Introduction
Ultrasonography (US) in medicine allows real time assessment of structure as “panoramic” and “dynamic” view where the procedure takes place. Panoramic view is the digital stitching of multiple ultrasound images into a broader one. It can display an entire abnormality and show its relationship to nearby structures based on dynamic behavior over time.
This feature and design could be more advantageous than radiological “static” view imaging. Radiological static imaging is the acquisition of a single image as a “snapshot” of the radiopharmaceutical distribution of a particular structure of the body.
The absence of ionizing radiation, availability and low cost are advantages of US.
It is the convincing imaging tool for many structural cardiovascular and gastrointestinal interventions [
1].
However, sonographic devices have trouble penetrating bone, performs very poorly when there is gas between the transducer and the organ of interest, due to the extreme differences in acoustic impedance and the depth penetration of ultrasound may be limited depending on the frequency of imaging. Consequently, Image quality and accuracy of diagnosis is limited with obese patients and overlying subcutaneous fat attenuates the sound beam.
These limitations could be minimized in transesophageal echocardiography (TOE), which could provide better image resolution due to the absence of intervening air or bone. However, transthoracic echocardiography (TTE) can assess certain cardiovascular structures better than that of TOE such as estimation of left ventricular function. Thus, TOE complement and cannot replace TTE.
Introduction of three-dimension innovation in transesophageal echocardiography (TOE) allows real time assessment of cardiovascular structure where the investigation takes place. It helps for understanding the complicated multiform morphology, and for evaluating its function. It has become an indispensable companion of two dimensional (2D) -TOE during structural cardiovascular diagnostic and interventions [
1].
On the other hand, endosonography (EUS) is the diagnostic tool with the highest resolution for the local staging of gastrointestinal tumors and, is recommended in current guidelines for cancer management [
2]. The benefits of investigating the cardiovascular structures using this diagnostic tool are unknown.
Materials and Methods
To understand the difference between echocardiographic and endosonographic ultrasound we summarized the main features of transesophageal and endosonographic ultrasound as a diagnostic modality and how do they work in this article.
Transesophageal Echocardiography in Focus
Images produced by echocardiography are created by analyzing reflected ultrasonic waves [
3]. The intensity and frequency of sound are its defining characteristics. Echo uses ultrasounds with frequencies between 1.5 and 7.5 Megahertz (MHz) [
4]. Cardiac examination through gastroenterological tract is called transesophageal echocardiography (TOE) [
5].
Three things—temporal, lateral, and longitudinal resolution—affect an ultrasound’s image resolution. Temporal resolution is the capacity to precisely determine the location of an anatomical structure at a specific moment in time [
6]. The eye can only see 25 frames per second (fps), which corresponds to a 40 ms temporal resolution. Sector size (width and depth) and line density affect the frame rate (which affects lateral resolution). Lateral resolution is the shortest distance between two adjacent structures that can be separated while still producing two different echoes. Longitudinal (axial) resolution is the ability to discern between two structures that are near to one another front to back [
6]. High frequency waves generally produce images with higher quality [
7].
Endosonographic Ultrasound in Focus
EUS equipment consists of ultrasound processor, connected to specific echoendoscopes, either with radial or linear transducer design coupled at the tip of an endoscope. Scopes are also connected to a standard video processor. It allows a simultaneous endoscopic and ultrasound imaging [
2]. Three major manufacturers, Fujifilm Endoscopy (Fujifilm Europe GmbH, Germany), Olympus (Olympus Europa SE and Co., KG), and Hitachi (Hitachi Medical Systems Europe, Zug, Switzerland), produce ultrasound processor, compatible with different types of echoendoscopes [
7].
The frequency used directly correlates with the quality of the image produced. So, a higher frequency results in a better image. However, the evaluation of the adjacent organs may be more challenging because high frequency ultrasonography may not penetrate as well as lower frequency ultrasound [
7].
The EUS differ in US tip design, flexibility, and balloon insufflation control design around its tip. Balloon inflation prior to insertion may reduce contact injury and severe discomfort pharyngeal pain. In addition, linear EUS produce ultrasound images in a plane parallel to the long axis of the echoendoscope. This ultrasound image orientation is a key point for tissue acquisition and therapeutic interventions as EUS devices are advanced from the distal tip of the echoendoscope in the same plane as the ultrasound image.
Presence of bend points at the distal end of the of the endoscope allow control of the angle of exit of EUS needles or other devices from the working channel with simultaneous visualization and intervention of the target lesion.
All the EUS transducers have a curved design and are located distal to the oblique-viewing endoscopic camera lens [
2].
There are 2 fundamental echoendoscope designs: curvilinear array and radial array. Radial-array EUS is mainly used for luminal imaging and evaluation of the wall layers of the GI tract, whereas curvilinear-array EUS in addition to imaging allows tissue sampling and therapeutic applications. The electronic radial-array transducers orient the individual piezoelectric elements around the distal tip in a 360° radial array, producing an image in a plane perpendicular to the long axis of the echoendoscope while linear EUS produce ultrasound images in a plane parallel to the long axis of the echoendoscope [
8].
An endoscope is made up of 1) a lighting system to illuminate internal cavities, 2) an image transmission system to send images outside the body, 3) channels for air to inflate the body cavity and for suction to remove fluids, 4) water to wash the objective lens and to introduce biopsy forceps, 5) and a bending mechanism to deflect the endoscope tip [
2]. Endoscopes transmit light from an external light source to their distal tip using an incoherent fiberoptic cable. The strong, white light required for videoendoscopy is commonly produced by 300-W xenon arc lamps in endoscopic light sources [
7].
High-resolution, or high definition (HD), endoscopes produce signal images with resolutions of up to a million pixels. Standard definition endoscopes are fitted with charge-coupled devices (CCD) chips that produce image signals with a resolution of 100,000 to 400,000 pixels [
7].
The endoscopic camera generally should meet the following criteria: a 400x400 camera sensor with attributes such as 1.75mm x 1.75mm pixel size and 714mm x 714mm picture area [
7].
Step-by-Step Approach of Endosonographic Standard Views and the Way to Look at Cardiac Structures
The EUS probe (viewing angle 120°) is advanced transesophageal by the experienced operator. Because of the lateral view optics of the endosonographic probe maneuvering especially inside the oral cavity, hypopharynx and the upper esophageal sphincter can be a challenge. We usually advance according to sonographic anatomic landmarks. Advancing smooth and without great resistance is of utmost importance to prevent iatrogenic damage.
After passing the oral cavity the first anatomic landmarks are the right carotid artery (C4 level) and the adjacent thyroid lobe. The probe is then advanced under moderate pressure (insufflation of carbon dioxide can be helpful) to pass the upper esophageal sphincter (C6 level) and advanced along the superior vena cava, the aortic arch (T4 level) and the ascending aorta. Cardiac structures can be examined from the esophagus around T4-T8 level. Around T5/6 the probe rests dorsal of the right pulmonary artery and the left atrium. Because of the close proximity and the adjustable ultrasound frequency of 5-10 MHz local resolution is very good to a depth of around 45 mm and acceptable to around 70-80 mm depending on tissue impedance. If the transducer is turned to the right at the level of the T4/5 aorta, you can also see the azygos vein, which can be traced to its continuity with the vena cava.
In contrast to a cardiac transesophageal ultrasound probe the endosonographic probe does not allow for plane rotation. This limits for example the assessment of different valvular planes. By rotating the probe from the mid axis around 45 degrees to the left and to the right we can assess the ascending aorta, right pulmonary artery, distal part of the pulmonary artery trunk, the aortic valve, the left atrium including the left atrial appendage, the mitral valve and large parts of the left ventricle. By advancing the probe further down the esophagus we reach the inferior vena cava hiatus and apical parts of the left ventricle around T8 level. We usually advance the probe further along the descending aorta passing the aortic hiatus around T11/12. By this time the probe is resting well past the lower esophageal sphincter inside the gastric body, and we can assess the celiac artery branches and the superior mesenteric artery. Transgastric image quality can be optimized by gastric fluid instillation to further lower impedance.
Available EUS Systems
There are typically two distinct EUS technologies available:
Radial or rotational arrays are used only for diagnostic purposes and have a single piezoelectric crystal positioned at the tip of a 6–10 French probe [
9]. Cross-sectional images are produced by a rotating transducer in a 360° radial plane that is perpendicular to the probe’s long axis [
9]. Rotational EUS operates between 9 and 12 MHz, which is ideal for near-field imaging up to 6 to 8 cm but not for far-field imaging [
9].
Longitudinal array EUS probes (used for both therapeutic and diagnostic purposes) consist of a 64-element transducer mounted on the distal end of an 8–10 French probe that may deflect in four different directions. A wedge-shaped image created by this probe is seen on a typical ultrasound workstation. In comparison to radial array systems, the longitudinal array probe provides several advantages, including a greater depth of penetration (up to 15 cm), improved maneuverability, and the capacity to capture Doppler and color flow imaging. A longitudinal array is preferred in the majority of interventional gastrointestinal operations due to these benefits [
9] (
Supp. Figure S7).
Longitudinal EUS performs imaging in the same plane as the shaft of an endoscope, whereas radial EUS viewing can be obtained in the plane perpendicular to that shaft [
7]
. Three dimension -based technology is still underway in endosonographic Ultrasound [
10].
The collaboration between Hitachi and Pentax in HI-VISION Preirus Ultrasound system increased the diagnostic accuracy in comparison to the conventional ultrasound systems and blending the outstanding contrast [
11]. Compounding high resolution imaging with mapping of the elastic properties and stiffness of soft tissue is the capabilities of Sonoelastography. Identification of whether the tissue is hard or soft will give diagnostic information about the status of disease. For example, cancerous tumors will often be harder than the surrounding tissue, and diseased livers are stiffer than healthy ones [
12].
This innovation improves resolution, delineation, and depth of imaging, while reducing noise, to provide optical and ultrasonic visualization and potentially increase detection of abnormalities [
10,
13].
Table 1 summarize the main features of both TOE and EUS as a diagnostic modality and how do they work and gives focus on other diagnostic applications of both in cardiovascular diseases.
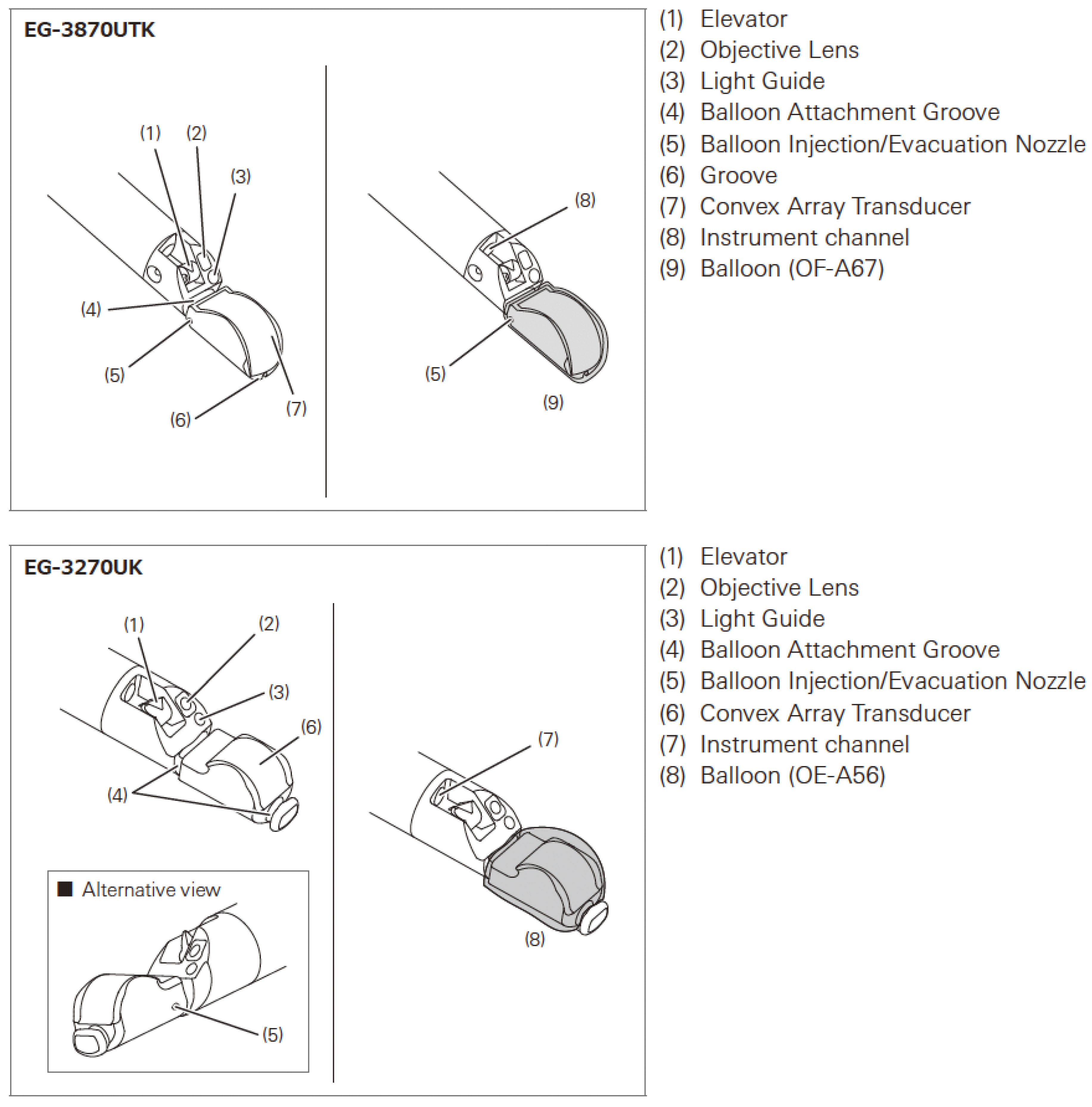
Table 2 and
Figure 1 and
Figure 2: summarize the main features of endosonographic ultrasound EG-3870TK and EG-3270UK.
The benefits of investigating the cardiovascular structures, during routine gastrointestinal procedure, using this diagnostic tool are unknown.
In this article, we discuss cases, in which a cardiovascular anatomy or structure was accidently detected using EUS as a diagnostic tool during routine gastrointestinal investigations and in some cases influenced a change in management strategies [
14]. The EUS used in all cases was Pentax EG-3870 UTK endosonography (diagnostic and therapeutic) and EG-3270UK endosonography (diagnostics) [
10], while the transesophageal echocardiography used was Philips Epic 7 [
15].
Results and Clinical Applications of EUS in Cardiovascular Medicine
The following applications are examples of the utility of endosonography in the field of cardiovascular diseases.
Aortic valve morphology, function, and vegetation (
Figure 3, Videos 1 and 2) [
14].
Mitral valve morphology, function, vegetation [
14] and Mitral clip (
Figure 4, and Videos 3–5). Mitral clip is a catheter-based edge-to-edge mitral valve repair for treating symptomatic functional mitral regurgitation (MR) in patients who are at high/prohibitive surgical risk.
- 2
Evaluation of tricuspid valve morphology and function (Video 1).
- 3
Main stem, right and left pulmonary artery morphology/diameter, structure, embolism, and pulmonary valve function and pulmonary artery embolism (Video 6).
- 4
- 5
Evaluation of atrial septal defect and patent foramen ovale with right/left shunt, thrombus or vegetation.
- 6
Left atrial appendage (LAA) morphology, thrombus/ myxoma, fibroelastoma, etc. (
Figure 5 and Videos 7–9). In addition, contrast endosonographic ultrasound can be used to image vascularity and vessel patterns in an organ of interest, especially for small volume and slow velocity blood flow. Consequently, EUS can differentiate both thrombus and myxoma not only by their distinguishing features of size, origin, shape, mobility, and prolapse but also by contrast enhancement. Compared with the adjacent myocardium, malignant and vascular tumors are hyper-enhanced, whereas stromal tumors and thrombi are hypo-enhanced [
16] (
Figure 6 and
Supp. Figure S3, and Videos 9 and 10).
Evalutation of the left atrial appendage occluder, device dislocation, device-related leak, vegetation, or thrombus (
Figure 7 and
Figure 8). The EUS can provide adequate and precise visualization of the LAA and could complement TOE in LAA evaluation. EUS in this context can (1) rule out LAA thrombus, (2) confirm device stability after release, (3) check for device-related leaks, (4) rule in/out device related thrombus and vegetation (4) monitor complications such as cardiac tamponade.
Percutaneous occlusion of the LAA devices is is a minimally invasive catheter-based therapy. When the device is positioned properly in the appendage, it covers the opening of the appendage. Over time, a thin layer of tissue will grow over the surface of the Amulet device. This keeps any blood clots in the left atrial appendage from entering the bloodstream.Thus, reduces the risk of thromboembolic complications associated with non-valvular atrial fibrillation.
- 8
Aorta ascendens, tranversus and desendens diameter, vegetation, thrombus, dissection, ulcers, aortic vasculer diseases, etc. (
Figure 4 and
Figure 5 and Supp. Video
Figure 2).
- 9
- 10
Evaluation of pericardial effusion (
Figure 9).
- 11
Evaluation of left ventriculer function and thrombus (Video 11).
Discussion
We report the clinical applications of EUS in cardiovascular medicine, which could be investigated during routine endosonographic gastrointestinal procedures. An early detection of cardiovasculer structures and pathologies can help in early differentiation between possible causes, and prompt management stratiges can be taken to minimize adverse consequences [
14].
The main strengths of EUS over TOE and its role in cardiology can be summarized as follows:
The higher resolution provides more precise information about the investigated pathology, which could help in management strategies [
13], e.g., for mass charchteristics, contrast enhancement, to image vascularity and vessel patterns in an organ of interest, precise descriptions of surrounding structures such as abscess formation, improves resolution, delineation, and depth of imaging, while reducing noise, to provide optical and ultrasonic visualization and potentially increase detection of abnormalities [
10].
The accidental detection of asymptomatic cardiac pathologies could infleunce changes in the management strategy, save time, reduce procedural complications [
17,
18], allow for the efficient use of resources and infrastructure, and improve economic outcomes.
Introducing the endoscope under direct visualization of gastroesophageal anatomy using an endoscopic camera, an advantage of EUS over TOE, could reduce procedural complications.
-
It stresses the importance of the interdisciplinary team work concept in diagnosis and treatment strategies especialy in accompaining symptoms and diseases.
o Patients with gastrointestinal tumor are immunocompromised and have a higher risk of pulmonary embolisms, ischemic events, and infective endocarditis.
o The secondary pain in tumor patient may mask and overshadow the symptoms of other pathologies, such as pulmonary embolism.
o Upper gastrointestinal pain may be due to angina pectoris/aortic dissection or a peptic ulcer.
o Patients with gastrointestinal bleeding under oral anticoagulation are admitted primarly at the internal medicine and not the cardiology department. A left atrial appendage closure device helps in this context to reduce the rate of repeated hospital admissions, the rates of gastrointestinal bleeding events, and drug–drug interactions. It can improve the patient’s quality of life, increase the efficiency of the use of resources, prevent double investigations, and improve economic outcomes.
o Fevers of unknown origin could be due to infective endocarditis or abscess formation.
o Gastrointestinal ischemic or thromboembolic events could be of primary cardiac origin.
o Dyspnea of unknown cause could be a pulmonary embolism or pulmnary artery sarcoma. An EUS or endobronchial ultrasound (EBUS) could differentiate and identify both structures.
o Intracardiac structures can be identified and evaluated for further differential diagnoses, such as intracardiac thrombus, myxoma, and tumors, using EUS with contrast.
o Heyde syndrome is a multisystem disorder characterized by the triad of aortic stenosis (AS), gastrointestinal bleeding, and acquired von Willebrand syndrome [
19].
As explained, the introduction of endosonography in cardiology allows a real-time assessment of cardiovascular anatomy and could complement transesophageal echocardiography as ideal high resolution imaging modality for detection of variable structural heart diseases. However, EUS requires more time for sterilization, preparation, and investigation.
It’s not surprising that both percutaneous and minimal invasive interventions have gradually replaced surgery for the treatment of gastrointestinal, and structural heart diseases. An essential condition of these game changer has been the parallel development of improved imaging modalities, capable of providing accurate anatomic and real time assessment during the procedures.
We hope to raise awareness among cardiologists and gastroentrologists of the significance of this diagonstic tool for both cardiovasculer and gastrointestinal diseases and highlights interdisciplinary teamwork benefits.
Finally, further studies are required to compare this procedure with other cardiac imaging modalities and to understand the exact applications and benefits of EUS in cardiovascular medicine and eventually, cardiovascular-based interventions.
Conclusions
The introduction of endosonography in cardiology allows for a real-time assessment of cardiac anatomy during gastrointestinal procedures. Due to the high resolution of the endoscope, detailed anatomical information, e.g., mass charachteristics, vascularity and vessel patterns in an organ of interest, and contrast enhancement can be obtained. The echoendoscope differs in the US tip design, flexibility, balloon insufflation control design, and bend points at the distal end of the echoscopes. EUS therefore could complement TOE in the evaluation of cardiovascular diseases and can provide accurate definitions of the variable cardiovascular anatomy, which is key to optimal management
In contrast to TOE, EUS eliminates the risk of esophageal trauma due to the direct visualization of the anatomy using a high-resolution camera. It prevents double investigations for both the patient and the operator, and it facilitates the early recognition and detection of asymptomatic pathologies, which could lead to management strategies that are safer, more effective, and improved economic outcomes by avoiding double investigation. It can complement TOE in the detection of structural heart disease. Its main disadvantage is its higher cost.
Future Perspectives
Future challenges include a higher image resolution, a reduction of probe size, and an integration of 3D technology, which will translate into a further expansion of clinical applications.
Recently, the introduction of real-time 3D-EUS probes have provided real-time volume images [
10]. Early experiences show promising results on its application to guide structural gastric procedures. This innovation could become a favored imaging mode for newer, more complex cardiovascular-based interventional techniques, such as percutaneous mitral leaflet repair and left atrial appendage closure procedures.
A promising innovation in medical imaging has been the development of micromachined ultrasonic transducers (CMUTs), based on microelectromechanical systems. A typical CMUT cell consists of a thin mobile membrane, a vacuum-sealed space, and two electrodes. When a voltage is applied between these electrodes, the membrane vibrates, generating ultrasound. Conversely, when soundwaves hit and displace the membrane, the capacitance between the electrode’s changes, and an electric current is produced. Compared with the traditional piezoelectric transducers, the advantages of CMUTs include miniaturization, amenability to integration with electronic circuits, a wide bandwidth, and a higher resolution. CMUTs can be integrated in several linear and ring arrays with different configurations and mounted on a catheter [
20].
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org. Figure S1: Ultrasonographic ultrasound demonstrated the morphology of left atrium in one view and the relation to pulmonary artery; Figure S2: Ultrasonographic ultrasound demonstrated the morphology of left atrium in another views and the relation to aortic valve; Figure S3: Ultrasonographic ultrasound demonstrated the anatomy of ascending, and aortic arch respectively; Figure S4: Ultrasonographic ultrasound demonstrated the anatomy of abdominal aorta; Figure S5: Endosonographic ultrasound demonstrated a moderate left pleural effusion; Figure S6: Endosonographic ultrasound-guided punction and aspiration of lymph nodes; Video S1: Aortic valve in short axis view and tricuspid valve in endosonographic ultrasound; Video S2: Aortic valve and ascending aorta in long axis view using endosonographic ultrasound; Video S3: Mitral valve in two chamber view in endosonographic ultrasound; Video S4: left atrial appendage, circumflex coronary artery, left atrium and mitral valve in endosonographic ultrasound; Video S5: mitral valve with mitral clip in endosonographic ultrasound; Video S6: pulmonary valve and main pulmonary artery in endosonographic ultrasound; Video S7: left atrium in endosonographic ultrasound; Video S8: left atrium and left atrial appendage in another view in endosonographic ultrasound; Video S9: Left atrial appendage with thrombus in endosonographic ultrasound; Video S10: Left atrial appendage with thrombus without contrast uptake in endosonographic ultrasound; Video S11: Left ventricle und longitudinal and short axis view in endosonographic ultrasound.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, A.E. and P. R; methodology, A.E, P.S and M.R.; M.E.; validation, A.E., P.R. and M.S.; formal analysis, A.E.; investigation, P.S. and M.R.; resources, A.E. and K.K.; data curation, M.S, A.E and K.K.; writing—original draft preparation, A.E., K.K, M.E and M.S.; writing—review and editing, M.S. and P.R.; visualization, M.E; supervision, M.S; project administration, A.E.; funding acquisition, A.E. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
The authors received no financial support for the publication of this article.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Ethical review and approval were waived for this study as all procedures were during routine gastrointestinal endosonographic investigations.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all individual participants involved in the study.
Data Availability Statement
The datasets used and all clinical and investigation images and laboratory results during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by my wife Aline Wenner and my son Yousef. Great thank to Boris Baetge for his support and Kadir Aybar for his efforts and comments during review of the article.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors AE, PR, MS, KK, MR, ME, and PS declare that they have no competing interests. The authors whose names are listed in this manuscript certify that they have NO affiliations with or involvement in any organization or entity with a financial or non-financial interest in the subject matter or materials discussed in this manuscript.
References
- Faletra, F.F.; Berrebi, A.; Pedrazzini, G.; Leo, L.A.; Paiocchi, V.L.; Cautilli, G.; Casso, G.; Cassina, T.; Moccetti, T.; Malouf, J.F. 3D transesophageal echocardiography: A new imaging tool for assessment of mitral regurgitation and for guiding percutaneous edge-to-edge mitral valve repair. Prog. Cardiovasc. Dis. 2017, 60, 305–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- T. Yamaguchi and B. Rinsho, The function of the endoscope. Jpn. J. Clin. Pathol. 1990, 38, 399–402. [Google Scholar]
- R. Freeman and C. Otto, Diagnostic Echocardiography (Ultrasound Imaging in Cardiovascular Diagnosis). Thoracic key, Fastest Thoracic Insight Engine, 2016.. Available online: https://thoracickey.com/diagnostic-echocardiography-ultrasound-imaging-in-cardiovascular-diagnosis/. [Accessed Dez. 2022].
- H. Heydarian and T. Kimball, Echocardiography: Basic Principles and Imaging, Thoracic key, Fastest Thoracic Insight Engine, 2016. Available online: https://thoracickey.com/echocardiography-basic-principles-and-imaging/.
- P. Currie,Transesophageal Echocardiography New Window to the Heart. AHA J. 1989, 80, 215–217. [Google Scholar]
- Mohamed, A. Arifi and A. Omran,The basics of echocardiography. J. Saudi Heart Assoc. 2010, 22, 71–76. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- F, F. F F. Murad, S. Komanduri, B. Dayyeh et al., Gastrointestinal endoscopy. Echoendoscopes 2015, 82, 189–202. [Google Scholar]
- Hocke, M.; Braden, B.; Jenssen, C.; Dietrich, C.F. Present status and perspectives of endosonography 2017 in gastroenterology. Korean J. Intern. Med. 2018, 33, 36–63. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DiMagno, E.P.; DiMagno, M.J. Endoscopic Ultrasonography: From the Origins to Routine EUS. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2015, 61, 342–353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- P. Medical, Endoscopic Ultrasound EG-3870UTK. Available online: https://www.pentaxmedical.com/pentax/download/fstore/uploadFiles/Pdfs/Product%20Datasheets/EMEA_PROD_ENDO_EG_3870URK_08.08.17.pdf.
- Medgadget, Hitachi and PENTAX Collaborate on HI VISION Preirus Ultrasound, Fujifilm Endoscopy, 2013. Available online: https://www.medgadget.com/2013/05/hi-vision-preirus.html (accessed on 8 December 2022).
- Wells, P.N.T.; Liang, H.-D. Medical ultrasound: imaging of soft tissue strain and elasticity. J. R. Soc. Interface 2011, 8, 1521–1549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jeong, S.H.; Yoon, H.H.; Kim, E.J.; Kim, Y.J.; Kim, Y.S.; Cho, J.H. High-resolution endoscopic ultrasound imaging and the number of needle passages are significant factors predicting high yield of endoscopic ultrasound-guided fine needle aspiration for pancreatic solid masses without an on-site cytopathologist. Medicine 2017, 96, e5782. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Elhakim, A.; Karkour, K.; Sauter, P.; Rode, M.; Elhakim, M.; Radke, P.W.; Saad, M. The role of endosonography in cardiology: case series and literature review. Eur. Hear. J. - Imaging Methods Pr. 2023, 1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Epiq-7-ultrasound-system-for-cardiology#specifications,Philips,. Available online: https://www.usa.philips.com/healthcare/product/HC795200C/. [Accessed 12 2022].
- Kirkpatrick, J.N.; Wong, T.; Bednarz, J.E.; Spencer, K.T.; Sugeng, L.; Ward, R.; DeCara, J.M.; Weinert, L.; Krausz, T.; Lang, R.M. Differential diagnosis of cardiac masses using contrast echocardiographic perfusion imaging. J. Am. Coll. Cardiol. 2004, 43, 1412–1419. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S. Krishnan, J. S. Krishnan, J. Ngai and M. Kanchuge, Complications of Transesophageal Echocardiography, Thoracic KeyFastest Thoracic Insight Engine, 2016. Available online: https://thoracickey.com/complications-of-transesophageal-echocardiography/.
- von Bartheld, M.; van Breda, A.; Annema, J. Complication Rate of Endosonography (Endobronchial and Endoscopic Ultrasound): A Systematic Review. Respiration 2014, 87, 343–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- S. Theis and S. Turner, Heyde Syndrome, StatPearls Publishing, Treasure Island (FL), 11 Jul. 2022. Available online: https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK551625/.
- Khuri-Yakub, B.T.; Oralkan. Capacitive micromachined ultrasonic transducers for medical imaging and therapy. J. Micromechanics Microengineering 2011, 21, 054004–054014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dietrich, C.; Sharma, M.; Hollerbach, S.; Fusaroli, P.; Löwe, A.; Koch, J.; Ignee, A.; Jenssen, C. General principles of image optimization in EUS. Endosc. Ultrasound 2021, 10, 168–184. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ng and, J. wanevelder, Resolution in ultrasound imaging, in Continuing Education in Anaesthesia Crit. Care Pain 2011, 11, 186–192. [Google Scholar]
- M. Anderson, Endoscope Camera: Medical Imaging Camera Quality, ATL technology, 2021. Available online: https://atltechnology.com/blog/endoscope-camera-imaging-camera-quality/.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).