1. Introduction
Scleroderma (systemic sclerosis; SSc) is a complex and heterogeneous connective tissue disease process that results in fibrosis in of the skin and internal organs[
1]. Dysregulated adaptive and innate immunity and endothelial damage are apparent at the earliest stages of disease, whereas persistent myofibroblast activation determines the subsequent skin and organ based fibrosis [
2]. In essence, SSc represents an abnormally enhanced wound healing or processes leading to fibrosis of skin and internal organs via extracellular matrix (ECM) deposition. This leads to organ dysfunction and failure linked to the increased mortality in this group of patients. The primary cause of death in SSc has now shifted from, historically, scleroderma renal crisis, to lung fibrosis, pulmonary hypertension and cardiac disease [
3]. It is also important to note that the morbidity in SSc can start at early stages of disease and that mostly organ systems involved in SSc are lined by epithelial cells. These cells have important homeostatic roles, have major immunoregulatory processes and represent the first barrier to any environmental trigger.
Whilst the precise cellular and molecular mechanisms are not fully elucidated, several types of autoantibodies have been identified in the sera of SSc patients, including a range of disease-specific anti-nuclear antibodies such as anti-RNA polymerase (ARA), anti-centromere (ACA) and anti-topoisomerase antibodies (ATA), used clinically to stratify patients [
4], but also less clinically characterised antibodies defined by binding to and activation of target cells; including anti-endothelial cell antibodies(AECA)[
5,
6], anti-fibroblast [
7] , anti-matrix metalloproteinase, anti-platelet-derived growth factor receptor (PDGFR) [
8] and antifibrillin-1 antibodies [
9], each of which could directly contribute to disease pathogenesis, or otherwise represent secondary phenomena induced by tissue damage. The presence of disease-specific auto-antibodies such ACA, ATA, ARA precedes the clinical diagnosis of SSc whereas this is not clearly established for the cellular activating antibodies [
10].
Accordingly, endothelial cells as a target for autoantibodies (AECAs) are considered especially relevant to SSc. These cells regulate leukocyte adhesion and transmigration, activate lymphocytes and are themselves a source of several key inflammation mediators. Activation of these cells may provide a link between the immune system and fibrosis seen in SSc, through cross-talk with migrating immune cells, and mobilization of perivascular stem cells which contribute to the pathogenic tissue myofibroblasts. AECA are reported in 44-84% of SSc patients and are associated with more severe vascular involvement [
11]. It remains unclear, however, whether AECA play a direct role in causing endothelial dysfunction
in vivo, in SSc.
Furthermore, SSc autoantibodies may stimulate normal fibroblasts via the Ha-Ras pathways, converting them into activated myofibroblasts, which produce increased levels of collagens and other extracellular matrix (ECM) components characteristically overexpressed by SSc fibroblasts [
12]. Thus, dysregulated production of self-damaging autoantibodies may be a pathogenic link between dysregulated immunity and fibrosis in SSc, however, further mechanistic evidence is needed, and whilst it is clear that activation of the cellular and humoral immune systems in SSc, direct evidence linking this to the damaging fibrosis is yet to be demonstrated.
There is growing recognition that epithelial cells play a crucial role in the development of fibrosis and the regulation of tissue [
13,
14], which may be highly relevant to SSc pathogenesis, given the increasing knowledge of epithelial phenotype changes in SSc [
15,
16,
17,
18,
19]. Epithelial cells covering the outermost layer of the skin, as well as forming the lining cell layer of internal organs such as the respiratory, renal and gastrointestinal tracts, representing an integumental cell surface with maximal exposure to environmental factors [
20] and collocating with major sites of clinically evident fibrosis in SSc. Moreover, the epithelia represent a large innate and adaptive immune organ and site of initiation of immune responses.
In this paper, we investigate and elucidate the role of IgG directed at epithelial cells in SSc patients as a potential driver of pathological keratocyte activation and promotor of the SSc fibrotic cascade.
2. Materials and Methods
Patients Patients under the care of the UCL Centre for Rheumatology and Connective Tissue Diseases (Royal Free Hospital) who fulfilled the 2013 ACR/EULAR criteria of diagnosis were recruited [
21]. Written informed consent was obtained from all patients and healthy controls included in the study. Plasma was isolated from blood sampled from sequential consenting patients attending for review and then stored at -80°C prior to assay.
Anti-epithelial cell IgG binding assay Primary human keratinocyte cells were cultured with serum free defined keratinocyte medium supplemented with L-glutamine. When confluent, cells were released by trypsinisation and then transferred into 96 well microtitre plates pre-coated with gelatin. Once the cells were confluent, usually at 48-72 hours, the media were removed and the cells fixed by adding 200 µL of 0.1% glutaraldehyde in PBS to each well, left for 10 min at 4°C. Cells were then washed gently 4 times in PBS and left to dry overnight. Fixed cells were examined for confluence by microscopy and stored at 4°C prior to use in the anti-epithelial cell assay.
At the start of the assay, non-specific binding protein was blocked with 10% milk powder in PBS. 200 µL of milk/PBS was added to each well and left at room temperature for 15 minutes followed by aspiration and replacement of milk/PBS. This was repeated for 4 cycles. Test sera were diluted 1/10, 1/80, 1/320, 1/1280 in 10% milk powder in PBS. 50 µL of the test sera were added to each microtitre well in duplicate for each sample. The plates were left at room temperature for 1 hour and then washed 6 times with 10% milk powder PBS. Keratinocyte binding IgG was detected by 60 minutes incubation with HRP conjugated rabbit anti-human IgG dilution (DAKO # P0214) diluted 1/500 in milk powder PBS. 50 µL of antibody was added per well and left at room temperature for 1 hour. Plates were then washed vigorously 5 times in PBS, and then the bound horse radish peroxidase activity was assayed by colorimetric analysis of the peroxidation of ortho-phenylenediamine dihydrochloride (OPD) at pH 5, using OPD buffer (12.4g of Na2HPO4.12H20, 350 ml water, pH adjusted to 5). 100 µL of the substrate solution was added to each microtitre well and optical density read at 450 nm with Titertek plate reader. Plates were read after 15 minutes.
Purification of SSc patients’ IgG using Protein A column purify kit (44667, Pierce/Perbio): The Pierce/Perbio Protein A column kit (#44667) was used to isolate IgG from SSc and healthy control plasma samples. The Protein A column was equilibrated with 5 ml of the Immunopure (A) IgG Binding buffer. Each diluted plasma sample was applied to the column and allowed to flow completely into the gel. The column was then washed with 15 ml of the Immunopure IgG Binding buffer, and then the bound IgG eluted with 5 ml of the Immunopure IgG Elution buffer. Each 1ml of elution buffer was collected in collection tubes and assayed by absorbance at 280nm for the total IgG protein content. The second 1ml fraction was found to contain the highest levels of IgG and was stored at -80°C and used in subsequent experiments.
Immunohistochemistry of Skin Biopsy Material 4 mm punch biopsies were obtained from the involved forearm skin of 6 early stage diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc) patients and matched sites of 6 healthy controls. Biopsies were formalin fixed and then embedded in paraffin prior to sectioning at 5µm. We then conducted immunohistochemistry of the obtained tissue samples, in order to investigate the epidermal expression of the IgG, using rabbit anti-human IgG polyclonal antibody (DAKO #P0214), and secondary fluorescent labelled goat anti-rabbit IgG. The fluorescent nuclear probe 4', 6-diamidino-2-phenylindole (DAPI) was as a counterstain to identify nucleated cells. The fields inspected were observed at x40 magnification. Slides were immersed in xylene for 10 minutes and then in 100% alcohol to remove the wax solvent. The slides were dipped in and out of the alcohol several times to allow thorough rinsing. They were subsequently immersed in a trough of 95% alcohol for 5 minutes, and then in a trough of 70% alcohol for 5 minutes. Lastly, the slides were immersed in distilled water (DH2O) for 5 minutes to remove all traces of alcohol.
Once dry, the sections were circled using a hydrophobic pen and allowed to dry. The sections were then re-hydrated by immersing in PBS 3 times for 5 minutes each time. The slides were boiled in citrate for 10 minutes. 25% secondary antibody species-specific serum was made up to block non-specific binding. The primary antibody (Anti-human IgG polyclonal) was made up and 40μl aliquoted onto each section covering each entire section then placed in the humidity chamber for 10 minutes. Tissue slides were placed back into the humidity chamber for 1 hour followed by 3 times 5 minutes PBS rinse. The secondary species-specific antibody was made up, 40μl aliquoted onto each section. Then tissue slides were placed into the humidity chamber for 30 minutes. The slides were then rinsed with PBS 3 times for 5 minutes each. Sections were incubated in FITC-Avidin D (1:500 Vector Labs) in PBS for 30 minutes at room temperature. Slides were protected against UV light with aluminium foil. They were washed in PBS three times for 2 minutes each time. The ABC (Vectastain Elite) was made up 30 minutes before usage by adding 1.5 ml of PBS to 1 drop of reagent A and 1 drop of reagent B. 40μl of the ABC was aliquoted until all the sections were completely covered, the slides then left for 30 minutes. They were then rinsed with PBS 3 times for 5 minutes each time. The sections were mounted with Vector-shield DAPI mounting solution, covered with Vector aqueous Anti-fade fluorescent mounting medium, and sealed with nail polish. The slides were stored in the dark at 4°C.
Cell-viability assay: The potential toxicity of the IgG on human keratinocytes was tested using the tetrazolium salt WST-1 (1644 807; Boehringer Mannheim Biochemicals Inc., Indianapolis, Indiana, USA). This assay depends on the conversion of the tetrazolium salt WST-1 (Boehringer Mannheim# 1644 807) (changes to dark red on conversion) by mitochondrial dehydrogenases in viable cells. 10µl of WST-1 is added per well to cells cultured in 100 µl of culture medium in 96 well plates. Cells were incubated for a further 4 hours and the colour conversion measured by reading the absorbance of light at 450 nm with reference wavelength of 600 nm.
Assay for IL-1α release by keratinocytes Keratinocytes were activated by purified SSc and control IgG. IgG was purified using immobilized Protein-A column from Fisher Scientific as above and normal human keratinocytes (NHK) were passaged two or three times in a 6-well dish containing fully supplemented keratinocyte basic medium (KBM). At nearly 70% subconfluency, the cells were cultured in basic KBM for 24 h, with or without the addition of SSc IgG sera (0, 10 and 100 μg/ml) in KSF-M, normal IgG sera (0, 10 and 100 μg/ml) in KSF-M, or else KSF-M media only. Conditioned media, as well as cell lysate, was collected at the end of the 24-hour treatment and assayed for cell layer and secreted media IL-1α levels by R&D Quantikine Human IL-1α Immunoassay (R&D # DLA50).
Human epithelial reporter cell lines for TLR 2 and 3 In order to investigate the potential for innate responses by the SSc IgG, HEK reporter cell lines (human embryonic tissue cell line) transfected with human TLR2 or TLR3 carrying a reporter gene for NFκB linked to SEAP (HEK-Blue™-hTLR2 Cells and -hTLR3 Cells, Invivogen, CA, #hkb-htlr2 &3) were cultured with or without a range of concentrations of SSc IgG (0.1-100µg/ml) for 3 hours. For these assays SSc IgG was purified from plasma samples demonstrating positive binding in the anti-epithelial cell antibody assay. Samples were included from 14 limited cutaneous subset (lcSSc) and 7 diffuse cutaneous (dcSSc) patients, as well as 5 healthy control (HC) individuals (
Table 1). Media were then removed after 3 hours stimulation by IgG and then assayed for the SEAP reporter gene product, used as an index of TLR signaling in the HEK cells.
Statistical analysis GrapPad Prism software was used throughout. Populations were first compared by ANOVA, followed by nonparametric testing for significance of treatment effects.
3. Results
Anti-epithelial cell antibody ELISA assay Initially we focused on testing whether IgGs from SSc plasma were able to bind fixed keratinocytes cultured
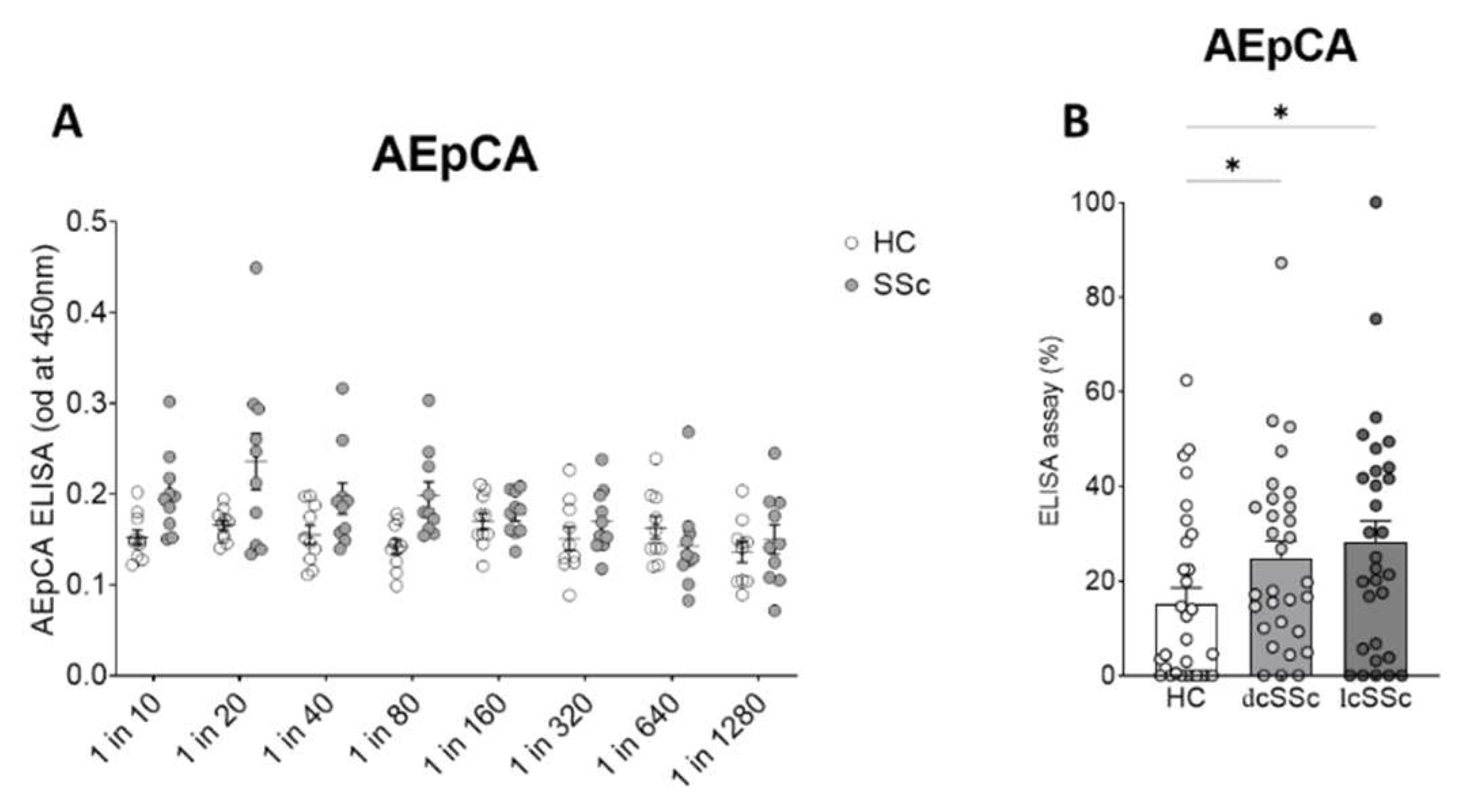
in vitro, using the anti-epithelial cell antibody ELISA (AEpCA) was performed as described. An initial screening study was performed to test the performance of the assay using 10 dcSSc samples and 10 healthy control samples at dilutions from 1/20 to 1/1280 which showed enhanced and dose dependent binding of the SSc IgG ( ANOVA,p<0.001 for overall effect SSc vs HC IgG, p<0.0048 for dose effect). A dilution of 1/80 was found to give the best performance in the assay with optimal differential between binding of scleroderma and control IgG and was used in subsequent assays (p<0.0044 for SSc vs HC at 1/80 dilution)(
Figure 1A).
At a dilution of 1 in 80, 30 further control samples, 30 dcSSc , and 30 lcSSc samples were screened by anti-epithelial cell ELISA (
Figure 1B,
Table 2), demonstrating overall differences between groups (ANOVA p<0.033) and elevated binding in both lcSSc and dcSSc patients samples (Kruskall-Wallace test p<0.014 for lcSSc vs HC, p<0.041 for dcSSc vs HC). Although there was a trend for median anti-epithelial cell ELISA values to be higher in lcSSc than in dcSSc subgroups, these effects did not reach significance.
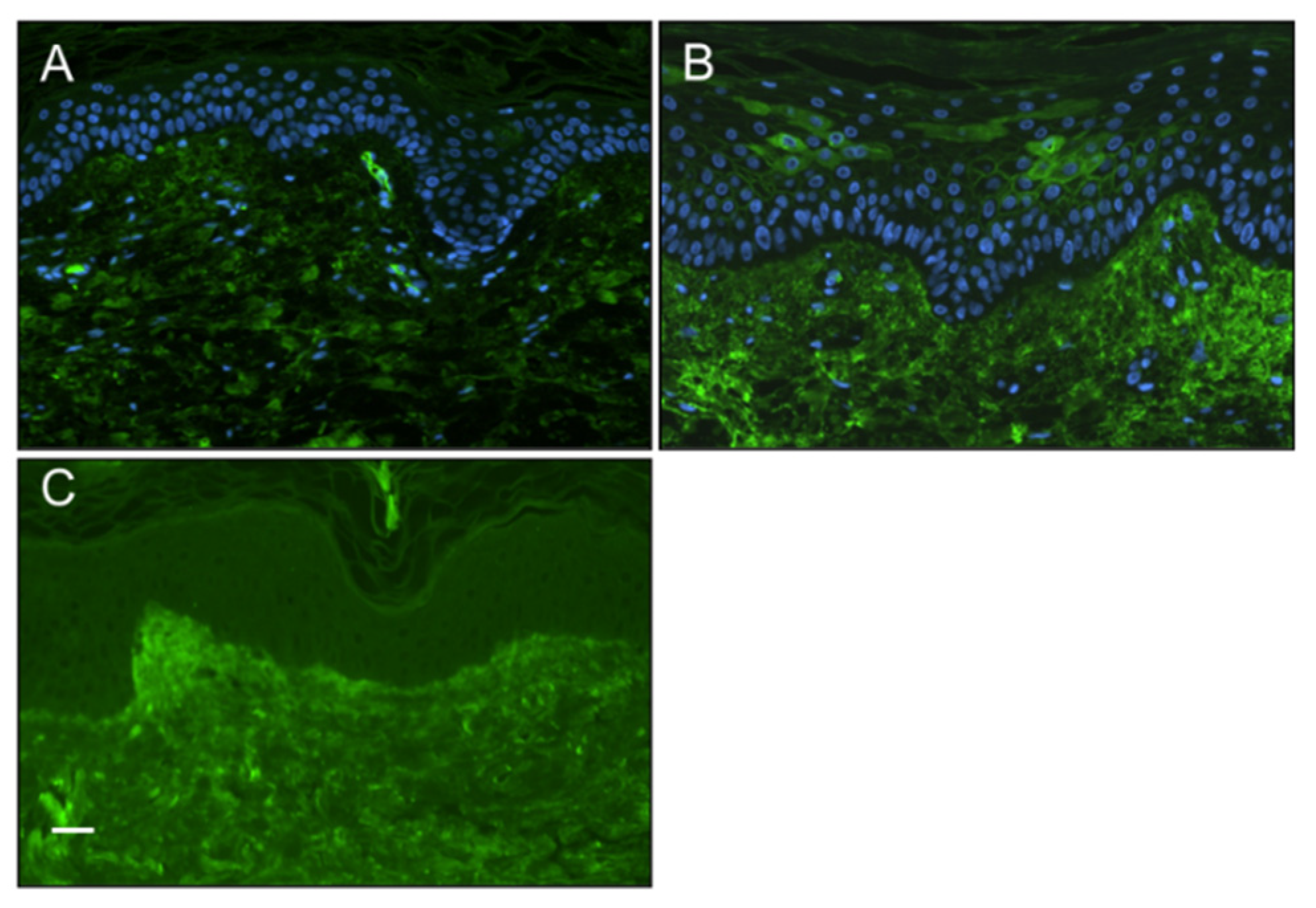
Positive staining for the presence of IgG in the epidermis of SSc patients skin biopsies Furthermore, to explore the possibility of patient IgG binding to keratinocytes
in vivo, we conducted immunostaining of sections of diffuse cutaneous SSc (dcSSc) and healthy skin biopsy material (both n=6) to detect evidence of autoantibody binding of the epidermis. Our results demonstrated the presence of IgG in cytoplasmic and cell surface distributions in some, but not all, SSc epidermal sections (observed in 2 out of 6 patients), whereas no healthy control sections showed positive staining (
Figure 2).
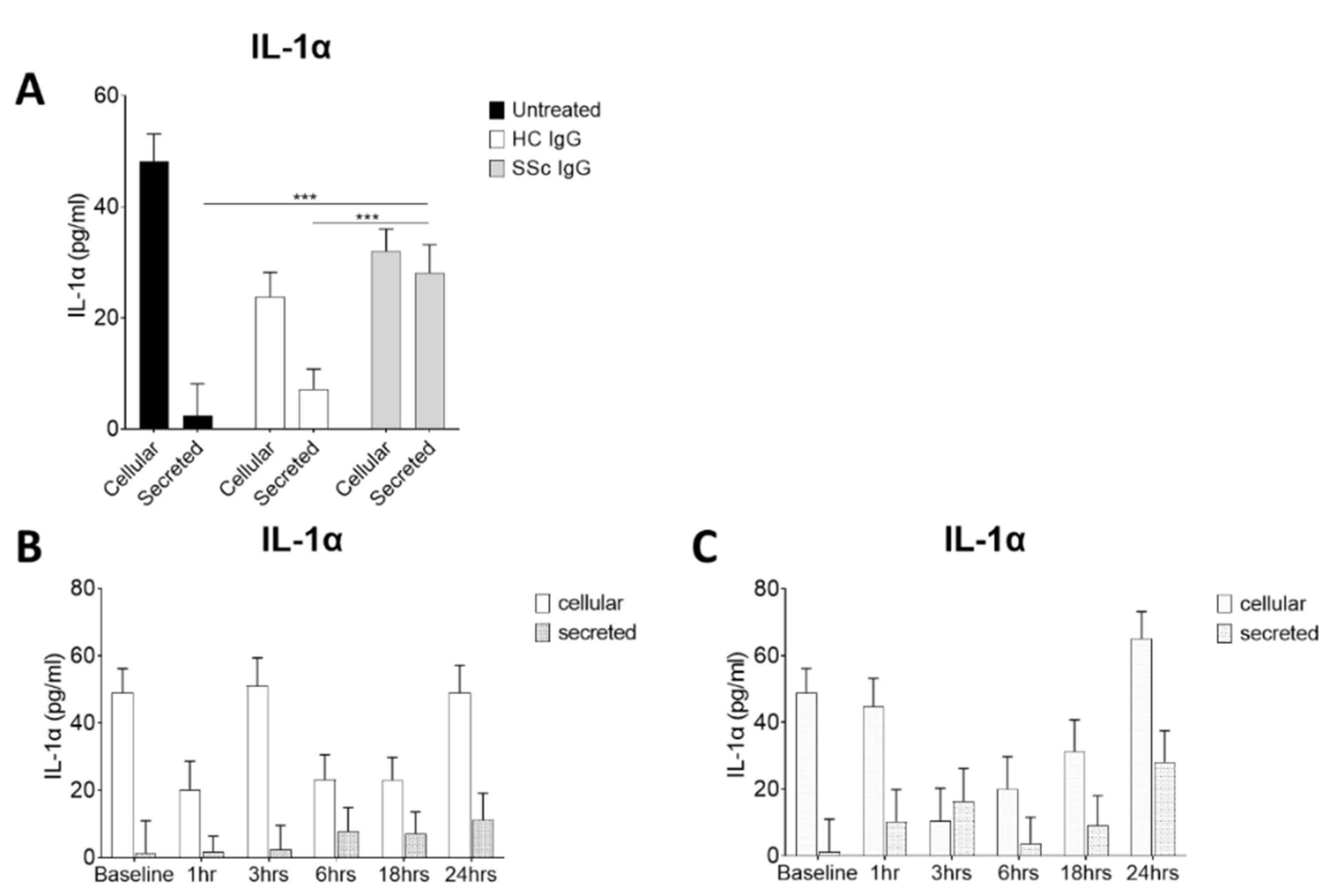
Activation of keratinocytes by systemic sclerosis IgG in vitro Because of the enhanced binding activity of SSc sera in AEpCA ELISA, it was hypothesised that SSc immunoglobulins could be binding to and activating keratinocytes in the disease tissue. IgG purified on protein A columns from severe SSc patients and from healthy controls were assayed for the capacity to activate keratinocytes
in vitro. Isolated IgG from 3 patients with recent onset diffuse SSc which tested with high titre in AEpCA ELISA and from 3 healthy control sera were used to activate cultured primary human keratinocytes. IL-1α levels in the conditioned media versus the keratinocyte cell layer levels were used as a readout of keratinocyte activation. Treatment with SSc IgG (10μg/ml) was associated with significantly higher levels of IL-1α secreted into the media, when compared to control IgG treated or media alone (
Figure 3A). In other experiments, a time course was determined by treating keratinocytes with these same SSc and HC IgG (10μg/ml) and removing media and cell layer at various time points for assay. Treatment with SSc IgG but not HC IgG, resulted in a rapid induction of IL-1α release, apparent by 3 hours with SSc IgG although this did not reach significance (
Figure 3B&C). No significant cytotoxicity was seen with concentrations of SSc IgG 10-120µg/ml in the MTT cyto-toxicity assay (data not shown).
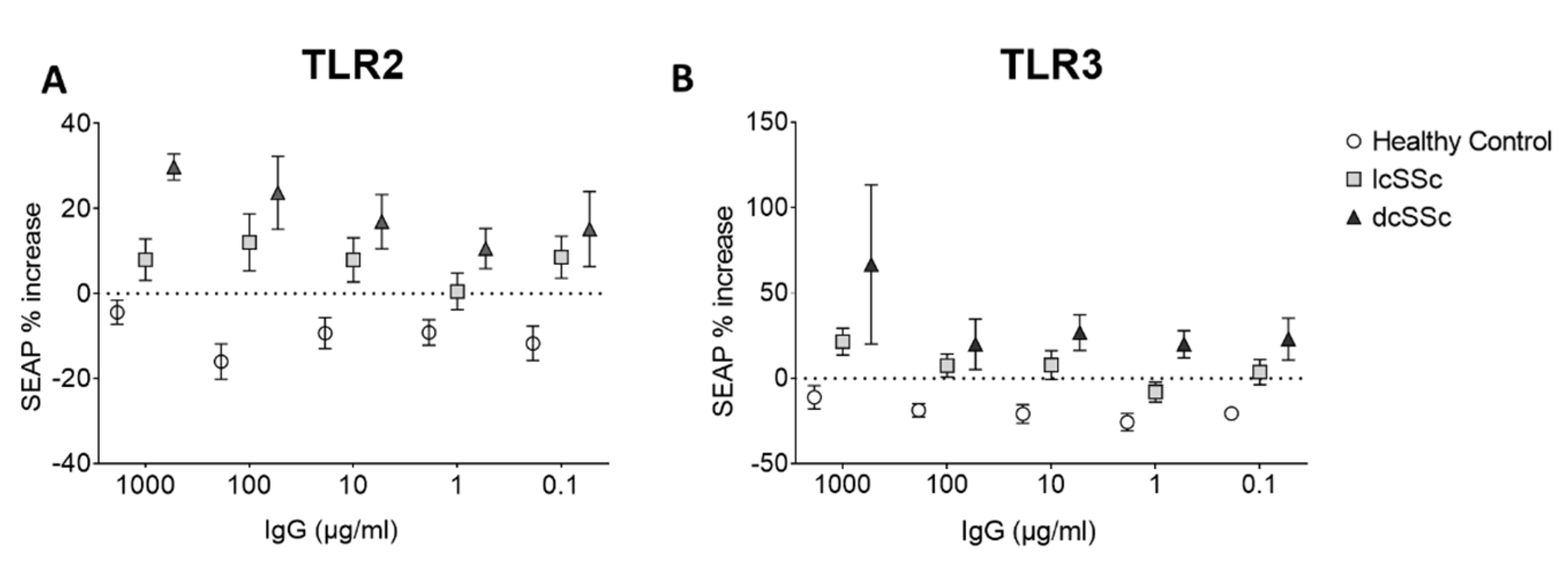
Effect of SSc IgG on TLR pathway signaling in HEK cells. Because of the induction of innate responses, an attempt was made to measure the effect of the SSc and HC IgG on the TLR pathway using HEK hTLR2 and hTLR3 reporter cell. Treatment with HC IgG led to a small decrease in reporter gene expression in both cell types, whereas lcSSc and dcSSc induced SEAP expression in both TLR2 and TLR3 cells (TLR2 cells ANOVA p<0.0001 for overall effect, p<0.012 for effect of lcSSc vs HC, p<0.0023 for dcSSc vs HC, higher levels in dcSSc vs lcSSc p<0.014, TLR3 cells p<0.0003 for overall effect, p<0.025 for effect of lcSSc vs HC, p<0.0002 for dcSSc vs HC, higher in dcSSc vs lcSSc p<0.032) (
Figure 4), indicating a possible effect on innate signal induction in these cells, more in dcSSc than lcSSc.
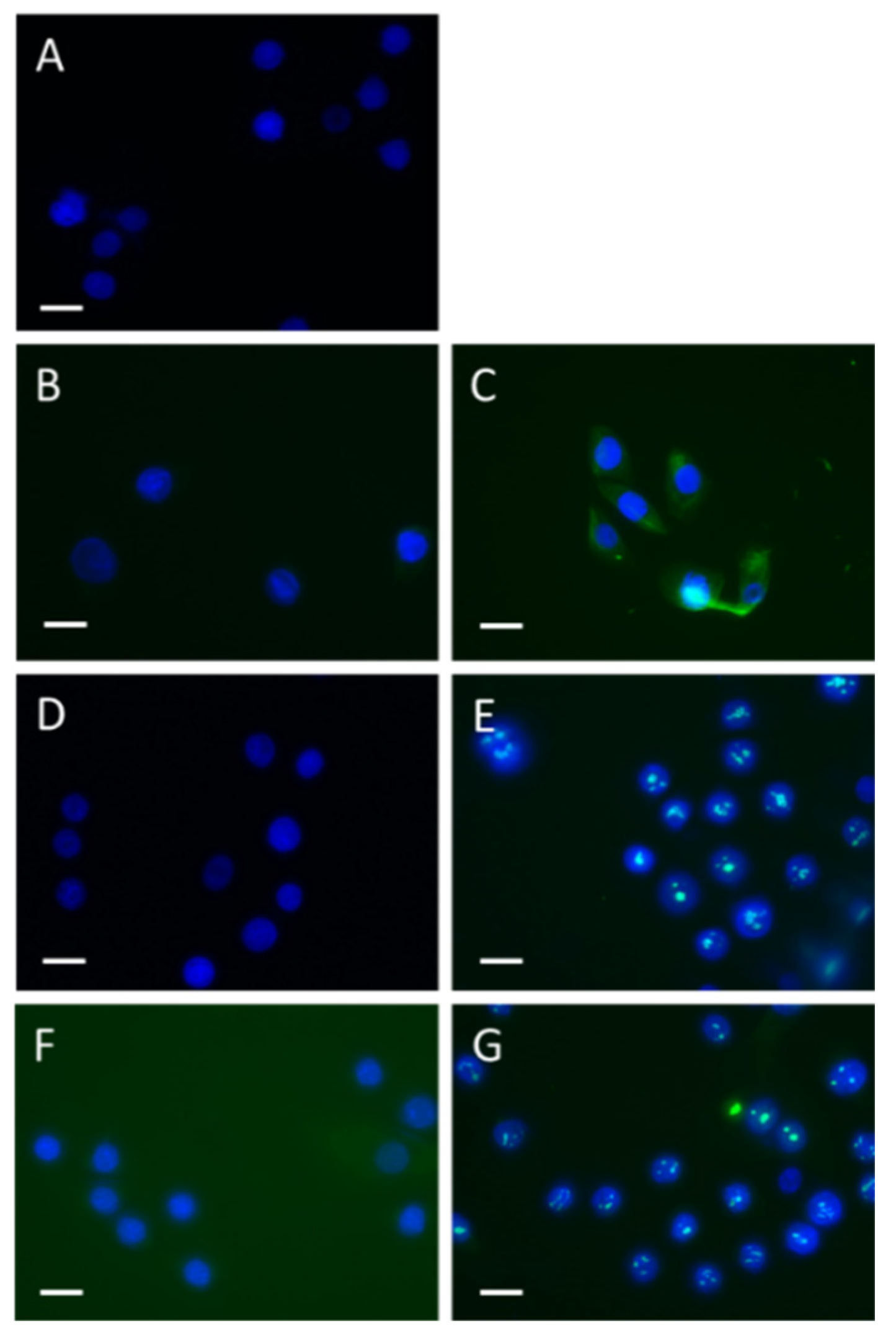
Uptake of SSc but not HC IgG by keratinocytes To determine whether SSc IgG was capable of entering keratinocytes, HaCat cells were cultured with or without the addition of SSc IgG or HC IgG. The cells were then fixed at two different time points, 10 minutes and 3 hours, and subject to immunostaining using both Fc-specific and Fab-specific antibodies for human IgG. The results demonstrated that at 10 minutes, SSc IgG had translocated to the cytoplasmic compartment, whereas HC IgG did not exhibit this. Additionally, after 3 hours, SSc IgG was found to further translocate to the nuclear compartment (
Figure 4).
4. Discussion
In this study, we demonstrate positive binding of SSc patients’ IgG to fixed human keratinocytes, which did not differ significantly between patient groups. It has been previously established that the epidermis in SSc patients undergoes critical changes, including a proposed model of TGF-β induced activation of epithelial cells, causing an epithelial to mesenchymal transition (EMT)-like phenomena and resulting in the hallmark damaging and pathogenic fibrosis of the disease[
19]. Reflecting on the potential for autoantibodies to initiate cellular damage in various other autoimmune diseases and due to the current gap in knowledge of the role of anti-epithelial cell antibodies specifically in SSc, we explored whether IgG antibodies targeting epithelial cells in skin lesions of SSc patients could be the potential drivers of pathological keratocyte activation and the initiation of the fibrotic cascade.
As a limitation we do not define the target antigen(s) involved and this has also been a limitation for other studies of pathogenic antibodies in the disease , for example the endothelial cell antibodies in the disease and even specific anti-PDGFR antibodies[
8] have not been a consistent finding between studies. Moreover, in our study, we found that SSc patients’ IgG activated keratinocytes inducing the release of IL-1a, a similar effect to that shown for endothelial cells [
5]. Moreover, SSc IgGs were found to induce signaling in reporter cells expressing TLR2 and TLR3, representing a potential mechanism, since these receptors are highly expressed by epithelial cells.
Certain of these findings are consistent with previous studies from Rubin demonstrating that SSc IgG induce innate responses via uptake into the endosomal compartment [
22]. Also of interest, in our study healthy control IgGs were found to dimmish the TLR signaling in reporter cells, indicating a potential immunoregulatory effect of healthy control IgG.
As discussed previously, the main early pathophysiological mechanisms in SSc are believed to include both microvascular damage as well as the presence of autoantibodies. IgG activation of epithelial cells could be included amongst the disease-initiating mechanisms, at least in some patients, as our results indicate variation in the extent of this effect. Where environmental factors have been implicated such as solvent exposures [
23] these might be of relevance to surface epithelial mechanisms, whereas endotheial cell damage could me triggered by systemic factors such as viral infection [
24] speculating that both external integumental activation and internal endothelial activation could operate as initiating factors. The inflammatory cascades induced could trigger transition of normal fibroblasts to myofibroblasts, which are responsible for abnormal extracellular matrix deposition in affected tissues, and eventual organ damage and deterioration.
Although our results demonstrate anti-epithelial cell antibodies as present in SSc patients’ plasma, our study has several limitations, including small sample size and lack of clear target antigen involved in the binding. However, the triggering of innate immune mechanisms in this cell layer by IgGs is of interest as a potential mechanism that could be addressed by therapeutic antagonists especially if the precise mechanisms can be better elucidated.
5. Conclusions
In conclusion, in this study, we have shown evidence of anti-epithelial cell antibodies in the plasma of SSc patients and demonstrated that SSc IgGs are capable of activating and triggering relevant innate immune mechanisms. This represents a potential mechanism triggering epithelial activation and contributing to downstream fibrosis in the skin, as well as a potential target for future attempts at therapy.
Author Contributions
C M Composed the article, characterized cases and provided patient samples, VW co-authored the article, provided patient samples and did bio-asays, JW perfomre TLR reporter cell line assays, LN co-authored the article, provided patient samples and performed assay, SLG purified SSc IgG samples and performed assays, SY co-authored the article and purified SSc IgG samples, , BAA performed assays, FN performed assays and characterised SSc patients, DA oversaw and supervised the translational research, RS conceived of the study, oversaw the translational research and coauthored the article. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Funding
Funding for the study was provided by the Rosetrees Trust, “Treating Scleroderma” #M429-F1, and by The Peltz Trust at the Prism Fund, “Investigating novel treatments for connective tissue disorders”.
Institutional Review Board Statement
The study was conducted according to the guidelines of the Declaration of Helsinki, and approved by the Institutional Review Board of Royal Free Hospital (North Thames NHRA REC, IRAS 270295: Elucidating Pathogenesis Study Implementation of SA6, 16th December 2022.
Informed Consent Statement
Informed consent was obtained from all subjects involved in the study.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Denton, C.P.; Khanna, D. Systemic sclerosis. Lancet (Lond. Engl. ) 2017, 390, 1685–1699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Allanore, Y.; Simms, R.; Distler, O.; Trojanowska, M.; Pope, J.; Denton, C.P.; et al. Systemic sclerosis. Nat. Rev. Dis. Primers 2015, 1, 15002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nihtyanova, S.I.; Schreiber, B.E.; Ong, V.H.; Rosenberg, D.; Moinzadeh, P.; Coghlan, J.G.; et al. Prediction of pulmonary complications and long-term survival in systemic sclerosis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2014, 66, 1625–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hamaguchi, Y. Autoantibody profiles in systemic sclerosis: predictive value for clinical evaluation and prognosis. J. Dermatol. 2010, 37, 42–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carvalho, D.; Savage, C.O.; Isenberg, D.; Pearson, J.D. IgG anti-endothelial cell autoantibodies from patients with systemic lupus erythematosus or systemic vasculitis stimulate the release of two endothelial cell-derived mediators, which enhance adhesion molecule expression and leukocyte adhesion in an autocrine manner. Arthritis Rheum. 1999, 42, 631–640. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Healy, C.M.; Carvalho, D.; Pearson, J.D.; Thornhill, M.H. Raised anti-endothelial cell autoantibodies (AECA), but not anti-neutrophil cytoplasmic autoantibodies (ANCA), in recurrent oral ulceration: modulation of AECA binding by tumour necrosis factor-alpha (TNF-alpha) and interferon-gamma (IFN-gamma). Clin Exp Immunol. 1996, 106, 523–528. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fineschi, S.; Cozzi, F.; Burger, D.; Dayer, J.M.; Meroni, P.L.; Chizzolini, C. Anti-fibroblast antibodies detected by cell-based ELISA in systemic sclerosis enhance the collagenolytic activity and matrix metalloproteinase-1 production in dermal fibroblasts. Rheumatology 2007, 46, 1779–1785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baroni, S.S.; Santillo, M.; Bevilacqua, F.; Luchetti, M.; Spadoni, T.; Mancini, M.; et al. Stimulatory autoantibodies to the PDGF receptor in systemic sclerosis. N Engl J Med. 2006, 354, 2667–2676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pandey, J.P.; Page, G.P.; Silver, R.M.; LeRoy, E.C.; Bona, C.A. Anti-fibrillin-1 autoantibodies in systemic sclerosis are GM and KM allotype-restricted. Exp Clin Immunogenet. 2001, 18, 123–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Burbelo, P.D.; Gordon, S.M.; Waldman, M.; Edison, J.D.; Little, D.J.; Stitt, R.S.; et al. Autoantibodies are present before the clinical diagnosis of systemic sclerosis. PLoS One 2019, 14, e0214202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, V.S.; Tripathy, N.K.; Misra, R.; Nityanand, S. Antiendothelial cell antibodies in scleroderma correlate with severe digital ischemia and pulmonary arterial hypertension. J. Rheumatol. 1998, 25, 462–466. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Smaldone, S.; Olivieri, J.; Gusella, G.L.; Moroncini, G.; Gabrielli, A.; Ramirez, F. Ha-Ras stabilization mediates pro-fibrotic signals in dermal fibroblasts. Fibrogenesis Tissue Repair. 2011, 4, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Werner, S.; Krieg, T.; Smola, H. Keratinocyte-fibroblast interactions in wound healing. J. Investig. Dermatology. 2007, 127, 998–1008. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Thiery, J.P.; Acloque, H.; Huang, R.Y.; Nieto, M.A. Epithelial-mesenchymal transitions in development and disease. Cell 2009, 139, 871–890. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aden, N.; Nuttall, A.; Shiwen, X.; de Winter, P.; Leask, A.; Black, C.M.; et al. Epithelial cells promote fibroblast activation via IL-1alpha in systemic sclerosis. J. Investig. Dermatology. 2010, 130, 2191–2200. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitorowicz-Buniak, J.; Shiwen, X.; Denton, C.P.; Abraham, D.; Stratton, R. Abnormally differentiating keratinocytes in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients show enhanced secretion of CCN2 and S100A9. J. Investig. Dermatology. 2014, 134, 2693–2702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tabata, H.; Hara, N.; Otsuka, S.; Yamakage, A.; Yamazaki, S.; Koibuchi, N. Correlation between diffuse pigmentation and keratinocyte-derived endothelin-1 in systemic sclerosis. Int J Dermatol. 2000, 39, 899–902. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, B.; Borowczyk, J.; Boehncke, W.H.; Truchetet, M.E.; Modarressi, A.; Brembilla, N.C.; et al. Dysfunctional Keratinocytes Increase Dermal Inflammation in Systemic Sclerosis: Results From Studies Using Tissue-Engineered Scleroderma Epidermis. Arthritis Rheumatol. 2021, 73, 1311–1317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nikitorowicz-Buniak, J.; Denton, C.P.; Abraham, D.; Stratton, R. Partially Evoked Epithelial-Mesenchymal Transition (EMT) Is Associated with Increased TGFbeta Signaling within Lesional Scleroderma Skin. PLoS One. 2015, 10, e0134092. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Povey, A.; Guppy, M.J.; Wood, M.; Knight, C.; Black, C.M.; Silman, A.J. Cytochrome P2 polymorphisms and susceptibility to scleroderma following exposure to organic solvents. Arthritis Rheumatism. 2001, 44, 662–665. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- van den Hoogen, F.; Khanna, D.; Fransen, J.; Johnson, S.R.; Baron, M.; Tyndall, A.; et al. 2013 classification criteria for systemic sclerosis: an American College of Rheumatology/European League against Rheumatism collaborative initiative. Arthritis Rheumatism. 2013, 65, 2737–2747. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eloranta, M.L.; Franck-Larsson, K.; Lovgren, T.; Kalamajski, S.; Ronnblom, A.; Rubin, K.; et al. Type I interferon system activation and association with disease manifestations in systemic sclerosis. Ann. Rheum. Diseases. 2010, 69, 1396–1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Muntyanu, A.; Milan, R.; Rahme, E.; Baron, M.; Netchiporouk, E.; Canadian Scleroderma Research Group. Canadian Scleroderma Research Group. Organic solvent exposure and systemic sclerosis: A retrospective cohort study based on the Canadian Scleroderma Research Group registry. J Am Acad Dermatol. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kahaleh, M.B.; LeRoy, E.C. Autoimmunity and vascular involvement in systemic sclerosis (SSc). Autoimmunity. 1999, 31, 195–214. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
Figure 1.
Anti-epithelial cell antibody ELISA in SSc and control plasma (A) Initial screening by serial dilution revealed optimal differential binding at dilution of 1 in 80. (B) Multiple plasma samples were assayed at 1 in 80 dilution from HC, limited cutaneous SSc, and diffuse cutaneous SSc (each N=30)* p<0.05.
Figure 1.
Anti-epithelial cell antibody ELISA in SSc and control plasma (A) Initial screening by serial dilution revealed optimal differential binding at dilution of 1 in 80. (B) Multiple plasma samples were assayed at 1 in 80 dilution from HC, limited cutaneous SSc, and diffuse cutaneous SSc (each N=30)* p<0.05.
Figure 2.
Presence of IgG in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients Immunostaining of SSc and healthy control skin biopsy material for the presence of IgG by indirect immunofluoresence (green). (A) Healthy controls epidermal cell layers did not stain positive for IgG. (B) Some but not all SSc patients (2 out of 6) stained positive for IgG which appeared to stain the surface of keratinocytes. (C) No primary IgG control, showing as expected autofluoresence of the dermis. (scale bar 50μm).
Figure 2.
Presence of IgG in the epidermis of systemic sclerosis patients Immunostaining of SSc and healthy control skin biopsy material for the presence of IgG by indirect immunofluoresence (green). (A) Healthy controls epidermal cell layers did not stain positive for IgG. (B) Some but not all SSc patients (2 out of 6) stained positive for IgG which appeared to stain the surface of keratinocytes. (C) No primary IgG control, showing as expected autofluoresence of the dermis. (scale bar 50μm).
Figure 3.
Systemic sclerosis IgG promotes release of IL-1α by human keratinocytes (A) Normal human keratinocytes cultured in 6 well plates were treated with IgG( 10μM) from SSc patients and controls. After 24 hours IL-1α was assayed in media and cell layers by ELISA. Treatment with SSc IgG at 10μg/ml lead to a significant increase in release of IL-1α, not seen with control IgG treatment or media only. (B) A time course of IL-1α release following treatment with control IgG and (C) SSc IgG (10µg/ml) was determined by treating keratinocytes in 6 well plates, removing media and lysing cell layer at various timepoints. Treatment with SSc IgG but not HC trended to a rapidly evoked and biphasic induction of IL-1α release. ***=p<0.001.
Figure 3.
Systemic sclerosis IgG promotes release of IL-1α by human keratinocytes (A) Normal human keratinocytes cultured in 6 well plates were treated with IgG( 10μM) from SSc patients and controls. After 24 hours IL-1α was assayed in media and cell layers by ELISA. Treatment with SSc IgG at 10μg/ml lead to a significant increase in release of IL-1α, not seen with control IgG treatment or media only. (B) A time course of IL-1α release following treatment with control IgG and (C) SSc IgG (10µg/ml) was determined by treating keratinocytes in 6 well plates, removing media and lysing cell layer at various timepoints. Treatment with SSc IgG but not HC trended to a rapidly evoked and biphasic induction of IL-1α release. ***=p<0.001.
Figure 4.
Effect of SSc patients’ plasma IgG on TLR2 and TLR3 expressing reporter cell lines. HEK reporter cell lines overexpressing TLR2 or TLR3 were stimulated with HC and SSc IgG for 3 hours after which media were removed and assayed for SEAP as a marker of reporter gene expression indication activation of the TLR pathway.
Figure 4.
Effect of SSc patients’ plasma IgG on TLR2 and TLR3 expressing reporter cell lines. HEK reporter cell lines overexpressing TLR2 or TLR3 were stimulated with HC and SSc IgG for 3 hours after which media were removed and assayed for SEAP as a marker of reporter gene expression indication activation of the TLR pathway.
Figure 4.
Time course and apparent nuclear translocation of SSc IgG in HaCat cells.HaCat epithelial cells were cultured with or without addition of SSc and HC IgG (40μg/ml) and then fixed at various timepoints and stained for human IgG. (A) Shows no primary antibody IgG control, (B) HC IgG Fc at 10 minutes, (C) SSc IgG Fc at 10 minutes (D) HC Fc at 3 hours, (E) SSc IgG Fc at 3 hours, (F) HC Fab at 3 hours (G) SSc IgG Fab at 3 hours. (Bar=20μm).
Figure 4.
Time course and apparent nuclear translocation of SSc IgG in HaCat cells.HaCat epithelial cells were cultured with or without addition of SSc and HC IgG (40μg/ml) and then fixed at various timepoints and stained for human IgG. (A) Shows no primary antibody IgG control, (B) HC IgG Fc at 10 minutes, (C) SSc IgG Fc at 10 minutes (D) HC Fc at 3 hours, (E) SSc IgG Fc at 3 hours, (F) HC Fab at 3 hours (G) SSc IgG Fab at 3 hours. (Bar=20μm).
Table 1.
Characteristics of SSc patients’ plasma samples included in HEK reporter cell line assays. (ACA=antcentromere, ANA=antinuclear factor, ARA=anti-RNApolyemrase antibody, ATA=anti-topoisomerase antibody, ENA=extractable nuclear antigen, Pm/Scl= anti-PM/Scl antibody, U3RNP=anti-U3RNP antibody).
Table 1.
Characteristics of SSc patients’ plasma samples included in HEK reporter cell line assays. (ACA=antcentromere, ANA=antinuclear factor, ARA=anti-RNApolyemrase antibody, ATA=anti-topoisomerase antibody, ENA=extractable nuclear antigen, Pm/Scl= anti-PM/Scl antibody, U3RNP=anti-U3RNP antibody).
| Disease Subset |
N |
Autoantibody Profile |
| Healthy control |
5 |
NA |
| Diffuse cutaneous SSc |
7 |
ATA n=1, ARA n=2, U3RNP n=1, ANA pos ENA neg n=2 ANA neg n=1 |
| Limited cutaneous SSc |
14 |
ACA n=5, ARA n=1, ATA n=1, PM/Scl n=1, ANA pos ENA neg n=1 |
Table 2.
Distribution of individual results for patients and control sera, showing median values for normal sera (NS), limited systemic sclerosis sera (dcSSc), and diffuse systemic sclerosis sera (lcSSc).
Table 2.
Distribution of individual results for patients and control sera, showing median values for normal sera (NS), limited systemic sclerosis sera (dcSSc), and diffuse systemic sclerosis sera (lcSSc).
| |
AEpCA (Median, Interquartile Range) |
p vs Control
(Kruskall-Wallace Test) |
| Healthy control (n=30) |
6.1 (0-28.3) |
|
| Limited SSc (n=30) |
23.8 (5.65-43.2) |
p<0.041 |
| Diffuse SSc (n=30) |
18.8 (10-35.6) |
p<0.014 |
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).