Submitted:
07 July 2023
Posted:
10 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Patients
2.2. Flow cytometry
2.3. Flow cytometry reagents
2.4. Definition of lymphocyte subpopulations
2.5. Statistical analysis
3. Results
3.1. Characteristics of SLE patients
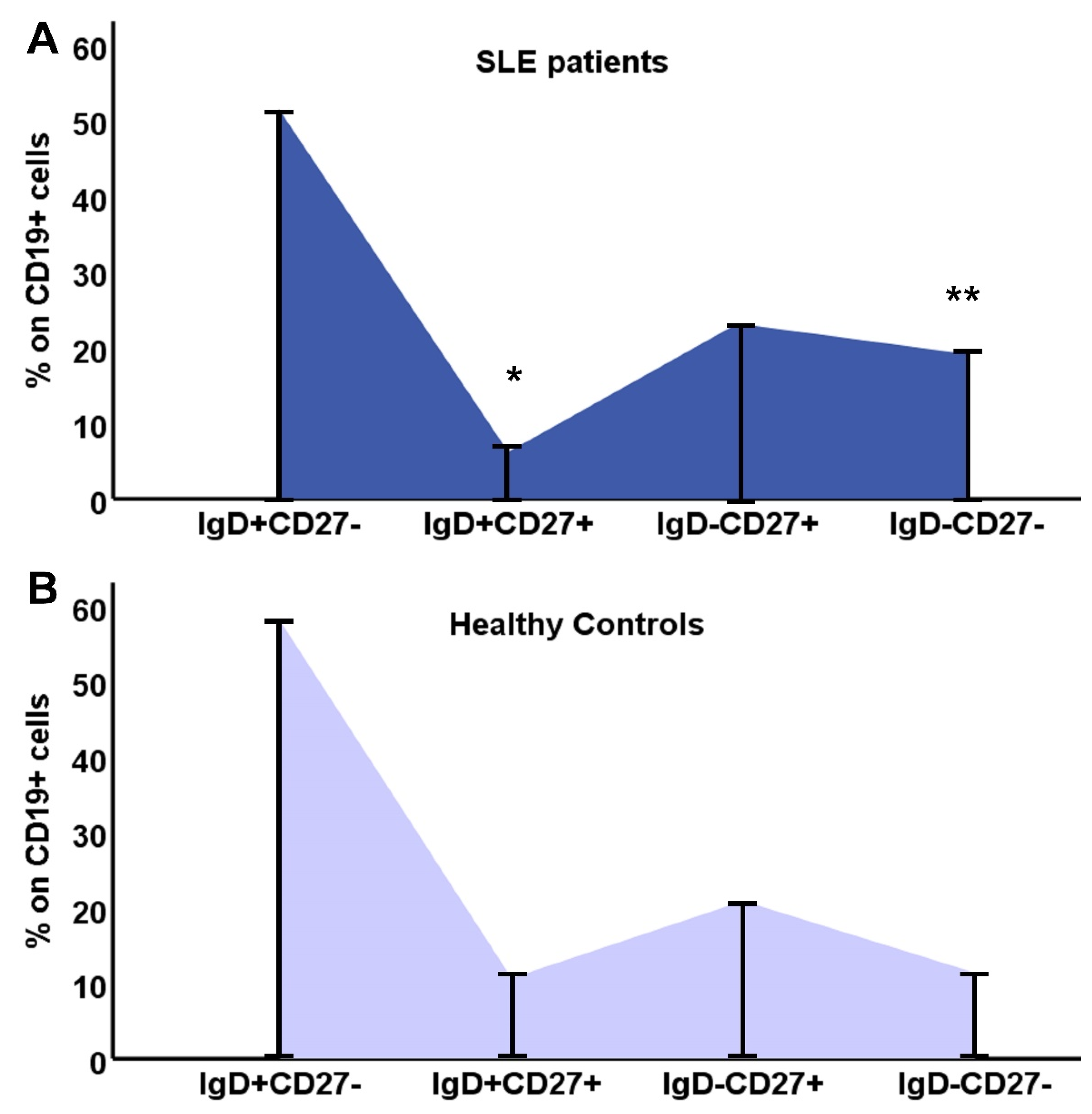
3.2. Phenotypic analysis of B lymphocytes in patients with SLE and in HC
3.3. Phenotypic analysis of T lymphocytes in SLE patients and HC
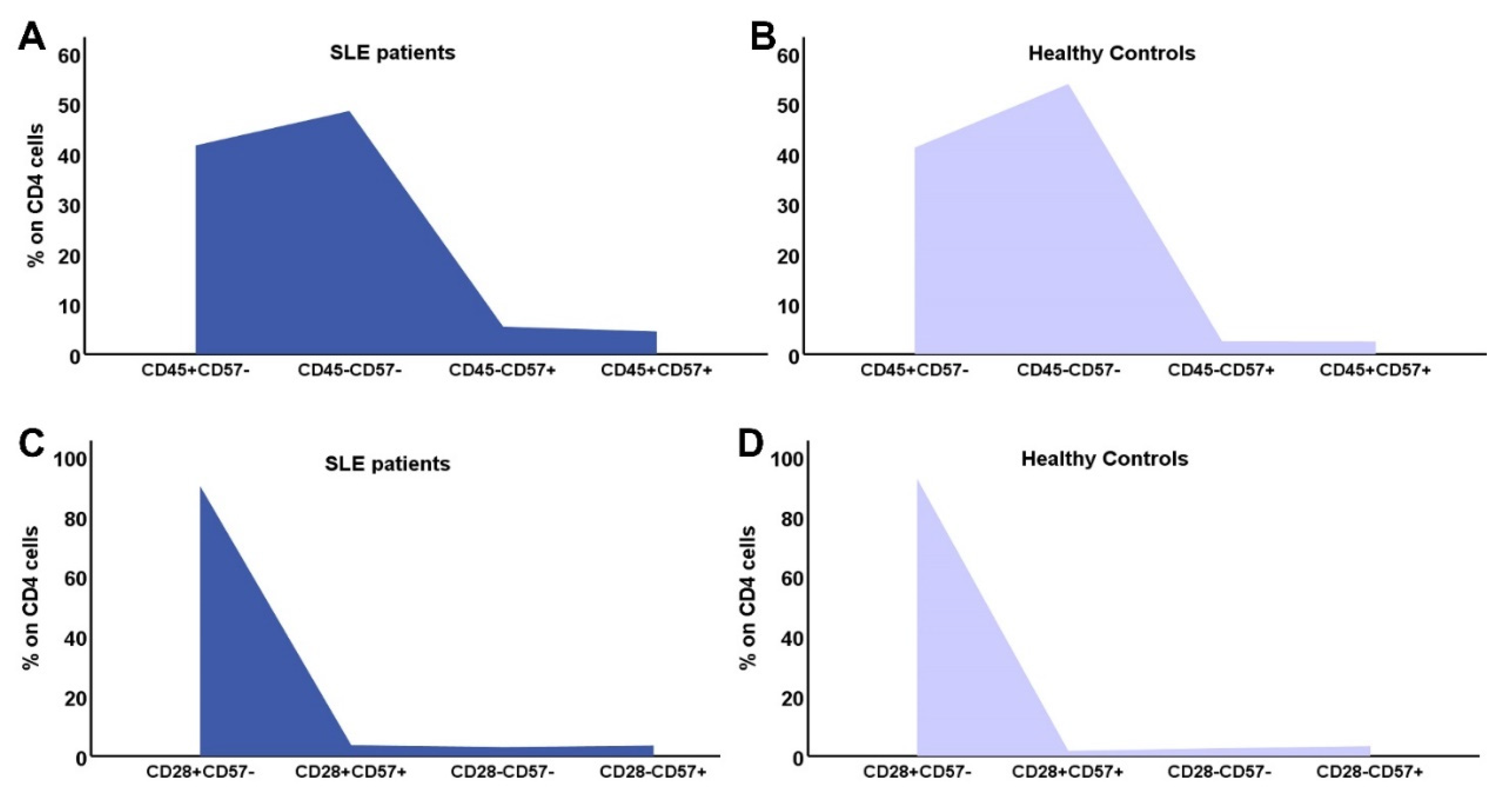
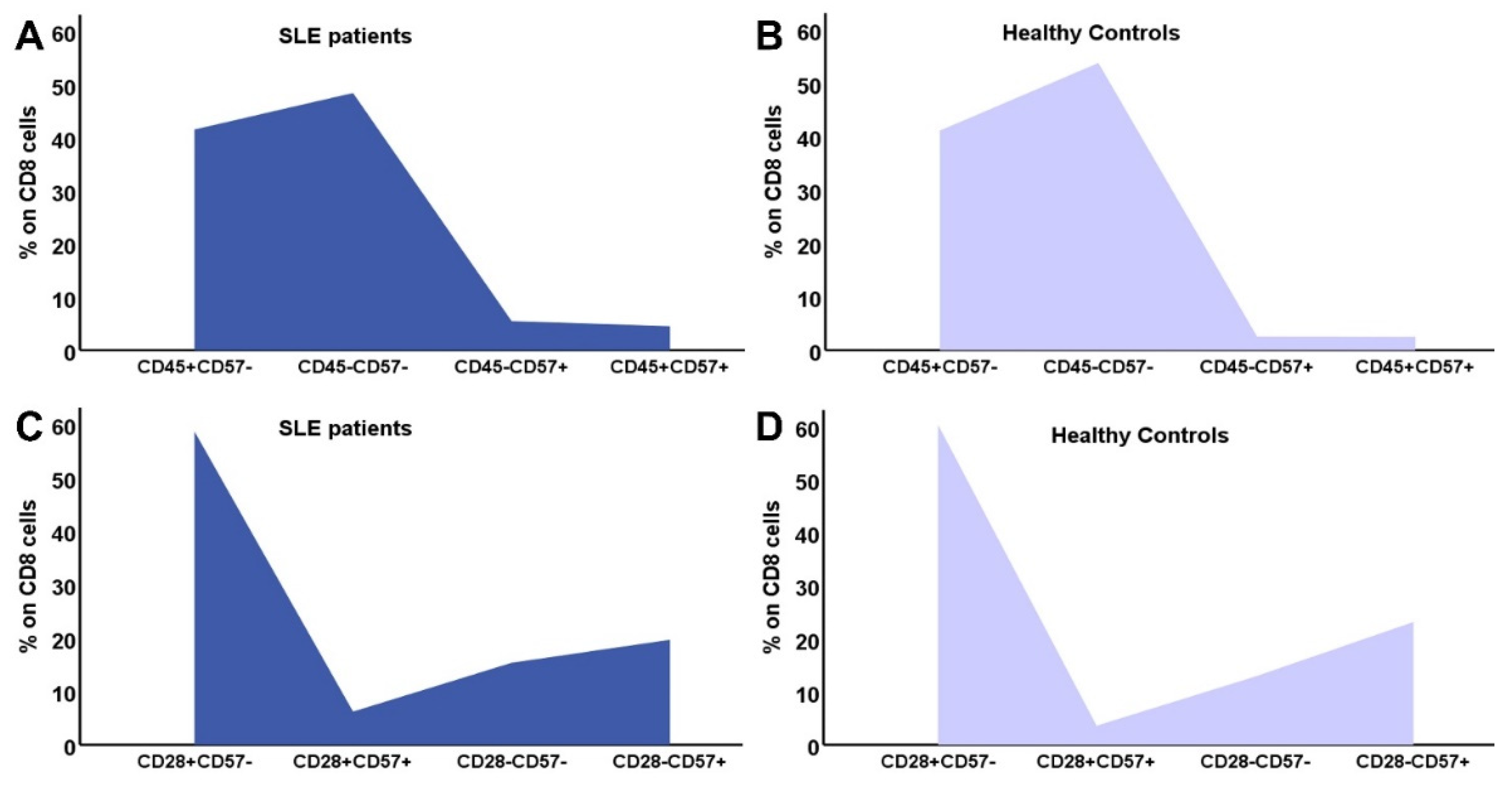
3.4. Distribution of CD4 and CD8 subtypes according to their differentiation status
3.5. Correlation of DN B cells with B lymphocyte subpopulations
3.6. Correlation of DN B cells with T lymphocyte subpopulations
3.6.1. Correlation with CD4 cells
3.6.2. Correlation with CD8 cells
4. Discussion
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Klein U, Rajewsky K, Küppers R. Human immunoglobulin (Ig)M+IgD+ peripheral blood B cells expressing the CD27 cell surface antigen carry somatically mutated variable region genes: CD27 as a general marker for somatically mutated (memory) B cells. J Exp Med 1998;188:1679–89. [CrossRef]
- Shi Y, Agematsu K, Ochs HD, Sugane K. Functional analysis of human memory B-cell subpopulations: IgD+CD27+ B cells are crucial in secondary immune response by producing high affinity IgM. Clin Immunol 2003;108(2):128-37. [CrossRef]
- Borst J, Hendriks J, Xiao Y. CD27 and CD70 in T cell and B cell activation. Curr Opin Immunol 2005;17(3):275-81. [CrossRef]
- Beckers L, Somers V, Fraussen J. IgD-CD27- double negative (DN) B cells: Origins and functions in health and disease. Immunol Lett 2023;255:67-76. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Li Z, Hu F. Double-negative (DN) B cells: An under-recognized effector memory B cell subset in autoimmunity. Clin Exp Immunol 2021;205(2):119-127. [CrossRef]
- Beckers L, Somers V, Fraussen J. IgD-CD27- double negative (DN) B cells: Origins and functions in health and disease. Immunol Lett 2023;255:67-76. [CrossRef]
- Li Y, Li Z, Hu F. Double-negative (DN) B cells: An under-recognized effector memory B cell subset in autoimmunity. Clin Exp Immunol 2021;205(2):119-127. [CrossRef]
- Lioulios G, Fylaktou A, Xochelli A, Sampani E, Tsouchnikas I, Giamalis P, Daikidou DV, Nikolaidou V, Papagianni A, Theodorou I, Stangou M. Clustering of End Stage Renal Disease Patients by Dimensionality Reduction Algorithms According to Lymphocyte Senescence Markers. Front Immunol 2022;13:841031. [CrossRef]
- Jenks SA, Cashman KS, Zumaquero E, Marigorta UM, Patel AV, Wang X, Tomar D, Woodruff MC, Simon Z, Bugrovsky R, Blalock EL, Scharer CD, Tipton CM, Wei C, Lim SS, Petri M, Niewold TB, Anolik JH, Gibson G, Lee FE, Boss JM, Lund FE, Sanz I. Distinct Effector B Cells Induced by Unregulated Toll-like Receptor 7 Contribute to Pathogenic Responses in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus. Immunity 2018;49(4):725-739.e6. [CrossRef]
- Szelinski F, Lino AC, Dörner T. B cells in systemic lupus erythematosus. Curr Opin Rheumatol 2022;34(2):125-132. PMID: 34939607. [CrossRef]
- Moysidou E, Lioulios G, Xochelli A, Nikolaidou V, Christodoulou M, Mitsoglou Z, Stai S, Fylaktou A, Papagianni A, Stangou M. Different Types of Chronic Inflammation Engender Distinctive Immunosenescent Profiles in Affected Patients. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(23):14688. [CrossRef]
- Lioulios G, Mitsoglou Z, Fylaktou A, Xochelli A, Christodoulou M, Stai S, Moysidou E, Konstantouli A, Nikolaidou V, Papagianni A, Stangou M.Exhausted but Not Senescent T Lymphocytes Predominate in Lupus Nephritis Patients. Int J Mol Sci 2022;23(22):13928. [CrossRef]
- Sampani E, Vagiotas L, Daikidou DV, Nikolaidou V, Xochelli A, Kasimatis E, Lioulios G, Dimitriadis C, Fylaktou A, Papagianni A, Stangou M. End stage renal disease has an early and continuous detrimental effect on regulatory T cells. Nephrology (Carlton) 2022;27(3):281-287. [CrossRef]
- Shang Q, Yip GW, Tam LS, Zhang Q, Sanderson JE, Lam YY, Li CM, Wang T, Li EK, Yu CM.SLICC/ACR damage index independently associated with left ventricular diastolic dysfunction in patients with systemic lupus erythematosus. Lupus. 2012;21(10):1057-62. [CrossRef]
- Gladman DD, Ibañez D, Urowitz MB.Systemic lupus erythematosus disease activity index 2000. J Rheumatol 2002;29(2):288-91.
- Zheng J, Zhu L, Ju B, Zhang J, Luo J, Wang Y, Lv X, Pu D, He L, Wang Peripheral immunophenotypes associated with the flare in the systemic lupus erythematosus patients with low disease activity state. J. Clin Immunol 2022;245:109166. [CrossRef]
- Liossis SC, Staveri C. The Role of B Cells in Scleroderma Lung Disease Pathogenesis. Front Med (Lausanne) 2022;9:936182. [CrossRef]
- Wang Y, Lloyd KA, Melas I, Zhou D, Thyagarajan R, Lindqvist J, Hansson M, Svärd A, Mathsson-Alm L, Kastbom A, Lundberg K, Klareskog L, Catrina AI, Rapecki S, Malmström V, Grönwall C.Rheumatoid arthritis patients display B-cell dysregulation already in the naïve repertoire consistent with defects in B-cell tolerance. Sci Rep 2019;9(1):19995. [CrossRef]
- Claes N, Fraussen J, Vanheusden M, Hellings N, Stinissen P, Van Wijmeersch B, Hupperts R, Somers V. Age-Associated B Cells with Proinflammatory Characteristics Are Expanded in a Proportion of Multiple Sclerosis Patients. J Immunol 2016;197(12):4576-4583. [CrossRef]
- Ehrhardt GR, Hijikata A, Kitamura H, Ohara O, Wang JY, Cooper MD. Discriminating gene expression profiles of memory B cell subpopulations. J. Exp. Med 2008;205, 1807–1817. [CrossRef]
- Buchta C, Bishop G. TRAF5 negatively regulates TLR signaling in B lymphocytes. J Immunol 2014;192, 145–150. [CrossRef]
- You X, Zhang R, Shao M, He J, Chen J, Liu J, Zhang X, Liu X, Jia R, Sun X, Li Z. Double Negative B Cell Is Associated With Renal Impairment in Systemic Lupus Erythematosus and Acts as a Marker for Nephritis Remission. Front Med (Lausanne). 2020;7:85. [CrossRef]
- Agematsu K, Hokibara S, Nagumo H, Shinozaki K, Yamada S, Komiyama A. Plasma cell generation from B-lymphocytes via CD27/CD70 interaction. Leuk Lymphoma 1999;35(3-4):219-25. [CrossRef]
- CD70-mediated CD27 expression downregulation contributed to the regulatory B10 cell impairment in rheumatoid arthritis. Shi L, Hu F, Zhu L, Xu C, Zhu H, Li Y, Liu H, Li C, Liu N, Xu L, Mu R, Li Z. Mol Immunol 2020;119:92-100. [CrossRef]
- Claes N, Dhaeze T, Fraussen J, Broux B, Van Wijmeersch B, Stinissen P, Hupperts R, Hellings N, Somers V. Compositional changes of B and T cell subtypes during fingolimod treatment in multiple sclerosis patients: A 12-month follow-up study. PLoS ONE. 2014 Oct 31;9(10):e111115. [CrossRef]
- Moura RA, Quaresma C, Vieira AR, Gonçalves MJ, Polido-Pereira J, Romão VC, Martins N, Canhão H, Fonseca JE.B-cell phenotype and IgD-CD27- memory B cells are affected by TNF-inhibitors and tocilizumab treatment in rheumatoid arthritis. PLoS ONE. 2017;12(9):e0182927. [CrossRef]
- Colonna-Romano G, Bulati M, Aquino A, Pellicanò M, Vitello S, Lio D, Candore G, Caruso C.A double-negative (IgD-CD27-) B cell population is increased in the peripheral blood of elderly people. Mech Ageing Dev. 2009;130(10):681-90. [CrossRef]
- Bulati M, Buffa S, Candore G, Caruso C, Dunn-Walters DK, Pellicanò M, Wu YC, Colonna Romano G.B cells and immunosenescence: A focus on IgG+IgD-CD27- (DN) B cells in aged humans. Ageing Res Rev. 2011;10(2):274-84. [CrossRef]
- Liu Z, Liang Q, Ren Y, Guo C, Ge X, Wang L, Cheng Q, Luo P, Zhang Y, Han X Immunosenescence: Molecular mechanisms and diseases. Signal Transduct Target Ther 2023;8(1):200. [CrossRef]
- Shen CY, Lu CH, Wu CH, Li KJ, Kuo YM, Hsieh SC, Yu CL. Molecular Basis of Accelerated Aging with Immune Dysfunction-Mediated Inflammation (Inflamm-Aging) in Patients with Systemic Sclerosis. Cells. 2021;10(12):3402. [CrossRef]
| SLE | HC | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 30 | 31 | SLE vs. HC |
| Age (yrs) | 43±14 | 49±13 | NS |
| Time since diagnosis (mo) | 84(45-125) | - | - |
| SLEDAI score | 2(1-5) | ||
| Laboratory results | |||
| WCC (cells/μL) | 7200(3350) | 6400(1800) | NS |
| Neutrophils (%) | 69.6(20.7) | 58.1(10.35) | <0.0001 |
| Neutrophils (cells/μL) | 4600(3500) | 3500(1200) | 0.03 |
| Lymphocytes (%) | 23.1(16.1) | 25.6(9) | 0.03 |
| Lymphocytes (cells/μL) | 1400(900) | 2100(900) | 0.005 |
| NLR | 3(4) | 1.8(0.85) | <0.0001 |
| SLE | HC | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 30 | 31 | SLE vs. HC |
| CD19 (%) | 7.9(2.1-28.6) | 11.8(5.4-24) | 0.012 |
| CD19 cells/μL | 75.4(14.4-520.8) | 214(84-576) | <0.001 |
| IgD+CD27- (%) | 51.5(0.4-94) | 58.7(4.5-86.9) | 0.34 |
| IgD+CD27- cells/μL | 37.71(0.26-434.84) | 117(5-364) | <0.001 |
| IgD+CD27+ (%) | 3.9(0.2-22) | 8.4(1.5-44) | 0.014 |
| IgD+CD27+ cells/μL | 5.12(0.13-17.55) | 23(2-700) | <0.001 |
| IgD-CD27+ (%) | 19.1(2.2-78) | 17.9(7.1-71.9) | 0.7 |
| IgD-CD27+ cells/μL | 18.58(0.47-89.58) | 38(11-258) | 0.001 |
| IgD-CD27- (%) | 12.9(2.3-74.2) | 8(1.7-35) | 0.04 |
| IgD-CD27- cells/μL | 10.84(0.93-122.91) | 21(3-202) | 0.007 |
| Ratio DN/[(IgD+CD27-)+ (IgD-CD27+)+ (IgD+CD27+)] | 0.14(0.02-2.9) | 0.08(0.02-0.54) | p=0.04 |
| SLE | HC | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 30 | 31 | p |
| CD4 (cells/μL) | 651.2(71.1-1478.2) | 986(344-1591) | 0.004 |
| Early differentiated cells | |||
| CD4+CD31+ | 216.38(16.3-904.7) | 250(69-967) | 0.14 |
| CD4CD45RA+CD28+ | 267.97 (20.62-1030.31) | 388 (139-1402) | 0.02 |
| CD4CD45RA+CD57- | 254.03 (21.05-1077.61) | 401 (160-1373) | 0.035 |
| CD4CD45RA-CD57- | 290.67 (38.96-884.43) | 539 (173-991) | <0.001 |
| CD4CD28+CD57- | 610.7 (54.68-1461.94) | 958 (332-1569) | 0.004 |
| CD4CD28+CD57+ | 4.7(0-806) | 7(0-245) | 0.21 |
| Memory cells | |||
| CD4CD45RA-CCR7+ | 402.35(38.7-972.4) | 563(40-1001) | 0.046 |
| CD4CD45RA-CCR7- | 1.62(0-73.49) | 11(0-590) | 0.002 |
| Advanced differentiated/Senescent cells | |||
| CD45RA+CCR7- | 7.29(0-180.62) | 23(0-487) | 0.027 |
| CD4CD28- | 20.12 (1.27 -139.06) | 38 (3-299) | 0.04 |
| CD4CD28-CD57+ | 9.90 (0.46-73.8) | 23 (0-274) | 0.1 |
| CD45RA+CCR7-CD28- | 1.2(0-82) | 2.5(0-106) | 0.21 |
| SLE | HC | p | |
|---|---|---|---|
| n | 30 | 31 | p |
| CD8 (cells/μL) | 414.8 (60.6-2017.8) | 454.5 (154-1310) | 0.26 |
| Early differentiated cells | |||
| CD8+CD31+ | 88.19 (8.2-1047) | 187.5 (8-541) | 0.26 |
| CD8CD45RA+CD28+ | 113.56 (1.81-753.7) | 212.5 (7-1257) | 0.17 |
| CD8CD45RA+CD57- | 63.65 (3.83-889.8) | 133 (8-552) | 0.17 |
| CD8CD45RA-CD57- | 194.52 (1.8-945.1) | 179 (28-555) | 0.99 |
| CD8CD28+CD57- | 249.45 (5.49-1362) | 298 (95-646) | 0.1 |
| CD8CD28+CD57+ | 12(0.4-132) | 8.5(0-424) | 0.58 |
| Memory cells | |||
| CD8CD45RA-CCR7+ | 171.52 (2.5-1417) | 123 (1-941) | 0.14 |
| CD8CD45RA-CCR7- | 13.94 (0.59-92.37) | 25 (0-355) | 0.53 |
| Advanced differentiated/Senescent cells | |||
| CD8CD45RA+CCR7- | 11.13 (0-279.6) | 49.5 (0-534) | 0.02 |
| CD8CD28- | 87.83 (4.56-1361.2) | 135 (36-633) | 0.14 |
| CD8CD28-CD57+ | 53.17 (0.83-571.04) | 71 (0-470) | 0.17 |
| CD45RA+CCR7-CD28- | 37.3(2.1-263) | 197(9-783) | <0.0001 |
| DN B Lymphocytes | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| SLE | HC | ||
| CD19+ cells | r | 0.696 | 0.554 |
| p | <0.001 | 0.001 | |
| Naïve cells (CD19+IgD+CD27-) | r | 0.446 | 0.282 |
| p | 0.013 | 0.123 | |
| Non-switched memory B cells (CD19+IgD-CD27+) | r | 0.671 | 0.540 |
| p | <0.001 | 0.001 | |
| Switched memory B cells (CD19+IgD+CD27+) | r | 0.424 | 0.094 |
| p | 0.019 | 0.614 | |
| CD19 IgD- CD27- | CD19 IgD-CD27- | ||||||
| SLE | HC | SLE | HC | ||||
| CD4 | r | 0.548 | 0.412 | CD8 | r | 0.425 | -0.239 |
| p | 0.002 | 0.021 | p | 0.019 | 0.196 | ||
| Early Differentiated cells | |||||||
| CD4 CD31+ | r | 0.587 | 0.243 | CD8 CD31+ | r | 0.366 | -0.286 |
| p | <0.001 | 0.188 | p | 0.047 | 0,119 | ||
| CD4 NAÏVE (CD45RA+ CCR7+) | r | 0.325 | 0.189 | CD8 NAÏVE (CD45RA+ CCR7+) | r | 0.432 | -0,308 |
| p | 0.079 | 0.316 | p | 0.017 | 0,091 | ||
| CD4CD45RA+CD28+ | r | 0.504 | 0.265 | CD8CD45RA+CD28+ | r | 0.234 | -0.086 |
| p | 0.005 | 0.15 | p | 0.214 | 0,646 | ||
| CD4CD45RA+CD57- | r | 0.419 | 0.42 | CD8CD45RA+CD57- | r | 0.201 | -0.251 |
| p | 0.021 | 0.021 | p | 0.287 | 0.173 | ||
| CD4CD45RA-CD57- | r | 0.397 | 0.24 | CD8CD45RA-CD57- | r | 0.444 | 0.166 |
| p | 0.03 | 0.201 | p | 0.014 | 0.371 | ||
| CD4CD28+CD57- | r | 0.487 | 0.439 | CD8CD28+CD57- | r | 0.363 | -0,088 |
| p | 0.006 | 0.013 | p | 0.048 | 0.638 | ||
| CD4CD28+CD57+ | r | 0.491 | 0.156 | CD8CD28+CD57+ | r | 0.483 | -0.092 |
| p | 0.006 | 0.402 | p | 0.007 | 0.624 | ||
| Memory cells | |||||||
| CD4 CM (CD45RA- CCR7+) | r | 0.381 | 0.188 | CD8 CM (CD45RA- CCR7+) | r | 0.33 | 0.138 |
| p | 0.038 | 0.32 | p | 0.075 | 0.459 | ||
| CD4 EM (CD45RA- CCR7-) | r | -0.075 | 0.008 | CD8 EM (CD45RA-CCR7-) | r | 0.099 | 0.088 |
| p | 0.695 | 0.965 | p | 0.601 | 0.637 | ||
| Senescent/Advanced differentiated cells | |||||||
| CD4 EMRA (CD45RA+ CCR7-) | r | 0.104 | 0.168 | CD8 EMRA (CD45RA+CCR7-) | r | 0.242 | 0.04 |
| p | 0.583 | 0.376 | p | 0.189 | 0.182 | ||
| CD4CD28null | r | 0.066 | -0.154 | CD8CD28null | r | 0.271 | -0.248 |
| p | 0.73 | 0.408 | p | 0.147 | 0.179 | ||
| CD4CD28-CD57+ | r | - 0.068 | -0.243 | CD8CD28-CD57+ | r | 0.291 | -0.254 |
| p | 0.722 | 0.187 | p | 0.119 | 0.169 | ||
| CD4 EMRA (CD45RA+ CCR7-) 28- | r | 0.042 | 0.198 | CD8 EMRA (CD45RA+ CCR7-) 28- | r | 0.191 | -0.032 |
| p | 0.825 | 0.294 | p | 0.312 | 0.862 | ||
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





