Submitted:
08 July 2023
Posted:
11 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Literature Review
2.1. What is ChatGPT
2.2. Its Application and Limitations
3. Research Questions
4. Methodology
- The case is critical and allows testing a well formulated theory;
- The case is unique or extreme;
- The case is representative or typical;
- The case allows analysis of a previously inaccessible phenomenon; and,
- The case is longitudinal in nature (i.e. covering an extended period of time) and allows analysis at different points of time [22] (pp. 39–46).
- Data related to experiences with Large Language Models (LLMs), such as ChatGPT, when coding android applications is not sufficiently available to allow a representative quantitative study; and,
- To the best of the authors’ knowledge, experiences of using ChatGPT for Android App development have so far not been investigated.
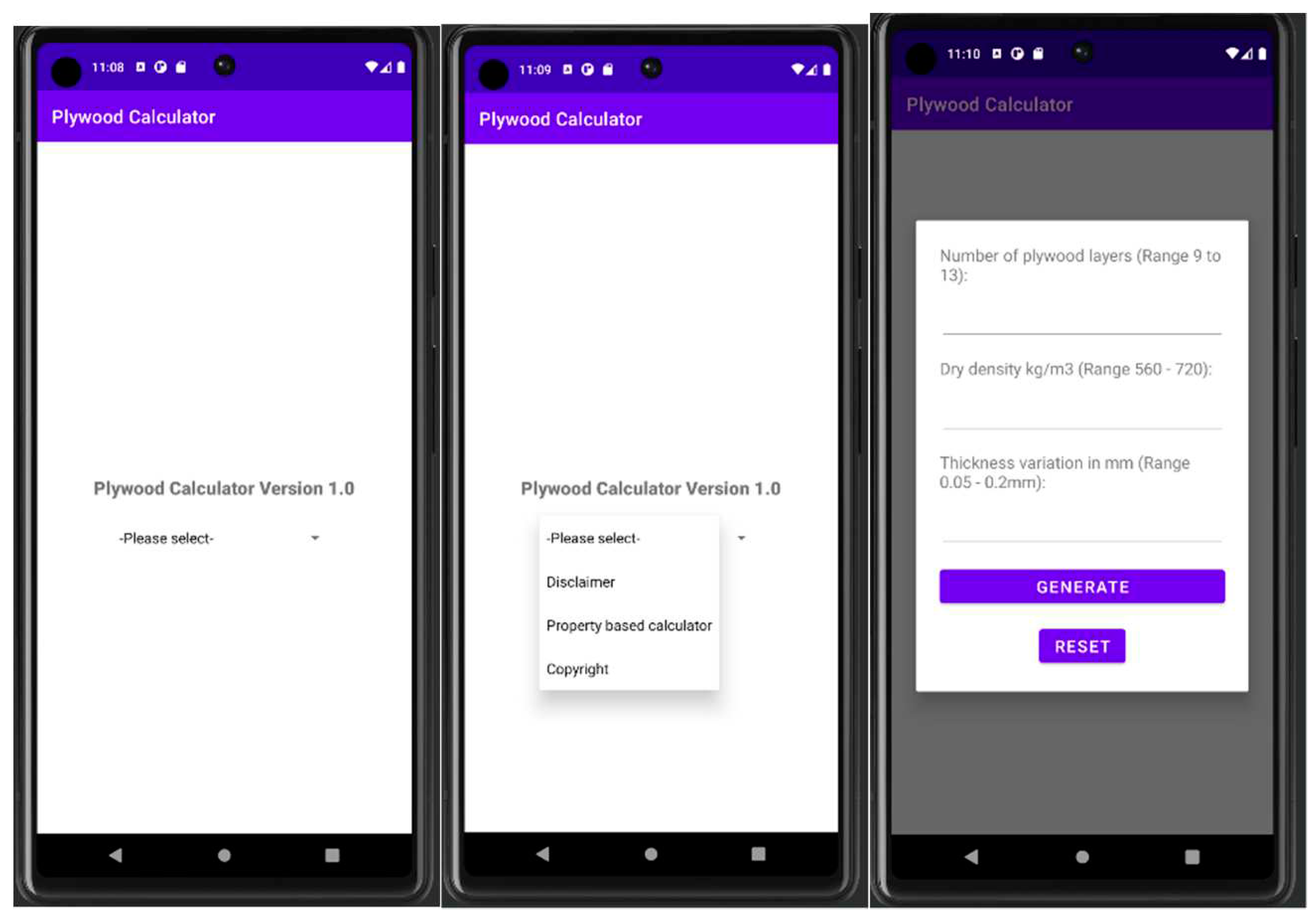
4.1. Case Identification
- Disclaimer
- Users that select the disclaimer should receive a disclaimer message.
- 2.
- Property Based Calculator (main function)
- Users that select the Property Based Calculator should be promoted to add the properties requested to add three variables.
- 3.
- Copyright
- Users that select the copyright option should receive the copyright message.
4.2. Data collection and data analysis
- Analyze “documentation”: Not applicable for this case, since no documentation related to coding of Android application using ChatGPT was identified.
- Analyze “interviews and discussions”: All “discussion” with ChatGPT was analyzed regarding the usefulness of responses.
- Analyze “physical artefacts”: ChatGPT generated code snippets (here considered as “artefacts”) were immediately transformed into Android MainActivity and tested. The output generated by the application was observed and analyzed. The analysis included one quantitative aspect and one qualitative aspect. The qualitative aspect refers to the difference between manually calculated values and application calculated values, whereas the qualitative aspect is concerned with the difference between expected application design and generated application design.
- Analyze “direct observations”: Not applicable for this case, since only the results of coding (principle #5) and the developer carrying out coding activities (principle #4) can be observed.
4.3. Analysis strategy
- Relying on theoretical propositions: These are derived from initial literature review, identification of issues and initial precursors for the case study. Final explanations will be based on comparing findings with these initial propositions. Since no body of knowledge could be identified in literature regarding the research question here, this study is based on the following two propositions:
- The developer can critically observe himself during the time of coding; and,
- “Archival records” allow a comparison with the experience of the developer.
- 2.
- Considering rival explanations: Alternative explanations might have caused the same phenomenon and need to be considered when discussing the results. For example, a code resulting in wrong values could be related to wrong information provided by ChatGPT, but it also could be related to a coding mistake although correct information was provided by ChatGPT.
- 3.
- Developing a descriptive framework (case description): This is principally used when the two proceeding strategies are not applicable [22] (pp. 109) and, therefore, is not further considered here.
5. Results and Discussion
5.1. Defining the platform
- Eclipse
- IntelliJ IDEA
- React Native
- Xamarin
- Netbeans
5.2. Creating the application
- Open Android Studio and create a new project.
- Select "Empty Activity" as the project template.
- Give your project a name and package name.
- Click "Finish" to create the project.
- Open the activity_main.xml file, located in the res/layout folder.
- Add the following code to create the layout for the application:”
- ChatGPT, when given a very long description, can generate wrong or incomplete codes.
- A step-by-step guide can enhance the developer’s understanding of the workflow used by Android Studio but does not necessarily allow for successful app development. Though simple steps in the early process of the app development can be successfully completed through a step-by-step request.
- Several follow-up questions must be asked by the developer to complete specific steps based on the complexity.
- None of the physical “artefacts”, were considered useful and required varying number of iterations.
5.2.1. Creating the spinner
5.2.2. Setting up the functionality of dropdown menu
6. Conclusion and Recommendations
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Appendix A
| Developer's Question | ChatGPT Response | Line number | Code |
| Q4 | R4 | 1 | import android.os.Bundle; |
| 2 | import android.view.Menu; | ||
| 3 | import android.view.MenuInflater; | ||
| 4 | import android.view.MenuItem; | ||
| 5 | import android.widget.ArrayAdapter; | ||
| 6 | import android.widget.Spinner; | ||
| 7 | import androidx.appcompat.app.AlertDialog; | ||
| 8 | import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; | ||
| 9 | public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { | ||
| 10 | private Spinner spinner; | ||
| 11 | private String[] options = {"Disclaimer", "Calculator", "Copyright"}; | ||
| 12 | private double input1 = 0.0; | ||
| 13 | private double input2 = 0.0; | ||
| 14 | private double input3 = 0.0; | ||
| 15 | private double U = 0.0; | ||
| 16 | @Override | ||
| 17 | protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { | ||
| 18 | super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); | ||
| 19 | setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); | ||
| 20 | setTitle("Material Calculator"); | ||
| 21 | // Set up the spinner for the drop-down menu | ||
| 22 | spinner = findViewById(R.id.spinner); | ||
| 23 | ArrayAdapter<String>adapter = new ArrayAdapter<>(this, android.R.layout.simple_spinner_item, options); | ||
| 24 | adapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item); | ||
| 25 | spinner.setAdapter(adapter); | ||
| 26 | // Set the logo of the University | ||
| 27 | getSupportActionBar().setDisplayShowHomeEnabled(true); | ||
| 28 | getSupportActionBar().setLogo(R.drawable.university_logo); | ||
| 29 | getSupportActionBar().setDisplayUseLogoEnabled(true); | ||
| 30 | } | ||
| 31 | @Override | ||
| 32 | public boolean onCreateOptionsMenu(Menu menu) { | ||
| 33 | MenuInflater inflater = getMenuInflater(); | ||
| 34 | inflater.inflate(R.menu.main_menu, menu); | ||
| 35 | return true; | ||
| 36 | } | ||
| 37 | @Override | ||
| 38 | public boolean onOptionsItemSelected(MenuItem item) { | ||
| 39 | switch (item.getItemId()) { | ||
| 40 | case R.id.action_disclaimer: | ||
| 41 | showDisclaimer(); | ||
| 42 | return true; | ||
| 43 | case R.id.action_calculator: | ||
| 44 | showCalculatorDialog(); | ||
| 45 | return true; | ||
| 46 | case R.id.action_copyright: | ||
| 47 | showCopyright(); | ||
| 48 | return true; | ||
| 49 | default: | ||
| 50 | return super.onOptionsItemSelected(item); | ||
| 51 | } | ||
| 52 | } | ||
| 53 | private void showDisclaimer() { | ||
| 54 | AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this); | ||
| 55 | builder.setTitle("Disclaimer"); | ||
| 56 | builder.setMessage("Disclaimer message"); | ||
| 57 | builder.setPositiveButton("OK", null); | ||
| 58 | builder.show(); | ||
| 59 | } | ||
| 60 | private void showCalculatorDialog() { | ||
| 61 | AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this); | ||
| 62 | builder.setTitle("Material Reusability Calculator"); | ||
| 63 | // Set up the input fields | ||
| 64 | final EditText input1EditText = new EditText(this); | ||
| 65 | input1EditText.setInputType(InputType.TYPE_NUMBER_FLAG_DECIMAL); | ||
| 66 | input1EditText.setHint("Input 1"); | ||
| 67 | final EditText input2EditText = new EditText(this); | ||
| 68 | input2EditText.setInputType(InputType.TYPE_NUMBER_FLAG_DECIMAL); | ||
| 69 | input2EditText.setHint("Input 2 (kg/m3)"); | ||
| 70 | final EditText input3EditText = new EditText(this); | ||
| 71 | input3EditText.setInputType(InputType.TYPE_NUMBER_FLAG_DECIMAL); | ||
| 72 | input3EditText.setHint("Input 3"); | ||
| 73 | LinearLayout layout = new LinearLayout(this); | ||
| 74 | layout.setOrientation(LinearLayout.VERTICAL); | ||
| 75 | layout.addView(input1EditText); | ||
| 76 | layout.addView(input2EditText); | ||
| 77 | layout.addView(input3EditText); | ||
| 78 | builder.setView(layout); | ||
| 79 | builder.setPositiveButton("Calculate", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { | ||
| 80 | @Override | ||
| 81 | public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) { | ||
| 82 | // Retrieve the values from the input fields | ||
| 83 | try { | ||
| 84 | input1 = Double.parseDouble(input1EditText.getText().toString()); | ||
| 85 | } catch (NumberFormatException e) { | ||
| 86 | input1 = 0.0; | ||
| 87 | } | ||
| 88 | try { | ||
| 89 | input2 = Double.parseDouble(input2EditText.getText().toString()); | ||
| 90 | } catch (NumberFormatException e) { | ||
| 91 | input2 = 0.0; | ||
| 92 | } | ||
| 93 | try { | ||
| 94 | input3 = Double.parseDouble(input3EditText.getText().toString()); | ||
| 95 | } catch (NumberFormatException e) { | ||
| 96 | input3 = 0.0; | ||
| 97 | } | ||
| 98 | // Calculate the number of uses | ||
| 99 | if (input1” |
| Developer's Question | ChatGPT Response | Line number | Code |
| Q4-Followup | R4-Followup | 1 | // Get the values of input 1, input 2 and input 3 |
| 2 | String input1Value = input1.getText().toString(); | ||
| 3 | String input2Value = input2.getText().toString(); | ||
| 4 | String input3Value = input3.getText().toString(); | ||
| 5 | // Check if any input field is empty | ||
| 6 | if (input1Value.isEmpty() || input2Value.isEmpty() || input3Value.isEmpty()) { | ||
| 7 | resultView.setText("Input missing"); | ||
| 8 | } else { | ||
| 9 | // Parse input 2 as a float value | ||
| 10 | float input2Float = Float.parseFloat(input2Value); | ||
| 11 | // Calculate the estimated max. number of uses using the formula | ||
| 12 | float U = (1000 * input2Float * 0.7f) / (Float.parseFloat(input1Value) * Float.parseFloat(input3Value)); | ||
| 13 | // Display the result in the resultView | ||
| 14 | resultView.setText("Estimated max. number of uses: " + String.format("%.2f", U)); | ||
| 15 | } | ||
| 16 | } | ||
| 17 | }); | ||
| 18 | } | ||
| 19 | } |
| Developer's Question | ChatGPT Response | Line number | Code |
| Q5 | R5 | 1 | <RelativeLayout xmlns:android="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res/android" |
| 2 | xmlns:app="http://schemas.android.com/apk/res-auto" | ||
| 3 | android:layout_width="match_parent" | ||
| 4 | android:layout_height="match_parent"> | ||
| 5 | <TextView | ||
| 6 | android:id="@+id/title" | ||
| 7 | android:text="Material Calculator" | ||
| 8 | android:textSize="20sp" | ||
| 9 | android:layout_width="wrap_content" | ||
| 10 | android:layout_height="wrap_content" | ||
| 11 | android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" | ||
| 12 | android:layout_marginTop="10dp" /> | ||
| 13 | <ImageView | ||
| 14 | android:id="@+id/logo" | ||
| 15 | android:src="@drawable/university_logo" | ||
| 16 | android:layout_width="wrap_content" | ||
| 17 | android:layout_height="wrap_content" | ||
| 18 | android:layout_below="@+id/title" | ||
| 19 | android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" | ||
| 20 | android:layout_marginTop="20dp" /> | ||
| 21 | <Spinner | ||
| 22 | android:id="@+id/menu" | ||
| 23 | android:layout_width="wrap_content" | ||
| 24 | android:layout_height="wrap_content" | ||
| 25 | android:layout_below="@+id/logo" | ||
| 26 | android:layout_centerHorizontal="true" | ||
| 27 | android:layout_marginTop="20dp" /> | ||
| 28 | Add the following code to the MainActivity.java file to set up the spinner: | ||
| 29 | public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity implements AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener { | ||
| 30 | private Spinner menuSpinner; | ||
| 31 | @Override | ||
| 32 | protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { | ||
| 33 | super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); | ||
| 34 | setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); | ||
| 35 | menuSpinner = (Spinner) findViewById(R.id.menu); | ||
| 36 | ArrayAdapter<CharSequence> adapter = ArrayAdapter.createFromResource(this, R.array.menu_options, android.R.layout.simple_spinner_item); | ||
| 37 | adapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item); | ||
| 38 | menuSpinner.setAdapter(adapter); | ||
| 39 | menuSpinner.setOnItemSelectedListener(this); | ||
| 40 | } | ||
| 41 | @Override | ||
| 42 | public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> adapterView, View view, int position, long l) { | ||
| 43 | switch (position) { | ||
| 44 | case 0: | ||
| 45 | showDisclaimer(); | ||
| 46 | break; | ||
| 47 | case 1: | ||
| 48 | showCalculatorDialog(); | ||
| 49 | break; | ||
| 50 | case 2: | ||
| 51 | showCopyright(); | ||
| 52 | break; | ||
| 53 | } | ||
| 54 | } | ||
| 55 | @Override | ||
| 56 | public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> adapterView) { | ||
| 57 | } | ||
| 58 | private void showDisclaimer() { | ||
| 59 | AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this); | ||
| 60 | builder.setTitle("Disclaimer"); | ||
| 61 | builder.setMessage("This application is for informational purposes only. Please consult a professional for accurate calculations."); | ||
| 62 | builder.setPositiveButton("OK", null); | ||
| 63 | builder.create().show(); | ||
| 64 | } | ||
| 65 | private void showCalculatorDialog() { | ||
| 66 | AlertDialog.Builder builder = new AlertDialog.Builder(this); | ||
| 67 | builder.setTitle("Calculator"); | ||
| 68 | LayoutInflater inflater = getLayoutInflater(); | ||
| 69 | View dialogView = inflater.inflate(R.layout.dialog_calculator, null); | ||
| 70 | builder.setView(dialogView); | ||
| 71 | final EditText input1EditText = (EditText) dialogView.findViewById(R.id.input1EditText); | ||
| 72 | final EditText input2EditText = (EditText) dialogView.findViewById(R.id.input2EditText); | ||
| 73 | final EditText input3EditText = (EditText) dialogView.findViewById(R.id.input3EditText); | ||
| 74 | builder.setPositiveButton("Calculate", new DialogInterface.OnClickListener() { | ||
| 75 | @Override | ||
| 76 | public void onClick(DialogInterface dialogInterface, int i) { | ||
| 77 | String input1 = input1EditText.getText” |
Appendix B
| Developer's Question | ChatGPT Response | Steps | Line number | Code |
| Q6 | R6 | 2 | 1 | <Spinner |
| 2 | android:id="@+id/spinner" | |||
| 3 | android:layout_width="match_parent" | |||
| 4 | android:layout_height="wrap_content" | |||
| 5 | android:entries="@array/countries" /> | |||
| 3 | 6 | <string-array name="countries"> | ||
| 7 | <item>USA</item | |||
| 8 | <item>Canada</item> | |||
| 9 | <item>Mexico</item> | |||
| 10 | <item>Brazil</item> | |||
| 11 | </string-array> | |||
| 4 | 12 | Spinner spinner = findViewById(R.id.spinner); | ||
| 13 | ArrayAdapter<CharSequence> adapter = ArrayAdapter.createFromResource(this, | |||
| 14 | R.array.countries, android.R.layout.simple_spinner_item); | |||
| 15 | adapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item); | |||
| 16 | spinner.setAdapter(adapter); | |||
| 5 | 17 | spinner.setOnItemSelectedListener(new AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener() { | ||
| 18 | @Override | |||
| 19 | public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) { | |||
| 20 | String selectedCountry = parent.getItemAtPosition(position).toString(); | |||
| 21 | Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Selected: " + selectedCountry, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); | |||
| 22 | } | |||
| 23 | @Override | |||
| 24 | public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> parent) { | |||
| 25 | } | |||
| 26 | }); |
| Developer's Question | ChatGPT Response | Line number | Code |
| Q6(a) | R6(a) | 1 | import android.os.Bundle; |
| 2 | import android.view.View; | ||
| 3 | import android.widget.AdapterView; | ||
| 4 | import android.widget.ArrayAdapter; | ||
| 5 | import android.widget.Spinner; | ||
| 6 | import android.widget.Toast; | ||
| 7 | import androidx.appcompat.app.AppCompatActivity; | ||
| 8 | public class MainActivity extends AppCompatActivity { | ||
| 9 | @Override | ||
| 10 | protected void onCreate(Bundle savedInstanceState) { | ||
| 11 | super.onCreate(savedInstanceState); | ||
| 12 | setContentView(R.layout.activity_main); | ||
| 13 | // Find the spinner view by its ID | ||
| 14 | Spinner spinner = findViewById(R.id.spinner); | ||
| 15 | // Create an ArrayAdapter using the string array and a default spinner layout | ||
| 16 | ArrayAdapter<CharSequence> adapter = ArrayAdapter.createFromResource(this, | ||
| 17 | R.array.countries, android.R.layout.simple_spinner_item); | ||
| 18 | // Specify the layout to use when the list of choices appears | ||
| 19 | adapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item); | ||
| 20 | // Apply the adapter to the spinner | ||
| 21 | spinner.setAdapter(adapter); | ||
| 22 | // Add a listener to the spinner | ||
| 23 | spinner.setOnItemSelectedListener(new AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener() { | ||
| 24 | @Override | ||
| 25 | public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) { | ||
| 26 | // Get the selected item from the spinner | ||
| 27 | String selectedCountry = parent.getItemAtPosition(position).toString(); | ||
| 28 | // Display a Toast message with the selected item | ||
| 29 | Toast.makeText(MainActivity.this, "Selected: " + selectedCountry, Toast.LENGTH_SHORT).show(); | ||
| 30 | } | ||
| 31 | @Override | ||
| 32 | public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> parent) { | ||
| 33 | } | ||
| 34 | }); | ||
| 35 | } | ||
| 36 | } |
Appendix C
| Developer's Question | ChatGPT Response | Steps | Line number | Code |
| Q7 | R7 | 3 | 1 | <Spinner |
| 2 | android:id="@+id/dropdown_menu" | |||
| 3 | android:layout_width="wrap_content" | |||
| 4 | android:layout_height="wrap_content" /> | |||
| 4 | 5 | <string-array name="menu_options"> | ||
| 6 | <item>Disclaimer Message</item> | |||
| 7 | <item>Material Calculator</item> | |||
| 8 | <item>Copyright</item> | |||
| 9 | </string-array> | |||
| 5 | 10 | Spinner dropdownMenu = findViewById(R.id.dropdown_menu); | ||
| 11 | ArrayAdapter<String> adapter = new ArrayAdapter<String>(this, | |||
| 12 | android.R.layout.simple_spinner_item, getResources().getStringArray(R.array.menu_options)); | |||
| 13 | adapter.setDropDownViewResource(android.R.layout.simple_spinner_dropdown_item); | |||
| 14 | dropdownMenu.setAdapter(adapter); | |||
| 6 | 15 | dropdownMenu.setOnItemSelectedListener(new AdapterView.OnItemSelectedListener() { | ||
| 16 | @Override | |||
| 17 | public void onItemSelected(AdapterView<?> parent, View view, int position, long id) { | |||
| 18 | switch (position) { | |||
| 19 | case 0: | |||
| 20 | // Display disclaimer message | |||
| 21 | break; | |||
| 22 | case 1: | |||
| 23 | // Launch material calculator layout | |||
| 24 | Intent intent = new Intent(MainActivity.this, CalculatorActivity.class); | |||
| 25 | startActivity(intent); | |||
| 26 | break; | |||
| 27 | case 2: | |||
| 28 | // Display copyright message | |||
| 29 | break; | |||
| 30 | } | |||
| 31 | } | |||
| 32 | @Override | |||
| 33 | public void onNothingSelected(AdapterView<?> parent) { | |||
| 34 | // Do nothing | |||
| 35 | } | |||
| 36 | }); | |||
| 37 | n |
References
- Aleksandra Fostikov. 2023. First impressions on using AI powered chatbots, tools and search engines: ChatGPT, Perplexity and other – possibilities and usage problems. (2023). [CrossRef]
- Azam Syukur Rahmatullah, E. Mulyasa, Syahrani Syahrani, Fien Pongpalilu, and Riana Eka Putri. 2022. Digital Era 4.0. Linguistics and Culture Review 6 (2022), 89–107. [CrossRef]
- Aline F.S. Borges, Fernando J.B. Laurindo, Mauro M. Spínola, Rodrigo F. Gonçalves, and Claudia A. Mattos. 2021. The strategic use of artificial intelligence in the Digital Era: Systematic Literature Review and Future Research Directions. International Journal of Information Management 57 (2021), 102225. [CrossRef]
- Ankit Kesharwani. 2020. Do (how) Digital Natives adopt a new technology differently than digital immigrants? A longitudinal study. Information & Management 57, 2 (2020), 103170. [CrossRef]
- Eleni Adamopoulou and Lefteris Moussiades. 2020. An overview of chatbot technology. IFIP Advances in Information and Communication Technology (2020), 373–383 . [CrossRef]
- Jürgen Rudolph, Samson Tan, and Shannon Tan. 2023. Chatgpt: Bullshit spewer or the end of traditional assessments in higher education? 1 6, 1 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Jie Zhou, Pei Ke, Xipeng Qiu, Minlie Huang, and Junping Zhang. 2023. CHATGPT: Potential, prospects, and limitations. Frontiers of Information Technology & Electronic Engineering (2023). [CrossRef]
- Michael Liebrenz, Roman Schleifer, Anna Buadze, Dinesh Bhugra, and Alexander Smith. 2023. Generating scholarly content with chatgpt: Ethical challenges for medical publishing. The Lancet Digital Health 5, 3 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Kindra Cooper. 2022. OpenAI GPT-3: Everything you need to know. (October 2022). Retrieved March 12, 2023 from https://www.springboard.com/blog/data-science/machine-learning-gpt-3-open-ai/.
- OpenAI. 2015. Introducing chatgpt. (2015). Retrieved March 12, 2023 from https://openai.com/blog/chatgpt.
- Dan Milmo. 2023. CHATGPT reaches 100 million users two months after launch. (February 2023). Retrieved March 12, 2023 from https://www.theguardian.com/technology/2023/feb/02/chatgpt-100-million-users-open-ai-fastest-growing-app.
- Zhicheng Lin. 2023. Why and how to embrace AI such as CHATGPT in your academic life. (2023). [CrossRef]
- Marcel Binz and Eric Schulz. 2023. Using cognitive psychology to understand GPT-3. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences 120, 6 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Ashley M. Hopkins, Jessica M. Logan, Ganessan Kichenadasse, and Michael J. Sorich. 2023. AI chatbots will revolutionize how cancer patients access information: CHATGPT represents a paradigm-shift. JNCI Cancer Spectrum (2023). [CrossRef]
- Aidan Gilson et al. 2023. How does CHATGPT perform on the United States Medical Licensing Examination? the implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. JMIR Medical Education 9 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Travis Ryan Pickell and Brian R. Doak. 2023. Five Ideas for How Professors Can Deal with GPT-3 ... For Now (2023).
- Muneer Alshater. 2022. Exploring the role of artificial intelligence in enhancing academic performance: A case study of chatgpt. SSRN Electronic Journal (2022). [CrossRef]
- Calum Macdonald, Davies Adeloye, Aziz Sheikh, and Igor Rudan. 2023. Can chatgpt draft a research article? an example of population-level vaccine effectiveness analysis. Journal of Global Health 13 (2023). [CrossRef]
- Ali Borji. 2023. A Categorical Archive of ChatGPT Failures. arXiv preprint (2023) . [CrossRef]
- Sakib Shahriar and Kadhim Hayawi. 2023. Let's have a chat! A Conversation with ChatGPT: Technology, Applications, and Limitations. arXiv preprint (2023) . [CrossRef]
- Domonik Sobania, Martin Briesch, Carol Hanna, and Justyna Petke. 2023. An Analysis of the Automatic Bug Fixing Performance of ChatGPT. arXiv preprint (2023). [CrossRef]
- Robert K. Yin. 2003. Case study research: Design and methods, Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications.
- Kimberly A. Neuendorf. 2002. The Content Analysis Guidebook, Thousand Oaks (California), Cleveland State University: Sage.
- G2. 2012. Business software and services reviews | G2. (2012). Retrieved March 10, 2023 from https://www.g2.com/.
- [Codes Easy]. (2017, December 29). Creating First Application In Android Studio in 2023 [Video]. Youtube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=p0ItPcqqXog.
- [Wasay Tech Tips]. (2020, September 29). How to Install Emulator in Android Studio 2020 [Video]. Youtube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=P1LFl5CYulc.
- [Coding in Flow]. (2017, December 29). How to Change the App Icon in Android Studio (With Adaptive Icons) [Video]. Youtube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=ts98gL1JCQU.
- Alex Moazed. 2017. How long does it take to build an IOS or Android mobile app? (May 2017). Retrieved March 21, 2023 from https://www.applicoinc.com/blog/long-take-build-ios-android-mobile-app/#:~:text=It%20will%20usually%20take%203,of%20building%20a%20mobile%20app.
- Spdload. 2023. Find out how long does it take to build an app in 2023. (January 2023). Retrieved March 21, 2023 from https://spdload.com/blog/how-long-does-it-take-to-develop-an-app/.

| # | Data analysis approach | Unit of analysis |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | “interviews and discussions” | Number of immediately useful ChatGPT response Number of not immediately useful ChatGPT response |
| 2 | “physical artefacts” | Frequency of wrong results generation Frequency of unmet expectation regarding application design |
| Platform | Ease of use | Quality of support | Ease of setup |
|---|---|---|---|
| Android studio | 8.6 | 8.4 | 7.8 |
| Cordova | 8 | 6.9 | 7.6 |
| Ionic | 8.9 | 8.2 | 8.5 |
| PhoneGap | - | - | - |
| Eclipse | 8.2 | 7.8 | 8.1 |
| IntelliJ IDEA | 8.7 | 8.5 | 8.6 |
| React Native | 8.2 | 8.1 | 8.4 |
| Xamarin | 7.7 | 7.6 | 7.6 |
| Netbeans | 8.5 | 7.8 | 8.4 |
| ChatGPT generated Steps in R5 |
Number of Iterations |
Success |
|---|---|---|
| 1 | 0 | yes |
| 2 | 0 | yes |
| 3 | 0 | yes |
| 4 | 0 | yes |
| 5 | 1 | yes |
| 6 | 3 | yes |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





