1. Introduction
At present, in order to improve the reproductive rate of sows and the survival rate of piglets, the pig breeding industry normally adopts early weaning isolation technology to shorten the traditional suckling period of approximately 2 months to 15-28 days [
1]. However, this technique will cause piglets to bear nutritional, psychological and environmental pressure in advance [
2], causing piglets stress response [
3]. Studies have found that excessive concentration of free radicals produced by the body during weaning stress will destroy the redox balance [
4], which will oxidize and damage the intestinal morphological structure and mucosal barrier of piglets. The damaged intestinal morphological structure will reduce the digestion and absorption ability of food, and the damaged intestinal mucosal barrier will easily lead to intestinal allergy and the activation of certain neuroregulatory pathways. Viruses and bacteria can invade and colonize the intestine, causing intestinal inflammation, flora imbalance, dyspepsia, diarrhea, slow growth and a series of intestinal diseases [
5].
The addition of excessive doses of zinc and copper in feed is a common international practice to prevent and alleviate intestinal diseases of piglets, although it can significantly improve the intestinal health of piglets, but the zinc and copper not absorbed by the animal body will seriously pollute the water and soil. This approach completely violates the conservation, green and environmental protection development concept advocated by the International Health Organization, so in recent years, many countries have begun to introduce regulations to limit the dosage of zinc and copper in feed, calling for exploring new ways to deal with intestinal diseases from greener and safer aspects such as enzyme preparations, acidifiers and amino acids.
Taurine (Tau) is a semi-essential
β-amino acid and is the most abundant free amino acid in animal tissues [
6], accounting for 25%, 50%, 53% and 19% of the total free amino acids in liver, kidney, muscle and brain tissues, respectively [
7]. The significance of its high concentration is not to provide raw materials for protein synthesis, nor to provide energy for body metabolism, but to play its rich biological functions as a body regulator, and antioxidant is one of its main functions. It has been found that Tau can avoid the mistranslation of proteins related to the electron transport chain by strengthening the precise positioning of codons and anti-codons, so as to maintain the structural and functional integrity of the electron transport chain more efficiently, thus avoiding the leakage of electrons during the transport process and reducing the generation of reactive oxygen species (ROS) [
8,
9]. Tau can act on the Keap1-Nrf2/ARE antioxidant signaling pathway, promote NF-E2-related factor 2 (Nrf2) to enter the nucleus and bind to the small Maf protein (Maf) in the nucleus into heterodimer, and then act on the antioxidant reaction element (ARE) on the nucleic acid sequence to induce the expression of antioxidant oxidase genes [
10]. In addition to acting as a pH regulator in the glutathione redox system [
11], exogenous supplementation of Tau can also increase the amount of glutathione synthesis in the body [
12], thereby improving the antioxidant capacity of the body.
Because Tau has a clear antioxidant effect, this study is of great significance to explore the antioxidant effect of Tau on the alleviation of intestinal oxidative damage in weaned piglets through three main aspects: intestinal morphology, mucosal barrier and microbial flora: On the one hand, expand the new understanding of the application value of Tau in livestock and poultry nutrition and medical circles, promote the development of related research, and further provide theoretical guidance for the application of Tau in livestock and poultry breeding industry; On the other hand, it provides a more efficient, green and safe solution to the intestinal oxidative damage induced by early weaning in livestock and poultry breeding, thereby improving the health of weaned piglets and improving the economic benefits of the farm.
4. Discussion
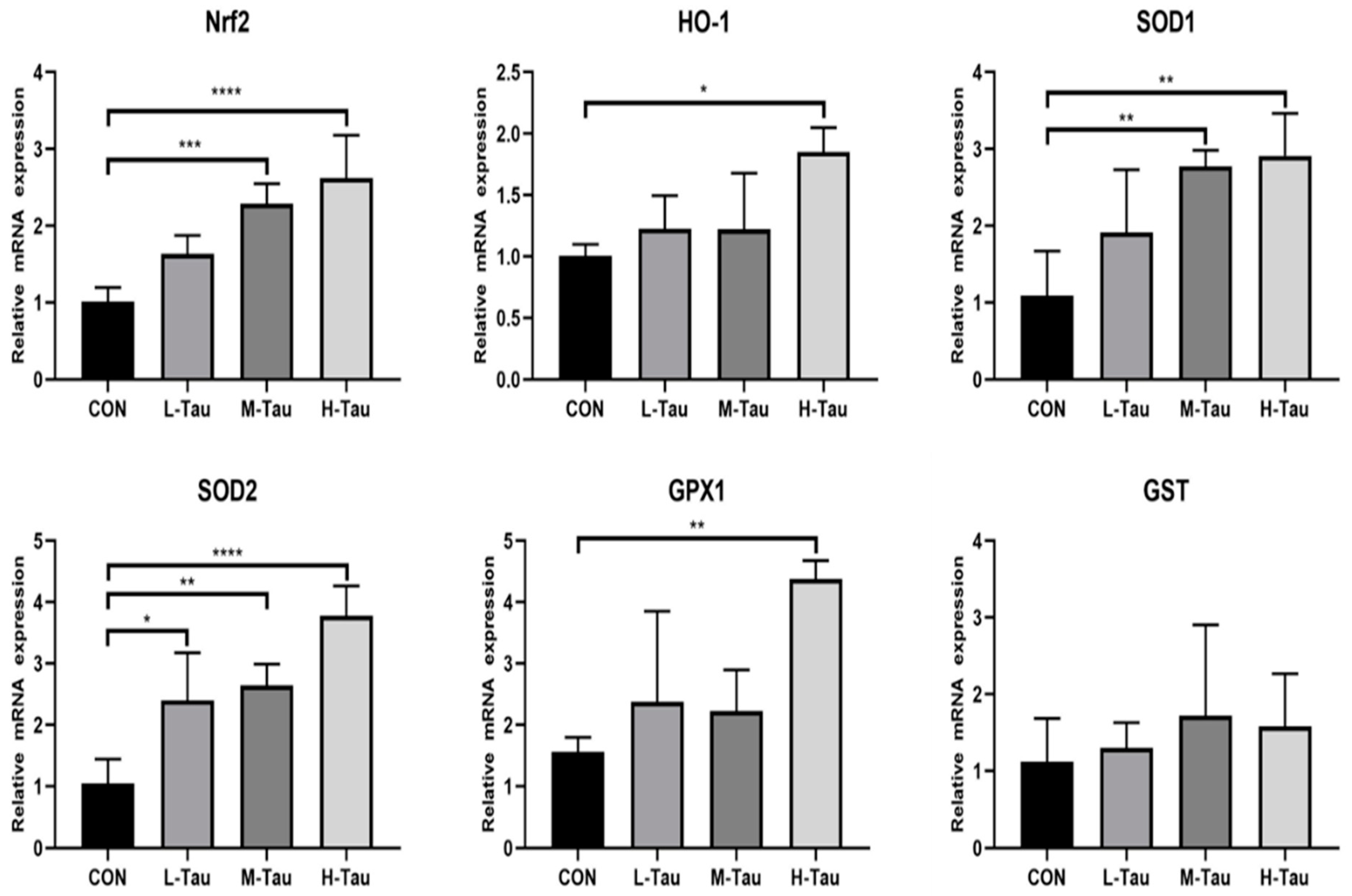
Early weaning is a necessary link in contemporary piglet breeding, and it is also an important means for farms to improve production benefit. However, after early weaning of piglets, the activity of antioxidant enzymes in the body is significantly decreased, resulting in increased concentrations of ROS and reactive nitrogen species (RNS), thus damaging proteins and lipids in the body and causing oxidative damage to tissues and organs [14-16]. Therefore, it is known that after early weaning of piglets, the body is in a peroxide state and there is an antioxidant demand. The results of this study showed that Tau could enhance its antioxidant activity by up-regulating the mRNA abundance of antioxidant oxidase genes, thereby improving the scavenging ability of ROS and RNS, and reducing the damage to the body. The reason for this result may be that Tau activates the Keap1-Nrf2/ARE antioxidant signaling pathway. Studies have shown that [17-19], hydrogen peroxide generates hypochlorous acid in the presence of chloride ions, and then hypochlorous acid reacts with Tau to produce nitrogen chloro-Tau, which can activate nuclear factor Nrf2 and make it enter the nucleus to interact with the antioxidant reaction element (ARE). The transcriptional levels of antioxidant enzyme genes HO-1, CAT, SOD and GSH-Px are up-regulated [
20], which increases the antioxidant capacity of the body. Tau not only enhances the scavenging ability of ROS and RNS, but also reduces its production rate. It has been found [
21,
22] that Tau can enhance the effective synthesis rate of mitochondrial electron transport chain related proteins by enhancing the precise location of codons and anti-codons,such as NADH dehydrogenase subunit 5(ND5), NADH dehydrogenase subunit 6(ND6)and cytochrome b(Cytb),in order to maintain the structural and functional integrity of the electron transport chain, so as to avoid electron leakage during the transport process, and thus greatly reduce the generation of ROS. In addition, the results of this study also showed that Tau significantly up-regulated the blood GSH concentration and GSH/GSSG ratio, indicating that Tau increased the reducing capacity of glutathione and weakened its oxidation capacity, and indirectly reflected that Tau could up-regulate the antioxidant potential of glutathione. Some scholars have also found that Tau can maintain the REDOX ability of glutathione by regulating the pH in mitochondria [
11]. At the same time, we also found that Tau up-regulated the activity of glutathione synthase in liver and jejunum mucosa, possibly because Tau and glutathione share the same synthetic raw material cysteine [
12]. Exogenous Tau supplementation can reduce the endogenous synthesis of Tau by hepatocytes, thus limiting the participation of cysteine in the pathway of Tau synthesis. This will save a lot of cysteine raw materials for the synthesis of glutathione, and a lot of saved cysteine activates glutathione synthase as a substrate, and then synthesizes more glutathione, increasing the antioxidant capacity of the body.
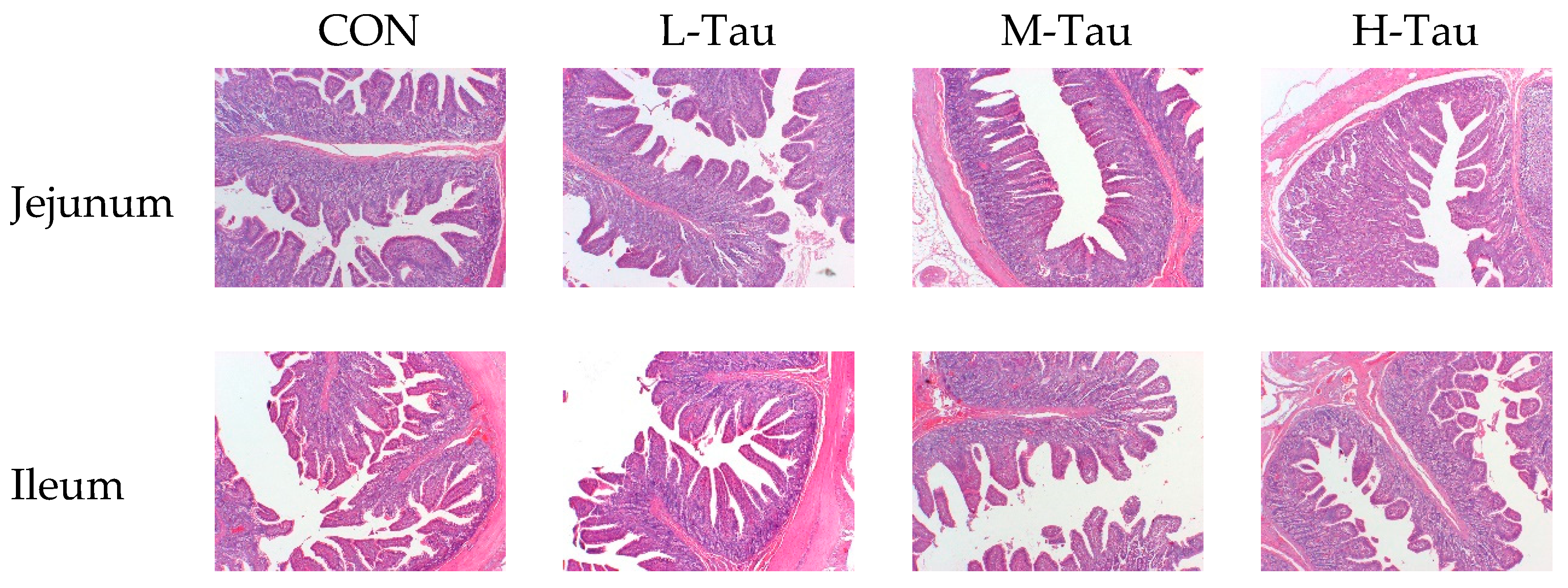
Whether the nutrients in the feed can be fully digested and absorbed depends to a certain extent on whether the animal has a good intestinal morphological structure. Because of its long retention time of food and large surface area of absorption, the gut is the main supplier of nutrients to the body. Studies have shown [
15] that oxidative stress caused by weaning can cause the destruction of jejunal villi accompanied by lamina propria edema, and significantly reduce the height and width of jejunal villi, and significantly increase the CD. These changes will seriously reduce the digestion and absorption function, and then seriously slow down the growth and development rate of piglets. In this study, Tau was found to significantly up-regulate VH and VH/CD in jejunum and ileum, which was consistent with previous studies [
23]. The increase of VH can increase the surface area of nutrient absorption in the intestine, improve the absorption capacity of nutrients in the intestine of piglets, and further promote the growth and development of piglets. The small intestine epithelium is renewed every 2-5 days and is the most regenerative tissue in mammals [
24]. The intestinal epithelium is composed of many repetitive crypt-villus units that undergo continuous cycle of renewal and repair [
25]. The crypt was proliferative areas, and early progenitor cells produced by the intestinal stem cells (ISCs) at the bottom migrated to the crypt-villus axis and differentiated into epithelial cells [
26], thereby repairing intestinal damage. However, the efficiency of ISCs in intestinal damage repair is closely related to the REDOX state. Excessive accumulation of ROS in mammals can inhibit the proliferation and differentiation of ISCs. Studies have found that the proliferation and differentiation process of ISCs is blocked under high ROS levels [
27]. Further studies have confirmed that the activation of Keap1/Nrf2 signaling pathway significantly reduces the ROS content in the intestine, creating an appropriate ROS content for intestinal cells and enhancing the activity of ISCs [
28]. In addition, Keap1/Nrf2 signaling may work synergistically with Notch signaling to determine the proliferation and differentiation of ISCs. Studies have found that the functional regulatory region of Notch1 gene is located at the proximal end of the Nrf2 promoter [
29], which may be activated with the activation of Nrf2. It can negatively regulate the Notch downstream effector Math1, thus disrupting the Notch cascade and accelerating the proliferation and differentiation of mouse ISCs [
30]. These results suggest that taurine can maintain the REDOX state required for the proliferation and differentiation of ISCs by activating the Keap1/Nrf2/ARE antioxidant pathway and increasing the abundance of glutathione, and may activate the functional regulatory region gene of Notch1 gene while activating Nrf2, thus interfering with Notch signaling pathway. The proliferation and differentiation ability of ISCs in piglets were enhanced, and the repair efficiency of intestinal damage was improved.
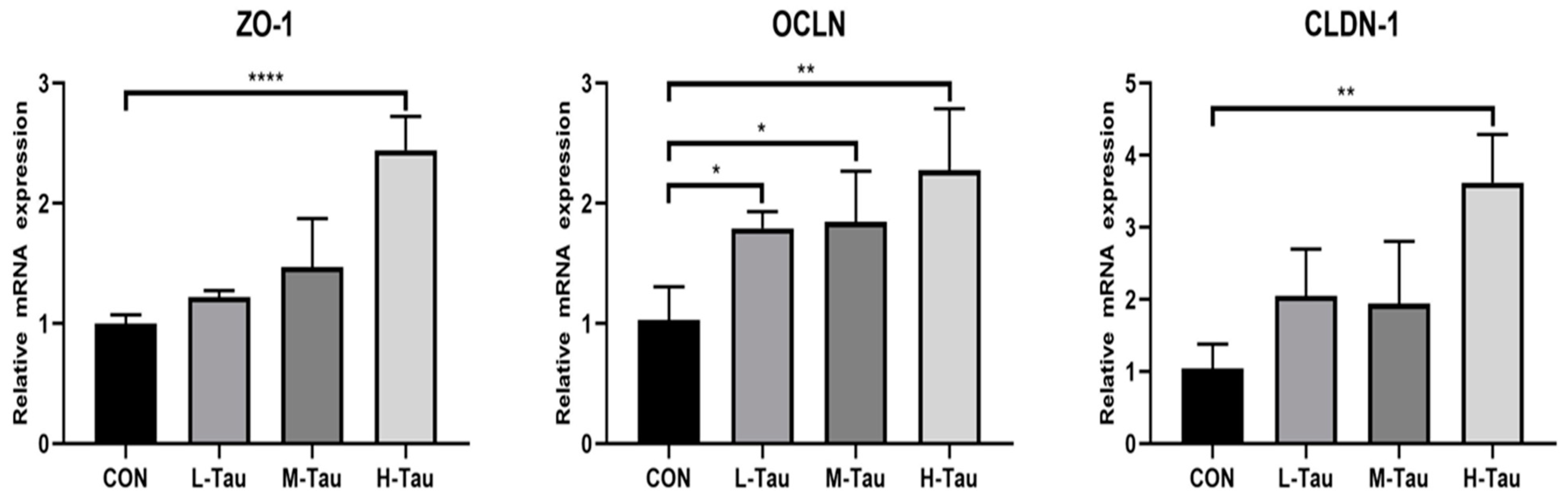
Intestinal mucosal barrier can effectively prevent harmful substances from passing through the intestinal mucosa and entering the blood, thus avoiding the occurrence of enteroborne infections. Studies have found that oxidative stress can reduce the abundance of intestinal protein expression of OCLN, CLDN-1 and ZO-1 in piglets [
31], and significantly increase the level of lipopolysaccharide in blood [
32]. This indicates that oxidative stress can indeed increase the permeability of intestinal mucosa, damage the intestinal defense barrier of piglets, and cause endotoxins to enter the blood through the mucosa to further threaten the health of piglets. However, in this study, this phenomenon was alleviated to a certain extent, and it was observed that dietary Tau supplementation could significantly up-regulate the mRNA abundance of ZO-1, OCLN and CLDN-1 protein genes in jejunal mucosa and their expression levels in jejunal mucosa, and significantly reduce the content of D-LA in blood. This suggests that Tau can reduce intestinal mucosal permeability by restoring the tight connections between cells, thereby inhibiting enteric metabolites from crossing the intestinal defense barrier into the bloodstream, reducing the risk of enteric diseases in piglets. The mechanism of taurine promoting the intestinal barrier has not been fully established. Since taurine have the ability to promote intestinal antioxidant capacity as well as barrier function and the study found that taurine promoted the tight junction protein expression and activated the Nrf2 signaling pathway, we further hypothesized that taurine promoted intestinal barrier function via the Nrf2 signaling pathway. Previous studies found that inhibition or deletion of Nrf2 decreased the tight junction protein expression in cells or mice [
33,
34]. The effect of Nrf2 on intestinal barrier function is possibly indirectly promoted in many ways, which may be associated with the regulation of Nrf2-mediated inflammation, oxidative stress, T cell activation, and autophagy [
35]. In addition, Nrf2 might directly regulate tight junction protein expression, and it has been reported that Nrf2 binds to the promoter of claudin 4, which has the potential to result in an increase in claudin 4 transcription [
36]. Future research is needed to determine whether Nrf2, as a transcription factor, binds the promoter of other tight junction genes to promote their transcription.
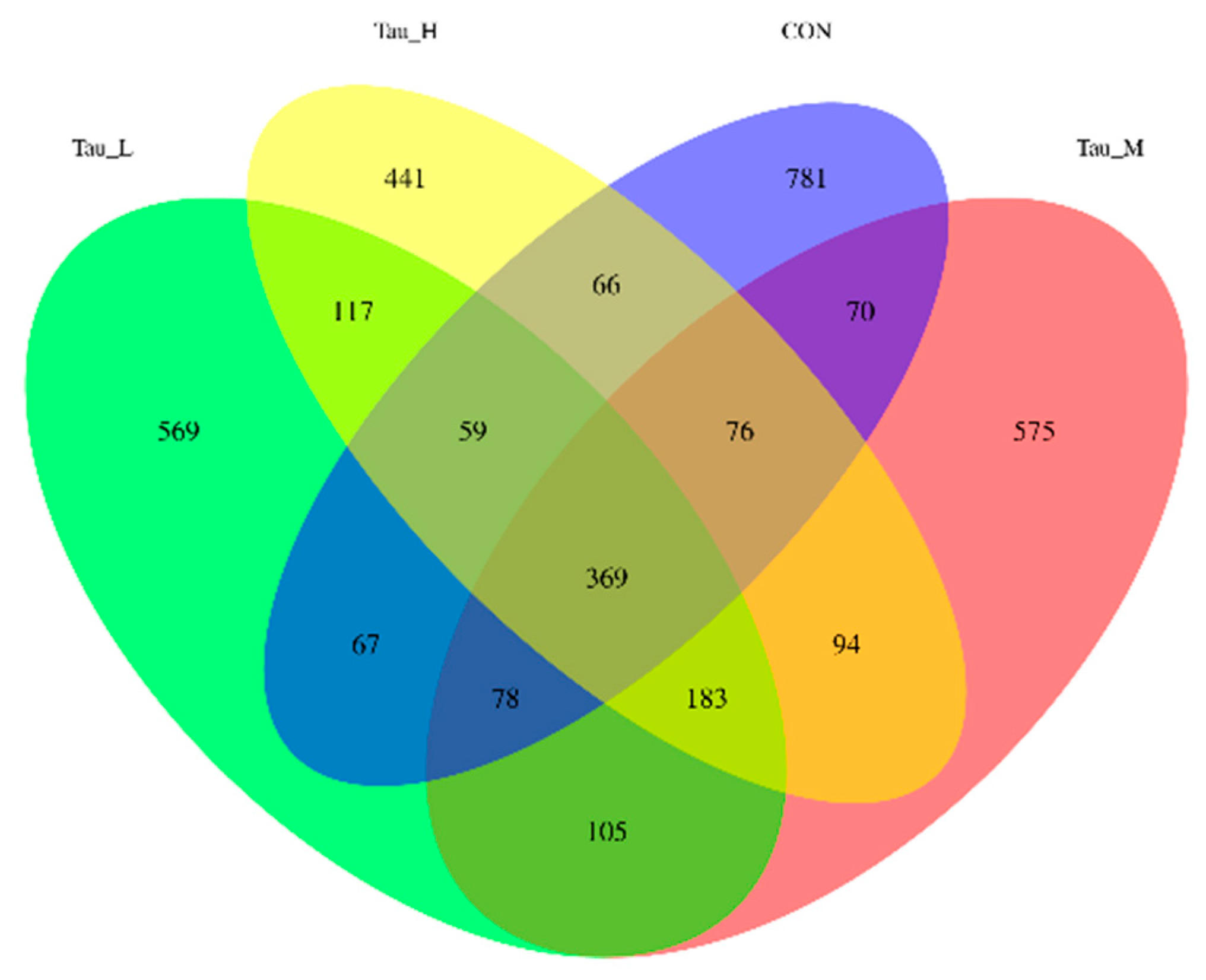
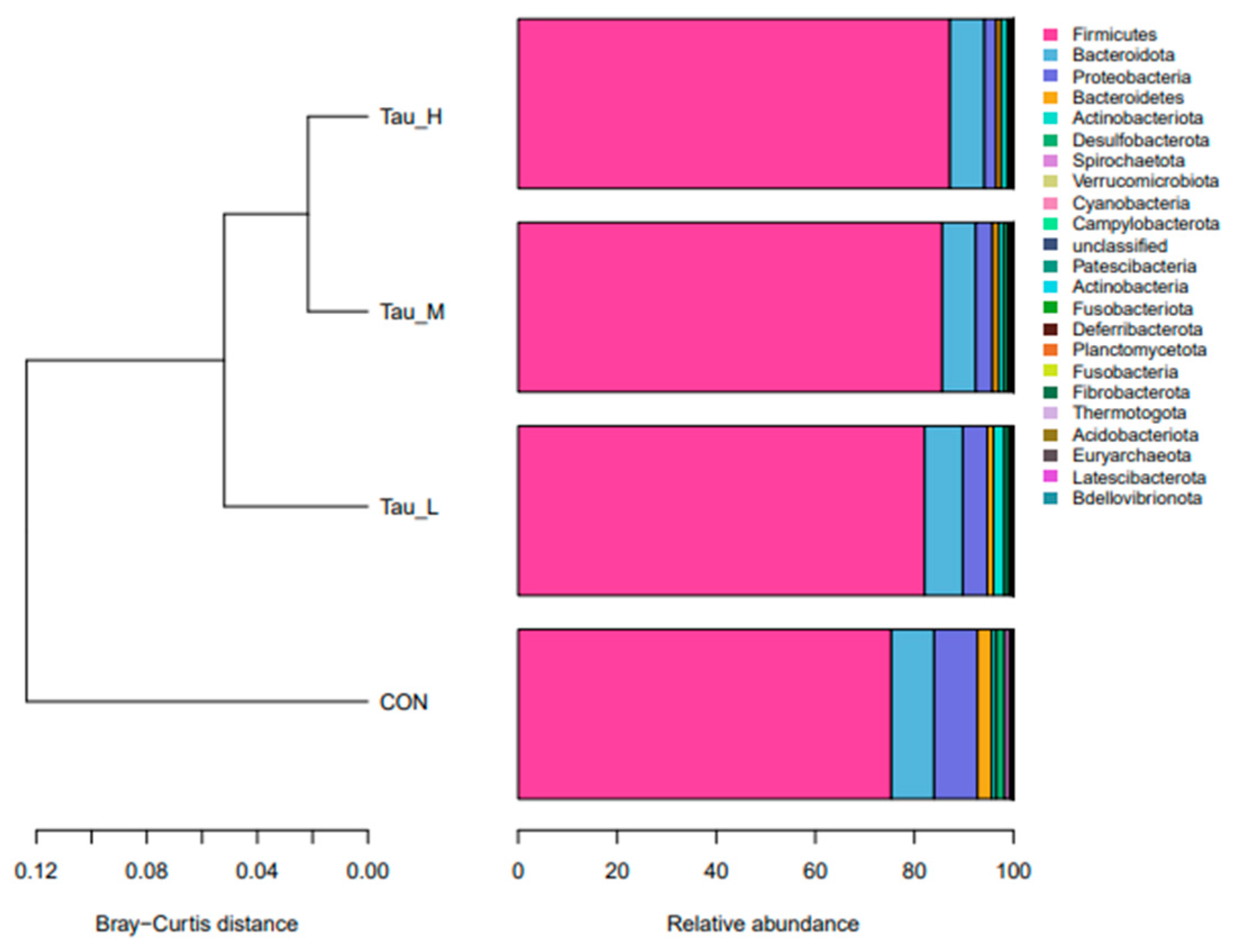
The microbiota inhabits the intestines of piglets in a dynamic composition and is regulated by a variety of factors. The imbalance of intestinal flora caused by oxidative stress may be one of the main causes of various intestinal diseases. Studies have shown [
37] that oxidative stress can significantly reduce the abundance of Lactobacillus and Faecalibacterium in the gut of piglets, while significantly increase the abundance of Clostridium cluster I. Lactobacillus is a beneficial bacterium that can resist the invasion and colonization of exogenous pathogenic microorganisms [
38], Faecalibacterium is a resident anti-inflammatory probiotic in the gut of healthy animals, and Clostridium cluster Ⅰ is a conditional pathogenic bacterium [
39]. The imbalance of intestinal microbiota can lead to a variety of intestinal diseases [
40]. Therefore, the above study found that after oxidative stress of piglets, the abundance of beneficial bacteria in the intestine is down, and the abundance of harmful bacteria is up, which indicates that oxidative stress can cause a variety of intestinal diseases by changing the microbial flora in the intestine, and then adversely affect the digestion, absorption, growth and development of piglets. Interestingly, this appears to be reversed when Tau is added to the feed. According to the Venn diagram of ASV distribution between groups, the addition of Tau made 781 ASV microorganisms disappear from the cecum colonization, but 183 ASV microorganisms were introduced into the cecum colonization. The reason why Tau changes the microflora of cecum may be that it changes the microenvironment of cecum in some way. It is reported [
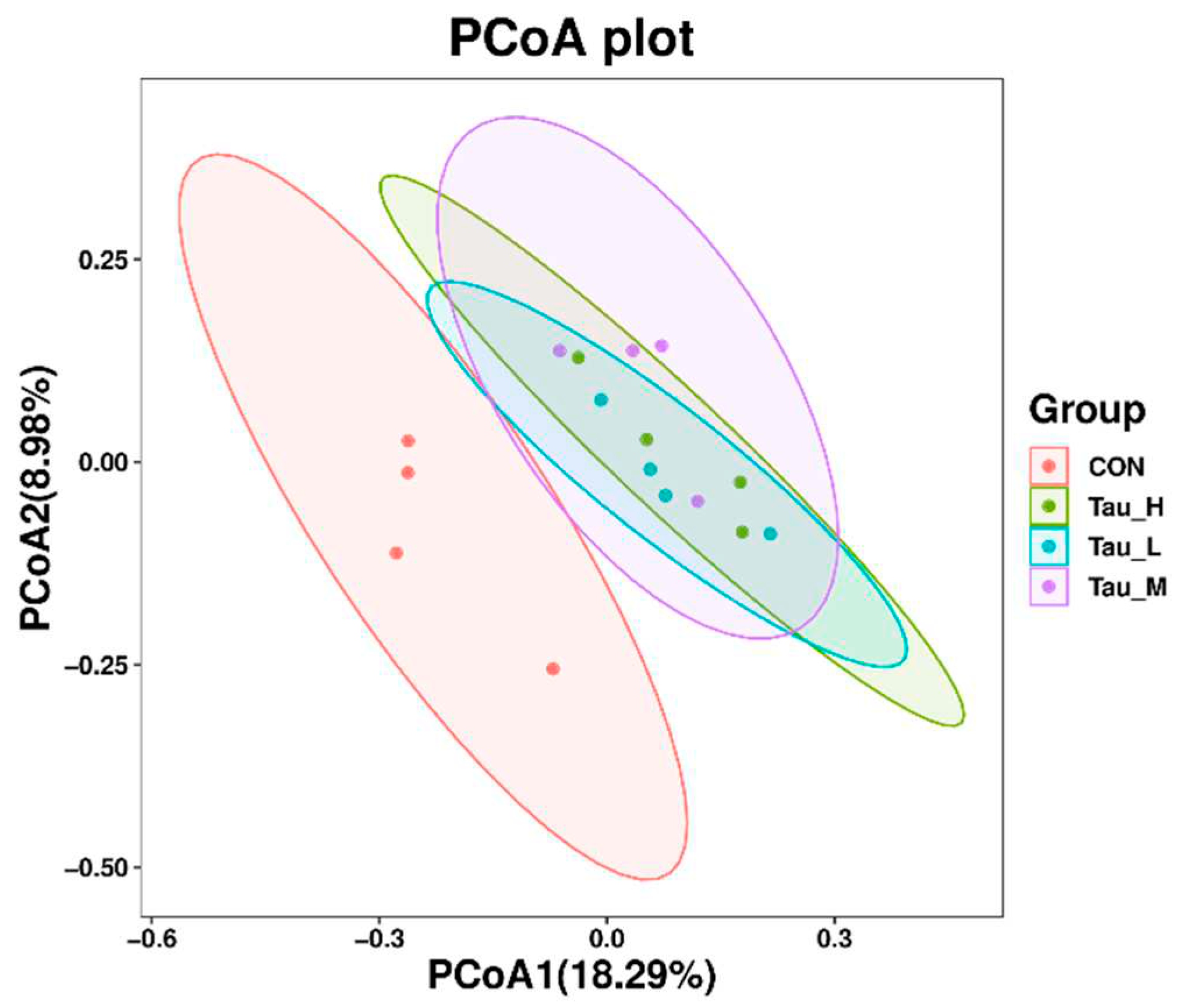
41] that Tau, as a sulfite donor, can produce hydrogen sulfide in the intestine, and hydrogen sulfide is an important metabolic product in the intestine, which can have both beneficial and harmful effects on the intestinal environment. In this way, it showed certain selectivity to the microorganisms colonized in the cecum. Although Tau had no significant effect on alpha diversity of cecum microflora, it had some effect on Beta diversity. This shows that Tau does not change the total number of microflora species and their quantitative distribution in the cecum, but causes changes in the composition and proportion of microflora species.
The test results showed that at the phylum level, Tau significantly increased the proportion of Firmicutes, and significantly decreased the proportion of spirobacteroides and Proteobacteria. Although there was no significant effect on Bacteroides, the proportion of Bacteroides showed a significant downward trend with the increase of Tau dose. According to relevant reports, Firmicutes can improve energy utilization in the diet, and Bacteroides are common microorganisms that degrade polysaccharides [
42], and the ratio of Firmicutes to Bacteroides is usually positively correlated with intestinal digestion and absorption [
43,
44]. It was also observed in this experiment that the feed utilization rate of piglets was significantly improved after the addition of Tau in the diet, which indicates that Tau may improve the production performance of animals by improving the intestinal flora. Proteobacteria are a group of highly adaptable and potentially pathogenic bacteria in the gastrointestinal tract, and the imbalance of intestinal flora in the colon is usually accompanied by the increase of Proteobacteria abundance [
45]. Spirochaeta is mostly pathogenic bacteria or conditional pathogenic bacteria, which has a potential induction effect on piglet diarrhea [
46]. The proportion of Proteobacteria and spirochaeta decreased significantly after the addition of Tau in the diet, which also indicates that the addition of Tau can limit the growth of harmful bacteria and is more conducive to the health of the body. At the generic level, Tau significantly increased the proportion of
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1,
Terrisporobacter and
Turicibacter.
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1,
Terrisporobacter and
Turicibacter all belong to the Firmicutes group of probiotics [
47]. The study found that
Clostridium_sensu_stricto_1 can utilize mucous derived sugars, such as glucose, and can also act as a fiber degrading bacterium that degrades cellulose and hemicellulose [
48], thereby improving the animal’s utilization capacity of coarse fiber in feed.
Terrisporter is a lactic acid-degrading bacterium. Under anaerobic conditions,
Terrisporter can degrade lactic acid [
49], thereby avoiding acidosis and intestinal damage caused by excessive lactic acid in the intestine. Therefore, the results of this experiment also indicate that Tau may improve the intestinal nutrient utilization capacity of piglets by increasing the proportion of beneficial bacteria, and then maintain intestinal health by improving the flora.
Intestinal health is closely related to the body’s digestion and absorption ability. The above results are sufficient to prove that the addition of Tau in feed can indeed alleviate the intestinal oxidative damage induced by early weaning of piglets. Meanwhile, we also observed that the addition of Tau in feed can significantly reduce the diarrhea index of piglets and improve the feed conversion rate. These results indicate that Tau can improve feed utilization ability of piglets by alleviating intestinal oxidative damage. In addition, we also speculate that this beneficial effect may be related to taurine improving the synthesis capacity of GSH, Because GSH can improve the body’s ability to absorb nutrients. Researches show that GSH can participate in the absorption of amino acids through the
γ-glutamyl cycle, and the extracellular amino acids react with GSH under the action of
γ-glutamul transpeptidase (
γ-GT) to generate
γ-glutamyl-amino-acids and cysteinyl-glycine into the cell. In the cytoplasm,
γ-glutamyl amino acids are catalyzed by
γ-glutamyl cyclotransferase to decompose into amino acids and 5-hydroxyproline. 5-hydroxyproline is hydrolyzed to glutamic acid under the catalysis of 5-hydroxyprolinase, and cysteine-glycine is hydrolyzed to cysteine and glycine by dipeptidase, and GSH can be synthesized in the cell [
50]. GSH can also reduce Fe
3+ to Fe
2+, and Fe
2+ is more easily absorbed by intestinal mucosa, thus promoting iron absorption [
51]. Studies have shown that changes in the ratio of GSSG/GSH can directly or indirectly affect the activity of enzymes related to carbohydrate metabolism [
52] and the activity of Na
+ dependent D-glucose carriers, and the reduction of this ratio can improve the carrying capacity of glucose [
53].
Although we also observed a decrease in feed intake after Tau supplementation, this was not a negative effect. The reason may be that with the increase of Tau dosage, intestinal oxidative damage can be repaired, the degree of diarrhea of piglets is significantly reduced, the digestion and absorption ability of feed is significantly improved, and the body’s demand for material and energy can be met by eating less feed. As for the CON group, the intestinal oxidative damage was not alleviated and the degree of diarrhea was serious, so they needed to eat more feed to meet the needs of the body in the state of free feeding. Some studies have found that Tau can significantly improve the growth performance of piglets fed a high plant protein diet, but has no effect on piglets fed a high animal protein diet [
54]. The reason for this divergence may be that almost all plant feeds do not contain Tau, while animal feeds are rich in Tau [
55]. The high concentration of Tau contained in high animal protein diets has met the needs of animals, and additional Tau supplementation has little effect on growth performance at this time. However, the high plant protein diet basically does not contain Tau, and the body has a relatively large demand for Tau. At this time, additional Tau supplementation can significantly improve the growth performance. The study found [
56] that after 1% Tau was added to the basic diet containing 7.5% animal protein feed (2.5% whey powder +5% fish meal), the feed to meat ratio of the experimental group on the 10th day after weaning was reduced by 12.5% compared with the control group, and the difference in daily gain was not significant, but there was a trend of improvement. Similarly, it was observed in this experiment that with the increase of Tau supplemental dose, the feed conversion rate showed a linear increase, H-Tau and M-Tau groups were significantly higher than CON group, and the difference in daily gain was not significant, but there was a trend of improvement. These directly indicate that the additional Tau does have a significant improvement effect on intestinal digestion and absorption, and indirectly reflect that the Tau provided in the basic diet supplemented with 15% animal protein feed (5% fish meal +10% whey meal) in this study still cannot meet the needs of the body. And because the price of animal protein feed is much higher than the price of plant protein feed, the proportion of animal protein feed added in the actual production will also be constrained, which leads to the actual production completely rely on the Tau in animal protein feed to meet the needs of the body is unrealistic, we must add additional Tau in the diet to meet the needs of the body.