Submitted:
19 July 2023
Posted:
20 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
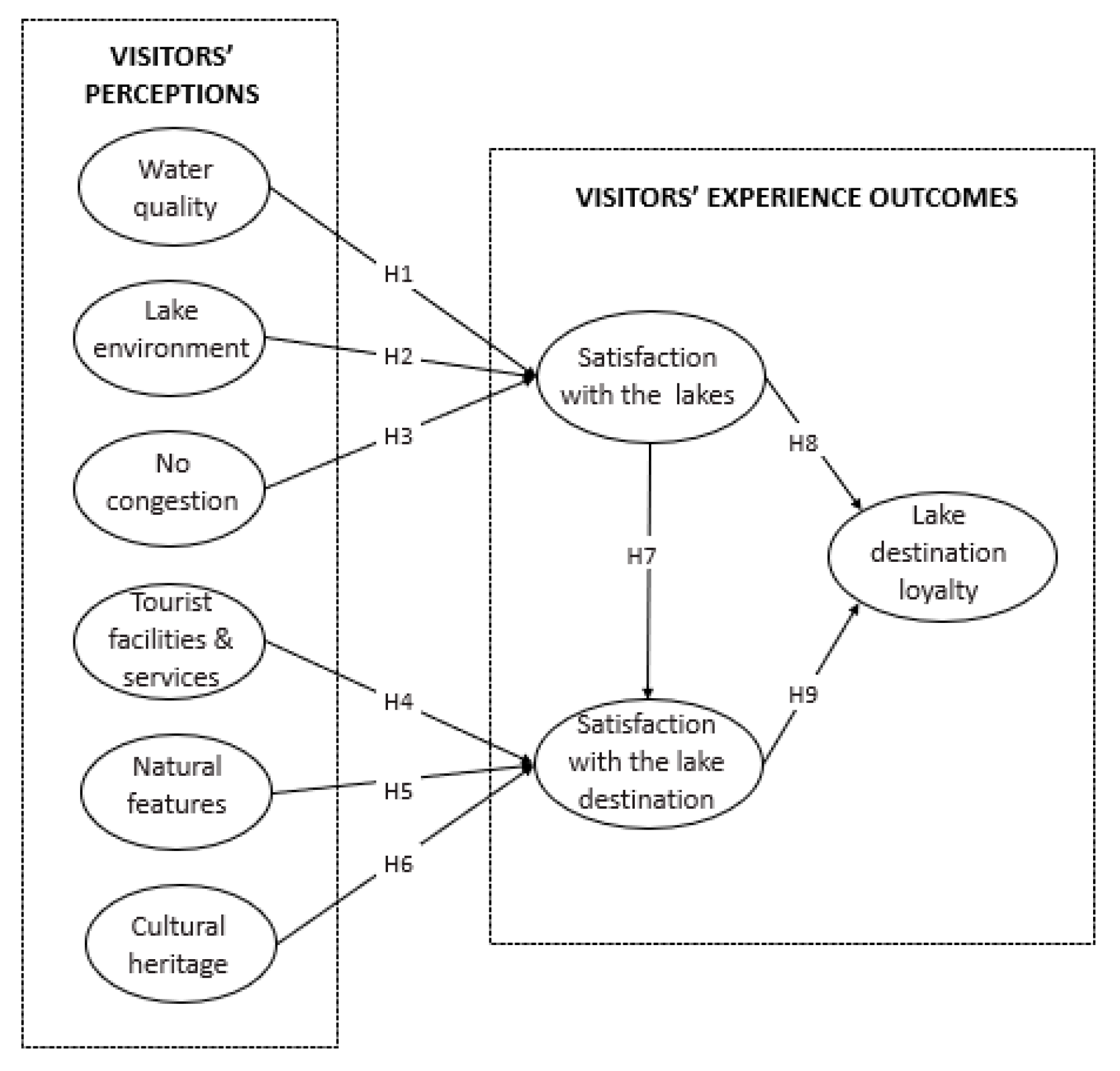
1. Introduction
2. The sustainability of lake destinations
3. Impacts of lake destination perceptions on satisfaction and loyalty
4. Materials and Methods
4.1. Context of the empirical study
4.2. Data collection
4.3. Data analysis
5. Discussion
5.1. Sample profile
5.2. Model assessment
5.2.1. Measurement model
5.2.2. Structural model
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- S. Obradović, V. Stojanović, S. Kovačić, T. Jovanovic, M. Pantelić, and M. Vujičić, “Assessment of residents’ attitudes toward sustainable tourism development - A case study of Bačko Podunavlje Biosphere Reserve, Serbia,” Journal of Outdoor Recreation and Tourism, vol. 35, p. 100384, Sep. 2021. [CrossRef]
- UNWTO, “Tourism in the green economy – Background report,” Madrid, 2012.
- United Nations Development Programme, “The 2030 Agenda for Sustainable Development,” 2015.
- D. Gössling, S., Hall, C. M., & Scott, Tourism and Water, 2nd ed. Bristol, Buffalo, Toronto: Channel View Publications.
- I. Potocka, “The lakescape in the eyes of a tourist,” Quaestiones Geographicae, vol. 32, no. 3, pp. 85–97, 2013. [CrossRef]
- C. Ryan, G. Huimin, and K. Chon, “Tourism to polluted lakes: Issues for tourists and the industry. an empirical analysis of four Chinese lakes,” Journal of Sustainable Tourism, vol. 18, no. 5, pp. 595–614, 2010. [CrossRef]
- T. Anja, In search of the sense of Finnish lakes - A geographical approach to lake tourism marketing, vol. 44, no. 5. 2015.
- A. Tuohino and K. Pitkänen, “The transformation of a neutral lake landscape into a meaningful experience-interpreting tourist photos,” Journal of Tourism and Cultural Change, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 77–93, 2004. [CrossRef]
- T. C. V. Publications. Cooper, C. (2006). Lakes as tourism destination resources. In C. M. Hall & T. Härkönen (Eds.), Lake tourism: An integrated approach to lacustrine tourism systems (pp. 27-42). Clevedon, Buffalo, “No Title,”.
- R. C. Stedman and R. B. Hammer, “Environmental perception in a rapidly growing, amenity-rich region: The effects of lakeshore development on perceived water quality in Vilas County, Wisconsin,” Soc Nat Resour, vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 137–151, 2006. [CrossRef]
- UNWTO, “World Tourism Day 27 September 2013. Tourism and Water: Protecting our Common Future,” 2013. 27 September.
- S. Gössling, C. Michael Hall, and D. Scott, Tourism and Water. Channel View Publications, 2015. [CrossRef]
- L. , B. Z. , P. C. , & T. A. David, “Lake tourism and global climate change: an integrative approach based on Finnish and Hungarian case-studies. ,” Carpathian Journal of Earth and Environmental Sciences, vol. 7, no. 1, 2012.
- R. Tandyrak, K. Parszuto, and J. Grochowska, “Water Quality of Lake Ełk as a Factor Connected with Tourism, Leisure and Recreation on an Urban Area,” Quaestiones Geographicae, vol. 35, no. 3, pp. 51–59, 2016. [CrossRef]
- M. Ramazanova, M. Bulai, A. Ursu, B. Deyá Tortella, and A. Kakabayev, “Effects of tourism development on surface area of main lakes of Shchuchinsk-Burabay resort area, Kazakhstan,” European Journal of Tourism Research, vol. 21, pp. 69–86, 2019. [CrossRef]
- C. M. and H. T. Hall, Lake tourism: an integrated approach to lacustrine tourism systems. Clevedon, UK: Channel View Publications, 2006.
- M. Castel-Branco and I. Soares Albergaria, “Los jardines de los lagos de las Azores como bien turístico: estudio por el método de las preferencias visuales,” methaodos revista de ciencias sociales, vol. 5, no. 1, May 2017. [CrossRef]
- L. J. Chen, J. S. Chen, and C. Basman, “Investigation on visitors’ perceptions of recreation impacts in Sun Moon Lake National Scenic Area in Taiwan,” Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, vol. 14, no. 3, pp. 241–253, 2009. [CrossRef]
- Y. Zhu, Z. Li, J. Li, and X. Xia, “Notice of Retraction: Water Pollution and Tourism Development - Case Study in Dongchang Lake in Shandong Province of China,” in 2011 5th International Conference on Bioinformatics and Biomedical Engineering, IEEE, May 2011, pp. 1–3. [CrossRef]
- Md. A. H. Bhuiyan, C. Siwar, and S. M. Ismail, “Sustainability Measurement for Ecotourism Destination in Malaysia: A Study on Lake Kenyir, Terengganu,” Soc Indic Res, vol. 128, no. 3, pp. 1029–1045, Sep. 2016. [CrossRef]
- K. Lőrincz, Z. Banász, and J. Csapó, “Customer Involvement in Sustainable Tourism Planning at Lake Balaton, Hungary—Analysis of the Consumer Preferences of the Active Cycling Tourists,” Sustainability, vol. 12, no. 12, p. 5174, Jun. 2020. [CrossRef]
- G. Mavrommati, M. M. Baustian, and E. A. Dreelin, “Coupling Socioeconomic and Lake Systems for Sustainability: A Conceptual Analysis Using Lake St. Clair Region as a Case Study,” Ambio, vol. 43, no. 3, pp. 275–287, Apr. 2014. [CrossRef]
- A. I. Rodrigues, A. Correia, M. Kozak, and A. Tuohino, “Lake-Destination Image Attributes: Content Analysis of Text and Pictures,” 2015, pp. 293–314. [CrossRef]
- E. B. Ogucha, G. K. Riungu, F. K. Kiama, and E. Mukolwe, “The influence of homestay facilities on tourist satisfaction in the Lake Victoria Kenya Tourism Circuit,” Journal of Ecotourism, vol. 14, no. 2–3, pp. 278–287, 2015. [CrossRef]
- M. L. Sun and Y. H. Lin, “The effects of motivation, background, attraction and loyalty in the 2010 international thousands swimming cross to Sun Moon Lake,” APBITM 2011 - Proceedings2011 IEEE International Summer Conference of Asia Pacific Business Innovation and Technology Management, pp. 19–23, 2011. [CrossRef]
- EUROSTAT, “Water and Tourism Pilot Study,” Luxemburg, 2009.
- M. C. Sudha, S. Ravichandran, and R. Sakthivadivel, “Water Bodies Protection Index for assessing the sustainability status of lakes under the influence of urbanization: A case study of south Chennai, India,” Environ Dev Sustain, vol. 15, no. 5, pp. 1157–1171, 2013. [CrossRef]
- S. Cole, “Tourism and water: from stakeholders to rights holders, and what tourism businesses need to do,” Journal of Sustainable Tourism, vol. 22, no. 1, pp. 89–106, 2014. [CrossRef]
- L. V. Lehmann, “The Relationship between tourism and water in dry land regions,” Proceedings of the Environmental Research Event 2009, Noosa, QLD, pp. 1–8, 2009, [Online]. Available: http://espace.library.uq.edu.au/view/UQ:179617.
- “Lee, S. W., & Xue, K. (2020). A model of destination loyalty: Integrating destination image and sustainable tourism. Asia Pacific Journal of Tourism Research, 25(4), 393-408. [CrossRef]
- W. R. Lin, “Structural model of hassles experienced at travel destinations,” Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, vol. 9, pp. 97–103, Sep. 2018. [CrossRef]
- R. B. Ditton and T. L. Goodale, “Water quality perception and the recreational uses of Green Bay, Lake Michigan,” Water Resour Res, vol. 9, no. 3, pp. 569–579, Jun. 1973. [CrossRef]
- R. C. Stedman et al., “Perceived environmental quality and place attachment in North American and European temperate lake districts,” Lake Reserv Manag, vol. 23, no. 4, pp. 330–344, 2007. [CrossRef]
- J. Priskin, “Implications of eutrophication for lake tourism in Québec,” Revue de Recherche en Tourisme, pp. 59–61, 2008.
- G. Schernewski, T. Neumann, V. Podsetchine, and H. Siegel, “Spatial impact of the Oder river plume on water quality along the south-western Baltic coast,” Int J Hyg Environ Health, vol. 204, no. 2–3, pp. 143–155, Jan. 2001. [CrossRef]
- L. Puczkó and T. Rátz, “Tourist and Resident Perceptions of the Physical Impacts of Tourism at Lake Balaton, Hungary: Issues for Sustainable Tourism Management,” Journal of Sustainable Tourism, vol. 8, no. 6, pp. 458–478, 2000. [CrossRef]
- A.A. Prasetyowati, N. Harahab, and S. Soemarno, “Tourist Perceptions On Supporting Infrastructure Facilities And Climate-Based Visiting Time Of Ngebel Lake, Ponorogo,” Journal of Indonesian Tourism and Development Studies, vol. 2, no. 2, pp. 47–54, 2014. [CrossRef]
- C. G. Q. Chi and H. Qu, “Examining the structural relationships of destination image, tourist satisfaction and destination loyalty: An integrated approach,” Tour Manag, vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 624–636, Aug. 2008. [CrossRef]
- N. P. Jin, S. Lee, and H. Lee, “The Effect of Experience Quality on Perceived Value, Satisfaction, Image and Behavioral Intention of Water Park Patrons: New versus Repeat Visitors,” International Journal of Tourism Research, vol. 17, no. 1, pp. 82–95, Jan. 2015. [CrossRef]
- J. Roper, E. M. Collins, and J. de Jong, “Lake Taupo: A multi-sector collaborative partnership towards sustainable development,” J Public Aff, vol. 15, no. 2, pp. 143–152, 2015. [CrossRef]
- A. I. Rodrigues, A. Correia, and M. Kozak, “Assessing lake-destination image: insights from the industry side,” International Journal of Culture, Tourism and Hospitality Research, vol. 11, no. 1, pp. 5–17, Mar. 2017. [CrossRef]
- Y. Yoon and M. Uysal, “An examination of the effects of motivation and satisfaction on destination loyalty: a structural model,” Tour Manag, vol. 26, no. 1, pp. 45–56, Feb. 2005. [CrossRef]
- C. G.-Q. Chi and H. Qu, “Examining the structural relationships of destination image, tourist satisfaction and destination loyalty: An integrated approach,” Tour Manag, vol. 29, no. 4, pp. 624–636, Aug. 2008. [CrossRef]
- M. Kozak, “Repeaters’ behavior at two distinct destinations,” Ann Tour Res, vol. 28, no. 3, pp. 784–807, Jan. 2001. [CrossRef]
- C. Y. Wang and M. K. Hsu, “The relationships of destination image, satisfaction, and behavioral intentions: An integrated model,” Journal of Travel and Tourism Marketing, vol. 27, no. 8, pp. 829–843, 2010. [CrossRef]
- W.-R. Lin, “Structural model of hassles experienced at travel destinations,” Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, vol. 9, pp. 97–103, Sep. 2018. [CrossRef]
- M. Ramazanova, B. D. Tortella, and A. Kakabayev, “Tourism development in Kazakhstan,” Journal of Tourism and Development, vol. 2019, no. 31, pp. 35–45, 2019.
- Sevkaznedra, “Results of hydrogeological work upon the object Compilation of modern hydrogeological map of the Shchuchinsk-Burabay resort area in Akmola region,” Kostanay, Kazakhstan, 2014.
- Kazhydromet, “Environmental monitoring bulletin,” 2018.
- Y.-S. Yoon, J.-S. Lee, and C.-K. Lee, “Measuring festival quality and value affecting visitors’ satisfaction and loyalty using a structural approach,” Int J Hosp Manag, vol. 29, no. 2, pp. 335–342, Jun. 2010. [CrossRef]
- Y. K. Lee, C. K. Lee, S. K. Lee, and B. J. Babin, “Festivalscapes and patrons’ emotions, satisfaction, and loyalty,” J Bus Res, vol. 61, no. 1, pp. 56–64, Jan. 2008. [CrossRef]
- G. Cepeda Carrión, J. Henseler, C. M. Ringle, and J. L. Roldán, “Prediction-oriented modeling in business research by means of PLS path modeling: Introduction to a JBR special section,” J Bus Res, vol. 69, no. 10, pp. 4545–4551, Oct. 2016. [CrossRef]
- J. F. , R. C. , & S. M. Hair, A Primer on Partial Least Squares Structural Equation Modeling (PLS-SEM).. Thousand Oaks: SAGE Publications., 2014.
- G. Shmueli, S. Ray, J. M. Velasquez Estrada, and S. B. Chatla, “The elephant in the room: Predictive performance of PLS models,” J Bus Res, vol. 69, no. 10, pp. 4552–4564, Oct. 2016. [CrossRef]
- C. M. Ringle, S. Wende, and J.-M. Becker, Smartpls 3. Hamburg. Germany, 2014.
- C. Garcia and J. Servera, “Impacts of tourism development on water demand and beach degradation on the island of mallorca (spain),” Geografiska Annaler: Series A, Physical Geography, vol. 85, no. 3–4, pp. 287–300, Oct. 2003. [CrossRef]
- Xuan Fuhua, “Notice of Retraction: Analysis on sustainable development of lake tourism in Heilongjiang province,” in 2010 IEEE International Conference on Advanced Management Science(ICAMS 2010), IEEE, Jul. 2010, pp. 102–104. [CrossRef]
- W.-R. Lin, “Structural model of hassles experienced at travel destinations,” Journal of Destination Marketing & Management, vol. 9, pp. 97–103, Sep. 2018. [CrossRef]
- C. F. Chen and D. C. Tsai, “How destination image and evaluative factors affect behavioral intentions?,” Tour Manag, vol. 28, no. 4, pp. 1115–1122, Aug. 2007. [CrossRef]
- J. J. Markovic, D. J. Pavic, M. M. Mészaros, and M. D. Petrovic, “Measuring the Quality of the Lakeside Tourist Destinations: Case Study of Lake Palić and Lake Srebrno (Serbia),” Journal of Environmental and Tourism Analyses, vol. 3, no. 1, pp. 63–81, 2015, [Online]. Available: http://search.proquest.com.proxy.unimib.it/docview/1737432328?accountid=16562.
- G. Moser, “Water quality perception, a dynamic evaluation,” J Environ Psychol, vol. 4, no. 3, pp. 201–210, Sep. 1984. [CrossRef]
- B. Jenkins, “Sustainability analysis of the management approach for six New Zealand lakes,” Lake Reserv Manag, vol. 32, no. 2, pp. 101–115, 2016. [CrossRef]
| Constructs / indicators | Indicator loading | t-value a | CR | AVE | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Water quality | 0.941 | 0.639 | |||||
| Lakes have a color that suggests there is no pollution | 0.815 | 29.068 | |||||
| Lakes have very clear water | 0.718 | 19.053 | |||||
| Lakes do not have a bad odor | 0.851 | 44.171 | |||||
| There is no animal waste | 0.742 | 30.082 | |||||
| There are not plenty of algae/reeds | 0.783 | 31.710 | |||||
| There are no sediments on the surface of the lakes | 0.837 | 34.322 | |||||
| There are no sediments on the bottom of the lakes | 0.862 | 50.902 | |||||
| Water is not polluted | 0.845 | 42.087 | |||||
| Lake’s water level is not decreasing | 0.724 | 22.020 | |||||
| Lake environment | 0.877 | 0.543 | |||||
| Lakes are accessible | 0.720 | 20.686 | |||||
| Lakes are favorable for water-based activities (swimming, boating, fishing) | 0.774 | 29.874 | |||||
| Lakes have many species of wildlife and plants | 0.771 | 26.514 | |||||
| Lakes are very peaceful | 0.700 | 19.707 | |||||
| Lake shore has enough tourism facilities | 0.787 | 33.700 | |||||
| Lakes are very scenic | 0.660 | 15.917 | |||||
| No congestion | 0.913 | 0.840 | |||||
| There is no conflict between users | 0,899 | 50.397 | |||||
| Lakes are not being harmed by overuse | 0.934 | 111.924 | |||||
| Tourist facilities and services | 0.958 | 0.657 | |||||
| High quality of balneology services | 0.723 | 21.258 | |||||
| Clean and tidy environment | 0.849 | 55.256 | |||||
| Cleanliness of beaches | 0.799 | 36.338 | |||||
| Diverse shop facilities | 0.848 | 50.639 | |||||
| Easy access to tourist information | 0.830 | 33.570 | |||||
| Good local transport services | 0.873 | 55.649 | |||||
| Good quality accommodation facilities | 0.835 | 42.657 | |||||
| Good quality restaurants and cafes | 0.860 | 58.702 | |||||
| High quality of wellbeing services | 0.782 | 37.915 | |||||
| Reasonable price for accommodation | 0.734 | 18.723 | |||||
| Reasonable price for attractions and activities | 0.759 | 23.992 | |||||
| Safe and secure environment | 0.820 | 42.530 | |||||
| Natural features | 0.868 | 0.689 | |||||
| Attractive lakes | 0.909 | 66.824 | |||||
| Scenic mountains and valleys | 0.814 | 35.685 | |||||
| Favourable and pleasant climate | 0.760 | 22.624 | |||||
| Cultural heritage | 0.889 | 0.728 | |||||
| Friendly local people | 0.814 | 28.257 | |||||
| The range of cultural events, shows and exhibitions | 0.885 | 46.841 | |||||
| Rich historical and cultural heritage | 0.860 | 51.409 | |||||
| Constructs / indicators | Indicator loading | t-value a | CR | AVE | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Satisfaction with the lakes | 0.972 | 0.946 | |||
| I am satisfied with the decision to visit these lakes | 0.974 | 207.041 | |||
| Overall, I am very pleased with the lakes | 0.972 | 168.940 | |||
| Satisfaction with the lake destination | 0.966 | 0.934 | |||
| I am satisfied with the decision to visit this destination | 0.966 | 182.621 | |||
| Overall, I am very pleased with the destination | 0.967 | 183.657 | |||
| Lake destination loyalty | 0.950 | 0.904 | |||
| I will recommend this destination to other people | 0.957 | 146.067 | |||
| I will do a trip to this destination next year | 0.944 | 70.064 | |||
| Constructs | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 1. Water quality | 0.799 | ||||||||
| 2. Lake environment | 0.501 | 0.737 | |||||||
| 3. No congestion | 0.678 | 0.445 | 0.917 | ||||||
| 4. Tourist facilities and services | 0.609 | 0.498 | 0.407 | 0.811 | |||||
| 5. Natural features | 0.420 | 0.623 | 0.368 | 0.615 | 0.830 | ||||
| 6. Cultural heritage | 0.404 | 0.480 | 0.276 | 0.740 | 0.577 | 0.853 | |||
| 7. Satisfaction with the lakes | 0.663 | 0.551 | 0.585 | 0.419 | 0.427 | 0.298 | 0.973 | ||
| 8. Satisfaction with the lake destination | 0.486 | 0.591 | 0.463 | 0.657 | 0.700 | 0.622 | 0.548 | 0.967 | |
| 9. Lake destination loyalty | 0.405 | 0.535 | 0.422 | 0.553 | 0.582 | 0.568 | 0.504 | 0.828 | 0.951 |
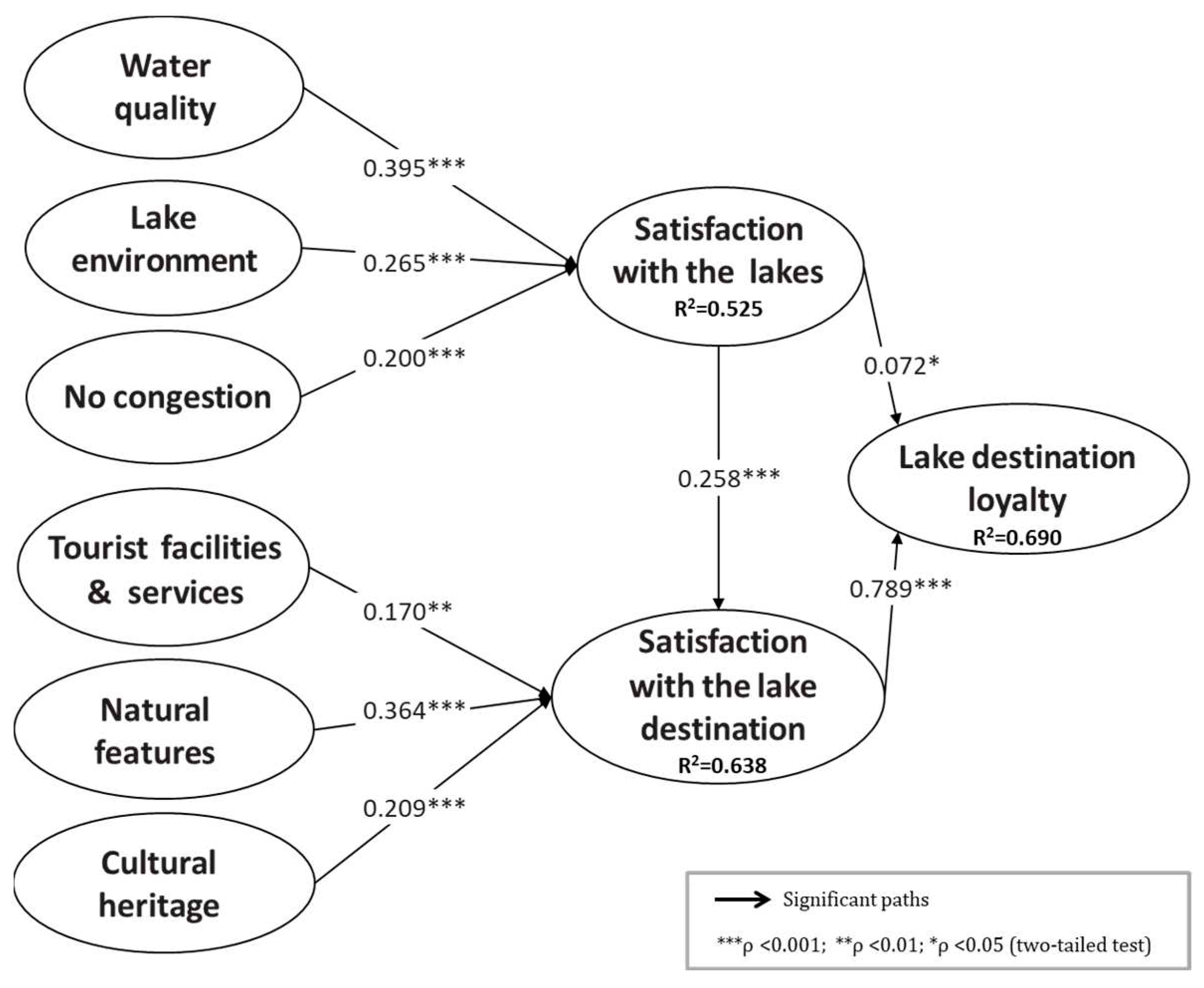
| Hypothesis | Path coefficient | t-value b | p-value | Supported |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| H1: Water quality –> Satisfaction with the lakes | 0.395 | 7.714 | 0.000 | Yes |
| H2: Lake environment –> Satisfaction with the lakes | 0.265 | 5.331 | 0.000 | Yes |
| H3: No congestion –> Satisfaction with the lakes | 0.200 | 3.504 | 0.000 | Yes |
| H4: Tourist facilities and services –> Satisfaction with the lake destination | 0.170 | 2.630 | 0.009 | Yes |
| H5: Natural features –> Satisfaction with the lake destination | 0.364 | 6.651 | 0.000 | Yes |
| H6: Cultural heritage –> Satisfaction with the lake destination | 0.209 | 3.320 | 0.001 | Yes |
| H7: Satisfaction with the lakes –> Satisfaction with the lake destination | 0.258 | 6.795 | 0.000 | Yes |
| H8: Satisfaction with the lakes –> Lake destination loyalty | 0.072 | 2.075 | 0.038 | Yes |
| H9: Satisfaction with the lake destination –> Lake destination loyalty | 0.789 | 27.283 | 0.000 | Yes |
| Path | Path coefficient | t-value | p-value |
|---|---|---|---|
| Water quality –> Satisfaction with the lake destination | 0.102 | 5.721 | 0.000 |
| Water quality –> Lake destination loyalty | 0.109 | 5.502 | 0.000 |
| Lake environment –> Satisfaction with the lake destination | 0.068 | 4.092 | 0.000 |
| Lake environment –> Lake destination loyalty | 0.073 | 3.936 | 0.000 |
| No congestion–> Satisfaction with the lake destination | 0.052 | 2.884 | 0.004 |
| No congestion–> Lake destination loyalty | 0.055 | 2.895 | 0.004 |
| Tourist facilities and services –> Lake destination loyalty | 0.134 | 2.596 | 0.009 |
| Natural features –> Lake destination loyalty | 0.288 | 6,399 | 0.000 |
| Cultural heritage –> Lake destination loyalty | 0.165 | 3.294 | 0.001 |
| Satisfaction with the lake–> Lake destination loyalty | 0.204 | 6.516 | 0.000 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





