Submitted:
07 July 2023
Posted:
07 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
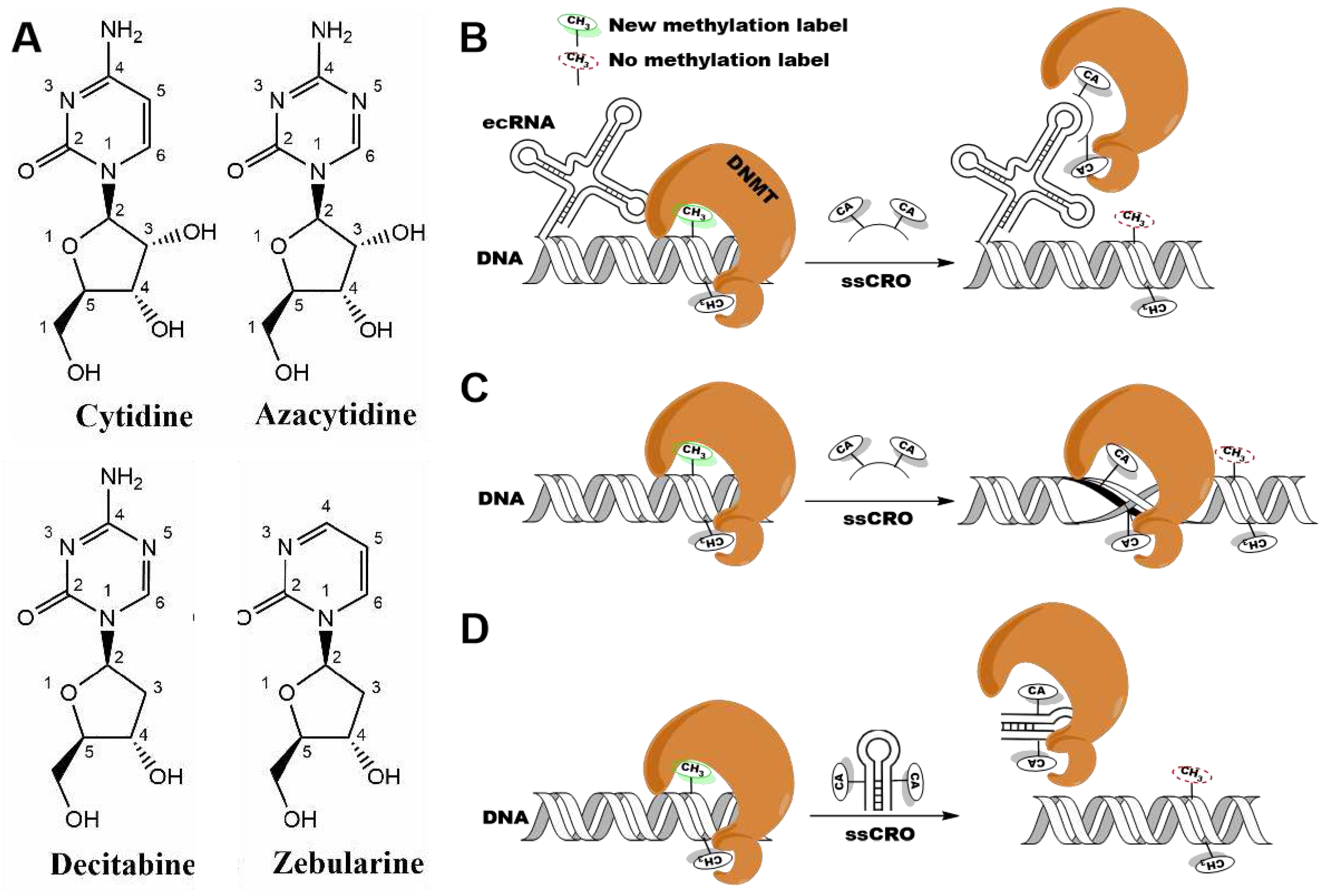
1. Introduction
2. Method
2.1. MD input preparation
2.2. MD process
2.3. QM/MM simulations.
3. Result
3.1. The characterization of the pre-reaction state.
3.2. Deprotonation of the Cys.
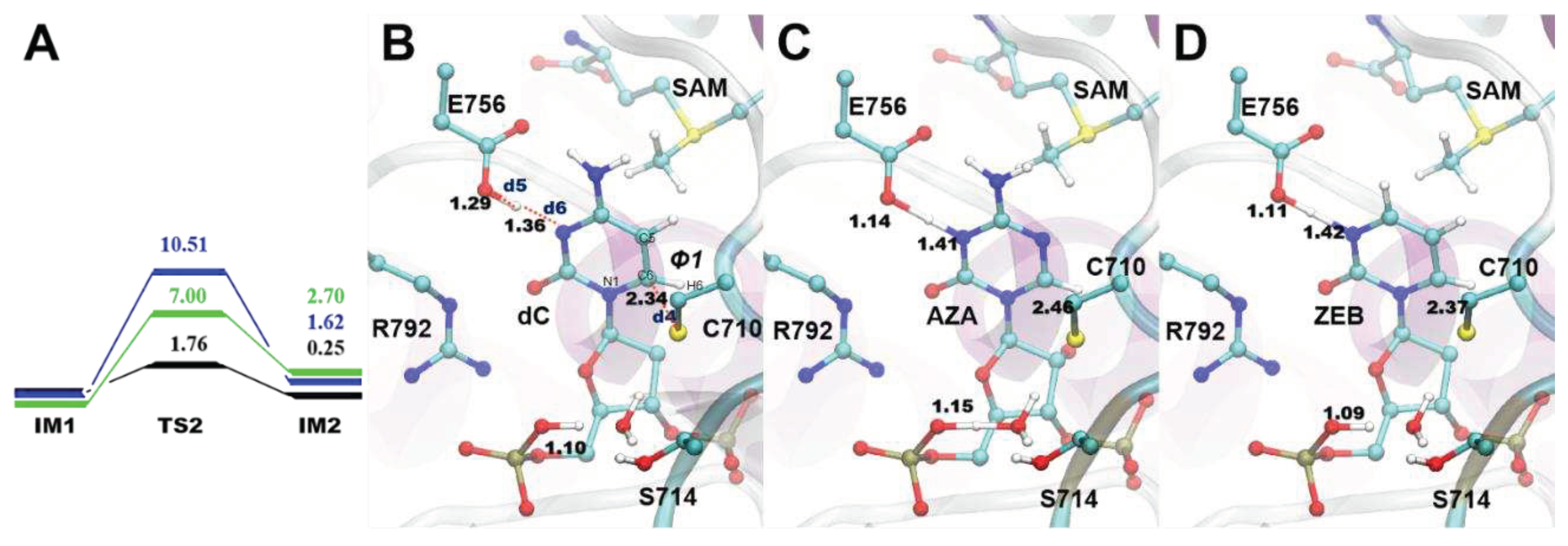
3.3. The S-C attack
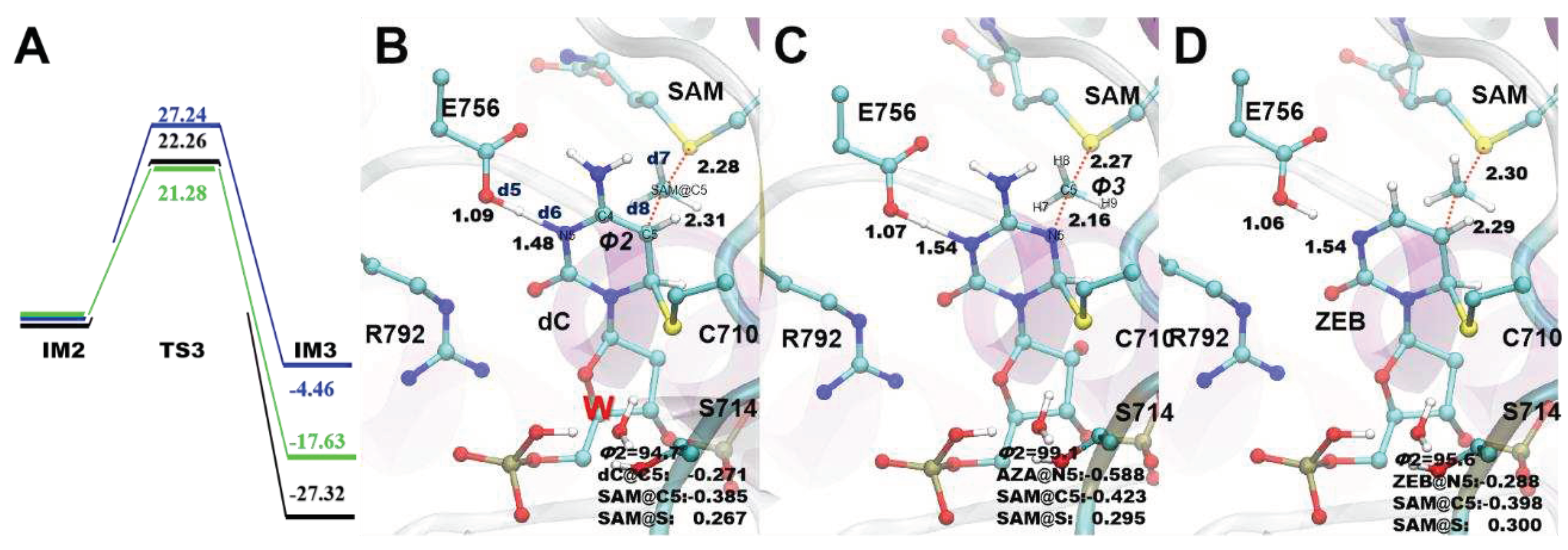
3.4. Methyl transfer process
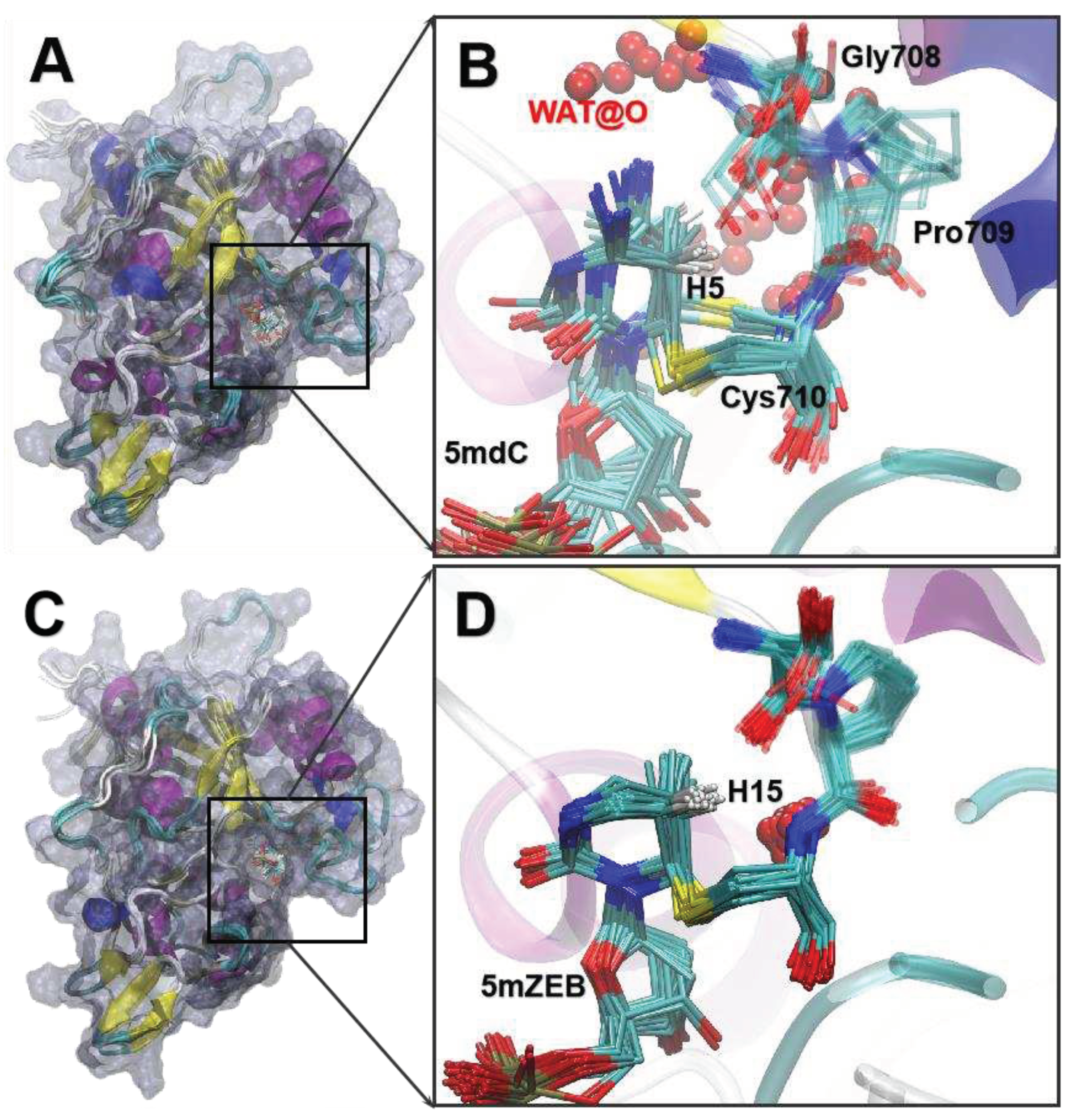
3.5. The MD of the IM3 states.
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Acknowledgments
References
- Riddihough, G.; Zahn, L.M. What is epigenetics? Assoc. Adv. Sci. 2010, 330, 611–611. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yoo, C.B.; Jones, P.A. Epigenetic therapy of cancer: Past, present and future. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2006, 5, 37–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ehrlich, M.; Wang, R.Y. 5-Methylcytosine in eukaryotic DNA. Science 1981, 212, 1350–1357. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- el-Deiry, W.S.; Nelkin, B.D.; Celano, P.; Yen, R.W.; Falco, J.P.; Hamilton, S.R.; Baylin, S.B. High expression of the DNA methyltransferase gene characterizes human neoplastic cells and progression stages of colon cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 1991, 88, 3470–3474. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Patra, S.K.; Patra, A.; Zhao, H.; Dahiya, R. DNA methyltransferase and demethylase in human prostate cancer. Mol. Carcinog. 2002, 33, 163–171. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Girault, I.; Lerebours, F.; Amarir, S.; Tozlu, S.l.; Tubiana-Hulin, M.; Lidereau, R.; Bièche, I. Expression analysis of estrogen receptor α coregulators in breast carcinoma: Evidence that NCOR1 expression is predictive of the response to tamoxifen. Clin. Cancer Res. 2003, 9, 1259–1266. [Google Scholar]
- Oh, B.K.; Kim, H.; Park, H.J.; Shim, Y.H.; Choi, J.; Park, C.; Park, Y.N. DNA methyltransferase expression and DNA methylation in human hepatocellular carcinoma and their clinicopathological correlation. Int. J. Mol. Med. 2007, 20, 65–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Melki, J.R.; Warnecke, P.; Vincent, P.C.; Clark, S.J. Increased DNA methyltransferase expression in leukaemia. Leukemia 1998, 12, 311–316. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jurkowska, R.Z.; Jurkowski, T.P.; Jeltsch, A. Structure and function of mammalian DNA methyltransferases. ChemBioChem 2011, 12, 206–222. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belinsky, S.A.; Nikula, K.J.; Baylin, S.B.; Issa, J.P.J. Increased cytosine DNA-methyltransferase activity is target-cell-specific and an early event in lung cancer. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. United States Am. 1996, 93, 4045–4050. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schubeler, D. Function and information content of DNA methylation. Nature 2015, 517, 321–326. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zeng, Y.; Ren, R.; Kaur, G.; Hardikar, S.; Ying, Z.; Babcock, L.; Gupta, E.; Zhang, X.; Chen, T.; Cheng, X. The inactive Dnmt3b3 isoform preferentially enhances Dnmt3b-mediated DNA methylation. Genes Dev 2020, 34, 1546–1558. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xu, P.; Hu, G.; Luo, C.; Liang, Z. DNA methyltransferase inhibitors: An updated patent review (2012-2015). Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2016, 26, 1017–1030. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Erdmann, A.; Halby, L.; Fahy, J.; Arimondo, P.B. Targeting DNA methylation with small molecules: what’s next? Miniperspective. J. Med. Chem. 2015, 58, 2569–2583. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Castillo-Aguilera, O.; Depreux, P.; Halby, L.; Arimondo, P.B.; Goossens, L. DNA methylation targeting: The DNMT/HMT crosstalk challenge. Biomolecules 2017, 7, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, C.H.; Marquez, V.E.; Mao, D.T.; Haines, D.R.; McCormack, J.J. Synthesis of pyrimidin-2-one nucleosides as acid-stable inhibitors of cytidine deaminase. J. Med. Chem. 1986, 29, 1374–1380. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.C.; Matsen, C.B.; Gonzales, F.A.; Ye, W.; Greer, S.; Marquez, V.E.; Jones, P.A.; Selker, E.U. Inhibition of DNA methylation and reactivation of silenced genes by zebularine. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stresemann, C.; Lyko, F. Modes of action of the DNA methyltransferase inhibitors azacytidine and decitabine. Int. J. Cancer 2008, 123, 8–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gabbara, S.; Bhagwat, A.S. The mechanism of inhibition of DNA (cytosine-5-)-methyltransferases by 5-azacytosine is likely to involve methyl transfer to the inhibitor. Biochem. J. 1995, 307, 87–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bowler, E.H.; Bell, J.; Divecha, N.; Skipp, P.; Ewing, R.M. Proteomic Analysis of Azacitidine-Induced Degradation Profiles Identifies Multiple Chromatin and Epigenetic Regulators Including Uhrf1 and Dnmt1 as Sensitive to Azacitidine. J. Proteome Res. 2019, 18, 1032–1042. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gros, C.; Fahy, J.; Halby, L.; Dufau, I.; Erdmann, A.; Gregoire, J.-M.; Ausseil, F.; Vispé, S.; Arimondo, P.B. DNA methylation inhibitors in cancer: Recent and future approaches. Biochimie 2012, 94, 2280–2296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Medina-Franco, J.L.; Méndez-Lucio, O.; Dueñas-González, A.; Yoo, J. Discovery and development of DNA methyltransferase inhibitors using in silico approaches. Drug Discov. Today 2015, 20, 569–577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fahy, J.; Jeltsch, A.; Arimondo, P.B. DNA methyltransferase inhibitors in cancer: A chemical and therapeutic patent overview and selected clinical studies. Expert Opin. Ther. Pat. 2012, 22, 1427–1442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abraham, M.J.; Murtola, T.; Schulz, R.; Páll, S.; Smith, J.C.; Hess, B.; Lindahl, E. GROMACS: High performance molecular simulations through multi-level parallelism from laptops to supercomputers. SoftwareX 2015, 1, 19–25. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, S.; Wang, Y.; Zhou, W.; Li, S.; Peng, J.; Shi, Z.; Hu, J.; Liu, Y.-C.; Ding, H.; Lin, Y. Identifying novel selective non-nucleoside DNA methyltransferase 1 inhibitors through docking-based virtual screening. J. Med. Chem. 2014, 57, 9028–9041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Datta, J.; Ghoshal, K.; Denny, W.A.; Gamage, S.A.; Brooke, D.G.; Phiasivongsa, P.; Redkar, S.; Jacob, S.T. A new class of quinoline-based DNA hypomethylating agents reactivates tumor suppressor genes by blocking DNA methyltransferase 1 activity and inducing its degradation. Cancer Res. 2009, 69, 4277–4285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.Z.; Chen, D.; Sun, Y.; Jin, Z.; Christman, J.K.; Yang, C.S. Reversal of hypermethylation and reactivation of p16INK4a, RARβ, and MGMT genes by genistein and other isoflavones from soy. Clin. Cancer Res. 2005, 11, 7033–7041. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fang, M.Z.; Wang, Y.; Ai, N.; Hou, Z.; Sun, Y.; Lu, H.; Welsh, W.; Yang, C.S. Tea polyphenol (−)-epigallocatechin-3-gallate inhibits DNA methyltransferase and reactivates methylation-silenced genes in cancer cell lines. Cancer Res. 2003, 63, 7563–7570. [Google Scholar]
- Fagan, R.L.; Cryderman, D.E.; Kopelovich, L.; Wallrath, L.L.; Brenner, C. Laccaic acid A is a direct, DNA-competitive inhibitor of DNA methyltransferase 1. J. Biol. Chem. 2013, 288, 23858–23867. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, J.; Zinovjev, K.; Swiderek, K.; Roca, M.; Tunon, I. Unraveling the Reaction Mechanism of Enzymatic C5-Cytosine Methylation of DNA. A Combined Molecular Dynamics and QM/MM Study of Wild Type and Gln119 Variant. ACS Catal. 2016, 6, 3262–3276. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aranda, J.; Attana, F.; Tunon, I. Molecular mechanism of inhibition of DNA methylation by zebularine. Acs Catal 2017, 7, 1728–1732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, L.; Shi, T.; Houk, K.N.; Zhao, Y. Understanding the R882H mutation effects of DNA methyltransferase DNMT3A: A combination of molecular dynamics simulations and QM/MM calculations. Rsc Adv 2019, 9, 31425–31434. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Zhuang, J.; Li, C.; Cheng, G.-J. Unveiling the Methyl Transfer Mechanisms in the Epigenetic Machinery DNMT3A-3L: A Comprehensive Study Integrating Assembly Dynamics with Catalytic Reactions. Comput. Struct. Biotechnol. J. 2023.
- Lamiable-Oulaidi, F.; Harijan, R.K.; Shaffer, K.J.; Crump, D.R.; Sun, Y.; Du, Q.; Gulab, S.A.; Khan, A.A.; Luxenburger, A.; Woolhouse, A.D.; et al. Synthesis and Characterization of Transition-State Analogue Inhibitors against Human DNA Methyltransferase 1. J. Med. Chem. 2022, 65, 5462–5494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Gao, Q.; Steine, E.J.; Barrasa, M.I.; Hockemeyer, D.; Pawlak, M.; Fu, D.; Reddy, S.; Bell, G.W.; Jaenisch, R. Deletion of the de novo DNA methyltransferase Dnmt3a promotes lung tumor progression. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2011, 108, 18061–18066. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhang, Z.M.; Lu, R.; Wang, P.; Yu, Y.; Chen, D.; Gao, L.; Liu, S.; Ji, D.; Rothbart, S.B.; Wang, Y.; et al. Structural basis for DNMT3A-mediated de novo DNA methylation. Nature 2018, 554, 387–391. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, F.-F.; Yang, W.; Shi, Y.-H.; Cheng, X.-R.; Le, G.-W. Structure-based approach for the study of thyroid hormone receptor binding affinity and subtype selectivity. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2016, 34, 2251–2267. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, W.; Hu, X. Discovery of high affinity receptors for dityrosine through inverse virtual screening and docking and molecular dynamics. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2018, 20, 115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, W.; Li, R.; Sui, Z.; Cheng, G.; Zhou, B. Molecular description of pyrimidine-based inhibitors with activity against FAK combining 3D-QSAR analysis, molecular docking and molecular dynamics. Arab. J. Chem. 2021, 14, 103144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, F.; Yang, W.; Liu, H.; Zhou, B. Identification of the structural features of quinazoline derivatives as EGFR inhibitors using 3D-QSAR modeling, molecular docking, molecular dynamics simulations and free energy calculations. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2022, 40, 11125–11140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, W.; Riley, B.T.; Lei, X.; Porebski, B.T.; Kass, I.; Buckle, A.M.; McGowan, S. Mapping the Pathway and Dynamics of Bestatin Inhibition of the Plasmodium falciparum M1 Aminopeptidase PfA-M1. ChemMedChem 2018, 13, 2504–2513. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, W.; Riley, B.T.; Lei, X.; Porebski, B.T.; Kass, I.; Buckle, A.M.; McGowan, S. Generation of AMBER force field parameters for zinc centres of M1 and M17 family aminopeptidases. J. Biomol. Struct. Dyn. 2018, 36, 2595–2604. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dolinsky, T.J.; Nielsen, J.E.; McCammon, J.A.; Baker, N.A. PDB2PQR: An automated pipeline for the setup of Poisson-Boltzmann electrostatics calculations. Nucleic Acids Res. 2004, 32, W665–667. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- D.A. Case, I.Y.B.-S., S.R. Brozell, D.S. Cerutti, T.E. Cheatham, III, V.W.D. Cruzeiro, T.A. Darden, R.E. Duke, D. Ghoreishi, M.K. Gilson, H. Gohlke, A.W. Goetz, D. Greene, R Harris, N. Homeyer, S. Izadi, A. Kovalenko, T. Kurtzman, T.S. Lee, S. LeGrand, P. Li, C. Lin, J. Liu, T. Luchko, R. Luo, D.J. Mermelstein, K.M. Merz, Y. Miao, G. Monard, C. Nguyen, H. Nguyen, I. Omelyan, A. Onufriev, F. Pan, R. Qi, D.R. Roe, A. Roitberg, C. Sagui, S. Schott-Verdugo, J. Shen, C.L. Simmerling, J. Smith, R. Salomon-Ferrer, J. Swails, R.C. Walker, J. Wang, H. Wei, R.M. Wolf, X. Wu, L. Xiao, D.M. York and P.A. Kollman, AMBER 18, University of California, San Francisco., 2018.
- Wang, J.; Wang, W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Automatic atom type and bond type perception in molecular mechanical calculations. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 2006, 25, 247–260. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayly, C.I.; Cieplak, P.; Cornell, W.D.; Kollman, P.A. A Well-Behaved Electrostatic Potential Based Method Using Charge Restraints for Deriving Atomic Charges - the Resp Model. J. Phys. Chem. 1993, 97, 10269–10280. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stephens, P.J.; Devlin, F.J.; Chabalowski, C.F.; Frisch, M.J. Ab-Initio Calculation of Vibrational Absorption and Circular-Dichroism Spectra Using Density-Functional Force-Fields. J. Phys. Chem. 1994, 98, 11623–11627. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Frisch, M.J.; Trucks, G.W.; Schlegel, H.B.; Scuseria, G.E.; Robb, M.A.; Cheeseman, J.R.; Scalmani, G.; Barone, V.; Mennucci, B.; Petersson, G.A.; et al. Gaussian 09, Gaussian, Inc.: Wallingford, CT, USA, 2009.
- Wang, J.; Wolf, R.M.; Caldwell, J.W.; Kollman, P.A.; Case, D.A. Development and testing of a general amber force field. J. Comput. Chem. 2004, 25, 1157–1174. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maier, J.A.; Martinez, C.; Kasavajhala, K.; Wickstrom, L.; Hauser, K.E.; Simmerling, C. ff14SB: Improving the Accuracy of Protein Side Chain and Backbone Parameters from ff99SB. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2015, 11, 3696–3713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ivani, I.; Dans, P.D.; Noy, A.; Perez, A.; Faustino, I.; Hospital, A.; Walther, J.; Andrio, P.; Goni, R.; Balaceanu, A.; et al. Parmbsc1: A refined force field for DNA simulations. Nat. Methods 2016, 13, 55–58. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jorgensen, W.L.; Chandrasekhar, J.; Madura, J.D.; Impey, R.W.; Klein, M.L. Comparison of Simple Potential Functions for Simulating Liquid Water. J. Chem. Phys. 1983, 79, 926–935. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Essmann, U.; Perera, L.; Berkowitz, M.L.; Darden, T.; Lee, H.; Pedersen, L.G. A Smooth Particle Mesh Ewald Method. J. Chem. Phys. 1995, 103, 8577–8593. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smith, W.; Forester, T. ChemShell-amodular software package for QM/MM simulation. J. Mol. Graph. Model. 1996, 14, 136–141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smith, W.; Yong, C.W.; Rodger, P.M. DL_POLY: Application to molecular simulation. Mol. Simul. 2002, 28, 385–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Vries, A.H.; Sherwood, P.; Collins, S.J.; Rigby, A.M.; Rigutto, M.; Kramer, G.J. Zeolite structure and reactivity by combined quantum-chemical− classical calculations. J. Phys. Chem. B 1999, 103, 6133–6141. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Billeter, S.R.; Turner, A.J.; Thiel, W. Linear scaling geometry optimisation and transition state search in hybrid delocalised internal coordinates. Phys. Chem. Chem. Phys. 2000, 2, 2177–2186. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senn, H.M.; Kastner, J.; Breidung, J.; Thiel, W. Finite-temperature effects in enzymatic reactions - Insights from QM/MM free-energy simulations. Can. J. Chem. 2009, 87, 1322–1337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, P.; Zhang, Y. Catalytic mechanism and product specificity of the histone lysine methyltransferase SET7/9: An ab initio QM/MM-FE study with multiple initial structures. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2006, 128, 1272–1278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Senn, H.M.; Thiel, S.; Thiel, W. Enzymatic Hydroxylation in p-Hydroxybenzoate Hydroxylase: A Case Study for QM/MM Molecular Dynamics. J. Chem. Theory Comput. 2005, 1, 494–505. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X.; Bruice, T.C. The mechanism of M.HhaI DNA C5 cytosine methyltransferase enzyme: A quantum mechanics/molecular mechanics approach. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2006, 103, 6148–6153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zangi, R.; Arrieta, A.; Cossio, F.P. Mechanism of DNA methylation: The double role of DNA as a substrate and as a cofactor. J. Mol. Biol. 2010, 400, 632–644. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, J.; Lior-Hoffmann, L.; Wang, S.; Zhang, Y.; Broyde, S. DNA cytosine methylation: Structural and thermodynamic characterization of the epigenetic marking mechanism. Biochemistry 2013, 52, 2828–2838. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheng, J.C.; Matsen, C.B.; Gonzales, F.A.; Ye, W.; Greer, S.; Marquez, V.E.; Jones, P.A.; Selker, E.U. Inhibition of DNA methylation and reactivation of silenced genes by zebularine. J. Natl. Cancer Inst. 2003, 95, 399–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shieh, F.-K.; Reich, N.O. AdoMet-dependent methyl-transfer: Glu119 is essential for DNA C5-cytosine methyltransferase M. HhaI. HhaI. J. Mol. Biol. 2007, 373, 1157–1168. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]


Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




