Submitted:
09 July 2023
Posted:
10 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
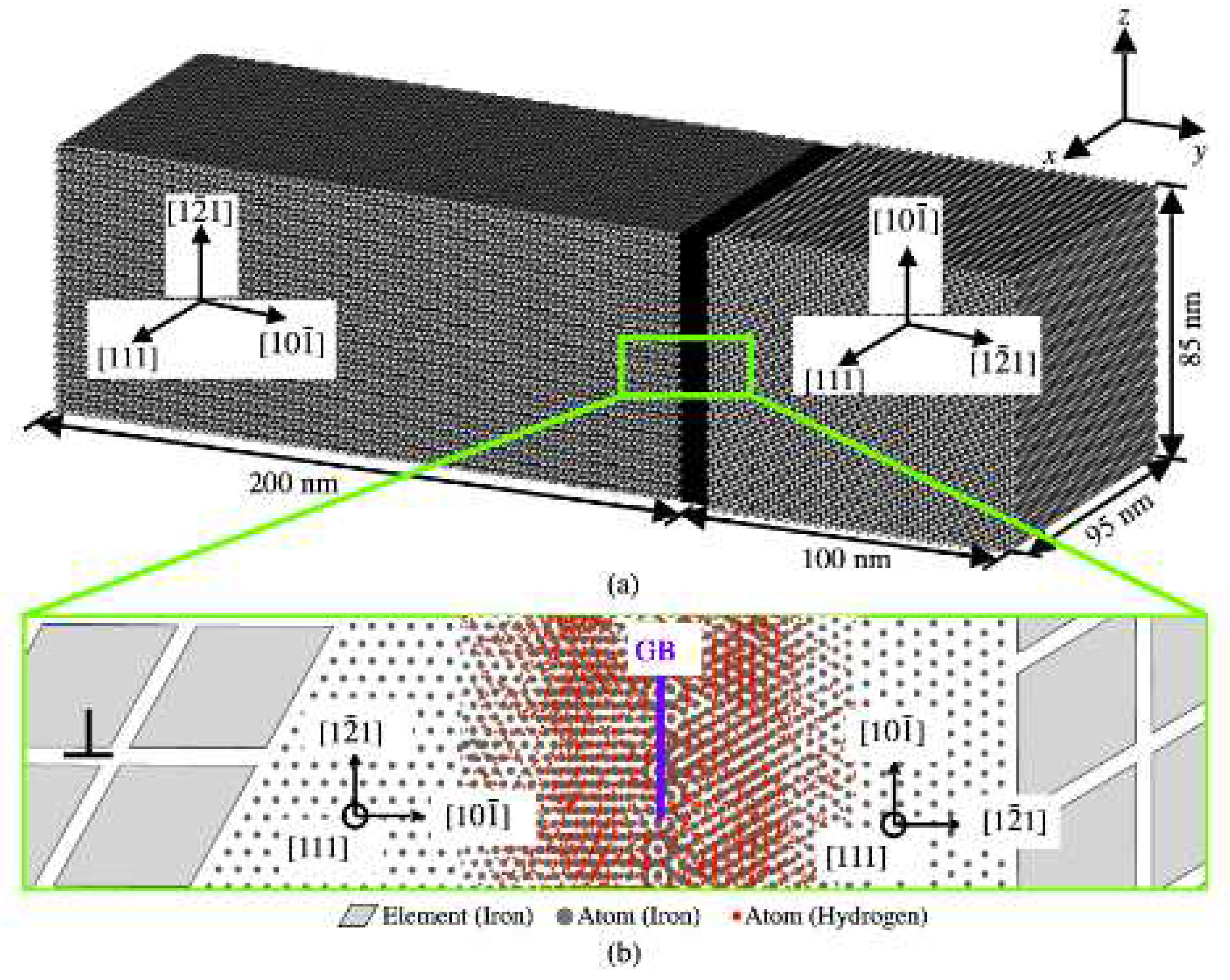
2. Computer Model Set-up
3. Simulation Results
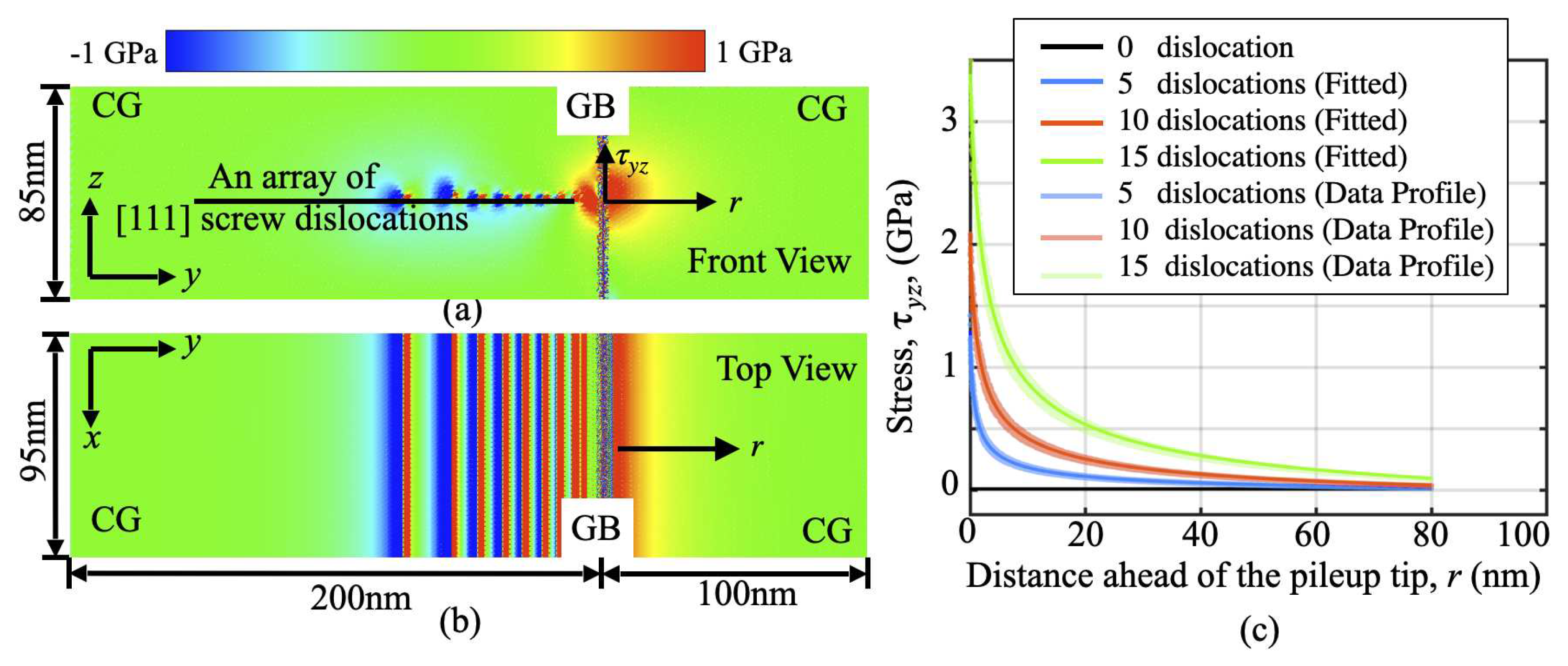
3.1. Dislocation pileup-induced internal stress nearby a H-charged GB
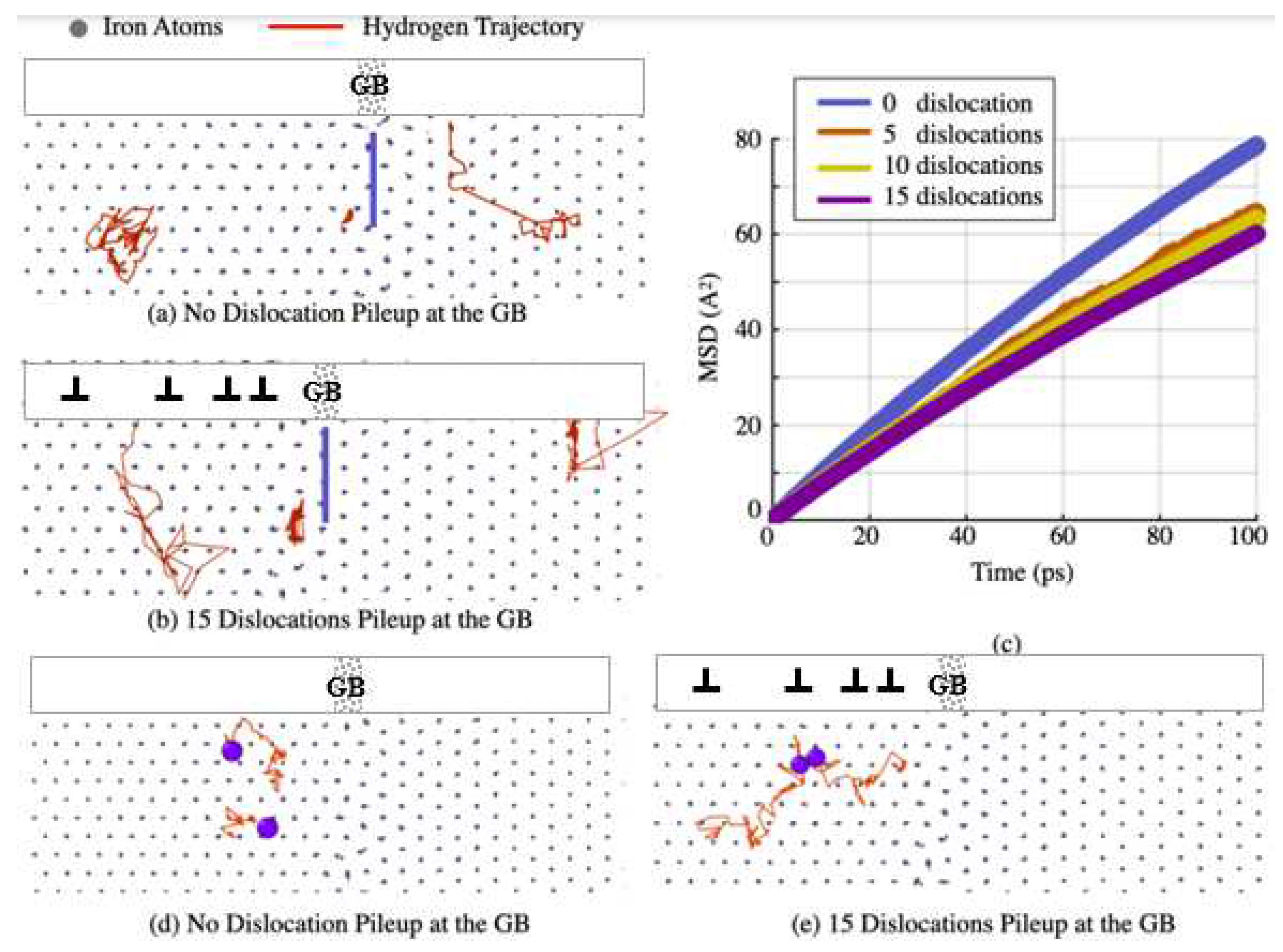
3.2. H atom diffusion nearby the slip-GB intersection
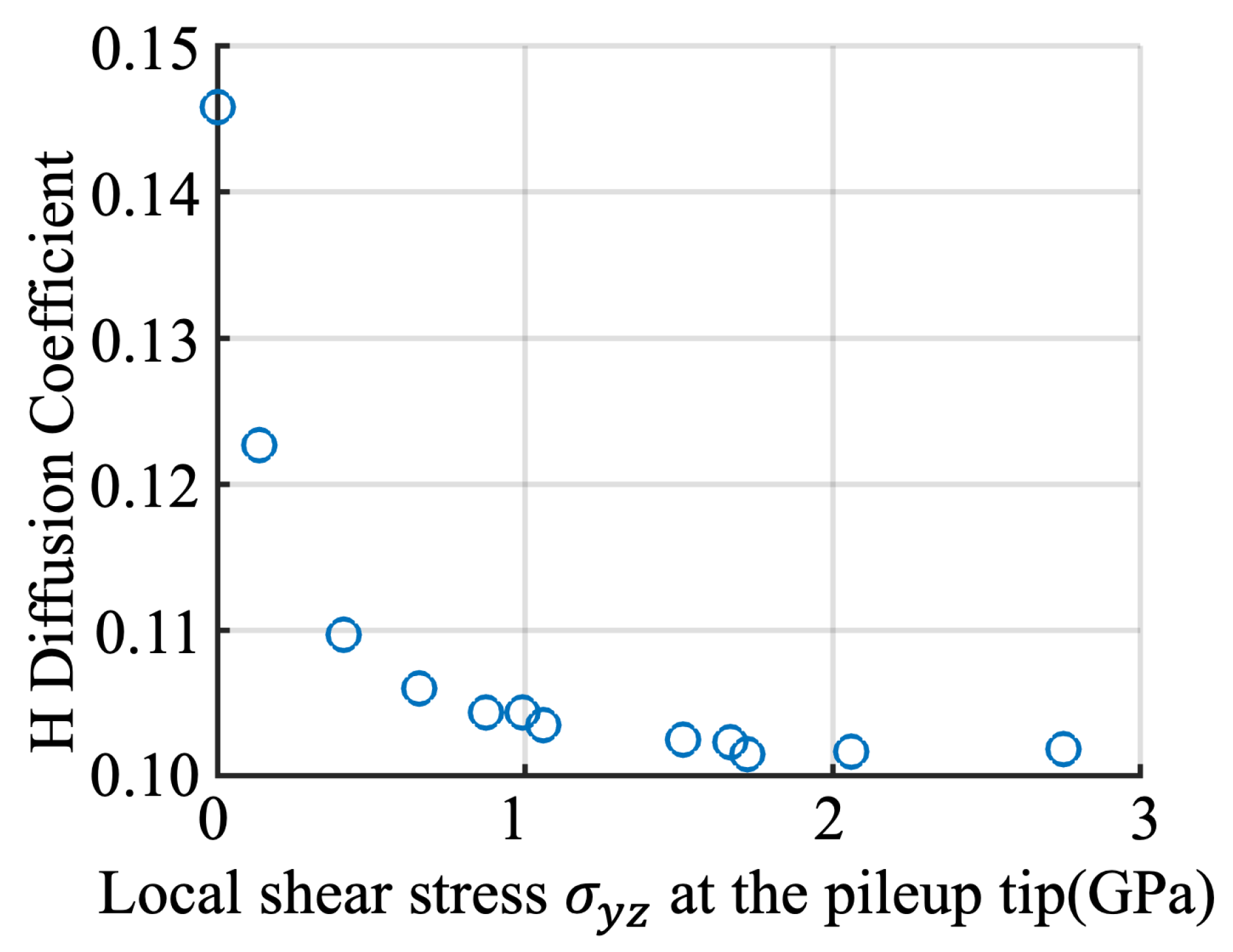
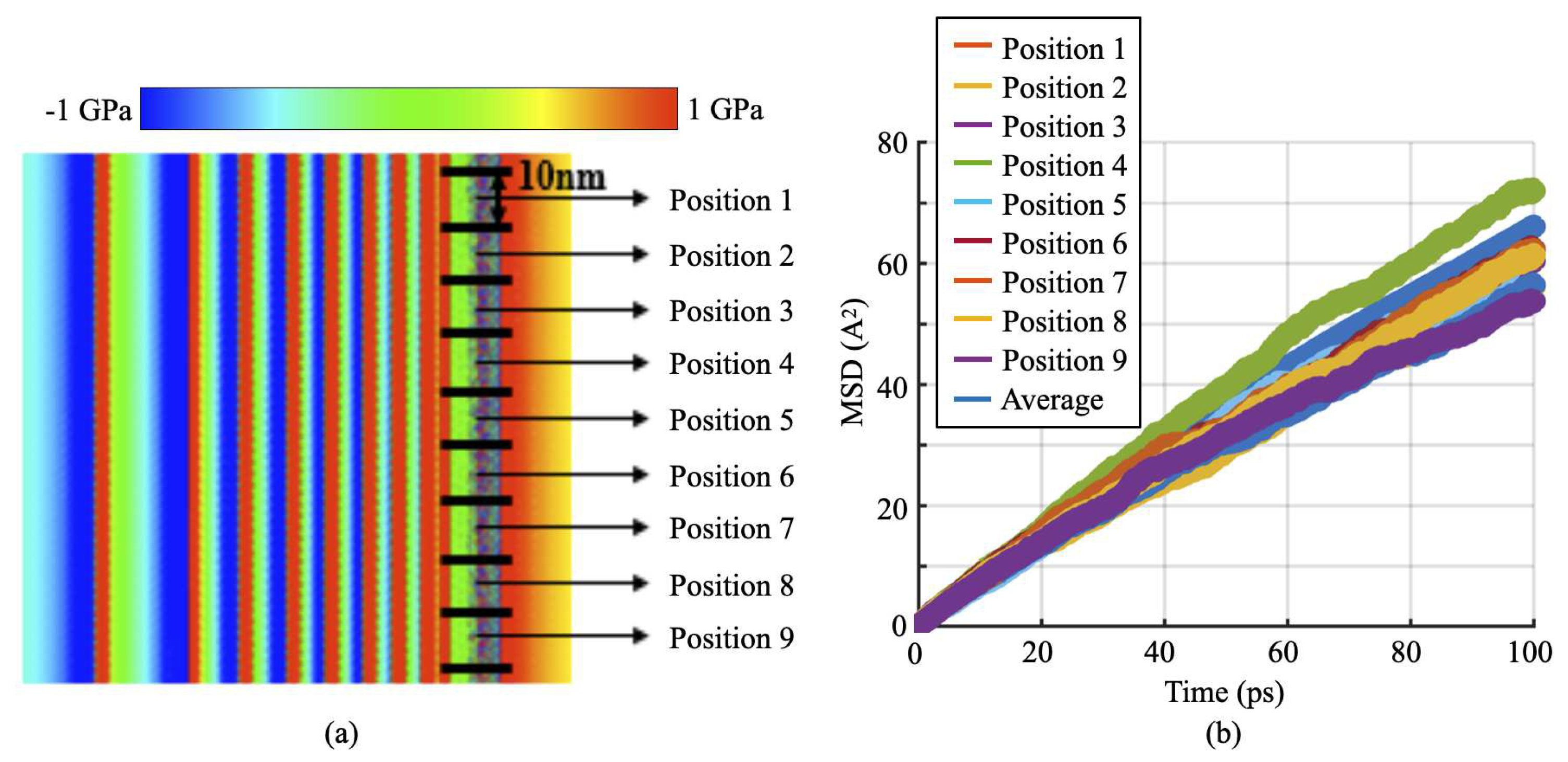
3.3. H Diffusion Heterogeneity and Its Dependence on Local Stresses
4. Summary and Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Ossai, C. Advances in asset management techniques: an overview of corrosion mechanisms and mitigation strategies for oil and gas pipelines. International Scholarly Research Network 2012, p. 570143. [CrossRef]
- Beachem, C. A new model for hydrogen-assisted cracking (hydrogen embrittlement). Met. Trans. 1972, 3, 437–451. [CrossRef]
- Birnbaum, H.; Sofronis, P. Hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity - a mechanism for hydrogen related fracture. Mater. Sci. & Eng. A 1994, 176, 191–202. [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, P.; Robertson, I.; Birnbaum, H. Hydrogen effects on the interaction between dislocations. Acta Materialia, 46. [CrossRef]
- Kacher, J.; Robertson, I. Quasi-four-dimensional analysis of dislocation interactions with grain boundaries in 304 stainless steel. Acta Materialia 2012, 60, 6657–6672. [CrossRef]
- Kacher, J.; Robertson, I. In situ and tomographic analysis of dislocation/grain boundary interactions in alpha-titanium. Philosophical Magazine 2014, 94, 814–829. [CrossRef]
- Guo, Y.; Collins, D.; Tarleton, E.; Hofmann, F.; Tischler, J.; Liu, W.; Xu, R.; Wilkinson, A.; Britton, T. Measurement of stress fields near a grain boundary exploring blocked arrays of dislocations in 3D. Acta Materialia 2015, 96, 229–236. [CrossRef]
- Andani, M.; Lakshmanan, A.; Sundararaghavan, V.; Allison, J.; Misra, A. Estimation of micro-Hall-Petch coefficients for prismatic slip system in Mg-4Al as a function of grain boundary parameters. Acta Materialia 2022, 226, 117613. [CrossRef]
- Lynch, S. Interpreting hydrogen-induced fracture surfaces in terms of deformation processes: A new approach. Scripta Materialia 2011, 65, 851–854. [CrossRef]
- Wang, L.; Yang, Y.; Eisenlohr, P.; Bieler, T.; Crimp, M.; Mason, D. Twin nucleation by slip transfer across grain boundaries in commercial purity titanium. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A 2010, 41, 421. [CrossRef]
- Kacher, J.; Eftink, B.; Cui, B.; Robertson, I. Dislocations interactions with grain boundaries. Current Opinion in Solid State and Materials Science 2014, 18, 227–243.
- Robertson, I.M.; Sofronis, P.; Nagao, A.; Martin, M.; Wang, S.; Gross, D.; Nygren, K. Hydrogen embrittlement understood. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A 2015, 46, 2323–2341. [CrossRef]
- Kimizuka, H.; Ogata, S. Slow diffusion of hydrogen at a screw dislocation core in α-iron. Physical Review B 2011, 84, 024116. [CrossRef]
- Sanchez, J.; Fullea, J.; Andrade, M.; De Andres, P. Ab initio molecular dynamics simulation of hydrogen diffusion in α-iron. Physical Review B 2010, 81, 132102.
- Zhou, X.Y.; Zhu, J.H.; Wu, H.H. Molecular dynamics studies of the grain-size dependent hydrogen diffusion coefficient of nanograined Fe. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2021, 46, 5842–5851. [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Curtin, W. Atomic mechanism and prediction of hydrogen embrittlement in iron. Nature materials 2013, 12, 145–151. [CrossRef]
- Zhou, X.; Ouyang, B.; Curtin, W.; Song, J. Atomistic investigation of the influence of hydrogen on dislocation nucleation during nanoindentation in Ni and Pd. Acta Materialia 2016, 116, 364–369. [CrossRef]
- Yavas, D.; Phan, T.; Xiong, L.; Hebert, K.; Bastawros, A. Mechanical degradation due to vacancies produced by grain boundary corrosion of steel. Acta Materialia 2020, 200, 471–480. [CrossRef]
- Huang, S.; Chen, D.; Song, J.; McDowell, D.; Zhu, T. Hydrogen embrittlement of grain boundaries in nickel: an atomistic study. npj Computational Materials 2017, 3. [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Curtin, W. Mechanisms of hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity: an atomistic study using alpha-Fe as a model system. Acta Materialia 2014, 68, 61–69. [CrossRef]
- Chen, J.; Zhu, Y.; Huang, M.; Zhao, L.; Liang, S.; Li, Z. Study on hydrogen-affected interaction between dislocation and grain boundary by MD simulation. Computational Materials Science 2021, 196, 110562. [CrossRef]
- Jin, Z.; Gumbsch, P.; Albe, K.; Ma, E.; Lu, K.; Gleiter, H.; Hahn, H. Interactions between non-screw lattice dislocations and coherent twin boundaries in face-centered cubic metals. Acta Materialia 2008, 56, 1126–1135. [CrossRef]
- Chassagne, M.; Legros, M.; Rodney, D. Atomic-scale simulation of screw dislocation-coherent twin boundary interaction in Al, Au, Cu, and Ni. Acta Materialia 2011, 59, 1456–1463. [CrossRef]
- Wang, J. Atomistic simulations of dislocation pileup: grain boundaries interactions. Journal of Materials 2015, 67, 1515–1525. [CrossRef]
- Szajewski, B.; Curtin, W. Analysis of spurious image forces in atomistic simulations of dislocations. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. and Eng. 2015, 23, 025008. [CrossRef]
- Sofronis, P.; McMeeking, R. Numerical analysis of hydrogen transport near a blunting crack tip. J. Mech. Phys. Solid 1989, 37, 317–350. [CrossRef]
- Liang, Y.; Sofronis, P. Micromechanics and numerical modeling of the hydrogen-particle-matrix interaction in nickel-base alloys. Model. Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2003, 11, 523–551. [CrossRef]
- Novak, P.; Yuan, R.; Somerday, B.; Sofronis, P.; Ritchie, R. A statistical, physical-based, micro-mechanical model of hydrogen-induced intergranular fracture in steel. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2010, 58, 206–226. [CrossRef]
- Oriani, R. The diffusion and trapping of hydrogen in steels. Acta Metallurgical 1970, 18, 147–157. [CrossRef]
- Sofronis, P.; Liang, Y.; Aravas, N. Hydrogen induced shear localization of the plastic flow in metals and alloys. Eur. J. Mech. A/Solids 2001, 20, 857–872. [CrossRef]
- Barrera, O.; Tarleton, E.; Tang, H.; Cocks, A. Modelling the coupling between hydrogen diffusion and the mechanical behaviour of metals. Computational Materials Science 2016, 122, 219–228. [CrossRef]
- Zirkle, T.; Costello, L.; McDowell, D. Crystal plasticity modeling of hydrogen and hydrogen-related defects in initial yield and plastic flow of single-crystal stainless steel 316L. Metallurgical and Materials Transactions A 2021, 52A, 3961–3977. [CrossRef]
- Song, J.; Curtin, W. Mechanisms of hydrogen-enhanced localized plasticity: an atomistic study using alpha-Fe as a model system. Acta Materialia 2014, 68, 61–69. [CrossRef]
- Asano, S.; Otsuka, R. The lattice hardening due to dissolved hydrogen in iron and steel. Scripta Materialia 1976, 10, 1015–1020. [CrossRef]
- Abraham, D.; Altstetter, C. The effect of hydrogen on the yield and flow stress of an austenitic stainless steel. Met. Trans. A 1995, 26, 2849–2858. [CrossRef]
- Matsui, H.; Kimura, H.; Moriya, S. The effect of hydrogen on the mechanical properties of high purity iron I. Softening and hardening of high purity iron by hydrogen charging during tensile deformation. Mat. Sci. Engng 1979, 40, 207–216. [CrossRef]
- Matsui, H.; Kimura, H.; Kimura, A. The effect of hydrogen on the mechanical properties of high purity iron III. The dependence of softening on specimen size and charging current density. Mat. Sci. Engng 1979, 40, 227–234. [CrossRef]
- Moriya, S.; Matsui, H.; Kimura, H. The effect of hydrogen on the mechanical properties of high purity iron II. Effect of quenched-in hydrogen below room temperature. Mat. Sci. Engng 1979, 40, 217–226. [CrossRef]
- Eastman, J.; Heubaum, N.; Matsumoto, T.; Birnbaum, H. The effect of hydrogen on the solid solution strengthening and softening of nickel. Acta Metall. 1982, 30, 1579–1586. [CrossRef]
- Meyers, S.; Baskes, M.; Birnbaum, H.; Corbett, J.; DeLeo, G.; Estreicher, S.; Haller, E.; Jena, P.; Johnson, N.; Kirchheim, R.; Pearton, S.; Stavola, M. Hydrogen interactions with defects in crystalline solids. Rev. Mod. Phys. 1992, 64, 559–617. [CrossRef]
- Ilin, D.; Saintier, N.; Olive, J.; Abgrall, R.; Aubert, I. Simulation of hydrogen diffusion affected by stress-strain heterogeneity in polycrystalline stainless steel. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2014, 39, 2418–2422. [CrossRef]
- Charles, Y.; Nguyen, H.; Gasperini, M. Comparison of hydrogen transport through pre-deformed synthetic polycrystals and homogeneous samples by finite element analysis. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2017, 42, 20336–20350. [CrossRef]
- Abdolvand, H. Progressive modelling and experimentation of hydrogen diffusion and precipitation in anisotropic polycrystals. International Journal of Plasticity 2019, 116, 39–61. [CrossRef]
- Arnaudov, N.; Kolyshkin, A.; Weihe, S. Micromechanical modeling of fatigue crack initiation in hydrogen atmosphere. Mechanics of Materials 2020, 149, 103557. [CrossRef]
- Hassan, U.; Govind, K.; Hartmaier, A. Micromechanical modelling of coupled crystal plasticity and hydrogen diffusion. Philos. Mag. 2019, 99, 92–115. [CrossRef]
- Hussein, A.; Krom, A.; Dey, P.; Sunnardianto, G.; Moultos, O.; Walters, C. The effect of hydrogen content and yield strength on the distribution of hydrogen in steel: a diffusion coupled micromechanical FEM study. Acta Mater. 2021, 209, 116799. [CrossRef]
- Tondro, A.; Taherijam, M.; Abdolvand, H. Diffusion and redistribution of hydrogen atoms in the vicinity of localized deformation zones. Mechanics of Materials 2023, 177, 104544. [CrossRef]
- Oh, C.; Kim, Y.; Yoon, K. Coupled analysis of hydrogen transport using ABAQUS. Journal of Solid Mechanics and Materials Engineering 2010, 4, 908–917. [CrossRef]
- Barrera, O.; Bombac, D.and Chen, Y.; Daff, T.; Galindo-Nava, E.; Gong, P.; Haley, D.; Horton, R.; Katzarov, I.; Kermode, J.; Liverani, C.; Stopher, M.; Sweeney, F. Understanding and mitigating hydrogen embrittlement of steels: a review of experimental, modelling and design progress from atomistic to continuum. Journal of Materials Science 2016, 53, 6251–6290. [CrossRef]
- Diaz, A.; Alegre, J.; Cuesta, I. Coupled hydrogen diffusion simulation using a heat transfer analogy. International Journal of Mechanical Sciences 2016, 115–116, 360–369. [CrossRef]
- Rimoli, J.; Ortiz, M. A three-dimensional multiscale model of intergranular hydrogen-assisted cracking. Philos. Mag. 2010, 90, 2939–2963. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Q.; Zikry, M. Prediction of diffusion assisted hydrogen embrittlement failure in high strength martensitic steels. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2015, 85, 143–159. [CrossRef]
- Pu, C.; Gao, Y.; Wang, Y.; Sham, T. Diffusion-coupled cohesive interface simulations of stress corrosion intergranular cracking in polycrystalline materials. Acta Materialia 2017, 136, 21–31. [CrossRef]
- Benabou, L. Coupled stress-diffusion modelling of grain boundary seggregation and dynamic embrittlement in a copper alloy. Modelling Simul. Mater. Sci. Eng. 2019, 27, 045007. [CrossRef]
- Valverde-Gonzalez, A.; Martinez-Paneda, E.; Quintanas-Corominas, A.; Reinoso, J.; Paggi, M. Computational modelling of hydrogen assisted fracture in polycrystalline materials. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy 2022, 47, 32235–32251. [CrossRef]
- Chakraborty, A.; Lebensohn, R.; Capolungo, L. Coupled chemo-mechanical modeling of point-defect diffusion in a crystal plasticity fast Fourier transform framework. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 2023, 173, 105190. [CrossRef]
- Kumar, A.; Mahajan, D. Hydrogen distribution in metallic polycrystals with deformation. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2020, 135, 103776. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Tucker, G.; McDowell, D.; Chen, Y. Coarse grained atomistic simulations of dislocations. J. Mech. Phys. Solids 2011, 59, 160–177. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Deng, Q.; Tucker, G.; McDowell, D.; Chen, Y. A concurrent scheme for passing dislocations from atomistic to continuum domains. Acta Materialia 2012, 60, 899–913. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; McDowell, D.; Chen, Y. Nucleation and growth of dislocation loops in Cu, Al, and Si by a concurrent atomistic-continuum method. Scripta Materialia 2012, 67, 633–636. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Ji, R.; Chen, X.; Xu, S.; McDowell, D.; Chen, Y. Coarse-grained elastodynamics of fast moving dislocations. Acta Materialia 2016, 104, 143–155. [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xu, S.; Li, W.; Ji, R.; Phan, T.; Xiong, L. A spatial decomposition parallel algorithm for a concurrent atomistic-continuum simulator and its preliminary applications. Computational Materials Science 2018, 144, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Payne, T.; Chen, H.; Liu, Y.; Xiong, L.; Chen, Y.; McDowell, D. PyCAC: The concurrent atomistic-continuum simulation environment. Journal of Materials Research 2018, 33, 857–871. [CrossRef]
- Xu, S.; Xiong, L.; Chen, Y.; McDowell, D. Validation of the concurrent atomistic-continuum method on screw dislocation/stacking fault interactions. Crystals 2017, 7, 120. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Chen, Y. Multiscale modeling and simulation of single-crystal MgO through an atomistic field theory. International Journal of Solids and Structures 2009, 46, 1448–1455. [CrossRef]
- Chen, Y. Reformulation of microscopic balance equations for multiscale materials modeling. Journal of Chemical Physics 2009, 130, 134706. [CrossRef]
- Ji, R.; Phan, T.; Chen, Y.; McDowell, D.; Xiong, L. A finite-temperature coarse-grained atomistic approach for understanding the kink-controlled dynamics of micrometer-long dislocations in high-Peierls-barrier materials. MRS Communications 2022, pp. 1–9. [CrossRef]
- Xiong, L.; Chen, Y.; Lee, J. Modeling and simulation of boron-doped nanocrystalline silicon carbide thin film by a field theory. Journal of Nanoscience and Nanotechnology 2009, 9, 1034. [CrossRef]
- Su, Y.; Phan, T.; Xiong, L.; Kacher, J. Multiscale computational and experimental analysis of the slip-GB reactions: in-situ high-resolution electron backscattered diffraction and concurrent atomistic-continuum simulations. Scripta Materialia 2023, p. under review. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y.; Ji, R.; Phan, T.; Capolungo, L.; Levitas, V.; Xiong, L. Effect of a micro-scale dislocation pileup on the atomic-scale multi-variant phase transformation and twinning. arXiv 2022, p. 2208.03592.
- Peng, Y.; Ji, R.; Phan, T.; Gao, W.; Levitas, V.; Xiong, L. An atomistic-to-microscale computational analysis of the dislocation pileup-induced local stresses near an interface in plastically deformed two-phase materials. Acta Materialia 2022, 226, 117663. [CrossRef]
- Eshelby, J.; Frank, F.; Nabarro, F. XLI. The equilibrium of linear arrays of dislocations. The London, Edinburgh, and Dublin Philosophical Magazine and Journal of Science 1951, 42, 351–364. [CrossRef]
- Eshelby, J.D. The determination of the elastic field of an ellipsoidal inclusion, and related problems. Proceedings of the royal society of London. Series A. Mathematical and physical sciences 1957, 241, 376–396. [CrossRef]
- Eshelby, J.D. The elastic field outside an ellipsoidal inclusion. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. Series A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences 1959, 252, 561–569. [CrossRef]
- Vasoya, M.; Kondori, B.; Benzerga, A.A.; Needleman, A. Energy dissipation rate and kinetic relations for Eshelby transformations. Journal of the Mechanics and Physics of Solids 2020, 136, 103699. [CrossRef]
- Phan, T.; Peng, Y.; Gao, W.; Xiong, L. Coarse-grained atomistic characterization the properties of micrometer-long dislocations charged with hydrogen. Scripta Materialia 2023, p. under review.
- Chen, Y.; Diaz, A.; Xiong, L.; McDowell, D.; Chen, Y. Passing waves from atomistic to continuum. Journal of Computational Physics 2018, 354, 393–402. [CrossRef]
- Meng, F.; Du, J.P.; Shinzato, S.; Mori, H.; Yu, P.; Matsubara, K.; Ishikawa, N.; Ogata, S. General-purpose neural network interatomic potential for the alpha-iron and hydrogen binary system: Toward atomic-scale understanding of hydrogen embrittlement. Physical Review Materials 2021, 5, 113606. [CrossRef]
- Peng, Y. An atomistic-to-mesocale prediction of the complex reaction between the plastic flow and the interfaces in heterogeneous materials. Iowa State University Ph.D. Dissertation 2023.
| Number of Dislocations | 0 | 5 | 10 | 15 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Stress Intensity Factor K (GPa/m) | 0 | 0.82 | 1.98 | 4.12 |
| H Diffusion Coefficient | 0.146 | 0.110 | 0.104 | 0.102 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





