1. Introduction
There is a recent increased interest in small modular reactors (SMRs) as a result of their lower initial capital investment compared to larger nuclear power plants (NPPs) and the increase in high renewable energy penetrated grids. The SMRs offer a small capacity, modularity and load following capabilities [
1]. Like most modern industrial systems, motors, particularly induction motors (IMs), dominate an NPP’s load capacities [
2]. Generally for pressurized water reactors, the reactor coolant pump (RCP) motors have the largest capacities. For enhanced safety, a good number of new SMR designs, such as KAERI’s System-integrated Modular Advanced ReacTor (SMART), use passive safety systems[
3], including canned motors (CM) in their RCPs [
4,
5].
CMs have a larger air gap between motor stator and rotor compared to similar sized general motors. Even though the air gap allows more cooling as a result of increased coolant flow, it has the disadvantage of reducing the electromagnetic interlinkage between the stator and rotor fields resulting in less torque [
6]. With SMR motor sizes designed to be as small as possible, the starting torque may be insufficiently small necessitating the use of variable frequency drives (VFDs) depending on factors such as allowable voltage drops, inrush current limitations, required acceleration times, thermal limits, costs and compliance with standards [
7].
This paper compares torque characteristics for general IMs with those of CMs. Motor starting studies are then done for the purpose of comparing IM RCPs with CMs RCPs and also comparing VFD driven CM RCPs with CM RCPs started across the line. To achieve the above, an SMR auxiliary power system (APS) was modelled in electrical transient analyzer program (ETAP) pegged on the SMART SMR with RCP canned motors.
2. Induction Motors and Motor Starting
2.1. Induction Motors and Canned Motors
Induction motors (IMs) work by electromagnetic induction. The interaction between the three-phase AC-supply-connected stator windings’ and the rotor windings’ electromagnetic fields produces slip according to Faraday’s Law and the Lorentz force on a conductor. The most common type, squirrel cage induction motor (SCIM), has a rotor made of conducting bars short-circuited at the ends.
The canned motor (CM) was invented in 1913 and became appreciated in the 1950s [
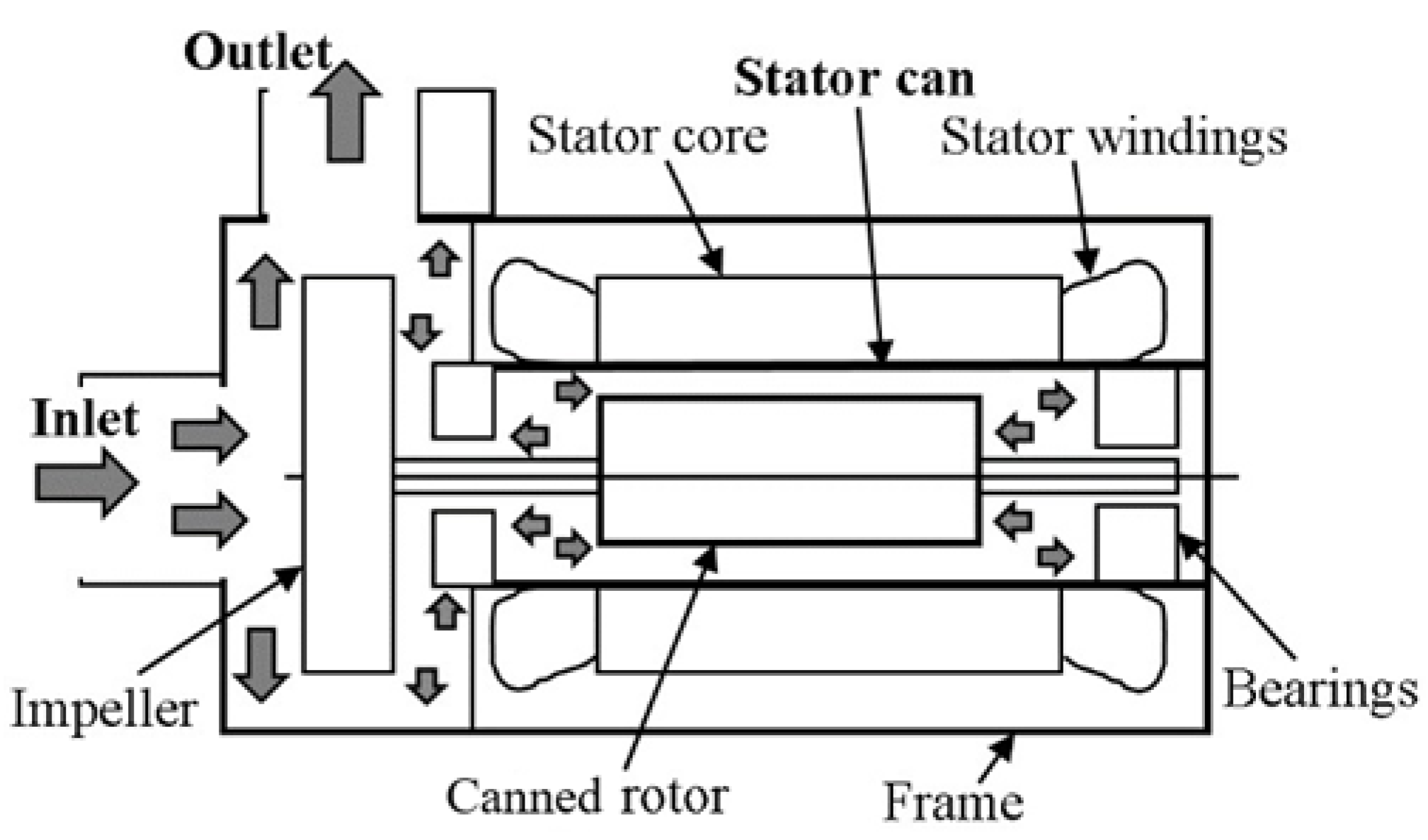
8] when the circumstances in the chemical and nuclear industry favored seal-less, leak-free operation of centrifugal pumps. The CM combines and hermetically seals a centrifugal pump with a SCIM using two cans placed inside the air gap: on the stator and rotor side respectively, as shown in the
Figure 1 [
9]. This leakage prevention property is immensely useful in SMRs since the CM drives RCPs that circulate radioactive reactor coolant. However, due to manufacturing limitations, the cans are made of a bulk metal material instead of laminations and this introduces eddy current losses that in turn interact with the air gap’s magnetic field, an effect called magnetic shielding [
10].
2.2. Motor Torque Characteristics or
Connecting a three-phase supply to the SCIM stator produces a rotating magnetic field (RMF) that cuts across the short-circuited rotor cage bars inducing a voltage that causes a huge current flow. The current interacts with the stator’s field to produce a torque which drags the rotor along the path of the RMF.
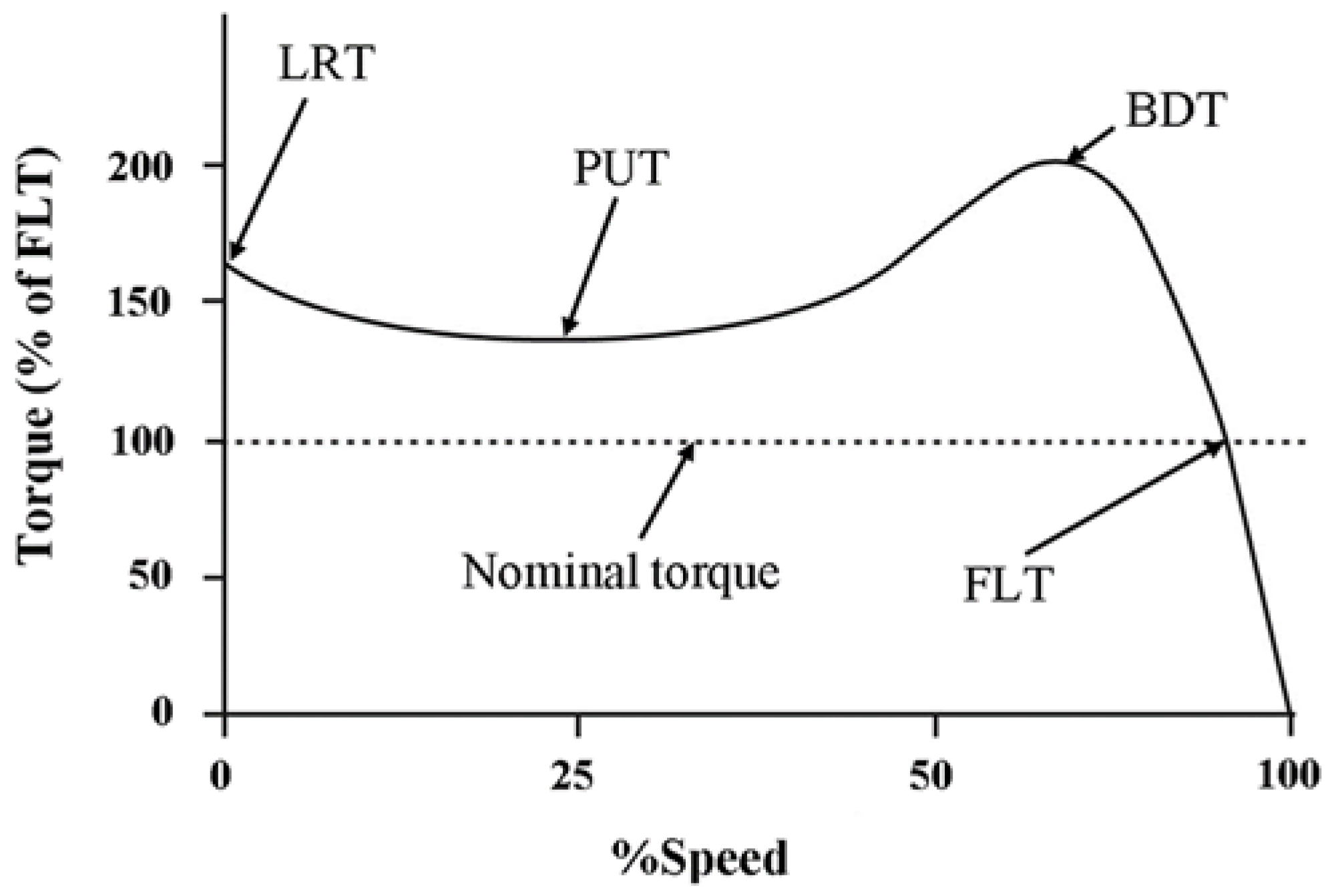
Figure 2 shows a typical IM torque speed curve [
7]. Notably, the torque developed at zero speed is the starting or locked rotor torque (LRT) while the one required to run a full load at rated speed is the full load torque (FLT). In between, the maximum and minimum torques are pull-up (PUT) and breakdown torques (BDT) respectively.
The RCP motor’s load torque is typical for a centrifugal pump i.e. it follows the square law. The accelerating torque, i.e. difference between the motor torque and load torque curves, accelerates the motor to its operating speed and within its thermal limits [
7]. Insufficient acceleration torque may lead to motor overheating and causing motor stator winding damage. The motor may also stall and draw large currents that may damage other motors or loads connected to the same or nearby buses.
The CM’s electromagnetic design affects eddy current losses and heavily depends on air gap and can thickness. There are three factors considered in the size determination of the air gap between the cans [
11]. Firstly, the clearance needs to be as small as possible such that the starting torque and the efficiency of electromagnetic conversion satisfy the pump requirements. The other two factors involve having the clearance as wide as possible to guarantee the motor cooling performance and also large enough to maintain rotor system stability.
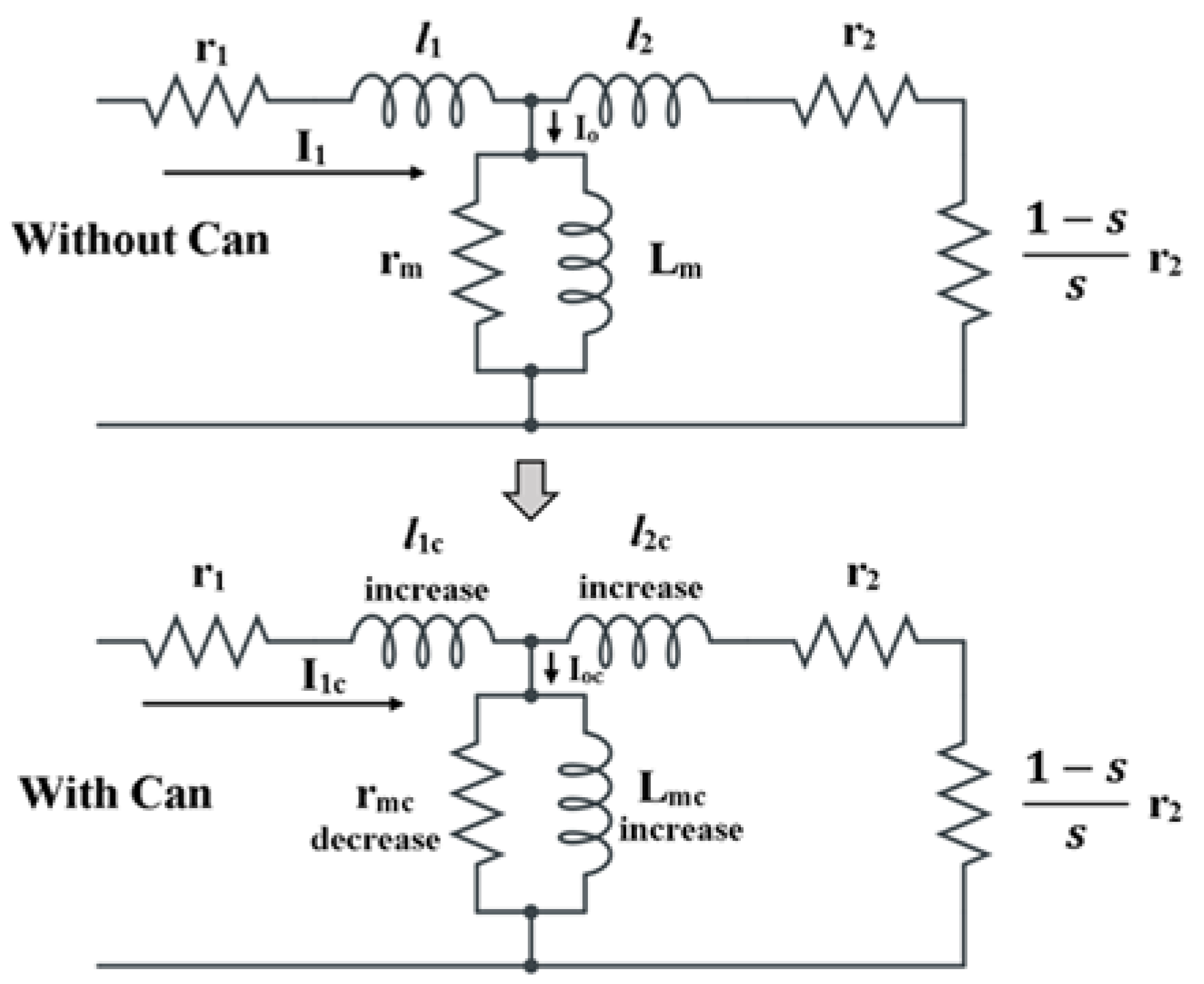
According to studies [
12] and as shown in
Figure 3, addition of cans to an IM decreases the magnetizing current (I
oc < I
o) resulting from increased magnetizing inductance (L
mc > L
m) and decreased magnetizing resistance (r
mc < r
m). Conversely, increased slot leakage flux causes a corresponding increased stator (l
1c > l
1) and rotor (l
2c > l
2) leakage inductance. Overall effect is a lower power factor (PF), efficiency and starting torque [
6,
10]. Stator (r
1) and rotor (r
2) resistances are mainly unchanged.
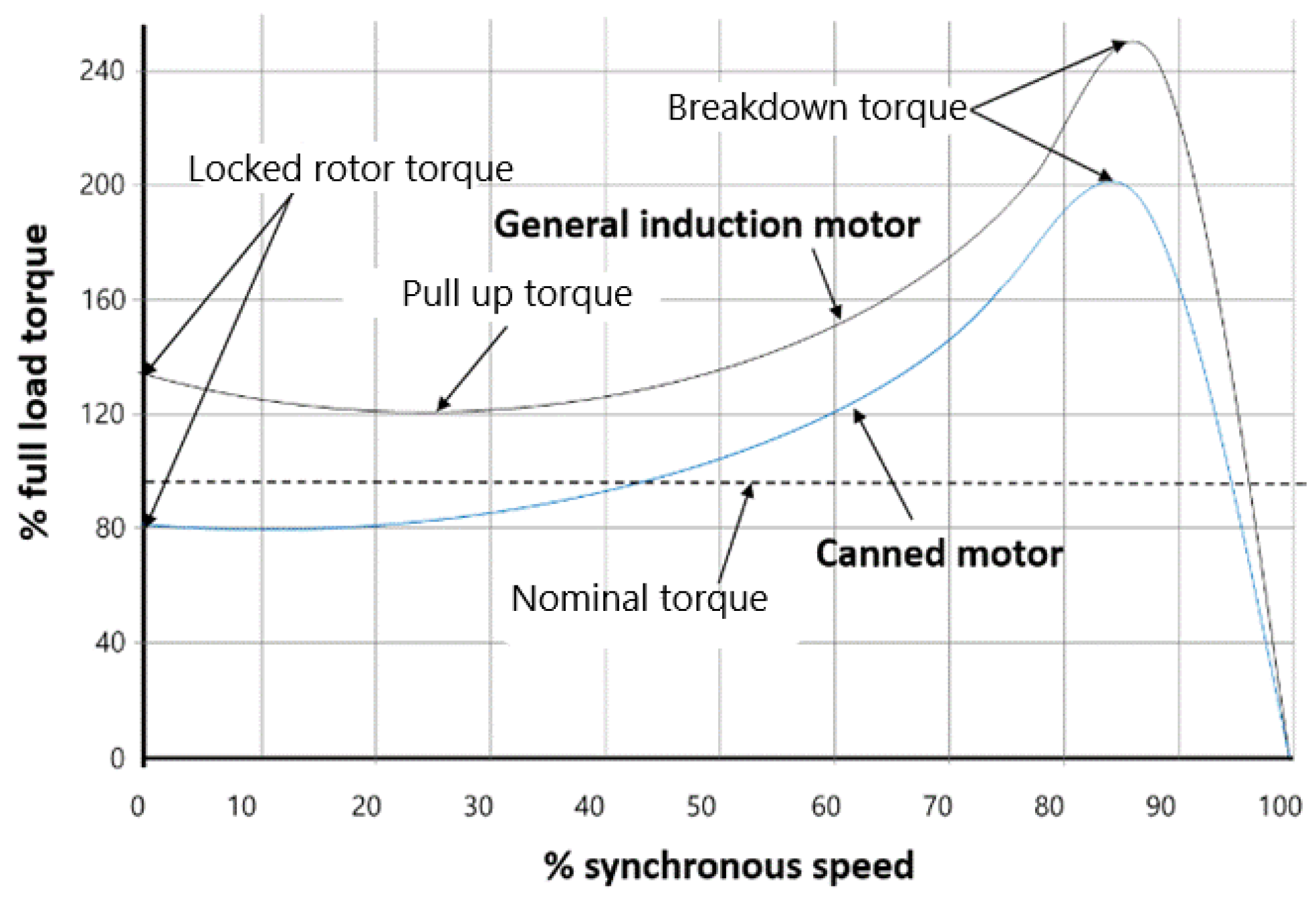
The usual efficiency of a CM is 50% to 70%, PF is 80% and BDT greater than 200% of FLT. It is shown by studies [
13] that these parameters are higher for larger capacity CMs. A 1.9kW CM is, for instance, shown to have a locked rotor torque that’s 92.2% that of same sized IM [
14].
Figure 4 shows typical NEMA design letter A or B torque-speed curve for an IM and the relative curve for a similar sized CM i.e. CM has lower LRT and BDT.
2.3. Motor Starting and Variable Frequency Drives
Strictly speaking, three-phase IMs are self-starting. However, a starter may be required in order to reduce the inrush current to the machine that can be as high as five to seven times the full load current (FLC), and provide overload protection. The starter method depends on various factors such as allowable voltage drops, inrush current limitations, torque, acceleration time, cost and compliance with standards such as IEEE 3002.7. The major commercially-used starting methods are full voltage-fixed frequency (direct online or across the line), reduced voltage-fixed frequency (wye-delta, autotransformer and soft starter), and variable frequency drive (VFD) starts.
Across-the-line starting (direct online) is used by default. If there is a need to limit inrush current or starting torque, reduced voltage starting is then used.
On the other hand, variable frequency drives (VFDs) convert a fixed voltage and frequency input into a variable voltage and frequency output using power electronics. The most common VFD, PWM-type, has improved stable voltage and frequency outputs, and eliminates cogging in motors [
15]. A constant voltage-to-frequency (volts-per-hertz) ratio leads to a fixed flux. If the volts-per-hertz ratio is based on the rated voltage and rated frequency, and kept constant by use of a VFD, then it follows that rated flux and rated motor torque are maintained without the risk of magnetic core saturation. The motor thus achieves rated torque at rated speed with constant rated motor flux[
16]. This speed and torque control is a big advantage over the other reduced voltage-fixed frequency methods.
The main issue with the canned motor RCP is low-torque development as a result of the smaller size of the motor (relative to larger NPPs) and the motor characteristics of a canned motor. This is particularly important when starting the motor because the voltage drop across the nearest buses (as a result of the inrush currents) is highest. If the motor takes too long to start due to a low developed motor torque, the motor insulation may be damaged for exceeding its thermal limits and the suppressed and sustained low voltage may stall other running motors in the same system. Even though full torque can be provided by both across the line and VFD starts VFD start has the added benefit of limiting the starting current the most which is crucial given that the RCP motor is the largest load in the SMR and will thus cause the largest voltage drops. The other benefit of using VFD with the RCP is that it also eliminates the need for an anti-reverse rotation system [
17]. The other methods (reduced voltage-fixed frequency starts) are also able to limit inrush currents but at the expense of the important torque development in the motor. This paper thus proposes the use of a VFD to start CMs and will therefore focus on direct online (DOL) and VFD starts.
However, introducing VFD start as a motor driving method also introduces challenges [
15,
18,
19]. Electromagnetic emissions can be produced from the VFD’s output terminal and cause interference. This can be mitigated by proper specification, using shielded power cables to connect VFD or using mitigation devices such as electromagnetic interference (EMI) filters and common-mode chokes. Another issue is that of harmonics produced by the power electronics that comprise the VFD and that have a negative impact on PF and other electronic equipment. Using adequate filtering to smoothen the input current can mitigate this and reduce the overall current harmonic distortion. Additionally, PWM pulse build-up can break down motor insulation and stress the windings and to mitigate the insulation damage, motor terminal voltage can be lowered by using line reactors, resistor-capacitor snubbers, and resistor-inductor-capacitor (RLC) low-pass filters. The other challenges associated with the use of VFDs are acoustic noises produced by VFD resonating with the system at certain speeds and that shortens the life of the VFD and connected motor, high initial investment costs due to the VFD complexity, and the need for reliability studies as a result of the increased failure chance of solid state components of the VFD.
2.4. Motor Starting Simulation using ETAP
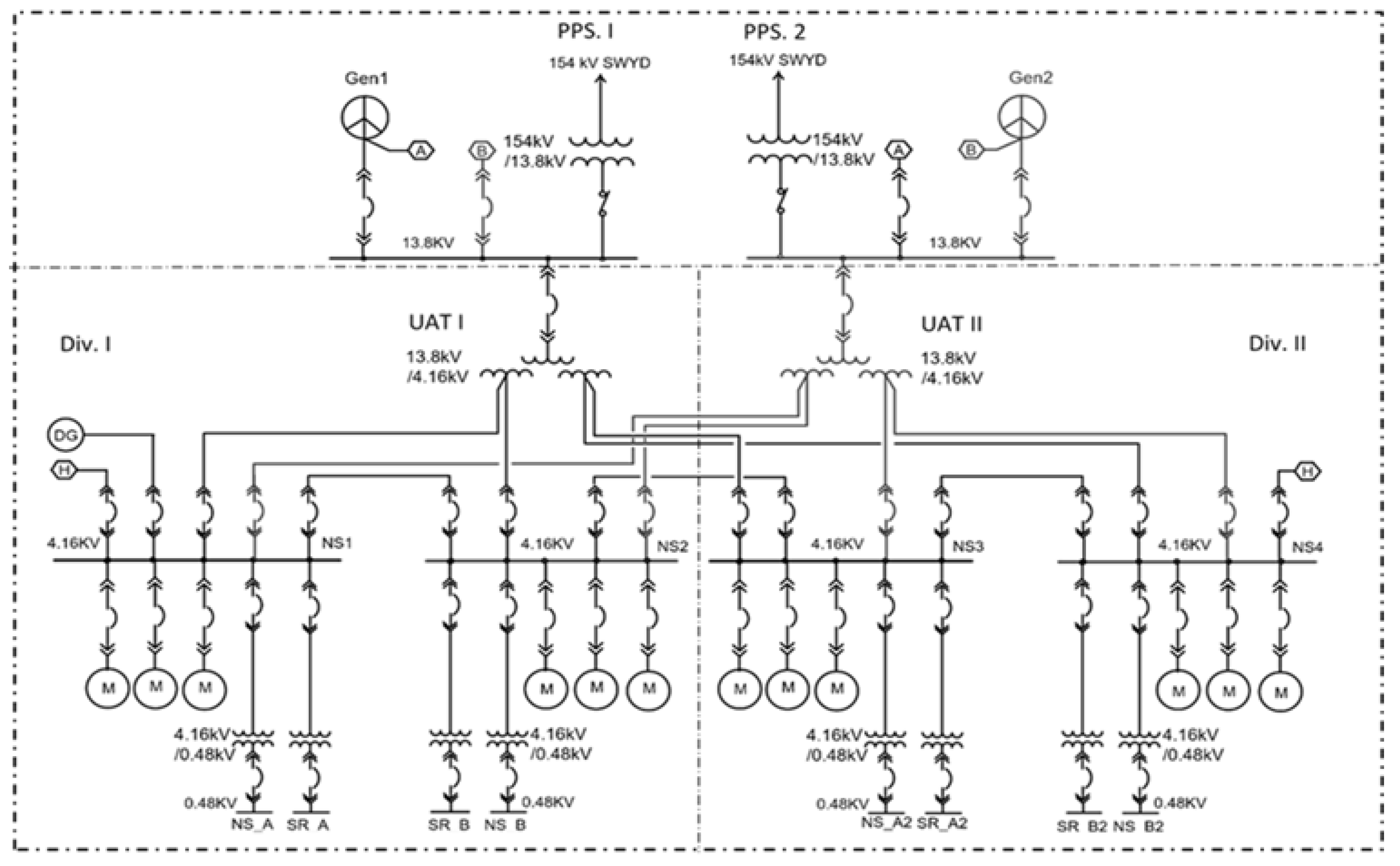
In order to perform this study, the SMR’s auxiliary power system (APS) is designed considering physical separation, redundancy, independence, and diversity criteria. The chosen configuration is shown in the conceptual diagram in
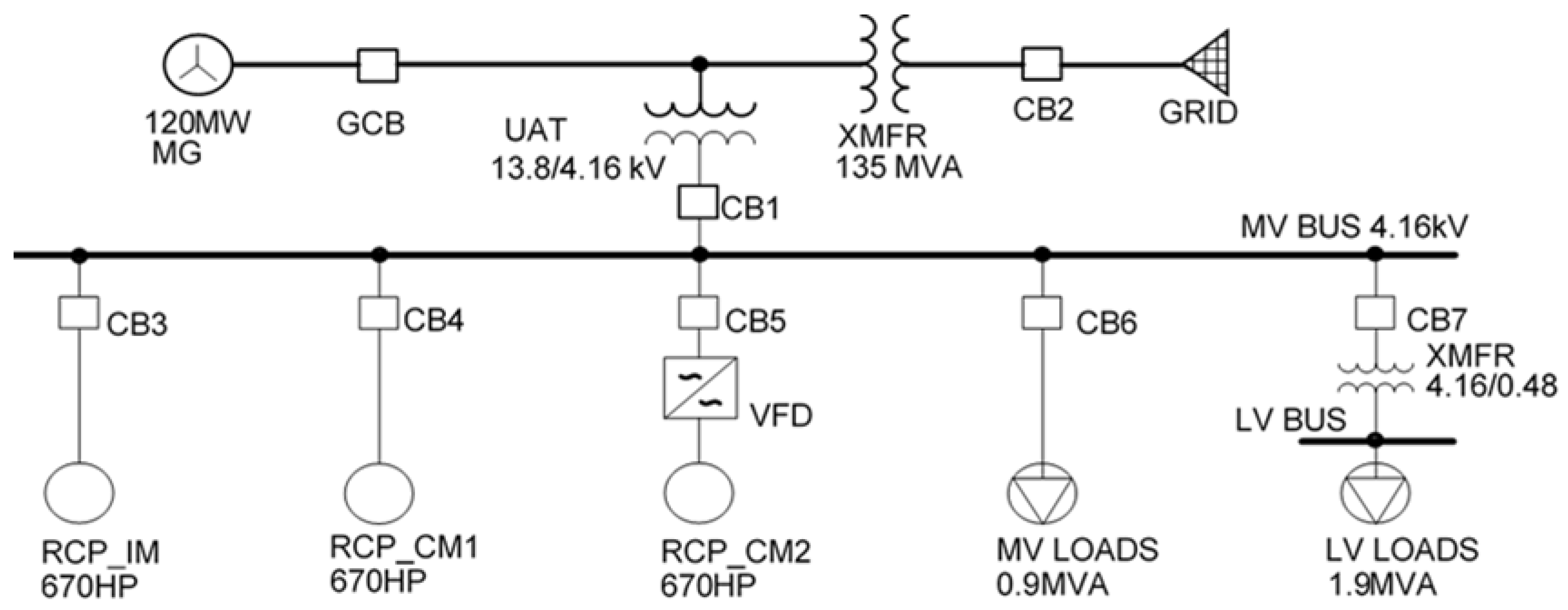
Figure 5. Additionally, and in order to compare the motor starting performances of general induction motor RCP with canned motor RCP, the SMR’s APS design is then summarized and modelled on ETAP as per
Figure 6. This is done because the focus of the study involves studying motor starting, and the determination of motor starting times and motor starting torques. One 4.16kV bus is conceived as enough to show voltage drops across the system while non-RCP loads are lumped. ‘Single Cage Motor IM with deep bars’ circuit model in ETAP library (
Table 1) is used to model the IM and CM RCPs by modifying equivalent circuit parameters (stator, rotor and core inductances). From literature reviews, the ratio between CM LRT and that of similar-sized IMs is used as a guide [
12].
3. Results and Discussion
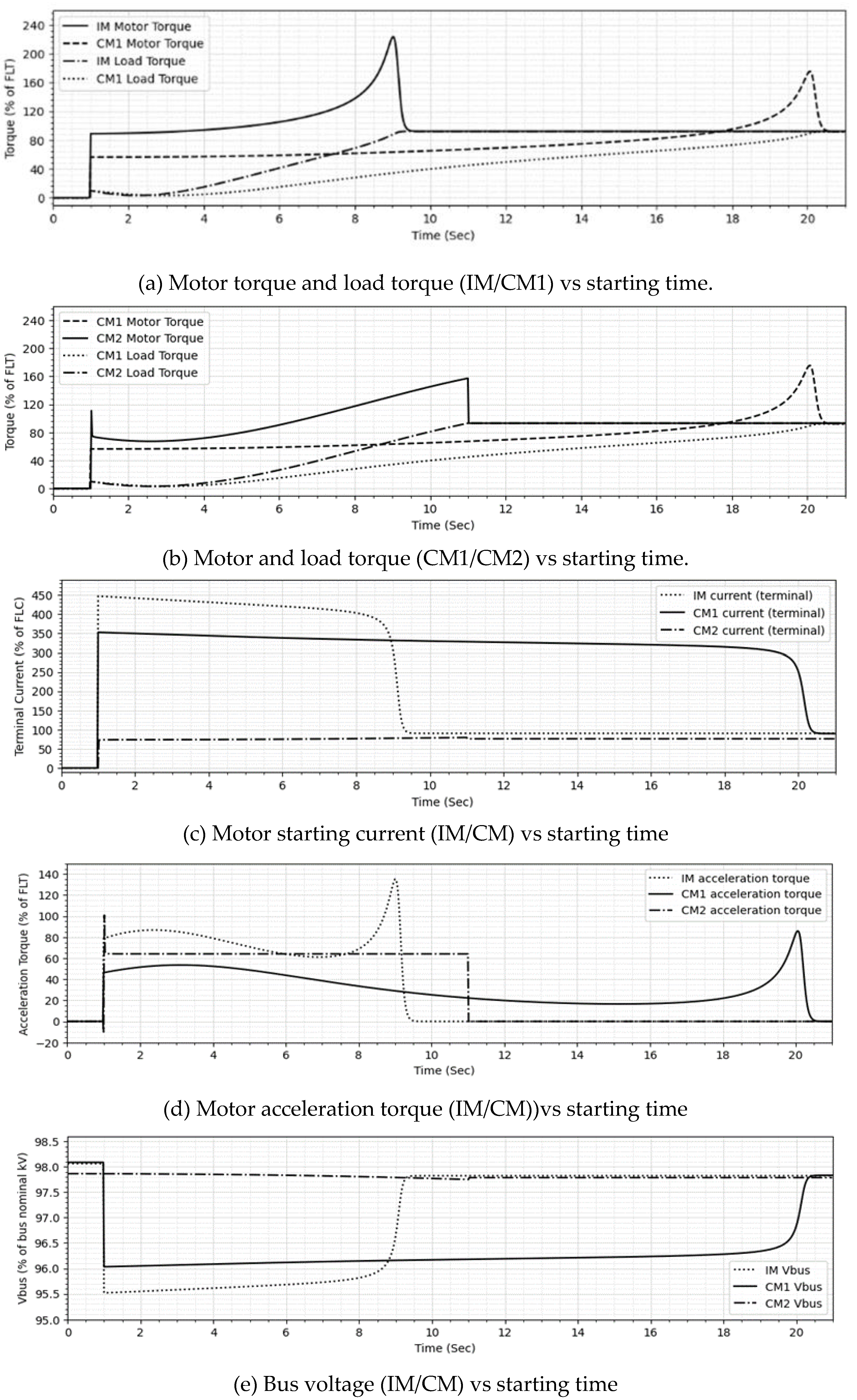
The study captures the comparison of direct online (DOL) starting one IM (IM), DOL starting one CM (CM1), and variable frequency drive (VFD) starting a second CM (CM2). The total simulation time is twenty one seconds. The results of the motor starting study are shown in
Figure 7a–e, discussed thereafter, and summarized in
Table 2.
The DOL started IM (IM) achieves full load torque and rated speed faster 8.7 seconds after starting compared to DOL started CM (CM1) that takes 19.7 seconds. VFD started CM (CM2), however, achieves full load torque and rated speed in 10 seconds compared to 19.7 seconds of direct online started CM1 (CM1).
Rated torque is achieved faster by the direct online started IM (IM) compared to the direct online started CM (CM1). This is because even though the load torques are similar, the IM has a higher starting torque resulting in a higher accelerating torque and shorter accelerating time. The reduced starting torque of CM1 is mainly caused by eddy current losses in the canned motors. Additionally, even though both direct online started CM (CM1) and VFD started CM (CM2) should have the same starting torque, employing the VFD starter results in a higher developed torque (almost full load torque) at the start for the CM2. This is because the VFD can utilize a V/Hz control scheme to achieve constant flux at reduced motor voltages all though to rated voltage. Consequently, for the same load torque, the CM2 has a higher resultant acceleration torque compared CM1, thus achieving rated torque faster. All these are illustrated in
Figure 7a–c.
The bus percentage voltage drops are similar for the direct online started IM (IM) and CM (CM1) but the IM has a slightly deeper drop (i.e. the bus voltage drops from 98.1% bus nominal kV to 95.5%, a difference of 2.6%) compared to the CM1′s (drops from 98.1% bus nominal kV to 96.0% bus nominal kV, a difference of 2.1%). Also as shown in
Figure 7d, there is a significant difference in the voltage drops for direct online started CM (CM1) and VFD started CM (CM2). CM2 has no discernible voltage drop compared CM1 i.e. CM2 bus voltage drops from 97.9% bus nominal kV to 97.7% bus nominal kV, a difference of only 0.2%. The difference in voltage drops is attributed to IM’s higher line current (inrush current of up to 446% of full load amps) compared to CM1 (352.7% of full load current) and CM2 (a maximum of 79.4% full load current) while the VFD significantly reduces the voltage drop with barely any inrush current to the motor. The VFD achieves this due to the reduced voltage applied to the motor at the start. However, even though CM1 has a lower maximum current compared to IM, the duration of its inrush current is longer and care may need to be taken to ensure the motor does not exceed its thermal limits. The inrush currents are shown in
Figure 7c.
4. Conclusions
The major motor in the SMR is the RCP. However a challenge is introduced: the smaller size of the motors due to the lower loads of the SMR means that the motors develop lower torques. Additionally, in a bid to enhance safety of the SMR, SMR RCPs use canned motors (CMs) to prevent leakage of radioactive coolant. The low torque as a result of these challenges increases the risk of the RCP motor not starting or even stalling. Furthermore, SMR’s are expected to do load following to cope with variable energy sources which means that the RCPs may be required to start and stop more frequently compared to base load nuclear power plants. Therefore, selection of the motor starting method is important. This study proposes using VFD starting as a suitable motor driving method to overcome the low torque issue. The solution also solves other challenges such as starting the motors smoothly to reduce mechanical shock and increase their lifetime. However, surge protection measures must be taken as VFD may cause surge voltage and damage to the motor.
Canned motors, compared to similar sized induction motors (IM), were shown through ETAP simulation to have a reduced inrush current compared to similar sized IMs. Further simulation showed that VFD start overcomes the reduced starting torque issue of the CMs, thereby improving the starting torque from around 46.3% of full load torque to 100.8% of full load torque. In addition to this, the starting times were reduced due to the higher motor torque developed that is sufficient to guarantee starting. The paper therefore concludes that VFD starting of SMART SMR’s RCP canned motors is a viable solution to the low starting torque problem associated with CMs.
Further study is required to determine if additional VFD associated costs can be justified in the long run, and determine if the introduced electromagnetic emissions and harmonics would be within the allowable limits.
Author Contributions
Timothy Kanyolo did simulation and wrote this paper as the first author. Harold Oyando designed auxiliary power system of SMR as the second author. Choong-koo Chang guided the design and analysis as a corresponding author. All authors have read and agreed to the published version of the manuscript.
Acknowledgments
This research was supported by 2023 Research Fund of the KEPCO International Nuclear Graduate School (KINGS), Ulsan, Republic of Korea.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- C. Chang and H. C. Oyando, “Review of the Requirements for Load Following of Small Modular Reactors,” Energies, vol. 15, no. 17, p. 6327, Aug. 2022. [CrossRef]
- M. Villaran and M. Subudhi, “Aging Assessment of Large Electric Motors in Nuclear Power Plants,” New York, Mar. 1996. [CrossRef]
- K. H. Bae et al., “Enhanced safety characteristics of SMART100 adopting passive safety systems,” Nucl. Eng. Des., vol. 379. 2021. [CrossRef]
- M. D. Carelli and D. T. Ingersoll, Handbook of Small Modular Nuclear Reactors: Second Edition. 2021.
- IAEA, “ADVANCES IN SMALL MODULAR REACTOR TECHNOLOGY DEVELOPMENTS - A Supplement to: IAEA Advanced Reactors Information System (ARIS).” IAEA, 2020.
- Xu Hu, Yong Li, and Li Luo, “The Influence of Air Gap Thickness between the Stator and Rotor on Nuclear Main Pump,” Aug. 2017. [CrossRef]
- IEEE, “3002.7-2018 - IEEE Recommended Practice for Conducting Motor-Starting Studies and Analysis of Industrial and Commercial Power Systems.” IEEE, Apr. 26, 2019.
- R. Neumaier, Hermetic Pumps: The Latest Innovations and Industrial Applications of Sealless Pumps, 1st ed. Gulf Professional Publishing, 1997.
- Li Weili, Zhang Xiaochen, Chen Wenbiao, and Cao Junci, “Numerical Analysis of Thermal Behavior of Canned Motor,” IEEE. 2007. [CrossRef]
- K. Hu, H. Zhuang, and Q. Yu, “Electromagnetic Shielding Effect of a Canned Permanent Magnet Motor,” Energies, vol. 13, no. 18, p. 4666, Sep. 2020. [CrossRef]
- R. Xu, Y. Song, X. Gu, B. Lin, and D. Wang, “Research on the clearance flow between stator and rotor cans in canned motor RCP,” Ann. Nucl. Energy, vol. 164, p. 108583, Dec. 2021. [CrossRef]
- Katsumi Yamazaki, “Modeling and Analysis of Canned Motors for Hermetic Compressors Using Combination of 2D and 3D Finite Element Method,” in Proc International Electric Machines and Drives Conference, ICEM, 1999, p. 337. [CrossRef]
- Yushi Wang, Zhenqiang Yao, Hong Shen, Yabo Xue, and De Cheng, “Modeling and Analysis of Canned Motor of the Nuclear Reactor Coolant Pump,” Appl. Mech. Mater. Vol 328, vol. 328, pp. 955–959, Jun. 2013. [CrossRef]
- A. Yuejun, Z. Zhiheng, L. Ming, W. Guangyu, K. Xiangling, and L. Zaihang, “Influence of asymmetrical stator axes on the electromagnetic field and driving characteristics of canned induction motor,” IET Electr. Power Appl., vol. 13, no. 8, pp. 1229–1239, Aug. 2019. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- T. H. Blair, “Variable Frequency Drive Systems,” in Energy Production Systems Engineering, 2016. [CrossRef]
- A. H. Vandermeulen, T. J. Natali, T. J. Dionise, G. Paradiso, and K. Ameele, “Exploring New and Conventional Starting Methods of Large Medium-Voltage Induction Motors on Limited kVA Sources,” in IEEE Transactions on Industry Applications, 2019, vol. 55, no. 5. [CrossRef]
- J. Park, R. M.Field, and T.-R. Kim, “Study on the VFD (Variable Frequency Drive) for RCP (Reactor Coolant Pump) Motors of APR1400.,” Oct. 2014.
- W. Moncrief, “Guide to the Industrial Application of Motors and Variable-Speed Drives. 1005983.,” Palo Alto, CA, Oct. 2001.
- S. Khan, Industrial power systems. 2007. [CrossRef]
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).