Submitted:
12 July 2023
Posted:
13 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
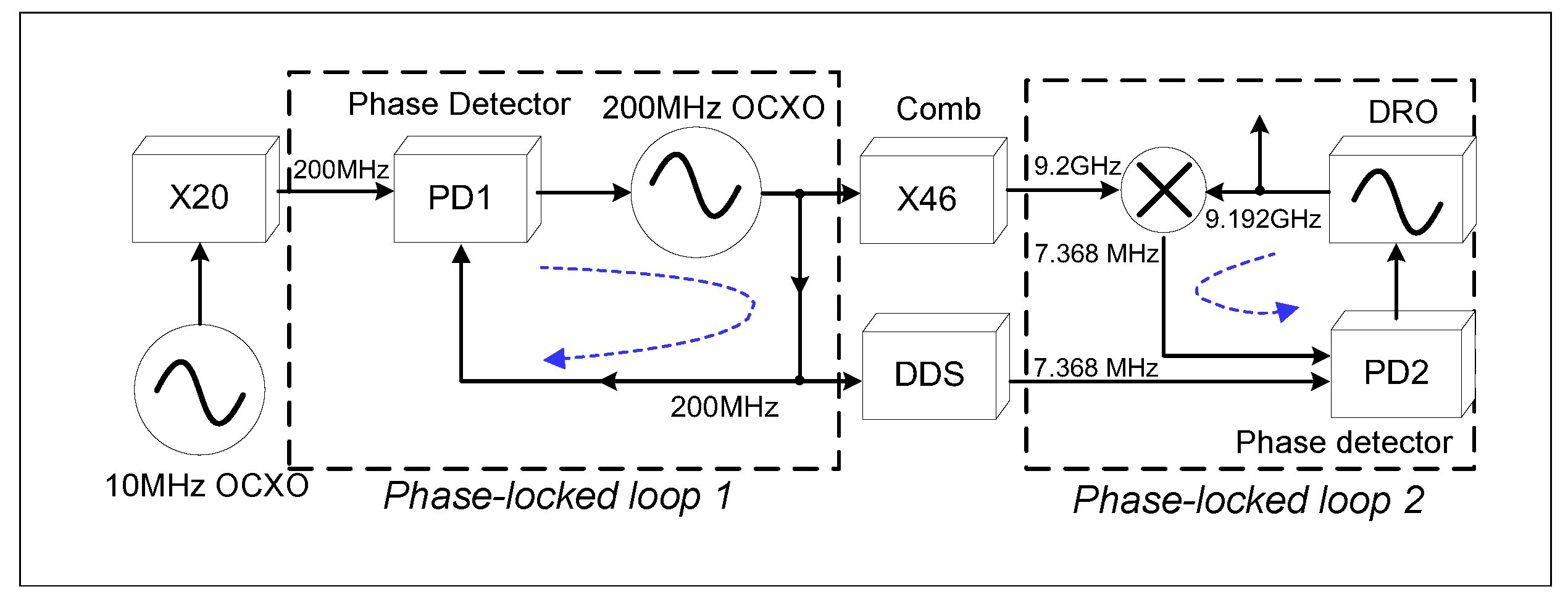
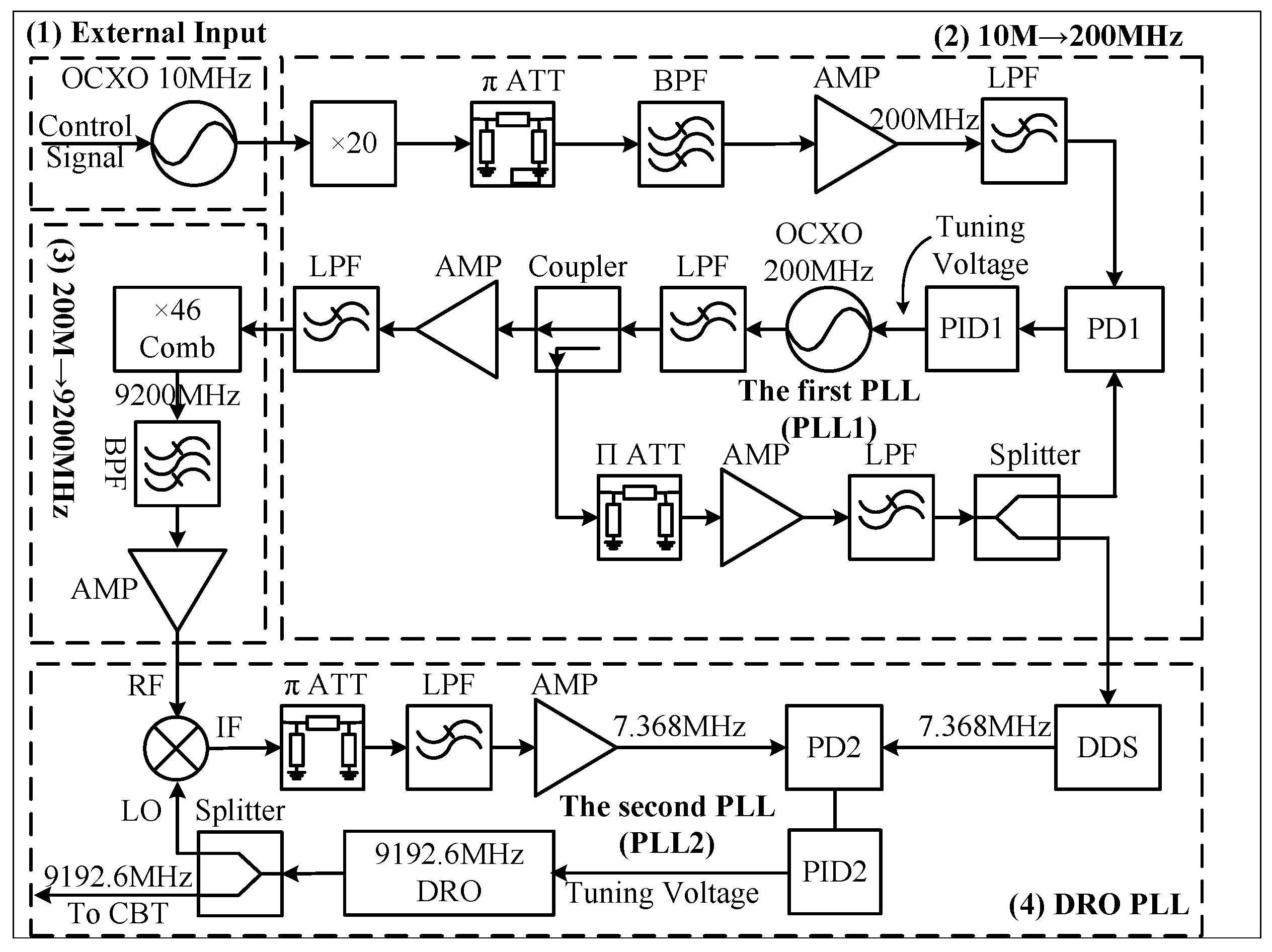
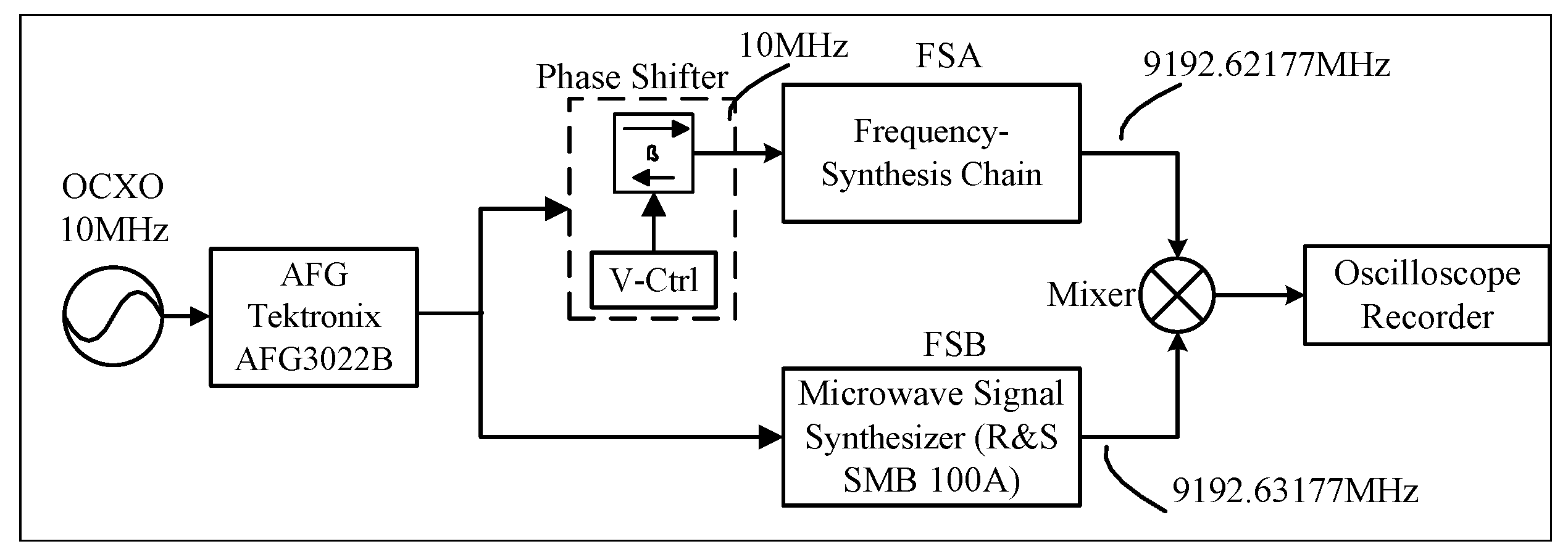
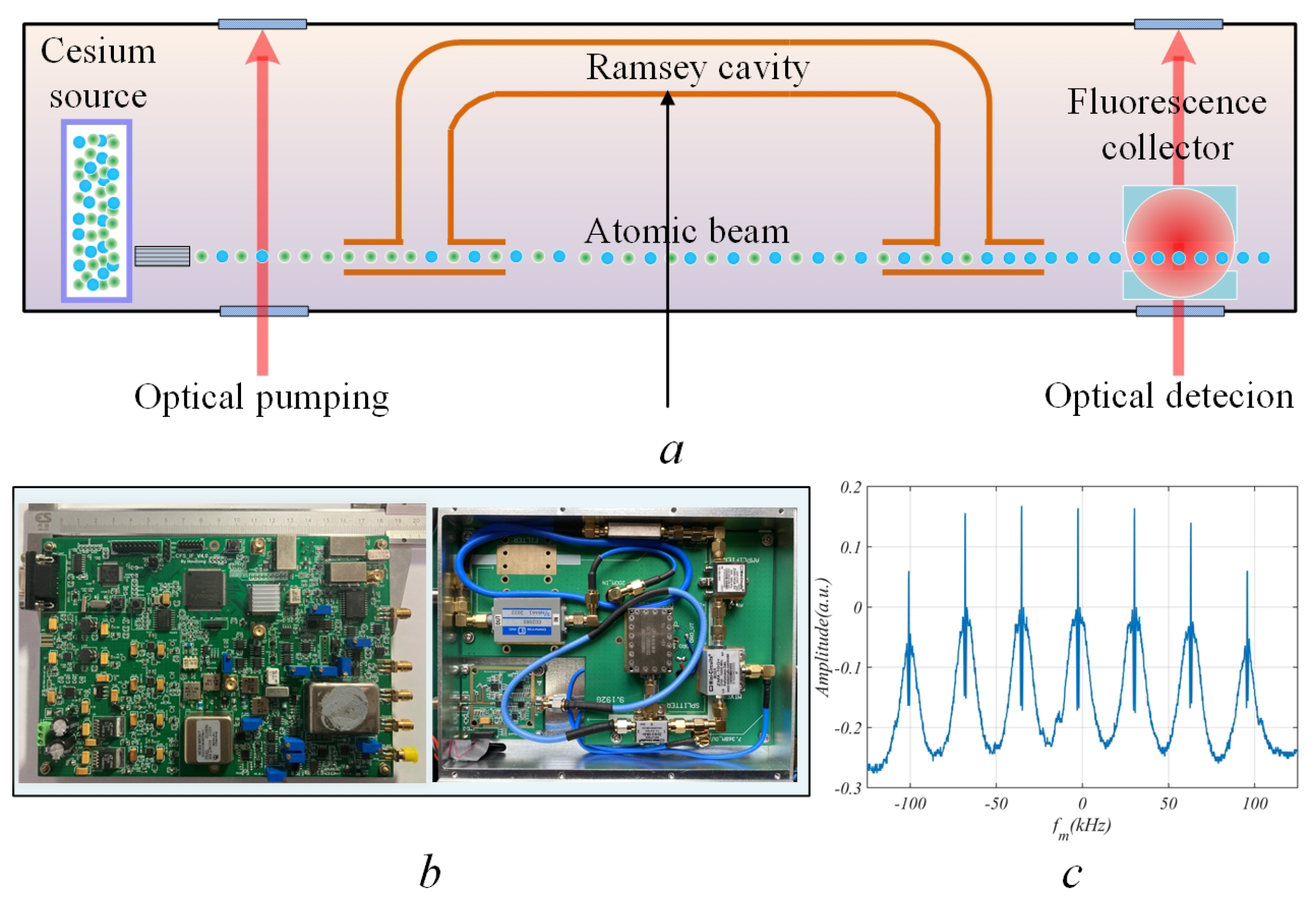
2. Schematic and Experimental Setup og the Frequency-Synthesis Chain
3. Theoretical Analysis and Simulation of the Frequency-Synthesis Chain
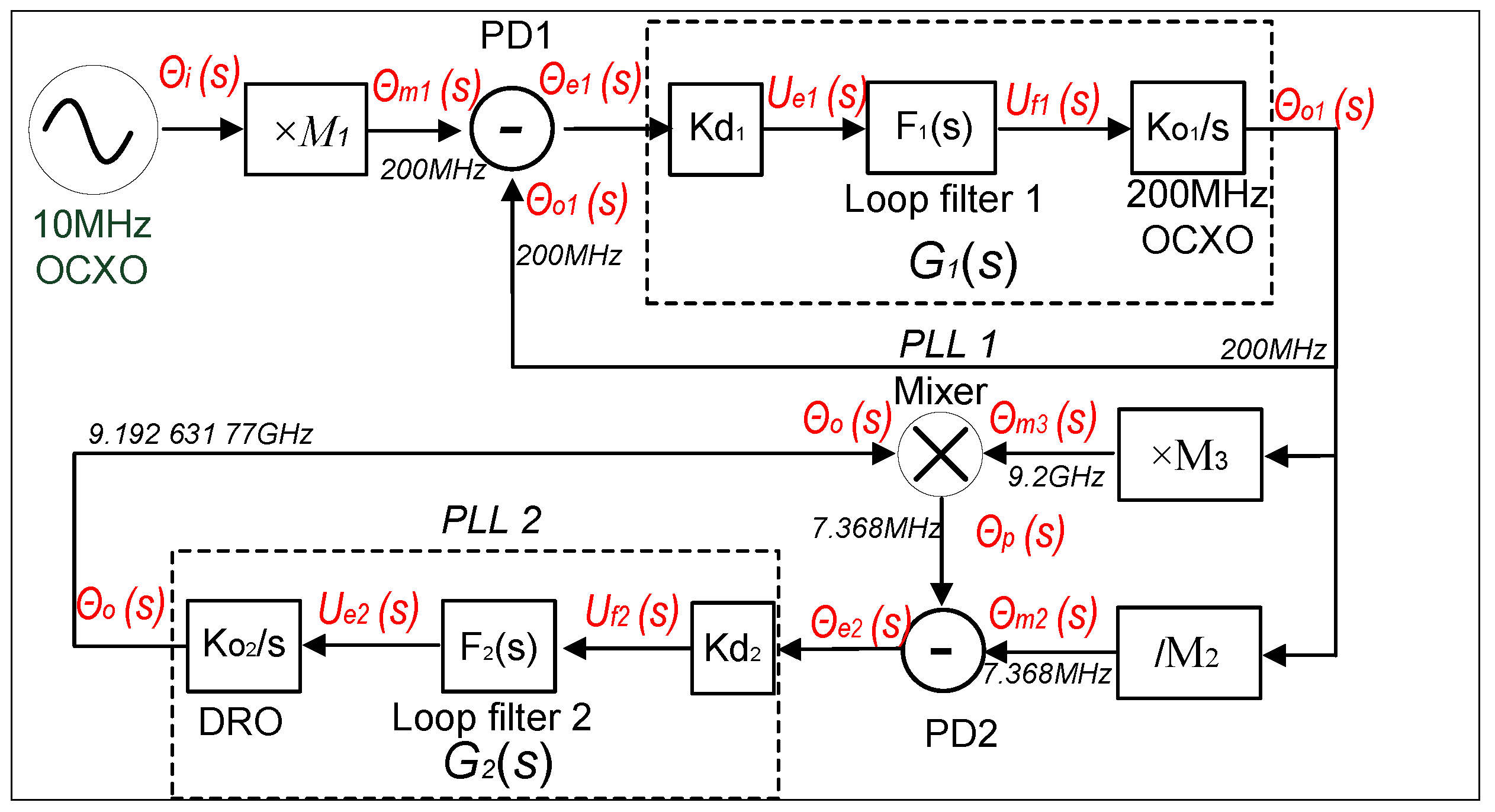
3.1. Analysis of the model for the PLLs
3.2. Simulation results
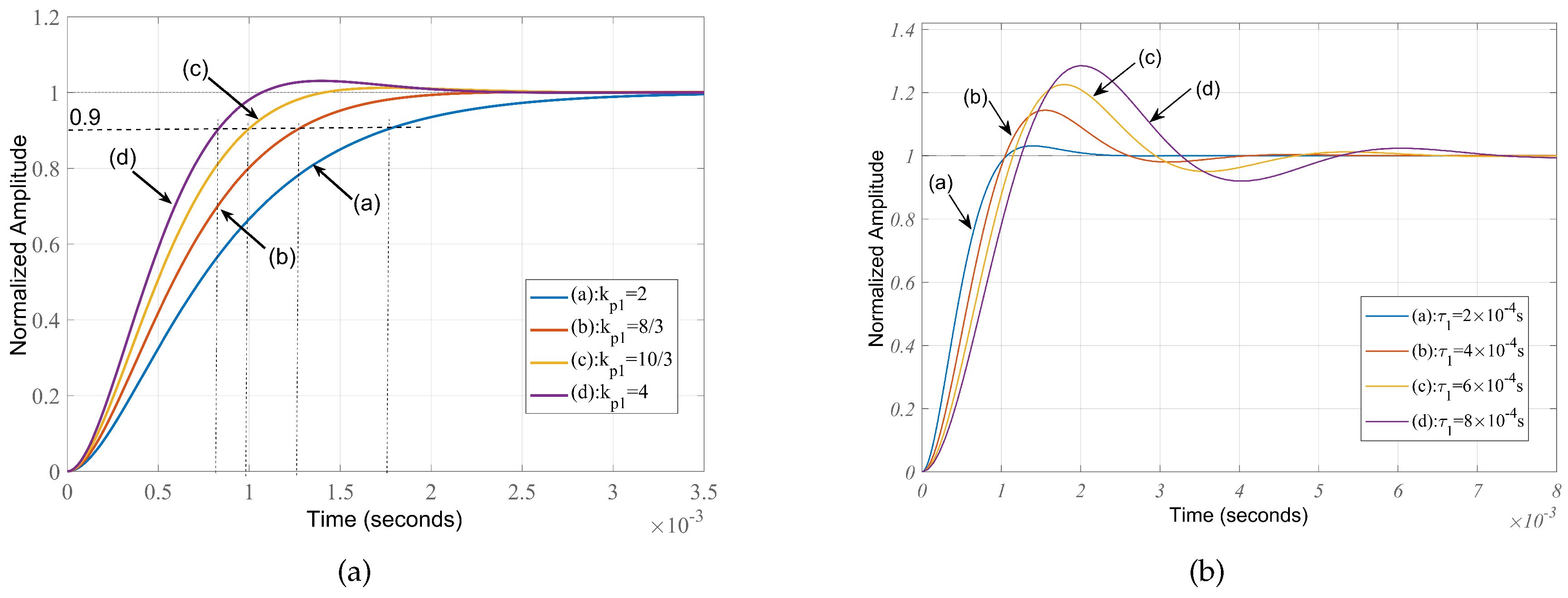
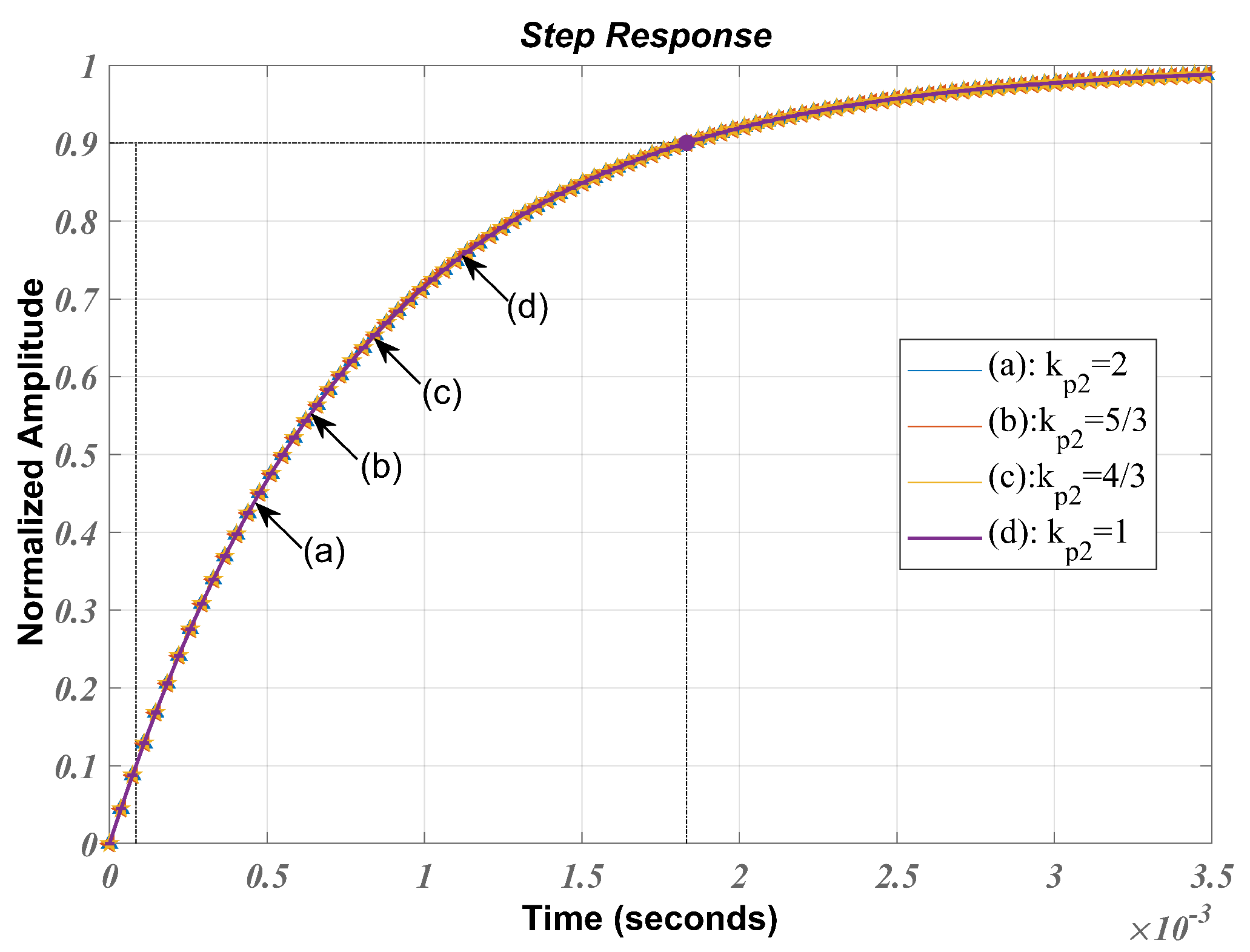
3.2.1. Transient analysis
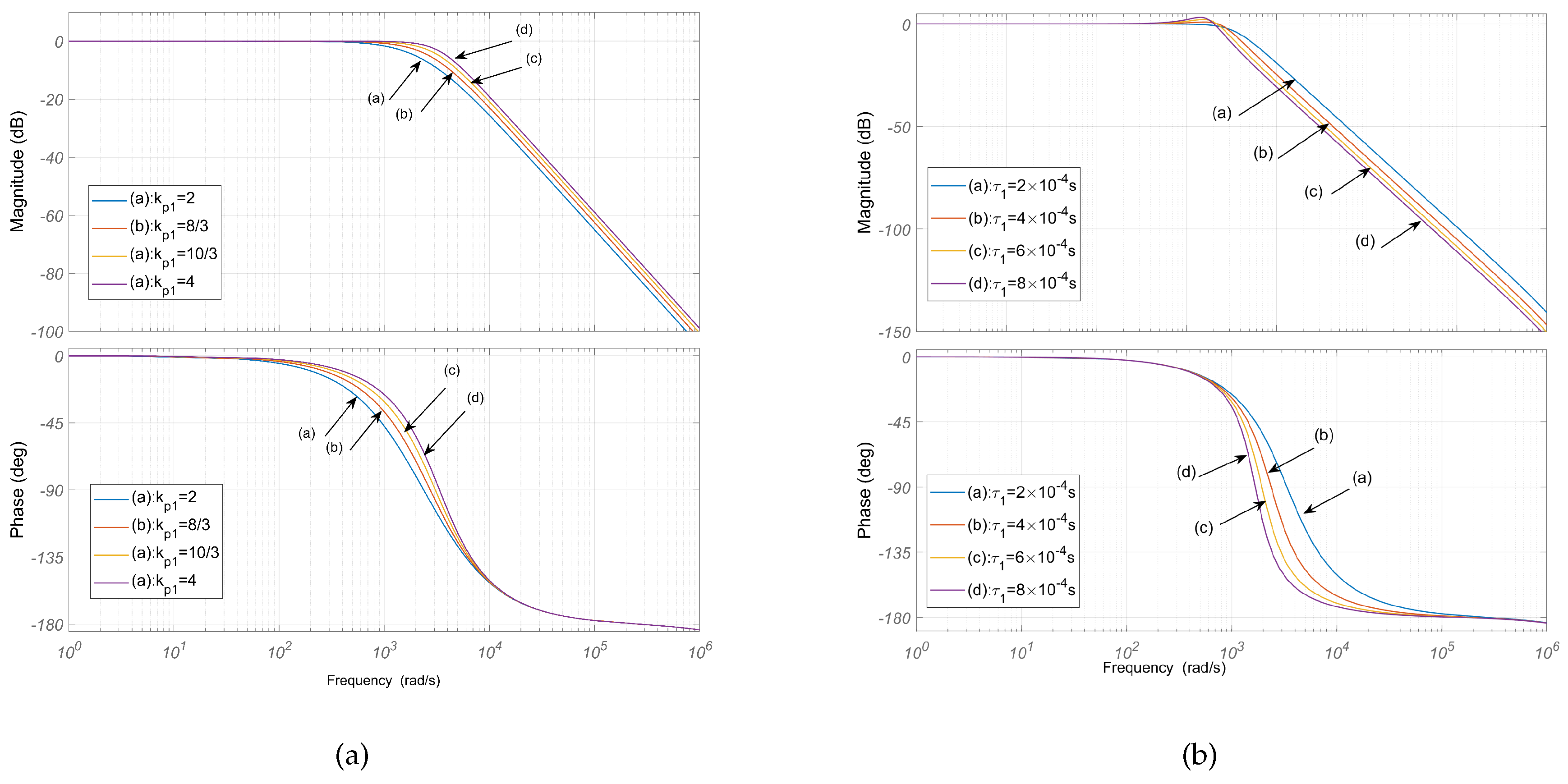
3.2.2. Stability analysis
4. Experimental Results and Verification
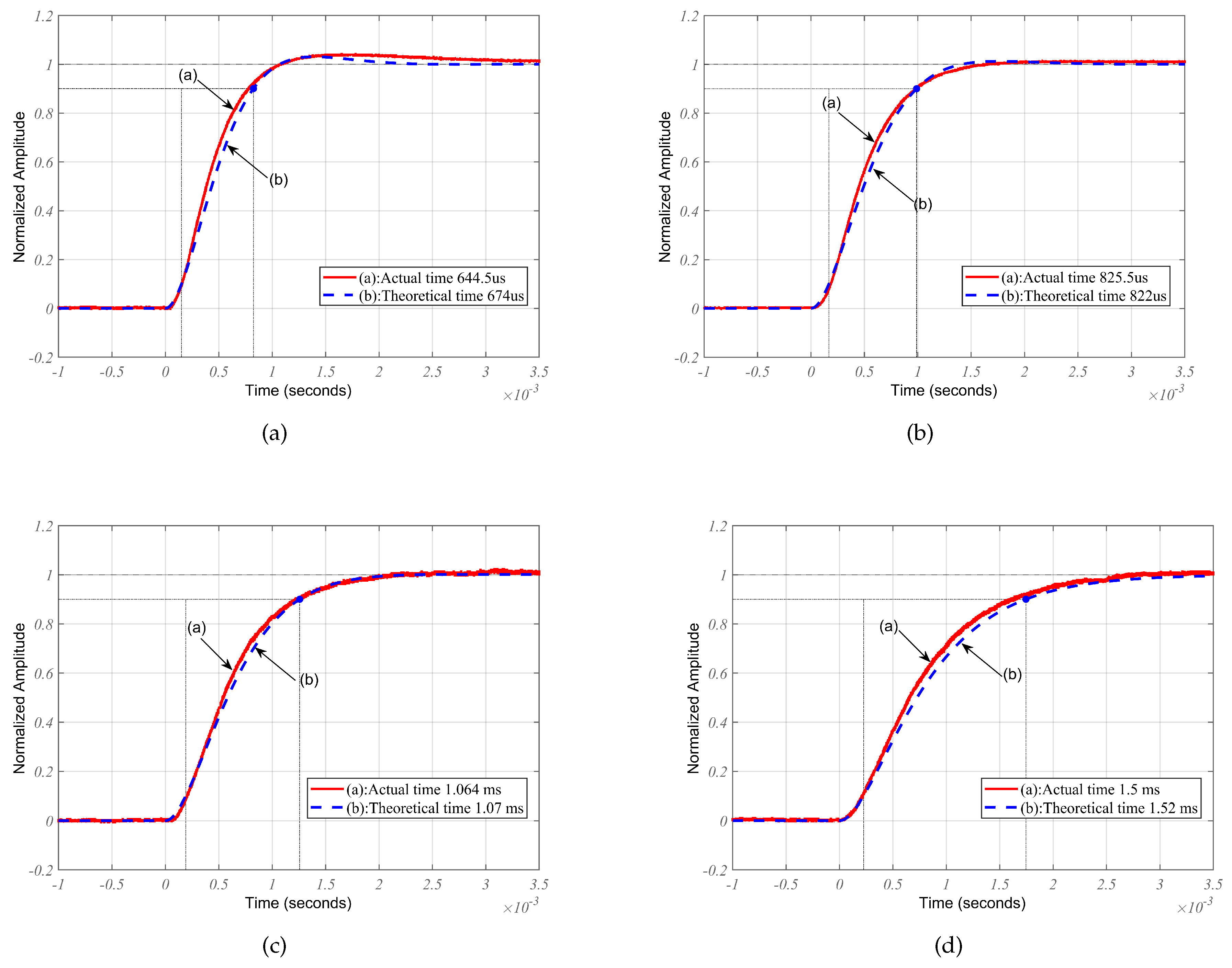
4.1. Settling time measurement
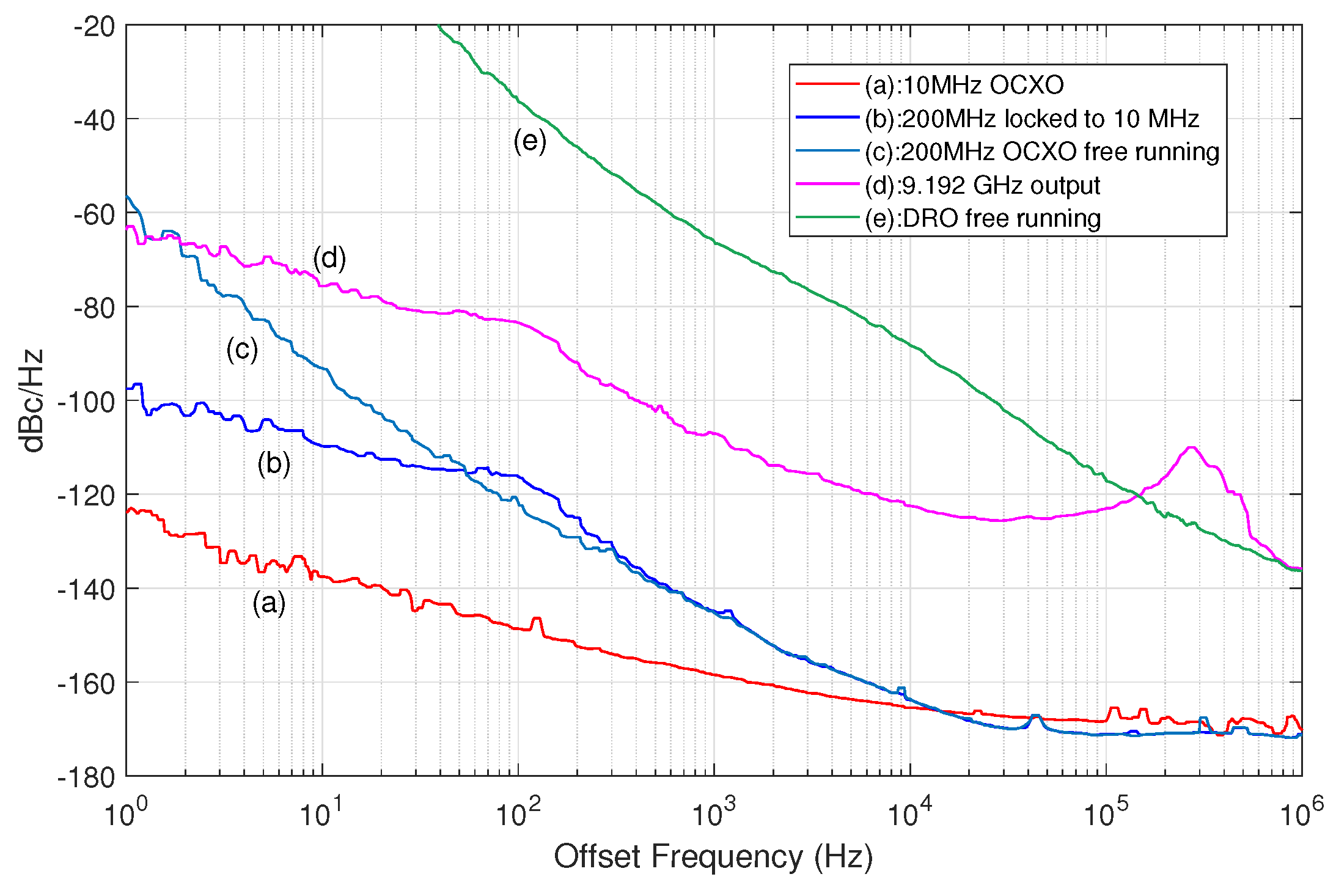
4.2. Phase noise measurement
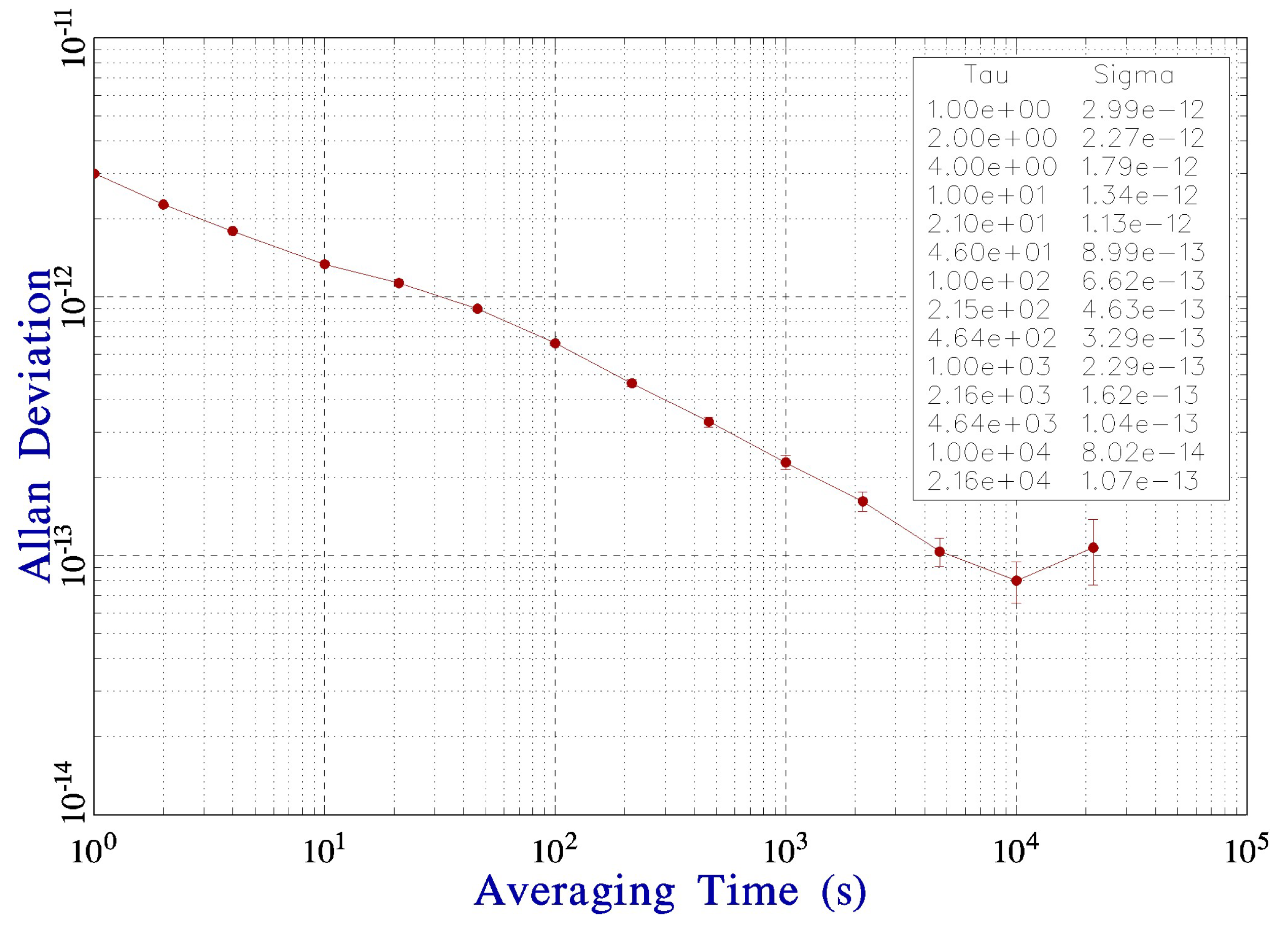
4.3. Frequency Stability measurement
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Gill, P. Raising the standards. Science 2001, 294, 1666–1668. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mohr, P.J.; Newell, D.B.; Taylor, B.N.; Tiesinga, E. Data and analysis for the CODATA 2017 special fundamental constants adjustment. Metrologia 2018, 55, 125–146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lodewyck, J. On a definition of the SI second with a set of optical clock transitions. Metrologia 2019, 56, 055009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, C.; Sun, F.; Liu, J.; Li, X.; Ma, J.; Guo, G.; Hou, D.; Zhang, S. Non 0–0 states magnetically insensitive transitions in alkali species. Physica Scripta 2020, 95, 045402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hafele, J.C.; Keating, R.E. Around-the-world atomic clocks: Observed relativistic time gains. Science 1972, 177, 168–170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McGrew, W.; Zhang, X.; Fasano, R.; Schäffer, S.; Beloy, K.; Nicolodi, D.; Brown, R.; Hinkley, N.; Milani, G.; Schioppo, M.; et al. Atomic clock performance enabling geodesy below the centimetre level. Nature 2018, 564, 87–90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, Q.; Zhou, M.; Han, C.; Li, S.; Zhang, S.; Yao, Y.; Li, B.; Qiao, H.; Ai, D.; Lou, G.; et al. Systematic evaluation of a 171Yb optical clock by synchronous comparison between two lattice systems. Scientific Reports 2018, 8, 8022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Oelker, E.; Hutson, R.; Kennedy, C.; Sonderhouse, L.; Bothwell, T.; Goban, A.; Kedar, D.; Sanner, C.; Robinson, J.; Marti, G.; et al. Demonstration of 4.8× 10- 17 stability at 1 s for two independent optical clocks. Nature Photonics 2019, 13, 714–719. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brewer, S.M.; Chen, J.S.; Hankin, A.M.; Clements, E.R.; Chou, C.w.; Wineland, D.J.; Hume, D.B.; Leibrandt, D.R. Al+ 27 quantum-logic clock with a systematic uncertainty below 10- 18. Physical review letters 2019, 123, 033201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bothwell, T.; Kedar, D.; Oelker, E.; Robinson, J.M.; Bromley, S.L.; Tew, W.L.; Ye, J.; Kennedy, C.J. JILA SrI optical lattice clock with uncertainty of. Metrologia 2019, 56, 065004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Świerad, D.; Häfner, S.; Vogt, S.; Venon, B.; Holleville, D.; Bize, S.; Kulosa, A.; Bode, S.; Singh, Y.; Bongs, K.; et al. Ultra-stable clock laser system development towards space applications. Scientific Reports 2016, 6, 33973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Antypas, D.; Tretiak, O.; Garcon, A.; Ozeri, R.; Perez, G.; Budker, D. Scalar dark matter in the radio-frequency band: atomic-spectroscopy search results. Physical Review Letters 2019, 123, 141102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sanner, C.; Huntemann, N.; Lange, R.; Tamm, C.; Peik, E.; Safronova, M.S.; Porsev, S.G. Optical clock comparison for Lorentz symmetry testing. Nature 2019, 567, 204–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kazda, M.; Gerginov, V.; Lipphardt, B.; Weyers, S. Microwave Synthesis for the PTB Cesium Fountain Clocks. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2019, 69, 3711–3718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlquist, R.K. A new RF architecture for cesium frequency standards. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 1992 IEEE Frequency Control Symposium. IEEE; 1992; pp. 134–142. [Google Scholar]
- Cutler, L.S.; Giffard, R.P. Architecture and algorithms for new cesium beam frequency standard electronics. In Proceedings of the Proceedings of the 1992 IEEE Frequency Control Symposium. IEEE; 1992; pp. 127–133. [Google Scholar]
- Francois, B.; Calosso, C.; Danet, J.; Boudot, R. A low phase noise microwave frequency synthesis for a high-performance cesium vapor cell atomic clock. Review of Scientific Instruments 2014, 85, 094709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- François, B.; Calosso, C.; Abdel Hafiz, M.; Micalizio, S.; Boudot, R. Simple-design ultra-low phase noise microwave frequency synthesizers for high-performing Cs and Rb vapor-cell atomic clocks. Review of Scientific Instruments 2015, 86, 094707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audoin, C. A limit to the frequency stability of passive frequency standards due to an intermodulation effect. IEEE Trans. Instrum Meas. 1991, 40, 121–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ju, B.; Yun, P.; Hao, Q.; Nie, S.; Liu, G. A low phase and amplitude noise microwave source for vapor cell atomic clocks. Review of Scientific Instruments 2022, 93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Danet, J.M.; Lours, M.; Guérandel, S.; De Clercq, E. Dick effect in a pulsed atomic clock using coherent population trapping. IEEE Transactions on Ultrasonics, Ferroelectrics, and Frequency Control 2014, 61, 567–574. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.B.; Hao, Q.; Du, Y.B.; Huang, S.Q.; Yun, P.; Lu, Z.H. Demonstration of a sub-sampling phase lock loop based microwave source for reducing dick effect in atomic clocks. Chinese Physics Letters 2019, 36, 070601. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petrov, A.; Davydov, V. Digital frequency synthesizer for 133 Cs-vapor atomic clock. Journal of Communications Technology and Electronics 2017, 62, 289–293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boudot, R.; Guérandel, S.; De Clercq, E. Simple-design low-noise NLTL-based frequency synthesizers for a CPT Cs clock. IEEE Transactions on Instrumentation and Measurement 2009, 58, 3659–3665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vanier, J. Atomic clocks based on coherent population trapping: a review. Applied Physics B 2005, 81, 421–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santarelli, G.; Audoin, C.; Makdissi, A.; Laurent, P.; Dick, G.J.; Clairon, A. Frequency stability degradation of an oscillator slaved to a periodically interrogated atomic resonator. IEEE transactions on ultrasonics, ferroelectrics, and frequency control 1998, 45, 887–894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Du, Y.; Li, W.; Ge, Y.; Li, H.; Deng, K.; Lu, Z. Note: A high-frequency signal generator based on direct digital synthesizer and field-programmable gate array. Review of Scientific Instruments 2017, 88, 096103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, K.; Tian, S.; Guo, G.; Xiao, Y. Precisely synchronous and cascadable multi-channel arbitrary waveform generator. Review of Scientific Instruments 2017, 88, 035110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Didier, A.; Millo, J.; Grop, S.; Dubois, B.; Bigler, E.; Rubiola, E.; Lacroûte, C.; Kersalé, Y. Ultra-low phase noise all-optical microwave generation setup based on commercial devices. Applied Optics 2015, 54, 3682–3686. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dick, G.J. Local oscillator induced instabilities in trapped ion frequency standards. In Proceedings of the 19th Annual Precise Time and Time Interval Systems and Applications Meeting; 1989; pp. 133–147. [Google Scholar]
- Nelson, C.W.; Hati, A.; Nava, J.; Howe, D.A. Phase noise suppression in frequency comb generators. In Proceedings of the 2010 IEEE International Frequency Control Symposium; IEEE, 2010; pp. 440–442. [Google Scholar]
- Bin, L. A decision-feedback phase-tracking receiver for continuous phase modulation. IEEE transactions on communications 1997, 45, 396–399. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).



