1. Introduction
Alzheimer’s disease (AD), the principal cause of senile dementia is a progressive neurodegenerative disease that distresses millions of patients over 65 years of age worldwide [
1,
2]. Deposition of β-amyloid (Aβ) senile plaques, neurofibrillary tangles, tau hyperphosphorylation, and cognitive dysfunctions are the well-accepted hallmarks of AD [
3]. Although the familial type of AD constitutes up to five percent of AD cases, the majority type found is late-onset sporadic AD (SAD) [
4]. SAD involves key etiopathogenic mechanisms including environmental, metabolic, genetic, and lifestyle factors causing numerous disturbances including chronic oxidative stress, cholinergic deficits, and neuroinflammation [
5]. Currently, available medications for the treatment of AD that include N-methyl-D-aspartate receptor antagonists, acetylcholinesterase inhibitors offer limited therapeutic advantages and do not prevent disease progression [
6].
The concept of drug repurposing by investigating established and old drugs used for other pharmacological benefits for the treatment of neurodegenerative diseases holds great potential [
7]. Calcium channel blockers (CCBs) clinically used as antihypertensive and antianginal agent are being used by millions of patients in a safe and efficacious manner [
8]. The broad array of epidemiologic data and translational science revealed a promising approach for CCBs to be repurposed for neuroprotection and delay progressive neurodegenerative disorders [
9,
10,
11]. Previous studies suggested that CCBs exhibited promising effects as therapeutics for treating AD [
12]. Calcium has been linked with cognitive function, neural plasticity, and neuronal physiology [
13]. Calcium imbalance and/or dysregulation is observed in the course of human aging and neurological disorders including AD [
14,
15,
16]. Evidence suggests that CCBs such as memantine, nimodipine, and verapamil are efficacious for treating AD by targeting receptor-operated calcium channels and voltage-gated calcium channels thereby protecting AD cells from Aβ oligomer production in various
in vitro and
in vivo animal models [
17,
18,
19]. Further, several other classes of CCBs including nicardipine, felodipine, and nifedipine ameliorated memory deficits associated with hypoxic conditions [
20,
21].
CCBs were well documented to possess immense antioxidant and anti-inflammatory effects [
11,
22,
23,
24]. Diltiazem (DTZ), a benzothiazepine class of voltage-gated CCB clinically used in angina and in the treatment of cardiovascular diseases exhibited various pharmacological benefits in experimental models [
25,
26]. DTZ exhibited protective effects against traumatic brain injury, cyanide-induced neurotoxicity, anti-inflammation, pentylenetetrazole-provoked amnesia, glutamate-induced excitotoxicity in ischemia model, spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury rabbit model, aluminum chloride-induced dementia, and lead toxicity [
27,
28,
29,
30,
31,
32,
33]. Further, DTZ, by blocking Ca
2+ is known to reduce the adverse effects of calcium dysregulation and has been proposed to be useful in AD [
17,
34]. However, the neuroprotective anti-dementia role and its underlying mechanisms of DTZ in sporadic AD-type conditions in experimental models were not documented.
Streptozotocin (STZ), a glucosamine-nitrosourea combination widely used in laboratory animals to induce diabetes, was reported to cause serious damage to the brain and other metabolic irregularities in the central nervous system (CNS) [
35]. Further, reports indicated that intra-cerebrovascular (ICV) injection of STZ impairs glucose and energy metabolism in the CNS, triggering neurodegeneration [
36,
37]. ICV injection of STZ increases β-amyloid protein expression, cognitive deficits, chronic neuroinflammation, anxiety, and increased oxidative stress and is identified as a classical model featuring SAD [
38,
39]. Given such reports, in the present study, DTZ was investigated for its neuroprotective role against ICV-STZ-induced SAD type model in rats. In addition, the pharmacological effect of DTZ on ICV-STZ-induced anti-oxidative defense factors, neuroinflammatory cytokines, and Aβ protein expression in rat brain tissue was investigated.
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Chemicals
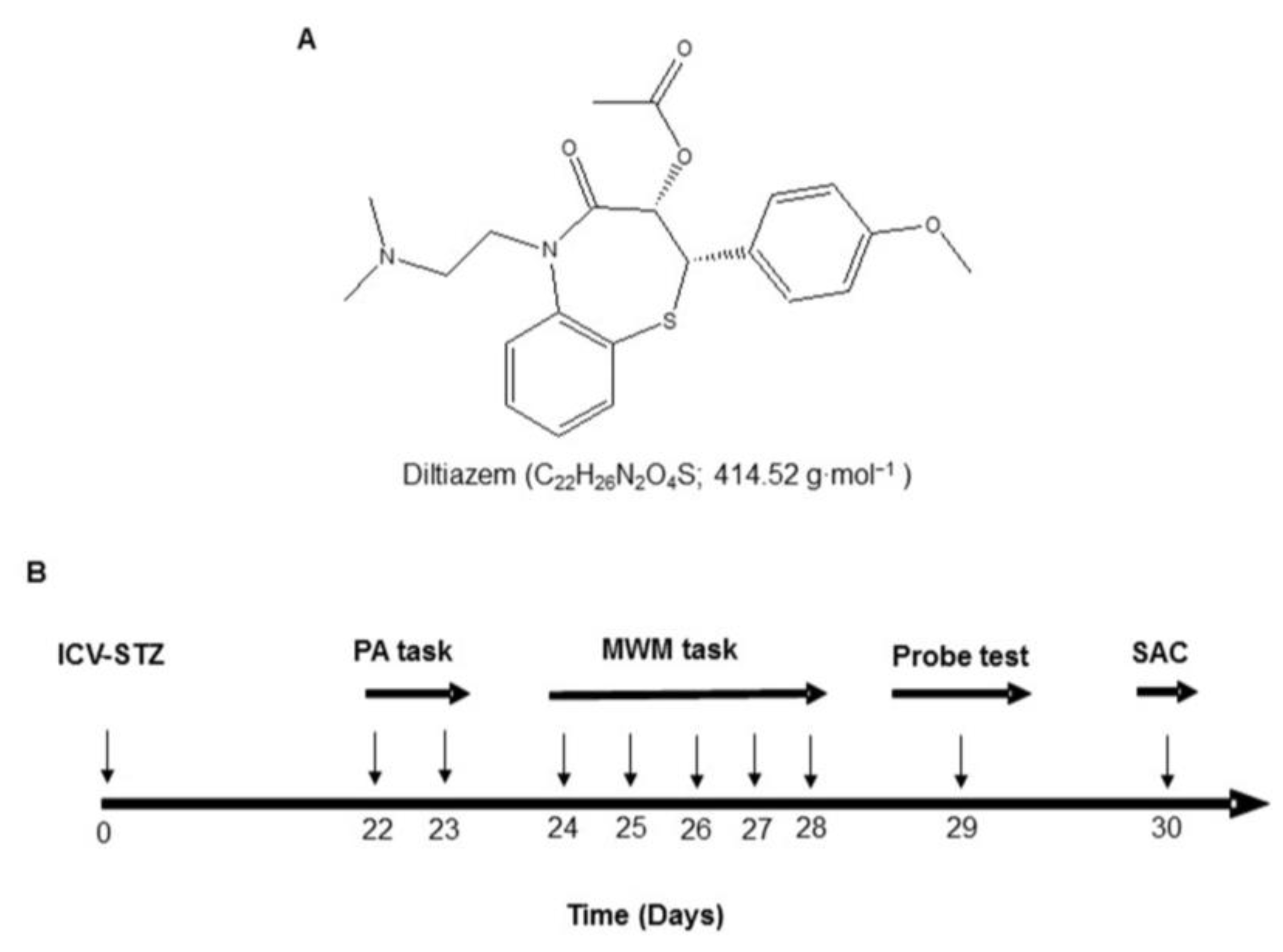
DTZ (
Figure 1A), 5,5'-Dithiobis-2-nitrobenzoic acid (DTNB), STZ, glutathione (GSH), 2-thiobarbituric acid (TBA), phosphate-buffered saline (PBS), bovine serum albumin (BSA), and analytical reagents for TNF-α and IL-1β were purchased from Sigma (St. Louis, United States). Antibodies for immunohistochemistry and western blotting (WB) were purchased from Invitrogen in Camarillo, California, United States of America. All drug solutions were prepared fresh prior to administration.
2.2. Animals
Wistar rats of both sexes weighing 150–200 g and aging at 8 to 12 weeks were used for the study. The animals were housed in colony cages in the Central Animal House of our facility, which had a 12 h light/dark period, an ambient temperature of 25 ± 2 °C, relative humidity of 45–55%, and unlimited access to a standard mouse pelleted food and water. Each of the studies was conducted in accordance with the "Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals" (CPCSEA) and our Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (No. 1358/ac/10/CPCSEA) guidelines.
2.3. Surgery and ICV-STZ Administration
STZ was administered via the ICV route as previously stated with a minor change [
36]. Animals were made unconscious by intraperitoneal (i.p.) injections of ketamine hydrochloride (70 mg/kg, i.p.) and diazepam (4 mg/kg, i.p.). The animal was positioned on the surgical board, the head was straightened, the hair was trimmed, and a midline sagittal scalp incision was made after cleansing the entire area with povidone-iodine alcoholic solution. On each lateral ventricle, two holes were drilled into the skull at coordinates of 0.8 mm posterior to the bregma, 1.5 mm lateral to the sagittal suture, and 3.6 mm below the surface of the brain. A 10 µL Hamilton syringe with a 28-gauge needle was lowered into the lateral ventricle using a micro-injector unit. Artificial cerebrospinal fluid (ACSF; 2.9 mM KCl; 147 mM NaCl, 1.7 mM CaCl
2, 1.6 mM MgCl
2, and 2.2 mM dextrose) containing STZ (3 mg/kg b.w.) was injected ICV into the lesioned groups on both sides. Similar procedures were performed on the control group, but ACSF was administered in the same volume in place of STZ. Rats were placed on a heated pad throughout the procedure and recovery period. The rats were kept in individual cages for recovery until their behavior was back to normal.
2.4. Animal groups and drug treatments
After a week of adaptation, the animals were divided into six groups (n=12). Control Group I receive a single injection of ACSF through an ICV line. Group II received a single infusion of STZ (3 mg/kg ICV) on day one. Groups III, IV, and V received a single dose of STZ (3 mg/kg, ICV) on day 1, followed by 21 days of treatment with DTZ (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg/day, respectively) administered orally (p.o.). Group VI received a single infusion of STZ (3 mg/kg; ICV) on day 1, followed by 21 days of treatment with a standard drug, donepezil (0.1 mg/kg; p.o.). DTZ and donepezil were dissolved in a vehicle (PBS), and the concentration of the resulting solution was adjusted to 10 ml/kg of body weight. After three weeks of STZ or ACSF infusions, the animals underwent behavioral and biochemical assessments. The body weights of all groups were noted in pre- and post-experimental schedules. The experimental design and treatment schedule was depicted in
Figure 1B.
2.5. Behavioral studies
Behavioral assessments were carried out beginning in the fourth week following ICV-STZ infusion and the subsequent administration of DTZ or DON, as previously described [
40].
2.5.1. Passive avoidance test
The memory retention deficits in ICV-STZ-induced rats were performed on days 22 and 23, using a passive avoidance test [
41]. Briefly, the equipment was a two-compartment dark/light shuttle box with a behead door separating the compartments. The floor of the dark compartment was made of stainless-steel shock grid. Each rat was placed in the light chamber during the acquisition trial. The guillotine door was unlocked after a 60 s habituation interval, and the animals' first latency to enter the dark chamber was recorded. Rats with an initial latency time of more than 60 s were ruled out of further testing. The guillotine door was locked immediately after the rat entered the dark chamber, and an electric foot shock (75 V; 0.2 mA, 50 Hz) was administered to the floor grid with a stimulator for 3 s. After 5sm the rat was taken from the dark chamber and returned to its home cage. After 24 h, the retention latency time was evaluated in the same manner as in the acquisition experiment, except that the foot shock was not administered and the latency time was limited to 600 s. Short latencies imply poor retention.
2.5.2. Morris water maze (MWM) test
Following the passive avoidance test, Morris water maze task was conducted to assess the special learning and memory abilities of the animals as described earlier [
42]. Briefly, MWM apparatus contains a cylindrical water tank with a diameter of 130 cm and a height of 62 cm, filled with water to a depth of 40 cm (at a temperature of 25 ± 2 °C). The water was made cloudy with non-toxic paint. The pool was partitioned into four equitably sized quadrants, denoted as North, South, East, and West. A concealed escape platform with a diameter of 10 cm was positioned at a fixed location within one of the quadrants, submerged 2 cm beneath the water's surface. The platform remains in the same quadrant throughout the duration of the experiment. Prior to the start of the training, rats were allowed to swim freely in the pool with the platform for 60 s. Upon ascending the platform, the animal maintained its position for a duration of 30 s prior to the commencement of the subsequent trial. If a rat took longer than 60 s to find and reach the escape platform, it was carefully placed on the platform and allowed to stay there for the same amount of time. Latency times (in seconds) were recorded for each platform. A probing test was conducted 24 h following the acquisition phase by removing the platform. Rats were allowed to swim freely in the pool for 60 s. The amount of time spent in the target quadrant, which formerly housed the hidden platform, was recorded. The amount of time spent in the intended quadrant represents the extent of consolidation of memory experienced after learning.
2.6. Biochemical analysis
2.6.1. Tissue préparations
Rats were euthanized with anesthesia 24 h following the MWM tests, and their brains were taken immediately and preserved on ice on a glass plate.. The hippocampus and cerebral cortex were removed using the rat brain matrix and the rat brain atlas [
43]. Six brains were hemisected across the center and frozen on dry ice for preservation. The tissues in one hemisphere were homogenized in lysis buffer for use in WB, and the tissues in the other hemisphere were independently homogenized in 10 mM tris-buffer (pH 7.4) with protease inhibitors. In order to estimate lipid peroxidation (LPO), the nuclear debris was separated from the homogenate by centrifuging it at 800 ×g for 5 min at 4 °C. The supernatant was further centrifuged at 10,000 ×g for 20 min at 4 °C to obtain post-mitochondrial supernatant (PMS), which was utilized for additional biochemical tests. After transcardial perfusion with saline and 4% paraformaldehyde, the brains of the remaining six rats in each group were removed and either fixed in 3.7% formaldehyde in PBS 1X solution, embedded in paraffin, and then 5 µm sections were cut for immunohistochemistry.
2.6.2. Measurement of LPO
As described previously [
44], the quantitative measurement of thiobarbituric acid-reactive species (TBARS), an indicator of lipid peroxidation in the brain, was evaluated. In brief, 0.1 mL of supernatant was incubated for 2 h with 0.5 mL Tris-HCl (0.1 M, pH 7.4). To this 1 mL of 10% w/v trichloroacetic acid was added and centrifuged at 1,000 ×g for 10 min. To 1 mL of supernatant, 1 ml (0.67%, w/v) thiobarbituric acid (TBA) was mixed and placed in a boiling water bath for 10 min before cooling and adding 1 ml distilled water. The LPO products were quantified by reacting them with TBA at a wavelength of 532 nM using the T60 UV/VIS spectrophotometer (PG Instruments Limited, India).
2.6.3. Effect on brain GSH level
The GSH content in the brain was determined using the method outlined by Ellman [
45]. The supernatant, measuring 1 ml, was subjected to precipitation using 1 mL of 4% sulfosalicylic acid. The resulting mixture was then cold-digested at a temperature of 4°C for a duration of 1 h. The samples underwent centrifugation at a speed of 1200×g for a duration of 15 min at a temperature of 4°C. To analyze the supernatant, a mixture was prepared by adding 2.7 mL of phosphate buffer (0.1 M, pH 8) and 0.2 mL of 5,5-dithio-bis (2-nitrobenzoic acid) to 1 mL of the supernatant. The yellow color that was produced was measured at a wavelength of 412 nm using a T60 UV/VIS spectrophotometer (PG Instruments Limited, India).
2.6.4. Effect on brain superoxide dismutase (SOD) activity
SOD activity was determined by measuring its ability to block the photochemical reduction of nitro blue tetrazolium (NBT), as previously stated [
46]. One unit (U) of SOD production is regarded as the quantity of enzyme necessary to reduce NBT by 50%. Maximum absorbance was measured at 550 nm using a T60 UV/VIS spectrophotometer (PG Instruments Limited, India), and enzymatic activity was expressed in units per milligram of protein.
2.6.5. Effect on brain nitrite and pro-inflammatory cytokine levels
Nitric oxide (NO) production in the supernatant was measured as described previously [
47]. Griess reagent and supernatant were mixed together in equal parts and the resultant mixture was incubated for 10 min at room temperature in the dark, and a T60 UV/VIS spectrophotometer was used to measure the absorbance at 540 nm (PG Instruments Limited, India). The nitrite concentration in the supernatant was calculated using a sodium nitrite standard curve and quantified as micromoles per milligram protein. To assess pro-inflammatory mediator levels, TNF-α and IL-1β levels were determined using respective immunoassay kits. Marker concentrations were calculated using standard curves and expressed as pg/mL protein.
2.7. Protein content and Western blotting analysis
Protein content was evaluated using the Lowry et al. method with bovine serum albumin (BSA) as a reference [
48]. Western blot analysis was carried out in accordance with the manufacturer's instructions (Invitrogen, Carlsbad, CA). The protein concentrations in frozen brain samples were determined using the Bradford protein assay (Bio-Rad Laboratories, Hercules, CA, USA). Proteins were separated by electrophoresis in 4-20% SDS-PAGE gels and electro-transcribed onto nitrocellulose membranes. After blocking the membranes with 5% nonfat milk, the membranes were subjected to immunoblot analysis by allowing them to lie overnight with primary antibodies of rabbit polyclonal anti-APP (Invitrogen, Camarillo, CA, USA, catalog number: 51-2700; 1:1000 dilution) and anti-tubulin to normalize the amount of protein loaded (Invitrogen, Camarillo, CA, USA, catalog number: 32-2600; dilution: dilution 1:4000). The blots were washed with PBS and then analyzed using goat anti-rabbit or goat anti-mouse secondary antibodies that were conjugated with horseradish peroxidase (dilution, 1: 100,000; A32735; Invitrogen, Camarillo, CA, USA). The visualization of protein bands was achieved through the utilization of a chemiluminescence reagent (ECL Plus), followed by exposure on X-ray film. (Kodak, Rochester, NY, USA). The intensity levels of the bands were assessed utilizing the alpha imager gel documentation system (FluorChem E; Cell Biosciences, USA), with β-tubulin serving as a loading control.
2.8. Immunocytochemistry
For immunohistochemistry, brain sections were prepared by deparaffinizing them and then washing them with 0.1 M phosphate-buffered saline (PBS) for a duration of 3-10 min. Following this, the sections were incubated in a blocking solution consisting of PBS with 0.3% Triton X-100, 0.1% BSA, and 2% normal goat serum for a period of 2 h at room temperature. The primary and secondary antibodies were diluted with the blocking solution. After blocking, the sections were treated with a polyclonal rabbit antibody to -amyloid 42 (1:1000, Invitrogen) overnight at 4 degrees Celsius with gentle shaking. Following overnight incubation, sections were washed twice in PBS and then incubated with horseradish peroxidase-conjugated goat anti-rabbit IgG (Invitrogen, 1:1,000) for 1 h to detect immunoreactivity. Following incubation, sections were washed three times in PBS, and 100 µL of 3,3′-diaminobenzidine (DAB) color reagent solution was added, and the response was seen under a microscope. With 0.1% Cresyl violet (Nissl stain), the sections were counterstained. Alcohol gradients were used to dehydrate sections, which were then sealed with neutral adhesive. Positive staining was identified as the appearance of brown DAB reaction products.
2.9. Statistical analysis
The findings are represented as means ± standard error of the mean (S.E.M). The behavioral and biochemical data were analyzed with one-way analysis of variance (ANOVA) and Bonferroni's post hoc test for multiple comparisons using GraphPad Prism (version 6.0; GraphPad Software, Inc., La Jolla, CA, USA). In every experiment, p < 0.05 was set to be statistically significant.
3. Results
3.1. Effect of DTZ on body weight changes in ICV-STZ-induced rats
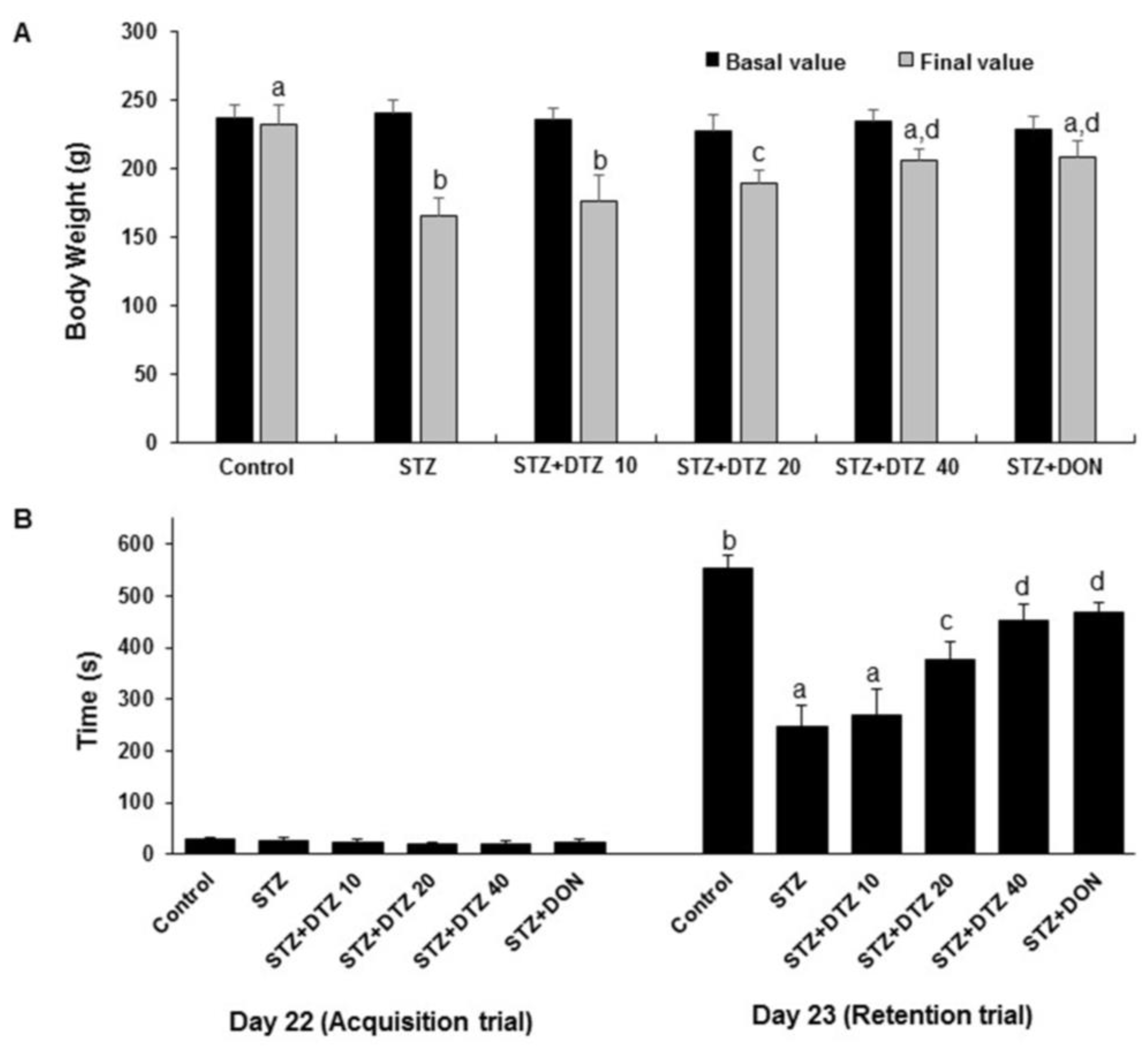
ICV-STZ (3 mg/kg; p.o.) alone treated rat group showed a significant (p < 0.01) decrease in body weight as compared to the control values (from 232.72 ± 14.54 g to 165.28 ± 13.24 g). Treatment with indicated doses of DTZ (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg) restored the body weight changes significantly (p < 0.01 at 20 and 40 mg/kg) when compared with ICV-STZ-induced rat groups (175.98 ± 18.94 g, 188.92 ± 10.58 g and 205.86 ± 12.55 g at 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg, respectively). Treatment with the standard drug DON (0.1 mg/kg) to ICV-STZ-induced rats also significantly (p < 0.01) improved the altered body weights (208.28 ± 11.86 g) and is comparable with DTZ treated at 40 mg/kg dose (
Figure 2A).
3.2. Effect of DTZ on cognitive deficits in passive avoidance task
To measure the effect of DTZ on ICV-STZ-induced learning and memory impairment in rat groups, acquisition latency (AL) and retention latency (RL) were measured. One day after the treatment schedule (day 22), the AL was unchanged in all the groups. On the following day (day 23), the RL was significantly (p< 0.001) decreased in the ICV-STZ-induced group when compared with the control group (from 554 ± 22 s to 248 ± 39 s). Treatment with DTZ at indicated doses (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg) significantly (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01 at 20 and 40 mg/kg).) and dose-dependently attenuated the RL values (270 ± 45 s, 376 ± 36 s and 452 ± 31 s at 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg, respectively) when compared with ICV-STZ treated groups indicating that DTZ significantly improved the cognitive functions. DON treated at 0.1 mg/kg showed similar significant effects (468 ± 19 s, p < 0.01) when compared with DTZ in attenuating the ICV-STZ-induced decrease in RL values (
Figure 2B).
3.3. Effects of DTZ on ICV-STZ-induced cognitive impairment in MWM task
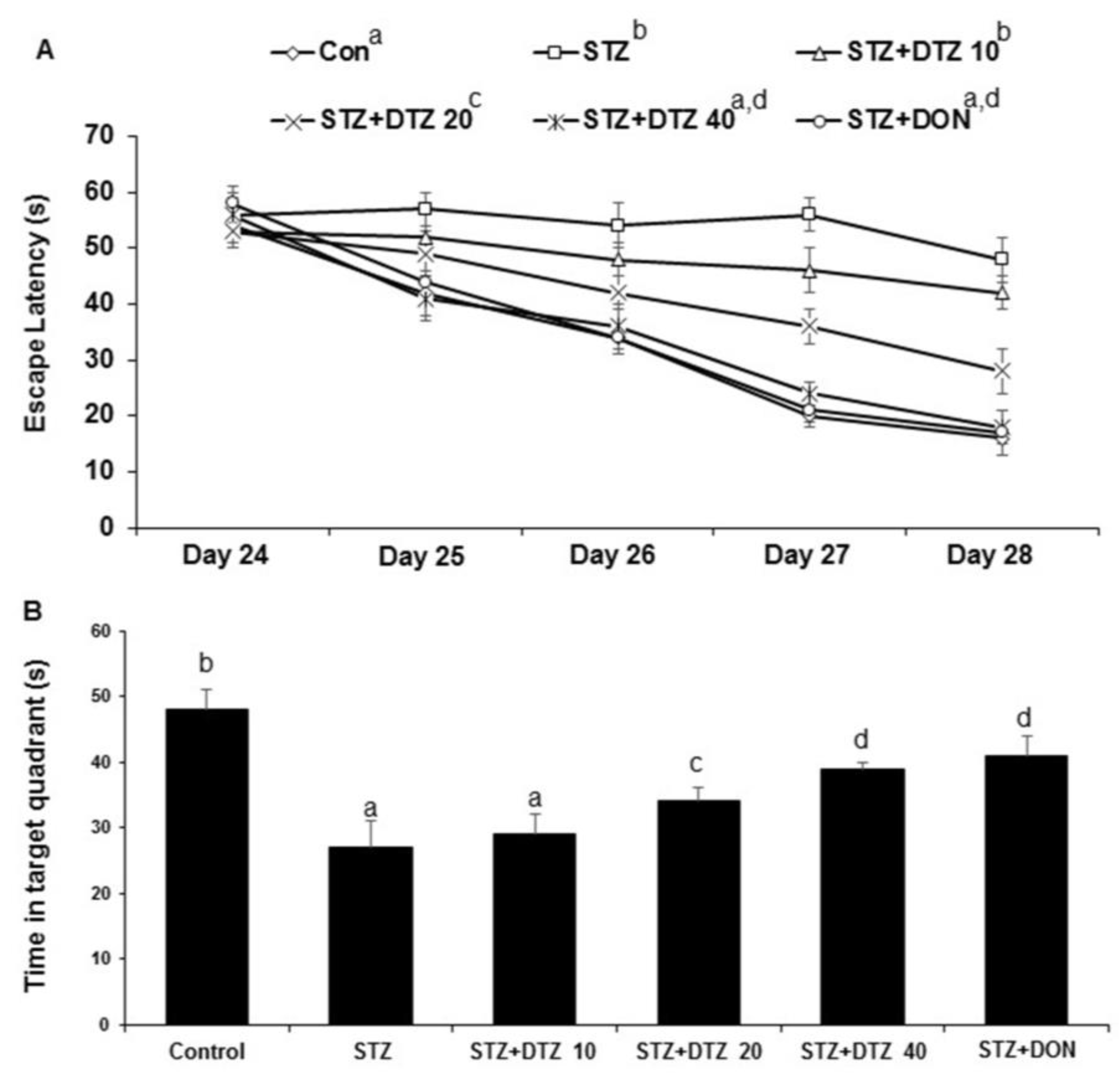
The escape latency to locate the hidden platform decreased during the course of the five training trials for the MWM task as compared to day one. ICV-STZ-induced rat group showed a significant (p < 0.001) increased average latency in finding the hidden platform when compared to the control group indicating reduced learning and memory capacities in ICV-STZ-induced rats (16 ± 3 s to 48 ± 4 s on day 5). Treatment with indicating doses of DTZ (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg) or standard drug DON (0.1 mg/kg), decreased the escape latency compared with ICV-STZ alone treated group 42 ± 3 s, 28 ± 4 s, 18 ± 3 s at 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg DTZ and 17 ± 4 s at 0.1 mg/kg DON). Similar effects were observed with DON (0.1 mg/kg) when compared with DTZ (40 mg/kg) treated group (
Figure 3A). Further, the spatial probe test evaluated by the time spent in the target quadrant after the removal of the hidden platform revealed a significant decrease (p < 0.001) in the ICV-STZ-induced group when compared with the control group (from 48 ± 3 s to 27 ± 4 s). Treatment with DTZ to ICV-STZ-induced rats at indicated doses significantly increased (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01 at 20 and 40 mg/kg) the amount of time spent in the target quadrant area indicating an increase in memory consolidation and learning performance (29 ± 3 s, 34 ± 2 s and 39 ± 1 s at 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg, respectively). DON treatment also exhibited a significant (p < 0.01) effect in ameliorating the ICV-STZ-induced memory and learning deficits in both escape latency and probe test and is comparable with DTZ at 40 mg/kg dose (
Figure 3B).
3.4. Effect of DTZ on the anti-oxidative enzyme status in ICV-STZ-induced rat brain tissues
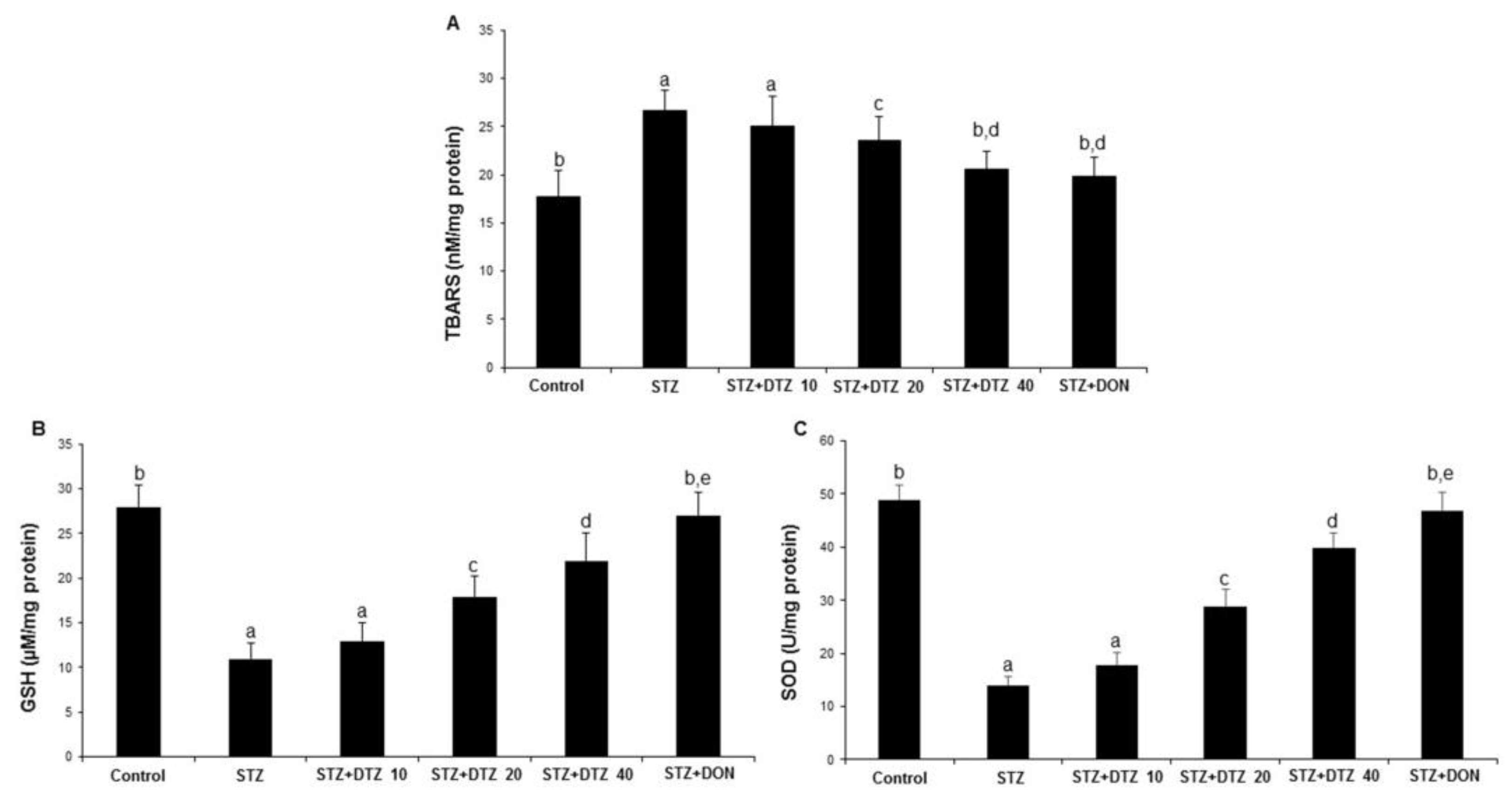
The oxidative damage caused by ICV-STZ injection was evaluated by measuring the anti-oxidative LPO, GSH, and SOD enzyme levels in rat brain tissues (
Figure 4). The LPO enzyme status as measured by TBARS content was significantly (p < 0.01) increased in ICV-STZ-induced rat brain tissues when compared with control samples (17.75 ± 2.74 to 26.78 ± 2.12 nM/mg protein). However, DTZ treatment to ICV-STZ-induced rats at indicated doses (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg), reduced the increased TBARS content significantly (p < 0.05 and p < 0.01 at 20 and 40 mg/kg) in a dose-dependent fashion (25.02 ± 3.14, 23.60 ± 1.85 and 20.68 ± 1.82 nM/mg protein at 10, 20 and 40 mg/kg, respectively;
Figure 4A). Further, the GSH and SOD enzyme levels showed a significant (p < 0.001) decrease in ICV-STZ-induced brain tissues when compared to the control groups (from 28.22 ± 2.45 to 11.24 ± 1.76 for GSH; from 49. 46 ± 2.78 to 14.20 ± 1.74 for SOD). Treatment with DTZ (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg) improved the depleted GSH and SOD levels in brain tissues when compared with ICV-STZ treated rats (p < 0.05 ~ p < 0.001 at 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg). The standard drug DON (0.1 mg/kg) treated group also attenuated the altered levels of LPO, GSH, and SOD enzymes, and the effect was similar to DTZ treated at 40 mg/kg dose (p < 0.01 and p < 0.001 for GSH and SOD, respectively;
Figure 4B and 4C). Considering the results obtained, DTZ has the potential to regulate the anti-oxidative enzyme status disrupted by ICV-STZ injections in SAD-type rats.
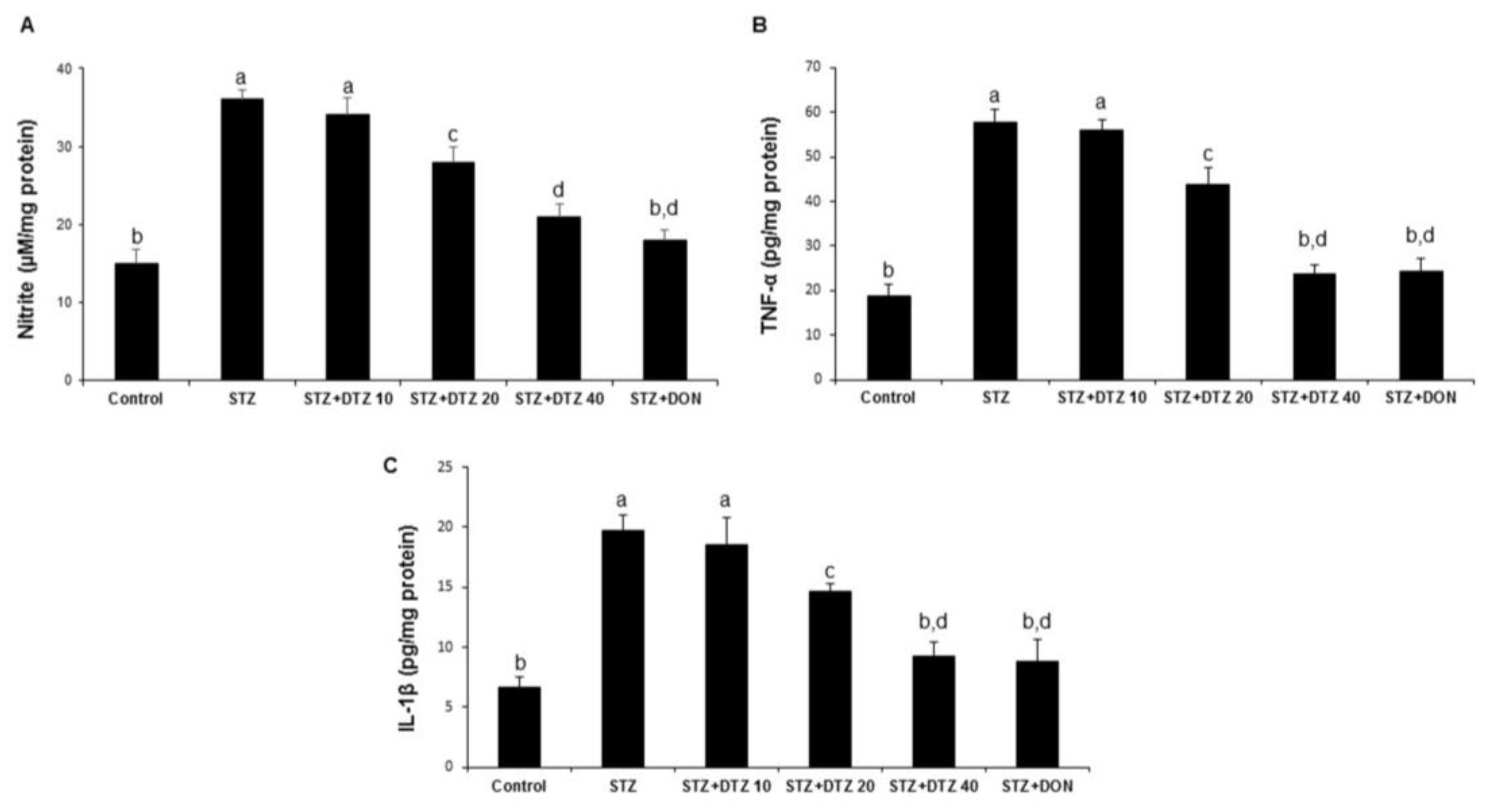
3.5. Effect of DTZ on the pro-inflammatory markers in rat brain tissues
To identify the neuroinflammatory protective role of DTZ, the nitrite levels and the pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α and IL-1β) in rat brain tissues were estimated (
Figure 5). ICV-STZ-induced rat groups produced a significant increase in brain nitrite levels when compared with the control samples (15.26 ± 1.78 to 36.28 ± 2.24 µM/mg protein;
Figure 5A). Similarly, the TNF-α and IL-1β levels were also significantly increased in ICV-STZ-induced groups when compared with control groups (18.65 ± 2.87 to 57.64 ± 3.12 and 6.64 ± 0.87 to 19.76 ± 1.24 pg/mg protein for TNF-α and IL-1β, respectively;
Figure 5B and 5C). Treatment with DTZ at indicated concentrations (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg) significantly (p < 0.05 and p < 0.001 at 20 and 40 mg/kg) attenuated the increased brain TNF-α and IL-1β levels as compared to ICV-STZ-induced rats. DON (0.1 mg/kg) treated groups also significantly (p < 0.001) reduced the increased nitrite, TNF-α, and IL-1β levels (18.24 ± 1.24 µM/mg protein, 24.18 ± 3.02 and 8.78 ± 1.89 pg/mg protein, respectively) and are comparable with DTZ treated at 40 mg/kg dose.
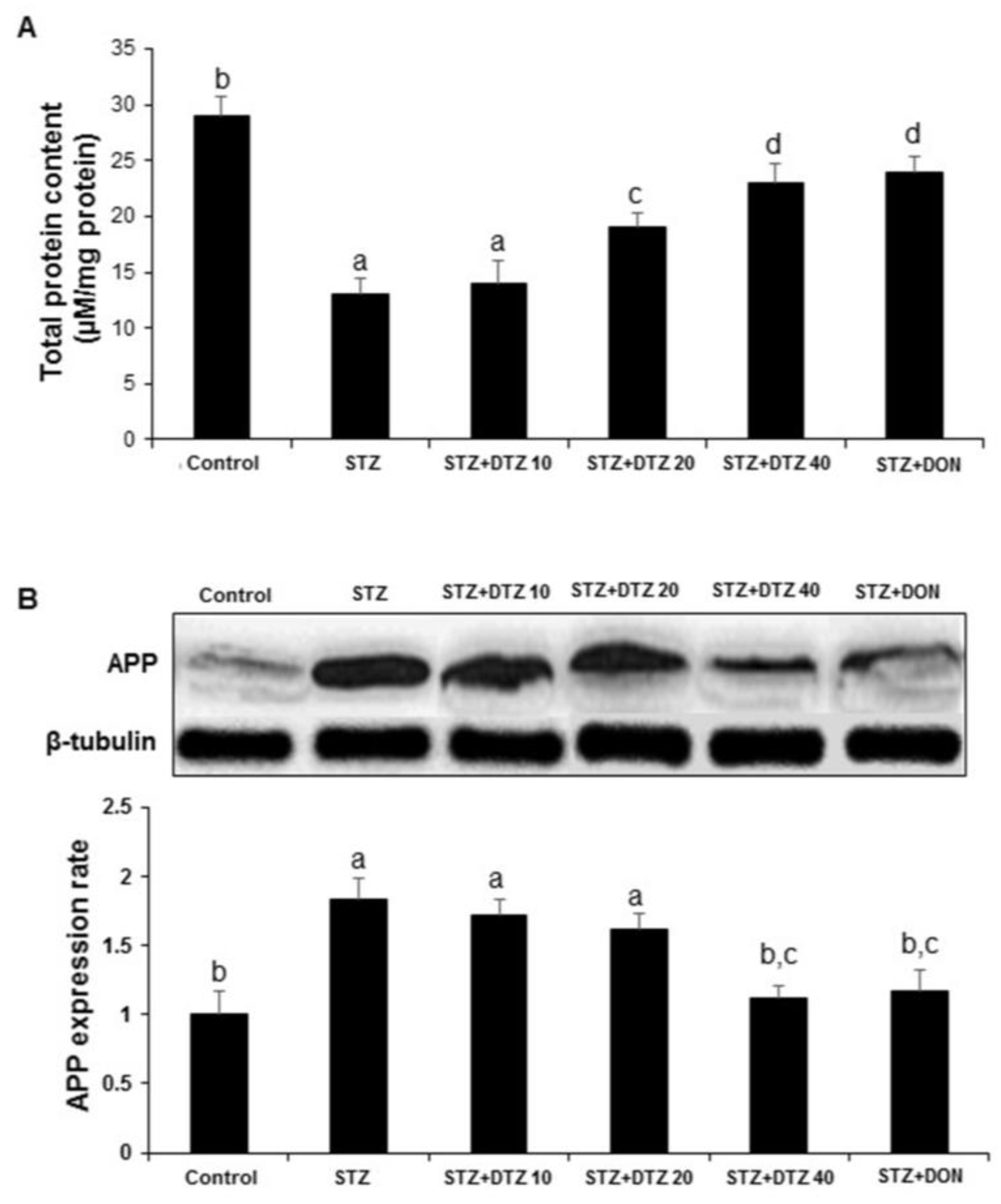
3.6. Effects of DTZ on the total protein content and APP expression
ICV-STZ-induced rats showed a significant decrease (p < 0.01) in brain total protein level when compared to the control group. Treatment with DTZ (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg) and DON (0.1 mg/kg) significantly (p < 0.01) and dose-dependently (14.26 ± 1.97, 19.56 ± 1.22, 23. 54 ± 1.68 and 24. 68 ± 1.44 µM/mg protein, respectively) prevented ICV-STZ-induced decrease in brain total protein level (
Figure 6A). Further, to understand the effect of DTZ on the Aβ protein, the expression of APP processing was analyzed by WB. In ICV-STZ-induced rats, the expression of APP in brain samples was markedly increased when compared with the control group samples. Treatment with DTZ (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg) suppressed the increased APP expression when compared with the ICV-STZ-induced group. DTZ at 40 mg/kg dose exhibited a similar effect with DON treated at 0.1 mg/kg dose. Densitometry analysis revealed a significant (p < 0.01) increase in APP expression rate (1.84 ± 0.15) in ICV-STZ-induced rat brain tissues and DTZ treatment ameliorated (1.12 ± 0.09) the changes significantly (p < 0.01 at 40 mg/kg). DON treatment to ICV-STZ-induced rats also showed a similar effect in attenuating the APP expression rate (1.17 ± 0.15) and is comparable with DTZ treated at 40 mg/kg dose (
Figure 6B).
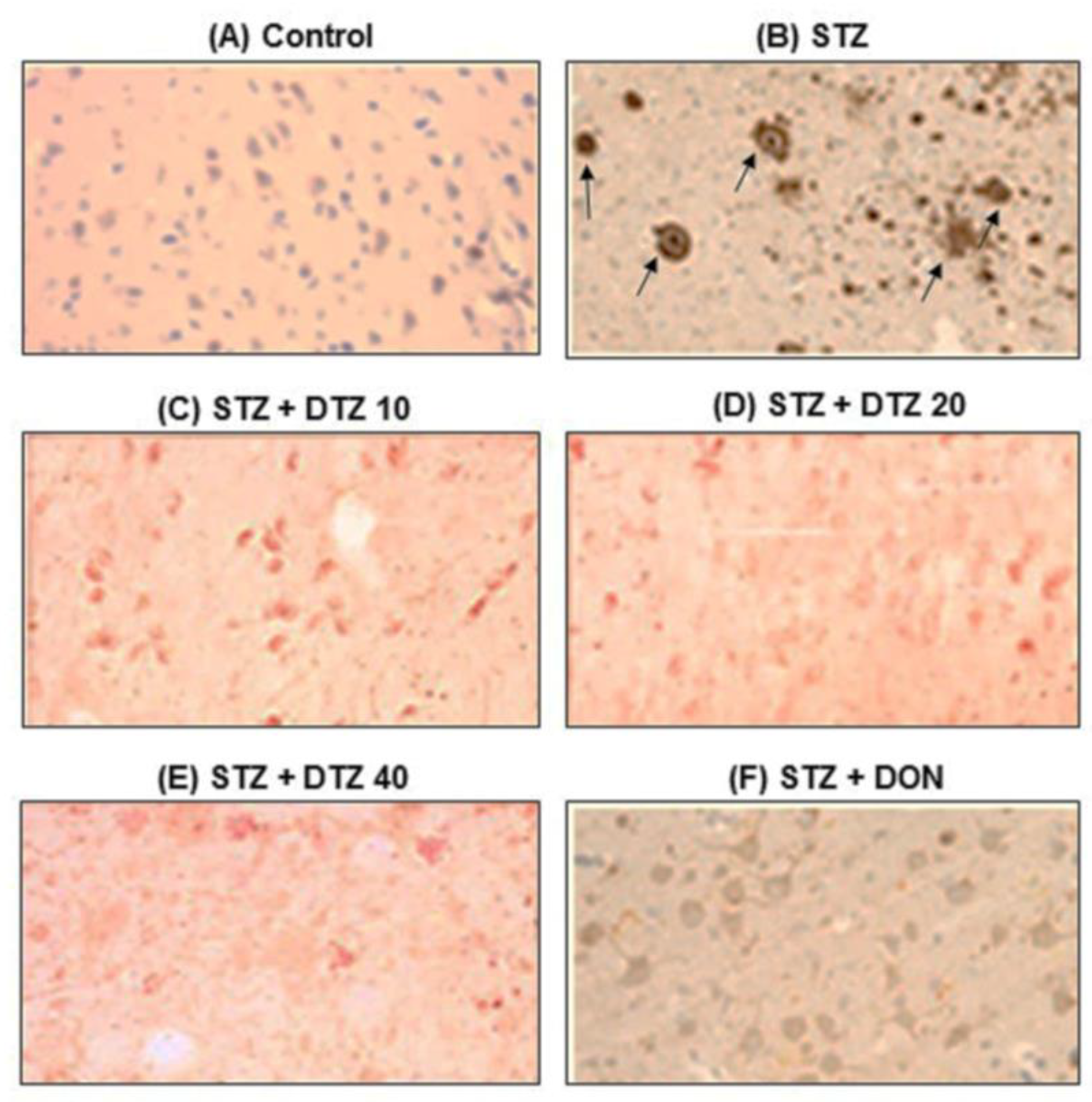
3.7. Effect of DTZ on ICV-STZ-induced Aβ accumulation in rat brain tissues
To evaluate the presence of Aβ accumulation, immunostaining of Aβ using the polyclonal rabbit antibody to β-amyloid 42, which recognizes the Aβ peptide signal was performed (
Figure 7). Marked brown reaction products (DAB) in hippocampal areas were observed in ICV-STZ-induced rat groups when compared with control brain samples, indicating a strong reaction with Aβ antibodies. In ICV-STZ-induced DTZ-treated rats, the Aβ peptide signal was decreased with increasing concentrations. DON treated at 0.1 mg/kg, also markedly reduced the Aβ signal exhibiting similar effects as that of DTZ treated at 40 mg/kg dose (
Figure 7). The results suggest that the SAD-type pathologies induced by ICV-STZ injection were ameliorated by DTZ by promoting clearance of soluble intracellular Aβ deposits which are the major hallmarks of AD.
4. Discussion
DTZ has been shown to be effective in the treatment of hypertension, angina, and cardiovascular disease [
49,
50]. DTZ exerts vasodilatory actions on arterial blood vessels and raises the sympathetic response reflex [
51]. Decrease in blood pressure and an increase in cardiac output, heart rate, and contractility are considered to be the main effects of DTZ on cardiovascular disorders [
26]. Previous studies have indicated the potential neurological effects of CCBs by regulating or blocking the neuronal voltage-gated calcium channels [
10,
52]. Further, the neuroprotective potential of CCBs in disorders such as AD, PD, focal cerebral ischemia, and spinal cord ischemia-reperfusion injury was well documented indicating that CCBs can be used as potential repurposing or repositioning agents for various CNS disorders [
17,
28,
53,
54,
55,
56]. In a recent study, CCBs were shown to exert greater potential in the treatment of psychiatric and neurodegenerative disorders and suggested that repurposing trials using the existing CCBs might increase the choice of drug selection for neuroprotection [
57]. In this study, DTZ exhibited a beneficial role against the ICV-STZ-induced SAD rats in various aspects by attenuating the altered cognitive deficits, anti-oxidative defense parameters, pro-inflammatory cytokines, and APP expression. In experimental animal models, DTZ has been utilized in a variety of doses ranging from 5 mg/kg to 800 mg/kg for up to 10–40 days [
58,
59,
60]. In this study, the treatment doses employed (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg) were selected after performing the pilot study and referring to the previous reports [
61].
Earlier studies indicated that a single ICV-STZ injection (3 mg/kg) to rodents exhibited cognitive impairments and altered other important oxidative and inflammatory biochemical parameters simulated like that are seen in SAD-like pathology in human AD patients [
36,
37,
62]. In agreement, a single ICV-STZ injection into rats induced significant pathological alterations by impairing the learning and memory functions in rats as evaluated in passive avoidance and MWM tasks. The latency time to enter the dark chamber was reduced significantly indicating cognitive deficits in ICV-STZ-induced rats. In the MWM task, increased escape latency time was observed in ICV-STZ-induced animals, and also a reduced time to spend in the target quadrant was observed. Treatment with DTZ at 20 and 40 mg/kg doses attenuated these changes in both passive avoidance and MWM task indicating a significant improvement in cognitive function disrupted by ICV-STZ injection. Our data agreed with earlier published works wherein DTZ at 40 mg/kg dose ameliorated the cognitive deficits induced by aluminum chloride in experimental mice [
29].
Oxidative stress by excessive production of ROS is known to be one of the important pathological hallmarks of brain aging and AD. Evidence suggests that STZ-induced experimental animals negatively affect the anti-oxidative stress-related enzymatic status leading to free radical-mediated AD progression [
61,
63]. Further, elevated calcium levels cause oxidative damage, mitochondrial overload, Aβ production, and tau phosphorylation [
64]. Increased Aβ further interacts with Fe
2+ and Cu
2+ to generate reactive oxygen species (ROS), and ROS leads to lipid peroxidation and altered antioxidative enzyme status [
65].
In this study, the anti-oxidative enzymatic parameters including LPO, GSH, and SOD were estimated in ICV-STZ-induced brain tissues. ICV-STZ-induced rats showed an increase in LPO as measured by TBARS levels and decreased the GSH and SOD levels significantly. DTZ at 10, 20, and 40 mg/kg dose-dependently restored the altered enzyme status which agreed with earlier studies that DTZ significantly attenuated oxidative stress in STZ-induced diabetic rabbits and aluminum chloride-induced oxidative stress in mice [
29,
66].
Neuroinflammation, by increased pro-inflammatory responses, is another major causative factor in several neurodegenerative disorders including AD [
67,
68]. Pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-6, IL-1β, and IL-10 increase the Aβ accumulation and promote abnormal tau phosphorylation [
69]. Further, single ICV administration of STZ to experimental animals was known to produce inflammation in the brain by increasing the expression of pro-inflammatory cytokines including TNF-α, IL-6, and IL-1β [
70,
71,
72]. It has been reported that inhibitors of Ca
2+ influx can regulate the excessive production of various pro-inflammatory cytokines and NO [
11]. Further, DTZ also showed anti-inflammatory effects by stimulating the production of anti-inflammatory mediators and inhibiting pro-inflammatory mediators [
28,
73]. In agreement with the previous reports, in the present work, the STZ-induced excessive production of NO and the pro-inflammatory cytokines (TNF-α, and IL-1β) in the brain tissue was ameliorated by DTZ significantly (p < 0.001 at 40 mg/kg dose).
Aβ accumulation together with neuronal cell death and cognitive impairments are known to be unique symptoms of AD. Previous studies indicated ICV-STZ-induced experimental animals showed a decrease in overall brain weight, memory dysfunction, and Aβ accumulation with increased expression of APP which are well-known pathological changes linked to SAD [
74]. In the present study, ICV-STZ-induced rat brain tissues exhibited an increased expression of APP and Aβ deposition analyzed by WB and immunohistochemistry. Treatment with DTZ (40 mg/kg) showed a significant reduction in APP expression dose-dependently. Further, the appearance of strong brown reaction products (DAB) of Aβ deposition immunoreactive signal as seen in ICV-STZ-induced groups when compared with the control group was markedly recovered in DTZ-treated rat groups. Although we found dose-dependent effects with DTZ treated at selected doses (10, 20, and 40 mg/kg), significant effects were observed at 20 and 40 mg/kg doses in the majority of the parameters evaluated. Further, no significant difference was observed with DTZ (40 mg/kg) and standard drug DON (0.1 mg/kg) treatments, and the results were comparable.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, the calcium channel blocker DTZ exhibited neuroprotective anti-dementia effects in ICV-STZ-induced SAD-type experimental rats. DTZ significantly improved the ICV-STZ-induced behavioral and cognitive impairments. Further, DTZ attenuated the altered oxidative stress parameters and neuroinflammation-related pro-inflammatory cytokines in ICV-STZ-induced rat brain tissues. In addition, DTZ suppressed the increased APP expression and restored the amyloid-β depositions in ICV-STZ-induced brain tissues. This study provided therapeutic importance of DTZ for its benefits in repurposing as a potential agent in the treatment and management of various neurodegenerative disorders including AD. However, to gain complete therapeutic benefit as a potential repurposed drug for neuroprotection, a detailed multifactorial mechanistic-based study of DTZ in other models of neurodegeneration is quite necessary.
Author Contributions
Conceptualization, R.A., E.K. and S.K.; methodology, R.A., S.K. and P.P.; software, S.K., and S.R.K., R.A.; validation, R.A., E.K., P.P. and S.K.; formal analysis, S.K., and R.A.; investigation, R.A., S.R.K., P.P., and E.K.; resources, S.K. and R.A.; data curation, R.A., S.R.K., P.P., E.K., and S.K.; writing—original draft preparation, R.A. and S.K.; writing—review and editing, S.K., E.K., and S.R.K.; visualization, S.K., and R.A.; supervision, R.A. and S.K.; project administration, R.A. and S.K.; funding acquisition, R.A., and S.K. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
This research received no external funding.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The animal study protocol was approved by the “Purpose of Control and Supervision of Experiments on Animals (CPCSEA)” guidelines and our Institutional Animal Care and Use Committee (No: 1358/ac/10/CPCSEA).
Informed Consent Statement
Not applicable.
Data Availability Statement
Data are contained within the article.
Acknowledgments
This work was supported by the Department of Science and Technology (DST), Ministry of Science and Technology, India, New Delhi, and partly by Konkuk University, South Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Guo, T.; Zhang, D.; Zeng, Y.; Huang, T.Y.; Xu, H.; Zhao, Y. Molecular and Cellular Mechanisms Underlying the Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease. Mol Neurodegener 2020, 15, 40. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haque, R.U.; Levey, A.I. Alzheimer’s Disease: A Clinical Perspective and Future Nonhuman Primate Research Opportunities. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 2019, 116, 26224–26229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sajjad, R.; Arif, R.; Shah, A.A.; Manzoor, I.; Mustafa, G. Pathogenesis of Alzheimer’s Disease: Role of Amyloid-Beta and Hyperphosphorylated Tau Protein. Indian J Pharm Sci 2018, 80. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Masters, C.L.; Bateman, R.; Blennow, K.; Rowe, C.C.; Sperling, R.A.; Cummings, J.L. Alzheimer’s Disease. Nat Rev Dis Primers 2015, 1, 15056. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, K.; Grundke-Iqbal, I. Alzheimer’s Disease, a Multifactorial Disorder Seeking Multitherapies. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2010, 6, 420–424. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chin, E.; Jaqua, E.; Safaeipour, M.; Ladue, T. Conventional Versus New Treatment: Comparing the Effects of Acetylcholinesterase Inhibitors and N-Methyl-D-Aspartate Receptor Antagonist With Aducanumab. Cureus 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Durães, F.; Pinto, M.; Sousa, E. Old Drugs as New Treatments for Neurodegenerative Diseases. Pharmaceuticals 2018, 11, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfraind, T. Discovery and Development of Calcium Channel Blockers. Front Pharmacol 2017, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zornow, M.H.; Prough, D.S. Neuroprotective Properties of Calcium-Channel Blockers. New Horiz 1996, 4, 107–114. [Google Scholar]
- Kopecky, B.J.; Liang, R.; Bao, J. T-Type Calcium Channel Blockers as Neuroprotective Agents. Pflugers Arch 2014, 466, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Huang, B.-R.; Chang, P.-C.; Yeh, W.-L.; Lee, C.-H.; Tsai, C.-F.; Lin, C.; Lin, H.-Y.; Liu, Y.-S.; Wu, C.Y.-J.; Ko, P.-Y.; et al. Anti-Neuroinflammatory Effects of the Calcium Channel Blocker Nicardipine on Microglial Cells: Implications for Neuroprotection. PLoS One 2014, 9, e91167. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lovell, M.A.; Abner, E.; Kryscio, R.; Xu, L.; Fister, S.X.; Lynn, B.C. Calcium Channel Blockers, Progression to Dementia, and Effects on Amyloid Beta Peptide Production. Oxid Med Cell Longev 2015, 2015, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burgoyne, R.D.; Haynes, L.P. Understanding the Physiological Roles of the Neuronal Calcium Sensor Proteins. Mol Brain 2012, 5, 2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radulescu, C.I.; Cerar, V.; Haslehurst, P.; Kopanitsa, M.; Barnes, S.J. The Aging Mouse Brain: Cognition, Connectivity and Calcium. Cell Calcium 2021, 94, 102358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yu, J.-T.; Chang, R.C.-C.; Tan, L. Calcium Dysregulation in Alzheimer’s Disease: From Mechanisms to Therapeutic Opportunities. Prog Neurobiol 2009, 89, 240–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zündorf, G.; Reiser, G. Calcium Dysregulation and Homeostasis of Neural Calcium in the Molecular Mechanisms of Neurodegenerative Diseases Provide Multiple Targets for Neuroprotection. Antioxid Redox Signal 2011, 14, 1275–1288. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, Y.; Deng, Y.; Qing, H. Calcium Channel Blockers and Alzheimer’s Disease. Neural Regen Res 2012, 7, 137–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tong, B.C.-K.; Wu, A.J.; Li, M.; Cheung, K.-H. Calcium Signaling in Alzheimer’s Disease & Therapies. Biochimica et Biophysica Acta (BBA) - Molecular Cell Research 2018, 1865, 1745–1760. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nimmrich, V.; Eckert, A. Calcium Channel Blockers and Dementia. Br J Pharmacol 2013, 169, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zupan, G.; Mrsić, J.; Simonić, A. Effects of Nicardipine, Felodipine and Nifedipine on Passive Avoidance Behavior of Intact and Hypoxia-Exposed Rats. Arch Int Pharmacodyn Ther 1993, 325, 61–69. [Google Scholar]
- Župan, G.; Vitezić, D.; Mršić, J.; Matešić, D.; Simonić, A. Effects of Nimodipine, Felodipine and Amlodipine on Electroconvulsive Shock-Induced Amnesia in the Rat. Eur J Pharmacol 1996, 310, 103–106. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mason, R.P.; Mak, I.T.; Trumbore, M.W.; Mason, P.E. Antioxidant Properties of Calcium Antagonists Related to Membrane Biophysical Interactions. Am J Cardiol 1999, 84, 16–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Godfraind, T. Antioxidant Effects and the Therapeutic Mode of Action of Calcium Channel Blockers in Hypertension and Atherosclerosis. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 2005, 360, 2259–2272. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Das, R.; Burke, T.; Van Wagoner, D.R.; Plow, E.F. L-Type Calcium Channel Blockers Exert an Antiinflammatory Effect by Suppressing Expression of Plasminogen Receptors on Macrophages. Circ Res 2009, 105, 167–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaffman, M.; Brogden, R.N. Diltiazem. Drugs 1985, 29, 387–454. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez Padial, L.; Barón-Esquivias, G.; Hernández Madrid, A.; Marzal Martín, D.; Pallarés-Carratalá, V.; de la Sierra, A. Clinical Experience with Diltiazem in the Treatment of Cardiovascular Diseases. Cardiol Ther 2016, 5, 75–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paquet-Durand, F.; Gierse, A.; Bicker, G. Diltiazem Protects Human NT-2 Neurons against Excitotoxic Damage in a Model of Simulated Ischemia. Brain Res 2006, 1124, 45–54. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fansa, I.; Altug, M.; Melek, I.; Ucar, E.; Kontas, T.; Akcora, B.; Atik, E.; Duman, T. The Neuroprotective and Anti-Inflammatory Effects of Diltiazem in Spinal Cord Ischaemia–Reperfusion Injury. Journal of International Medical Research 2009, 37, 520–533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Neha; Sodhi, R. K.; Kaur, A. Protective Effect of a Calcium Channel Blocker “Diltiazem” on Aluminum Chloride-Induced Dementia in Mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2015, 388, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vallazza-Deschamps, G.; Fuchs, C.; Cia, D.; Tessier, L.-H.; Sahel, J.A.A.; Dreyfus, H.; Picaud, S. Diltiazem-Induced Neuroprotection in Glutamate Excitotoxicity and Ischemic Insult of Retinal Neurons. Documenta Ophthalmologica 2005, 110, 25–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J.; Cao, H.; Zhang, Y.; Zhang, Y.; Ma, J.; Wang, J.; Gao, Y.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, F.; Chu, L. Nephroprotective Effect of Calcium Channel Blockers against Toxicity of Lead Exposure in Mice. Toxicol Lett 2013, 218, 273–280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mathangi, D.C.; Namasivayam, A. Protective Effect of Diltiazem on Cyanide-Induced Neurotoxicity in Wistar Strain Rats. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2004, 42, 605–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Genkova-Papazova, M.G.; Petkova, B.; Shishkova, N.; Lazarova-Bakarova, M. Effect of the Calcium Channel Blockers Nifedipine and Diltiazem on Pentylenetetrazole Kindling-Provoked Amnesia in Rats. European Neuropsychopharmacology 2001, 11, 91–96. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quartermain, D.; Garcia deSoria, V. The Effects of Calcium Channel Antagonists on Short- and Long-Term Retention in Mice Using Spontaneous Alternation Behavior. Neurobiol Learn Mem 2001, 76, 117–124. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamat, P. Streptozotocin Induced Alzheimer′s Disease like Changes and the Underlying Neural Degeneration and Regeneration Mechanism. Neural Regen Res 2015, 10, 1050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moreira-Silva, D.; Vizin, R.; Martins, T.; Ferreira, T.; Almeida, M.; Carrettiero, D. Intracerebral Injection of Streptozotocin to Model Alzheimer Disease in Rats. Bio Protoc 2019, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grieb, P. Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin Injections as a Model of Alzheimer’s Disease: In Search of a Relevant Mechanism. Mol Neurobiol 2016, 53, 1741–1752. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Villar, M.F.Z.; Hanotte, J.L.; Peralta, F.; Reggiani, P.C. Streptozotocin-induced Sporadic Alzheimer’s Disease: Behavioral Effects in Female Rats. Alzheimer’s & Dementia 2021, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zappa Villar, M.F.; López Hanotte, J.; Falomir Lockhart, E.; Trípodi, L.S.; Morel, G.R.; Reggiani, P.C. Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin Induces Impaired Barnes Maze Spatial Memory and Reduces Astrocyte Branching in the CA1 and CA3 Hippocampal Regions. J Neural Transm 2018, 125, 1787–1803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Alluri, R.; Ambati, S.R.; Routhu, K.; Kopalli, S.R.; Koppula, S. Phosphoinositide 3-Kinase Inhibitor AS605240 Ameliorates Streptozotocin-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease like Sporadic Dementia in Experimental Rats. EXCLI J 2020, 19, 71–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Raghavendra, V.; Kulkarni, S.K. Possible Antioxidant Mechanism in Melatonin Reversal of Aging and Chronic Ethanol-Induced Amnesia in plus-Maze and Passive Avoidance Memory Tasks. Free Radic Biol Med 2001, 30, 595–602. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Morris, R. Developments of a Water-Maze Procedure for Studying Spatial Learning in the Rat. J Neurosci Methods 1984, 11, 47–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- BUTTNER-ENNEVER, J. The Rat Brain in Stereotaxic Coordinates, 3rd Edn. By George Paxinos and Charles Watson. (Pp. Xxxiii+80; Illustrated; F$69.95 Paperback; ISBN 0 12 547623; Comes with CD-ROM.) San Diego: Academic Press. 1996. J Anat 1997, 191, 315–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ohkawa, H.; Ohishi, N.; Yagi, K. Assay for Lipid Peroxides in Animal Tissues by Thiobarbituric Acid Reaction. Anal Biochem 1979, 95, 351–358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ellman, G.L. Tissue Sulfhydryl Groups. Arch Biochem Biophys 1959, 82, 70–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Durak, I.; Yurtarslanl, Z.; Canbolat, O.; Akyol, Ö. A Methodological Approach to Superoxide Dismutase (SOD) Activity Assay Based on Inhibition of Nitroblue Tetrazolium (NBT) Reduction. Clinica Chimica Acta 1993, 214, 103–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, L.C.; Wagner, D.A.; Glogowski, J.; Skipper, P.L.; Wishnok, J.S.; Tannenbaum, S.R. Analysis of Nitrate, Nitrite, and [15N]Nitrate in Biological Fluids. Anal Biochem 1982, 126, 131–138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LOWRY, O.H.; ROSEBROUGH, N.J.; FARR, A.L.; RANDALL, R.J. Protein Measurement with the Folin Phenol Reagent. J Biol Chem 1951, 193, 265–275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, L.; Gamal El-Din, T.M.; Lenaeus, M.J.; Zheng, N.; Catterall, W.A. Structural Basis for Diltiazem Block of a Voltage-Gated Ca 2+ Channel. Mol Pharmacol 2019, 96, 485–492. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamargo, J.; Ruilope, L.M. Investigational Calcium Channel Blockers for the Treatment of Hypertension. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2016, 25, 1295–1309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mohanty, P.K.; Sowers, J.R.; Thames, M.D. Effects of Hydrochlorothiazide and Diltiazem on Reflex Vasoconstriction in Hypertension. Hypertension 1987, 10, 35–42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ortner, N.J.; Striessnig, J. L-Type Calcium Channels as Drug Targets in CNS Disorders. Channels 2016, 10, 7–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pasternak, B.; Svanström, H.; Nielsen, N.M.; Fugger, L.; Melbye, M.; Hviid, A. Use of Calcium Channel Blockers and Parkinson’s Disease. Am J Epidemiol 2012, 175, 627–635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tseng, Y.-F.; Lin, H.-C.; Chao, J.C.-J.; Hsu, C.-Y.; Lin, H.-L. Calcium Channel Blockers Are Associated with Reduced Risk of Parkinson’s Disease in Patients with Hypertension: A Population-Based Retrospective Cohort Study. J Neurol Sci 2021, 424, 117412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nimmrich, V.; Eckert, A. Calcium Channel Blockers and Dementia. Br J Pharmacol 2013, 169, 1203–1210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lukic-Panin, V.; Kamiya, T.; Zhang, H.; Hayashi, T.; Tsuchiya, A.; Sehara, Y.; Deguchi, K.; Yamashita, T.; Abe, K. Prevention of Neuronal Damage by Calcium Channel Blockers with Antioxidative Effects after Transient Focal Ischemia in Rats. Brain Res 2007, 1176, 143–150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Colbourne, L.; Harrison, P.J. Brain-Penetrant Calcium Channel Blockers Are Associated with a Reduced Incidence of Neuropsychiatric Disorders. Mol Psychiatry 2022, 27, 3904–3912. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y.-C.; Wu, C.-T.; Chen, J.-H.; Tsai, C.-F.; Wu, C.-Y.; Chang, P.-C.; Yeh, W.-L. Diltiazem Inhibits Breast Cancer Metastasis via Mediating Growth Differentiation Factor 15 and Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition. Oncogenesis 2022, 11, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadrożniak, A.; Trojnar, M.; Trojnar, M.; Kimber-Trojnar, Ż.; Dudra-Jastrzębska, M.; Andres-Mach, M.; Łuszczki, J.J. Diltiazem Enhances the Protective Activity of Oxcarbazepine against Maximal Electroshock-Induced Seizures in Mice. Journal of Pre-Clinical and Clinical Research 2008, 2, 147–152. [Google Scholar]
- Corrêa, F. de O.B.; Giro, G.; Gonçalves, D.; Spolidorio, L.C.; Orrico, S.R.P. Diltiazem Did Not Induce Gingival Overgrowth in Rats: A Clinical, Histological and Histometric Analysis. Braz Oral Res 2005, 19, 163–168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rani, A.; Neha; Sodhi, R. K.; Kaur, A. Protective Effect of a Calcium Channel Blocker “Diltiazem” on Aluminum Chloride-Induced Dementia in Mice. Naunyn Schmiedebergs Arch Pharmacol 2015, 388, 1151–1161. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shalaby, M.A.; Nounou, H.A.; Deif, M.M. The Potential Value of Capsaicin in Modulating Cognitive Functions in a Rat Model of Streptozotocin-Induced Alzheimer’s Disease. Egypt J Neurol Psychiatr Neurosurg 2019, 55, 48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sharma, M.; Gupta, Y.K. Chronic Treatment with Trans Resveratrol Prevents Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin Induced Cognitive Impairment and Oxidative Stress in Rats. Life Sci 2002, 71, 2489–2498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ge, M.; Zhang, J.; Chen, S.; Huang, Y.; Chen, W.; He, L.; Zhang, Y. Role of Calcium Homeostasis in Alzheimer’s Disease. Neuropsychiatr Dis Treat 2022, Volume 18, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheignon, C.; Tomas, M.; Bonnefont-Rousselot, D.; Faller, P.; Hureau, C.; Collin, F. Oxidative Stress and the Amyloid Beta Peptide in Alzheimer’s Disease. Redox Biol 2018, 14, 450–464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Anjaneyulu, M.; Chopra, K. Diltiazem Attenuates Oxidative Stress in Diabetic Rats. Ren Fail 2005, 27, 335–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Heneka, M.T.; Carson, M.J.; Khoury, J. El; Landreth, G.E.; Brosseron, F.; Feinstein, D.L.; Jacobs, A.H.; Wyss-Coray, T.; Vitorica, J.; Ransohoff, R.M.; et al. Neuroinflammation in Alzheimer’s Disease. Lancet Neurol 2015, 14, 388–405. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubey, L. Anti-Inflammatory Action of Diltiazem in Patients with Unstable Angina. Postgrad Med J 2006, 82, 594–597. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Domingues, C.; da Cruz e Silva, O.A.B.; Henriques, A.G. Impact of Cytokines and Chemokines on Alzheimer’s Disease Neuropathological Hallmarks. Curr Alzheimer Res 2017, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wrona, D.; Majkutewicz, I.; Świątek, G.; Dunacka, J.; Grembecka, B.; Glac, W. Dimethyl Fumarate as the Peripheral Blood Inflammatory Mediators Inhibitor in Prevention of Streptozotocin-Induced Neuroinflammation in Aged Rats. J Inflamm Res 2022, Volume 15, 33–52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mishra, S.K.; Singh, S.; Shukla, S.; Shukla, R. Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin Impairs Adult Neurogenesis and Cognitive Functions via Regulating Neuroinflammation and Insulin Signaling in Adult Rats. Neurochem Int 2018, 113, 56–68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kraska, A.; Santin, M.D.; Dorieux, O.; Joseph-Mathurin, N.; Bourrin, E.; Petit, F.; Jan, C.; Chaigneau, M.; Hantraye, P.; Lestage, P.; et al. In Vivo Cross-Sectional Characterization of Cerebral Alterations Induced by Intracerebroventricular Administration of Streptozotocin. PLoS One 2012, 7, e46196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Begum, A. Comparative Study of Anti-Inflammatory Property of Calcium Channel Blocker and Aspirin in Albino Rats. Int J Basic Clin Pharmacol 2018, 8, 21. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arora, R.B.; Kumar, K.; Deshmukh, R.R. FK506 Attenuates Intracerebroventricular Streptozotocin-Induced Neurotoxicity in Rats. Behavioural Pharmacology 2013, 24, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
A : Structure, chemical formula, and molar mass of DTZ. B: The method of treatment, the intervals for estimating different parameters, and the experimental design. ICV-STZ: intra-cerebroventricular-streptozotocin, DTZ: diltiazem, MWM: Morris water maze, PA: passive avoidance, SAC: sacrificed.
Figure 1.
A : Structure, chemical formula, and molar mass of DTZ. B: The method of treatment, the intervals for estimating different parameters, and the experimental design. ICV-STZ: intra-cerebroventricular-streptozotocin, DTZ: diltiazem, MWM: Morris water maze, PA: passive avoidance, SAC: sacrificed.
Figure 2.
Effect of DTZ on body weight and passive avoidance task in ICV-STZ-induced rats. (A) Body weight changes. (B) Acquisition trial and retention trial in passive avoidance task. A maximum of 600 s of latency time was measured. Values are expressed as means ± S.E.M. (n=12). Different letters (a-d) denote statistically significant variations between the samples. (p < 0.05). STZ: streptozotocin (3 mg/kg), STZ+DTZ 10: diltiazem (10 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 20: diltiazem (20 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 40: diltiazem (40 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DON: donepezil (0.1 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group.
Figure 2.
Effect of DTZ on body weight and passive avoidance task in ICV-STZ-induced rats. (A) Body weight changes. (B) Acquisition trial and retention trial in passive avoidance task. A maximum of 600 s of latency time was measured. Values are expressed as means ± S.E.M. (n=12). Different letters (a-d) denote statistically significant variations between the samples. (p < 0.05). STZ: streptozotocin (3 mg/kg), STZ+DTZ 10: diltiazem (10 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 20: diltiazem (20 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 40: diltiazem (40 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DON: donepezil (0.1 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group.
Figure 3.
Effect of DTZ in ICV-STZ-induced rat memory performance in Morris water maze (MWM) task. A: MWM escape latency in ICV-STZ rats. (B) Time (%) spent in the target quadrant in ICV-STZ rats. Values are expressed as means ± S.E.M. (n=12). Different letters (a–d) denote statistically significant differences among the samples (p < 0.05). STZ: streptozotocin (3 mg/kg), STZ+DTZ 10: diltiazem (10 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 20: diltiazem (20 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 40: diltiazem (40 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DON: donepezil (0.1 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group.
Figure 3.
Effect of DTZ in ICV-STZ-induced rat memory performance in Morris water maze (MWM) task. A: MWM escape latency in ICV-STZ rats. (B) Time (%) spent in the target quadrant in ICV-STZ rats. Values are expressed as means ± S.E.M. (n=12). Different letters (a–d) denote statistically significant differences among the samples (p < 0.05). STZ: streptozotocin (3 mg/kg), STZ+DTZ 10: diltiazem (10 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 20: diltiazem (20 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 40: diltiazem (40 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DON: donepezil (0.1 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group.
Figure 4.
Effect of DTZ on brain anti-oxidative parameters in ICV-STZ-induced rat brain homogenates. (A) Lipid peroxidation (LPO) as measured by TBARS, (B) Glutathione (GSH) levels, (C) Superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 6. Different letters (a–d) indicate statistically significant differences among the samples (p < 0.05). STZ: streptozotocin (3 mg/kg), STZ+DTZ 10: diltiazem (10 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 20: diltiazem (20 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 40: diltiazem (40 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DON: donepezil (0.1 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group.
Figure 4.
Effect of DTZ on brain anti-oxidative parameters in ICV-STZ-induced rat brain homogenates. (A) Lipid peroxidation (LPO) as measured by TBARS, (B) Glutathione (GSH) levels, (C) Superoxide dismutase (SOD) levels. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 6. Different letters (a–d) indicate statistically significant differences among the samples (p < 0.05). STZ: streptozotocin (3 mg/kg), STZ+DTZ 10: diltiazem (10 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 20: diltiazem (20 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 40: diltiazem (40 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DON: donepezil (0.1 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group.
Figure 5.
Effect of DTZ on the nitrite and pro-inflammatory cytokines in ICV-STZ-induced rat brain tissues. (A) nitrite levels, (B) TNF-α levels and (C) IL-1β. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 6. Different letters (a–d) indicate statistically significant differences among the samples (p < 0.05). STZ: streptozotocin (3 mg/kg), STZ+DTZ 10: diltiazem (10 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 20: diltiazem (20 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 40: diltiazem (40 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DON: donepezil (0.1 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group.
Figure 5.
Effect of DTZ on the nitrite and pro-inflammatory cytokines in ICV-STZ-induced rat brain tissues. (A) nitrite levels, (B) TNF-α levels and (C) IL-1β. Values are expressed as mean ± SEM; n = 6. Different letters (a–d) indicate statistically significant differences among the samples (p < 0.05). STZ: streptozotocin (3 mg/kg), STZ+DTZ 10: diltiazem (10 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 20: diltiazem (20 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 40: diltiazem (40 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DON: donepezil (0.1 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group.
Figure 6.
Effect of DTZ on the total protein content and amyloid β precursor protein (APP) expression in ICV-STZ-induced rat brain tissues. (A) Total protein content was measured in brain homogenates four weeks after ICV-STZ injection. (B) APP protein levels in rat brain homogenates were determined by immunoblot analysis and quantified by image analysis (lower panel). Equal loading of proteins was illustrated by β-tubulin bands. Values are expressed as means ± S.E.M. (n=6). Different letters (a–d) indicate statistically significant differences among the samples (p < 0.05). APP: Amyloid β precursor protein, STZ: streptozotocin (3 mg/kg), STZ+DTZ 10: diltiazem (10 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 20: diltiazem (20 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 40: diltiazem (40 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DON: donepezil (0.1 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group. .
Figure 6.
Effect of DTZ on the total protein content and amyloid β precursor protein (APP) expression in ICV-STZ-induced rat brain tissues. (A) Total protein content was measured in brain homogenates four weeks after ICV-STZ injection. (B) APP protein levels in rat brain homogenates were determined by immunoblot analysis and quantified by image analysis (lower panel). Equal loading of proteins was illustrated by β-tubulin bands. Values are expressed as means ± S.E.M. (n=6). Different letters (a–d) indicate statistically significant differences among the samples (p < 0.05). APP: Amyloid β precursor protein, STZ: streptozotocin (3 mg/kg), STZ+DTZ 10: diltiazem (10 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 20: diltiazem (20 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DTZ 40: diltiazem (40 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group, STZ+DON: donepezil (0.1 mg/kg) plus streptozotocin (3 mg/kg) injected group. .
Figure 7.
Effect of DTZ on immunohistostaining in ICV-STZ-induced rat brain sections. Immunoreactive signal of amyloid-β visualized by polyclonal rabbit antibody to amyloid-β-42. (A) Control group, (B) ICV-STZ injected group (3 mg/kg), (C) DTZ (10 mg/kg) plus ICV-STZ (3 mg/kg) injected group, (D) DTZ (20 mg/kg) plus ICV-STZ (3 mg/kg) injected group, (E) DTZ (40 mg/kg) plus ICV-STZ (3 mg/kg) injected group, (F) DON (0.1 mg/kg) plus ICV-STZ (3 mg/kg) injected group. The brown reaction products (DAB) shown in arrows, clearly indicates marked amyloid deposition in ICV-STZ-induced group and weak staining was observed in DTZ (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg) and DON (0.1 mg/kg) treated groups. Nissl counterstain. Scale as 100µM. Magnification 200X. ICV-STZ: intra-cerebroventricular-streptozotocin, DTZ: diltiazem, DON: donepezil.
Figure 7.
Effect of DTZ on immunohistostaining in ICV-STZ-induced rat brain sections. Immunoreactive signal of amyloid-β visualized by polyclonal rabbit antibody to amyloid-β-42. (A) Control group, (B) ICV-STZ injected group (3 mg/kg), (C) DTZ (10 mg/kg) plus ICV-STZ (3 mg/kg) injected group, (D) DTZ (20 mg/kg) plus ICV-STZ (3 mg/kg) injected group, (E) DTZ (40 mg/kg) plus ICV-STZ (3 mg/kg) injected group, (F) DON (0.1 mg/kg) plus ICV-STZ (3 mg/kg) injected group. The brown reaction products (DAB) shown in arrows, clearly indicates marked amyloid deposition in ICV-STZ-induced group and weak staining was observed in DTZ (10, 20 and 40 mg/kg) and DON (0.1 mg/kg) treated groups. Nissl counterstain. Scale as 100µM. Magnification 200X. ICV-STZ: intra-cerebroventricular-streptozotocin, DTZ: diltiazem, DON: donepezil.
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).