1. Introduction
Laurencia is a well-known chemically defended seaweed genus whose many species produce mainly terpenes and acetogenins, which act on defense against microbes, herbivores, competitors and epiphytes [
1]. The halogenated sesquiterpene elatol is one of the major specialized metabolites common in this genus, and occurs in variable intra-thallus concentrations [
2]. In red seaweeds, diverse intracellular structures were previously characterized as sites for the storage and/or biosynthesis of defensive chemicals, such as gland cells [
3] and mevalonosomes [
4]. Halogenated metabolites in
L. dendroidea are stored inside specialized vesicles called corps en cerise (CC) [
5,
6] and their main metabolite may be the sesquiterpene elatol [
2]. These substances are released to cell surface through regulated vesicle trafficking [
7,
8] activated by epiphytic bacteria whose growth are, thereafter, chemically inhibited [
9].
Recent advances to the knowledge of defensive strategies in
L. dendroidea included the characterization of a large array of genes involved on the biosynthesis of terpenes [
10], and the recognition of diverse molecular mechanisms activated in response to epiphytic marine pathogenic bacteria [
11]. Nevertheless, although
L. dendroidea has been developing as a model study for seaweed chemical defense [6-9], the transport systems involved in the accumulation of specialized metabolites inside CC remain unknown.
In plants, vacuoles are not only the end-storage cellular compartment for defense compounds, but also host biosynthetic intermediates and the final steps of biosynthetic pathways. For example, the transport of defensive compounds is promoted by three types of transporters: ATP-binding cassette- (ABC) protein; Multidrug and toxin extrusion protein (MATE); and Nitrate/peptide family transporters (NPFs) [
12]. The ABC superfamily is one of the largest proteins in all organism, comprising membrane-bound transporters and soluble proteins that are grouped in 8 subfamilies – from ABCA to ABCH [
13]. ABC transporters play diverse roles in plant cell events, acting as importers and exporters, and also playing a leading in the growth, nutrition and resistance to stress [
14].
Moreover, ABC transporters are considered biotechnological targets, since they are involved in the compartmentalization of specialized metabolites (= secondary metabolites) to avoid autotoxicity, which improves cell growth in microbial cultures for the heterologous biosynthesis of plant valuable compounds [12-14]. Besides, microbes harboring not only biosynthetic genes but also genes for certain ABC transporters could exudate the specialized metabolites in the culture medium, increasing the recovery efficiency [
15]. In that sense, expanding the knowledge about ABC proteins would help setting up heterologous systems for the biosynthesis of biotechnologically relevant seaweeds specialized metabolites.
According to a transcriptome-based study, ABC transporter genes are widespread among seaweed species [
16]. Other studies, based on gene expression, suggested that ABC transporters may be involved on seaweeds resistance to the effects of heavy metal [
17] and desiccation [
18]. Nonetheless, the role of ABC proteins on seaweed secondary metabolites transport and their association with the chemical defense mechanism remains largely unknown. Aiming to elucidate the roles of ABC proteins in seaweeds, this article investigated the intracellular localization of ABC transporters in
L. dendroidea, as well as their role in the transport and accumulation of secondary metabolites, and the consequent chemical defense mechanism against biofouling.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Intracellular localization of ABC proteins
Clones obtained from L. dendroidea specimens collected in the intertidal zone at Rasa Beach (Búzios, Rio de Janeiro State, Brazil) were cultivated in seawater enriched with Von Stosch (VS). The culture conditions were temperature 20 ± 2 °C, salinity 32 ± 1, irradiance 40 ± 5 µmol photons.m-2.s-1 and 14 h light/10 h dark. These culture conditions were used for all experiments, unless otherwise stated.
The presence of ABC proteins on the membrane of
L. dendroidea organelles was investigated by incubating trichoblasts with the fluorescent dye Rhodamin-123 (Rho 123) [
25] and with the inhibitor of ABC activity, Cyclosporin A (CSA; obtained from Novartis, Brazil) [
20]. Trichoblasts are hyaline uniserial and branched filaments grown over seaweed thallus apex and they were chosen for this experiment due to their high liability, rapid growth and plasticity to environmental factors, and to the absence of auto-fluorescence (from chlorophyll), which interferes with fluorescent dye detection. The assay was set as follows: Assay 1: trichoblasts were incubated with Rho 123 (200 ng.mL
-1) for 30 min.; Assay 2: seaweed fragments were incubated with Rho 123 (200 ng.mL
-1) for 60 min.; Assay 3: trichoblasts were incubated with both Rho 123 (200 ng.mL
-1) and CSA (1000 ng.mL
-1) for 60 min. Following, cells were washed with culture medium and maintained alive at 4 ºC until observed at fluorescence optical microscope (Olympus BX 50, 100X objective lens, N.A. 1.3, oil). Images were acquired with a CCD camera Cool Snap-Pro Color RS Photometrics coupled to a computer.
2.2. Morphology of corps en cerise (CC), elatol content and chemical defense
To evaluate the effects of ABC inhibition on the morphology of CC, the main secondary metabolites storage organelle, and on elatol content, L. dendroidea specimens were cultivated with sterile seawater for 10 days and submitted to daily CSA incubation times of 6 h. The CSA concentrations used were: Control: 0 ng.mL-1; Low: CSA - 200 ng.mL-1; and High: CSA - 1000 ng.mL-1. The same experiment setting was used to evaluate the effects of ABC inhibition on antifouling defense, but clones were cultured in non-sterile seawater.
The area of CC (N= 100) in trichoblast cells was analyzed as a function of CSA concentration. Cells were observed with an Olympus BX 50 microscope (100X objective lens, N.A. 1.3, oil) and the Differential Interferential Contrast (DIC) images were acquired with a CCD camera Cool Snap-Pro Color RS Photometrics coupled to a computer. The area of CC was analyzed and measured with ImageJ software [
26]. Elatol concentration was quantified in hexanic extracts of
L. dendroidea trichoblasts (N = 5
per treatment) by using a Gas Chromatograph (Crompack CP 900X) coupled to an Electron Capture Detector (GC-ECD) and based on analytical curves obtained from five standard solutions of purified elatol [
2].
To evaluate the effects of ABC inhibition on antifouling defense, the relative surface area of
L. dendroidea biofouled thalli was evaluated as a function of CSA concentration. Thalli surface images (N= 40) were acquired with an Olympus ZX microscope equipped with a digital Olympus SC30 Color Camera coupled to a computer. The surface area of biofouled thalli was analyzed and measured with ImageJ software [
26]. Samples were also processed for scanning electron microscopy, fixed in 2.5 % glutaraldehyde and 4 % formaldehyde (diluted in sodium cacodilate buffer (0.1 M, pH 7.4). After post-fixation in 1 % osmium tetroxide for 1 h, the samples were dehydrated in crescent series of ethanol and dried by CO
2 critical point method. Representative images of biofouled thalli area from each treatment were obtained with a Zeiss EVO 40 Scanning Electron Microscope.
2.3. Statistical analysis
Most statistical analyses were performed using ANOVA with a post hoc analysis (Tukey HSD), to resolve differences among levels of significant factors (p < 0.05). Other analyses were performed with PERMANOVA (D1 Euclidean distance) with the software PRIMER (version 6) + PERMANOVA software. Pairwise comparisons were used to resolve differences among levels of significant factors (p < 0.05).
2.4. Expression level of ABC protein candidate genes
Clones obtained from
L. dendroidea specimens collected at Castelhanos beach (Anchieta, Espírito Santo State, Brazil) were treated with antibiotics cocktail (100 µg. ml
-1 ampicillin, 120 µg. ml
-1 streptomycin and 60 µg. ml
-1 gentamicin) and maintained in sterile seawater with germanium dioxide (1 mg. L
-1) and 50 % Provasoli solution (sterile enriched seawater - SESW) for 2 days before the experiment. The culture and experimental conditions were temperature 22 ± 1 °C, salinity 32 ± 1, irradiance 80 ± 5 µmol photons.m
-2.s
-1 and 14 h light/10 h dark. The bacteria
Vibrio madracius, isolated from the coral
Madracis decactis [
27] was grown at 30
oC in sterile Marine broth to the OD
600 0.8, corresponding to 10
8 CFU.ml
-1 and precipitated for 5 min. at 3.000 rpm (Centrifuge 5415R, Eppendorf). The supernatant was discarded, and the pellet was resuspended in sterile seawater.
Vibrio madracius is associated with bleached coral and induces the up-regulation of genes related to defense responses in
L. dendroidea, including the biosynthesis of terpenes [
11,
27].
Control tubes were set up with 250 mg of L. dendroidea and 40 ml of SESW (n= 3), and inoculated tubes contained 250 mg of L. dendroidea, 40 ml of SESW and V. madracius at 107 CFU ml-1 (n= 3). After 24, 48 and 72 h, control and inoculated L. dendroidea specimens were frozen and ground in liquid nitrogen. Total RNA was extracted using the TRIzol protocol (Life Technologies), cDNA libraries were prepared using the TruSeq stranded mRNA LT Sample Preparation Kit (Illumina) and paired-end sequencing (2 × 250 bp) was performed on a MiSeq (Illumina).
Sequences were assembled using Trinity [
28], and sequences larger than 199 bp were used in the downstream analysis. To identify the transcripts coding for ABC proteins, we prospected the transcriptome of
L.
dendroidea using hidden Markov models available at PFAM and the HMMER 3.0 software [
29]. The ABC protein candidate genes were annotated through a BLAST search against the NCBI-nr and Uniprot databases (e-value < 10
-5). Sequences from each sample coding for ABC protein were mapped against the assembled reads using Bowtie 2 [
30], and statistically relevant differentially expressed genes between the control and the inoculated samples were identified using the edgeR software package associated to Fisher’s exact test and Bonferroni correction for multiple tests (considering corrected p-value ≤ 0.001 and logFC ≥ 2.0) [
31]. The functional annotation and classification of candidate genes into ABC protein subfamilies was confirmed through SmartBLAST, and the best hits were aligned with
L. dendroidea candidate genes.
3. Results
This section may be divided by subheadings. It should provide a concise and precise description of the experimental results, their interpretation, as well as the experimental conclusions that can be drawn.
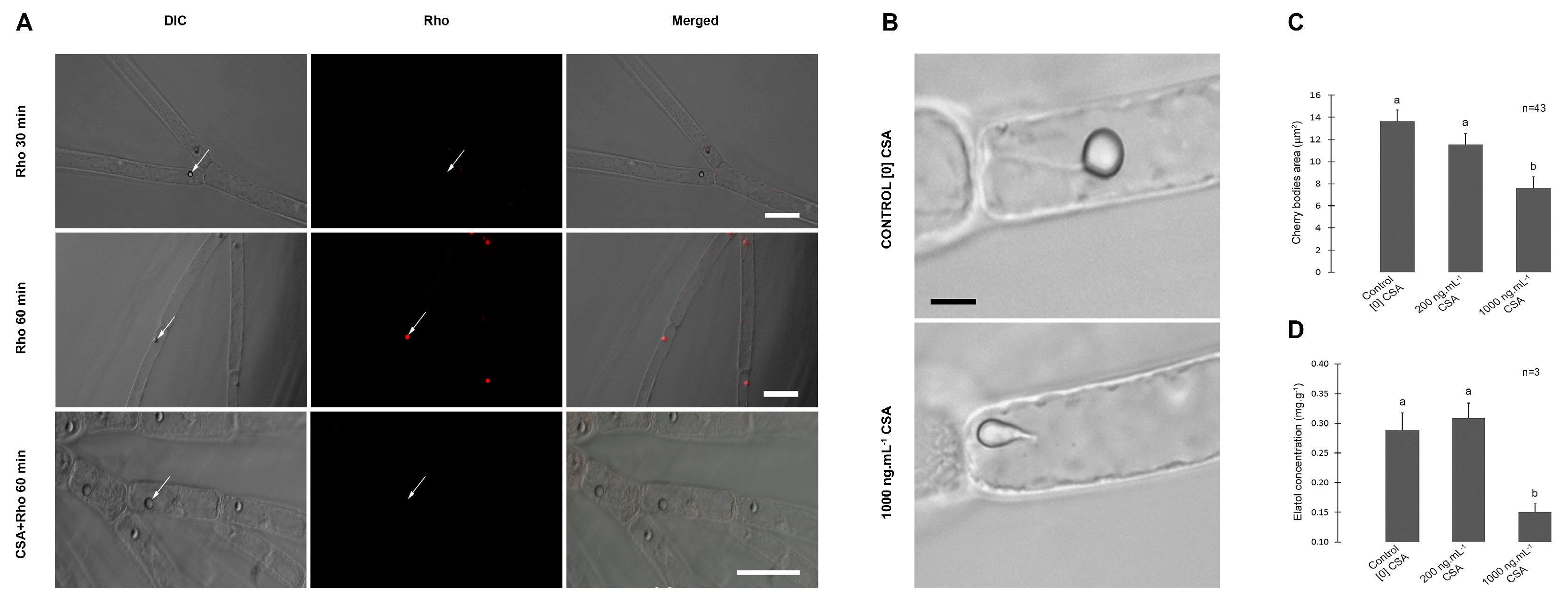
Laurencia dendroidea trichoblast cells showed no fluorescent dye compartmentation after incubation with Rho 123 for 30 min. (
Figure 1A). However, Rho 123 fluorescence was observed exclusively inside the CC (
Figure 1A) after 60 min of incubation. The simultaneous incubation of trichoblast cells with Rho 123 and CSA for 60 min. resulted in no fluorescence inside CC, revealing that fluorescent dye compartmentation was interrupted (
Figure 1A).
We also observed morphological alterations in CC of trichoblast cells incubated with CSA (
Figure 1B). The area of CC decreased significantly in cells treated with 1.000 ng. mL
-1 CSA, when compared to the respective control and the 200 ng. mL
-1 treatment (
Figure 1C). Elatol concentration reduced in extracts of trichoblast cells under high CSA treatment, when compared to control and low CSA treatment (
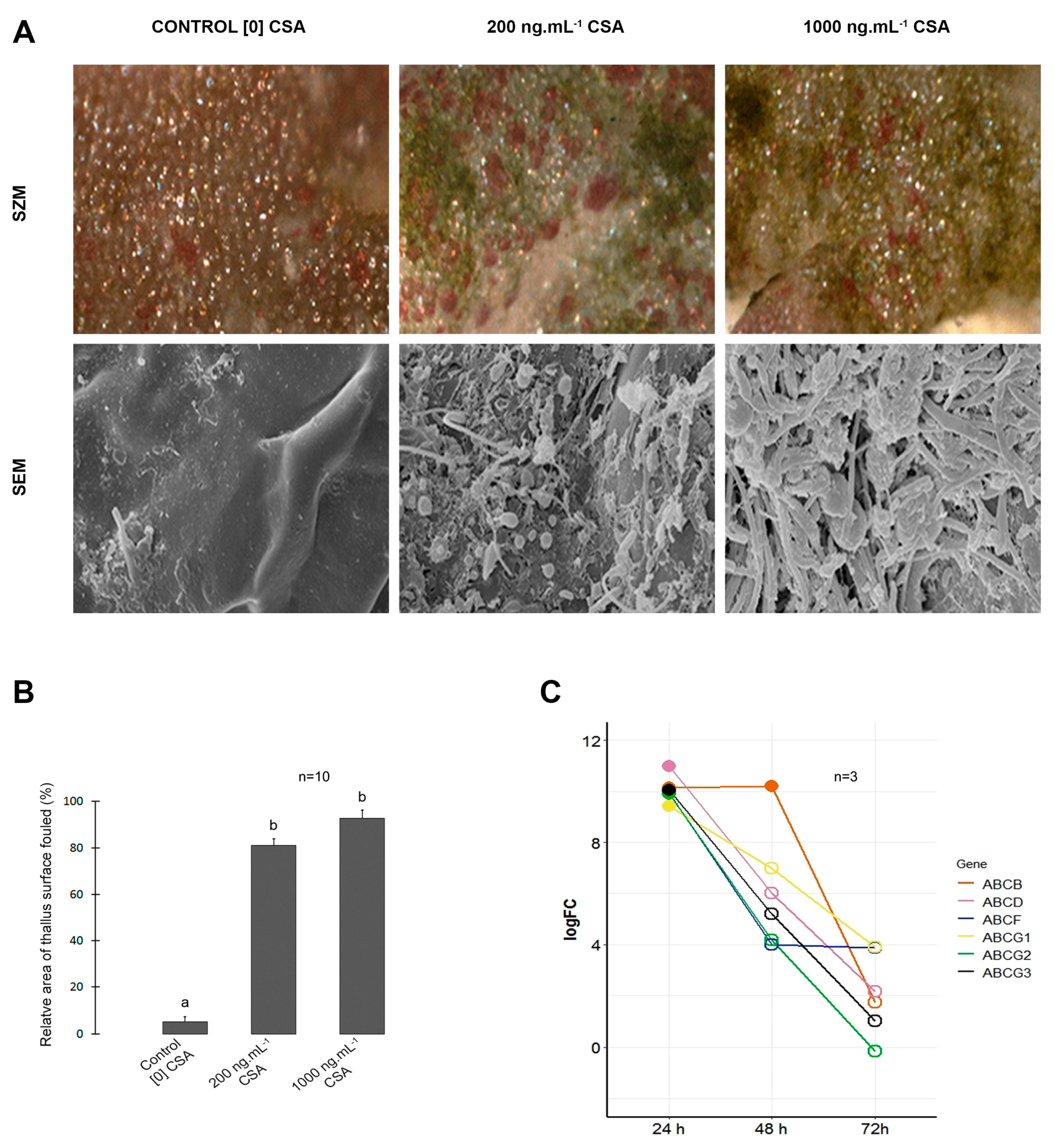
Figure 1D). The relative surface area of
L. dendroidea thalli covered by biofouling increased from ~ 5% in control samples to ~ 80% in low CSA and ~ 90 % in high CSA treatments (
Figure 2A,B).
Genes coding for the following subfamilies of ABC proteins were up-regulated in
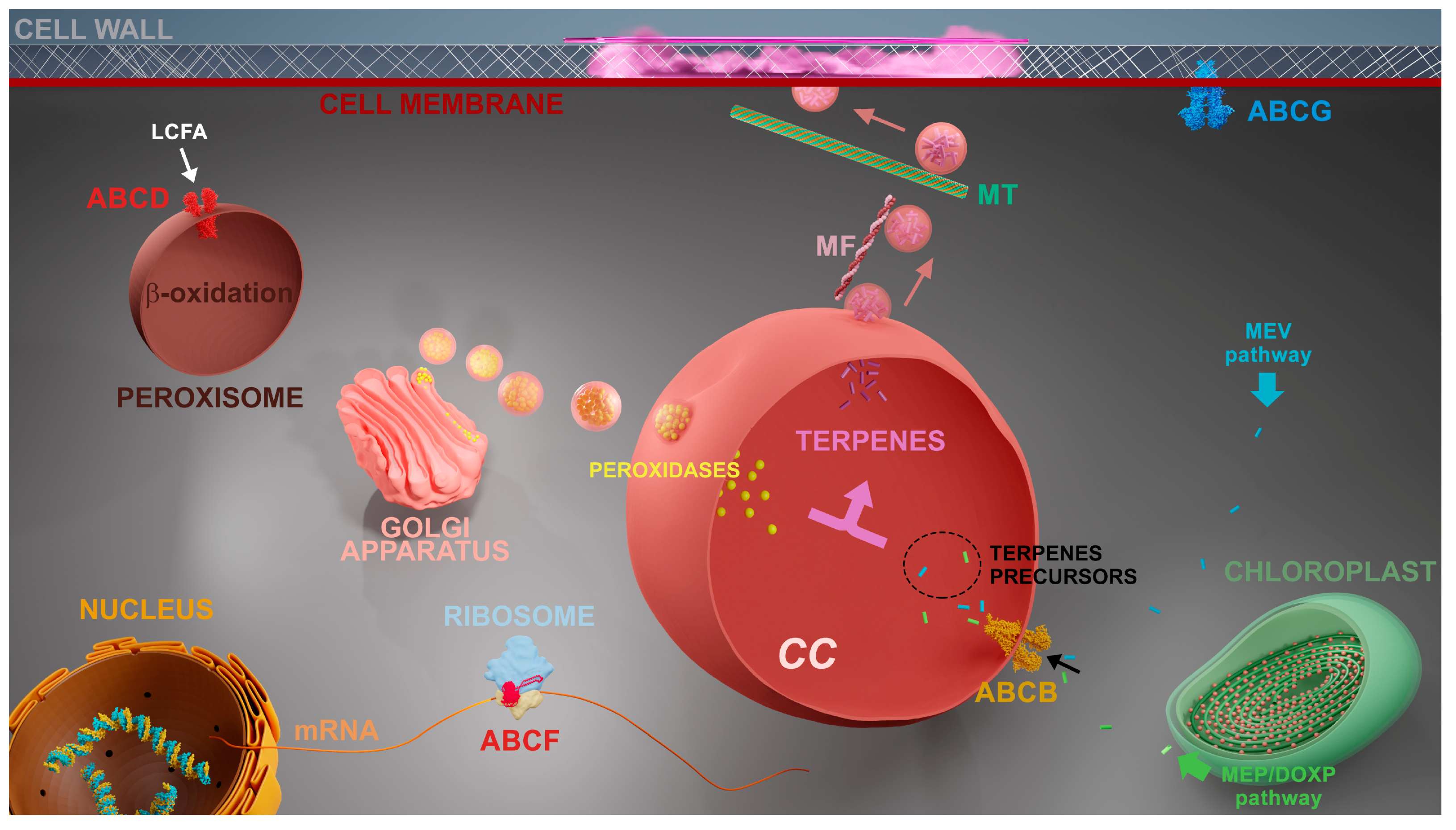
L. dendroidea 24 h after the inoculation by marine pathogenic bacteria: ABCB, ABCD, ABCF and ABCG. Three different ABCG genes were up-regulated 24 h after bacterial inoculation, named ABCG1, ABCG2 and ABCG3. The overexpression of the gene coding for ABCB transporter was also observed 48 h post inoculation (Fig 2C). The cytological and molecular evidences presented here were combined with previous knowledge to propose a cellular model regarding the chemical defense mechanisms in
L. dendroidea (
Figure 3).
4. Discussion
The ability of seaweeds to store secondary metabolites in specialized vesicles provides protection against cell auto-toxicity [
19] and allows the regulated release of defensive compounds in response to stimulus – fouling colonization [
9]. The presence of ABC transporters in
corps en cerise (CC) membrane of
L. dendroidea was demonstrated in this study by the compartmentation of Rho 123 in the lumen of this vesicle. Accordingly, this compartmentation ceased after the addition of CSA, which is known to impair the activity of ABC transporters [
20]. Experimental approaches using Rho123 and CSA to locate ABC proteins are often applied and, while providing indirect evidence, are quite efficient. The presence of ABC in
L. dendroidea CC membrane was reiterated due to compromised development of the organelle under the influence of CSA maintained in culture medium. In this sense, the reduced size of CC of cells submitted to higher CSA concentrations indicates that ABC transporters are responsible for the transmembrane transport and accumulation of elatol inside CC, since this organelle is responsible for the storage of such compound [
6].
Moreover, the concentration of elatol in
L. dendroidea trichoblasts reduced after the addition of high concentrations of CSA, which suggests that ABC transporters could also be (indirectly) involved in the biosynthesis of elatol by acting on the compartmentation of biosynthetic intermediates. For instance, vesicle-like intracellular structures, considered to be the precursors of CC, were shown to contain biosynthetic intermediates for terpenoid biosynthesis through the mevalonate pathway in
L. dendroidea [
10]. Consistently, the inhibition of ABC transporters resulted in lower defense amounts against biofouling, as observed by the progressive increase in thallus area biofouled following the increase on CSA concentration.
Furthermore, the presence of a pathogenic marine bacteria induced in
L. dendroidea the overexpression of genes belonging to four ABC subfamilies: ABCB (MDR), ABCD (PMP), ABCF and ABCG (PDR). Recent studies suggested a role for ABCB transporters on monoterpene compartmentation and toxicity tolerance in lavender plants [
21], and on the import of the alkaloid berberine in the plant species
Coptis japonica [
22]. As such, we hypothesize that ABCB transporters could be involved on the accumulation of defensive chemicals inside the CC in
L. dendroidea, but further studies will be necessary to investigate the specific role of ABCB transporters in seaweeds.
The genes coding for ABCD subfamily members are twice more abundant in red seaweed species (Rhodophyta) than in plants [
16], even though their function is still unclear. In plants, these peroxisome-localized transporters are important for long-chain fatty acid metabolism [
23].
Accordingly, the oxidation of fatty acids, was among the up-regulated pathways in
L. dendroidea as a response to pathogenic bacteria, possibly providing alternative sources of energy during biotic stress [
11]. The ABCF subfamily comprises soluble proteins with unknown functions, even in plants. Studies in yeast and humans have indicated an indirect role of ABCF protein in the regulation of stress response factors, by acting on protein synthesis and ribosome assembly [
16]. We suppose that ABCF could be involved in orchestrating biotic stress response in
L. dendroidea, but specific studies in this topic are required. Finally, ABCG proteins are recognized transporters of terpenoid compounds with antimicrobial activities towards plant surface [
15,
24]
. These proteins could be relevant for the exudation of defense compounds in
L. dendroidea, additionally to the well-established vesicle trafficking process [
7]. Considering the high diversity of molecular size and chemical characteristics of secondary metabolites in
L. dendroidea, it is expected that more than one strategy is deployed for intracellular transport and exudation of defense compounds.
In conclusion, the cellular and molecular evidences presented here suggest that ABC transporters play multiple roles in seaweeds chemical defense metabolism, possibly acting on secondary metabolites’ accumulation in vesicles, participating in stress-response signaling and energy metabolism and promoting the delivery of defensive compounds at pathogen or biofouling contact areas. Therefore, this study enhances the comprehension of the complex and dynamic mechanisms involved in seaweed chemical defense. Following a biotechnological perspective, this article presents valuable information for the future heterologous biosynthesis of seaweed secondary metabolites. Even so, the proposed roles for ABC proteins in seaweed should be also investigated through analysis of ABC protein mutants, or overexpression and silencing of ABC proteins through seaweed metabolic engineering. Finally, the results presented here demonstrate that the chemical defense mechanisms in seaweeds and land plants are more similar than known so far, despite 400 million years of distinct and independent evolutionary histories.
Supplementary Materials
The following supporting information can be downloaded at the website of this paper posted on Preprints.org.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, L.T.S., L.S.O. and F.L.T; methodology, L.T.S, L.S.O., J.E.L., V.M.R. and D.B.S..; validation, L.T.S., L.S.O. and R.C.P.; formal analysis, L.T.S., V.M.R., D.B.S., J.E.L. and L.S.O.; investigation, L.S.O.; D.B.S.; J.E.L. and V.M.R; resources, L.T.S., F.L.T. and R.C.P.; data curation, L.S.O., V.M.R. and J.E.L.; writing—original draft preparation, L.T.S., L.S.O. and R.C.P.; writing—review and editing, L.T.S., L.S.O. and R.C.P.; supervision, L.T.S., R.C.P. and F.L.T; project administration, L.T.S., F.L.T. and R.C.P.; funding acquisition, L.T.S., F.L.T. and R.C.P. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research was funded by Fundação de Amparo à Pesquisa do Estado do Rio de Janeiro, grant number E-26/202.589/2019.
Institutional Review Board Statement
Not applicable.
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Harizani, M.; Ioannou, E.; Roussis, V. The Laurencia paradox: an endless source of chemodiversity. Prog. Chem. Org. Nat. Prod. 2016, 102, 91–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudatti, D.B; Rodrigues, S.V.; Pereira, R.C. Quantitative GC-ECD analysis of halogenated metabolites: determination of surface and within-thallus elatol of Laurencia obtusa. J. Chem. Ecol. 2006, 32, 835–843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, N.A.; Cole, L.; De Nys, R.; Steinberg, P.D. Ultrastructure of the gland cells of the red alga Asparagopsis armata (Bonnemaisoniaceae). J. Phycol. 2006, 42, 637–645. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paradas, W.C.; Crespo, T.M.; Salgado, L.T.; Andrade, L.R.; Soares, A.R.; Hellio, C.; Paranhos, R.R.; Hill, L.J.; Souza, G.M.; Kelecom, A.G.A.C.; et al. Mevalonosomes: specific vacuoles containing the mevalonate pathway in Plocamium brasiliense cortical cells (Rhodophyta). J. Phycol. 2015, 51, 225–235. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, D.N.; Howard, B.M.; Fenical, W. Subcellular localization of brominated secondary metabolites in the red alga Laurencia snyderae. J. Phycol. 1980, 16, 182–185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Salgado, L.T.; Viana, N.B.; Andrade, L.R.; Leal, R.N.; Da Gama, B.A.P.; Pereira, R.C.; Amado Filho, G.M. Intra-cellular storage, transport and exocytosis of halogenated compounds in marine red alga Laurencia obtusa. J. Struct. Biol. 2008, 162, 345–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reis, V.M.; Oliveira, L.S.; Passos, R.M.F.; Viana, N.B.; Mermelstein, C.; Sant’Anna, C.; Pereira, R.C.; Paradas, W.C.; Thompson, F.L.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; et al. Traffic of secondary metabolites to cell surface in the red alga Laurencia dendroidea depends on a two-step transport by the cytoskeleton. PLoS One 2018, 8, e63929. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sudatti, D.B.; Rodrigues, S.V.; Coutinho, R.; Da Gama, B.A.P.; Salgado, L.T.; Amado-Filho, G.M.; Pereira, R.C. Transport and defensive role of elatol at the surface of the red seaweed Laurencia obtusa (Ceramiales, Rhodophyta). J. Phycol. 2008, 44, 584–591. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Paradas, W.C.; Salgado, L.T.; Sudatti, D.B.; Crapez, M.A.; Fujii, M.T.; Coutinho, R.; Pereira, R.C.; Amado Filho, G.M. Induction of halogenated vesicle transport in cells of the red seaweed Laurencia obtusa. Biofouling 2010, 26, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oliveira, L.S.; Tschoeje, D.A.; Oliveira, A.S.; Hill, L.J.; Paradas, W.C.; Salgado, L.T.; Thompson, C.C.; Pereira, R.C.; Thompson, F.L. New Insights on the terpenome of the red seaweed Laurencia dendroidea (Florideophyceae, Rhodophyta). Mar. Drugs 2015, 13, 879–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oliveira, L.S.; Tschoeke, D.A.; Lopes, A.C.R.M.; Sudatii, D.B.; Meirelles, P.M.; Thompson, C.C.; Pereira, R.C.; Thompson, F.L. Molecular mechanisms for microbe recognition and defense by the red seaweed Laurencia dendroidea. MSphere 2017, 2, e00094–17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brito, F.R.; Martinoia, E. The vacuolar transportome of plant specialized metabolites. Plant Cell Physiol. 2018, 59, 1326–1336. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrier, P.J.; Bird, D.; Burla, B.; Dassa, E.; Forestier, C.; Geisler, M.; Klein, M.; Kolukisaoglu, U.; Lee, Y.; Martinoia, E.; et al. Plant ABC proteins - a unified nomenclature and updated inventory. Trends Plant Sci. 2008, 13, 151–159. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.U.; Song, W.-Y.; Hong, D.; Ko, D.; Yamaoka, Y.; Jang, S.; Yim, S.; Lee, E.; Khare, D.; Kim, K.; et al. Plant ABC transporters enable many unique aspects of a terrestrial plant’s lifestyle. Mol. Plant. 2016, 9, 338–355. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shitan, N. Secondary metabolites in plants: Transport and self-tolerance mechanisms. Biosci. Biotechnol. Biochem. 2016, 80, 1283–1293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lane, T.S.; Rempe, C.S.; Davitt, J.; Station, M.E.; Peng, Y.; Soltis, D.E.; Melkonian, M.; Deyholos, M.; Leebens-Mack, C.M.; Rothfels, C.J.; et al. Diversity of ABC transporter genes across the plant kingdom and their potential utility in biotechnology. BMC Biotechnol. 2016, 16, 47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ritter, A.; Dittami, S.M.; Goultquer, S.; Correa, J.A.; Boyen, C.; Potin, P.; Tonon, T. Transcriptomic and metabolomic analysis of copper stress acclimation in Ectocarpus siliculosus highlights signaling and tolerance mechanisms in brown algae. BMC Plant Biol. 2014, 14, 116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fierro, C.; Lópes-Cristoffanini, C.; Meynard, A.; Lovazzano, C.; Castañeda, F.; Guajardo, E.; Conttreras-Porcia, L. Expression profile of desiccation tolerance factors in intertidal seaweed species during the tidal cycle. Planta 2017, 245, 1149–1164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sudatti, D.B.; Duarte, H.M.; Soares, A.R.; Salgado, L.T.; Pereira, R.C. New ecological role of seaweed secondary metabolites as autotoxic and allelopathic. Front. Plant Sci. 2020, 11, 347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qadir, M.; O’Loughlin, K.L.; Fricke, S.M.; Williamson, N.A.; Greco, W.R.; Minderman, H.; Baer, M.R. Cyclosporin A is a broad-spectrum multidrug resistance modulator. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 2320–2326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Demissie, Z.A.; Tarnowycz, M.; Adai, A.M.; Sarjer, L. A lavender ABC transporter confers resistance to monoterpene toxicity in yeast. Planta 2019, 249, 139–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otani, M.; Shitan, N.; Sakai, K.; Martinoia, E.; Sato, F.; Yazaki, K. Characterization of vacuolar transport of the endogenous alkaloid berberine in Coptis japonica. Plant Physiol. 2005, 138, 1939–1946. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Charton, L.; Plett, A.; Linka, N. Plant peroxisomal solute transporter proteins. J. Integr. Plant Biol. 2019, 61, jipb–12790. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lefèvre, F.; Boutry, M. Towards identification of the substrates of ATP-binding cassette transporters. Plant Physiol. 2018, 178, 18–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Forster, S.; Thumser, A.E.; Hood, N.; Plant, N. Characterization of Rhodamine-123 as a tracer dye for use in in vitro drug transport assays. PLoS One 2012, 7, e33253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schindelin, J.; Rueden, C.T.; Hiner, M.C.; Eliceiri, K.W. The ImageJ ecosystem: An open platform for biomedical image analysis. Mol. Rep. Dev. 2015, 82, 518–529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira, A.P.B.; Duytschaever, G.; Tonon, L.A.C.; Dias, G.M.; Mesquita, M.; Cnockaert, M.; Francini-Filho, R.B.; De Vos, P.; Thompson, C.C.; Thompson, F.L. Vibrio madracius sp. nov. isolated from Madracis decactis (Scleractinia) in St Peter & St Paul Archipelago, Mid-Atlantic Ridge, Brazil. Curr. Microbiol. 2014, 69, 405–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grabherr, M.G.; Haas, B.J.; Yassour, M.; Levin, J.Z; Thomspn, D.A.; Amit, I.; Adiconis, X.; Fan, L.; Raychowdhury, R.; Zeng, Q.; et al. Full-length transcriptome assembly from RNA-Seq data without a reference genome. Nat. Biotechnol. 2011, 29, 644–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Finn, R.D.; Clements, J.; Eddy, S.R. HMMER web server: interactive sequence similarity searching. Nucleic Acids Res. 2011, 39, W29–W37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langmead, B.; Salzberg, S.L. Fast gapped-read alignment with Bowtie 2. Nat Methods 2012, 9, 357–359. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Robinson, M.D.; McCarthy, D.J.; Smyth, G.K. EdgeR: a Bioconductor package for differential expression analysis of digital gene expression data. Bioinformatics 2010, 139–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).