Submitted:
08 July 2023
Posted:
10 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
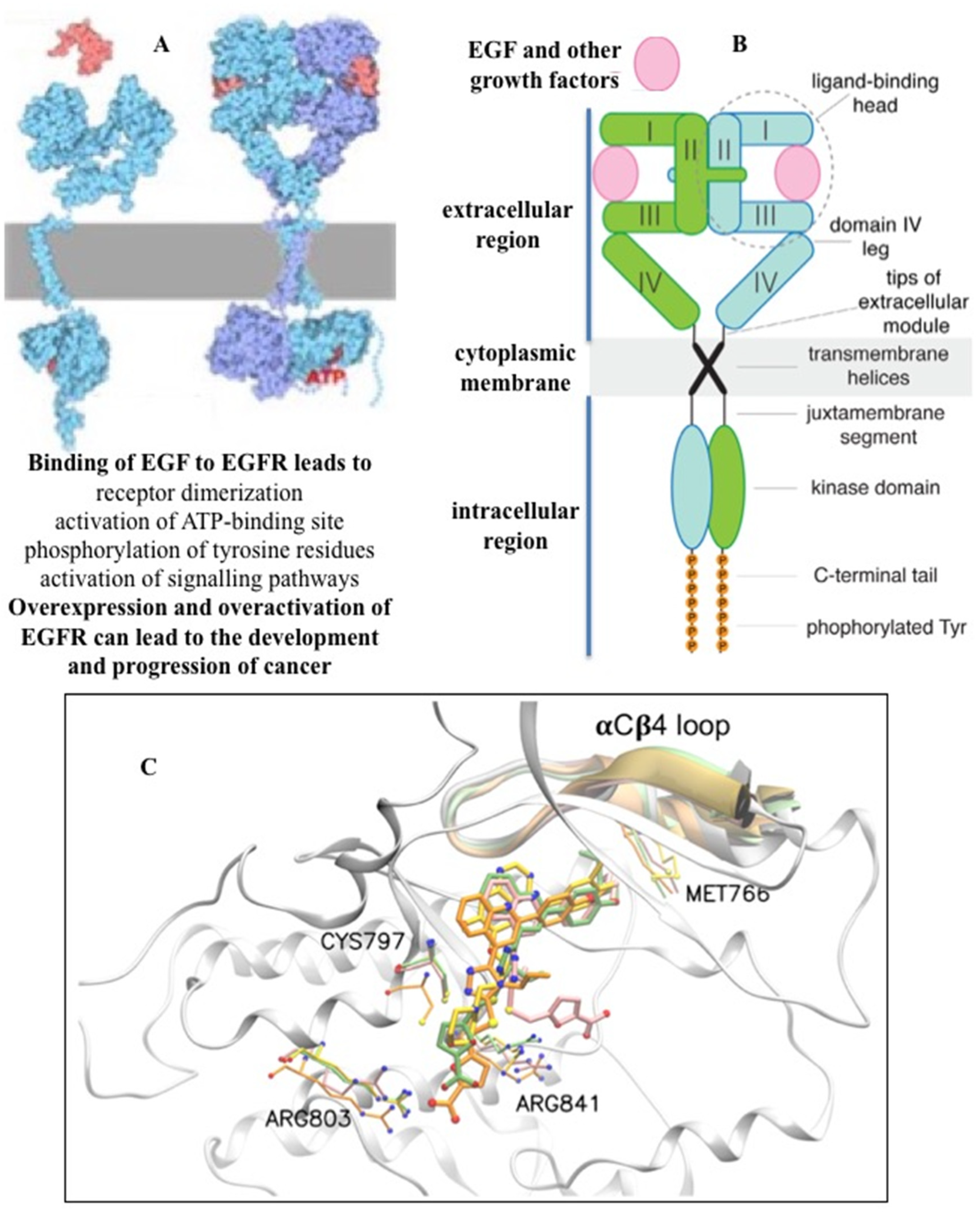
2. Targeted inhibition of receptor tyrosine kinase EGFR
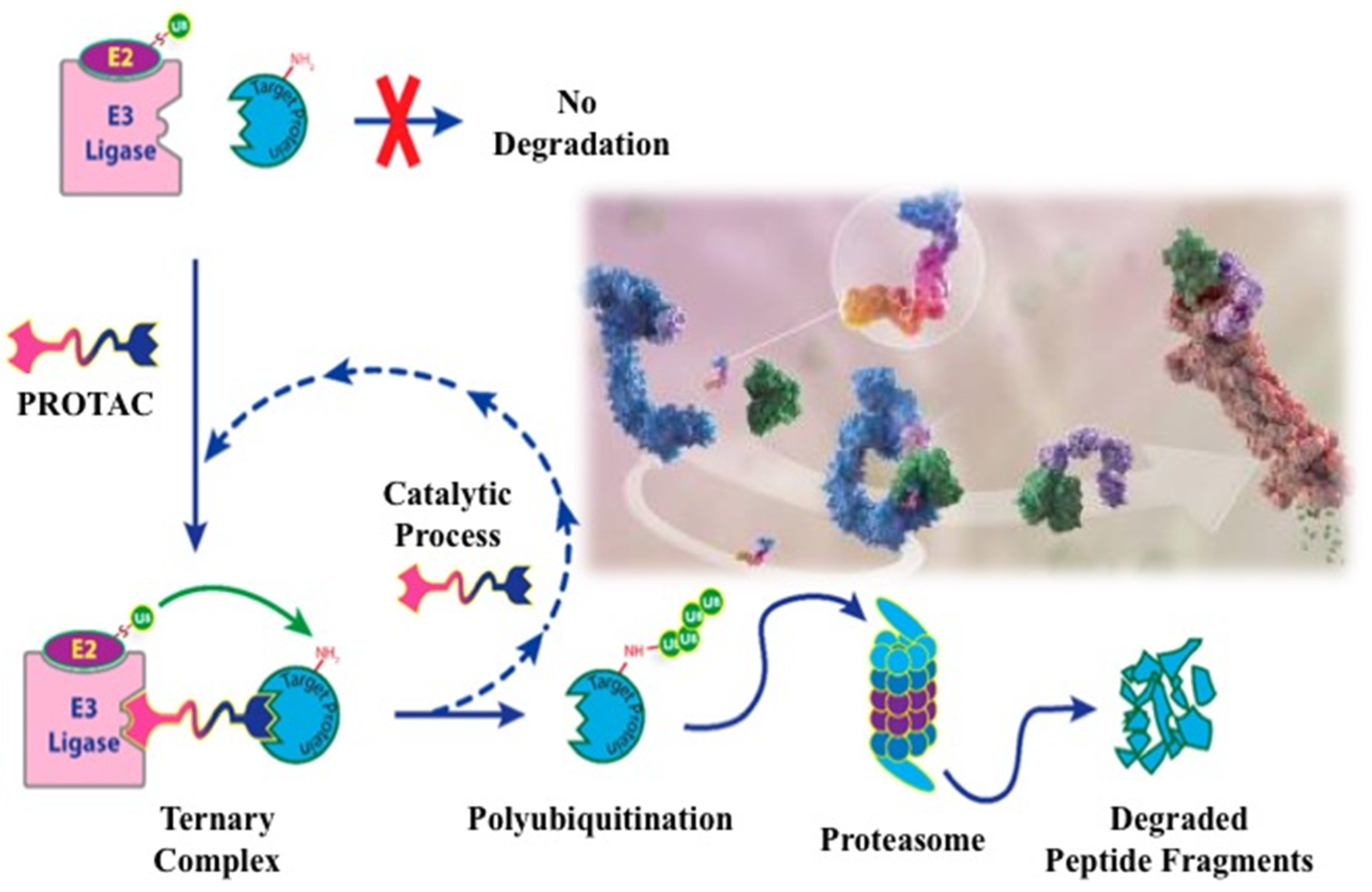
3. EGFR degradation by Protac technology
4. Alternative strategies for EGFR degradation
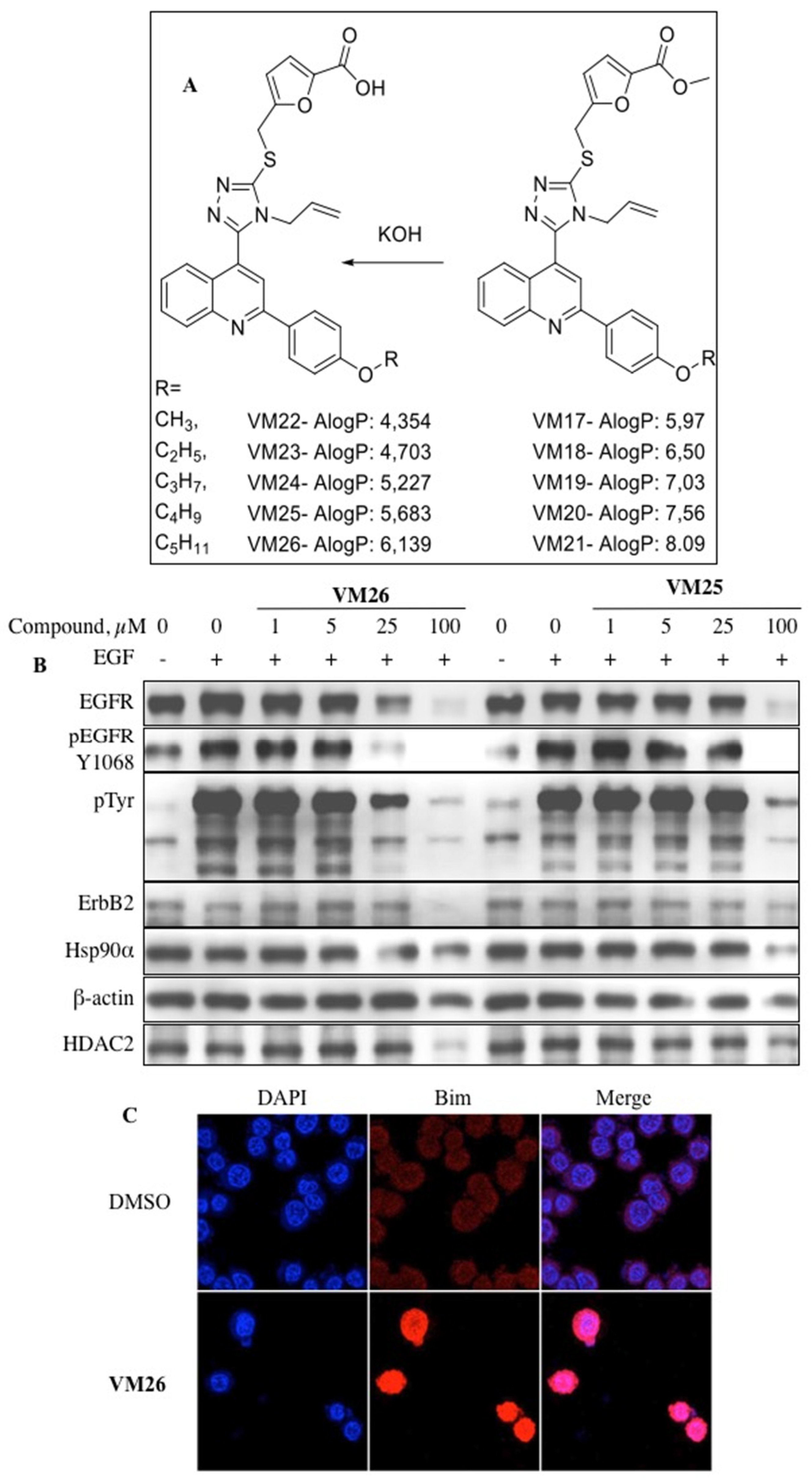
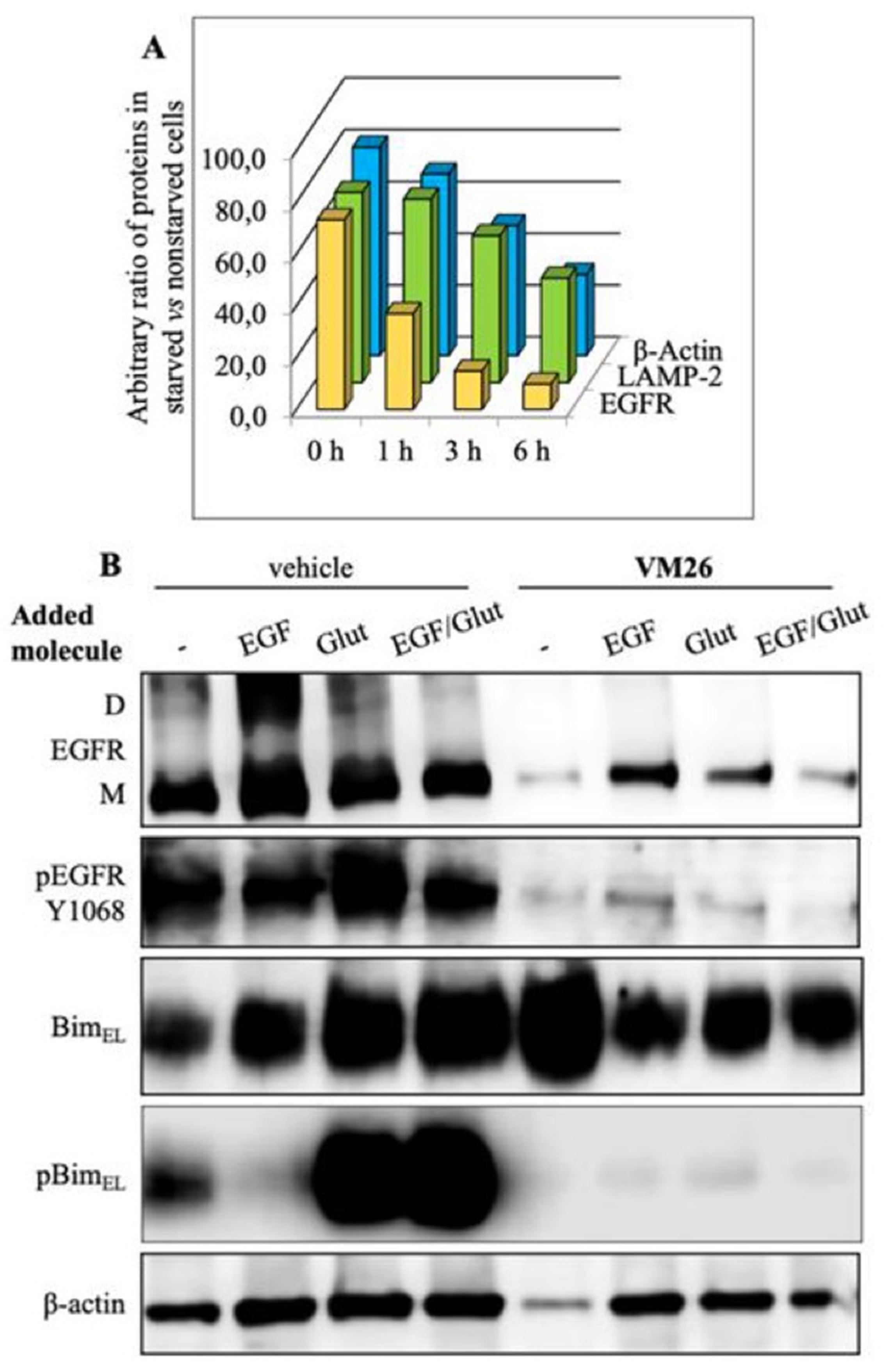
5. New allosteric chemicals bind to EGFR and lead to cancer cell death
6. New vision on cancer chemotherapy
7. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Acknowledgements
Conflict of Interest and other Ethics Statements
References
- Soneji S., Beltrán-Sánchez H., Sox H.C. Assessing progress in reducing the burden of cancer mortality, 1985–2005. J. Clin. Oncol., 2014, 32, 444-448. [CrossRef]
- Miller K.D., Nogueira L., Devasia T., Mariotto A.B., Yabroff K.R., Jemal A., Kramer J., Siegel R.L. Cancer treatment and survivorship statistics, 2022. CA Cancer J. Clin., 2022, 72(5):409-436. [CrossRef]
- Willemsen M.C., Mons U., Fernández E. Tobacco control in Europe: progress and key challenges. Tob Control 2022, 31:160–163. [CrossRef]
- Patel V.R., Qasim Hussaini S.M., Blaes A.H., Morgans A.K., Haynes A.B., Adamson A.S., Gupta A. Trends in the prevalence of functional limitations among US cancer survivors, 1999–2018. JAMA Oncol., 11 May 2023. [CrossRef]
- Jotte R.M., Spigel D.R. Advances in molecular-based personalized non-small-cell lung cancer therapy: targeting epidermal growth factor receptor and mechanisms of resistance. Cancer Med., 2015, 4(11), 1621-1632. [CrossRef]
- Castañeda A.M., Meléndez C.M., Uribe D., Pedroza-Díaz J. Synergistic effects of natural compounds and conventional chemotherapeutic agents: recent insights for the development of cancer treatment strategies. Heliyon, 2022, 8(6), e09519. [CrossRef]
- Seshacharyulu P., Ponnusamy M.P., Haridas D., Jain M., Ganti A.K., Batra S.K. Targeting the EGFR signaling pathway in cancer therapy. Expert Opin. Ther. Targets. 2012, 16(1), 15-31. [CrossRef]
- Patnaik S.K., Chandrasekar M.J.N., Nagarjuna P., Ramamurthi D., Swaroop A.K. Targeting of ErbB1, ErbB2, and their dual targeting using small molecules and natural peptides: blocking EGFR cell signaling pathways in cancer: A mini-review. Mini Rev. Med. Chem., 2022, 21, 22(22), 2831-2846. [CrossRef]
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R.A. The hallmarks of cancer. Cell, 2000, 100(1), 57-70. [CrossRef]
- Hanahan D., Weinberg R.A. Hallmarks of cancer: the next generation. Cell, 2011, 144(5), 646-674. [CrossRef]
- Hanahan D. Hallmarks of cancer: new dimensions. Cancer Discov. 2022 Jan;12(1):31-46. [CrossRef]
- Falzone L., Salomone S., Libra M. Evolution of cancer pharmacological treatments at the turn of the third millennium. Front. Pharmacol., 2018, 9:1300. [CrossRef]
- Du Z., Lovly C.M. Mechanisms of receptor tyrosine kinase activation in cancer. Mol Cancer., 2018, 17(1), 58. [CrossRef]
- Levantini E., Maroni G., Del Re M., Tenen D.G. EGFR signaling pathway as therapeutic target in human cancers. Semin. Cancer Biol., 2022, 85, 253-275. [CrossRef]
- Pucci, C., Martinelli C., Ciofani G. Innovative approaches for cancer treatment: current perspectives and new challenges. Ecancermedicalscience, 2019, 13:961. [CrossRef]
- Zhang C., Xu C., Gao X., Yao Q. Platinum-based drugs for cancer therapy and anti-tumor strategies. Theranostics, 2022, 12(5), 2115-2132. [CrossRef]
- Schlessinger J. Receptor tyrosine kinases: legacy of the first two decades. Cold Spring Harb. Perspect. Biol., 2014, 6(3), a008912. [CrossRef]
- Sigismund S., Avanzato D., Lanzetti L. Emerging functions of the EGFR in cancer. Mol Oncol. 2018, 12(1), 3-20. [CrossRef]
- Uribe M.L., Marrocco I., Yarden Y. EGFR in Cancer: Signaling Mechanisms, Drugs, and Acquired Resistance. Cancers (Basel). 2021, 13(11), 2748. [CrossRef]
- Dawson J.P., Berger M.B., Lin C.C., Schlessinger J., Lemmon M.A., Ferguson K.M. Epidermal growth factor receptor dimerization and activation require ligand-induced conformational changes in the dimer interface. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2005 Sep, 25(17), 7734-42. [CrossRef]
- Stamos J., Sliwkowski M.X., Eigenbrot C. Structure of the epidermal growth factor receptor kinase domain alone and in complex with a 4-anilinoquinazoline inhibitor. J. Biol. Chem. 2002 Nov 29, 277(48), 46265-46272. [CrossRef]
- Bae Y.S., Kang S.W., Seo M.S., Baines I.C., Tekle E., Chock P.B., Rhee S.G. Epidermal growth factor (EGF)-induced generation of hydrogen peroxide. Role in EGF receptor-mediated tyrosine phosphorylation. J. Biol. Chem. 1997, 272(1), 217-221. [CrossRef]
- Paulsen C.E., Truong T.H., Garcia F.J., Homann A., Gupta V., Leonard S.E., Carroll K.S. Peroxide-dependent sulfenylation of the EGFR catalytic site enhances kinase activity. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2011 Dec 11, 8(1), 57-64. [CrossRef]
- Pan J., Carroll K. S. Chemical biology approaches to study protein cysteine sulfenylation. Biopolymers. 2014 Feb, 101(2), 165-172. [CrossRef]
- Sakanyan V., Angelini M., Le Béchec M., Lecocq M.F., Benaiteau F., Rousseau B., Gyulkhandanyan A., Gyulkhandanyan L., Logé C., Reiter E., Roussakis C., Fleury F. Screening and discovery of nitro-benzoxadiazole compounds activating epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) in cancer cells. Sci. Rep. 2014 Feb 5, 4:3977. [CrossRef]
- Sakanyan V., Hulin P., Alves de Sousa R., Silva V.A., Hambardzumyan A., Nedellec S., Tomasoni C., Logé C., Pineau C., Roussakis C., Fleury F., Artaud I. Activation of EGFR by small compounds through coupling the generation of hydrogen peroxide to stable dimerization of Cu/Zn SOD1. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 21088. [CrossRef]
- Sakanyan V., Benaiteau F., Alves de Sousa R., Pineau C., Artaud, I. Straightforward detection of reactive compound binding to multiple proteins in cancer cells: Towards a better understanding of electrophilic stress. Ann. Clin. Exp. Metabol. 2016, 1, 1006.
- Silva V.A., Lafont F., Benhelli-Mokrani H., Breton M.L., Hulin P., Chabot T., Paris F., Sakanyan V., Fleury F. Rapid diminution in the level and activity of DNA-dependent protein kinase in cancer cells by a reactive nitro-benzoxadiazole compound. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2016 May 11, 17(5), 703. [CrossRef]
- Sakanyan V. Reactive Chemicals and Electrophilic Stress in Cancer: A Minireview. High Throughput. 2018 Apr 27, 7(2), 12. [CrossRef]
- Parzych K.R., Klionsky D.J. An overview of autophagy: morphology, mechanism, and regulation. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2014 Jan 20, 20(3), 460-473. [CrossRef]
- von Zastrow M., Sorkin A. Mechanisms for Regulating and Organizing Receptor Signaling by Endocytosis. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2021 Jun 20, 90, 709-737. [CrossRef]
- Tomas A., Futter C.E., Eden E.R. EGF receptor trafficking: consequences for signaling and cancer. Trends Cell Biol. 2014 Jan, 24(1), 26-34. [CrossRef]
- Caldieri G., Malabarba M.G., Di Fiore P.P., Sigismund S. EGFR Trafficking in Physiology and Cancer. Prog. Mol. Subcell. Biol. 2018, 57, 235-272. [CrossRef]
- Zhou Y., Sakurai H. New trend in ligand-induced EGFR trafficking: A dual-mode clathrin-mediated endocytosis model. J. Proteomics. 2022 Mar 20, 255, 104503. [CrossRef]
- Mendelsohn J., Baselga J. Epidermal growth factor receptor targeting in cancer. Semin Oncol., 2006, 33(4):369-385. [CrossRef]
- Cohen P., Cross D., Jänne P.A. Kinase drug discovery 20 years after imatinib. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov., 2021, 20, 551−569. [CrossRef]
- Red Brewer M., Yun C.H., Lai D., Lemmon M.A., Eck M.J., Pao W. Mechanism for activation of mutated epidermal growth factor receptors in lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA. 2013, 110(38), E3595-604. Erratum in: Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2013, 110(50), 20344. [CrossRef]
- Arter C., Trask L., Ward S., Yeoh S., Bayliss R. Structural features of the protein kinase domain and targeted binding by small-molecule inhibitors. J. Biol. Chem. 2022 Aug, 298(8), 102247. [CrossRef]
- Herbst R.S., Fukuoka M., Baselga J. Gefitinib - a novel targeted approach to treating cancer. Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2004, 4, 956−965. [CrossRef]
- Cappuzzo F., Ciuleanu T., Stelmakh L., Cicenas S., Szczésna A., Juhász E., Esteban E., Molinier O., Brugger W., Melezínek I., Klingelschmitt G., Klughammer B., Giaccone G. SATURN investigators. Erlotinib as maintenance treatment in advanced non-small-cell lung cancer: a multicentre, randomised, placebo-controlled phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol. 2010 Jun, 11(6), 521-529. [CrossRef]
- Jänne P.A. Challenges of detecting EGFR T790M in gefitinib/erlotinib-resistant tumours. Lung Cancer. 2008 Jun, 60 Suppl 2, S3-9. [CrossRef]
- Shah R., Lester J.F. Tyrosine kinase inhibitors for the yreatment of EGFR mutation-positive Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer: A clash of the generations. Clin. Lung Cancer. 2020 May, 21(3), e216-e228. [CrossRef]
- Hirsch F. R., Scagliotti G. V., Mulshine J. L., Kwon R., Curran W. J., Wu Y.-L., Paz-Ares L. Lung cancer: current therapies and new targeted treatments. Lancet 2017, 389, 299−311. [CrossRef]
- Li L., Luo S., Lin H., Yang H., Chen H., Liao Z., Lin W., Zheng W., Xie X. Correlation between EGFR mutation status and the incidence of brain metastases in patients with non-small cell lung cancer. J. Thorac. Dis. 2017, 9, 2510–2520. [CrossRef]
- Russo A., Franchina T., Ricciardi G.R.R., Picone A., Ferraro G., Zanghì M., Toscano G., Giordano A., Adamo V. A decade of EGFR inhibition in EGFR-mutated non-small-cell lung cancer (NSCLC): Old successes and future perspectives. Oncotarget 2015, 6, 26814–26825. [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi S., Boggon T. J., Dayaram T., Janne P. A., Kocher O., Meyerson M., Johnson B. E., Eck M. J., Tenen D. G., Halmos B. EGFR mutation and resistance of non-small-cell lung cancer to gefitinib. N. Engl. J. Med. 2005, 352, 786−792. [CrossRef]
- Pao W., Miller V. A., Politi K. A., Riely G. J., Somwar R., Zakowski M. F., Kris M. G., Varmus H. Acquired resistance of lung adenocarcinomas to gefitinib or erlotinib is associated with a second mutation in the EGFR kinase domain. PLoS Med. 2005 Mar, 2(3):e73. [CrossRef]
- Godin-Heymann N., Ulkus L., Brannigan B. W., McDermott U., Lamb J., Maheswaran S., Settleman J., Haber D. A. The T790M “gatekeeper” mutation in EGFR mediates resistance to low concentrations of an irreversible EGFR inhibitor. Mol. Cancer Ther. 2008 Apr, 7(4), 874-879. [CrossRef]
- Yun C. H., Mengwasser K. E., Toms A. V., Woo M. S., Greulich H., Wong K. K., Meyerson M., Eck M. J. The T790M mutation in EGFR kinase causes drug resistance by increasing the affinity for ATP. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U.S.A. 2008, 105, 2070−2075. [CrossRef]
- Yu H.A., Riely G.J. Second-generation epidermal growth factor receptor tyrosine kinase inhibitors in lung cancers. J. Natl. Compr. Canc. Netw. 2013 Feb 1, 11(2), 161-169. [CrossRef]
- Meng Y., Yu B., Huang H., Peng Y., Li E., Yao Y., Song C., Yu W., Zhu K., Wang K., Yi D., Du J., Chang J. Discovery of dosimertinib, a highly potent, selective, and orally efficacious deuterated EGFR targeting clinical candidate for the treatment of Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. J. Med. Chem., 2021, 64, 925−937.
- Liu Q., Sabnis Y., Zhao Z., Zhang T., Buhrlage S.J., Jones L.H., Gray N.S. Developing irreversible inhibitors of the protein kinase cysteinome. Chem. Biol. 2013 Feb 21, 20(2), 146-159. [CrossRef]
- da Cunha Santos G., Shepherd F. A., Tsao M. S. EGFR mutations and lung cancer. Annu. Rev. Pathol., 2011, 6, 49−69.
- Herbst R. S., Morgensztern D., Boshoff C. The biology and management of non-small cell lung cancer. Nature, 2018, 553, 446− 454. [CrossRef]
- Huang F., Han X., Xiao X., Zhou J. Covalent warheads targeting cysteine residue: the promising approach in drug development. Molecules. 2022 Nov 10, 27(22), 7728. [CrossRef]
- , Ercan D., Chen L.., Yun C. H., Li D., Capelletti M., Cortot A. B., Chirieac L., Iacob R. E., Padera R., Engen J. R., Wong,K. K., Eck M. J., Gray N. S., Janne, P. A. Novel mutant-selective EGFR kinase inhibitors against EGFR T790M. Nature, 2009, 462, 1070−1074. [CrossRef]
- Finlay M. R., Anderton M., Ashton S., Ballard P., Bethel P. A., Box M. R., Bradbury R. H., Brown S. J., Butterworth S., Campbell A., Chorley C., Colclough N., Cross D. A., Currie G. S., Grist M., Hassall L., Hill G. B., James D., James M., Kemmitt P., Klinowska T., Lamont G., Lamont S. G., Martin N., McFarland H. L., Mellor M. J., Orme J. P., Perkins D., Perkins P., Richmond G., Smith P., Ward R. A., Waring M. J., Whittaker D., Wells S., Wrigley G. L. Discovery of a potent and selective EGFR inhibitor (AZD9291) of both sensitizing and T790M resistance mutations that spares the wild type form of the receptor. J. Med. Chem., 2014, 57, 8249−8267. [CrossRef]
- Shah M.P., Neal J.W. Targeting acquired and intrinsic resistance mechanisms in Epidermal Growth Factor Receptor mutant Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Drugs. 2022 Apr, 82(6), 649-662. [CrossRef]
- He J., Zhou Z., Sun X., Yang Z., Zheng P., Xu S., Zhu W. The new opportunities in medicinal chemistry of fourth-generation EGFR inhibitors to overcome C797S mutation. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021 Jan 15, 210, 112995. [CrossRef]
- Wang Z., Yang J.J., Huang J., Ye J.Y., Zhang X.C., Tu H.Y., Han-Zhang H., Wu Y.L. Lung adenocarcinoma harboring EGFR T790M and in trans C797S responds to combination therapy of first- and third-generation EGFR TKIs and shifts allelic configuration at resistance. J. Thorac. Oncol. 2017 Nov,12(11), 1723-1727. [CrossRef]
- Jia Y., Yun C.H., Park E., Ercan D., Manuia M., Juarez J., Xu C., Rhee K., Chen T, Zhang H, Palakurthi S, Jang J, Lelais G, DiDonato M, Bursulaya B, Michellys PY, Epple R., Marsilje T.H., McNeill M., Lu W., Harris J., Bender S., Wong K.K., Jänne P.A., Eck M.J. Overcoming EGFR(T790M) and EGFR(C797S) resistance with mutant-selective allosteric inhibitors. Nature, 2016, 534(7605), 129-132. [CrossRef]
- Wang S., Song Y., Liu D. EAI045: The fourth-generation EGFR inhibitor overcoming T790M and C797S resistance. Cancer Lett., 2017, 385:51-54. [CrossRef]
- To C., Jang J., Chen T., Park E., Mushajiang M., De Clercq D.J.H., Xu M., Wang S, Cameron MD, Heppner DE, Shin BH, Gero TW, Yang A, Dahlberg SE, Wong KK, Eck M.J., Gray N.S., Jänne P.A. Single and dual targeting of mutant EGFR with an allosteric inhibitor. Cancer Discov., 2019, 9(7), 926-943. [CrossRef]
- Jang J., To C., De Clercq D.J.H., Park E., Ponthier C.M., Shin B.H., Mushajiang M., Nowak R.P., Fischer E.S., Eck M.J., Jänne P.A., Gray N.S. Mutant-selective allosteric EGFR degraders are effective against a broad range of drug-resistant mutations. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl., 2020, 59(34), 14481-14489. [CrossRef]
- Dong H., Ye X., Zhu Y., Shen H., Shen H, Chen W., Ji M., Zheng M., Wang K., Cai Z., Sun H., Xiao Y., Yang P. Discovery of potent and wild-type-sparing fourth-generation EGFR Inhibitors for treatment of osimertinib-resistance NSCLC. J. Med. Chem., 2023, May 4. [CrossRef]
- Marasco M., Misale S. Resistance is futile with fourth-generation EGFR inhibitors. Nat. Cancer, 2022, 3(4):381-383. [CrossRef]
- Xu L., Xu B., Wang J., Gao Y., He X., Xie T., Ye X.Y. Recent advances of novel fourth generation EGFR inhibitors in overcoming C797S mutation of lung cancer therapy. Eur. J. Med. Chem., 2023, 245(Pt 1):114900. [CrossRef]
- Chirnomas D., Hornberger K.R., Crews C.M. Protein degraders enter the clinic - a new approach to cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Clin. Oncol. 2023 Apr, 20(4), 265-278. [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto K.M., Kim K.B., Kumagai A., Mercurio F., Crews C.M., Deshaies R.J. Protacs: chimeric molecules that target proteins to the Skp1-Cullin-F box complex for ubiquitination and degradation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA, 2001, 98(15), 8554-8559. [CrossRef]
- Sakamoto K.M., Kim K.B., Verma R., Ransick A., Stein B., Crews C.M., Deshaies R.J. Development of Protacs to target cancer-promoting proteins for ubiquitination and degradation. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2003 Dec; 2(12), 1350-8. [CrossRef]
- Bondeson D., Mares A., Smith I., Ko E., Campos S., Miah A.H., Mulholland K.E., Routly N., Buckley D.L., Gustafson J.L., Zinn N., Grandi P., Shimamura S., Bergamini G., Faelth-Savitski M., Bantscheff M., Cox C., Gordon D.A., Willard R.R., Flanagan J.J., Casillas L.N., Votta B.J., den Besten W., Famm K., Kruidenier L., Carter P.S., Harling J.D., Churcher I., Crews C.M. Catalytic in vivo protein knockdown by small-molecule PROTACs. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2015, 11, 611–617. [CrossRef]
- Dale B., Cheng M., Park K.S., Kaniskan H.Ü., Xiong Y., Jin J. Advancing targeted protein degradation for cancer therapy. Nat. Rev. Cancer, 2021, 21(10), 638-654. [CrossRef]
- Békés M., Langley D.R., Crews CM. PROTAC targeted protein degraders: the past is prologue. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2022 Mar, 21(3), 181-200. [CrossRef]
- Hipp M.S., Kasturi P., Hartl F.U. The proteostasis network and its decline in ageing. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2019 Jul, 20(7), 421-435. [CrossRef]
- Li X., Pu W., Zheng Q., Ai M., Chen S., Peng Y. Proteolysis-targeting chimeras (PROTACs) in cancer therapy. Mol Cancer. 2022 Apr 11, 21(1), 99. [CrossRef]
- Yau R., Rape M. The increasing complexity of the ubiquitin code. Nat. Cell Biol. 2016 May 27, 18(6), 579-586. [CrossRef]
- Bard J.A.M., Goodall E.A., Greene E.R., Jonsson E., Dong K.C., Martin A. Structure and function of the 26S proteasome. Annu. Rev. Biochem. 2018 Jun 20, 87, 697-724. [CrossRef]
- Wolska-Washer A., Smolewski, P. Targeting protein degradation pathways in tumors: Focusing on their role in hematological malignancies. Cancers (Basel). 2022 Aug 3, 14(15), 3778. [CrossRef]
- Ishida T., Ciulli A. E3 ligase ligands for PROTACs: How they were found and How to discover new ones. SLAS Discovery 2021, 26, 484−502. [CrossRef]
- Li M., Zhi Y., Liu B., Yao Q. Advancing strategies for proteolysis-targeting chimera design. J. Med. Chem. 2023 Feb 23; 66(4), 2308-2329. [CrossRef]
- Smith B. E., Wang S. L., Jaime-Figueroa S., Harbin A., Wang J., Hamman B. D., Crews C. M. Differential PROTAC substrate specificity dictated by orientation of recruited E3 ligase. Nat. Commun. 2019 Jan 10, 10(1), 131. [CrossRef]
- Kofink C., Trainor N., Mair B., Wohrle S., Wurm M., Mischerikow N., Roy M.J., Bader G., Greb P., Garavel G., Diers E., McLennan R., Whitworth C., Vetma V., Rumpel K., Scharnweber M., Fuchs J.E., Gerstberger T., Cui Y., Gremel G., Chetta P., Hopf S., Budano N., Rinnenthal J., Gmaschitz G., Mayer M., Koegl M., Ciulli A., Weinstabl H., Farnaby W. A selective and orally bioavailable VHL-recruiting PROTAC achieves SMARCA2 degradation in vivo. Nat. Commun. 2022 Oct 10, 13(1), 5969. [CrossRef]
- Lu J., Huang, Y., Huang J., He R., Huang M., Lu X., Xu Y., Zhou F., Zhang Z., Ding K. Discovery of the first examples of threonine tyrosine kinase PROTAC degraders. J. Med. Chem. 2022 Feb 10, 65(3), 2313-2328. [CrossRef]
- Hu J., Hu B., Wang M., Xu F., Miao B., Yang C.-Y., Wang M., Liu Z. Hayes D.F., Chinnaswamy K., Delproposto J., Stuckey J., Wang S. Discovery of ERD-308 as a highly potent proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) degrader of estrogen receptor (ER). J. Med. Chem. 2019, 62, 1420−1442.
- Yokoo H., Shibata N., Naganuma M., Murakami Y., Fujii K., Ito T., Aritake K., Naito M., Demizu Y. Development of a hematopoietic prostaglandin D synthase-degradation inducer. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2021, 12, 236−241. [CrossRef]
- Khan S., Zhang X., Lv D., Zhang Q., He Y., Zhang P., Liu X., Thummuri D., Yuan Y., Wiegand J.S., Pei J., Zhang W., Sharma A., McCurdy C.R., Kuruvilla V.M., Baran N., Ferrando A.A., Kim Y., Rogojina A., Houghton P.J., Huang G., Hromas R., Konopleva M., Zheng G., Zhou D. A selective BCL-XL PROTAC degrader achieves safe and potent antitumor activity. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 1938−1947. [CrossRef]
- Li X., Song Y. Proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) for targeted protein degradation and cancer therapy. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2020, 13, 50.
- Zhao Q., Lan T., Su S., Rao Y. Induction of apoptosis in MDAMB-231 breast cancer cells by a PARP1-targeting PROTAC small molecule. Chem. Commun. (Camb). 2019 Jan 2, 55(3), 369-372. [CrossRef]
- Yan W., Pan B., Shao J., Lin H., Li H. Feasible column chromatography-free, multi-gram scale synthetic process of VH032 amine, which could enable rapid PROTAC library construction. ACS Omega. 2022 Jul 19, 7(30), 26015-26020. [CrossRef]
- Burslem G. M., Smith B. E., Lai A. C., Jaime-Figueroa S., McQuaid D. C., Bondeson D. P., Toure M., Dong H., Qian Y., Wang J., Crew A. P., Hines J., Crews C. M. The advantages of targeted protein degradation over inhibition: An RTK case study. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018, 25, 67−77.e3. [CrossRef]
- Jones L.H., Mitchell C.A., Loberg L., Pavkovic M., Rao M., Roberts R., Stamp K., Volak L., Wittwer M.B., Pettit S. Targeted protein degraders: a call for collective action to advance safety assessment. Nat. Rev. Drug Discovery. 2022, 21, 401−402. [CrossRef]
- Zeng S., Huang W., Zheng X., Cheng L., Zhang Z., Wang, J., Shen Z. Proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC) in drug discovery paradigm: Recent progress and future challenges. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021, 210, 112981. [CrossRef]
- Ottis, P.; Crews, C. M. Proteolysis-targeting chimeras: induced protein degradation as a therapeutic strategy. ACS Chem. Biol. 2017 Apr 21, 12(4), 892-898. [CrossRef]
- Bondeson D.P., Smith B.E., Burslem G.M., Buhimschi A.D., Hines J., Jaime-Figueroa S., Wang J., Hamman B. D., Ishchenko A., Crews C. M. Lessons in PROTAC design from selective degradation with a promiscuous warhead. Cell Chem. Biol. 2018 Jan 18, 25(1), 78-87.e5. [CrossRef]
- Cromm P. M., Samarasinghe K.T.G., Hines J., Crews C. M. Addressing kinase-independent functions of Fak via PROTAC mediated degradation. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2018 Dec 12, 140(49), 17019-17026. [CrossRef]
- Burslem G.M., Crews C.M. Proteolysis-targeting chimeras as therapeutics and tools for biological discovery. Cell. 2020 Apr 2,181(1), 102-114. [CrossRef]
- Cheng M., Yu X., Lu K., Xie L., Wang L., Meng F., Han X., Chen X., Liu J., Xiong Y., Jin J. Discovery of potent and selective epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) bifunctional small-molecule degraders. J. Med. Chem. 2020, 63, 1216−1232. [CrossRef]
- He K., Zhang Z., Wang W., Zheng X., Wang X., Zhang X. Discovery and biological evaluation of proteolysis targeting chimeras (PROTACs) as EGFR degraders based on osimertinib and lenalidomide. Bioorg. Med. Chem. Lett. 2020 Jun 15, 30(12), 127167. [CrossRef]
- Qu X., Liu H., Song X., Sun N., Zhong H., Qiu X., Yang X., Jiang B. Effective degradation of EGFRL858R+T790M mutant proteins by CRBN-based PROTACs through both proteosome and autophagy/lysosome degradation systems. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2021 Jun 5, 218, 113328. [CrossRef]
- Zhang X., Xu F., Tong L., Zhang T., Xie H., Lu X., Ren X., Ding K. Design and synthesis of selective degraders of EGFRL858R/T790M mutant. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020 Apr 15, 192, 112199. [CrossRef]
- Zhao H.-Y., Yang X.-Y., Lei H., Xi X.-X., Lu S.-M., Zhang J.-J., Xin M., Zhang S.-Q. Discovery of potent small molecule PROTACs targeting mutant EGFR. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020 Dec 15, 208, 112781. [CrossRef]
- Kabeya Y., Mizushima N., Ueno T., Yamamoto A., Kirisako T., Noda T., Kominami E., Ohsumi Y., Yoshimori T. LC3, a mammalian homologue of yeast Apg8p, is localized in autophagosome membranes after processing. EMBO J. 2000 Nov 1, 19(21), 5720-5728. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H., Zhao H.-Y., Xi X.-X., Liu Y.-J., Xin M., Mao S., Zhang J.-J., Lu A. X., Zhang S.-Q. Discovery of potent epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) degraders by proteolysis targeting chimera (PROTAC). Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2020 Mar 1, 189, 112061. [CrossRef]
- Zhao H.-Y., Wang H.P., Mao Y.Z., Zhang H., Xin M., Xi X-X., Lei H., Mao S., Li D.H, Zhang S-Q. Discovery of potent PROTACs targeting EGFR mutants through the optimization of covalent EGFR ligands. J. Med. Chem. 2022 Mar 24; 65(6), 4709-4726. [CrossRef]
- Ricordel C., Friboulet L., Facchinetti F., Soria J. C. Molecular mechanisms of acquired resistance to third-generation EGFR-TKIs in EGFR T790M-mutant lung cancer. Ann. Oncol. 2018 Jan 1, 29(suppl_1), 128-137. [CrossRef]
- Wang S. H., Tsui S. T., Liu C., Song Y. P., Liu D. L. EGFR C797S mutation mediates resistance to third-generation inhibitors in T790M-positive non-small cell lung cancer. J. Hematol. Oncol. 2016 Jul 22, 9(1), 59. [CrossRef]
- Zhang H., Xie R., AI-Furas H., Li Y., Wu Q., Li J., Xu F., Xu T. Design, synthesis, and biological evaluation of novel EGFR PROTACs targeting del19/T790M/C797S mutation. ACS Med. Chem. Lett. 2022 Jan 14, 13(2), 278-283. [CrossRef]
- Chen Y., Tandon I., Heelan W., Wang Y.X., Tang W.P., Hu Q.Y. Proteolysis-targeting chimera (PROTAC) delivery system: advancing protein degraders towards clinical translation. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022, 51, 5330−5350.
- Raina K., Lu J., Qian Y., Altieri M., Gordon D., Rossi A.M.K., Wang J., Chen X., Dong H.Q., Siu K., Winkler J.D., Crew A.P., Crews C.M., Coleman K.G. PROTAC-induced BET protein degradation as a therapy for castration-resistant prostate cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U. S. A. 2016, 113, 7124−7129.
- Moreau K., Coen M., Zhang A.X., Pachl F., Castaldi M.P., Dahl G., Boyd H., Scott C., Newham P. Proteolysis-targeting chimeras in drug development: A safety perspective. Brit. J. Pharmacol. 2020, 177, 1709−1718. [CrossRef]
- Hong K.B., An H. Degrader-antibody conjugates: Emerging new modality. J. Med. Chem. 2023 Jan 12, 66(1), 140-148. [CrossRef]
- Li K., Crews C.M. PROTACs: past, present and future. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022 Jun 20, 51(12), 5214-5236. [CrossRef]
- Dragovich P.S. Degrader-antibody conjugates. Chem. Soc. Rev. 2022 May 23, 51(10), 3886-3897. [CrossRef]
- Yu N., Huang L., Zhou Y., Xue T., Chen Z., Han G. Near-infrared-light activatable nanoparticles for deep-tissue-penetrating wireless optogenetics. Adv. Health. Mater. 2019 Mar, 8(6), e1801132. [CrossRef]
- Zhang Y., Zhang Y., Song G., He Y., Zhang X., Liu Y., Ju H. A DNA-azobenzene nanopump fueled by upconversion luminescence for controllable intracellular drug release. Angew. Chem. Int. Ed. Engl. 2019 Dec 9, 58(50), 18207-18211. [CrossRef]
- He Q., Zhou L., Yu D., Zhu R., Chen Y., Song M., Liu X., Liao Y., Ding T., Fan W., Yu W. Near-infrared-activatable PROTAC nanocages for controllable target protein degradation and on-demand antitumor therapy. J. Med. Chem. 2023 Jun 6. [CrossRef]
- Schirrmacher V. From chemotherapy to biological therapy: A review of novel concepts to reduce the side effects of systemic cancer treatment (Review). Int. J. Oncol. 2019 Feb, 54(2), 407-419. [CrossRef]
- Pirker, R. EGFR-directed monoclonal antibodies in non-small cell lung cancer. Target. Oncol. 2013 Mar, 8(1), 47-53. [CrossRef]
- Tabasinezhad M., Omidinia E., Talebkhan Y., Omrani M.D., Mahboudi F., Ghaedi H., Wenzel W. The effects of somatic mutations on EGFR interaction with anti-EGFR monoclonal antibodies: Implication for acquired resistance. Proteins, 2020 Jan, 88(1), 3-14. [CrossRef]
- Capdevila J., Elez E., Macarulla T., Ramos F.J., Ruiz-Echarri M., Tabernero J. Anti-epidermal growth factor receptor monoclonal antibodies in cancer treatment. Cancer Treat. Rev. 2009 Jun, 35(4), 354-363. [CrossRef]
- Ermondi G., Garcia-Jimenez D., Caron G. PROTACs and building blocks: The 2D chemical space in very early drug discovery. Molecules. 2021 Jan 28, 26(3), 672. [CrossRef]
- Weng G., Cai X., Cao D., Du H., Shen C., Deng Y., He Q., Yang B., Li D., Hou T. PROTAC-DB 2.0: an updated database of PROTACs. Nucleic Acids Res. 2023 Jan 6, 51(D1), D1367-D1372. [CrossRef]
- O'Brien Laramy M.N., Luthra S., Brown M.F., Bartlett D.W. Delivering on the promise of protein degraders. Nat Rev Drug Discov. 2023 May, 22(5), 410-427. [CrossRef]
- Li S., de Camargo Correia G.S., Wang J., Manochakian R., Zhao Y., Lou Y. Emerging targeted therapies in advanced Non-Small-Cell Lung Cancer. Cancers (Basel). 2023 May 24, 15(11), 2899. [CrossRef]
- Banik S.M., Pedram K., Wisnovsky S., Ahn G., Riley N.M., Bertozzi C.R. Lysosome- targeting chimaeras for degradation of extracellular proteins. Nature, 584 (2020) 291–297. [CrossRef]
- Li Z., Zhu C., Ding Y., Fei Y., Lu B. ATTEC: a potential new approach to target proteinopathies. Autophagy, 2020 Jan, 16(1), 185-187. [CrossRef]
- Takahashi D., Arimoto H. Targeting selective autophagy by AUTAC degraders. Autophagy, 2020 Apr, 16(4), 765-766. [CrossRef]
- Ji C.H., Lee M.J., Kim H.Y., Heo A. J., Park D.Y., Kim Y.K., Kim B.Y., Kwon Y.T. Targeted protein degradation via the autophagy-lysosome system: AUTOTAC (AUTOphagy-TArgeting Chimera). Autophagy, 2022, 18, 2259−2262.
- Ballabio A., Bonifacino J.S. Lysosomes as dynamic regulators of cell and organismal homeostasis. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 2020, 21, 101−118. [CrossRef]
- Ahn G., Banik S.M., Bertozzi C.R. Degradation from the outside in: Targeting extracellular and membrane proteins for degradation through the endolysosomal pathway. Cell Chem. Biol. 2021 Jul 15, 28(7), 1072-1080. [CrossRef]
- Hong D, Zhou B, Zhang B, Ren H, Zhu L, Zheng G, Ge M, Ge J. Recent advances in the development of EGFR degraders: PROTACs and LYTACs. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2022 Sep 5, 239, 114533. [CrossRef]
- Maity P., Chatterjee J., Patil K.T., Arora S., Katiyar M.K., Kumar M., Samarbakhsh A., Joshi G., Bhutani P., Chugh M., Gavande N.S., Kumar R. Targeting the epidermal growth factor receptor with molecular degraders: state-of-the-art and future opportunities. J. Med. Chem. 2023 Mar 9, 66(5), 3135-3172. [CrossRef]
- Li X., Liu Q., Xie X., Peng C., Pang Q., Liu B., Han B. Application of novel degraders employing autophagy for expediting medicinal research. J. Med. Chem. 2023 Feb 9, 66(3), 1700-1711. [CrossRef]
- Ahn G., Banik S.M., Miller C.L., Riley N.M., Cochran J.R., Bertozzi C.R. LYTACs that engage the asialoglycoprotein receptor for targeted protein degradation. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2021, 17, 937-946. [CrossRef]
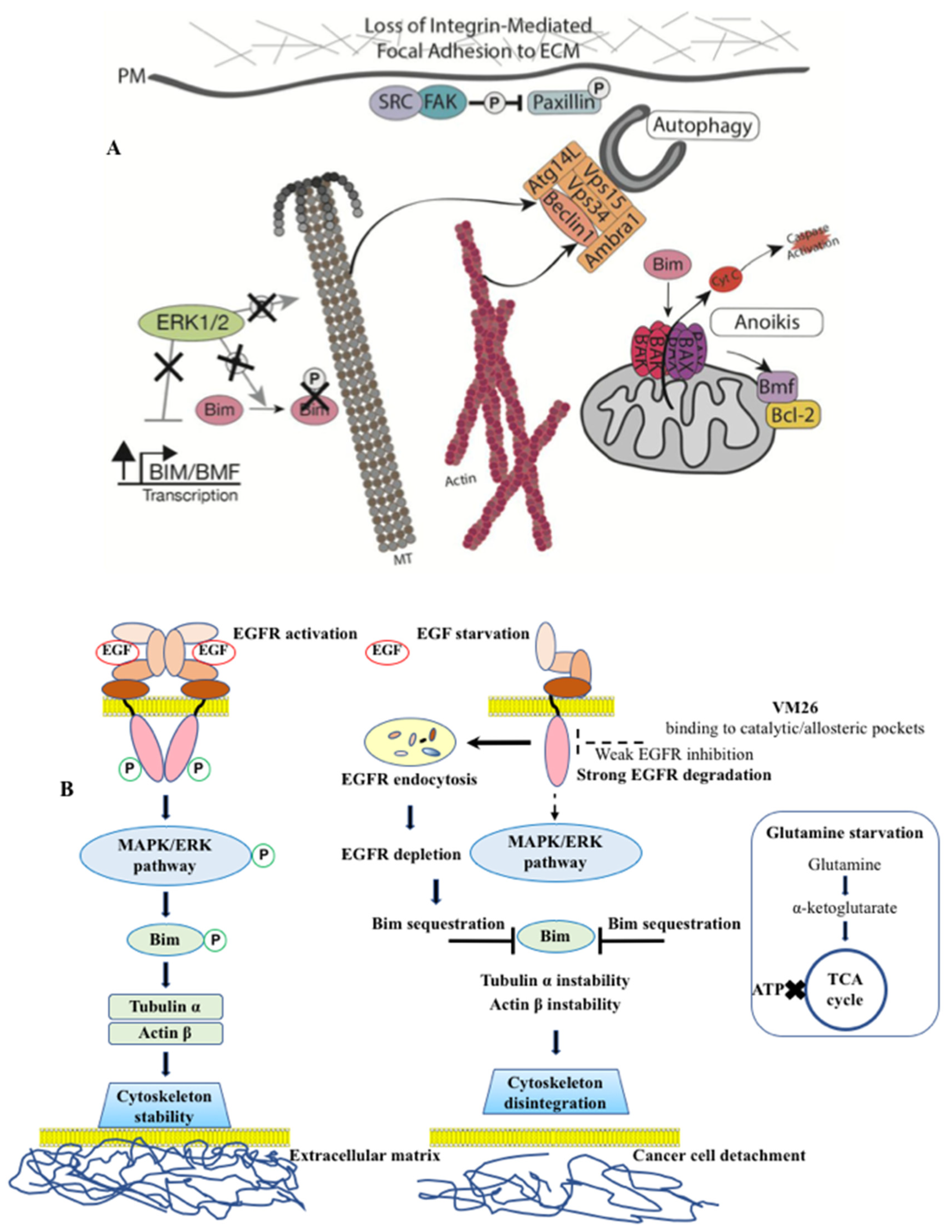
- Iradyan M., Iradyan N., Hulin P., Hambardzumyan A., Gyulkhandanyan A., Alves de Sousa R., Hessani A., Roussakis C., Bollot G., Bauvais C., Sakanyan V. Targeting degradation of EGFR through the allosteric site leads to cancer cell detachment-promoted death. Cancers (Basel). 2019 Aug 1, 11(8), 1094. [CrossRef]
- Foulkes W.D., Smith I.E., Reis-Filho J.S. Triple-negative breast cancer. N. Engl. J. Med. 2010 Nov 11, 363(20),1938-1948. [CrossRef]
- Tanida I., Ueno T., Kominami E. LC3 conjugation system in mammalian autophagy. Int. J. Biochem. Cell. Biol. 2004 Dec, 36(12), 2503-2518. [CrossRef]
- Taipale M., Jarosz D.F., Lindquist S. HSP90 at the hub of protein homeostasis: emerging mechanistic insights. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell. Biol. 2010 Jul, 11(7), 515-528. [CrossRef]
- Miyata Y., Nakamoto H., Neckers L. The therapeutic target Hsp90 and cancer hallmarks. Curr. Pharm. Des. 2013, 19(3), 347-365. [CrossRef]
- Citri A., Harari D., Shohat G., Ramakrishnan P., Gan J., Lavi S., Eisenstein M., Kimchi A., Wallach D., Pietrokovski S., Yarden Y. Hsp90 recognizes a common surface on client kinases. J. Biol. Chem. 2006 May 19, 281(20), 14361-14369. [CrossRef]
- Pick E., Kluger Y., Giltnane J.M., Moeder C., Camp R.L., Rimm D.L., Kluger H.M. High HSP90 expression is associated with decreased survival in breast cancer. Cancer Res. 2007 Apr 1, 67(7), 2932-2937. [CrossRef]
- Sakanyan V.A., Iradyan M.A., Iradyan N.S. Development of targeted EGFR degradation for cancer treatment. Nat. Academy Sci. Armenia Reports. 2022, 122(3), 218-227. [CrossRef]
- Paoli P., Giannoni E., Chiarugi P. Anoikis molecular pathways and its role in cancer progression. Biochim. Biophys. Acta. 2013 Dec,1833(12), 3481-3498. [CrossRef]
- V lahakis A., Debnath J. The Interconnections between autophagy and integrin-mediated cell adhesion. J. Mol. Biol. 2017 Feb 17, 429(4), 515-530. [CrossRef]
- Reginato M.J., Mills K.R., Paulus J.K., Lynch D.K., Sgroi D.C., Debnath J., Muthuswamy S.K., Brugge J.S. Integrins and EGFR coordinately regulate the pro-apoptotic protein Bim to prevent anoikis. Nat. Cell. Biol. 2003 Aug, 5(8), 733-740. [CrossRef]
- Chi X., Nguyen D., Pemberton J.M., Osterlund E.J., Liu Q., Brahmbhatt H., Zhang Z., Lin J., Leber B., Andrews D.W. The carboxyl-terminal sequence of bim enables bax activation and killing of unprimed cells. eLife. 2020, 9:e44525. [CrossRef]
- O’Connor L., Strasser A., O’Reilly L.A., Hausmann G., Adams J.M., Cory S., Huang D.C. Bim: a novel member of the Bcl-2 family that promotes apoptosis. EMBO J. 1998, 17, 384–395. [CrossRef]
- Wilfling F., Weber A., Potthoff S., Vögtle F.N., Meisinger C., Paschen S.A., Häcker G. BH3-only proteins are tail-anchored in the outer mitochondrial membrane and can initiate the activation of bax. Cell Death Differentiation 2012, 19, 1328–1336. [CrossRef]
- Gogada R., Yadav N., Liu J., Tang S., Zhang D., Schneider A., Seshadri A., Sun L., Aldaz C.M., Tang D.G., Chandra D. Bim, a proapoptotic protein, up-regulated via transcription factor E2F1-dependent mechanism, functions as a prosurvival molecule in cancer. J. Biol. Chem. 2013 Jan 4, 288(1), 368-381. [CrossRef]
- Singh R., Letai A., Sarosiek, K. Regulation of apoptosis in health and disease: the balancing act of BCL-2 family proteins. Nat. Rev. Mol. Cell Biol. 20, 175–193 (2019). [CrossRef]
- Tong J., Taylor P., Moran M.F. Proteomic analysis of the epidermal growth factor receptor (EGFR) interactome and post-translational modifications associated with receptor endocytosis in response to EGF and stress. Mol. Cell. Proteomics. 2014 Jul, 13(7), 1644-1658. [CrossRef]
- Galluzzi L., Vitale I., Aaronson S.A., Abrams J.M., Adam D., Agostinis P., Alnemri E.S., Altucci L., Amelio I., Andrews D.W. Molecular mechanisms of cell death: recommendations of the Nomenclature Committee on Cell Death 2018. Cell Death Differ., 2018, 25(3), 486-541. [CrossRef]
- Tang D., Kang R., Berghe T.V., Vandenabeele P., Kroemer G. The molecular machinery of regulated cell death. Cell Res., 2019, 29(5), 347-364. [CrossRef]
- Yan G., Elbadawi M., Efferth T. Multiple cell death modalities and their key features (Review). World Acad. Sci. J., 2020, 2, 39-48. [CrossRef]
- Le Gall M., Chambard J.C., Breittmayer J.P., Grall D., Pouyssegur J., Obberghen-Schilling E. The p42/p44 MAP kinase pathway prevents apoptosis induced by anchorage and serum removal. Mol. Biol. Cell, 2000, 11, 1103–1112. [CrossRef]
- Quadros M.R., Peruzzi F., Kari C., Rodeck U. Complex regulation of signal transducers and activators of transcription 3 activation in normal and malignant keratinocytes. Cancer Res., 2004, 64, 3934–3939. [CrossRef]
- Chamberlain P.P., Hamann L.G. Development of targeted protein degradation therapeutics. Nat. Chem. Biol. 2019 Oct, 15(10), 937-944. [CrossRef]
- Iradyan M.A., Iradyan N.S., Hambardzumyn A.A., Panosyan H.A., Tamazyan R.A., Ayvazyan A.G., Hovhannisyan G.S., Alves de sousa R., Sakanyan V.A. Selective N-, S-alkylation of 4-allyl-3-[2-(4-alkoxyphenyl)-quinolin-4-yl]-4,5-dihydro-1h-1,2,4-triazole-5-thiones with substituted benzylchlorides. synthesis, docking analysis and cytotoxic action. Chem. J. Arm. 2018, 71, 389–406.
- Iradyan M.A., Iradyan N.S., Hambardzumyan A.A., Minasyan N.S., Roussakis C., Sakanyan V.A. Synthesis of furfuryl derivatives of 4-allyl-1-(4-hydroxy-3-nitrobenzyl)-3-[2- (4-alkoxyphenyl)-quinolin-4-yl]-4,5-dihydro-1H-1,2,4-triazole-5-thions and their toxicity in cancer cells. Chem. J. Arm. 2018, 71, 559–570.
- Iradyan M.A., Iradyan N.S., Hambardzumyan A.A., Nersesyan L.E., Aharonyan A.S., Danielyan I.S., Muradyan R.E., Paronikyan R.V., Stepanyan G.M. Docking analysis and some biological properties of furfuryl derivatives of 4-allyl-5-[2-(4-alkoxyphenyl) quinolin-4-yl]-4H-1,2,4-triazol-3-thiol. Biol. J. Arm. 2018, 70, 100–107.

Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




