Submitted:
21 July 2023
Posted:
21 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Visual Odometry
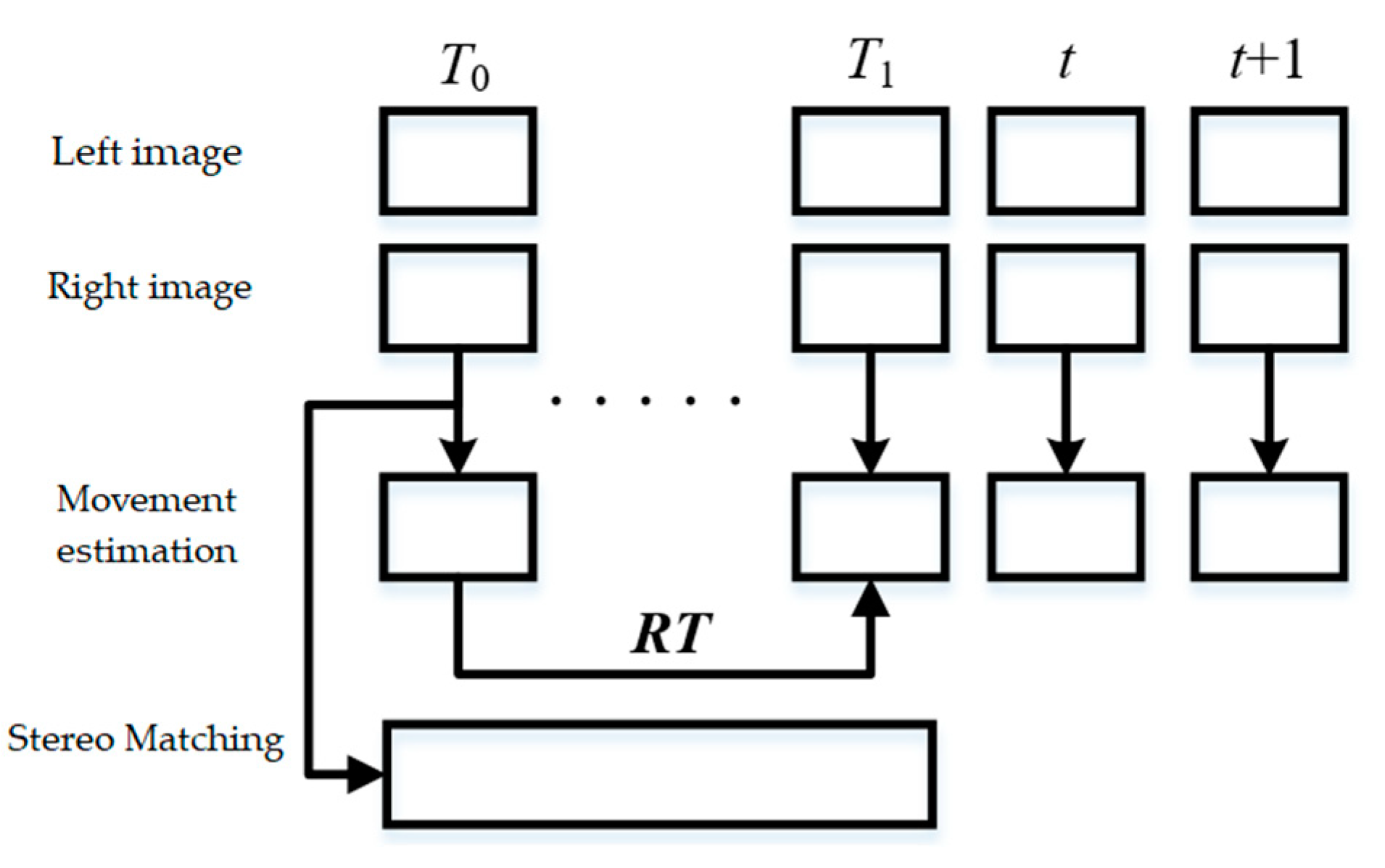
2.1. System Framework
2.2. ORB algorithm parameters selection
3. Improvement of ORB features
3.1. Calculation of different texture area weights
3.2. Keyframe-based predictive motion model
4. Experimental verification
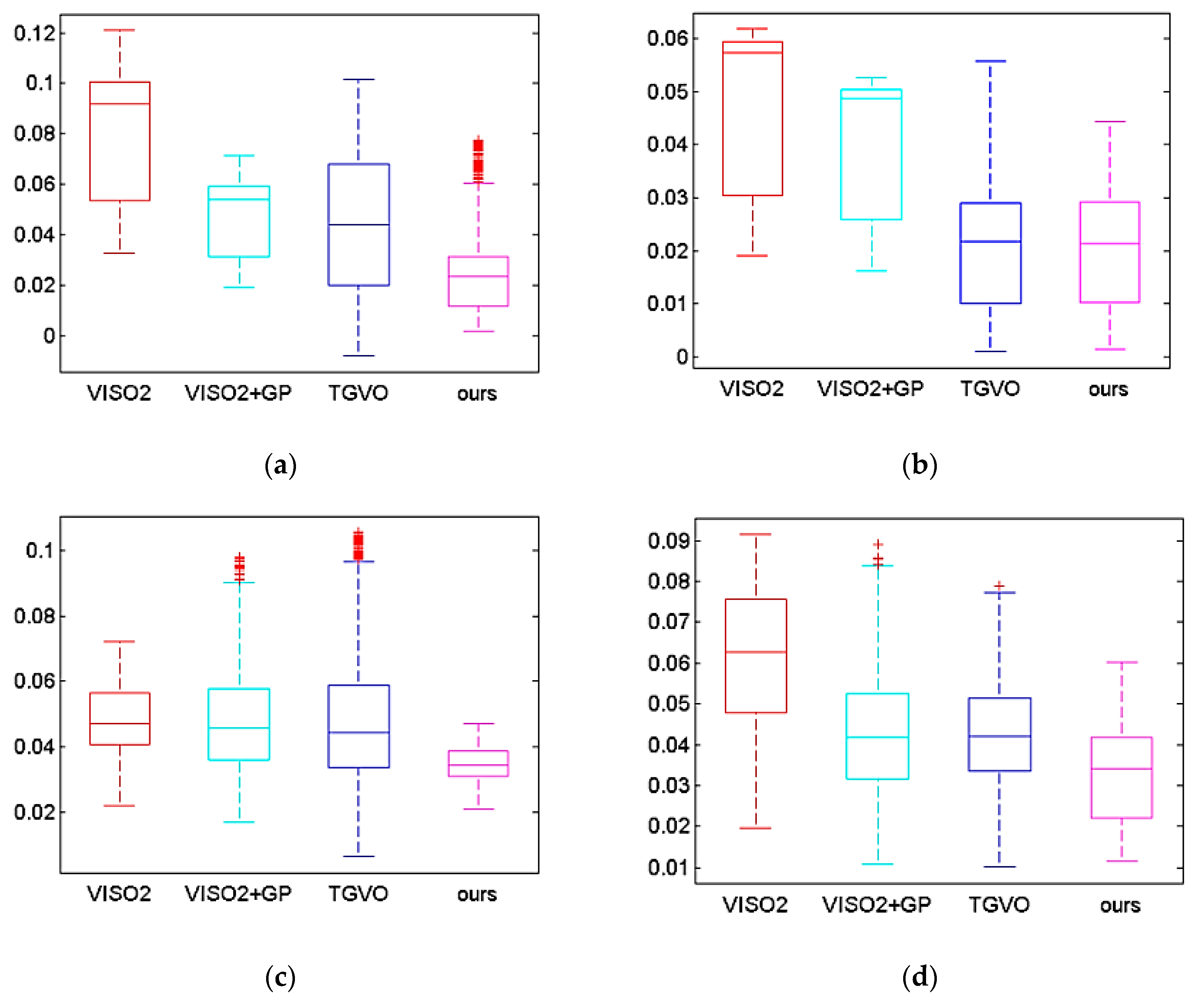
4.1. System Validation
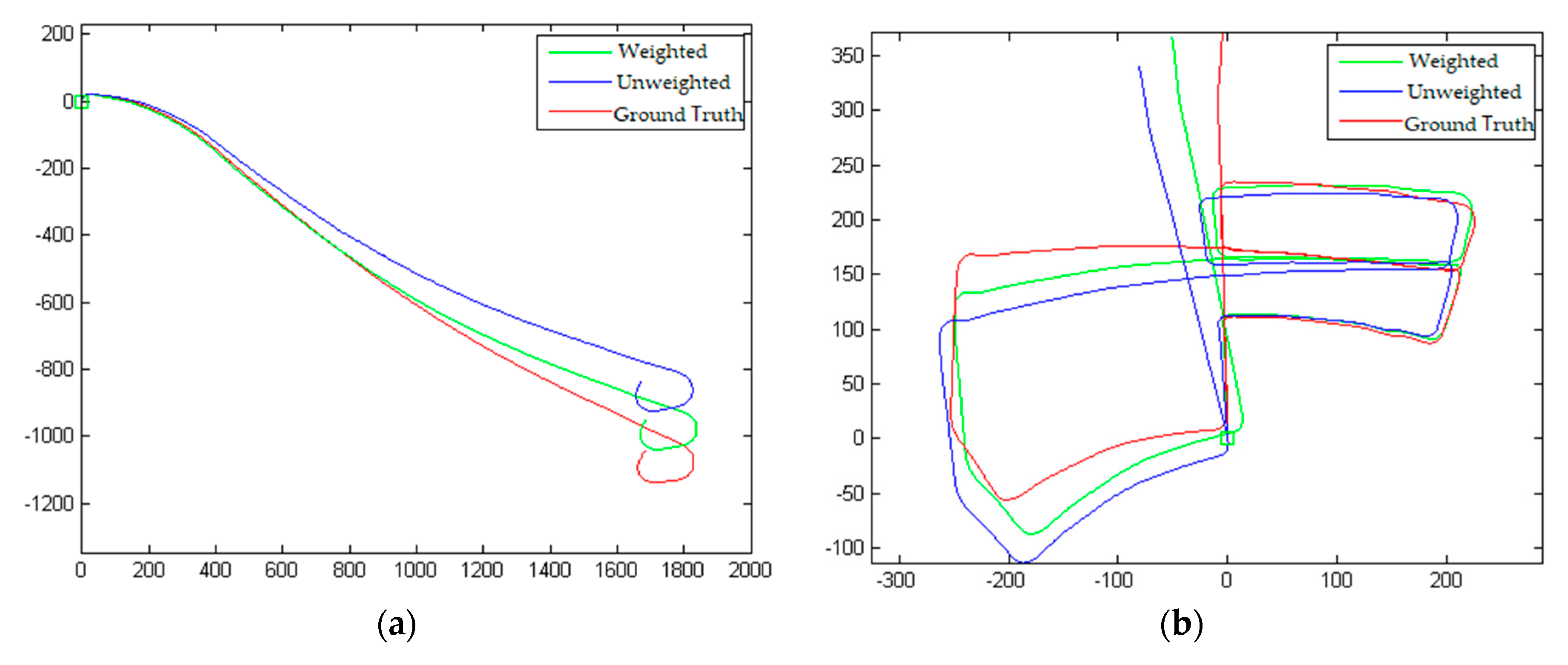
4.2. Verify texture weighting impact
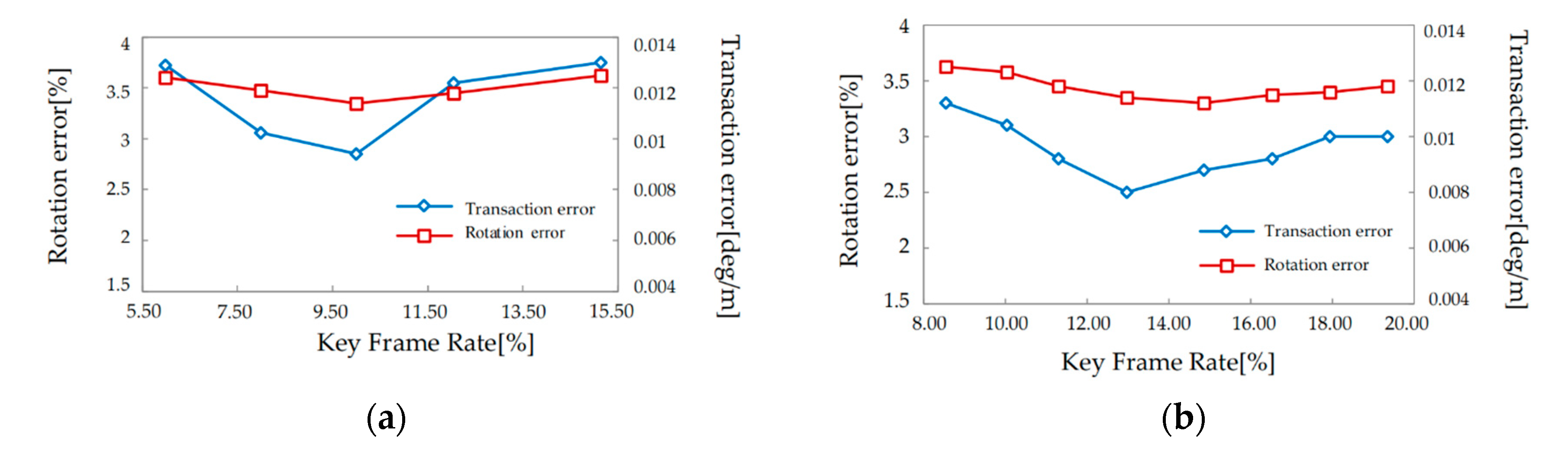
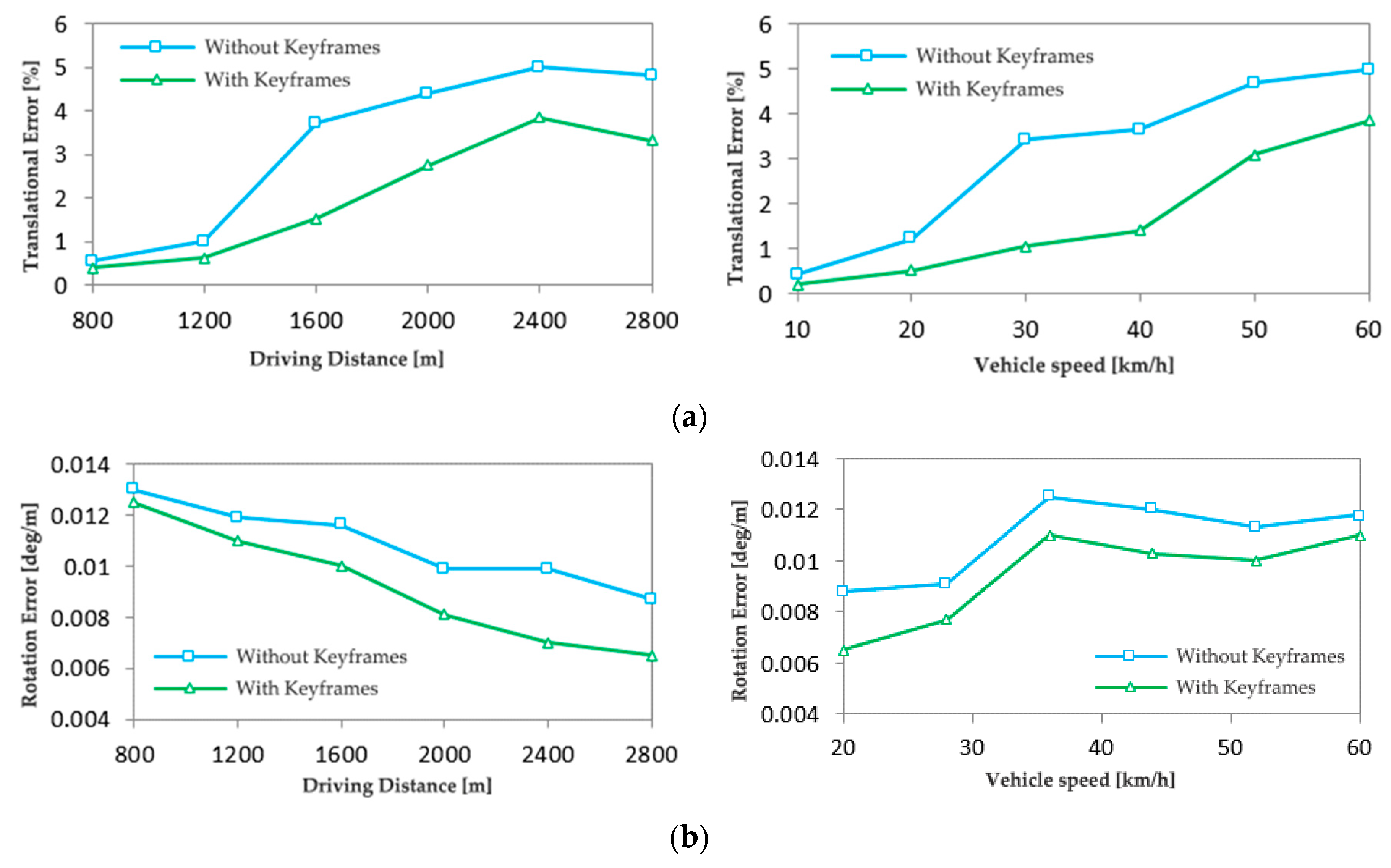
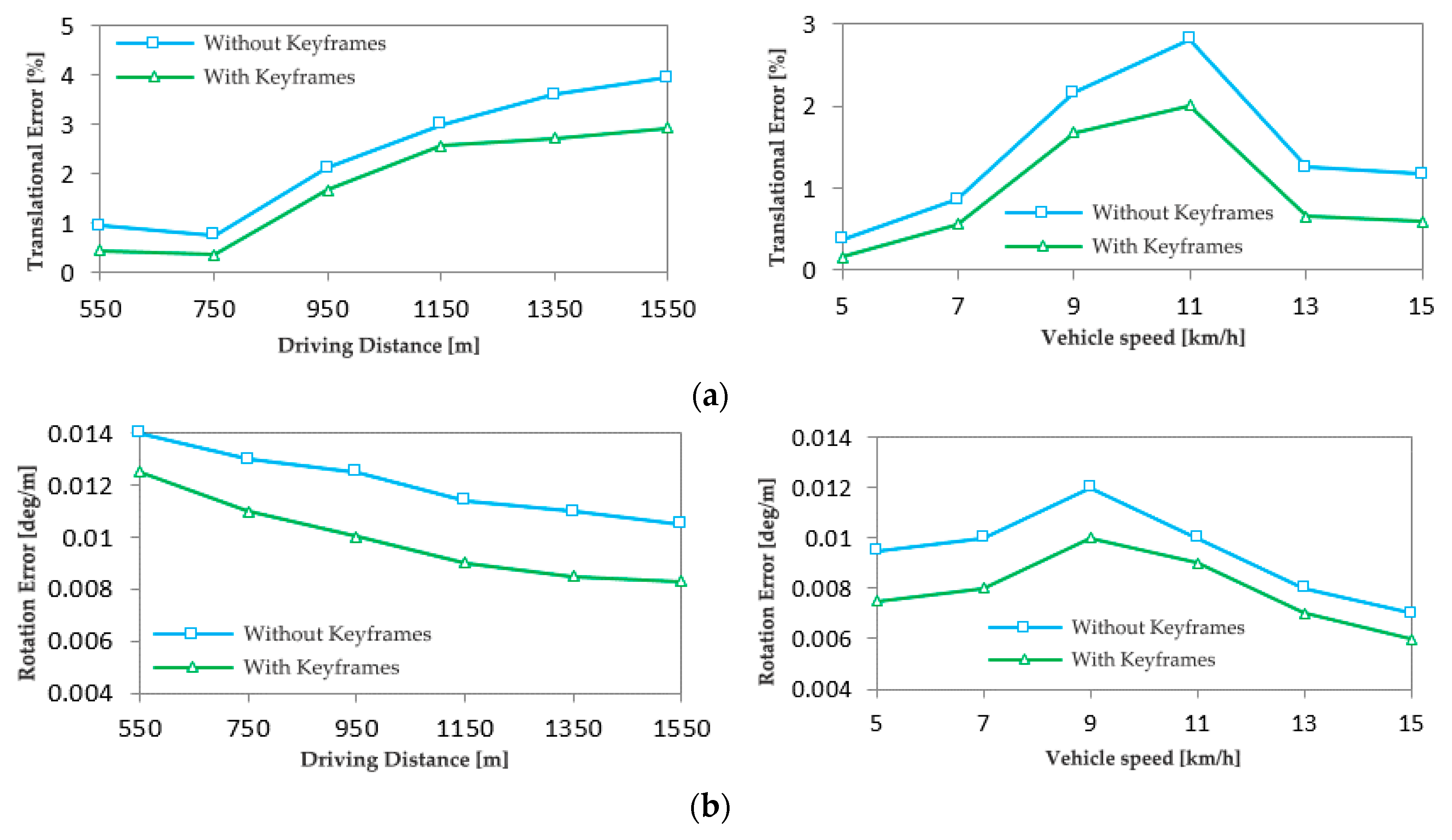
4.3. Verification of keyframes
5. Conclusions
- Propose the calculation of weights for different texture regions, with high matching weights for high texture regions and low matching weights for low texture regions, so that feature points can be evenly dispersed throughout the image and better matching results.
- Using the predicted motion model of keyframes, i.e., the motion of feature points between adjacent keyframes is obvious so that the system is more stable and less prone to errors when the vehicle is driving at slow speed. The test using KITTI dataset shows that the key frame rate reaches 10%-12% error minimum. When comparing the translation and rotation errors with and without keyframes using the KITTI dataset, the presence of keyframes clearly shows a reduction in translation and rotation errors.
- This system compares the performance of the VISO2, VISO2+GP, and TGVO verification systems, and the comparison experiments were conducted on four sequences of the KITTI dataset, and the errors were lower than those of the above three systems.
References
- Li, S.; Wang, G.; Yu, H.; Wang, X. Engineering Project: The Method to Solve Practical Problems for the Monitoring and Control of Driver-Less Electric Transport Vehicles in the Underground Mines. World Electr. Veh. J. 2021, 12, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boersma, R.; Van Arem, B.; Rieck, F. Application of Driverless Electric Automated Shuttles for Public Transport in Villages: The Case of Appelscha. World Electr. Veh. J. 2018, 9, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C.; Lei, L.; Ma, X.; Zhou, R.; Shi, Z.; Guo, Z. Map Construction Based on LiDAR Vision Inertial Multi-Sensor Fusion. World Electric Vehicle Journal. 2021, 12, 261. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, F.W.; Shi, J.Z.; Ge, L.H.; et al. Research progress of monocular vision odometer for unmanned vehicles. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering Edition) 2020, 50, 765–775. [Google Scholar]
- Zeng, Q.H.; Luo, Y.X.; Sun, K.C.; et al. A review on the development of SLAM technology for vision and its fused inertia[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics 2022, 54, 1007–1020. [Google Scholar]
- Zhou, F.Y.; Gu, P.L.; Wan, F.; et al. Methods and techniques for multi-motion visual odometry. Journal of Shandong University (Engineering Edition) 2021, 51, 1–10. [Google Scholar]
- Campos, C.; Elvira, R.; Rodríguez, J.J.; et al. ORB-SLAM3: An Accurate Open-Source Library for Visual, Visual-Inertial and Multi-Map SLAM. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2020, 37, 1874–1890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Liu, L. Navigable Space Construction from Sparse Noisy Point Clouds. IEEE Robotics and Automation Letters 2021, 6, 4720–4727. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, B.; Zhu, D. A Stereo SLAM System with Dense Mapping. IEEE Access 2021, 9, 151888–151896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Seichter, D.; Köhler, M.; Lewandowski, B.; Wengefeld, T.; Gross, H.M. Efficient RGB-D Semantic Segmentation for Indoor Scene Analysis[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Robotics and Automation (ICRA), 2021: 13525-13531.
- Raúl Mur-Artal, J.M.; Montiel, M.; Tardós, J.D. ORB-SLAM: A Versatile and Accurate Monocular SLAM System[J]. IEEE Transactions on Robotics 2015, 3, 1147–1163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bei, Q.; Liu, H.; Pei, Y.; Deng, L.; Gao, W. An Improved ORB Algorithm for Feature Extraction and Homogenization Algorithm[C]. 2021 IEEE International Conference on Electronic Technology, Communication and Information (ICETCI), 2021: 591-597.
- Chen, J.S.; Yu, L.L.; Li, X.N.; et al. Loop detection based on uniform ORB[J]. Journal of Jilin University (Engineering and Technology Edition), 2022: 1-9.
- Yao, J.J.; Zhang, P.C.; Wang, Y.; et al. An algorithm for uniform distribution of ORB features based on improved quadtrees[J]. Computer Engineering and Design 2020, 41, 1629–1634. [Google Scholar]
- Zhao, C. Research on the uniformity of SLAM feature points and the construction method of semantic map in dynamic environment[D]. Xi’an University of Technology, 2022.
- Lai, L.; Yu, X.; Qian, X.; Ou, L. 3D Semantic Map Construction System Based on Visual SLAM and CNNs[C]. IECON 2020 The 46th Annual Conference of the IEEE Industrial Electronics Society, 2020: 4727-4732.
- Ranftl, R.; Bochkovskiy, A.; Koltun, V. Vision Transformers for Dense Prediction[C]. 2021 IEEE/CVF International Conference on Computer Vision (ICCV), 2021: 12159-12168.
- Li, G.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, H.; et al. A Multi-Feature Fusion Slam System Attaching Semantic In-Variant to Points and Lines[J]. Sensors 2021, 21, 1196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fan, X.N.; Gu, Y.F.; Ni, J.J. Application of improved ORB algorithm in image matching[J]. Computer and Modernization 2019, 282, 5–10. [Google Scholar]
- Xu, H.; Yang, C.; Li, Z. OD-SLAM: Real-Time Localization and Mapping in Dynamic Environment through Multi-Sensor Fusion[C]. 2020 5th International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM), 2020:172-177.
- Xu, H.; Yang, C.; Li, Z. OD-SLAM: Real-Time Localization and Mapping in Dynamic Environment through Multi-Sensor Fusion[C]. 2020 5th International Conference on Advanced Robotics and Mechatronics (ICARM). 2020(7): 75604-75614.
- Zhao, L.; Liu, Z.; Chen, J.; Cai, W.; Wang, W.; Zeng, L. A Compatible Framework for RGB-D SLAM in Dynamic Scenes[J]. IEEE Access 2019, 7, 75604–75614. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geiger, A.; Ziegler, J.; Stiller, C. StereoScan: Dense 3d reconstruction in real-time[J]. IEEE Intelligent Vehicles Symposium 2011, 32, 963–968. [Google Scholar]
- Geiger, A. Are we ready for autonomous driving? The KITTI vision benchmark suite[C]// Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition. IEEE, 2012:3354-3361.
- Kitt, B.; Geiger, A.; Lategahn, H. Visual odometry based on stereo image sequences with RANSAC-based outlier rejection scheme[C]// Intelligent Vehicles Symposium. IEEE, 2010: 486-492.
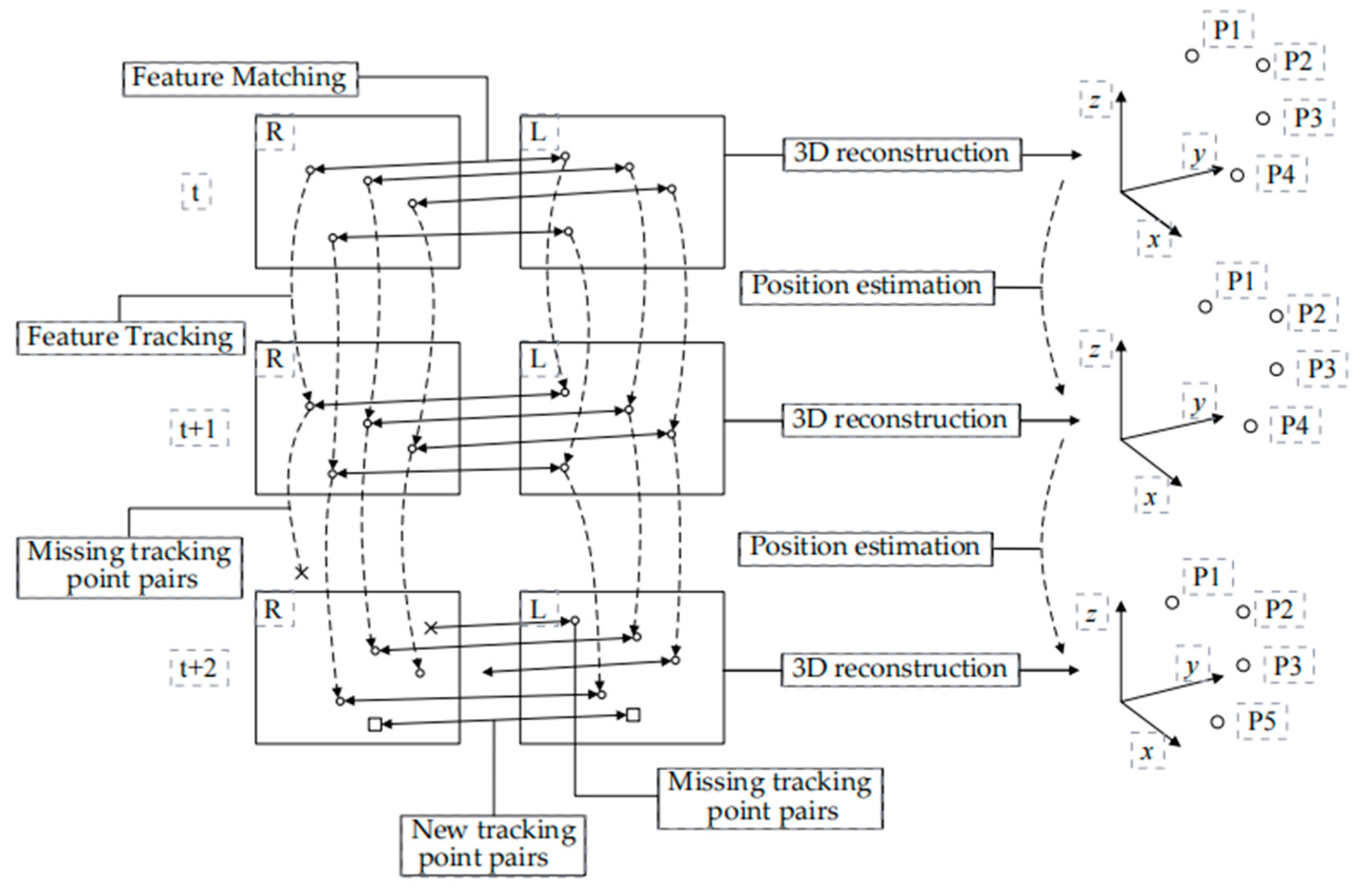
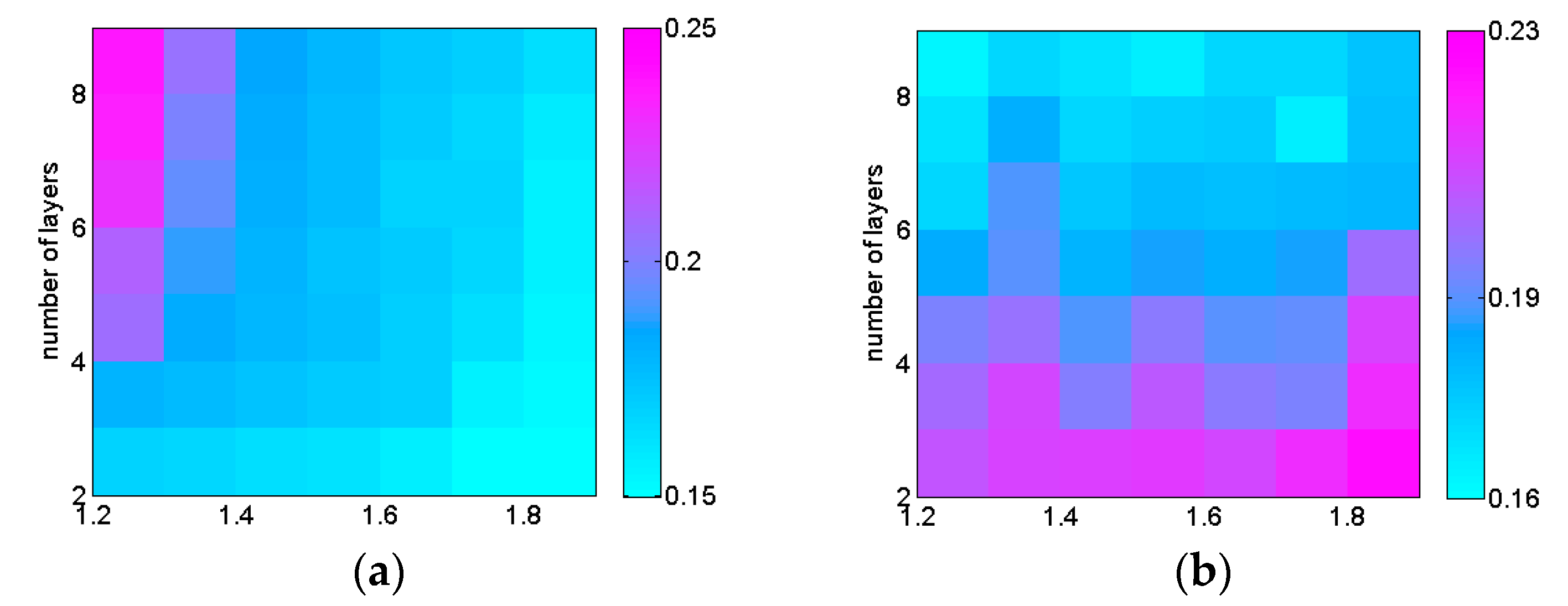
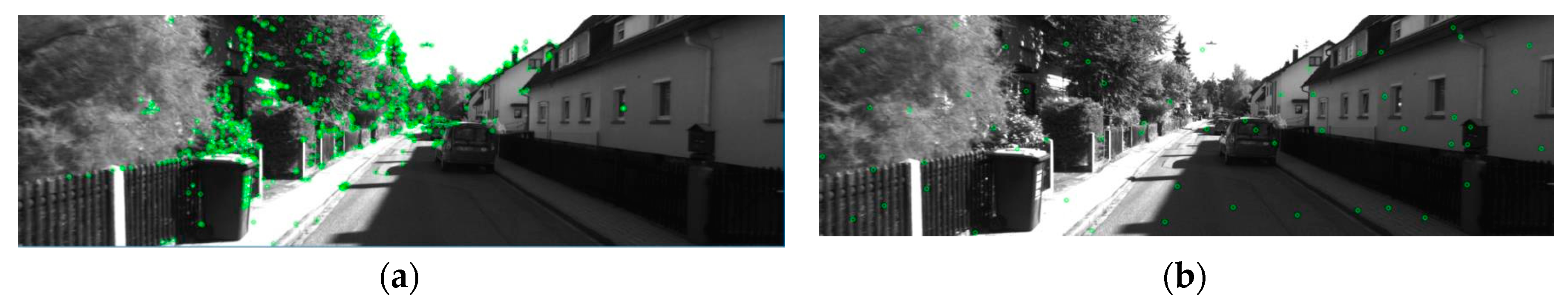
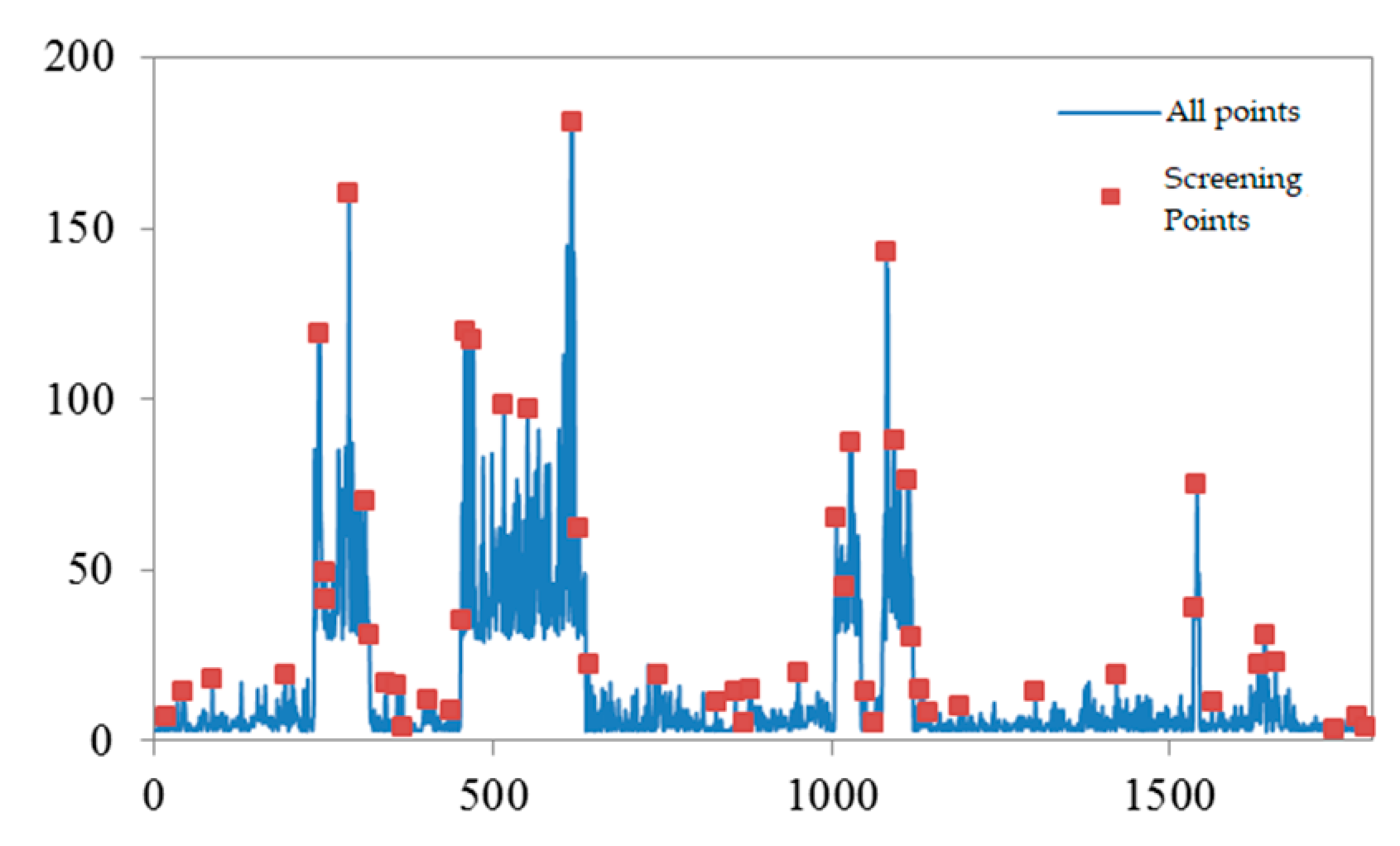
| Focal length/mm | Coordinates of main point | Aberration factor | Baseline /m |
| 718.86 | (607.19,185.22) | 0.00 | 0.54 |
| Serial number | Number of frames | Key Frame Count | Key Frame Rate(%) |
| 1 | 1101 | 66 | 5.99 |
| 2 | 1101 | 88 | 8.00 |
| 3 | 1101 | 110 | 10.00 |
| 4 | 1101 | 133 | 12.05 |
| 5 | 1101 | 167 | 15.15 |
| Serial number | Number of frames | Key Frame Count | Key Frame Rate(%) |
| 1 | 2761 | 236 | 8.55 |
| 2 | 2761 | 277 | 10.03 |
| 3 | 2761 | 312 | 11.30 |
| 4 | 2761 | 358 | 12.97 |
| 5 | 2761 | 410 | 14.85 |
| 6 | 2761 | 456 | 16.52 |
| 7 | 2761 | 495 | 17.93 |
| 8 | 2761 | 534 | 19.34 |
| Time(ms) | Min | Max | Avg |
| Feature extraction and matching | 14.6 | 34.6 | 20.7 |
| 3D reconstruction | 5.1 | 12.6 | 8.5 |
| Movement estimation | 2.9 | 10.7 | 6.4 |
| Total time | 23.9 | 52.3 | 35.6 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




