Submitted:
10 July 2023
Posted:
12 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Ergonomic Challenges
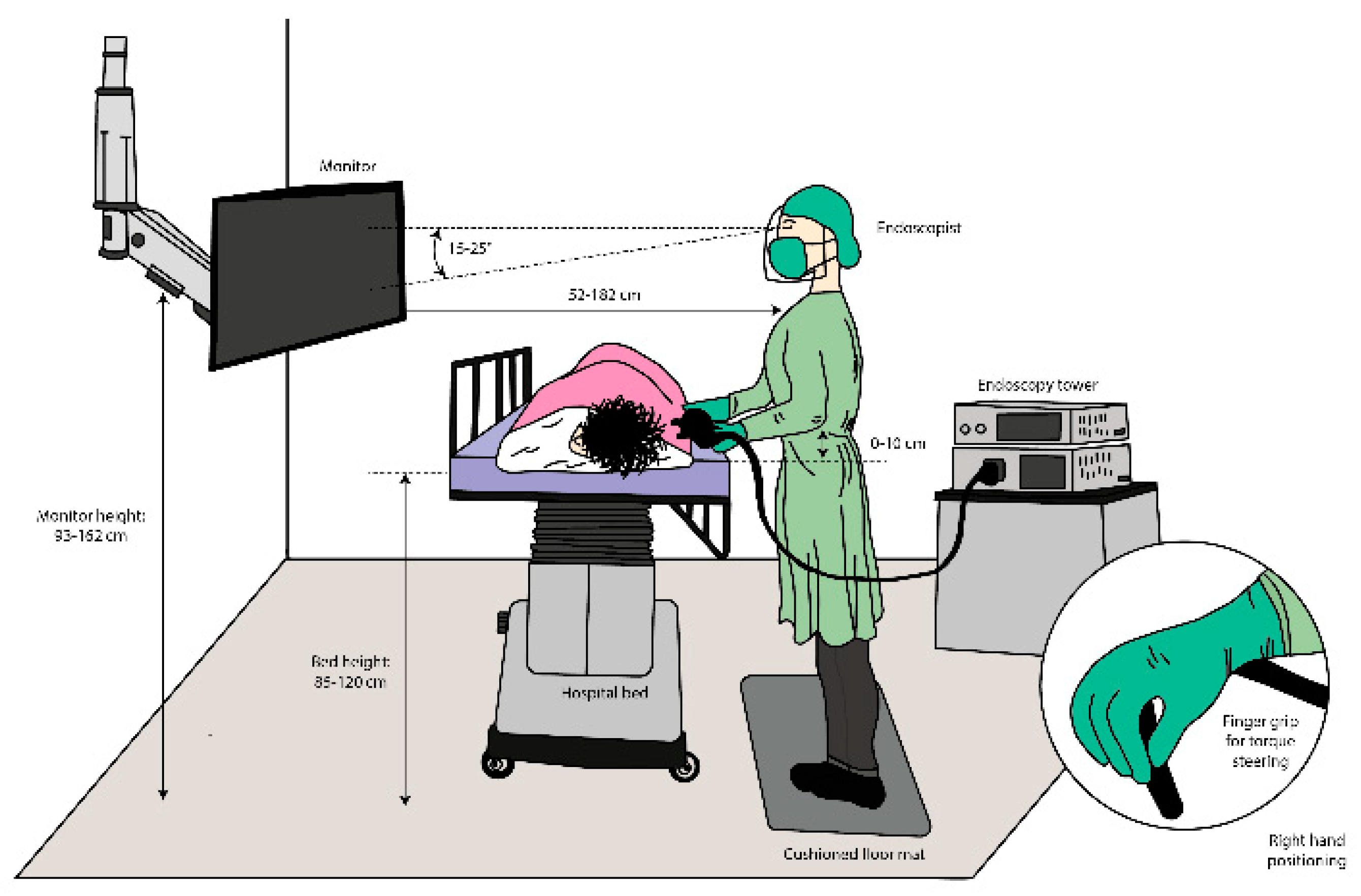
3. General Problem of the Endoscope Layout
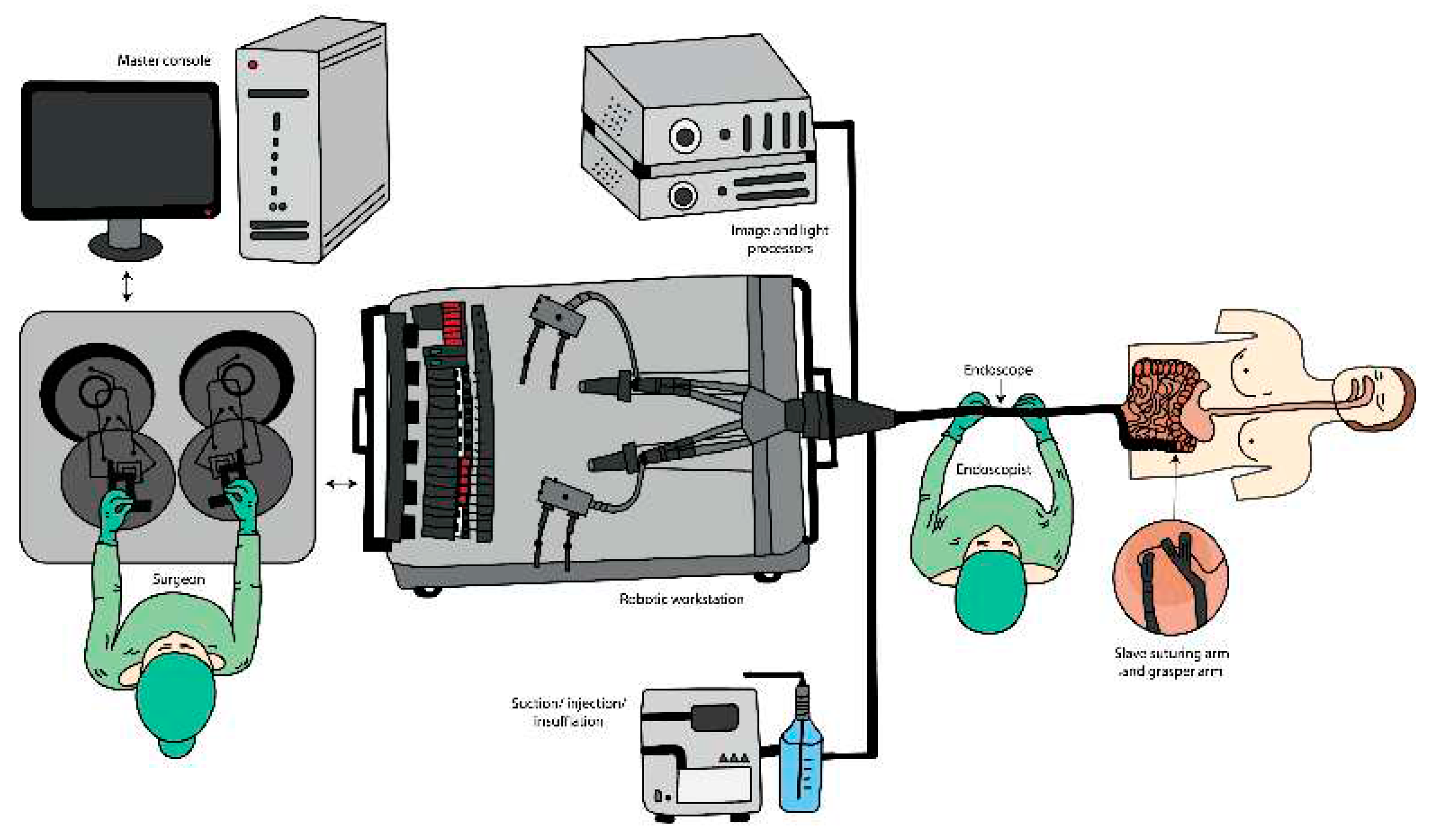
3.1. Robotics
- Platforms capable of high degrees of freedom on forceps manipulation for ESD (endoscopic submucosal dissection) and NOTES (natural orifice transluminal endoscopic surgery).
- Active introduction of the endoscopes to reduce the influence of the operator ability and to reduce the discomfort and pain referred by the patients.
- Endoscopic capsule evolution to use it as screening for GI pathologies and as a therapeutic method[24].
3.2. “Hands-Free” Endoscopy
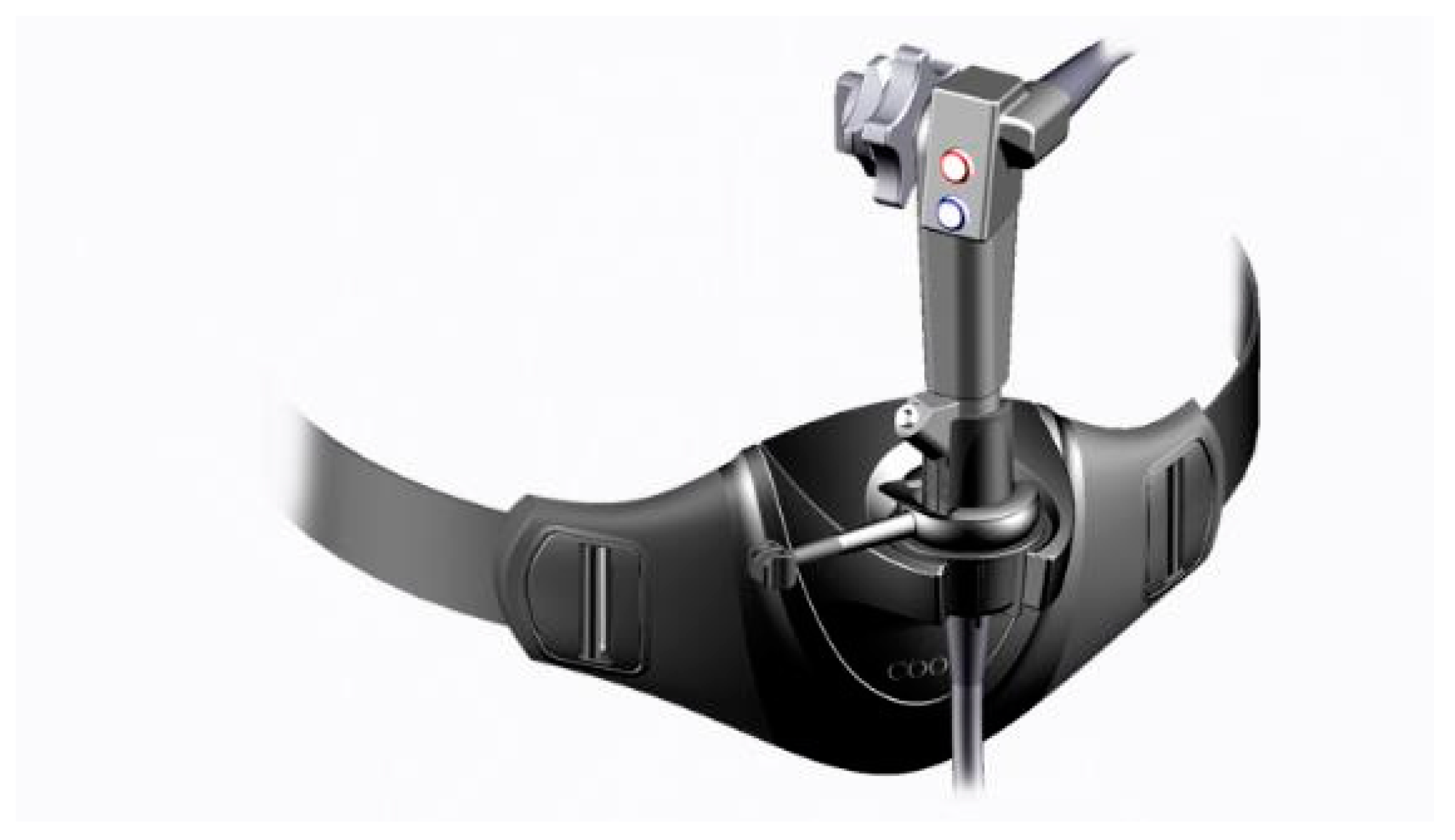
3.3. Personal Care Strategies—Floor Mat and Cushioned Insoles
4. Discussion and Conclusions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Shergill AK, Harris Adamson C. Failure of an engineered system: The gastrointestinal endoscope. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2019 Jul 1;21(3):116–23.
- Yung DE, Banfi T, Ciuti G, Arezzo A, Dario P, Koulaouzidis A. Musculoskeletal injuries in gastrointestinal endoscopists: a systematic review. Expert Rev Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2017 Oct 3;11(10):939–47.
- Villa E, Attar B, Trick W, Kotwal V. Endoscopy-related musculoskeletal injuries in gastroenterology fellows. Endosc Int Open. 2019 Jun;07(06):E808–12.
- Austin K, Schoenberger H, Sesto M, Gaumnitz E, Teo Broman A, Saha S. Musculoskeletal Injuries Are Commonly Reported Among Gastroenterology Trainees: Results of a National Survey. Dig Dis Sci. 2019 Jun 1;64(6):1439–47.
- Shergill AK, McQuaid KR, Rempel D. Ergonomics and GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2009 Jul 1;70(1):145–53.
- Siau K, Anderson JT. Ergonomics in endoscopy: Should the endoscopist be considered and trained like an athlete? Endosc Int Open. 2019 Jun;07(6):E813–5.
- Walsh CM, Qayed E, Aihara H, Anand GS, Byrne K, Chahal P, et al. Core curriculum for ergonomics in endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2021 Jun 1;93(6):1222–7.
- Shergill AK, McQuaid KR. Ergonomic endoscopy: An oxymoron or realistic goal? Gastrointest Endosc. 2019 Dec;90(6):966–70.
- Chang MA, Mitchell J, Abbas Fehmi SM. Optimizing ergonomics during endoscopy. VideoGIE. 2017 Apr 10;2(7):170.
- Anderson JT. Optimizing ergonomics during endoscopy training. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2019 Jul 1;21(3):143–9.
- Singla M, Kwok RM, Deriban G, Young PE. Training the Endo-Athlete: An Update in Ergonomics in Endoscopy. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2018 Jul 1;16(7):1003–6.
- Ridtitid W, Coté GA, Leung W, Buschbacher R, Lynch S, Fogel EL, et al. Prevalence and risk factors for musculoskeletal injuries related to endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2015 Feb 1;81(2):294-302.e4.
- Harvin G. Review of Musculoskeletal Injuries and Prevention in the Endoscopy Practitioner. J Clin Gastroenterol. 2014 Aug;48(7):590–4.
- Han S, Hammad HT, Wagh MS. High prevalence of musculoskeletal symptoms and injuries in third space endoscopists: an international multicenter survey. Endosc Int Open. 2020 Oct;08(10):E1481–6.
- Kamani L, Kalwar H. Ergonomic Injuries in Endoscopists and Their Risk Factors. Clin Endosc. 2021 Mar 3;54(3):356–62.
- Shah SZ, Rehman ST, Khan A, Hussain MM, Ali M, Sarwar S, et al. Ergonomics of gastrointestinal endoscopies: Musculoskeletal injury among endoscopy physicians, nurses, and technicians. World J Gastrointest Endosc. 2022 Mar 16;14(3):142–52.
- Anderson J. Colonoscopy: do operator motions and posture count? Endosc Int Open. 2015 Dec;03(6):E627–8.
- Hierarchy of Controls | NIOSH | CDC [Internet]. 2023 [cited 2023 Jul 7]. Available from: https://www.cdc.gov/niosh/topics/hierarchy/default.html.
- Park AE, Zahiri HR, Hallbeck MS, Augenstein V, Sutton E, Yu D, et al. Intraoperative “Micro Breaks” With Targeted Stretching Enhance Surgeon Physical Function and Mental Focus. Ann Surg. 2017 Feb 1;265(2):340–6.
- Baillie J. The endoscope. Gastrointest Endosc. 2007 May 1;65(6):886–93.
- De Groen PC. History of the Endoscope [Scanning Our Past]. Proc IEEE. 2017 Oct;105(10):1987–95.
- Yeung BPM, Chiu PWY. Application of robotics in gastrointestinal endoscopy: A review. World J Gastroenterol. 2016 Feb 7;22(5):1811–25.
- Kume K, Sakai N, Goto T. Development of a novel endoscopic manipulation system: the Endoscopic Operation Robot ver.3. Endoscopy. 2015 Sep;47(09):815–9.
- Visconti TA de C, Otoch JP, Artifon EL de A. Robotic endoscopy. A review of the literature. Acta Cirúrgica Bras [Internet]. 2020 Apr 27 [cited 2022 Jul 11];35. Available from: http://www.scielo.br/j/acb/a/yJT7PtqMn85gC7VkKQHNysL/?format=html&stop=next&lang=en.
- Lim SG. The development of robotic flexible endoscopic platforms. Int J Gastrointest Interv. 2020 Jan 31;9:9–12.
- Li Z, Chiu PWY. Robotic Endoscopy. Visc Med. 2018;34(1):45–51.
- Kim SH, Choi HS, Keum B, Chun HJ. Robotics in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy. Appl Sci. 2021 Nov 30;11:11351.
- Bianchi F, Masaracchia A, Shojaei Barjuei E, Menciassi A, Arezzo A, Koulaouzidis A, et al. Localization strategies for robotic endoscopic capsules: a review. Expert Rev Med Devices. 2019 May 4;16(5):381–403.
- Pullens HJM, Stap N van der, Rozeboom ED, Schwartz MP, Heijden F van der, Oijen MGH van, et al. Colonoscopy with robotic steering and automated lumen centralization: a feasibility study in a colon model. Endoscopy. 2016 Mar;48(03):286–90.
- Kang M, Joe S, An T, Jang H, Kim B. A novel robotic colonoscopy system integrating feeding and steering mechanisms with self-propelled paddling locomotion: A pilot study. Mechatronics. 2021 Feb;73:102478.
- Duric T. Ergonometry in Endoscopic Procedures: Prevention of Musculoskeletal Injuries During Endoscopic Procedures by Using Belt-Like Manouvring Device with Joystick Capabilities. In: Endoscopy [Internet]. Georg Thieme Verlag KG; 2021 [cited 2023 Jan 8]. p. eP193. Available from: http://www.thieme-connect.de/DOI/DOI?10.1055/s-0041-1724689.
- Luttmann A, Jäger M, Laurig W. Electromyographical indication of muscular fatigue in occupational field studies. Int J Ind Ergon. 2000 Jul 1;25(6):645–60.
- Albayrak A, van Veelen MA, Prins JF, Snijders CJ, de Ridder H, Kazemier G. A newly designed ergonomic body support for surgeons. Surg Endosc. 2007 Oct 1;21(10):1835–40.
- Wiggermann N, Keyserling W. Effects of Anti-Fatigue Mats on Perceived Discomfort and Weight-Shifting During Prolonged Standing. Hum Factors. 2013 Aug 1;55:764–75.
- Noor SNAM, Ahmad IN, Wahab NA, Ma’arof MIN. A Review of Studies Concerning Prolonged Standing Working Posture. Adv Eng Forum. 2013;10:131–6.
- King PM. A comparison of the effects of floor mats and shoe in-soles on standing fatigue. Appl Ergon. 2002 Sep 1;33(5):477–84.
- Speed G, Harris K, Keegel T. The effect of cushioning materials on musculoskeletal discomfort and fatigue during prolonged standing at work: A systematic review. Appl Ergon. 2018 Jul 1;70:300–14.
- Korman LY. An ounce of prevention: ergonomic training in GI endoscopy. Gastrointest Endosc. 2020 Nov 1;92(5):1081–2.
- Singh S, Sedlack RE, Cook DA. Effects of Simulation-Based Training in Gastrointestinal Endoscopy: A Systematic Review and Meta-analysis. Clin Gastroenterol Hepatol. 2014 Oct 1;12(10):1611-1623.e4.
- Khanicheh A, Shergill AK. Endoscope design for the future. Tech Gastrointest Endosc. 2019 Jul 1;21(3):167–73.

| Author | Year | Ref. No | Title | Methodology | Key argument |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Harvin | 2014 | [13] | Review of Musculoskeletal Injuries and Prevention in the Endoscopy Practitioner | Systematic review | Strategies for the management of the risk of musculoskeletal injuries related to the practice of endoscopy include compliance with currently recommended ergonomic practices, education of trainees in ergonomic technique when practicing endoscopy, and research toward the modification and development of more ergonomic endoscopes and procedure spaces. |
| Ridtitid et al | 2015 | [12] | Prevalence and risk factors for musculoskeletal injuries related to endoscopy | Survey | Among endoscopists there is a high prevalence of injuries definitely or potentially related to endoscopy. Higher procedure volume, more time doing endoscopy per week, and cumulative years performing endoscopy are associated with more work-related injuries. |
| Yung et al | 2017 | [2] | Musculoskeletal injuries in gastrointestinal endoscopists: a systematic review | Systematic review | Comprehensive investigation into the prevalence, types, pathophysiology and methods to minimise endoscopy-related musculoskeletal injuries is vital to ensure the continued efficient provision of endoscopy services in the face of rising demands worldwide. A paradigm shift is required in endoscopic devices and techniques to improve safety and comfort. |
| Villa et al | 2019 | [3] | Endoscopy-related musculoskeletal injuries in gastroenterology fellows | Survey, cross-sectional study | Injuries were more common in fellows who did not receive proper ergonomical training and education |
| Austin et al | 2019 | [4] | Musculoskeletal Injuries Are Commonly Reported Among Gastroenterology Trainees: Results of a National Survey | Electronic survey | Musculoskeletal injuries may affect up to 20% of GI fellows. Female fellows more frequently report injuries and may be at particularly high risk which has not been found in previously reported surveys of practicing gastroenterologists. Standardized curricula on ergonomic considerations and injury prevention are needed to enhance GI fellowship training and reduce injury rates. |
| Han et al | 2020 | [14] | High prevalence of musculoskeletal symptoms and injuries in third space endoscopists: an international multicenter survey | International multicenter survey | Over two-thirds of endoscopists performing TSE suffer from MSI, with many reporting onset of their symptoms after starting TSE in their practice. Further studies are needed to understand and reduce the risk of MSI in TSE given the growing demand for these procedures and the potential long-term impact of this occupational hazard. |
| Lubna Kamani,Hamid Kalwar | 2021 | [15] | Ergonomic Injuries in Endoscopists and Their Risk Factors | Survey, cross-sectional study | Endoscopists are at high risk of developing ergonomic injuries, representing the negative potential of the endoscopyassociated workload. To overcome these issues, an appropriate strategic framework needs to be designed to avoid occupational compromises. |
| Shah et al | 2022 | [16] | Ergonomics of gastrointestinal endoscopies: Musculoskeletal injury among endoscopy physicians, nurses, and technicians | Observational cross-section study | Three-fourth of our endoscopists reported MSI, of which more than half are not sure or attributed this problem to endoscopy. The prevalence of MSI warrants urgent attention. |
| NAME | APPROVAL STATUS | CLINICAL TRIAL | PURPOSE OF USE | TECHNICAL FEATURES |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| ENDOMASTER EASE SYSTEM (ENDOMASTER PTE., SINGAPORE) | No | AnimalguifenHuman | Stomach ESDguifenColon ESD | Console for remote control of the robotic arms, Independent endoscopic platform |
| ENDOLUMINAL ASSISTANT FOR SURGICAL ENDOSCOPY guifen(ICUBE LABORATORY, STRASBOURG, FRANCE) | No | Animal | Colon ESD | Master console and a detachable flexible endoscope with three working channels |
| FLEX ROBOTIC SYSTEM (MEDROBOTICS, RAYNHAM, MA, USA) | FDA | AnimalguifenHuman | Colon ESD | Robotic endoscope, mechanical single-use flexible instruments and a master console with a touchscreen, HD visual display, a joystick |
| K-FLEX guifen(EASYENDO SURGICAL, DAEJEON, KOREA) | No | Explanted animal organs | Colon ESD | Bendable overtube, two exchangeable surgical instrument modules, a driving robot arm, and a master console |
| NAME | SINGLE USE | APPROVAL STATUS | ACTUATION PRINCIPLE | TECHNICAL FEATURES |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| THE AER-O-SCOPETM COLONOSCOPE SYSTEM guifen(GI VIEW LTD., TEL AVIV, ISRAEL) | Yes | FDA, CE | Electro – pneumatic mechanisms | Self-propelled, disposable colonoscope |
| ENDOTICS guifen(ERA ENDOSCOPY SRL, CASCINA, ITALY) | Yes | CE | Electro – pneumatic mechanisms | Self-propelled, joystick-controlled endoscope |
| COLONOSIGHT (STRYKER GI, HAIFA, ISRAEL) | Yes | FDA | Electro – pneumatic mechanisms | Self-advancing system composed of a reusable colonoscope and a wrapped disposable multi-lumen sheath |
| NEOGUIDE ENDOSCOPY SYSTEM guifen(INTUITIVE SURGICAL INC., SUNNYVALE, CA, USA) | Yes | FDA | Electro-mechanical actuation | 16-segment insertion tube that controls the snake-like movement of the endoscope |
| ENDOCULUS (UNIVERSITY OF COLORADO, BOULDER, CO, USA) | No | No | Electrically actuated mechanisms | Small tank-like robot that can navigate the colon |
| MAGNETIC FLEXIBLE ENDOSCOPE (VANDERBILT UNIVERSITY, NASHVILLE, TN, USA) | No | No | Magnetic-actuated tethered robotic colonoscopes | Magnet-embedded endoscope, an actuated permanent magnet external to the patient, and a control software |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





