Submitted:
10 July 2023
Posted:
11 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Preparation and characterization
2.2. Antimicrobial activities
2.2.1. Agar well diffusion methods
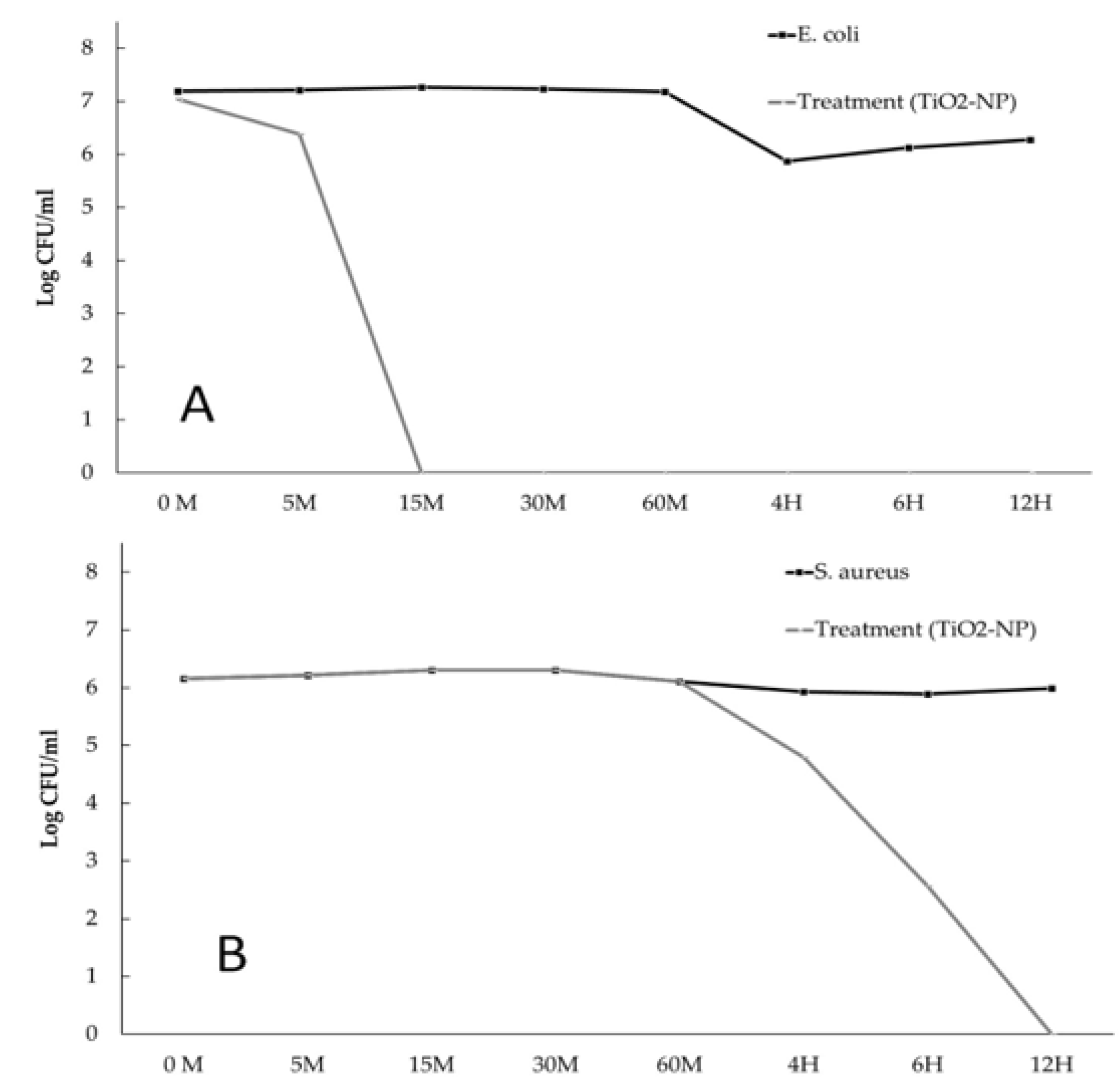
2.2.2. Time-kill kinetic assay
2.3. Antibiofilm forming activity
2.4. In-vitro wound healing assay
2.4.1. Cell culture
2.4.2. Scratching wound healing assay
2.5. In-vivo wound healing assay (animal model)
2.5.1. Ethical approval
2.5.2. Experimental animals
2.5.3. Early wound healing score (EHS)
2.5.4. Wound microbial assay
2.5.5. Wound contraction
2.5.6. Tissue collection and histological analysis
2.6. Statistical analysis
3. Results
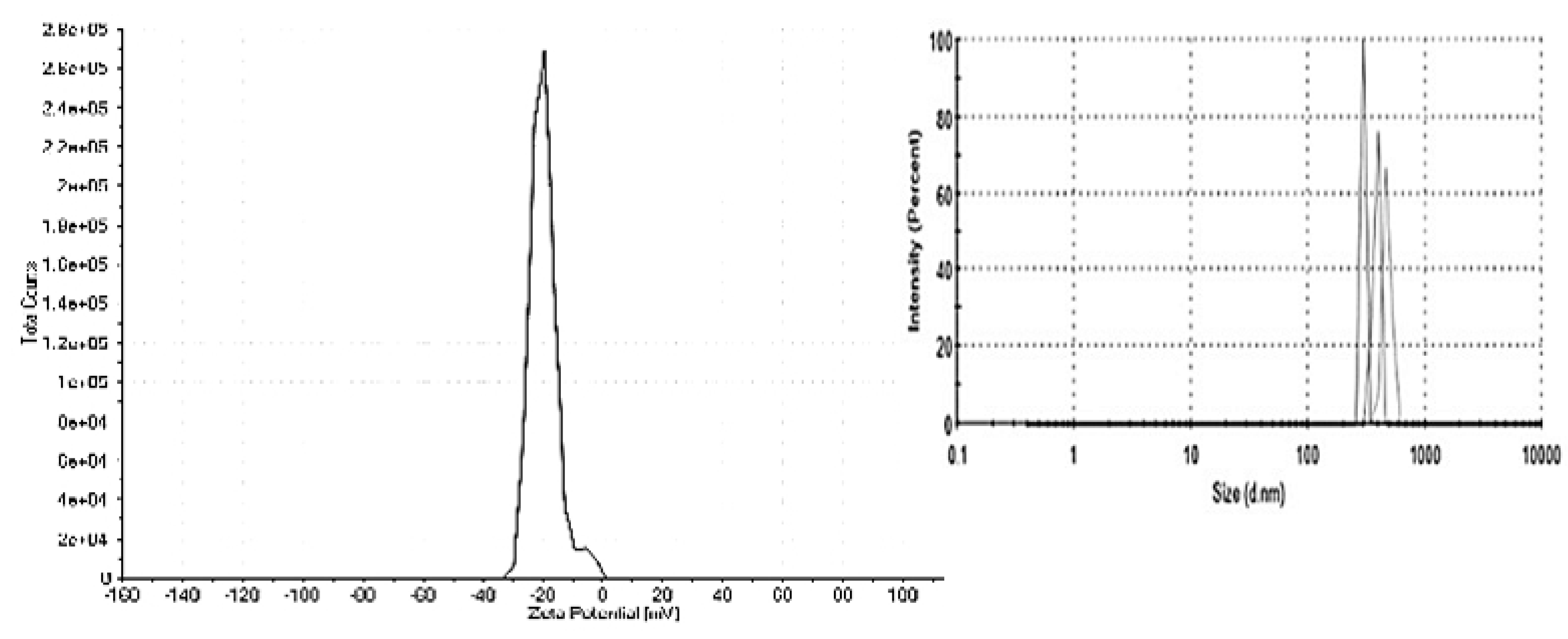
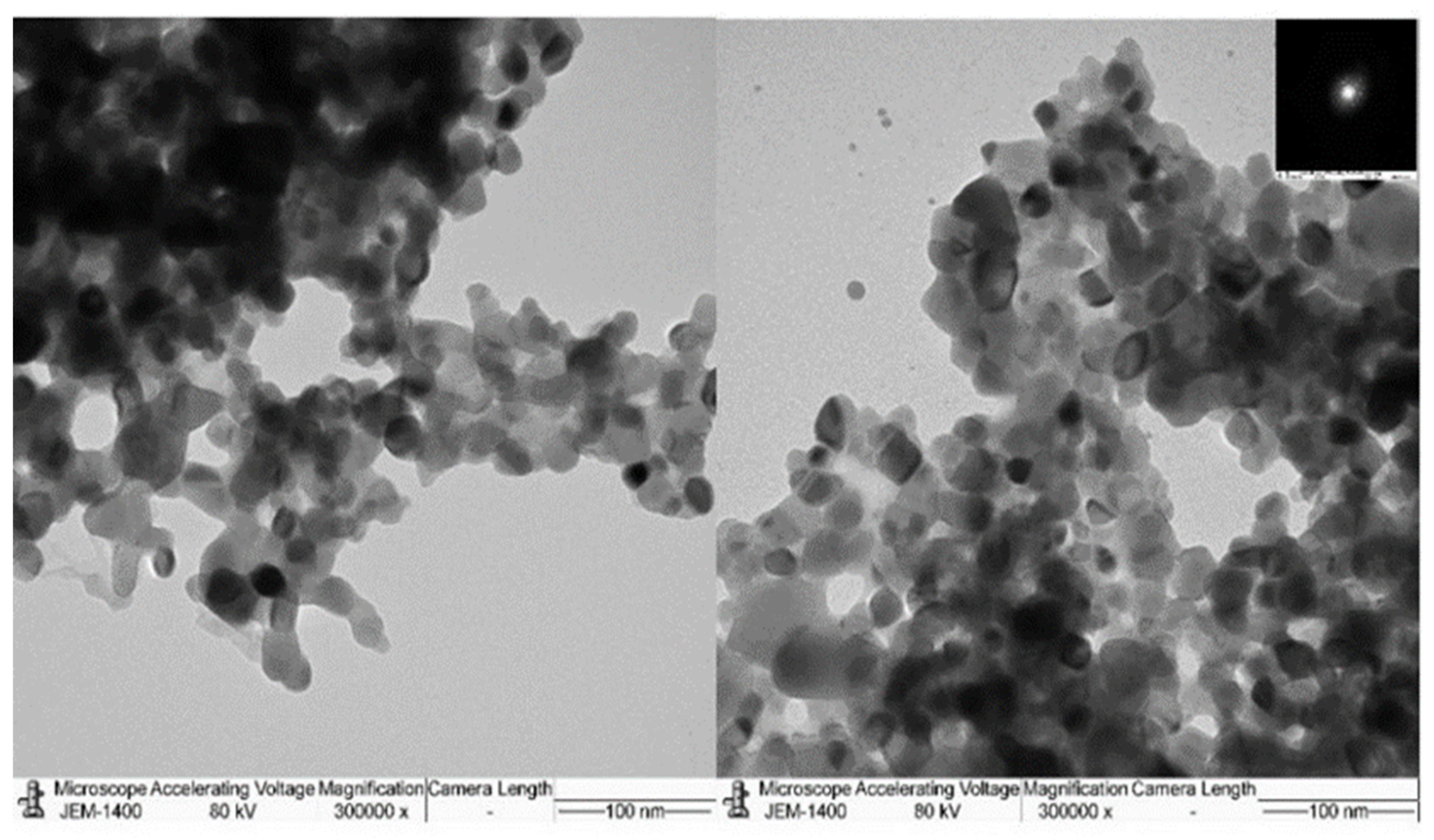
3.1. Characterization of TiO2-NP formulation
3.2. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm forming activities
3.3. Wound healing assay
3.3.1. In-vitro
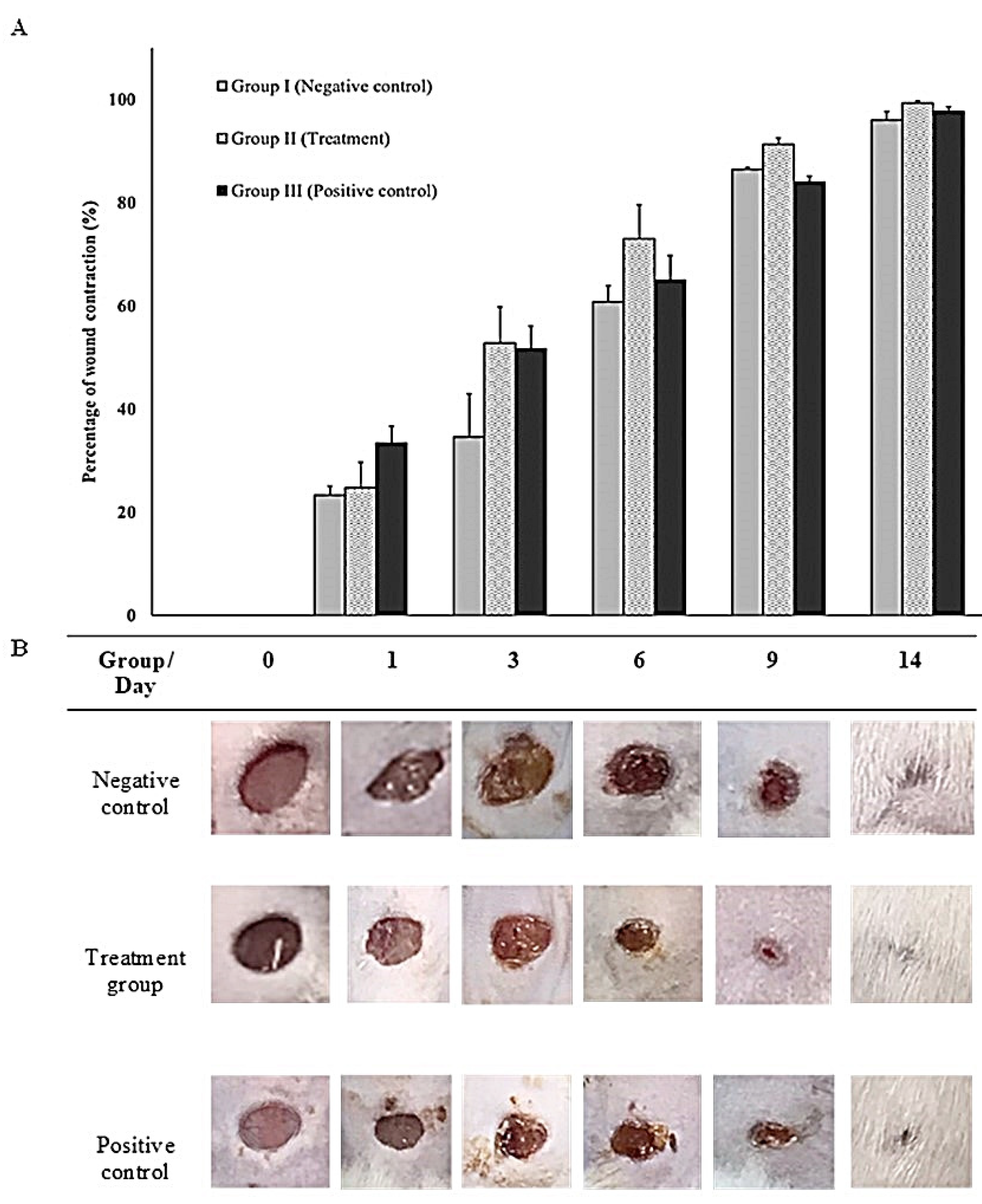
3.3.2. In-vivo (animal model)
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Puca, V.; Marulli, R.Z.; Grande, R.; Vitale, I.; Niro, A.; Molinaro, G.; Prezioso, S.; Muraro, R.; Di Giovanni, P. Microbial species isolated from infected wounds and antimicrobial resistance analysis: Data emerging from a three-years retrospective study. Antibiotics (Basel). 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roy, S.; Ahmed, M.U.; Uddin, B.M.M.; Ratan, Z.A.; Rajawat, M.; Mehta, V.; Zaman, S.B. . Evaluation of antibiotic susceptibility in wound infections: A pilot study from Bangladesh. F1000Res 6 2017, 2103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frykberg, R.G.; Banks, J. Challenges in the treatment of chronic wounds. Adv. Wound Care (New Rochelle). 2015, 4, 560–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kadam, S.; Nadkarni, S.; Lele, J.; Sakhalkar, S.; Mokashi, P.; Kaushik, K.S. Bioengineered platforms for chronic wound infection studies: How can we make them more human-relevant? Front. Bioeng. 2019, 7. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gueltzow, M.; Khalilpour, P.; Kolbe, K.; Zoellner, Y. Budget impact of antimicrobial wound dressings in the treatment of venous leg ulcers in the German outpatient care sector: A budget impact analysis. J. Mark Access Health Policy. 2018, 6, 1527654. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Norman, R.E.; Gibb, M.; Dyer, A.; Prentice, J.; Yelland, S.; Cheng, Q.; Lazzarini, P.A.; Carville, K.; Innes-Walker, K.; Finlayson, K.; Edwards, H.; Burn, E.; Graves, N. Improved wound management at lower cost: A sensible goal for Australia. Int. Wound J. 2016, 13, 303–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, P.G.; Welsby, S.; Towers, V.; Booth, R.; Hogarth, A.; Rowlands, V.; Joseph, A.; Jones, S.A. Multidrug-resistant organisms, wounds and topical antimicrobial protection. Int. Wound J. 2012, 9, 387–396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Corsini, C.M.M.; Silva, V.O.; Carvalho, O.V.; Sepúlveda, R.V.; Valente, F.; Reis, E.; Moreira, M.; Silva, A.; Borges, A. emergence of multidrug-resistant bacteria isolated from surgical site infection in dogs and cats. Arq. Med. Vet. 2020, 72, 1213–1220. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, J.; Cao, J.; Zhu, Y.-G.; Chen, Q.; Shen, F.; Wu, Y.; Xu, S.; Fan, H.; Da, G.; Huang, R.-j.; Wang, J.; de Jesus, A.L.; Morawska, L.; Chan, C.K.; Peccia, J.; Yao, M. Global survey of antibiotic resistance genes in air. Environ. Sci. Technol. 2018, 52, 10975–10984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wee, B.A.; Muloi, D.M.; van Bunnik, B.A.D. Quantifying the transmission of antimicrobial resistance at the human and livestock interface with genomics. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2020, 26, 1612–1616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uruén, C.; Chopo-Escuin, G.; Tommassen, J.; Mainar-Jaime, R.C.; Arenas, J. Biofilms as promoters of bacterial antibiotic resistance and tolerance. Antibiotics (Basel). 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shkodenko, L.; Kassirov, I.; Koshel, E. Metal oxide nanoparticles against bacterial biofilms: Perspectives and limitations. Microorganisms. 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jesline, A.; John, N.P.; Narayanan, P.M.; Vani, C.; Murugan, S. Antimicrobial activity of Zinc and Titanium dioxide nanoparticles against biofilm-producing methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus. Appl. Nanosci. 2015, 5, 157–162. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rajendran, N.K.; Kumar, S.S.D.; Houreld, N.N.; Abrahamse, H. A review on nanoparticle-based treatment for wound healing. J. Drug Deliv. Sci. Technol. 2018, 44, 421–430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ziental, D.; Czarczynska-Goslinska, B.; Mlynarczyk, D.T.; Glowacka-Sobotta, A.; Stanisz, B.; Goslinski, T.; Sobotta, L. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Prospects and applications in medicine. Nanomaterials (Basel). 2020, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gudkov, S.V.; Burmistrov, D.E.; Serov, D.A.; Rebezov, M.B.; Semenova, A.A.; Lisitsyn, A.B. ; A mini review of antibacterial properties of ZnO nanoparticles. Front. Phys. 2021, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Barroso, A.; Mestre, H.; Ascenso, A.; Simões, S.; Reis, C. Nanomaterials in wound healing: From material sciences to wound healing applications. Nano. Select. 2020, 1, 443–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mallick, S.; Nag, M.; Lahiri, D.; Pandit, S.; Sarkar, T.; Pati, S.; Nirmal, N. P.; Edinur, H. A.; Kari, Z. A.; Ahmad Mohd Zain M., R.; Ray R., R. Engineered nanotechnology: An effective therapeutic platform for the chronic cutaneous wound. Nanomaterials. 2022, 12(5), 778. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carol López de, D.; Matias Guerrero, C.; Fernanda, B.M.; Camilo, S.; Maria José, G. Antimicrobial effect of Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: Antimicrobial resistance. Intech. Open. Rijeka 2020, 5. [Google Scholar]
- Nikpasand, A.; Parvizi, M.R. Evaluation of the effect of Titatnium dioxide nanoparticles/gelatin composite on infected skin wound Healing; An Animal Model Study. Bull Emerg. Trauma. 2019, 7, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Anpo, M.; Kamat, P. Environmentally benign photocatalysts: Applications of Titanium oxide-based materials. 2010.
- Hamdan, S.; Pastar, I.; Drakulich, S.; Dikici, E.; Tomic-Canic, M.; Deo, S.; Daunert, S. Nanotechnology-Driven Therapeutic Interventions in Wound Healing: Potential Uses and Applications. ACS. Central Science. 2017, 3, 163–175. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Balouiri, M.; Sadiki, M.; Ibnsouda, S.K. Methods for in vitro evaluating antimicrobial activity: A review, J. Pharm. Anal. 2016, 6, 71–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Appiah, T.; Boakye, Y.D.; Agyare, C. Antimicrobial activities and time-kill kinetics of extracts of selected ghanaian mushrooms. Evid Based Complement Alternat Med. 2017, 4534350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Stepanović, S.; Vuković, D.; Hola, V.; Di Bonaventura, G.; Djukić, S.; Cirković, I.; Ruzicka, F. Quantification of biofilm in microtiter plates: overview of testing conditions and practical recommendations for assessment of biofilm production by staphylococci. APMIS. 2007, 115, 891–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C. D.; Shah, S.; Tammela, P. Defining conditions for biofilm inhibition and eradication assays for gram-positive clinical reference strains. BMC Microbiology. 2018, 18(1), 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Marini, L.; Rojas, M.A.; Sahrmann, P.; Aghazada, R.; Pilloni, A. Early wound healing score: a system to evaluate the early healing of periodontal soft tissue wounds. J. Periodontal Implant. Sci. 2018, 48, 274–283. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Naghili, H.; Tajik, H.; Mardani, K.; Razavi Rouhani, S.M.; Ehsani, A.; Zare, P. Validation of drop plate technique for bacterial enumeration by parametric and nonparametric tests. Vet. Res. Forum. 2013, 4, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Sultana, J.; Molla, M.R.; Kamal, M.; Shahidullah, M.; Begum, F.; Bashar, M.A. Histological differences in wound healing in maxillofacial region in patients with or without risk factors. Bangladesh J. Pathol. 2009, 24, 3–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santos, T.S.; Santos, I.; Pereira-Filho, R.N.; Gomes, S.V.F.; Lima-Verde, I.B.; Marques, M.N.; Cardoso, J.C.; Severino, P.; Souto, E.B.; Albuquerque-Júnior, R.L.C. Histological evidence of wound healing improvement in rats treated with oral administration of hydroalcoholic extract of Vitis labrusca. Curr. Issues Mol. Biol. 2021, 43, 335–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadrazilova, I.; Pospisilova, S.; Pauk, K.; Imramovsky, A.; Vinsova, J.; Cizek, A.; Jampilek, J. In vitro bactericidal activity of 4- and 5-chloro-2-hydroxy-N-[1-oxo-1-(phenylamino) alkan-2-yl benzamides against MRSA. Biomed. Res. Int. 2015, 349534. [Google Scholar]
- Joseph, E.; Singhvi, G. Chapter 4-Multifunctional nanocrystals for cancer therapy: a potential nanocarrier, In: Nanomaterials for drug delivery and therapy. William Andrew Publishing, 2019, 91-116.
- Ostolska, I.; Wiśniewska, M. Application of the zeta potential measurements to explanation of colloidal Cr(2)O(3) stability mechanism in the presence of the ionic polyamino acids. Colloid Polym. Sci. 2014, 292, 2453–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Godoy-Gallardo, M.; Eckhard, U.; Delgado, L.M.; de Roo Puente, Y.J.D.; Hoyos-Nogues, M.; Gil, F.J.; Perez, R.A. Antibacterial approaches in tissue engineering using metal ions and nanoparticles: From mechanisms to applications. Bioact. Mater. 2021, 6, 4470–4490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Breijyeh, Z.; Jubeh, B.; Karaman, R. Resistance of gram-egative bacteria to current antibacterial agents and approaches to resolve it. Molecules. 2020, 25. [Google Scholar]
- Shi, H.; Magaye, R.; Castranova, V.; Zhao, J. Titanium dioxide nanoparticles: a review of current toxicological data. Part. Fibre. Toxicol. 2013, 10, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ruppé, É.; Woerther, P.L.; Barbier, F. Mechanisms of antimicrobial resistance in gram-negative bacilli. Ann. Intensive Care. 2015, 5, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pulgarin, C.; Kiwi, J.; Nadtochenko, V. Mechanism of photocatalytic bacterial inactivation on TiO2 films involving cell-wall damage and lysis. Applied Catalysis B. Environmental. 2012, 128, 179–183. [Google Scholar]
- Di Pilato, V.; Ceccherini, F.; Sennati, S. F. D'Agostino, F. Arena, N. D'Atanasio, F. P. Di Giorgio, S. Tongiani, L. Pallecchi and G. M. Rossolini. In vitro time-kill kinetics of dalbavancin against Staphylococcus spp. biofilms over prolonged exposure times. Diagn. Microbiol. Microbiol. Microbiol. 2020, 96(2), 114901.
- Archer, N. K.; Mazaitis, M. J.; Costerton, J. W.; Leid, J. G.; Powers, M. E.; Shirtliff, M. E. Staphylococcus aureus biofilms: properties, regulation, and roles in human disease. Virulence. 2011, 2(5), 445–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carrouel, F.; Viennot, S.; Ottolenghi, L.; Gaillard, C.; Bourgeois, D. Nanoparticles as antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, and remineralizing agents in oral care cosmetics: A review of the current situation. Nanomaterials. 2020, 10(1), 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Sun, T.; Xu, Q.; Duan, C.; Dai, Y.; Wang, L.; Song, Q. Preparation and antibiofilm properties of Zinc oxide/porous anodic alumina composite films. Nanoscale Res. Lett. 2018, 13, 201. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khatoon, Z.; McTiernan, C.D.; Suuronen, E.J.; Mah, T.-F.; Alarcon, E.I. Bacterial biofilm formation on implantable devices and approaches to its treatment and prevention. Heliyon. 2018, 4. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hou, Y.; Cai, K.; Li, J.; Chen, X.; Lai, M.; Hu, Y.; Luo, Z.; Ding, X.; Xu, D. Effects of Titanium nanoparticles on adhesion, migration, proliferation, and differentiation of mesenchymal stem cells. Int J. Nanomedicine. 2013, 8, 3619–3630. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Chermprapai, S.; Ederveen, T. H. A.; Broere, F.; Broens, E. M.; Schlotter, Y. M.; van Schalkwijk, S.; Boekhorst, J.; van Hijum S. A. F., T.; Rutten, V. P. M. G. The bacterial and fungal microbiome of the skin of healthy dogs and dogs with atopic dermatitis and the impact of topical antimicrobial therapy, an exploratory study. Vet. Microbiol. 2019, 229, 90–99. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mathew-Steiner, S. S.; Roy, S.; Sen, C. K. Collagen in wound healing. Bioengineering (Basel). 2021, 8, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
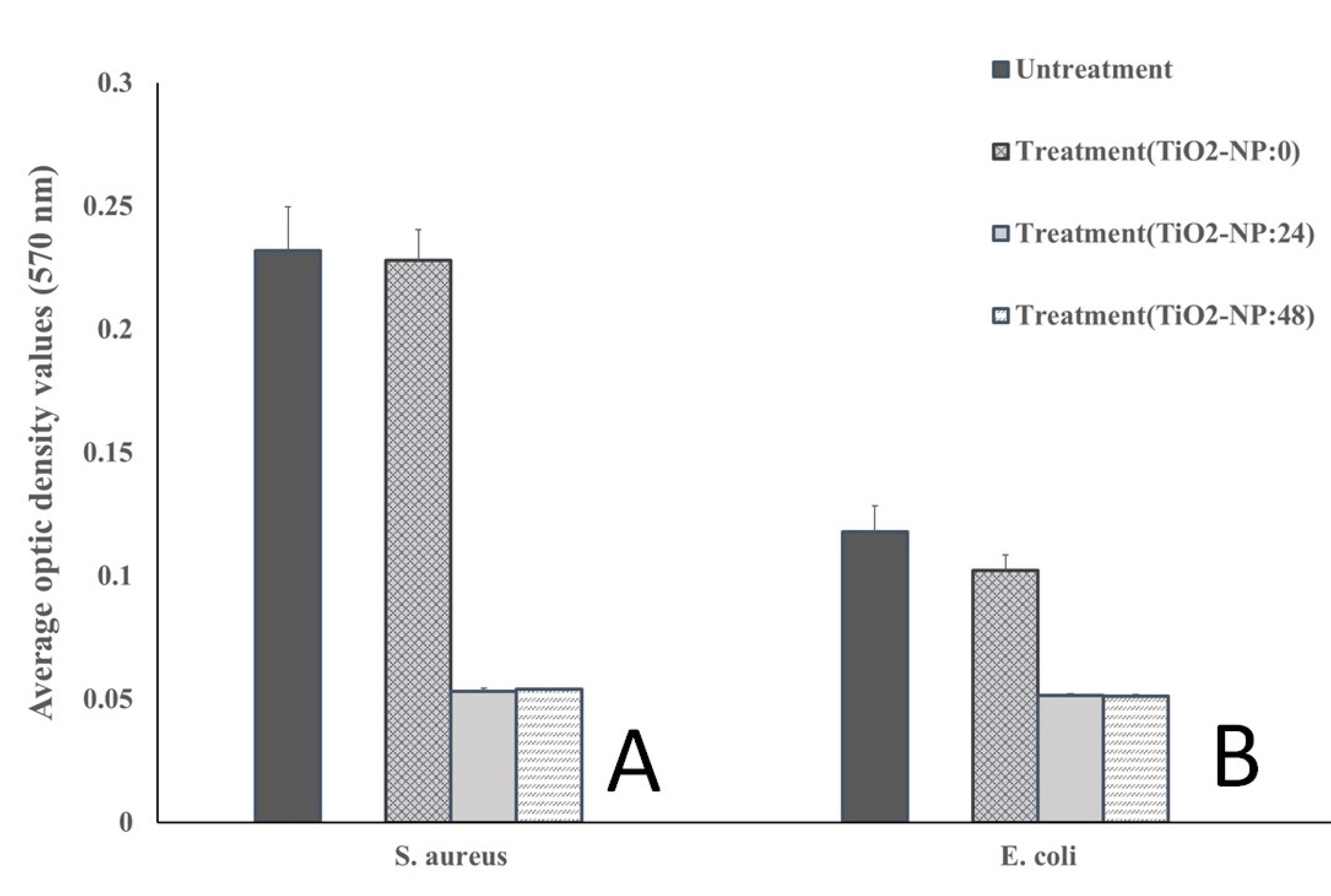
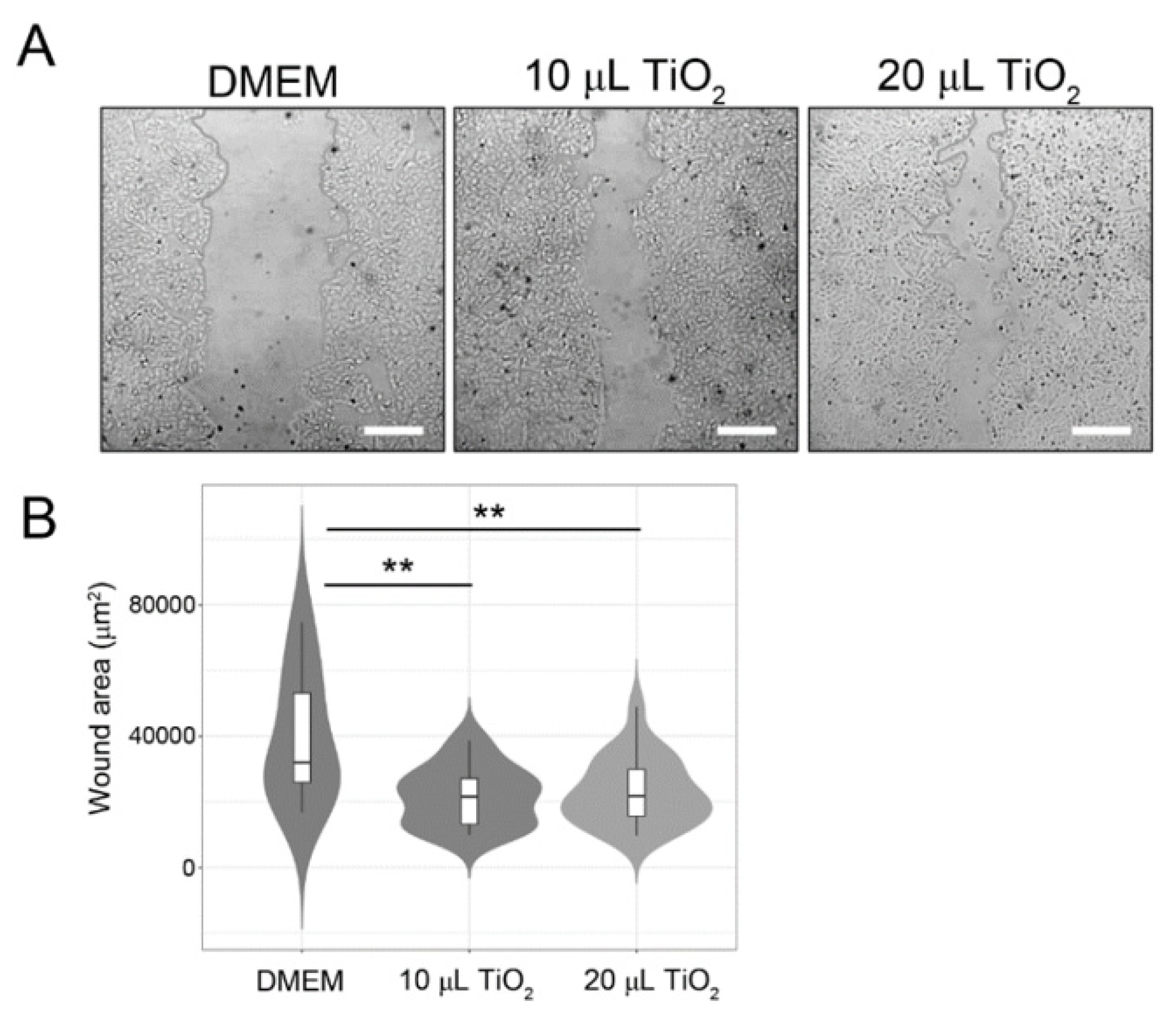
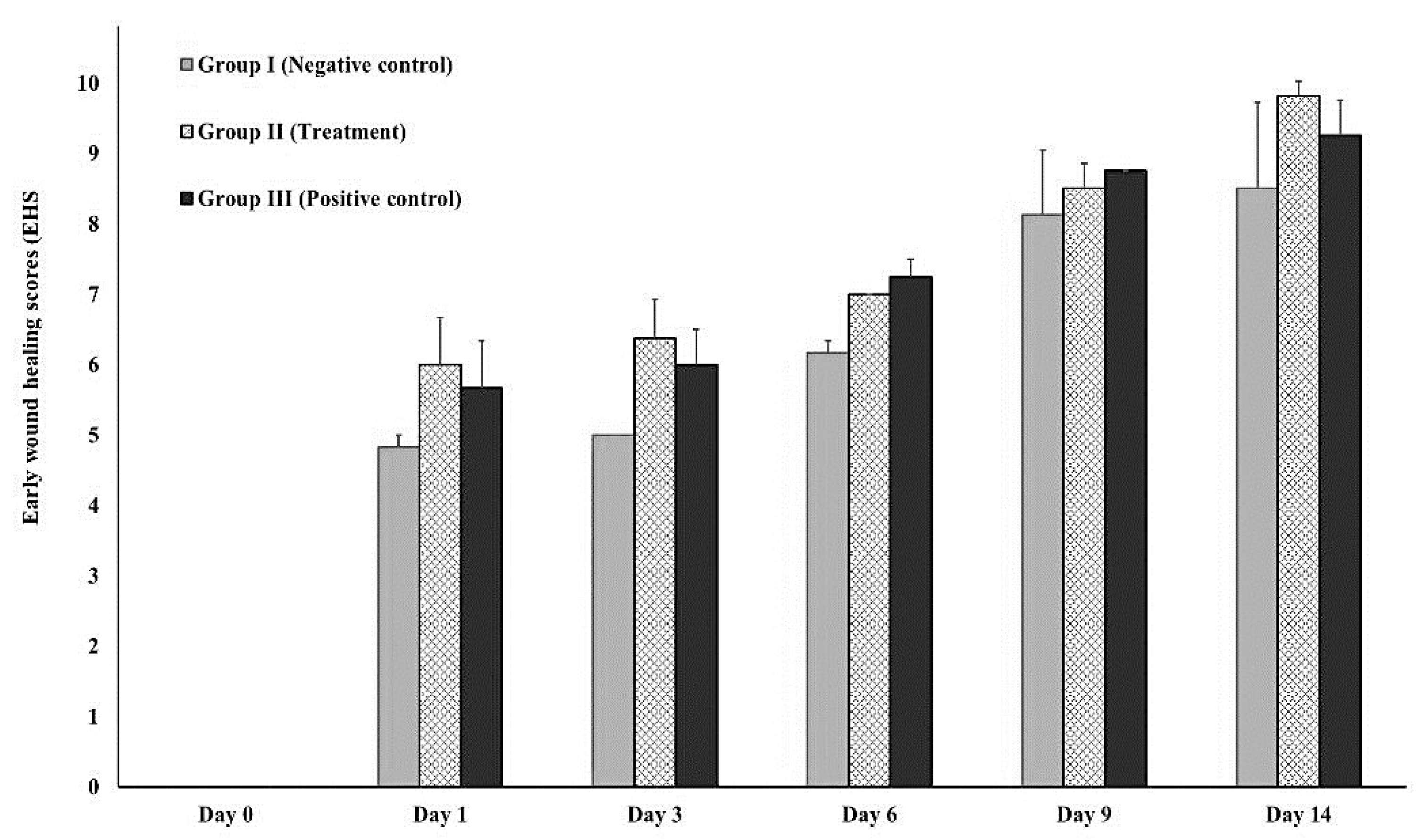
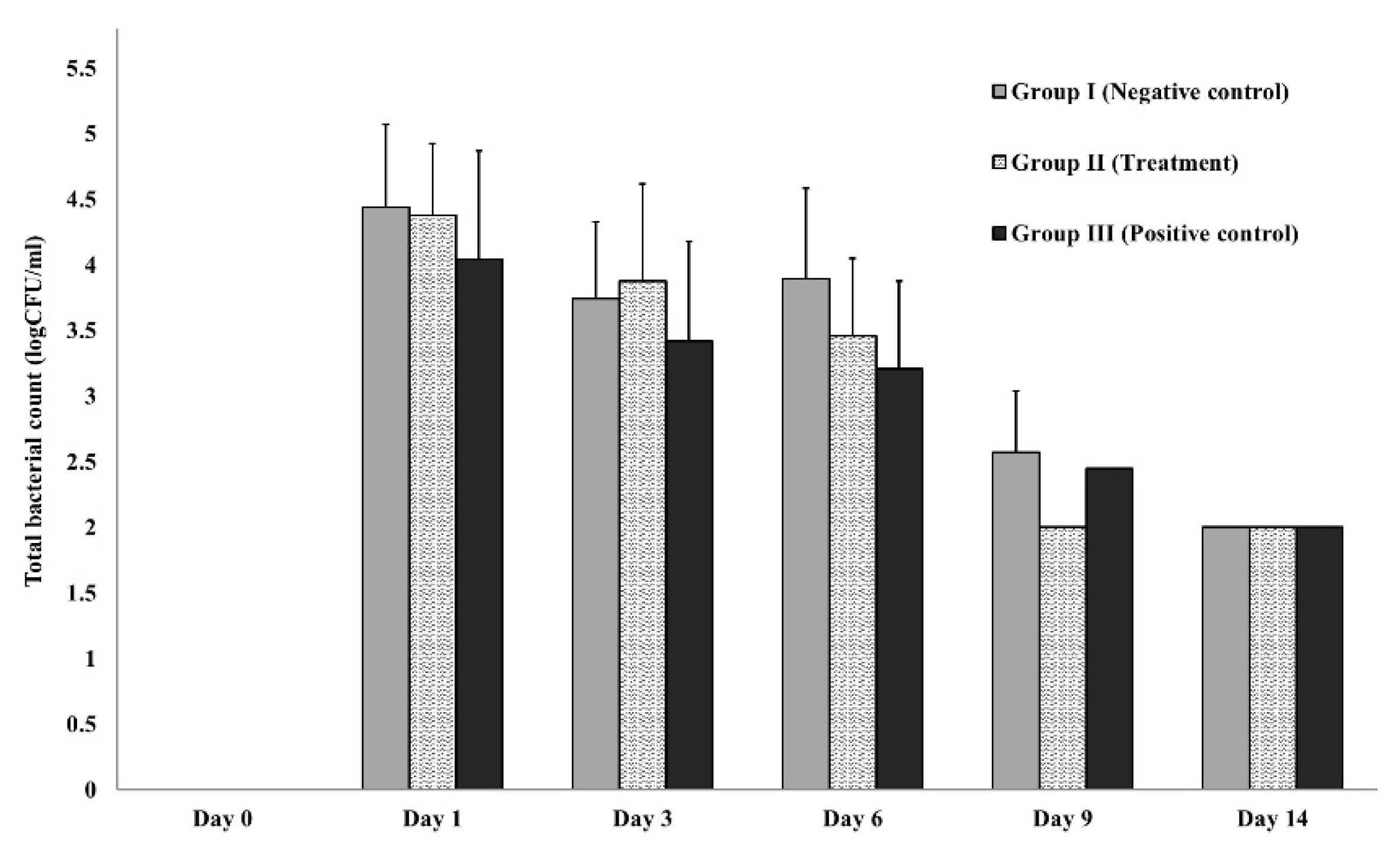

| Cut-Off Value Calculation | Biofilm-Formation Abilities |
|---|---|
| OD ≤ ODNC | Non-biofilm forming |
| ODNC < OD < 2ODNC | Weak-biofilm forming |
| 2ODNC < OD < 4ODNC | Moderate-biofilm forming |
| 4ODNC < OD | Strong-biofilm forming |
| Parameter | Descriptions | Score |
|---|---|---|
| CSR | Merged surgical wound margins | 6 |
| Surgical wound margins in contact | 3 | |
| Visible distance between surgical wound margins | 0 | |
| CSH | Absence of fibrin on the surgical wound margins | 2 |
| Presence of fibrin on the surgical wound margins | 1 | |
| Bleeding at the surgical wound margins | 0 | |
| CSI | Absence of redness along the surgical wound diameter | 2 |
| Redness involve < 50% of the diameter | 1 | |
| Redness involve > 50% of the diameter and/or pronounced swelling | 0 |
| Histological Parameters | Scoring System |
Histological Grading |
|---|---|---|
| Amount of granulation tissue | Profound | 1 |
| Moderate | 2 | |
| Scanty | 3 | |
| Absent | 4 | |
| Inflammatory infiltrate | Plenty | 1 |
| Moderate | 2 | |
| A few | 4 | |
| Collagen fiber orientation | Vertical | 1 |
| Mixed | 2 | |
| Horizontal | 4 | |
| Reticular | 1 | |
| Pattern of collagen | Mixed | 2 |
| Fascicle | 4 |
| Bacteria | Inhibition Zones (mm) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| N | TiO2-NP | Ag-NP | Iodine Solution | Gentamycin | |||
| S. aureus | 3 | 20.00 ± 5.42 | 20.12 ± 0.18 | 22.23 ± 0.24 | 31.75 ± 0.37* | ||
| E. coli | 3 | 24.00 ± 1.91 | 29.50 ± 0.50* | 24.51 ± 0.43 | 30.50 ± 0.75* | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





