G and Notch signaling. Thus, SEC61G is a new prognostic marker that may be used for the prediction of survival of GBM patients [
74].
There is a clinical relationship between the tumor vascular laminin-411 (a4b1g1) expression with GBM tumor grade and CSC associated genes, such as Notch signaling memberships, Nestin, c-Myc, and CD133. High expression of Laminin-411 is also associated with a higher reappearance degree and a shorter survival of a patient with glioma [
75,
76]. Expression of Laminin-411 in the microenvironment of GBM associates with Notch and other markers of cancer stemness which caused GBM proliferation [
77].
Receptors of Notch transfer into the endoplasmic reticulum and Golgi apparatus and are altered by several glycosyltransferases, comprising O-glucosyltransferase 1 (Poglut1), Pofut1, and KDEL (Lys-Asp-Glu-Leu) containing 2 (KDELC2) and Poglut2 (KDELC1) [
78]. KDELC1 and KDELC2 help transmission of O-glucose to Notch1 EGF11 and Notch3 EGF10 [
79]. KDELC2 can prompt invasion and migration of GBM via inducing MMP-2, enhances proliferation of the tumor by inhibition of two caspases (3 and 9), and increases cell cycle speed [
80]. Moreover, the high expression of KDELC2 induces the cascade of Notch signaling, containing NF-kB and PI3K/Akt/mTOR signaling pathways. Thus, KDELC2 is a marker for the measurement of the aggressiveness of GBM [
80].
Deltex (DTX) is a protein with Notch interacting characteristics, which includes a basic area at the N-terminal where it binds to the ankyrin sequences of the intracellular part of Notch. Deltex has been suggested to control Notch action by antagonizing the crosstalk between repressor of Hairless, a highly conserved protein that acts as the transducing transcription factor for the Notch cell-cell signaling pathway, and Notch [
81]. The non-canonical Notch signaling acts via DTX1 and mediates main characteristics related to GBM invasion. For instance, DTX1 triggers the MAPK/ERK and the RTK/PI3K/PKB key signaling pathways and stimulates anti-apoptotic factors. The DTX1 levels have a strong association with the proliferation of GBM cells. High expression of DTX1 enhances cells invasion and migration relating to ERK stimulation; in contrast, GBM patients with low DTX1 rates have a better prognosis [
82].
Stimulation of Notch signaling pathways performed by proteases belonging the family of disintegrins and metalloproteinases (ADAM), including ADAM-17 and ADAM-10, mediates other signaling factors downstream [
83]. ADAM-17 supervises the cut via proteolysis of Notch in its extracellular area, resulting in the stimulation of the Notch signaling pathway, which is involved in the production and maintenance of GSCs. GBM cells (CD133 positive) express a higher amount of ADAM-17 in comparison to the CD133 negative GBM cells. ADAM-17 may preserve the GSCs stemness by hindering their differentiation and stimulating their self-renewal through the Notch signaling pathway [
84].
Resistance against available drugs is a key barrier to the progression of therapeutic effects for patients of GBM. The endoplasmic reticulum stress response (ERSR) has been reported as a factor to resistance against chemotherapy agents in GBM because radiation can induce ERSR and related downstream signaling. Alteration in ROS equilibrium is the second reason for ER stress after irradiation. Inhibition of a key regulator of the ERSR, such as activating transcription factor 6 (ATF6), is adequate to increase radiation-prompted death in cells. Also, induction of ATF6 helps the upregulation (via radiation) of Notch1 and glucose-regulated protein 78 (GRP78). So ATF6 can be a probable therapeutic aim to increase the efficiency of radiation treatment [
85].
It has been revealed that a secretory glycoprotein, Stanniocalcin-1 (STC1), acts as a new inducer for stem-like properties of GBM cells. STC1 crosstalks with the extracellular region of Notch1 to activate NOTCH1-SOX2 signaling, and enhances the stemlike characters of glioma cells. Consequently, STC1 is a new Notch ligand (non-canonical pathway) and functions as a vital marker and regulator of stemness in GBM [
86].
The axonal leadership protein, netrin-1 or laminin-associated secreted protein is overexpressed in biopsies of GBM tumors. Netrin-1 makes a complex with both Jagged1 and Notch2, and subsequently increases GBM cells invasion. Therefore, netrin-1 can be a potential marker for evaluating GBM invasion [
87]. Tenascin-C (TNC) is an extracellular matrix protein pronounced in aggressive GBM; it enhances Notch function to increase proliferation in brain cancer-initiating cells [
88].
7. microRNAs Effects on Notch Pathway in Glioma Progression
Several microRNAs are regulated in the Notch pathway that play a crucial role in nervous system progress and brain tumor types [
89]. Tumor suppressor miR-34a expression is decreased in GBM tissues, c-Met, Notch1, and Notch2 expression have been regulated by miR-34a in GBM stem cells [
90]. miR-34a-5p intermediates interaction between Notch1/EGFR signaling pathways and M2 type muscarinic receptors in U87 GBM Cells [
3,
91,
92]. Based on the suppressive character of this miRNA in the histotypes of different types of tumors [
93,
94,
95,
96], miR-34a-5p expression is intensely decreased in cell lines of GBM in comparison to typical brain tissue. Remarkably, the Notch expression seems to be associated with expression of miR-34a-5p; actually, in the normal human brain, tissues with high expressions of miR-34a-5p, have decreased Notch-1 expression, while in GBM cell lines, the reduced expression of miR-34-5p is related to Notch-1 upregulation [
97].
Bcl2/adenovirus E1b 19-kDa interacting protein 3 (BNIP3) is a member of Bcl2 homology 3 (BH3), and it is situated in the mitochondria. It cooperates with ischemia-reperfusion (I/R) damage by stimulating mitochondrial inappropriate action [
98,
99,
100,
101] and is expressed highly by the Hypoxia-Inducible Factor (HIF)-1 transcription factor in the hypoxic region of tumors types [
102,
103]. It was demonstrated that BNIP3 is involved in Notch regulation in glioma cells. In malignant conditions, BNIP3 is located chiefly in the nucleus and hinders the apoptosis process [
104]. It has been stated that the expression of miR-145 is reduced in human GBM, and rat glioma tissues and GBM cell lines, whereas BNIP3 expression was enhanced in the same tissues. High expression of miR-145 or low expression of BNIP3 stimulates cellular apoptosis in GBM. miR-145 targets BNIP3 mRNA by binding to its 3′ UTR site. These results showed that miR-145 controls GBM cell apoptosis by controlling and regulating the Notch-associated genes including Notch1, Hes1, and p21 by targeting BNIP3 [
10].
miR-524-5p and miR-524-3p recover the general survival phase of patients with GBM, and their high expression can restrain proliferation, migration, cell cycle, and regulate tumor development in vivo. Briefly, both miRNAs have an inhibitory synergistic outcome on GBM cells. Moreover, studies approve that EGFR amplification and EGFRvIII mutations can suppress the pri-miR-524 expression by histone modification. miR-524-5p and miR-524-3p also hinder Notch, TGFβ factors and the Hippo pathway by targeting Hes1, Smad2 and Tead1, respectively. C-myc as a shared transcription factor of three pathways is suppressed after miRNA induction as well [
105].
It was reported that miR-326 increases following Notch1 silencing. This microRNA is not only repressed by Notch factors but also functions as a feedback loop via hindering Notch factors and activity. miR-326 is downregulated in GBM samples and transfection of this miRNA in both GBM and stem cell-like glioma lines showed a cytotoxic effect. Moreover, in vivo miR-326 induction decreases the tumorigenesis of GBM [
89].
miRNAs including miR-190-5p, miR-488-3p, miR-325, miR-34a, and miR-524-5p/3p involved in Notch negative regulation however other miRNAs like miR-145 and miR-4775 increase Notch signaling. On the other hand, lncRNAs including PVT-1, LINC00152, increase the Notch signaling pathway by masking the miRNA which targets Notch expression, others involved in Notch regulation indirectly include LINC0021, HOXA-AS2 and OPI-5, and PlncRNA-1 target Notch directly including.
8. Notch Pathway and Circular RNAs in Glioma Progression
An ncRNA with significant regulatory strength, Circular RNA (circRNA) has obtained enhanced consideration from RNA examiners in the last few years [
106]. circRNA nuclear factor I X (circNFIX) is the circRNA to be expressed highly in GBM. Furthermore, Notch signaling is significantly expressed in tumor tissues related to the brain in comparison to normal tissues. It has been recognized that circNFIX acts as a miR-34a-5p sponge. Low expression of circNFIX and high expression of miR-34a-5p will impede cell migration and proliferation. Additionally, an inhibitor of miR-34a-5p deactivates the repressive influence of si-circNFIX on GBM tumor cells. Also, miR-34a-5p and si-circNFIX mimic the apoptosis process. It has been revealed that si-circNFIX can repress GBM cells proliferation by controlling Notch1 and miR-34a-5p
in vivo [
107].
9. lncRNAs Regulation on the Notch Pathway in GBM Progression
Recently, evidence has revealed that lncRNA not only stimulates or hinders the Notch signaling pathway but also controls the expansion of cancer by regulating the Notch pathway [
108]. Interaction between lncRNAs and the Notch pathway makes those key molecules prospective biomarkers in the hyperactive Notch pathway cancer types [
5]. The expression rates of prostate cancer-up-regulated long non-coding RNA 1(PlncRNA-1) is predominantly increased in GBM tissues and cell lines [
109]. PlncRNA-1 knockdown markedly decreased cell proliferation, colony formation, and induced apoptosis of glioma cell lines via reducing of Notch-1, Jag-1, and Hes-1 expression.
Plasmacytoma Variant Translocation 1 (PVT1) is a lncRNA involved in tumorigenesis and the development of different malignancies. PVT1 has a key role in regulating the biological behaviors of GBM cells. PVT1 masks both tumor suppressor miR-190a-5p and miR-488-3p in glioma cells. miR-190a-5p and miR-488-3p directly target Myocyte enhancer factor 2C (MEF2C), which upregulates JAGGED1 by increasing its promoter activity in GBM [
110].
Zinc finger antisense 1 (ZFAS1) lncRNAs, overexpressed in GBM cell lines and tissues, is strongly related to the tumor aggressiveness phase and reduced overall survival rate. Moreover, in vitro experiments have revealed that inhibition of ZFAS1 potentially reduces proliferation, invasion, and migration of GBM cells. Notably, it has been confirmed that the Notch signaling and epithelial-mesenchymal transition (EMT) are deactivated in the GBM cells after the knockdown of ZFAS1 [
24]. LncRNA FEZF1-AS1 sponge miR-34a and cause upregulation of Notch-1 in GBM cells. The phenotypic results of this sponge were promoting GBM cell invasion and migration [
111].
Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 1410 (LINC01410) is overexpressed in GBM. It was reported that LINC01410 regulated Notch2 by miR-506-3p sponging. Additionally, overexpression of Myc in GBM increases the transcription of LINC01410 in a feedback loop. Studies have also shown that LINC01410 accelerates the development of glioma tumor via an agent acting as a ceRNA for miR-506-3p and increasing expression of Notch2 to further stimulate the Notch pathway [
112]. Temozolomide resistant GBM cell is also regulated by Long intergenic non-protein coding RNA 0021 (LINC00021). LINC00021 promoted the TMZ resistance and reduced apoptosis via the Notch pathway and suppression of p21 expression through recruitment of EZH2 in GBM [
113].
Various studies have evaluated the efficacy of inhibiting ncRNAs and Notch signaling as a therapeutic strategy for GBM. Opa interacting protein 5 (OIP5) belongs to the cancer-testis specific gene and is situated in the chromosome 15q15.1. Numerous studies reported that it is constantly expressed in GBM tumor [
114]. Knockdown or down-regulation of linc-OIP5 expression via a siRNA (linc-OIP5-small interfering RNA) hinders tumorigenesis, migration, and proliferation of glioma cells by the effect on the Notch signaling related to Yes-associated-protein (YAP) [
115]. Knockdown of prostate cancer-up-regulated long non-coding RNA 1 (PlncRNA-1) decreases GBM proliferation, colony development, and stimulates the apoptosis process in GBM cells. Furthermore, expression of PlncRNA-1 caused proliferation, increased colony numbers, and suppresses apoptosis in usual human astrocytes.
It was reported that PlncRNA-1 induces activation of the Notch signal by regulation of Notch1, Hes-1, and Jag-1 expression. Together, investigations imply that lncRNA PlncRNA-1 may have tumor-inducing character in the progression and expansion of gliomas via controlling the Notch pathway and inhibition of Notch signal pathway and can reverse the proliferation, colony, and apoptosis in overexpressed PlncRNA-1 GBM cells [
109].
HOXA cluster antisense RNA 2 (HOXA-AS2), located between the human HOXA4 and HOXA3 genes in the HOXA group, acts as an important oncogene in several malignancies such as gastric, breast, and pancreatic cancers, and hepatocellular carcinoma [
116]. HOXA-AS2 overexpressed in GBM cells and tissues. High HOXAAS2 expression levels are related to an increase in tumor mass and advanced pathological phase. The knockdown of HOXA-AS2 represses the cells invasion and growth and induces apoptosis. Instinctively, HOXA-AS2 genetically hinders minor RhoGTPase RhoE (also recognized as Rnd3) transcription via binding to the Zeste homolog 2 enhancer.
Furthermore, increasing the expression of RND3 has tumor-repressive effects by inactivation of the Notch signal pathway. Mechanistically, RND3 physically interacted with the proteins involved in the Notch transcriptional complex factors including NICD, CSL, and MAML1, promoted NICD ubiquitination, and contributed to the removal of these cofactor proteins. It was revealed that RND3 facilitated the binding of NICD to a ubiquitin ligase known as FBW7 and hence the improved NICD protein degradation (
https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/26108681/). Moreover, the anti-cancer properties stimulated through si-HOXA-AS2 are significantly inverted by increasing RND3 expression [
117].
Knockdown of ncRNA 152 (LINC00152) considerably represses cell migration, viability, and invasion potency and stimulates apoptosis in vitro. Moreover, LINC00152 worked as a molecular sponge of miR-4775, which resulted in inhibition converses the tumor-suppressive properties of LINC00152 silencing on GBM cells. Additionally, cell division protein kinase 6 (CDK6) has been proved to be a key target of miR-4775. Overexpression of CDK6 decreases the apoptosis and block miR-4775, and results in inhibitory effects on cells viability, invasion, and migration. It was demonstrated that overexpression CDK6 triggers the Notch and PI3K/Akt/MAPK pathway [
118].
Plasmacytoma variant translocation 1 (PVT1) gene originates from an intergenic region on chromosome 8 (8q24), It was reported that PVT1 knockdown suppressed the oncogenic feature of GBM cells through the repression of invasion, migration, and proliferation, as well as via increasing apoptosis. Also, PVT1 has been recognized to exert its effects on the GBM cells through binding to miR-488-3p and miR-190a-5p, which play as tumor suppressors by regulating PVT1 in GBM cell lines. miR-488-3p and miR-190a-5p directly target Myocyte enhancer factor 2C (MEF2C). It was demonstrated that MEF2C, an oncogene in GBM, and its overexpression increases promoter activity of JAGGED1 and results in JAGGED1 up-regulation. Knockdown of PVT1 together with induction of miR-488-3p and miR-190a-5p help to the minimum tumor size and the extended survival in immunodeficient mice [
41]. It was reported miR-524-3p and -5p reduced Notch, TGF/β, and the Hippo pathway through targeting Hes1, Smad2 and Tead1, respectively; this results in repression of C-myc, which is their common downstream transcription factor [
105].
Recombination signal binding protein for immunoglobulin kappa J region (RBPJ) is the main transcription factor of the Notch signaling pathway, and it is essential for Notch canonical signaling [
119,
120,
121]. RBPJ increases cell invasion, proliferation, stemness, and tumor initiation potency in GBM cells by stimulating the IL6-STAT3 pathway [
122].
10. Conclusions
Glioblastoma (GBM) stands out as the most aggressive form of brain tumor, with the Notch pathway playing a pivotal role in its tumorigenesis. Non-coding RNAs (ncRNAs) have emerged as crucial regulators of this pathway, particularly at the post-transcriptional level. Notably, long non-coding RNAs (lncRNAs) and microRNAs (miRNAs) exhibit potential as diagnostic, prognostic, and therapeutic targets for GBM. The interplay between lncRNAs and the Notch signaling pathway presents these molecules as promising biomarkers for assessing Notch pathway activity and as exciting prospects for RNA-based therapeutic interventions. Moreover, certain miRNAs exert their functions by inhibiting or modulating Notch signaling. Consequently, targeting molecular biomarkers within this pathway holds promise for predicting patient survival outcomes. Genomics-based analysis of GBM-derived exosomes from blood samples offers a promising avenue for predicting malignancy levels. Additionally, the effective delivery of tumor suppressor miRNAs targeting critical Notch members or activators represents a potential therapeutic strategy for GBM treatment.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, S.H.S., M.L., and M.M.T.; literature search and analysis, S.H.S., E.R.A., M.L., J.A., S.H.K., A.A.A.A., H.B., M.El-T., N.S.-S., A.G. A., Á.S.-A., V.M., Y.M., R.G., A.H.-J., V.N.U., M.L., and M.M.T.; validation, S.H.S., E.R.A., M.L., J.A., S.H.K., A.A.A.A., H.B., M.El-T., N.S.-S., A.G. A., Á.S.-A., V.M., Y.M., R.G., A.H.-J., V.N.U., M.L., and M.M.T.; writing—original draft preparation, S.H.S., E.R.A., M.L., J.A., S.H.K., A.A.A.A., H.B., M.El-T., V.M., Y.M., R.G.; writing—review and editing M.M.T., M.L., V.N.U., A.H-J., A.S-A., N.S-S., A.G.A.. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
This is a review article. No new data were generated.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest. The funders had no role in the design of the study; in the collection, analyses, or interpretation of data; in the writing of the manuscript; or in the decision to publish the results.
References
- Louis, D.N.; Ohgaki, H.; Wiestler, O.D.; Cavenee, W.K.; Burger, P.C.; Jouvet, A.; Scheithauer, B.W.; Kleihues, P. The 2007 WHO Classification of Tumours of the Central Nervous System. Acta Neuropathol. 2007, 114, 97–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anton, K.; Baehring, J.M.; Mayer, T. Glioblastoma Multiforme: overview of current treatment and future perspectives. Hematol. Clin. North Am. 2012, 26, 825–853. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Di Bari, M.; Bevilacqua, V.; De Jaco, A.; Laneve, P.; Piovesana, R.; Trobiani, L.; Talora, C.; Caffarelli, E.; Tata, A.M. Mir-34a-5p Mediates Cross-Talk between M2 Muscarinic Receptors and Notch-1/EGFR Pathways in U87MG Glioblastoma Cells: Implication in Cell Proliferation. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 19, 1631. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cenciarelli, C.; Marei, H.E.; Zonfrillo, M.; Casalbore, P.; Felsani, A.; Giannetti, S.; Trevisi, G.; Althani, A.; Mangiola, A. The interference of Notch1 target Hes1 affects cell growth, differentiation and invasiveness of glioblastoma stem cells through modulation of multiple oncogenic targets. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 17873–17886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reicher, A.; Foßelteder, J.; Kwong, L.N.; Pichler, M. Crosstalk between the Notch signaling pathway and long non-coding RNAs. Cancer Lett. 2018, 420, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, J.-B.; Jiang, H.; Zhan, R.-Y. Aberrant Notch signaling in glioblastoma stem cells contributes to tumor recurrence and invasion. Mol. Med. Rep. 2016, 14, 1263–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Slack, F.J.; Chinnaiyan, A.M. The Role of Non-coding RNAs in Oncology. Cell 2019, 179, 1033–1055. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yamamura, S.; Imai-Sumida, M.; Tanaka, Y.; Dahiya, R. Interaction and cross-talk between non-coding RNAs. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2018, 75, 467–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rynkeviciene, R.; Simiene, J.; Strainiene, E.; Stankevicius, V.; Usinskiene, J.; Kaubriene, E.M.; Meskinyte, I.; Cicenas, J.; Suziedelis, K. Non-Coding RNAs in Glioma. Cancers 2018, 11, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Du, Y.; Li, J.; Xu, T.; Zhou, D.-D.; Zhang, L.; Wang, X. MicroRNA-145 induces apoptosis of glioma cells by targeting BNIP3 and Notch signaling. Oncotarget 2017, 8, 61510–61527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Prokopi, M.; Kousparou, C.A.; Epenetos, A.A. The Secret Role of microRNAs in Cancer Stem Cell Development and Potential Therapy: A Notch-Pathway Approach. Front. Oncol. 2015, 4, 389–389. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mattick, J.S.; Makunin, I.V. Non-coding RNA. Hum. Mol. Genet. 2006, 15, R17–R29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schmitz, S.U.; Grote, P.; Herrmann, B.G. Mechanisms of long noncoding RNA function in development and disease. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2016, 73, 2491–2509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ransohoff, J.D.; Wei, Y.; Khavari, P.A. The functions and unique features of long intergenic non-coding RNA. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2018, 19, 143–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibb, E.A.; Brown, C.J.; Lam, W.L. The functional role of long non-coding RNA in human carcinomas. Mol. Cancer 2011, 10, 38. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qureshi, I.A.; Mattick, J.S.; Mehler, M.F. Long non-coding RNAs in nervous system function and disease. Brain Res. 2010, 1338, 20–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, F.F. Non-coding RNAs: Lost in translation? Gene 2007, 386, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sato-Kuwabara, Y.; Melo, S.A.; Soares, F.A.; Calin, G.A. The fusion of two worlds: Non-coding RNAs and extracellular vesicles - diagnostic and therapeutic implications (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2014, 46, 17–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Staněk, D. Long non-coding RNAs and splicing. Essays Biochem. 2021, 65, 723–729. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Møller, H.G.; Rasmussen, A.P.; Andersen, H.H.; Johnsen, K.B.; Henriksen, M.; Duroux, M. A Systematic Review of MicroRNA in Glioblastoma Multiforme: Micro-modulators in the Mesenchymal Mode of Migration and Invasion. Mol. Neurobiol. 2012, 47, 131–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masoudi, M.S.; Mehrabian, E.; Mirzaei, H. MiR-21: A key player in glioblastoma pathogenesis. J. Cell. Biochem. 2017, 119, 1285–1290. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tivnan, A.; McDonald, K.L. Current Progress for the Use of miRNAs in Glioblastoma Treatment. Mol. Neurobiol. 2013, 48, 757–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, S.; Mitra, R.; Zhao, M.-M.; Fan, W.; Eischen, C.M.; Yin, F.; Zhao, Z. The Potential Roles of Long Noncoding RNAs (lncRNA) in Glioblastoma Development. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2016, 15, 2977–2986. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, K.; Ji, Z.; She, K.; Yang, Q.; Shao, L. Long non-coding RNA ZFAS1 is an unfavourable prognostic factor and promotes glioma cell progression by activation of the Notch signaling pathway. BioMedicine 2017, 87, 555–560. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rezaei, O.; Tamizkar, K.H.; Sharifi, G.; Taheri, M.; Ghafouri-Fard, S. Emerging Role of Long Non-Coding RNAs in the Pathobiology of Glioblastoma. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, G.; Pan, Y.; Li, Y.; Xu, H. lncRNA and mRNA signature for prognosis prediction of glioblastoma. Futur. Oncol. 2020, 16, 837–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Q.; Qi, C.; Li, G.; Su, W. Prediction of the Outcome for Patients with Glioblastoma with lncRNA Expression Profiles. BioMed Res. Int. 2019, 2019, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, D.; Tang, L.; Wu, Y.; Fan, C.; Zhang, S.; Xiang, B.; Zhou, M.; Li, X.; Li, Y.; Li, G.; et al. Abnormal X chromosome inactivation and tumor development. Cell. Mol. Life Sci. 2020, 77, 2949–2958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mercer, T.R.; Mattick, J.S. Structure and function of long noncoding RNAs in epigenetic regulation. Nat. Struct. Mol. Biol. 2013, 20, 300–307. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.T. Epigenetic Regulation by Long Noncoding RNAs. Science 2012, 338, 1435–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Feng, W.; Li, L.; Xu, X.; Jiao, Y.; Du, W. Up-regulation of the long non-coding RNA RMRP contributes to glioma progression and promotes glioma cell proliferation and invasion. Arch. Med Sci. 2017, 13, 1315–1321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cai, J.; Zuo, X.; Chen, Z.; Zhao, W.; Zhu, Y.; Zhang, Z.; Ye, X. Prognostic value and clinical significance of long noncoding RNA CASC2 in human malignancies: a meta-analysis. Cancer Manag. Res. 2018, ume 10, 1403–1412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, R.; Li, Y.; Zhu, G.; Tian, B.; Zeng, W.; Yang, Y.; Li, Z. Long noncoding RNA CASC2 predicts the prognosis of glioma patients and functions as a suppressor for gliomas by suppressing Wnt/β-catenin signaling pathway. Neuropsychiatr. Dis. Treat. 2017, ume 13, 1805–1813. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Siebel, C.; Lendahl, U. Notch signaling in development, tissue homeostasis, and disease. Physiological reviews 2017, 97, 1235–1294. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nandagopal, N.; Santat, L.A.; LeBon, L.; Sprinzak, D.; Bronner, M.E.; Elowitz, M.B. Dynamic ligand discrimination in the notch signaling pathway. Cell 2018, 172, 869–880 e819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henrique, D.; Schweisguth, F. Mechanisms of Notch signaling: a simple logic deployed in time and space. Development 2019, 146, dev172148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Meurette, O.; Mehlen, P. Notch Signaling in the Tumor Microenvironment. Cancer Cell 2018, 34, 536–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovall, R.A.; Gebelein, B.; Sprinzak, D.; Kopan, R. The Canonical Notch Signaling Pathway: Structural and Biochemical Insights into Shape, Sugar, and Force. Dev. Cell 2017, 41, 228–241. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sivasankaran, B.; Degen, M.; Ghaffari, A.; Hegi, M.E.; Hamou, M.-F.; Ionescu, M.-C.S.; Zweifel, C.; Tolnay, M.; Wasner, M.; Mergenthaler, S.; et al. Tenascin-C Is a Novel RBPJκ-Induced Target Gene for Notch Signaling in Gliomas. Cancer Res 2009, 69, 458–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, X.; Mikolaenko, I.; Elhassan, I.; Ni, X.; Wang, Y.; Ball, D.; Brat, D.J.; Perry, A.; Eberhart, C.G. Notch1 and notch2 have opposite effects on embryonal brain tumor growth. Cancer research 2004, 64, 7787–7793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Purow, B.W.; Sundaresan, T.K.; Burdick, M.J.; Kefas, B.A.; Comeau, L.D.; Hawkinson, M.P.; Su, Q.; Kotliarov, Y.; Lee, J.; Zhang, W.; et al. Notch-1 regulates transcription of the epidermal growth factor receptor through p53. Carcinog. 2008, 29, 918–925. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Merlo, A. Genes and pathways driving glioblastomas in humans and murine disease models. Neurosurg. Rev. 2003, 26, 145–158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libermann, T.A.; Nusbaum, H.R.; Razon, N.; Kris, R.; Lax, I.; Soreq, H.; Whittle, N.; Waterfield, M.D.; Ullrich, A.; Schlessinger, J. Amplification, enhanced expression and possible rearrangement of EGF receptor gene in primary human brain tumours of glial origin. Nature 1985, 313, 144–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Libermann, T.A.; Nusbaum, H.R.; Razon, N.; Kris, R.; Lax, I.; Soreq, H.; Whittle, N.; Waterfield, M.D.; Ullrich, A.; Schlessinger, J. Amplification and Overexpression of the EGF Receptor Gene in Primary Human Glioblastomas. J. Cell Sci. 1985, 1985, 161–172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhen, Y.; Zhao, S.; Li, Q.; Li, Y.; Kawamoto, K. Arsenic trioxide-mediated Notch pathway inhibition depletes the cancer stem-like cell population in gliomas. Cancer Lett. 2010, 292, 64–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Ji, Z.; Liu, H.; Liu, Y.; Han, D.; Shi, C.; Shi, C.; Wang, C.; Yang, G.; Chen, X.; et al. Arsenic trioxide depletes cancer stem-like cells and inhibits repopulation of neurosphere derived from glioblastoma by downregulation of Notch pathway. Toxicol. Lett. 2013, 220, 61–69. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guichet, P.-O.; Guelfi, S.; Teigell, M.; Hoppe, L.; Bakalara, N.; Bauchet, L.; Duffau, H.; Lamszus, K.; Rothhut, B.; Hugnot, J.-P. Notch1 Stimulation Induces a Vascularization Switch With Pericyte-Like Cell Differentiation of Glioblastoma Stem Cells. STEM CELLS 2014, 33, 21–34. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hulleman, E.; Quarto, M.; Vernell, R.; Masserdotti, G.; Colli, E.; Kros, J.M.; Levi, D.; Gaetani, P.; Tunici, P.; Finocchiaro, G.; et al. A role for the transcription factor HEY1 in glioblastoma. J. Cell. Mol. Med. 2008, 13, 136–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, N.I.; Guilhamon, P.; Desai, K.; McAdam, R.F.; Langille, E.; O’connor, M.; Lan, X.; Whetstone, H.; Coutinho, F.J.; Vanner, R.J.; et al. ASCL1 Reorganizes Chromatin to Direct Neuronal Fate and Suppress Tumorigenicity of Glioblastoma Stem Cells. Cell Stem Cell 2017, 21, 209–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brun, M.; Jain, S.; Monckton, E.A.; Godbout, R. Nuclear Factor I Represses the Notch Effector HEY1 in Glioblastoma. Neoplasia 2018, 20, 1023–1037. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, J.; Zhang, X.-M.; Yang, J.-C.; Ye, Y.-B.; Luo, S.-Q. γ-Secretase Inhibitor-I Enhances Radiosensitivity of Glioblastoma Cell Lines by Depleting CD133+ Tumor Cells. Arch. Med Res. 2010, 41, 519–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Schreck, K.C.; Taylor, P.; Marchionni, L.; Gopalakrishnan, V.; Bar, E.E.; Gaiano, N.; Eberhart, C.G. The Notch Target Hes1 Directly Modulates Gli1 Expression and Hedgehog Signaling: A Potential Mechanism of Therapeutic Resistance. Clin. Cancer Res. 2010, 16, 6060–6070. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, W.; Zhang, C.; Ren, X.; Jiang, Y.; Han, S.; Liu, Y.; Cai, J.; Li, M.; Wang, K.; Liu, Y.; et al. Bioinformatic analyses reveal a distinct Notch activation induced by STAT3 phosphorylation in the mesenchymal subtype of glioblastoma. J. Neurosurg. 2017, 126, 249–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Phillips, E.; Lang, V.; Bohlen, J.; Bethke, F.; Puccio, L.; Tichy, D.; Herold-Mende, C.; Hielscher, T.; Lichter, P.; Goidts, V. Targeting atypical protein kinase C iota reduces viability in glioblastoma stem-like cellsviaa notch signaling mechanism. Int. J. Cancer 2016, 139, 1776–1787. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chigurupati, S.; Venkataraman, R.; Barrera, D.; Naganathan, A.; Madan, M.; Paul, L.; Pattisapu, J.V.; Kyriazis, G.A.; Sugaya, K.; Bushnev, S.; et al. Receptor Channel TRPC6 Is a Key Mediator of Notch-Driven Glioblastoma Growth and Invasiveness. Cancer Res 2010, 70, 418–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, M.; Inoue, K.; Leng, T.; Guo, S.; Xiong, Z.-G. TRPM7 channels regulate glioma stem cell through STAT3 and Notch signaling pathways. Cell. Signal. 2014, 26, 2773–2781. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clark, K.; Langeslag, M.; van Leeuwen, B.; Ran, L.; Ryazanov, A.G.; Figdor, C.G.; Moolenaar, W.H.; Jalink, K.; van Leeuwen, F.N. TRPM7, a novel regulator of actomyosin contractility and cell adhesion. EMBO J. 2006, 25, 290–301. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Takezawa, R.; Schmitz, C.; Demeuse, P.; Scharenberg, A.M.; Penner, R.; Fleig, A. Receptor-mediated regulation of the TRPM7 channel through its endogenous protein kinase domain. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2004, 101, 6009–6014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, C.; Perraud, A.-L.; Johnson, C.O.; Inabe, K.; Smith, M.K.; Penner, R.; Kurosaki, T.; Fleig, A.; Scharenberg, A.M. Regulation of vertebrate cellular Mg2+ homeostasis by TRPM7. Cell 2003, 114, 191–200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shen, F.; Song, C.; Liu, Y.; Zhang, J.; Song, S.W. IGFBP2 promotes neural stem cell maintenance and proliferation differentially associated with glioblastoma subtypes. Brain Res. 2018, 1704, 174–186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Kesari, S.; Rooney, C.; Strack, P.R.; Shen, H.; Wu, L.; Griffin, J.D. Inhibition of Notch Signaling Blocks Growth of Glioblastoma Cell Lines and Tumor Neurospheres. Genes Cancer 2010, 1, 822–835. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Floyd, D.H.; Kefas, B.; Seleverstov, O.; Mykhaylyk, O.; Dominguez, C.; Comeau, L.; Plank, C.; Purow, B. Alpha-secretase inhibition reduces human glioblastoma stem cell growth in vitro and in vivo by inhibiting Notch. Neuro-Oncology 2012, 14, 1215–1226. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Panza, S.; Russo, U.; Giordano, F.; Leggio, A.; Barone, I.; Bonofiglio, D.; Gelsomino, L.; Malivindi, R.; Conforti, F.L.; Naimo, G.D.; et al. Leptin and Notch Signaling Cooperate in Sustaining Glioblastoma Multiforme Progression. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 886. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aithal, M.G.S.; Rajeswari, N. Bacoside A Induced Sub-G0 Arrest and Early Apoptosis in Human Glioblastoma Cell Line U-87 MG through Notch Signaling Pathway. Brain Tumor Res. Treat. 2019, 7, 25–32. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hiddingh, L.; Tannous, B.A.; Teng, J.; Tops, B.; Jeuken, J.; Hulleman, E.; Boots-Sprenger, S.H.; Vandertop, W.P.; Noske, D.P.; Kaspers, G.J.; et al. EFEMP1 induces γ-secretase/Notch-mediated temozolomide resistance in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2013, 5, 363–374. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dantas-Barbosa, C.; Bergthold, G.; Daudigeos-Dubus, E.; Blockus, H.; Boylan, J.F.; Ferreira, C.; Puget, S.; Abely, M.; Vassal, G.; Grill, J.; et al. Inhibition of the NOTCH pathway using γ-secretase inhibitor RO4929097 has limited antitumor activity in established glial tumors. Anti-Cancer Drugs 2015, 26, 272–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Cheng, Z.; Liu, J.; Torre-Healy, L.; Lathia, J.D.; Nakano, I.; Guo, Y.; Thompson, R.C.; Freeman, M.L.; Wang, J. Inhibition of Farnesyltransferase Potentiates NOTCH-Targeted Therapy against Glioblastoma Stem Cells. Stem Cell Rep. 2017, 9, 1948–1960. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Opačak-Bernardi, T.; Ryu, J.S.; Raucher, D. Effects of cell penetrating Notch inhibitory peptide conjugated to elastin-like polypeptide on glioblastoma cells. J. Drug Target. 2017, 25, 523–531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bruick, R.K. Expression of the gene encoding the proapoptotic Nip3 protein is induced by hypoxia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2000, 97, 9082–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moutal, A.; Honnorat, J.; Massoma, P.; Désormeaux, P.; Bertrand, C.; Malleval, C.; Watrin, C.; Chounlamountri, N.; Mayeur, M.-E.; Besançon, R.; et al. CRMP5 Controls Glioblastoma Cell Proliferation and Survival through Notch-Dependent Signaling. Cancer Res 2015, 75, 3519–3528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Greenfield, J.J.A.; High, S. The Sec61 complex is located in both the ER and the ER-Golgi intermediate compartment. J. Cell Sci. 1999, 112, 1477–1486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oakes, S.A.; Papa, F.R. The Role of Endoplasmic Reticulum Stress in Human Pathology. Annu. Rev. Pathol. Mech. Dis. 2015, 10, 173–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, Y.; Ji, W.; Shergalis, A.; Xu, J.; Delaney, A.M.; Calcaterra, A.; Pal, A.; Ljungman, M.; Neamati, N.; Rehemtulla, A. Activation of the Unfolded Protein Response via Inhibition of Protein Disulfide Isomerase Decreases the Capacity for DNA Repair to Sensitize Glioblastoma to Radiotherapy. Cancer Res 2019, 79, 2923–2932. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, B.; Liu, J.; Liao, Y.; Jin, C.; Zhang, Z.; Zhao, J.; Liu, K.; Huang, H.; Cao, H.; Cheng, Q. Identification of SEC61G as a Novel Prognostic Marker for Predicting Survival and Response to Therapies in Patients with Glioblastoma. Experiment 2019, 25, 3624–3635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guo, J.; Li, P.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. NOTCH signaling pathway and non-coding RNAs in cancer. Pathol. - Res. Pr. 2019, 215, 152620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wei, W.; Ai, X.; Pang, Y.; Bian, Y. Upregulation of lncRNA PlncRNA-1 indicates the poor prognosis and promotes glioma progression by activation of Notch signal pathway. BioMedicine 2018, 103, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sun, T.; Patil, R.; Galstyan, A.; Klymyshyn, D.; Ding, H.; Chesnokova, A.; Cavenee, W.K.; Furnari, F.B.; Ljubimov, V.A.; Shatalova, E.S.; et al. Blockade of a Laminin-411–Notch Axis with CRISPR/Cas9 or a Nanobioconjugate Inhibits Glioblastoma Growth through Tumor-Microenvironment Cross-talk. Cancer Res 2019, 79, 1239–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Gong, W.; Zheng, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, J.; Wang, P.; et al. PVT1 regulates the malignant behaviors of human glioma cells by targeting miR-190a-5p and miR-488-3p. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1783–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, B.; Cai, M. LncRNA FEZF1-AS1 Sponges miR-34a to Upregulate Notch-1 in Glioblastoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, ume 12, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsai, Y.-L.; Chang, H.-H.; Chen, Y.-C.; Chang, Y.-C.; Tsai, Y. Molecular Mechanisms of KDELC2 on Glioblastoma Tumorigenesis and Temozolomide Resistance. Biomedicines 2020, 8, 339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsuno, K.; Diederich, R.J.; Go, M.J.; Blaumueller, C.M.; Artavanis-Tsakonas, S. Deltex acts as a positive regulator of Notch signaling through interactions with the Notch ankyrin repeats. Development 1995, 121, 2633–2644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Huber, R.M.; Rajski, M.; Sivasankaran, B.; Moncayo, G.; Hemmings, B.A.; Merlo, A. Deltex-1 Activates Mitotic Signaling and Proliferation and Increases the Clonogenic and Invasive Potential of U373 and LN18 Glioblastoma Cells and Correlates with Patient Survival. PLOS ONE 2013, 8, e57793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bozkulak, E.C.; Weinmaster, G. Selective Use of ADAM10 and ADAM17 in Activation of Notch1 Signaling. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2009, 29, 5679–5695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, X.; Chen, L.; Zhang, R.; Yi, Y.; Ma, Y.; Yan, K.; Jiang, X.; Wang, X. ADAM17 regulates self-renewal and differentiation of U87 glioblastoma stem cells. Neurosci. Lett. 2013, 537, 44–49. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dadey, D.Y.; Kapoor, V.; Khudanyan, A.; Urano, F.; Kim, A.H.; Thotala, D.; Hallahan, D.E. The ATF6 pathway of the ER stress response contributes to enhanced viability in glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2015, 7, 2080–2092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; He, Z.-C.; Zhang, X.-N.; Liu, Q.; Chen, C.; Zhu, Z.; Chen, Q.; Shi, Y.; Yao, X.-H.; Cui, Y.-H.; et al. Stanniocalcin-1 augments stem-like traits of glioblastoma cells through binding and activating NOTCH1. Cancer Lett. 2018, 416, 66–74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ylivinkka, I.; Hu, Y.; Chen, P.; Rantanen, V.; Hautaniemi, S.; Nyman, T.A.; Keski-Oja, J.; Hyytiäinen, M. Netrin-1 induced activation of Notch signaling mediates glioblastoma cell invasion. J. Cell Sci. 2013, 126, 2459–2469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sarkar, S.; Mirzaei, R.; Zemp, F.J.; Wei, W.; Senger, D.L.; Robbins, S.M.; Yong, V.W. Activation of NOTCH Signaling by Tenascin-C Promotes Growth of Human Brain Tumor-Initiating Cells. Cancer Res 2017, 77, 3231–3243. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kefas, B.; Comeau, L.; Floyd, D.H.; Seleverstov, O.; Godlewski, J.; Schmittgen, T.; Jiang, J.; Dipierro, C.G.; Li, Y.; Chiocca, E.A.; et al. The Neuronal MicroRNA miR-326 Acts in a Feedback Loop with Notch and Has Therapeutic Potential against Brain Tumors. J. Neurosci. 2009, 29, 15161–15168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Katsushima, K.; Kondo, Y. Non-coding RNAs as epigenetic regulator of glioma stem-like cell differentiation. Front. Genet. 2014, 5, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cristofaro, I.; Alessandrini, F.; Spinello, Z.; Guerriero, C.; Fiore, M.; Caffarelli, E.; Laneve, P.; Dini, L.; Conti, L.; Tata, A.M. Cross Interaction between M2 Muscarinic Receptor and Notch1/EGFR Pathway in Human Glioblastoma Cancer Stem Cells: Effects on Cell Cycle Progression and Survival. Cells 2020, 9, 657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xing, Z.-Y.; Sun, L.-G.; Guo, W.-J. Elevated expression of Notch-1 and EGFR induced apoptosis in glioblastoma multiforme patients. Clin. Neurol. Neurosurg. 2015, 131, 54–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pang, R.T.; Leung, C.O.; Ye, T.-M.; Liu, W.; Chiu, P.C.; Lam, K.K.; Lee, K.-F.; Yeung, W.S. MicroRNA-34a suppresses invasion through downregulation of Notch1 and Jagged1 in cervical carcinoma and choriocarcinoma cells. Carcinog. 2010, 31, 1037–1044. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-J.; Ji, M.-H.; Zhong, S.-L.; Zha, Q.-B.; Xu, J.-J.; Zhao, J.-H.; Tang, J.-H. MicroRNA-34a Modulates Chemosensitivity of Breast Cancer Cells to Adriamycin by Targeting Notch1. Arch. Med Res. 2012, 43, 514–521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Zhou, W.; Kong, F.; Xiao, X.; Kuang, H.; Zhu, Y. microRNA-34a overexpression inhibits cell migration and invasion via regulating SIRT1 in hepatocellular carcinoma. Oncol. Lett. 2017, 14, 6950–6954. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Guessous, F.; Zhang, Y.; Kofman, A.; Catania, A.; Li, Y.; Schiff, D.; Purow, B.; Abounader, R. microRNA-34a is tumor suppressive in brain tumors and glioma stem cells. Cell Cycle 2010, 9, 1031–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Betel, D.; Wilson, M.; Gabow, A.; Marks, D.S.; Sander, C. The microRNA.org resource: Targets and expression. Nucleic Acids Res. 2008, 36 (Suppl. 1), D149–D153. [CrossRef]
- Wang, P.; Liang, X.; Lu, Y.; Zhao, X.; Liang, J. MicroRNA-93 Downregulation Ameliorates Cerebral Ischemic Injury Through the Nrf2/HO-1 Defense Pathway. Neurochem. Res. 2016, 41, 2627–2635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, T.; Yao, Q.; Wang, W.; Yao, H.; Chao, J. iNOS Induces Vascular Endothelial Cell Migration and Apoptosis Via Autophagy in Ischemia/Reperfusion Injury. Cell. Physiol. Biochem. 2016, 38, 1575–1588. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rayner, B.S.; Duong, T.T.H.; Myers, S.J.; Witting, P.K. Protective effect of a synthetic anti-oxidant on neuronal cell apoptosis resulting from experimental hypoxia re-oxygenation injury. J. Neurochem. 2006, 97, 211–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jiang, Y.; Li, L.; Ma, J.; Zhang, L.; Niu, F.; Feng, T.; Li, C. Auricular vagus nerve stimulation promotes functional recovery and enhances the post-ischemic angiogenic response in an ischemia/reperfusion rat model. Neurochem. Int. 2016, 97, 73–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bacon, A.; Harris, A. Hypoxia-inducible factors and hypoxic cell death in tumour physiology. Ann. Med. 2004, 36, 530–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bruick, R.K. Expression of the gene encoding the proapoptotic Nip3 protein is induced by hypoxia. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2000, 97, 9082–9087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burton, T.R.; Henson, E.S.; Baijal, P.; Eisenstat, D.D.; Gibson, S.B. The pro-cell death Bcl-2 family member, BNIP3, is localized to the nucleus of human glial cells: Implications for glioblastoma multiforme tumor cell survival under hypoxia. Int. J. Cancer 2005, 118, 1660–1669. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, K.; Wang, Q.; Wang, Y.; Huang, K.; Yang, C.; Li, Y.; Yi, K.; Kang, C. EGFR/c-myc axis regulates TGFβ/Hippo/Notch pathway via epigenetic silencing miR-524 in gliomas. Cancer Lett. 2017, 406, 12–21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Zheng, Q.; Bao, C.; Li, S.; Guo, W.; Zhao, J.; Chen, D.; Gu, J.; He, X.; Huang, S. Circular RNA is enriched and stable in exosomes: a promising biomarker for cancer diagnosis. Cell Res. 2015, 25, 981–984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, H.; Zhang, Y.; Qi, L.; Ding, L.; Jiang, H.; Yu, H. NFIX Circular RNA Promotes Glioma Progression by Regulating miR-34a-5p via Notch Signaling Pathway. Front. Mol. Neurosci. 2018, 11, 225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guo, J.; Li, P.; Liu, X.; Li, Y. NOTCH signaling pathway and non-coding RNAs in cancer. Pathol. - Res. Pr. 2019, 215, 152620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Yan, Y.; Zhang, C.; Wei, W.; Ai, X.; Pang, Y.; Bian, Y. Upregulation of lncRNA PlncRNA-1 indicates the poor prognosis and promotes glioma progression by activation of Notch signal pathway. BioMedicine 2018, 103, 216–221. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xue, W.; Chen, J.; Liu, X.; Gong, W.; Zheng, J.; Guo, X.; Liu, Y.; Liu, L.; Ma, J.; Wang, P.; et al. PVT1 regulates the malignant behaviors of human glioma cells by targeting miR-190a-5p and miR-488-3p. Biochim. et Biophys. Acta (BBA) - Mol. Basis Dis. 2018, 1864, 1783–1794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luo, L.; Zhang, Y.; He, H.; Chen, C.; Zhang, B.; Cai, M. LncRNA FEZF1-AS1 Sponges miR-34a to Upregulate Notch-1 in Glioblastoma. Cancer Manag. Res. 2020, ume 12, 1827–1833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Shen, F.; Yang, B. LncRNA LINC01410 Induced by MYC Accelerates Glioma Progression via Sponging miR-506-3p and Modulating NOTCH2 Expression to Motivate Notch Signaling Pathway. Cell. Mol. Neurobiol. 2021, 42, 1513–1521. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Guo, S.; Liang, C.; Lian, M. Long intergenic noncoding RNA 00021 promotes glioblastoma temozolomide resistance by epigenetically silencing p21 through Notch pathway. IUBMB Life 2020, 72, 1747–1756. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Freitas, M.R.P.; Malheiros, S.M.F.; Stávale, J.N.; Biassi, T.P.; Zamunér, F.T.; Begnami, M.D.F.d.S.; Soares, F.A.; Vettore, A.L. Expression of Cancer/Testis Antigens is Correlated with Improved Survival in Glioblastoma. Oncotarget 2013, 4, 636–646. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, G.-W.; Wu, L.; Kuang, W.; Chen, Y.; Zhu, X.-G.; Guo, H.; Lang, H.-L. Knockdown of linc-OIP5 inhibits proliferation and migration of glioma cells through down-regulation of YAP-NOTCH signaling pathway. Gene 2017, 610, 24–31. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Su, Z.; Lu, S.; Fu, W.; Liu, Z.; Jiang, X.; Tai, S. LncRNA HOXA-AS2 and its molecular mechanisms in human cancer. Clin. Chim. Acta 2018, 485, 229–233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, X.; Song, Z.; Chen, D.; Guo, M.; Liang, J.; Ding, D.; Wang, W.; Yan, D. Long Non-Coding RNA HOXA-AS2 Enhances The Malignant Biological Behaviors In Glioma By Epigenetically Regulating RND3 Expression. OncoTargets Ther. 2019, ume 12, 9407–9419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, Z.; Dai, J.; Liao, Y.; Ma, J.; Zhou, W. [ARTICLE WITHDRAWN] Knockdown of Long Noncoding RNA LINC00152 Suppresses Cellular Proliferation and Invasion in Glioma Cells by Regulating miR-4775. Oncol. Res. Featur. Preclin. Clin. Cancer Ther. 2018, 26, 857–867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Díaz-Trelles, R.; Scimia, M.C.; Bushway, P.; Tran, D.; Monosov, A.; Monosov, E.; Peterson, K.; Rentschler, S.; Cabrales, P.; Ruiz-Lozano, P.; et al. Notch-independent RBPJ controls angiogenesis in the adult heart. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 12088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hori, K.; Cholewa-Waclaw, J.; Nakada, Y.; Glasgow, S.M.; Masui, T.; Henke, R.M.; Wildner, H.; Martarelli, B.; Beres, T.M.; Epstein, J.A.; et al. A nonclassical bHLH–Rbpj transcription factor complex is required for specification of GABAergic neurons independent of Notch signaling. Genes Dev. 2008, 22, 166–178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masui, T.; Long, Q.; Beres, T.M.; Magnuson, M.A.; MacDonald, R.J. Early pancreatic development requires the vertebrate Suppressor of Hairless (RBPJ) in the PTF1 bHLH complex. J. Bone Jt. Surg. 2007, 21, 2629–2643. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, G.; Tanaka, S.; Jiapaer, S.; Sabit, H.; Tamai, S.; Kinoshita, M.; Nakada, M. RBPJ contributes to the malignancy of glioblastoma and induction of proneural-mesenchymal transition via IL-6-STAT3 pathway. Cancer Sci. 2020, 111, 4166–4176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).