Submitted:
10 July 2023
Posted:
11 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Phytochemical reports
2.1. Essential oil
2.2. Pharmacological activities of volatile constituents of R. michauxii
2.3. Dillapiole
2.4. Caryophyllene oxide
2.5. Eugenol and eugenol acetate
2.6. Carvacrol
2.7. Non-volatile compounds
3. Pharmacological activities
3.1. Antimicrobial activity
3.2. Antimicrobial activity
3.3. Antioxidant activity
3.4. Cytotoxic activity
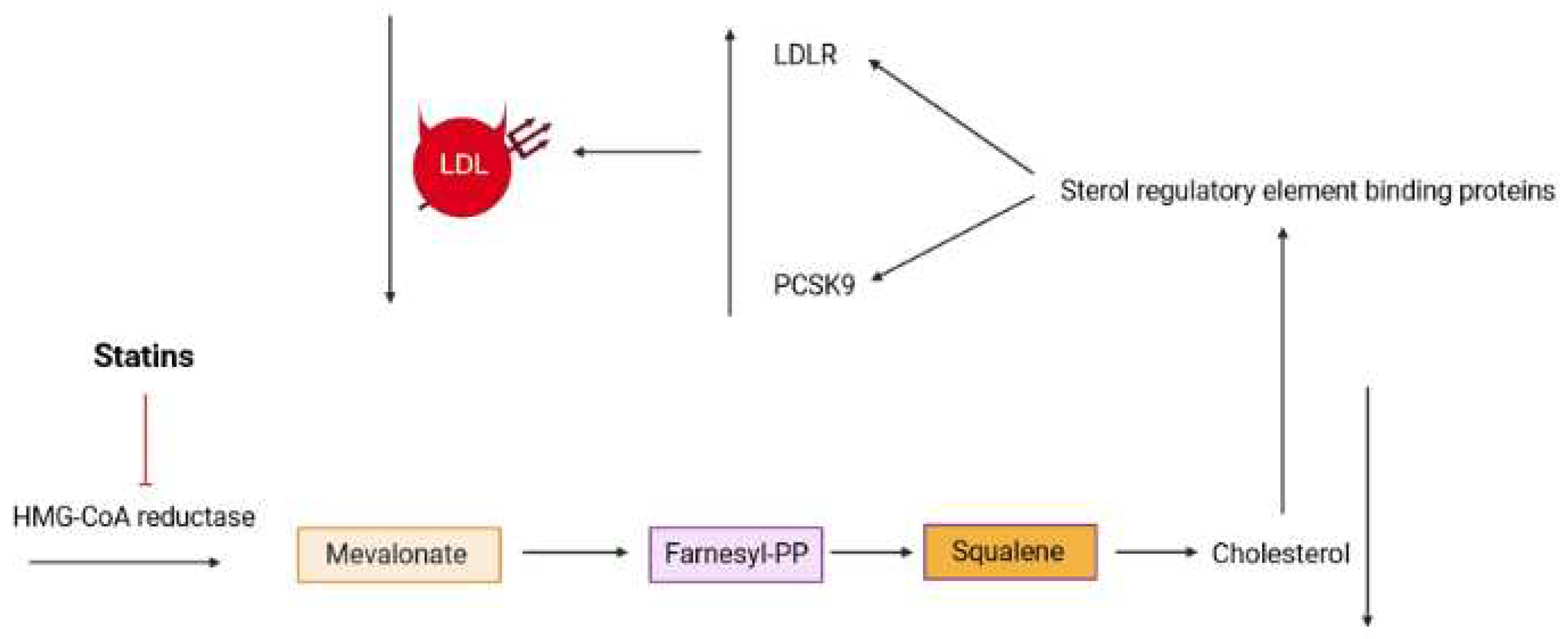
3.5. Lipid lowering activity
4. Pharmacological activities of non-volatile constituents of R. michauxii
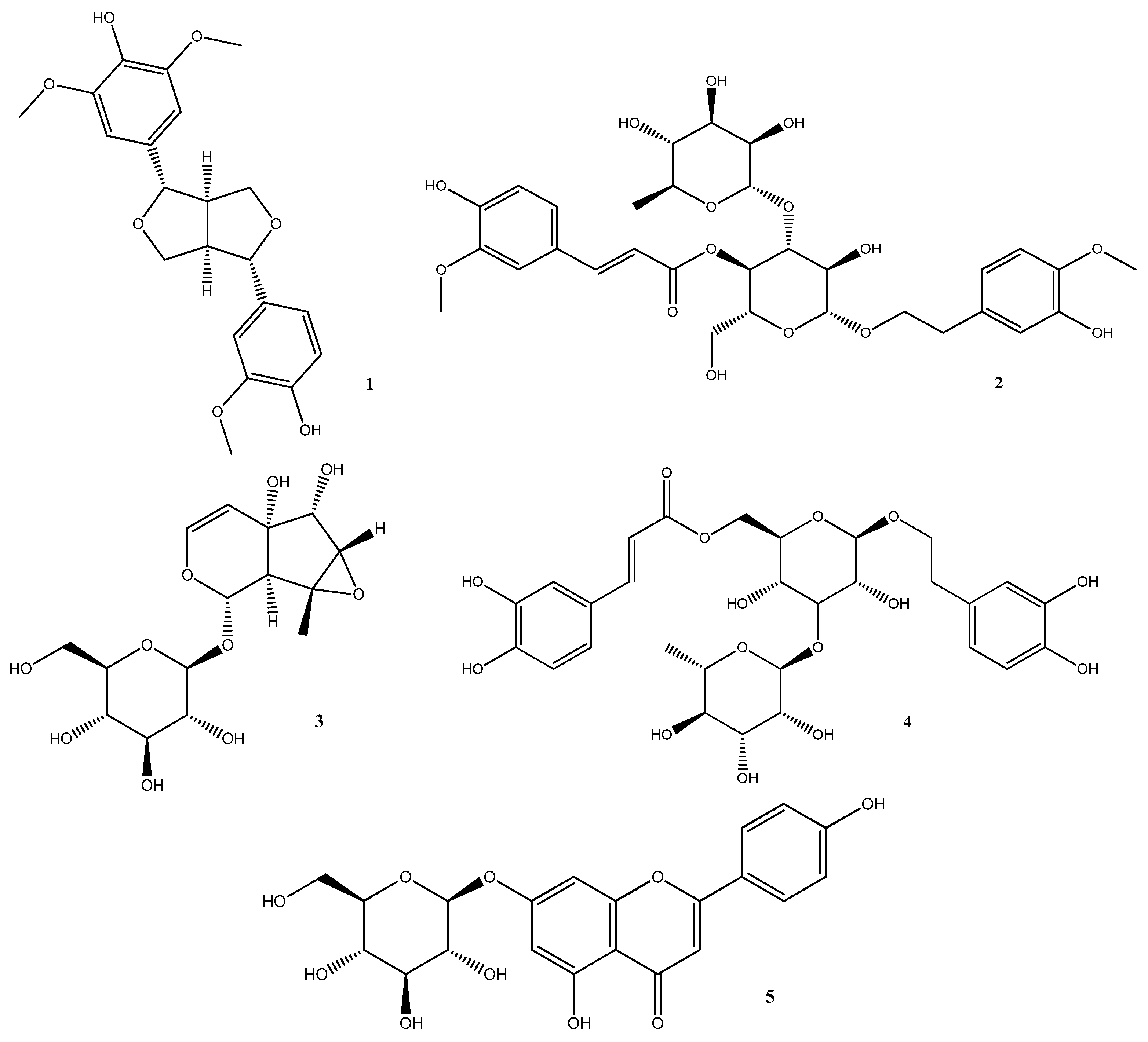
4.1. Medioresinol (MD)
4.2. Martynoside (MR)
4.3. Antirrhinoside
4.4. Isoverbascoside (IVer)
4.5. Apigenin-7-O-glucoside (AG)
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Halberstein, R.A. Medicinal plants: historical and cross-cultural usage patterns. Annals of epidemiology 2005, 15, 686–699. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Katz, L.; Baltz, R.H. Natural product discovery: past, present, and future. Journal of Industrial Microbiology and Biotechnology 2016, 43, 155–176. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Tamokou, J.; Mbaveng, A.; Kuete, V. Antimicrobial activities of African medicinal spices and vegetables. In Medicinal spices and vegetables from Africa; Elsevier: 2017; pp. 207-237.
- Kokkini, S.; Karousou, R.; Hanlidou, E. HERBS| Herbs of the Labiatae. 2003.
- Mabberley, D.J. The plant-book: a portable dictionary of the vascular plants; Cambridge university press: 1997.
- Scheen, A.-C.; Albert, V.A. Nomenclatural and taxonomic changes within the Leucas clade (Lamioideae; Lamiaceae). Systematics and Geography of Plants 2007, 229–238. [Google Scholar]
- Ghahremaninejad, F.; Hoseini, E. Identification of Medicinal and Aromatic Plants of Iran, Valiollah Mozaffarian. Farhang Moaser Publishers, Tehran (2012). 1444 pp., 2470 colored images (Language: Mainly Persian with English preface and several indexes). Hardback, ISBN: 978-600-1050-31-2. Format: 23.5× 15.5 cm. Price: 900000 IR-Rials. 2015.
- Javidnia, K.; Miri, R.; Soltani, M.; Khosravi, A. Chemical constituents of the essential oil of Otostegia michauxii Briq. from Iran. Journal of Essential Oil Research 2010, 22, 1–2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karami, A.; Esmaeili, H.; Shahbazian, D. Essential oil composition of Rydingia michauxii (Briq.) Scheen & VA Albert endemic of Iran. Natural product research 2018, 32, 229–233. [Google Scholar]
- Sut, S.; Tahmasebi, A.; Ferri, N.; Ferrarese, I.; Rossi, I.; Panighel, G.; Lupo, M.G.; Maggi, F.; Karami, A.; Dall’Acqua, S. NMR, LC-MS Characterization of Rydingia michauxii Extracts, Identification of Natural Products Acting as Modulators of LDLR and PCSK9. Molecules 2022, 27, 2256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghian, S.; Hatami, A.; Hamzeh’ee, B. CHROMOSOME COUNTS OF SIX TAXA OF LAMIACEAE FROM IRAN. The Iranian Journal of Botany 2021, 27, 58–61. [Google Scholar]
- Rosselli, S.; Fontana, G.; Bruno, M. A review of the phytochemistry, traditional uses, and biological activities of the Genus Ballota and Otostegia. Planta medica 2019, 85, 869–910. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadeghi, Z.; Akaberi, M.; Valizadeh, J. Otostegia persica (Lamiaceae): A review on its ethnopharmacology, phytochemistry, and pharmacology. Avicenna journal of phytomedicine 2014, 4, 79. [Google Scholar]
- Khan, S.; Syed, F. Bioactive constituents from genus Otostegia. SARJ of Physical Sci 2013, 1, 15–25. [Google Scholar]
- Safa, O.; Soltanipoor, M.A.; Rastegar, S.; Kazemi, M.; Dehkordi, K.N.; Ghannadi, A. An ethnobotanical survey on hormozgan province, Iran. Avicenna journal of phytomedicine 2013, 3, 64. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Toori, M.A.; Joodi, B.; Sadeghi, H.; Sadeghi, H.; Jafari, M.; Talebianpoor, M.S.; Mehraban, F.; Mostafazadeh, M.; Ghavamizadeh, M. Hepatoprotective activity of aerial parts of Otostegia persica against carbon tetrachloride-induced liver damage in rats. Avicenna journal of phytomedicine 2015, 5, 238. [Google Scholar]
- Tofighi, Z.; Ostad, S.; Khezrrahdoost, S.; Salehizadeh, H.; Yassa, N. Potent anti-nociceptive and anti-inflammatory effects of methanol fraction of Otostegia persica extract and its components. Research Journal of Pharmacognosy 2017, 4, 23–29. [Google Scholar]
- Ganjali, A.; Sotoudeh, A.; Jahanshahi, A.; Takhtfooladi, M.A.; Bazzazan, A.; Roodbari, N.; Harati, M.P. Otostegia persica extraction on healing process of burn wounds. Acta Cirurgica Brasileira 2013, 28, 407–411. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Safaeian, L.; Ghasemi-Dehkordi, N.; Javanmard, S.H.; Namvar, H. Antihypertensive and antioxidant effects of a hydroalcoholic extract obtained from aerial parts of Otostegia persica (Burm.) Boiss. Research in Pharmaceutical Sciences 2015, 10, 192. [Google Scholar]
- Tahmasebi, A.; Hosseini, S.M.; Karami, A.; Afsharifar, A.; Sharifi Olounabadi, A.R. Variation in essential oil composition of Rydingia michauxii at the three developmental stages. Natural product research 2021, 35, 342–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Handa, S.; Dewan, R. Evaluation of dillapiole and dihydrodillapiole as synergists for pyrethrins in dust formulations. Pyrethrum post 1975. [Google Scholar]
- Tomar, S.S.; Maheshwari, M.L.; Mukerjee, S.K. Syntheses and synergistic activity of some pyrethrum synergists from dillapiole. Agricultural and Biological Chemistry 1979, 43, 1479–1483. [Google Scholar]
- Tomar, S.; Maheshwari, M.; Mukerjee, S. Synthesis and synergistic activity of dillapiole based pyrethrum synergists. Journal of Agricultural and Food chemistry 1979, 27, 547–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bernard, C.B.; Arnason, J.; Philogene, B.; Lam, J.; Waddell, T. In vivo effect of mixtures of allelochemicals on the life cycle of the European corn borer, Ostrinia nubilalis. Entomologia experimentalis et applicata 1990, 57, 17–22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, W.-H. Cytotoxic effects of dillapiole on embryonic development of mouse blastocysts in vitro and in vivo. International Journal of Molecular Sciences 2014, 15, 10751–10765. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Parise-Filho, R.; Pastrello, M.; Pereira Camerlingo, C.E.; Silva, G.J.; Agostinho, L.A.; de Souza, T.; Motter Magri, F.M.; Ribeiro, R.R.; Brandt, C.A.; Polli, M.C. The anti-inflammatory activity of dillapiole and some semisynthetic analogues. Pharmaceutical Biology 2011, 49, 1173–1179. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Musdja, M.Y.; Asmara, D.; Musir, A. Effect of ethanol extract of Foeniculum Vulgare Mill on inhibition of uric acid crystals formation in male rats. 2018.
- Parise-Filho, R.; Pasqualoto, K.F.M.; Magri, F.M.M.; Ferreira, A.K.; da Silva, B.A.V.G.; Damião, M.C.F.C.B.; Tavares, M.T.; Azevedo, R.A.; Auada, A.V.V.; Polli, M.C. Dillapiole as antileishmanial agent: discovery, cytotoxic activity and preliminary SAR studies of dillapiole analogues. Archiv der Pharmazie 2012, 345, 934–944. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- AMIN, I.M.; RUSLAN, N.B.; ZULKIPLI, Z.A.; ZAKARIA, N.A.; JALIL, M.T.M.; ARIS, F. CYTOTOXIC EFFECT OF DILLAPIOLE ON HUMAN BREAST CANCER MCF-7 CELLS. Malaysian Applied Biology 2022, 51, 29–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brazao, M.A.B.; Brazao, F.V.; Guilherme, J.; Monteiro, M.C. Antibacterial activity of the Piper aduncum oil and dillapiole, its main constituent, against multidrug-resistant strains. Boletín Latinoamericano y del Caribe de Plantas Medicinales y Aromáticas 2014, 13, 517–526. [Google Scholar]
- Razzaghi-Abyaneh, M.; Yoshinari, T.; Shams-Ghahfarokhi, M.; Rezaee, M.-B.; Nagasawa, H.; Sakuda, S. Dillapiol and apiol as specific inhibitors of the biosynthesis of aflatoxin G1 in Aspergillus parasiticus. Bioscience, biotechnology, and biochemistry 2007, 71, 2329–2332. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de Almeida, R.R.; Souto, R.N.; Bastos, C.N.; da Silva, M.H.; Maia, J.G. Chemical variation in Piper aduncum and biological properties of its dillapiole-rich essential oil. Chemistry & biodiversity 2009, 6, 1427–1434. [Google Scholar]
- Ferreira, R.; Monteiro, M.; Silva, J.; Maia, J. Antifungal action of the dillapiole-rich oil of Piper aduncum against dermatomycoses caused by filamentous fungi. British Journal of Medicine and Medical Research 2016, 15, 1–10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morais, V.P.; Cabral, F.V.; Fernandes, C.C.; Miranda, M.L.D. Brief Review on Piper aduncum L., its Bioactive Metabolites and its Potential to Develop Bioproducts. Brazilian Archives of Biology and Technology 2023, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, A.K.; de-Sá-Júnior, P.L.; Pasqualoto, K.F.M.; de Azevedo, R.A.; Câmara, D.A.D.; Costa, A.S.; Figueiredo, C.R.; Matsuo, A.L.; Massaoka, M.H.; Auada, A.V.V. Cytotoxic effects of dillapiole on MDA-MB-231 cells involve the induction of apoptosis through the mitochondrial pathway by inducing an oxidative stress while altering the cytoskeleton network. Biochimie 2014, 99, 195–207. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ruslan, N.B. Dillapiole effects on apoptosis in human nasal epithelial carcinoma, RPMI 2650 cells involves BCL-2 and caspase-8 signalling pathway. Universiti Teknologi MARA, 2021.
- Farag, R.; Shalaby, A.; El-Baroty, G.; Ibrahim, N.; Ali, M.; Hassan, E. Chemical and biological evaluation of the essential oils of different Melaleuca species. Phytotherapy Research: An International Journal Devoted to Pharmacological and Toxicological Evaluation of Natural Product Derivatives 2004, 18, 30–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bettarini, F.; Borgonovi, G.; Fiorani, T.; Gagliardi, I.; Caprioli, V.; Massardo, P.; Ogoche, J.; Hassanali, A.; Nyandat, E.; Chapya, A. Antiparasitic compounds from East African plants: Isolation and biological activity of anonaine, matricarianol, canthin-6-one and caryophyllene oxide. International Journal of Tropical Insect Science 1993, 14, 93–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langenheim, J.H. Higher plant terpenoids: a phytocentric overview of their ecological roles. Journal of chemical ecology 1994, 20, 1223–1280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Russo, E.B.; Marcu, J. Cannabis pharmacology: the usual suspects and a few promising leads. Advances in pharmacology 2017, 80, 67–134. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Schmidt, E.; Bail, S.; Friedl, S.M.; Jirovetz, L.; Buchbauer, G.; Wanner, J.; Denkova, Z.; Slavchev, A.; Stoyanova, A.; Geissler, M. Antimicrobial activities of single aroma compounds. Natural product communications 2010, 5, 1934578X1000500906. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bodiba, D.; Lall, N. Heteropyxis dehniae. In Underexplored Medicinal Plants from Sub-Saharan Africa; Elsevier: 2020; pp. 167-171.
- Morgan, E.D.; Wilson, I.D. Insect hormones and insect chemical ecology. ChemInform 2001, 32, no. [Google Scholar]
- Tung, Y.-T.; Chua, M.-T.; Wang, S.-Y.; Chang, S.-T. Anti-inflammation activities of essential oil and its constituents from indigenous cinnamon (Cinnamomum osmophloeum) twigs. Bioresource technology 2008, 99, 3908–3913. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hammami, S.; Jmii, H.; El Mokni, R.; Khmiri, A.; Faidi, K.; Dhaouadi, H.; El Aouni, M.H.; Aouni, M.; Joshi, R.K. Essential oil composition, antioxidant, cytotoxic and antiviral activities of Teucrium pseudochamaepitys growing spontaneously in Tunisia. Molecules 2015, 20, 20426–20433. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zheng, G.-Q.; Kenney, P.M.; Lam, L.K. Sesquiterpenes from clove (Eugenia caryophyllata) as potential anticarcinogenic agents. Journal of natural products 1992, 55, 999–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, T.P.; Singh, R.K.; Malik, P. Analgesic and anti-inflammatory activities of Annona squamosa Linn bark. J. Scientific and Innov. Res 2014, 3, 60–64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jun, N.J.; Mosaddik, A.; Moon, J.Y.; Ki-Chang, J.; Dong-Sun, L.; Ahn, K.S.; Cho, S.K. Cytotoxic activity of [beta]-Caryophyllene oxide isolated from jeju guava (Psidium cattleianum sabine) leaf. Records of Natural Products 2011, 5, 242. [Google Scholar]
- Fidyt, K.; Fiedorowicz, A.; Strządała, L.; Szumny, A. β-caryophyllene and β-caryophyllene oxide—natural compounds of anticancer and analgesic properties. Cancer medicine 2016, 5, 3007–3017. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.-x.; Qian, P.; Guo, Y.-t.; Gu, L.; Jurat, J.; Bai, Y.; Zhang, D.-f. Myrtenal and β-caryophyllene oxide screened from Liquidambaris Fructus suppress NLRP3 inflammasome components in rheumatoid arthritis. BMC Complementary Medicine and Therapies 2021, 21, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xiu, Z.; Zhu, Y.; Han, J.; Li, Y.; Yang, X.; Yang, G.; Song, G.; Li, S.; Li, Y.; Cheng, C. Caryophyllene oxide induces ferritinophagy by regulating the NCOA4/FTH1/LC3 pathway in hepatocellular carcinoma. Frontiers in Pharmacology 2022, 13, 930958. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sánchez-Mendoza, M.E.; Cruz-Antonio, L.; GuadalupeCupido-Sánchez, M.; GarcíaCastillo, G.; Arrieta, J. Gastroprotective activity of caryophyllene oxide: the role of nitric oxide, prostaglandins and sulfhydryls. Journal of Applied Pharmaceutical Science 2014, 4, 001–005. [Google Scholar]
- Sharma, A.; Bhardwaj, G.; Sohal, H.S.; Gohain, A. Eugenol. In Nutraceuticals and health care; Elsevier: 2022; pp. 177-198.
- Abdou, A.; Elmakssoudi, A.; El Amrani, A.; JamalEddine, J.; Dakir, M. Recent advances in chemical reactivity and biological activities of eugenol derivatives. Medicinal Chemistry Research 2021, 30, 1011–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nisar, M.F.; Khadim, M.; Rafiq, M.; Chen, J.; Yang, Y.; Wan, C.C. Pharmacological properties and health benefits of eugenol: A comprehensive review. Oxidative Medicine and Cellular Longevity 2021, 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Tripathi, A.K.; Mishra, S. Plant monoterpenoids (prospective pesticides). In Ecofriendly pest management for food security; Elsevier: 2016; pp. 507-524.
- Musthafa, K.S.; Hmoteh, J.; Thamjarungwong, B.; Voravuthikunchai, S.P. Antifungal potential of eugenyl acetate against clinical isolates of Candida species. Microbial pathogenesis 2016, 99, 19–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrasco A, H.; Espinoza C, L.; Cardile, V.; Gallardo, C.; Cardona, W.; Lombardo, L.; Catalán M, K.; Cuellar F, M.; Russo, A. Eugenol and its synthetic analogues inhibit cell growth of human cancer cells (Part I). Journal of the Brazilian Chemical Society 2008, 19, 543–548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pasay, C.; Mounsey, K.; Stevenson, G.; Davis, R.; Arlian, L.; Morgan, M.; Vyszenski-Moher, D.; Andrews, K.; McCarthy, J. Acaricidal activity of eugenol based compounds against scabies mites. PloS one 2010, 5, e12079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nejad, S.M.; Özgüneş, H.; Başaran, N. Pharmacological and toxicological properties of eugenol. Turkish journal of pharmaceutical sciences 2017, 14, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alagawany, M.; Farag, M.R.; Abdelnour, S.A.; Elnesr, S.S. A review on the beneficial effect of thymol on health and production of fish. Reviews in Aquaculture 2021, 13, 632–641. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayir, A.G.; Kiziltan, H.S.; Kocyigit, A. Plant family, carvacrol, and putative protection in gastric cancer. In Dietary interventions in gastrointestinal diseases; Elsevier: 2019; pp. 3-18.
- Salehi, B.; Mishra, A.P.; Shukla, I.; Sharifi-Rad, M.; Contreras, M.d.M.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fathi, H.; Nasrabadi, N.N.; Kobarfard, F.; Sharifi-Rad, J. Thymol, thyme, and other plant sources: Health and potential uses. Phytotherapy research 2018, 32, 1688–1706. [Google Scholar]
- Sharifi-Rad, M.; Varoni, E.M.; Iriti, M.; Martorell, M.; Setzer, W.N.; del Mar Contreras, M.; Salehi, B.; Soltani-Nejad, A.; Rajabi, S.; Tajbakhsh, M. Carvacrol and human health: A comprehensive review. Phytotherapy Research 2018, 32, 1675–1687. [Google Scholar]
- Han, F.; Ma, G.-q.; Yang, M.; Yan, L.; Xiong, W.; Shu, J.-c.; Zhao, Z.-d.; Xu, H.-l. Chemical composition and antioxidant activities of essential oils from different parts of the oregano. Journal of Zhejiang University. Science. B 2017, 18, 79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Miara, M.D.; Bendif, H.; Ouabed, A.; Rebbas, K.; Hammou, M.A.; Amirat, M.; Greene, A.; Teixidor-Toneu, I. Ethnoveterinary remedies used in the Algerian steppe: Exploring the relationship with traditional human herbal medicine. Journal of ethnopharmacology 2019, 244, 112164. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luna, A.; Labaque, M.; Zygadlo, J.; Marin, R. Effects of thymol and carvacrol feed supplementation on lipid oxidation in broiler meat. Poultry Science 2010, 89, 366–370. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soltan, Y.A.; Morsy, A.S.; Araujo, R.C.; Elziat, H.; Sallam, S.M.A.; Louvandini, H.; Abdalla, A.L. Carvacrol and eugenol as modifiers of rumen microbial fermentation, and methane production in vitro. In Proceedings of the Proc. Of 4th Animal Wealth Research Conference in the middle East and North Africa pp; 2011; pp. 354–364. [Google Scholar]
- Hashemipour, H.; Kermanshahi, H.; Golian, A.; Veldkamp, T. Effect of thymol and carvacrol feed supplementation on performance, antioxidant enzyme activities, fatty acid composition, digestive enzyme activities, and immune response in broiler chickens. Poultry science 2013, 92, 2059–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bravo, D.; Pirgozliev, V.; Rose, S. A mixture of carvacrol, cinnamaldehyde, and capsicum oleoresin improves energy utilization and growth performance of broiler chickens fed maize-based diet. Journal of Animal Science 2014, 92, 1531–1536. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Can Baser, K. Biological and pharmacological activities of carvacrol and carvacrol bearing essential oils. Current pharmaceutical design 2008, 14, 3106–3119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Suntres, Z.E.; Coccimiglio, J.; Alipour, M. The bioactivity and toxicological actions of carvacrol. Critical reviews in food science and nutrition 2015, 55, 304–318. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rathod, N.B.; Kulawik, P.; Ozogul, F.; Regenstein, J.M.; Ozogul, Y. Biological activity of plant-based carvacrol and thymol and their impact on human health and food quality. Trends in Food Science & Technology 2021, 116, 733–748. [Google Scholar]
- Ultee, A.; Kets, E.; Smid, E. Mechanisms of action of carvacrol on the food-borne pathogen Bacillus cereus. Applied and environmental microbiology 1999, 65, 4606–4610. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bakır, M.; Geyikoglu, F.; Colak, S.; Turkez, H.; Bakır, T.O.; Hosseinigouzdagani, M. The carvacrol ameliorates acute pancreatitis-induced liver injury via antioxidant response. Cytotechnology 2016, 68, 1131–1146. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Imran, M.; Aslam, M.; Alsagaby, S.A.; Saeed, F.; Ahmad, I.; Afzaal, M.; Arshad, M.U.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; El-Ghorab, A.H.; Khames, A. Therapeutic application of carvacrol: A comprehensive review. Food Science & Nutrition 2022, 10, 3544–3561. [Google Scholar]
- Tahmasebi, A.; Karami, A.; Hosseini, S.M.; Afsharifar, A.; Moghadam, A.; Biniaz, Y. Cytotoxic and antimicrobial activities of Rydingia michauxii methanolic extracts during various growth stages. Cleaner Engineering and Technology 2021, 4, 100225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tahmasebi, A.; Karami, A.; Hosseini, S.M. Evaluation of antifungal activity of Rydingia michauxii extracts at the three different growth stages. In Proceedings of the 21th National & 9th International Congress on Biology, Semnan, Iran; 2021. [Google Scholar]
- Bhore, S.J.; Ravichantar, N.; Loh, C.Y. Screening of endophytic bacteria isolated from leaves of Sambung Nyawa [Gynura procumbens (Lour.) Merr.] for cytokinin-like compounds. Bioinformation 2010, 5, 191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Compant, S.; Duffy, B.; Nowak, J.; Clément, C.; Barka, E.A. Use of plant growth-promoting bacteria for biocontrol of plant diseases: principles, mechanisms of action, and future prospects. Applied and environmental microbiology 2005, 71, 4951–4959. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Egamberdieva, D.; Wirth, S.; Behrendt, U.; Ahmad, P.; Berg, G. Antimicrobial activity of medicinal plants correlates with the proportion of antagonistic endophytes. Frontiers in microbiology 2017, 8, 199. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Esmaeili, S.; Naghibi, F.; Mosaddegh, M. Indigenous knowledge of traditionally used plants from Iran for fever/malaria treatment. Planta Medica 2010, 76, P509. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Irani, M.; Esmaeili, S.; Pirani, A.; Naghibi, F.; Mosaddegh, M. Evaluation of antiplasmodial activity of some plants ethnopharmacologically used to treat malaria in Iran. 2015.
- Firuzi, O.; Javidnia, K.; Gholami, M.; Soltani, M.; Miri, R. Antioxidant activity and total phenolic content of 24 Lamiaceae species growing in Iran. Natural product communications 2010, 5, 1934578X1000500219. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dehghani Nazhvani, A.; Razmkhah, M.; Jassbi, A.; Khademalizadeh, M.; Mahmoodi, A. Evaluation of anticancer effect of Hibiscus Sabdarifa, Otostegia Persica Otostegia Aucheri, and Otostegia Michauxii on oral squamous cell carcinoma cell line. Journal of Dental Medicine 2020, 32, 208–215. [Google Scholar]
- Esmaeili, S.; Hamzeloo-Moghadam, M.; Ghaffari, S.; Mosaddegh, M. Cytotoxic activity screening of some medicinal plants from south of Iran. Research Journal of Pharmacognosy 2014, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar]
- Alipieva, K.; Korkina, L.; Orhan, I.E.; Georgiev, M.I. Verbascoside - A review of its occurrence, (bio)synthesis and pharmacological significance. Biotechnology Advances 2014, 32, 1065–1076. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, W.G.; Wang, P.; Yang, Z.Q.; Li, M.X.; Tian, X.Y. Pharmacological effects of verbascoside: research advances. Journal of International Pharmaceutical Research 2020, 47, 1078–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- He, W.; Fang, T.; Tu, P. Research progress on pharmacological activities of echinacoside. Zhongguo Zhongyao Zazhi 2009, 34, 476–479. [Google Scholar]
- Liu, J.; Yang, L.; Dong, Y.; Zhang, B.; Ma, X. Echinacoside, an Inestimable Natural Product in Treatment of Neurological and other Disorders. Molecules 2018, 23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.K.; Singla, R.K.; Pandey, A.K. Chlorogenic Acid: A Dietary Phenolic Acid with Promising Pharma-cotherapeutic Potential. Current Medicinal Chemistry 2023, 30, 3905–3926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sova, M.; Saso, L. Natural sources, pharmacokinetics, biological activities and health benefits of hydroxycinnamic acids and their metabolites. Nutrients 2020, 12, 1–30. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Çetinkaya, M.; Baran, Y. Therapeutic Potential of Luteolin on Cancer. Vaccines 2023, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Punia Bangar, S.; Kajla, P.; Chaudhary, V.; Sharma, N.; Ozogul, F. Luteolin: A flavone with myriads of bioactivities and food applications. Food Bioscience 2023, 52. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bhardawaj, H.; Vasudeva, N.; Sharma, S. Phytochemistry and Pharmacological Aspects of Apigenin: A Review. Natural Products Journal 2023, 13, 64–82. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahbaz, M.; Imran, M.; Alsagaby, S.A.; Naeem, H.; Al Abdulmonem, W.; Hussain, M.; Abdelgawad, M.A.; El-Ghorab, A.H.; Ghoneim, M.M.; El-Sherbiny, M.; et al. Anticancer, antioxidant, ameliorative and therapeutic properties of kaempferol. International Journal of Food Properties 2023, 26, 1140–1166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Hwang, I.-s.; Liu, Q.-H.; Woo, E.-R.; Lee, D.G. (+)-Medioresinol leads to intracellular ROS accumulation and mitochondria-mediated apoptotic cell death in Candida albicans. Biochimie 2012, 94, 1784–1793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kang, Y.J.; Seo, D.-G.; Park, S.-Y. Phenylpropanoids from cinnamon bark reduced β-amyloid production by the inhibition of β-secretase in Chinese hamster ovarian cells stably expressing amyloid precursor protein. Nutrition Research 2016, 36, 1277–1284. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badawi, M.M.; Handa, S.S.; Kinghorn, A.D.; Cordell, G.A.; Farnsworth, N.R. Plant anticancer agents XXVII: antileukemic and cytotoxic constituents of Dirca occidentalis (Thymelaeaceae). Journal of pharmaceutical sciences 1983, 72, 1285–1287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hwang, J.H.; Choi, H.; Hwang, I.-s.; Kim, A.R.; Woo, E.-R.; Lee, D.G. Synergistic antibacterial and antibiofilm effect between (+)-medioresinol and antibiotics in vitro. Applied biochemistry and biotechnology 2013, 170, 1934–1941. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sauvain, M.; Kunesch, N.; Poisson, J.; Gantier, J.C.; Gayral, P.; Dedet, J.P. Isolation of leishmanicidal triterpenes and lignans from the Amazonian liana Doliocarpus dentatus (Dilleniaceae). Phytotherapy research 1996, 10, 1–4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Guan, X.; Gao, C.-L.; Ruan, W.; Zhao, S.; Kai, G.; Li, F.; Pang, T. Medioresinol as a novel PGC-1α activator prevents pyroptosis of endothelial cells in ischemic stroke through PPARα-GOT1 axis. Pharmacological Research 2021, 169, 105640. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sasaki, H.; Taguchi, H.; ENDo, T.; Yosioka, I.; Higashiyama, K.; OTOMASU, H. The glycosides of Martynia louisiana Mill. A new phenylpropanoid glycoside, martynoside. Chemical and Pharmaceutical Bulletin 1978, 26, 2111–2121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendota, S.; Aderogba, M.; Van Staden, J. In vitro antimicrobial activity of extracts and an isolated compound from Boscia albitrunca leaves. South African Journal of Botany 2015, 96, 91–93. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tóth, E.; Tóth, G.; Máthé, I.; Blunden, G. Martynoside, forsythoside B, ladanein and 7a-acetoxyroyleanone from Ballota nigra L. Biochemical Systematics and Ecology 2007, 12, 894–897. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jianjun, G.; Rongzhao, L.; Guiqiu, H.; Zhongjian, J. Studies on the topoisomerase inhibitors of phenylpropanoid glycosides from Pedicularis alaschanica Maxim. Beijing yi ke da xue xue bao= Journal of Beijing Medical University 1996, 28, 50–51. [Google Scholar]
- Miao, J.; Wang, W.; Yao, S.; Navaratnam, S.; Parsons, B. Antioxidative properties of Martynoside: pulse radiolysis and laser photolysis study. Free radical research 2003, 37, 829–833. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liao, F.; Zheng, R.; Gao, J.; Jia, Z. Retardation of skeletal muscle fatigue by the two phenylpropanoid glycosides: verbascoside and martynoside from Pedicularis plicata Maxim. Phytotherapy Research: An International Journal Devoted to Pharmacological and Toxicological Evaluation of Natural Product Derivatives 1999, 13, 621–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, M.; Tan, N.; Zhu, H.; Zeng, G.; He, W.; Yu, B.; Chen, X. Anti-sports anaemia effects of verbascoside and martynoside in mice. International journal of sports medicine 2010, 31, 537–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hu, Y.; Guan, X.; He, Z.; Xie, Y.; Niu, Z.; Zhang, W.; Wang, A.; Zhang, J.; Si, C.; Li, F. Apigenin-7-O-glucoside alleviates DSS-induced colitis by improving intestinal barrier function and modulating gut microbiota. Journal of Functional Foods 2023, 104, 105499. [Google Scholar]
- Papoutsi, Z.; Kassi, E.; Mitakou, S.; Aligiannis, N.; Tsiapara, A.; Chrousos, G.P.; Moutsatsou, P. Acteoside and martynoside exhibit estrogenic/antiestrogenic properties. The Journal of Steroid Biochemistry and Molecular Biology 2006, 98, 63–71. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Gowan, E.; Lewis, B.A.; Turgeon, R. Phloem transport of antirrhinoside, an iridoid glycoside, in Asarina scandens (Scrophulariaceae). Journal of chemical ecology 1995, 21, 1781–1788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beninger, C.W.; Cloutier, R.R.; Grodzinski, B. The iridoid glucoside, antirrhinoside, from Antirrhinum majus L. has differential effects on two generalist insect herbivores. Journal of Chemical Ecology 2008, 34, 591–600. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Venditti, A.; Frezza, C.; Serafini, I.; Ciccòla, A.; Sciubba, F.; Serafini, M.; Bianco, A. Iridoids of chemotaxonomy relevance, a new antirrhinoside ester and other constituents from Kickxia spuria subsp. integrifolia (Brot.) R. Fern. Chemistry & Biodiversity 2018, 15, e1700473. [Google Scholar]
- Akkol, E.K.; Ercil, D. Antinociceptive and anti-inflammatory activities of some Linaria species from Turkey. Pharmaceutical Biology 2009, 47, 188–194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frezza, C.; Venditti, A.; Marcucci, E.; Parroni, A.; Reverberi, M.; Serafini, M.; Bianco, A. Phytochemical analysis of Linaria purpurea (L.) Mill. and inhibitory activity on the production of aflatoxin B1 (AFB1) in Aspergillus flavus Link. of one of its metabolites, antirrhinoside. Industrial crops and products 2019, 139, 111554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quirantes-Piné, R.; Herranz-López, M.; Funes, L.; Borrás-Linares, I.; Micol, V.; Segura-Carretero, A.; Fernández-Gutiérrez, A. Phenylpropanoids and their metabolites are the major compounds responsible for blood-cell protection against oxidative stress after administration of Lippia citriodora in rats. Phytomedicine 2013, 20, 1112–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luhata, L.P.; Usuki, T. Free radical scavenging activities of verbascoside and isoverbascoside from the leaves of Odontonema strictum (Acanthaceae). Bioorganic & Medicinal Chemistry Letters 2022, 59, 128528. [Google Scholar]
- Chen, C.-Y.; Tung, H.-Y.; Tseng, Y.-F.; Huang, J.-S.; Shi, L.-S.; Ye, Y.-L. Verbascoside and isoverbascoside ameliorate transforming growth factor β1-induced collagen expression by lung fibroblasts through Smad/non-Smad signaling pathways. Life Sciences 2022, 308, 120950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kashyap, B.; Barge, S.R.; Bharadwaj, S.; Deka, B.; Rahman, S.; Ghosh, A.; Manna, P.; Dutta, P.P.; Sheikh, Y.; Kandimalla, R. Evaluation of therapeutic effect of Premna herbacea in diabetic rat and isoverbascoside against insulin resistance in L6 muscle cells through bioenergetics and stimulation of JNK and AKT/mTOR signaling cascade. Phytomedicine 2021, 93, 153761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rui-Chuan, C.; Jin-Hua, S.; Gao-Liang, O.; Ke-Xia, C.; Jin-Quan, L.; Xiao-Guang, X. Induction of differentiation in human hepatocarcinoma cells by isoverbascoside. Planta medica 2002, 68, 370–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chen, R.-C.; Su, J.-H.; Yang, S.-M.; Li, J.; Wang, T.-J.; Zhou, H. Effect of isoverbascoside, a phenylpropanoid glycoside antioxidant, on proliferation and differentiation of human gastric cancer cell. Acta Pharmacol Sin 2002, 23, 997–1001. [Google Scholar]
- Wang, T.; Yang, S.; Huang, Z.; Li, Q.; Li, Q.; Zhou, H.; Zheng, R.; Jia, Z. Induced-differentiation and cytotoxicity of isoverbascoside on HL-60 cells. Shi yan Sheng wu xue bao 1999, 32, 321–327. [Google Scholar]
- Dimitrova, P.; Alipieva, K.; Stojanov, K.; Milanova, V.; Georgiev, M.I. Plant-derived verbascoside and isoverbascoside regulate Toll-like receptor 2 and 4-driven neutrophils priming and activation. Phytomedicine 2019, 55, 105–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Huang, Y.; Wen, X.; Wu, Y.; Zhao, Y.; Ni, Y. Extraction, purification, and hydrolysis behavior of apigenin-7-O-Glucoside from Chrysanthemum morifolium tea. Molecules 2018, 23, 2933. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Minda, D.; Avram, S.; Pavel, I.Z.; Kis, B.; Ghitu, A.; Zupkó, I.; Dehelean, C.; Buda, V.; Diaconeasa, Z.; Scurtu, A. An in vitro evaluation of apigenin and apigenin-7-o-glucoside against hela human cervical cancer cell line. Revista de Chimie 2020, 71, 140–144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, W.; Yue, R.-F.; Jin, Z.; He, L.-M.; Shen, R.; Du, D.; Tang, Y.-Z. Efficiency comparison of apigenin-7-O-glucoside and trolox in antioxidative stress and anti-inflammatory properties. Journal of Pharmacy and Pharmacology 2020, 72, 1645–1656. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, M.-M.; Ma, R.-H.; Ni, Z.-J.; Thakur, K.; Cespedes-Acuña, C.L.; Jiang, L.; Wei, Z.-J. Apigenin 7-O-glucoside promotes cell apoptosis through the PTEN/PI3K/AKT pathway and inhibits cell migration in cervical cancer HeLa cells. Food and Chemical Toxicology 2020, 146, 111843. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smiljkovic, M.; Stanisavljevic, D.; Stojkovic, D.; Petrovic, I.; Vicentic, J.M.; Popovic, J.; Grdadolnik, S.G.; Markovic, D.; Sankovic-Babice, S.; Glamoclija, J. Apigenin-7-O-glucoside versus apigenin: Insight into the modes of anticandidal and cytotoxic actions. EXCLI journal 2017, 16, 795. [Google Scholar]
- Abugri, D.A.; Witola, W.H. Interaction of apigenin-7-O-glucoside with pyrimethamine against Toxoplasma gondii growth. Journal of Parasitic Diseases 2020, 44, 221–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gulluce, M.; Orhan, F.; Yanmis, D.; Arasoglu, T.; Guvenalp, Z.; Demirezer, L.O. Isolation of a flavonoid, apigenin 7-O-glucoside, from Mentha longifolia (L.) Hudson subspecies longifolia and its genotoxic potency. Toxicology and industrial health 2015, 31, 831–840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pei, Z.J.; Li, C.; Dai, W.; Lou, Z.; Sun, X.; Wang, H.; Khan, A.A.; Wan, C. The Anti-Biofilm Activity and Mechanism of Apigenin-7-O-Glucoside Against Staphylococcus aureus and Escherichia coli. Infection and Drug Resistance 2023, 16, 2129–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]

| Dominant constituents of the essential oils | Percentage | Developmental stage | Location | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Dillapiole | 23.9 | Flowering | Chahzangooleh, Fars province, Iran | [8] |
| 2-methylbenzofuran | 12.9 | Flowering | Chahzangooleh, Fars province, Iran | [8] |
| α-pinene | 8.1 | Flowering | Chahzangooleh, Fars province, Iran | [8] |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 20.1 | Flowering | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [9] |
| Trans-verbenol | 10.2 | Flowering | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [9] |
| Linalool | 5.3 | Flowering | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [9] |
| Humulene epoxide II | 4.6 | Flowering | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [9] |
| Eugenol | 36.81 | Dormant | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [20] |
| Eugenol acetate | 21.02 | Dormant | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [20] |
| Carvacrol | 9.35 | Dormant | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [20] |
| Carvacrol | 16.08 | Vegetative | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [20] |
| Eugenol | 13.23 | Vegetative | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [20] |
| Cumin aldehyde | 9.63 | Vegetative | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [20] |
| Linalool | 8.28 | Vegetative | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [20] |
| Carvacrol | 14.20 | Flowering | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [20] |
| Eugenol | 8.98 | Flowering | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [20] |
| δ-cadinene | 8.90 | Flowering | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [20] |
| Caryophyllene oxide | 8.43 | Flowering | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [20] |
| n-hexadecanoic acid | 7.07 | Flowering | Kazeroon, Fars province, Iran | [20] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





