Submitted:
18 July 2023
Posted:
20 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Basic Theory of Fractional Calculus
2.1. Fractional Calculus Theory
- Grümwald-Letnikov of fractional calculus is defined as follows,
- The definition of Riemann-Liouville for fractional order integration and Riemann Liouville for fractional order differentiation are as follows,
- Caputo of fractional calculus is defined as follows,
2.2. Amplitude Frequency Characteristics of Fractional Calculus Operators
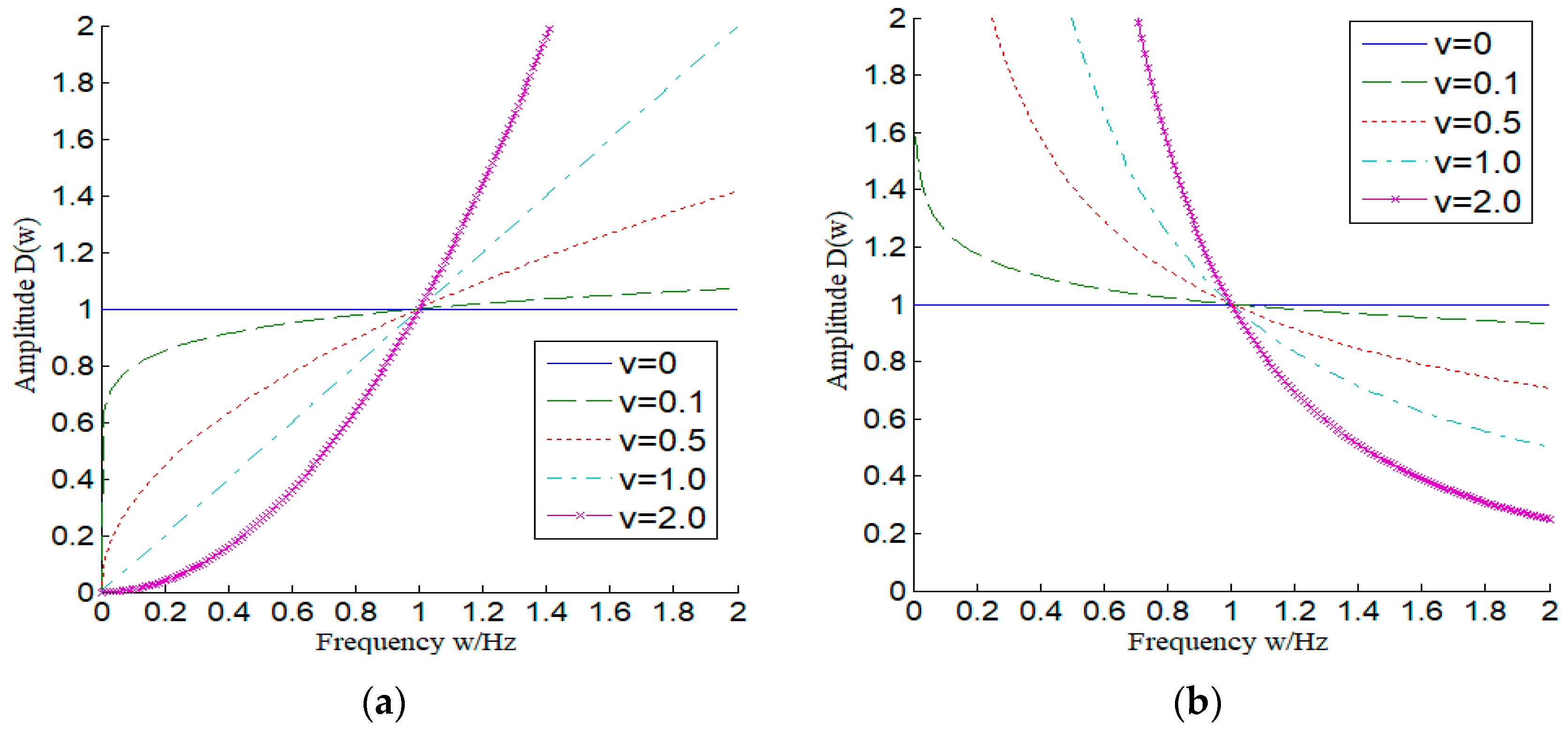
2.2.1. Fractional Order Differential Operator
2.2.2. Fractional Order Integral Operator
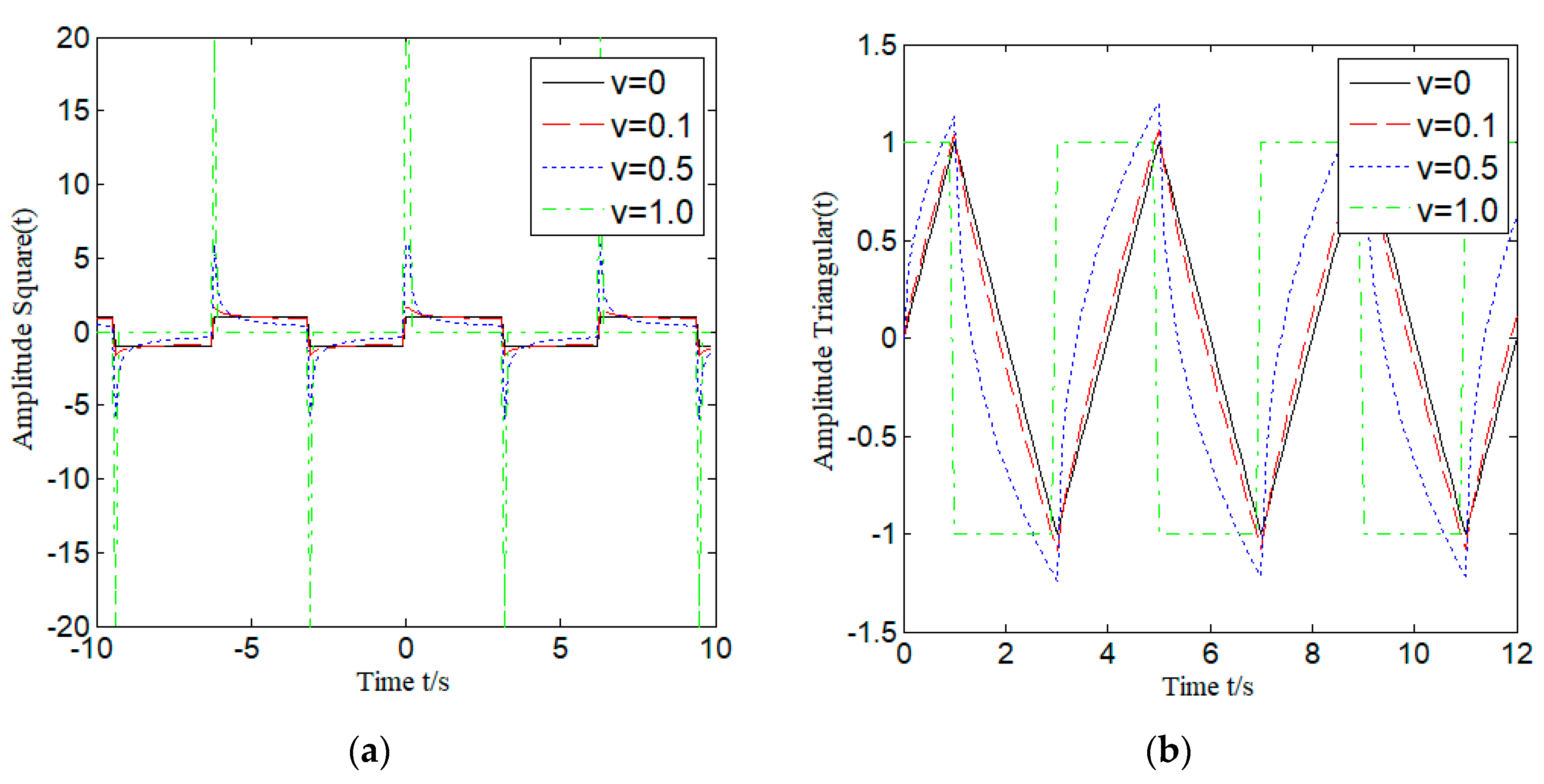
2.3. Fractional Order Calculus Processing and Analysis of Common Signals
3. Research on the Application of Fractional Differential in Image Enhancement
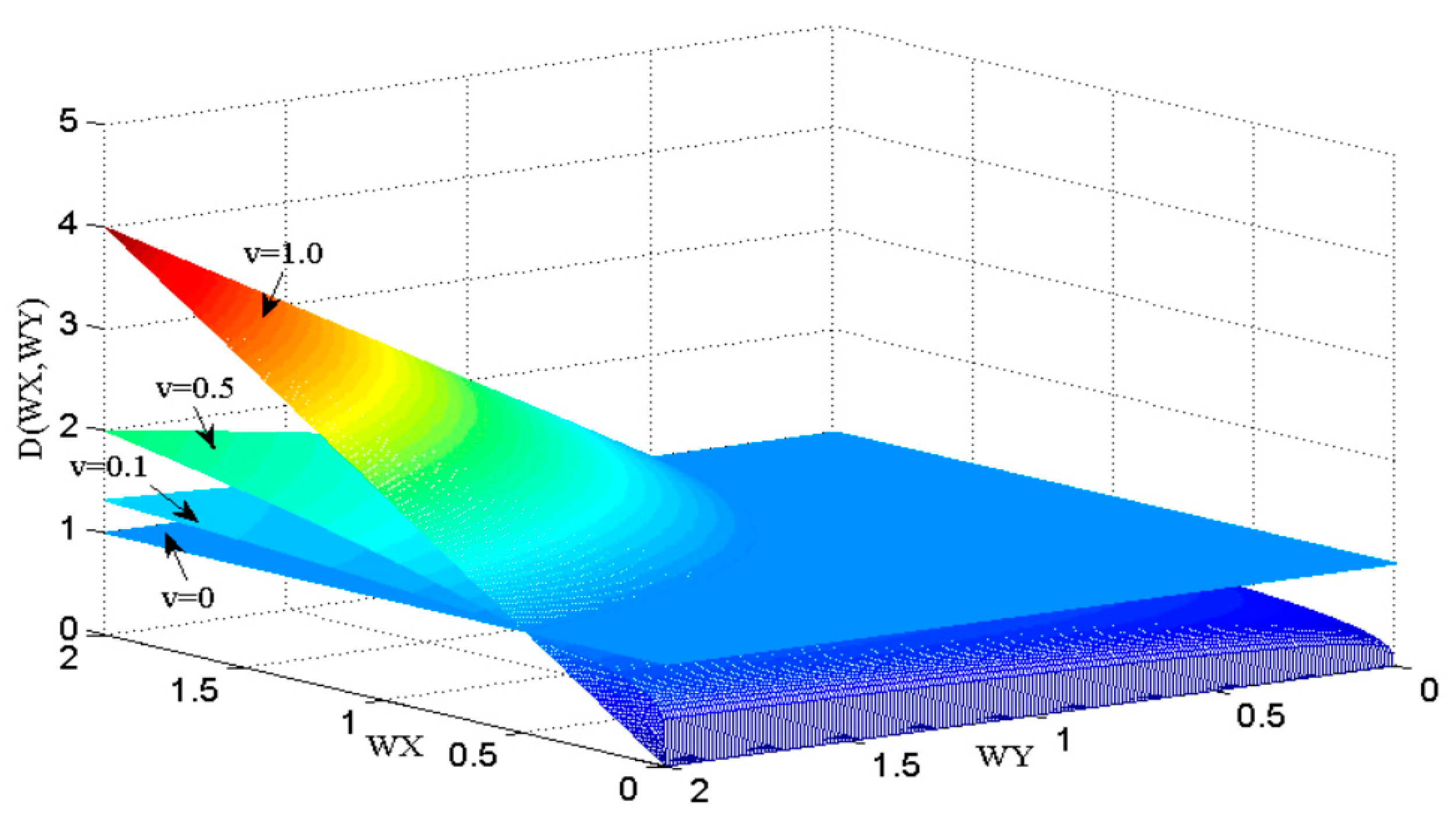
3.1. Amplitude Frequency Characteristics of Fractional Order Differential Image Enhancement Operators
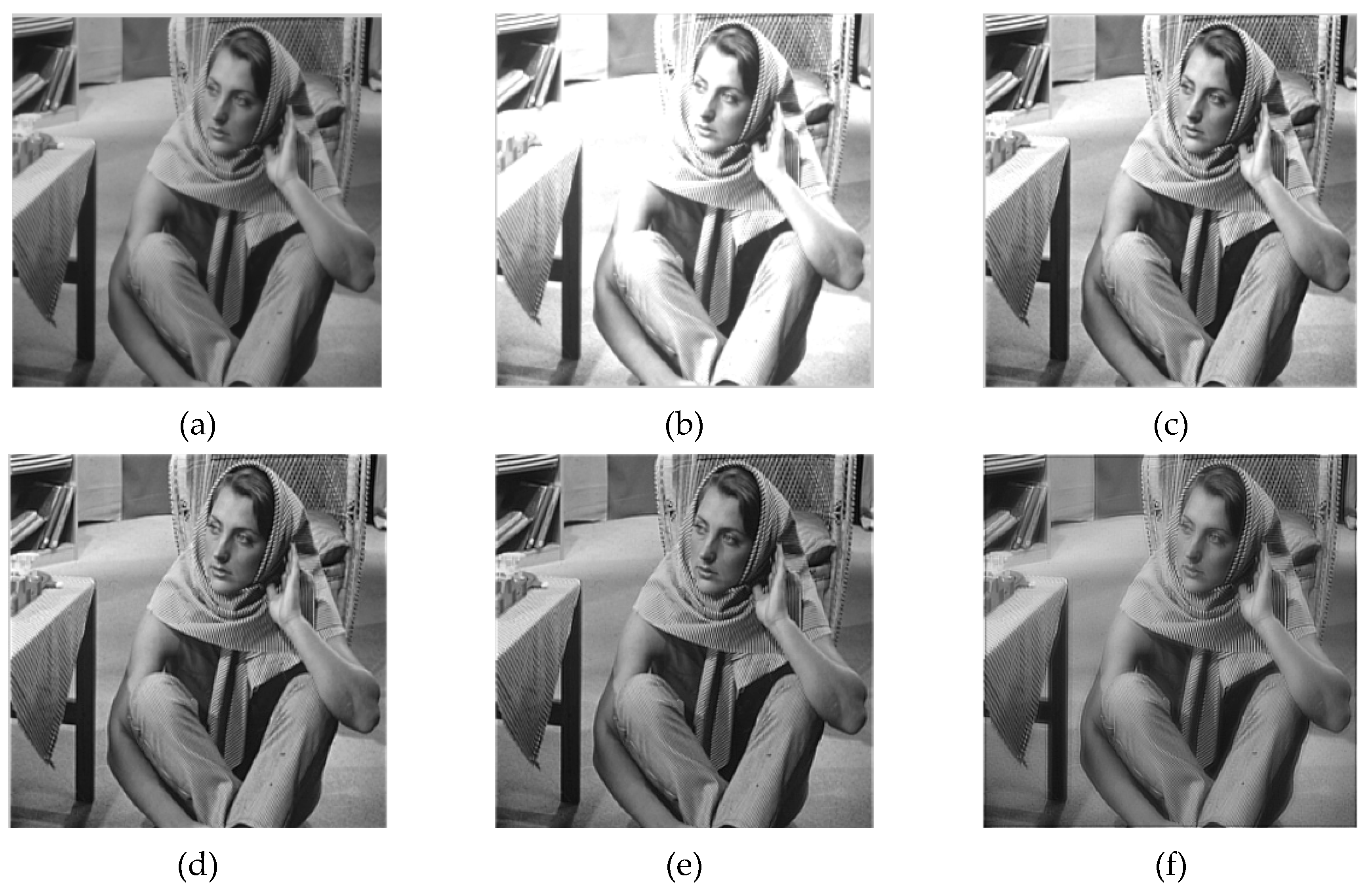
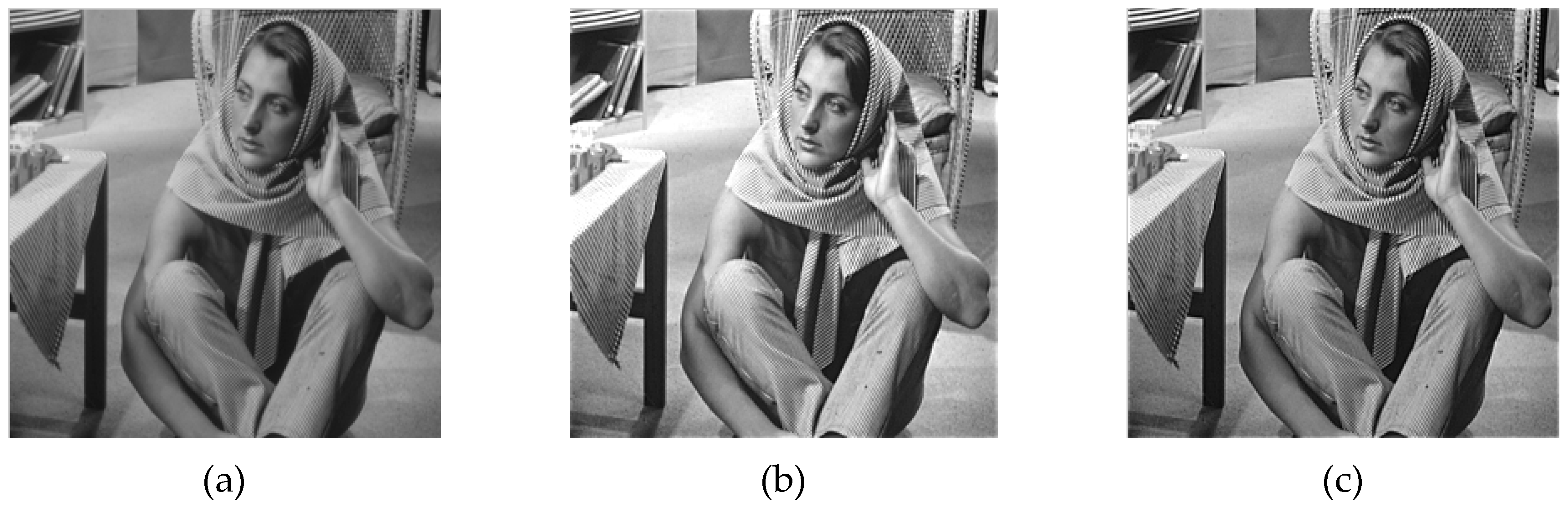
3.2. Image Enhancement Experiment and Analysis of Fractional Differential Operator
4. Research on the Application of Fractional Integral in Image Denoising
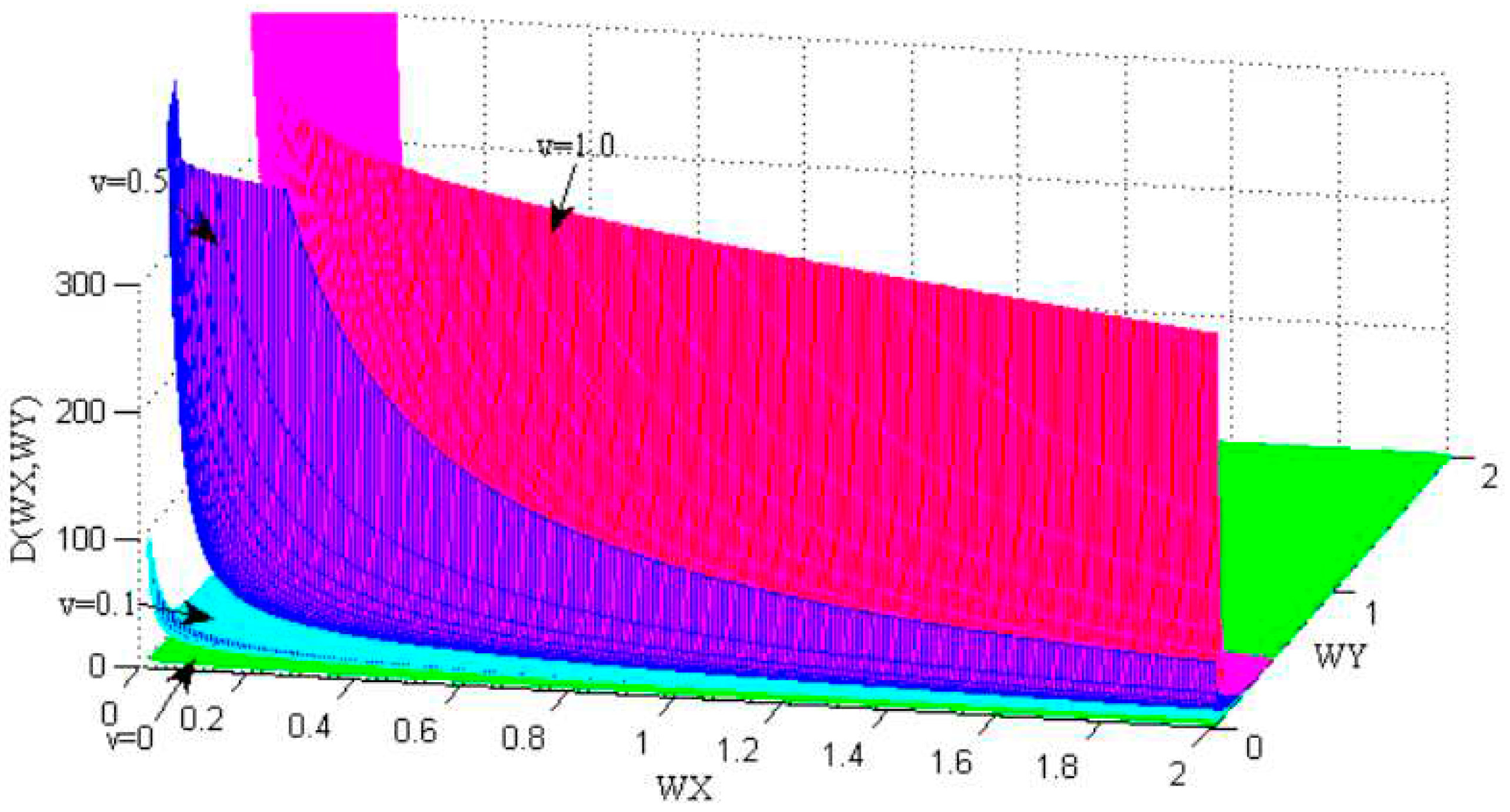
4.1. The Amplitude Frequency Characteristics of Fractional Order Integral Operator Image Denoising Operator
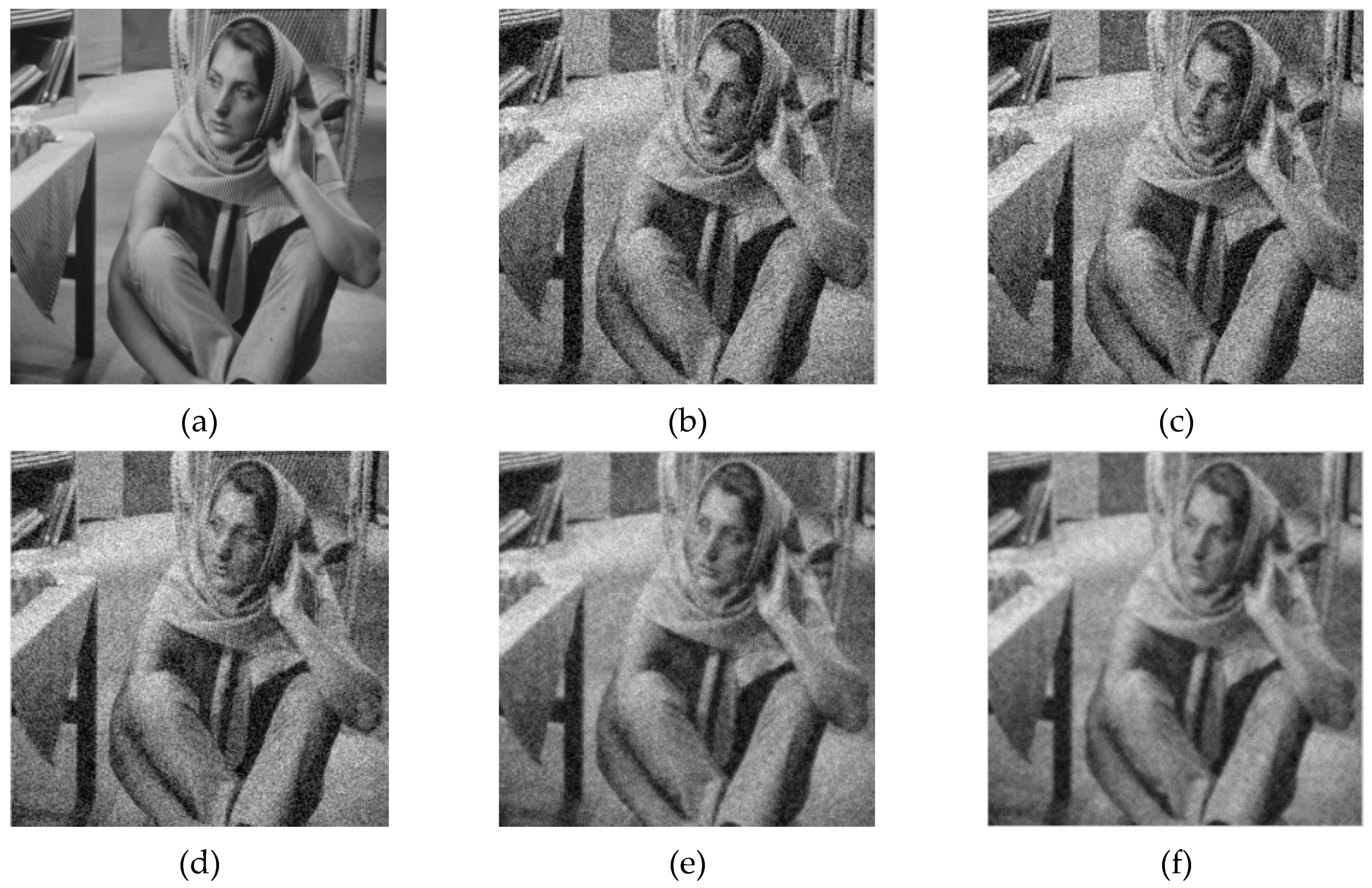
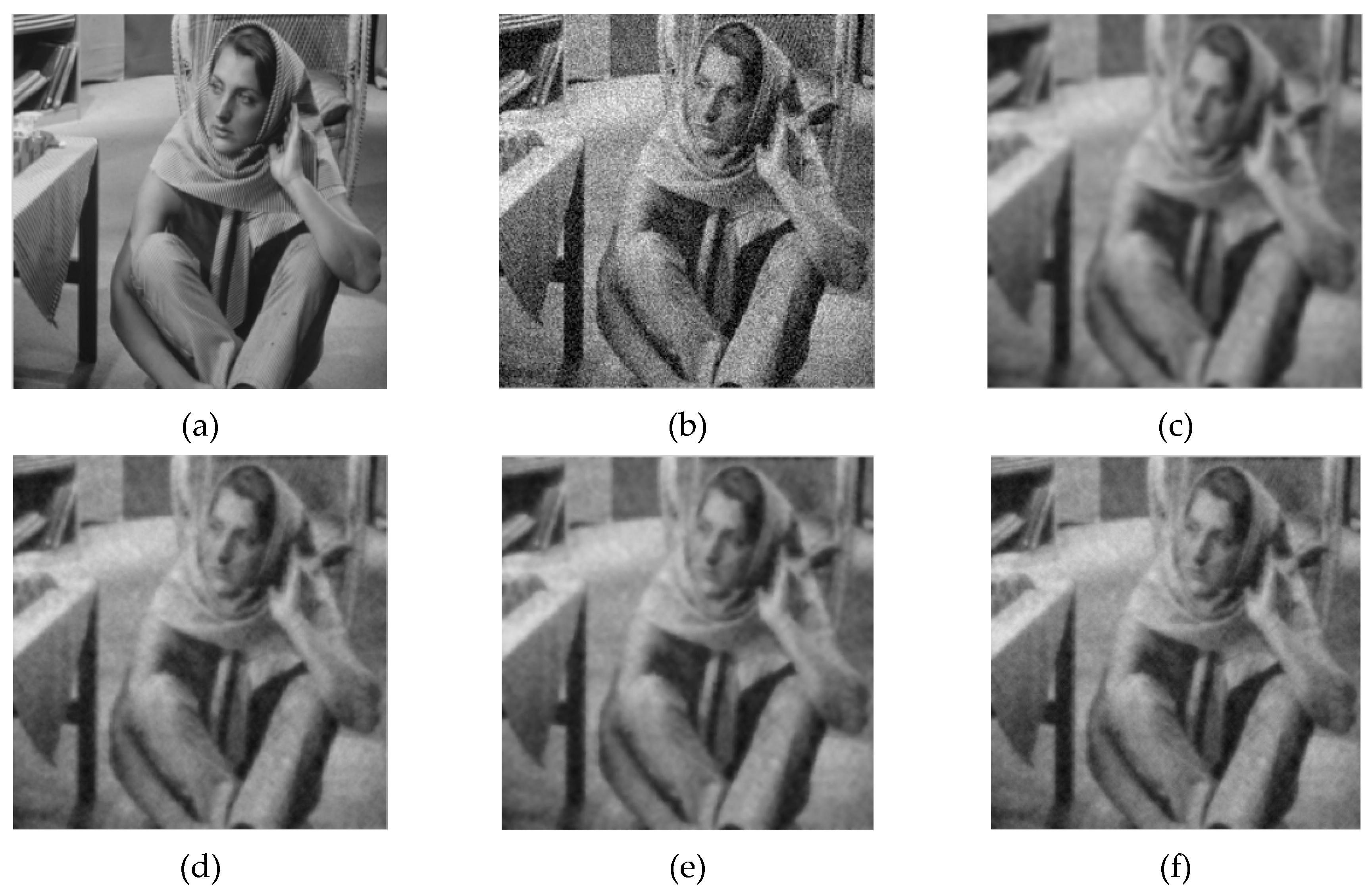
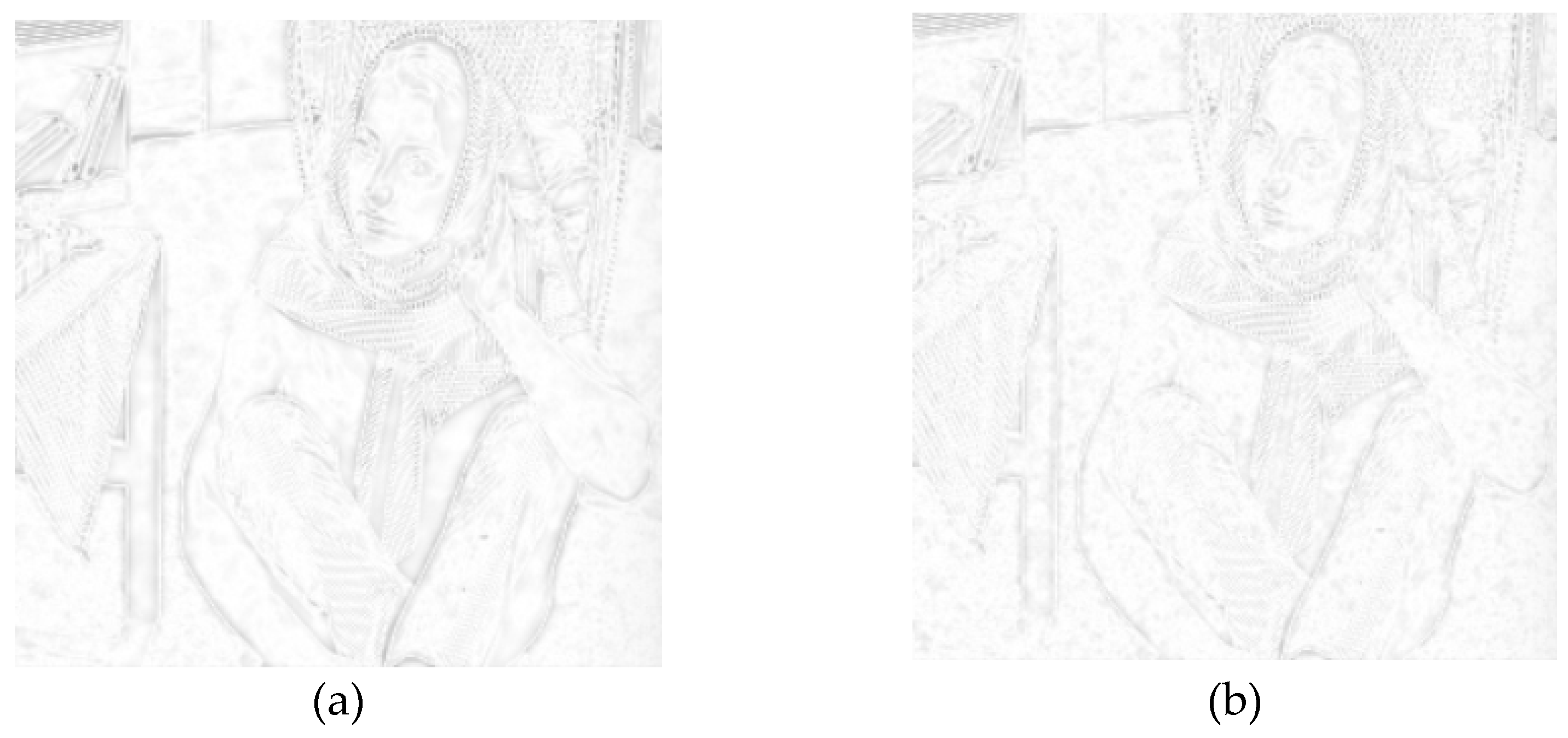
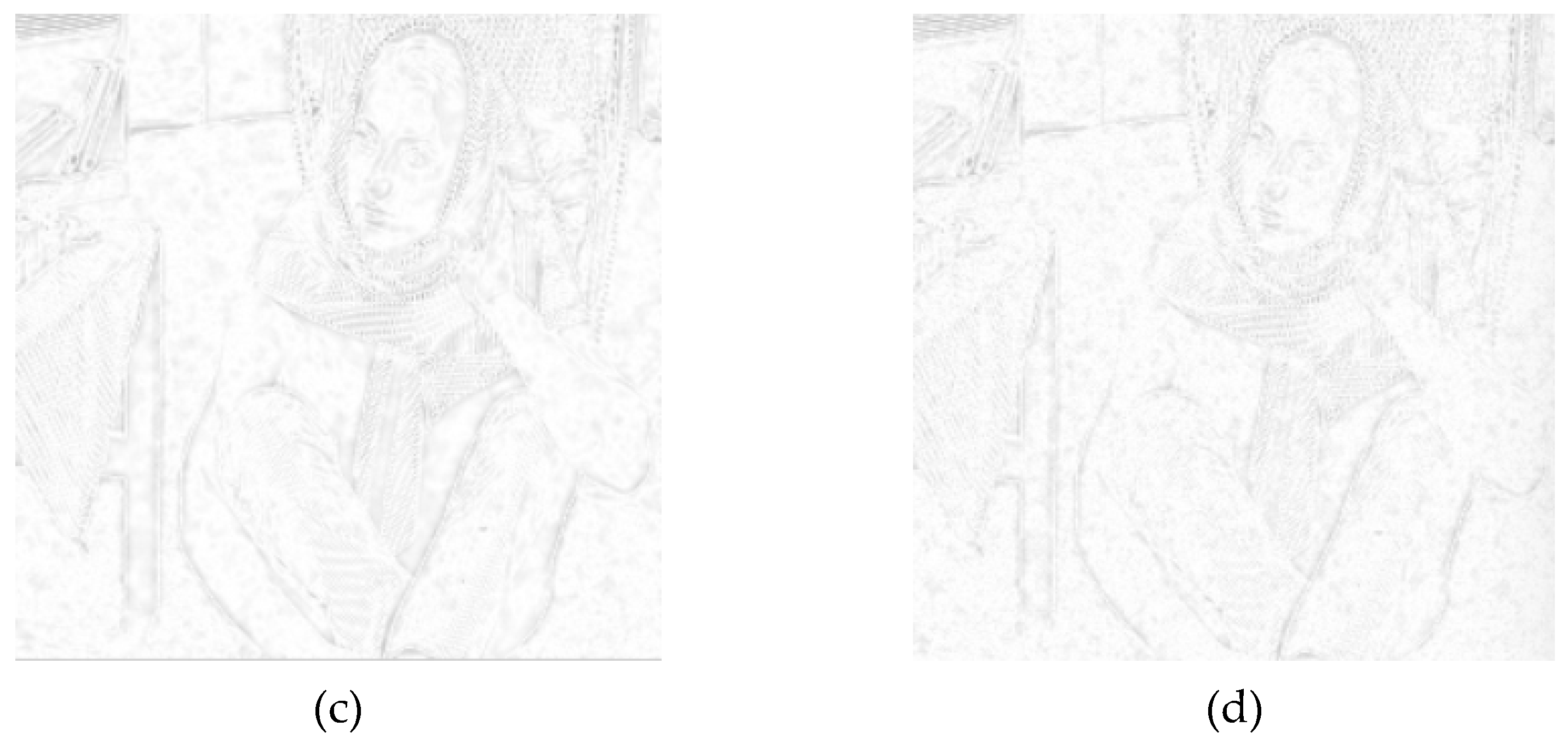
4.2. Experiment and Analysis of Fractional Order Integral Operator for Image Denoising
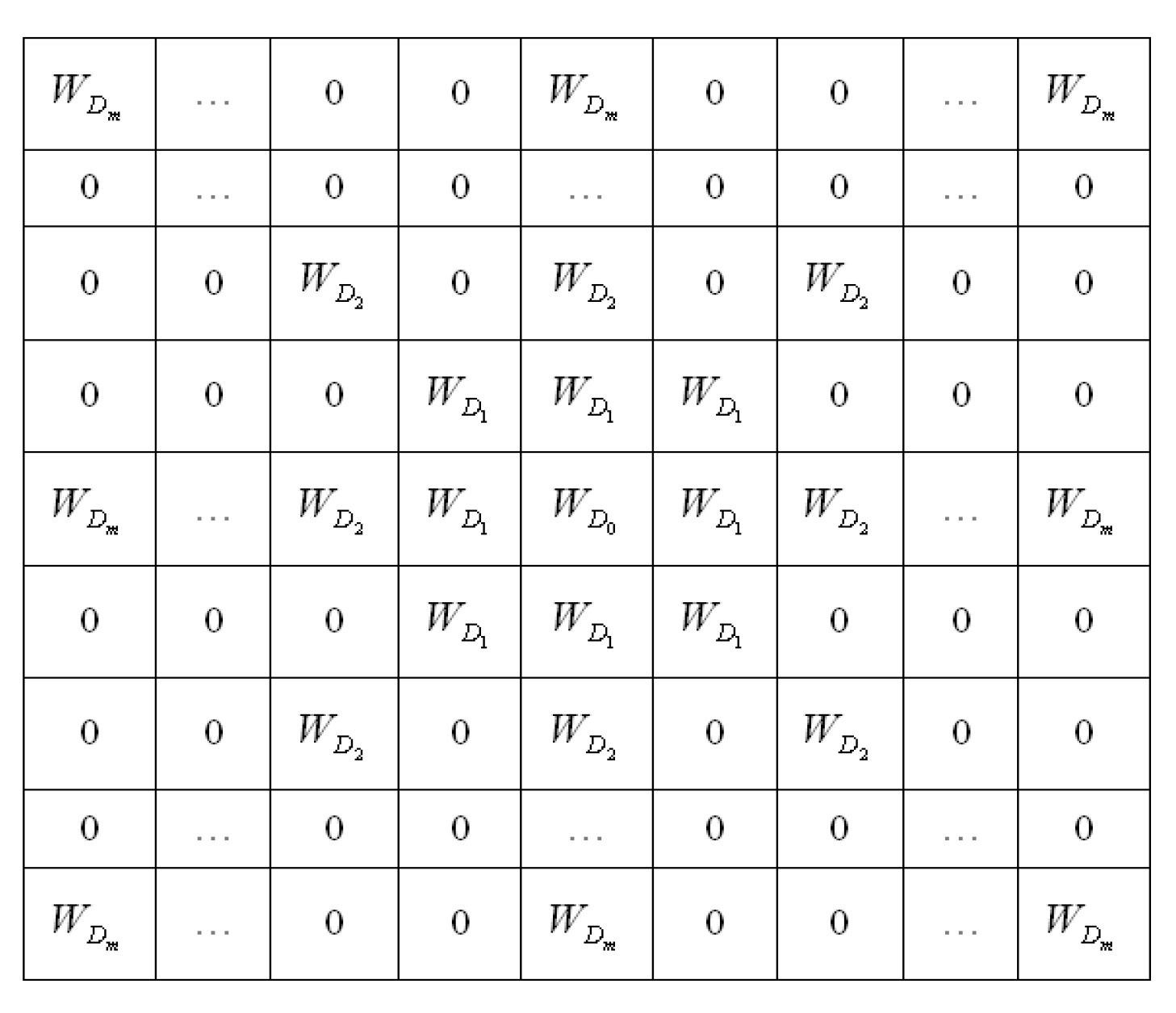
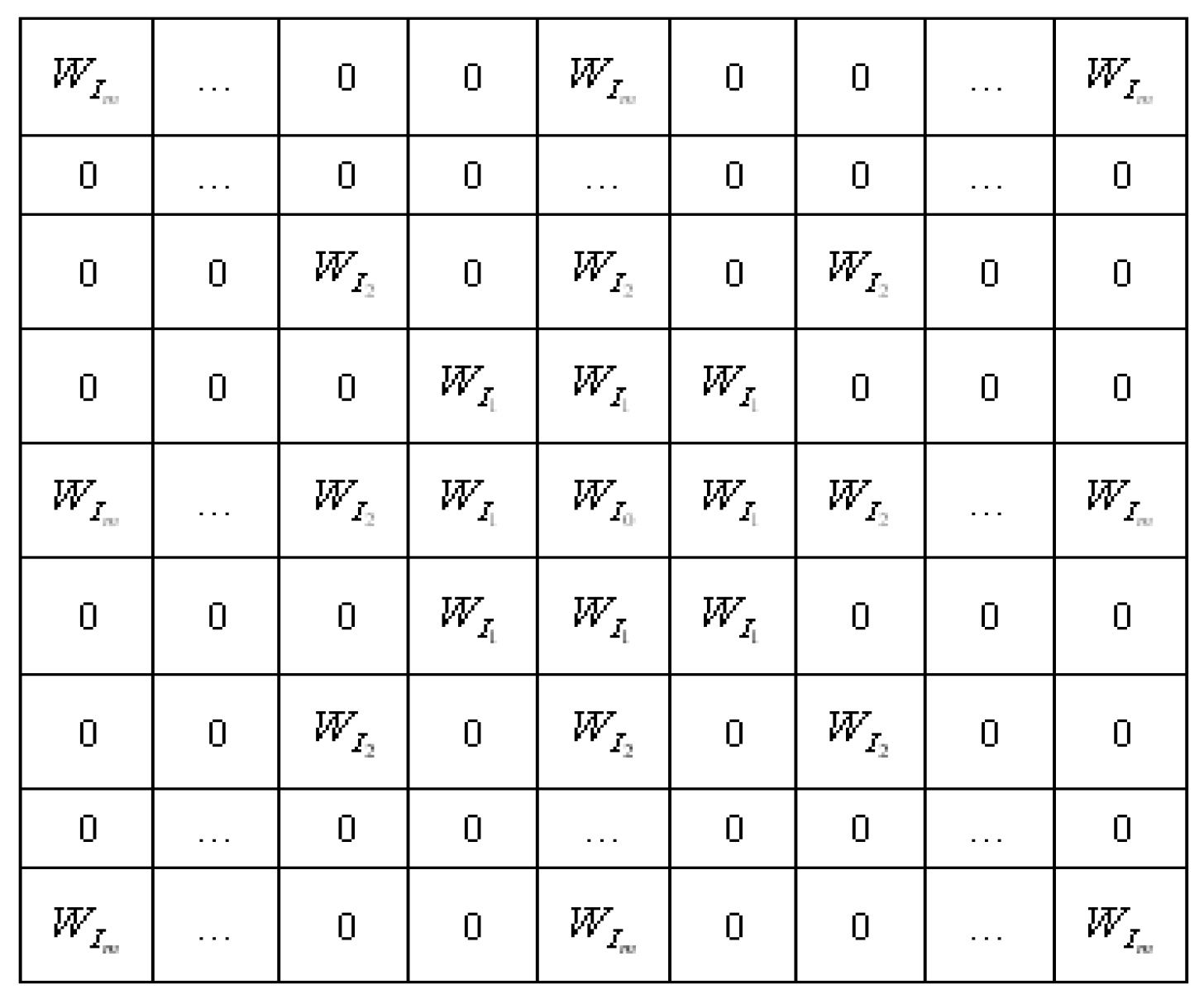
4.2.1. Construction of Fractional Order Integral Operators
4.2.2. Evaluation Criterion
- Average Gradient (AG)
- Edge Preservation Index (EPI)
- Signal-Noise Ratio(SNR)
4.2.3. Experimental Results and Comparative Analysis
5. Conclusions
References
- K. B. Ordham; J. Spanier. The Fractional Calculus, Academic Press, New York, NY, USA, 1974.
- K. S. Miller; B. Ross. An Introduction to the Fractional Calculus and Fractional Differential Equations, John Willey, New York, NY, USA, 1993.
- Petras, I. Fractional derivatives, fractional integrals, and fractional differential equations in Matlab, in ‘Engineering education and research using MATLAB’ vol. 10 (In-TechOpen, London, 2011), pp. 239–264.
- Mandelbrot; B.B.; van Ness; J.W.: ‘Factional Brownian motion, fractional noises and applications’, Geophys. J. R. Astron. SIAM Rev., 1968,10, (4), pp.422–437.
- Manderlbrot; B.B.; Wallis; J.R. Computer experiments with fractional Gaussian noises. Water Resour. Res., 1969, 5, (1), pp. 228–267.
- Huang Guo; XuLi; Pu Yi-fei.Summary of research on image processing using fractional calculus J. Application Research of Com- puters, 2012,29(02):414-420+426.
- Yi-Fei Pu, Bo Yu, Qiu-Yan He, and Xiao Yuan. Fracmemristor Oscillator: Fractional-Order Memristive Chaotic Circuit. IEEE Transactions on Circuits and Systems I: Regular Papers, vol. 69, no. 12, pp. 5219 – 5232, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Yi-Fei Pu, Bo Yu, Qiu-Yan He, and Xiao Yuan. “Fractional-Order Memristive Neural Synaptic Weighting Achieved by Pulse-Based Fracmemristor Bridge Circuit,” Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, vol. 22, no. 6, pp. 862-876, 2021. [CrossRef]
- Qiu-Yan He;Yi-Fei Pu ; Bo Yu;Xiao Yuan.Electrical Characteristics of Quadratic Chain Scaling Fractional-Order Memristor IEEE TRANSACTIONS ON CIRCUITS AND SYSTEMS—II: EXPRESS BRIEFS, VOL. 69, NO. 11, NOVEMBER 2022.
- Yi-Fei Pu; Patrick SIARRY;Wu-Yang ZHU et al. Fractional-Order Ant Colony Algorithm: A Fractional Long Term Memory Based Cooperative Learning Approach. Swarm and Evolutionary Computation, vol. 69, Article ID 101014, 18 pages, 2022. [CrossRef]
- Hq A;Xuan L A ;Zs A . Neural network method for fractional-order partial differential equations.J. Neurocomputing, 2020, 414:225-237.
- Yi-Fei Pu, Zhang Yi, and Ji-Liu Zhou. “Fractional Hopfield Neural Networks: Fractional Dynamic Associative Recurrent Neural Networks,” IEEE Transactions on Neural Networks and Learning Systems, vol. 28, no. 10, pp. 2319-2333, 2017. [CrossRef]
- Dong Y, Liao W, Wu M, et al. Convergence analysis of Riemann-Liouville fractional neural network[J]. Mathematical Methods in the Applied Sciences, 2022(10):45.
- Li X; Zhan Y; Tong S. Adaptive neural network decentralized fault-tolerant control for nonlinear interconnected fractional-order systems.J. Neurocomputing, 2022, 488:14-22. [CrossRef]
- Yi-Fei Pu; Ji-Liu Zhou; Xiao Yuan. Fractional Differential Mask: A Fractional Differential Based Approach for Multi-scale Texture Enhancement, IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol.19, no.2, pp. 491-511, 2010.
- Pu; Y.-F.; Siarry; P. Chatterjee, A., et al.: ‘A fractional-order variational framework for retinex: fractional-order partial differential equation-based formulation for multi-scale nonlocal contrast enhancement with texture preserving’, IEEE Trans. Image Process., 2018, 27, (3), pp. 1214–1229. [CrossRef]
- Hacini M ;Hachouf F; Charef A. A new Bi-Directional Fractional-Order Derivative Mask for Image Processing Applications[J]. IET Image Processing, 2020, 14(11): 2512-2524.
- Zhang, X., Dai, L. Image Enhancement Based on Rough Set and Fractional Order Differentiator. Fractal Fract., 2022, 6, 214. [CrossRef]
- Meng-Meng Li, Bing-Zhao Li. A novel active contour model for noisy image segmentation based on adaptive fractional order differentiation. IEEE Transactions on Image Processing, vol. 29, pp.9520-9531, 2020. [CrossRef]
- Nandal S , Kumar S . Single image fog removal algorithm in spatial domain using fractional order anisotropic diffusion[J]. Multimedia Tools and Applications, (2019) 78: 10717–10732.
- A. Abirami, “A new fractional order total variational model for multiplicative noise removal,” Journal of Applied Science and Computations, vol. 6, no. 3, pp. 483–491, 2019.
- A. Abirami, P. Prakash, and K. -angavel, “Fractional diffusion equation-based image denoising model using CN-GL scheme,” International Journal of Computer Mathematics, vol. 95, no. 6-7, pp. 1222–1239, 2018.
- Bai J, Feng X C. Image decomposition and denoising using fractional-order partial differential equations[J]. IET Image Processing, 2020, 14(7).
- Abirami A, Prakash P, Ma Y K. Variable-Order Fractional Diffusion Model-Based Medical Image Denoising[J]. Mathematical Problems in Engineering: Theory, Methods and Applications, 2021(Pt.51):2021.
- Xu L, Huang G, Chen Q L, et al. An improved method for image denoising based on fractional-order integration[J]. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering, 2020, 21(10):1485-1493.
- Xiuhong, Y., Baolong, G.: ‘Fractional-order tensor regularization for image inpainting’, IET Image Process., 2017, 11, (9), pp. 734–745.
- WANG Yong-xing;PU Yi-fei;GONG Xiao-qian;ZHOU Ji-liu. Fractional block matching three-dimensional filter.J. Application Research of Computers.2015,32(1),287-290.
- FENG Chenbo;QIN Yali;CHEN Hui;CHANG Liping;XUE Linlin. Fractional Total Variation Algorithm Based on Improved Non-local Means. J.Computer Engineering.2019,45(4),241-247.
- Liu, K.; Tian, Y. Research and analysis of deep learning image enhancement algorithm based on fractional differential. Chaos Solitons Fractals 2020, 131, 109507. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, K.; Jindal, N.; Singh, K. Fractional Fourier Transform based Riesz fractional derivative approach for edge detection and its application in image enhancement. Signal Process. 2021, 180, 107852. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Téllez-Velázquez, Cruz-Barbosa R. On the Feasibility of Fast Fourier Transform Separability Property for Distributed Image Processing[J]. Scientific Programming, 2021.
- RanTao;Feng Zhang;Yue Wang.Research progress on discretization of fractional Fourier transform.J. Chinese Science Series E: Information Science. 2008 38(4), 481- 503.
- K. Gu, J. Zhou, J. F. Qiao, G. Zhai, W. Lin, and A. C. Bovik, “No-reference quality assessment of screen content pictures,” IEEE Trans. Image Process., vol. 26, no. 8, pp. 4005–4018, Aug. 2017.
- K. Gu et al., “Blind quality assessment of tone-mapped images via analysis of information, naturalness and structure,” IEEE Trans. Multimedia, vol. 18, no. 3, pp. 432–443, Mar. 2016.
- HUANG Guo, XU Li, CHEN Qingli, et al. Research on Non-local Multi-scale Fractional Differential Image Enhancement Algorithm[J].Journal of Electronics & Information Technology,2019,41(12):2972-2979.





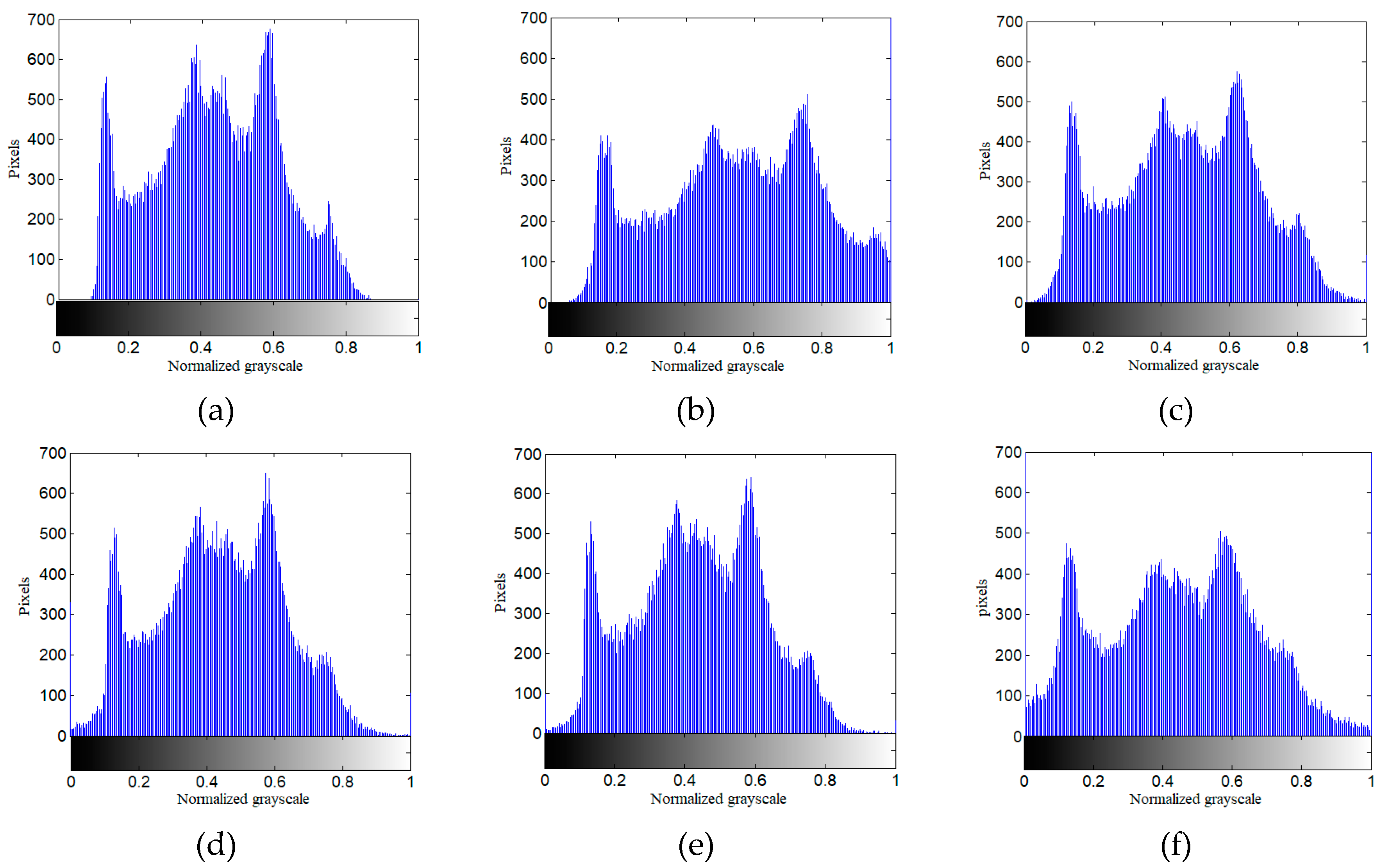




| Denoising average | gradient method | Edge retention coefficient | Signal to Noise Ratio |
|---|---|---|---|
| mean value Gaussian Wiener fractional order |
0.0138 0.0186 0.0165 0.0208 |
0.3547 0.5388 0.4356 0.7084 |
18.2964 19.3706 19.2437 19.8679 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




