Submitted:
06 July 2023
Posted:
07 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Genetic Polymorphisms Associated with Susceptibility COVID-19
2.1. ACE2
2.2. IFNAR2
2.3. OAS
| Gene | SNP | Patient # | SNP Effects | Significans | Features | Population | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| IFNAR2 | rs 2236757 G/A | 694 | Associated with severe forms of COVID-19 and increased mortality | p = 0,031 | In patients of non-white ethnicity, the presence of the A allele was linked to an increased risk of both intensive care unit (ICU*) admission and mortality | Brazil population | [21] |
| 2244 | Associated with severe forms of COVID-19 | p < 0,005 | The A allele demonstrated an association with an elevated risk of developing severe COVID-19. Additionally, lower expression of IFNAR2 was observed in individuals with life-threatening cases of COVID-19 | UK population | [19] | ||
| 1202 | Associated with mortality risk among patients with severe COVID-19 | p = 0,023 | N/A | Mexico population | [20] | ||
| ACE2 | rs 2074192 G/A | 318 | Associated with the disease severity caused by SARS-CoV-2 | p = 0,016 | Heterozygosity of rs2074192 was identified as a protective factor against COVID-19 infection in women | Spain population | [81] |
| rs 2074192 C/T | 104 | Correlated with more severe outcomes of SARS-CoV-2 infection | p = 0,0088 (for female) p < 0,0001 (for male) |
The T allele exhibited a higher prevalence in symptomatic patients compared to asymptomatic individuals | Italian population | [55] | |
| 293 | Was not associated with COVID-19 | p > 0,005 | The ACE2 rs2074192 variant does not confer a predisposition to the development of long-COVID symptoms in individuals who were previously hospitalized due to COVID-19 | Spain population | [59] | ||
| 191 | Was not associated with COVID-19 | p > 0,005 | N/A | China population | [58] | ||
| 481 | Was not associated with COVID-19 | Severe: p = 0,49 Critical: p = 0,6 |
N/A | Mexico population | [57] | ||
| 456 | Associated with COVID-19 | p < 0,001 | Rs2074192 may potentially correlate with susceptibility to COVID-19-related cardiovascular complications and acute inflammatory infections | China population | [56] | ||
| 188 | Associated with an increased risk of a more severe disease course of SARS-CoV-2 infection | p = 0,002 | A strong correlation was observed between the TT-genotype of ACE2 rs2074192 and unfavorable outcomes in individuals with severe forms of COVID-19 | [54] | |||
| OAS1 | rs10774671 A allele | 3084 | Associated with susceptibility to COVID-19 | Europeans: p < 0,005; Africans: p = 0,079 |
The presence of the A allele in rs10774671 may lead to decreased expression of OAS1, thereby increasing the specific human risk of developing severe COVID-19 | Europeans, Asians, Africans, African American, Hispanic | [80] |
| OAS3 | rs10735079 A/G | 2244 | Associated with severe forms of COVID-19 | p < 0,001 | N/A | UK population | [19] |
3. Genetic Polymorphisms Associated with Susceptibility to MAFLD
3.1. PNPLA3
3.2. TM6SF2
3.3. GCKR
3.4. LYPLAL1
| Gene | SNP | The number of patients | SNP Effects | Significance | Features | NAFLD diagnosed by | Population | Reference(s) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNPLA3 | rs738409 C > G (I148M) | 9515 | Associated with NAFLD risk, steatosis and NASH | p > 0,001 | Hepatic fat content exhibited a more than twofold increase in PNPLA3-148M homozygotes compared to individuals without this genetic variant | H-MRS | African American; European American; Hispanic; | [84] |
| 1117 | Associated with steatosis and histological severity of NAFLD | p = 0,039 steatosis); p < 0,001 (portal inflammation);, p = 0.004 (NAS); p < 0.001 (fibrosis | The presence of the G allele in rs738409 was associated with the development of steatosis and greater histological severity of NAFLD. In pediatric patients, the high-risk G allele in rs738409 was linked to an earlier onset of the disease | Histologically | Americans (894 adults/223 children) | [116] | ||
| 1092 | Associated with steatosis and hepatocyte ballooning | p > 0,001 (steatosis); p=0,006 (ballooning); | PNPLA3 rs738409 G allele was correlated with liver steatosis and an elevated risk of progression from simple steatosis to NASH | Histologically | Americans | [43] | ||
| 126 | Increased the risk for NAFLD | p < 0,001 | The risk of NAFLD increased by 3,7-fold in subjects carrying the PNPLA3 GG genotype | Ultrasonography | Hispanic children | [117] | ||
| 1709 | Associated with NAFLD steatosis | p < 0,001 | The G allele was associated with elevated levels ALT, HOMA-IR*, and insulin | Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) | African Americans; Japanese Americans; Latinos; Native Hawaiians; European Americans |
[118] | ||
| 7176 | Associated with NAFLD risk and steatosis | p < 0,001 (both) | N/A | CT, Histologically | European population | [38] | ||
| 417 | Associated with steatosis | p < 0,0001 | Individuals with the PNPLA3 GG genotype at rs738409 exhibited 2,7-fold higher liver fat content compared to those with the CC genotype | proton NMR (Proton nuclear magnetic resonance) | Finnish population | [119] | ||
| 405 | Associated with the ultrasonography-determined steatosis | p < 0,001 | The 148M allele was linked to reduced levels of LDL-C* in patients with NAFLD | Ultrasonography | Chinese population | [120] | ||
| 1027 | Associated with NAFLD and moderate-to-severe steatosis | p = 0,006 (NAFLD); p = 0,001 (steatosis). | The G-allele of PNPLA3 rs738409 exhibited an association with NAFLD and a 1,09 IU/L increase in ALT levels | Ultrasonography | Chinese children | [121] | ||
| 768 | Associated with NAFLD | p = 0.00087 | PNPLA3 GC and GG genotypes were significantly linked to an elevated risk of the disease | Ultrasonography | Chinese population. | [113] | ||
| 4300 | Associated with hepatic steatosis, and developed NAFLD and liver fibrosis | p <0,001 (NAFLD) |
Compared to CC homozygotes, GG homozygotes presented higher liver fat and liver fibrosis scores, despite having a better metabolic status (P < 0,05) | Ultrasonography | Chinese population | [122] | ||
| 879 | Associated with NAFLD and insulin resistance | p = 0,004 | The prevailing paradigm surrounding the PNPLA3 I148M (GG+GC) polymorphism indicates a positive correlation with elevated waist circumference, fasting insulin levels, HOMA-IR* scores, as well as higher concentrations of ALT and ferritin | Ultrasonography | Normoglycaemic population | [123] | ||
| 270 | Associated with NAFLD risk, steatosis, and fibrosis | p < 0,001 (NAFLD); p = 0,0003 (steatosis); p = 0,0445 (fibrosis) |
Characterized by a pattern of steatosis, inflammation, and fibrosis, which are interconnected factors | Histologically | German population (70 adolescents; 200 adult control cohort) | [124] | ||
| 515 | Associated with liver steatosis, and fibrosis | p < 0,001 (steatosis); p < 0,001 (fibrosis) |
The presence of the PNPLA3 risk allele exhibited heightened serum AST and ALT activities, with statistical significance observed at a p-value less than 0,05 | Histologically (320 biopsied patients) | German population | [125] | ||
| 1326 | Associated with steatosis, NAS* and fibrosis | p < 0,001 (NAFLD); p = 0,0016 (steatosis); p < 0,001 (NAS*) |
The PNPLA3 risk allele was found to be linked with elevated levels of AST and ALT in individuals diagnosed with NAFLD | Histologically and CT | Japanese population | [126] | ||
| 445 | Associated with NAFLD risk, steatosis, fibrosis, and cirrhosis | p < 0,001 (NAFLD) |
The ability to export VLDLs* from the liver is influenced by certain factors. | Ultrasonography | Italian population | [127] | ||
| 574 | Associated with the severity of steatosis and fibrosis and the presence of NASH | 95% CI = 1,04-1,76 (steatosis); CI = 1,12-2,04 (NASH) |
The G allele was observed to be disproportionately transmitted to children affected by the condition | Histologically | Italian (253) and United Kingdom (321) population | [128] | ||
| 246 | Associated with the risk of cirrhotic evolution | р < 0,001 | In the NAFLD population, each copy of the G allele was found to be associated with nearly a twofold increase in the risk of cirrhosis. Furthermore, individuals who were GG homozygous exhibited a tripled risk compared to those who were CC homozygous | Histologically | Italian population | [89] | ||
| 1380 | Associated with NAFLD risk, steatosis, NASH, fibrosis, cirrhosis and HCC* | p < 0,0001 (steatosis, NASH, fibrosis); p = 0,0007 (cirrhosis) |
Such results are caused by the co-presence of the 3 at-risk variants: rs738409 C>G (PNPLA3 I148M), rs58542926 C>T (TM6SF2 E167K), and rs641738 C>T MBOAT7 | Histologically | European population | [129] | ||
| 470 | Associated with NAFLD risk, steatosis and NASH | p < 0.001 (steatosis); p < 0,001 (lobular inflammation); p = 0,002 (ballooning) | The presence of specific features of steatohepatitis was found to be linked to the identified factor, but no significant associations were observed with liver fibrosis, anthropometry (body measurements), or insulin resistance | Histologically | Belgian population | [130] | ||
| 285 | Associated with NAFLD risk and NASH | p = 0,002 (NAFLD); p <0,001 (NASH) |
While the PNPLA3 genotype did not exhibit an association with the grade of steatosis, individuals with GG homozygosity had an increased likelihood of significant NASH activity and fibrosis | Ultrasonography | Brazilian population | [131] | ||
| 342 | Associated with NAFLD risk, NASH severity and fibrosis | p < 0,0001 (NAFLD); p < 0,0001 (NASH); p = 0,013 (fibrosis) |
No associations were identified between the PNPLA3 genotype and simple steatosis or other histological parameters | Histologically | Chinese, Indian and Malay | [132] | ||
| 365 | Associated with the development of NAFLD and the severity of liver histology | p = 0,002 (NAFLD development); p < 0,005 (NAFLD severity) |
Patients who possessed the PNPLA3 GG genotype exhibited higher levels of NAS* compared to those with the PNPLA3 CC genotype | Histologically | Turkish population | [133] | ||
| 225 | Associated with NAFLD and NASH risk, and fibrosis | p = 0,04 (NASH); p = 0,016 (fibrosis) |
The GG genotype demonstrated an association with decreased platelet counts | Histologically | Turkish population | [134] | ||
| 232 | Associated with NAFLD, fibrosis but not steatosis | 95% [CI] = 1,98-6,71 (NAFLD) |
No significant associations were found between the GG genotype and body mass index, triglyceride levels, high- and low-density lipoprotein levels, or diabetes, as well as the steatosis grade (with a p-value greater than 0,05) | Histologically | Chinese population | [135] | ||
| 904 | Associated with NAFLD in lean individuals | p = 0,003 (NAFLD) |
Among individuals diagnosed with (NAFLD, a higher frequency of lean subjects (30.3%) carried the PNPLA3 rs738409 GG genotype compared to overweight (17.9%) and obese subjects (17.4%) | Proton-magnetic resonance spectroscopy | Chinese population | [136] | ||
| 831 | Associated with NAFLD and fibrosis, but not steatosis | p < 0,0001 (NAFLD); p = 0,011 (fibrosis) |
The GG genotype was associated with elevated levels of AST (p = 0,00013), ALT (p < 0,0001), and ferritin (p = 0,014) | Histologically | Japanese population | [137] | ||
| 1461 | Associated with NAFLD and NASH | p < 0,0001 (NAFLD, NASH) | Was also linked to hyaluronic acid levels, HbA1c* levels, and iron deposition in the liver | Histologically | Japanese population | [138] | ||
| 339 | Associated with NAFLD and fibrosis | p = 0,028 (NAFLD); p = 0,01 (fibrosis) |
Within the NAFLD patient population, the frequency of CG+GG genotypes was significantly higher in individuals with advanced fibrosis | Ultrasonography | Korean population | [139] | ||
| 1363 | Associated with NAFLD | p < 0,0001 (NAFLD) | Carriers of the rs738409-G allele had a 1,19-fold increased risk for NAFLD and exhibited significantly lower levels of visceral and subcutaneous adiposity, body mass index, triglycerides, and insulin resistance compared to CC carriers | Ultrasonography and CT | Korean population | [140] | ||
| 244 | Associated with NAFLD, NASH risk. | p < 0,0005 (NAFLD); p < 0,05 (NASH) | N/A | Proton magnetic resonance spectroscopy | Indian population | [141] | ||
| 335 | Associated with NAFLD risk | p = 0,04 (NAFLD) | The presence of the G allele exhibited a significant association with higher levels of fasting insulin, HOMA-IR*, ALT, and AST values specifically among affected cases, while no such association was observed in the control group | Ultrasonography | Asian Indians | [142] | ||
| 200 | Associated with NAFLD risk and steatosis | p < 0,05 (steatosis) | Patients carrying the G allele demonstrated elevated levels of ALT, dyslipidemia, and insulin resistance | Ultrasonography | Indian population | [143] | ||
| 306 | Associated with NAFLD risk | p = 0,001 (NAFLD) | PNPLA3 gene polymorphism was found to be linked to higher levels of ALT | Ultrasonography | Indian population | [144] | ||
| 207 | Associated with NAFLD risk | p < 0,001 (NAFLD) | The PNPLA3 rs738409 gene polymorphism significantly increases the risk of NAFLD by up to four-fold in individuals with elevated triglyceride levels | Ultrasonography | Indian population | [145] | ||
| 224 | Associated with NAFLD, NASH, fibrosis, and cirrhosis. | p < 0,05 | The GG genotype exhibited a 20,25-fold higher odds of developing NAFLD, as well as a 6,53-fold higher odds of experiencing non-alcoholic steatohepatitis (NASH) | Ultrasonography | Indian population | [146] | ||
| 144 | Associated with MAFLD | p = 0,017 | In a multivariable analysis, hypertriglyceridemia, BMI, and the PNPLA3 GG genotype were identified as factors associated with MAFLD | CT, MRT | Chinese population. | [147] | ||
| 143 | Associated with NAFLD | p = 0,002 | The presence of PNPLA3 risk alleles impairs the response to dietary interventions in individuals diagnosed with NAFLD | Ultrasonography | German population | [148] | ||
| 525 | Associated with NASH and fibrosis | p = 0,008 (NASH); p = 0,020 (fibrosis) |
The PNPLA3 genotype showed an association with the HOMA-IR* and insulin resistance in adipose tissue | Histologically | Korean population | [149] | ||
| 211 | Associated with NAS* (NAFLD Activity Score) | NAS: ≤2 vs ≥3, p = 0,667; ≤4 vs ≥5, p = 0,034) |
The PNPLA3 genotype was found to have a partial impact on the NAFLD activity score |
Histologically | Japanese population | [150] | ||
| 4804 | Associated with steatosis | p = 0,01 | The presence of PNPLA3 variants was found to be associated with elevated levels of ALT | Ultrasonography | Non-Hispanic white, non-Hispanic black, and Mexican American participants in the US population | [151] | ||
| 797 | Associated with NAFLD | p = 0,008 | PNPLA3 variants may contribute to the susceptibility of NAFLD in obese individuals across various ethnic groups | Ultrasonography | Chinese children | [105] | ||
| 307 | Associated with NAFLD | p < 0,01 | No significant effect modification was observed with BMI | FibroScan | Mexican population | [114] | ||
| 382 | Associated with NAFLD, and fibrosis | p = 0,0044 (NAFLD); p = 0,0272 (fibrosis) |
Individuals with the PNPLA3 GG genotype had a significantly increased risk (3,29-fold) of developing NAFLD compared to those with the CC genotype | Histologically | Brazilian population | [152] | ||
| 349 | Increased the risk of NAFLD | p = 0,29 | Although the presence of the GG genotype showed a 1.39 times increased risk of NAFLD, this association did not reach statistical significance | Histologically and Ultrasonography | Turkey population | [153] | ||
| GCKR | rs780094 C > T | 1092 | Was not associated with NAFLD | p > 0,05 | The GCKR SNP rs780094 exhibited a significant association with elevated serum triglyceride levels (p = 0,04) | Histologically | American | [43] |
| 270 | Associated with NAFLD risk, steatosis, and especially fibrosis | p = 0,0281 (NAFLD); p = 0,0275 (fibrosis) |
In individuals with the rs738409 G/G genotype, proteome profiling analysis revealed a reduction in the levels of GCKR protein and a downregulation of the retinol pathway | Histologically | German population (70 adolescents; 200 adult control cohort) | [124] | ||
| 7176 | Associated with NAFLD risk and steatosis | p < 0,001 (NAFLD risk); p = 0,01 (steatosis) |
N/A | CT; Histologically | European population | [38] | ||
| 4804 | Associated with steatosis | p = 0,03 | Was associated with a high level of ALT | Ultrasonography | Non-Hispanic white, non-Hispanic black, and Mexican American participants in the US population | [151] | ||
| 366 | Associated with the severity of liver fibrosis | p < 0,001 | Associated with higher serum triglyceride levels (p = 0,02) | Histologically | Italian population | [154] | ||
| 797 | Associated with NAFLD | p = 0,008 | Associated with higher mean serum ALT concentration | Ultrasonography | Chinese children | [105] | ||
| 620 | Associated with NAFLD | 95% CI: 1,14-1,28 (NAFLD) | Demonstrated an association with specific dietary habits, such as the consumption of soda, eggs, and soybean. | Ultrasonography | Uyghur population | [115] | ||
| 342 | Associated with NAFLD, NASH, and fibrosis | p = 0,013 (NAFLD); р = 0,012 ( NASH); p = 0,038 ( fibrosis) |
The combined effect of GCKR and adiponutrin rs738409 indicated a substantially increased risk of NAFLD (p = 0,010) | Histologically | Malaysians (Malays, Chinese, and Indians) | [106] | ||
| 903 | Associated with NAFLD | p = 0,0072 | The T-allele of GCKR rs780094 showed a significant association with an elevation in fasting triglyceride levels | Ultrasonography | Chinese population | [107] | ||
| TM6SF2 | rs58542926 C>T | 768 | Associated with NAFLD | p = 0,0016 | The T allele of TM6SF2 rs58542926 showed a higher prevalence among subjects diagnosed with NAFLD | Ultrasonography | Chinese population | [113] |
| 515 | Associated with NAFLD risk and steatosis but not fibrosis | p = 0,003 (steatosis) | Associated with significantly increased AST but not ALT | Histologically (320 biopsied patients) | German population | [125] | ||
| 445 | Associated with NAFLD risk | p = 0,008 (NAFLD) | Affects the liver's ability to export very low-density lipoproteins (VLDLs) | Ultrasonography | Italian population | [127] | ||
| 1380 | Associated with NAFLD risk, steatosis, NASH, fibrosis, cirrhosis and HCC* | p < 0,0001 (steatosis, NASH, fibrosis); p = 0,0007 (cirrhosis) |
Such results are caused by the co-presence of the 3 at-risk variants: rs738409 C > G (PNPLA3 I148M), rs58542926 C>T (TM6SF2 E167K), and rs641738 C > T MBOAT7 | Histologically | European population | [129] | ||
| 3260 | Associated with NAFLD | p = 0,02 | No significant effect on inflammation was observed for the rs58542926 T allele | Histologically | International | [155] | ||
| 361 | Associated with NAFLD, steatosis and disease severity | p = 0,038 (NAFLD) | rs58542926 was not associated with levels of liver enzymes, lobular inflammation and fibrosis | Ultrasonography and Histologically | Argentina population | [101] | ||
| 300 | Associated with liver fat | p < 0,05 | Individuals with this variant exhibit preserved insulin sensitivity in relation to processes such as lipolysis and hepatic glucose production, and they do not typically experience hypertriglyceridemia | H-MRS | Finnish population | [156] | ||
| 143 | Associated with NAFLD | p = 0,041 | The presence of TM6SF2 risk alleles hinders the response to dietary interventions in individuals diagnosed with NAFLD | Ultrasonography | German population | [148] | ||
| 1010 | Associated with steatosis | p < 0,0001 (steatosis) | It is associated with higher levels of ALT and lower levels of total cholesterol, low-density lipoprotein cholesterol, triglycerides, and non-high-density lipoprotein cholesterol | Ultrasonography | Italian children | [157] | ||
| 878 | Associated with steatosis | p = 0,002 | Carriers of the TM6SF2 167K variant have a threefold increased risk of developing hepatic steatosis, which often manifests early in life | Ultrasonography | Italian children | [158] | ||
| 957 | Associated with NAFLD risk, steatosis and fibrosis | p = 0,05 (NAFLD); p < 0,05 (steatosis) |
Associated with high HFF% in Caucasians and African Americans, with high ALT levels in Hispanics and with a more favorable lipoprotein profile in Caucasians and Hispanics | Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and Histologically | Caucasians, African, Americans, and Hispanics children and adolescents | [42] | ||
| 1074 | Associated with NAFLD risk, steatosis, NASH, advanced hepatic fibrosis | p = 0,0008 (NAFLD); P < 0,001 (steatosis); p = 0,039 (NASH); p = 0,0074 (fibrosis) |
Carriage of the TM6SF2 variant does not appear to further increase HCC* risk independent of its effect on fibrosis stage | Histologically | Caucasians and Europeans | [99] | ||
| 316 | Associated with NAFLD risk and steatosis | p = 0,003 (NAFLD); p = 0.023 (steatosis) |
Associated with increased ALT but no other clinical parameters, such as AST, ALP* and lipids | FibroScan | Chinese population | [95] | ||
| 768 | Associated with NAFLD risk | p = 0,0007 | TM6SF2 167K allele was associated with NAFLD after adjustment for age, sex, body mass index and status of diabetes |
Ultrasonography | Chinese population | [159] | ||
| 1201 | Associated with NASH and fibrosis | p < 0,05 | Associated with more-severe steatosis, necroinflammation, ballooning, and fibrosis | Histologically | Italian, Finnish, and Swedish | [160] | ||
| 525 | Associated with NASH and fibrosis | p = 0.008 (NASH); p = 0.020 (fibrosis) |
Even after adjustment for metabolic risk factors rs58542926 increased the risk of NASH and significant fibrosis | Histologically | Korean population | [149] | ||
| 503 | Associated with NAFLD risk | p = 0,0004 | The presence of rs58542926 variant in the TM6SF2 gene exhibited a significant association with NAFLD, indicating a 2,7-fold higher risk of developing the condition | Ultrasonography | South Indians and North-East Indians | [161] | ||
| 285 | Was not associated with NAFLD risk | p = 0,78 | The presence of the T allele was not found to be associated with NAFLD or NASH, and it did not show any association with histological features related to these conditions | Ultrasonography | Brazilian population | [131] | ||
| 144 | Was not associated with NAFLD risk | p > 0,05 | There was no association between rs58542926 and liver steatosis (p = 0.62), ballooning (p = 0.14), lobular inflammation (p = 0.99) and fibrosis (p = 0.89) | CT, MRT | Chinese population | [147] | ||
| 211 | Was not associated with NAS | p > 0,05 | The TM6SF2 genotype did not affect the NAFLD activity score ( ≤ 2 vs ≥ 3, p = 0.867; ≤ 4 vs ≥ 5, p = 0,936) | Histologically | Japanese population | [150] | ||
| LYPLAL1 | rs12137855 C > T | 7176 | Associated with NAFLD risk and steatosis | p < 0,001; (NAFLD risk) | C-allele was associated with CT defined steatosis and biopsy-proven NAFLD | CT; Histologically | European | [38] |
| 797 | Was not associated with NAFLD | p > 0,05 | N/A | Ultrasonography | Chinese children | [105] | ||
| 307 | Was not associated with NAFLD | p > 0,05 | N/A | FibroScan | Mexican population | [114] | ||
| 620 | Was not associated with NAFLD | p > 0,05 | N/A | Ultrasonography | Uyghur population | [115] |
4. The Influence of MAFLD-Associated Polymorphisms on the Severity of COVID-19
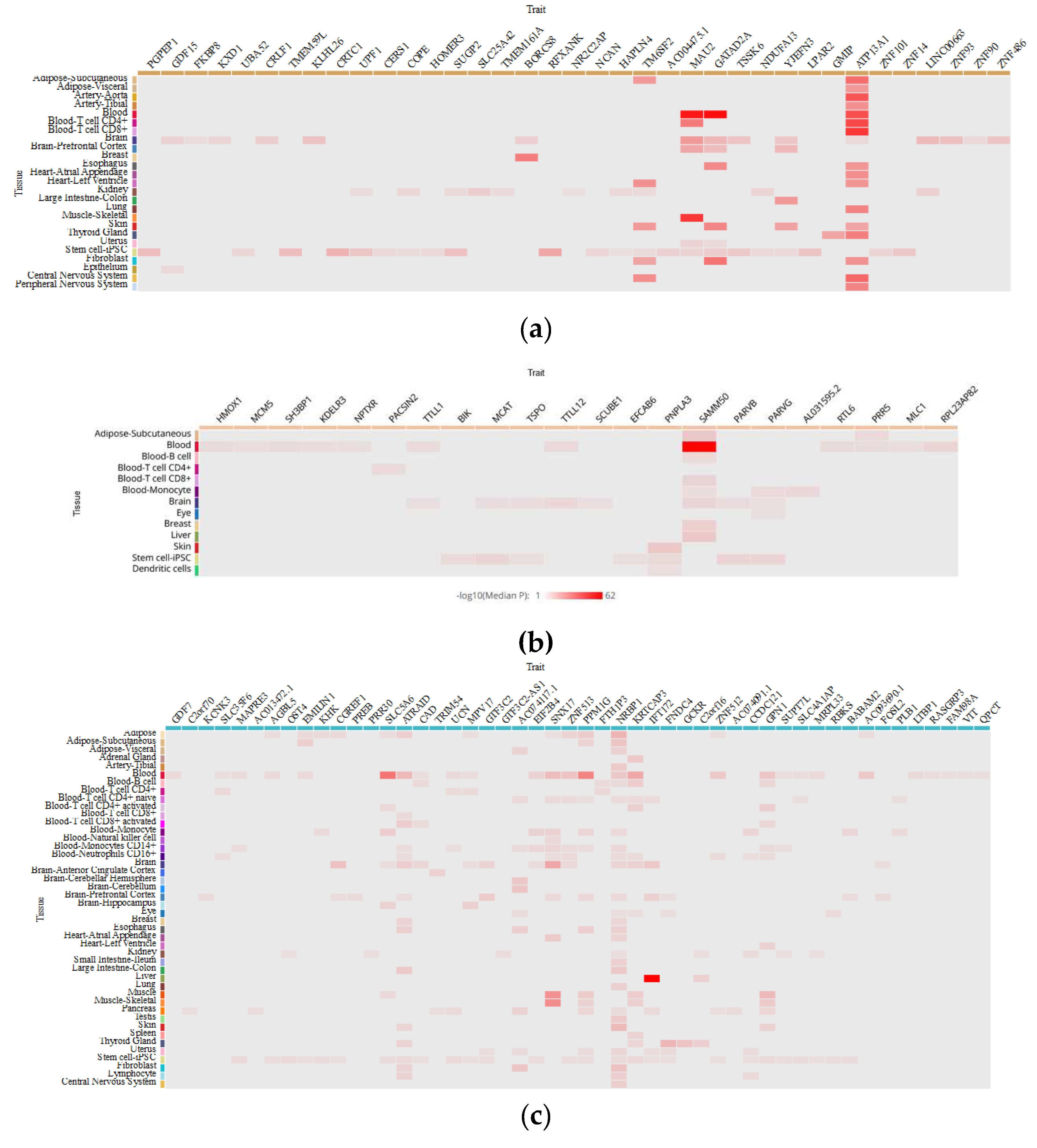
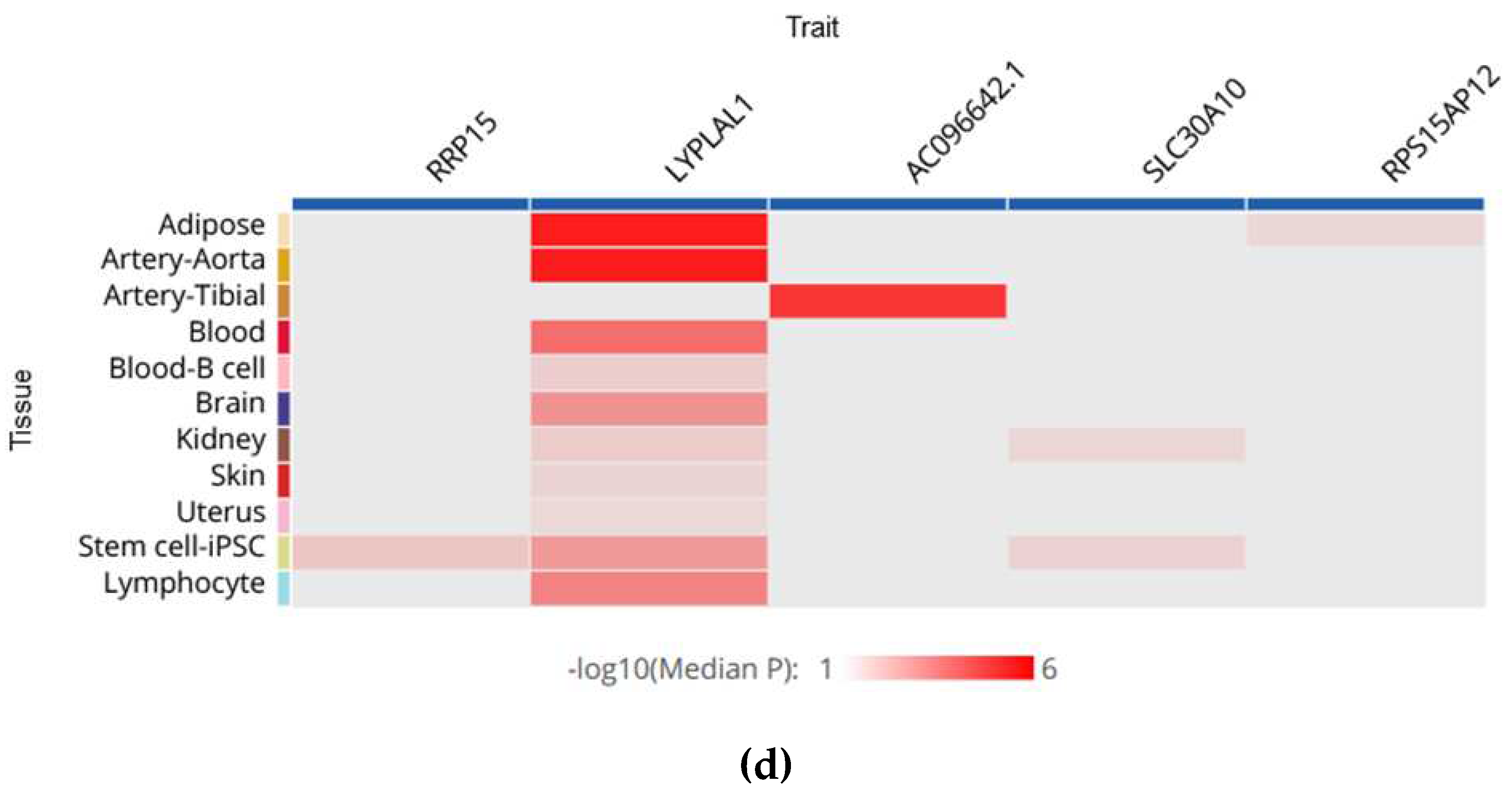
5. How do MAFLD-Associated Polymorphisms Affect Gene Expression in Different Tissues?
6. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- World Health Organization WHO Coronavirus Disease (COVID-19) Dashboard With Vaccination Data | WHO Coronavirus (COVID-19) Dashboard With Vaccination Data. World Heal. Organ. 2021, 1–5.
- Rapp, J.L.; Lieberman-Cribbin, W.; Tuminello, S.; Taioli, E. Male Sex, Severe Obesity, Older Age, and Chronic Kidney Disease Are Associated With COVID-19 Severity and Mortality in New York City. Chest 2021, 159, 112–115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, J. jin; Cao, Y. yuan; Tan, G.; Dong, X.; Wang, B. chen; Lin, J.; Yan, Y. qin; Liu, G. hui; Akdis, M.; Akdis, C.A.; et al. Clinical, Radiological, and Laboratory Characteristics and Risk Factors for Severity and Mortality of 289 Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Allergy Eur. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2021, 76, 533–550. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ebinge, J.E.; Achamallah, N.; Ji, H.; Clagget, B.L.; Sun, N.; Botting, P.; Nguyen, T.T.; Luong, E.; Ki, E.H.; Park, E.; et al. Pre-Existing Traits Associated with COVID-19 Illness Severity. PLoS One 2020, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Williamson, E.J.; Walker, A.J.; Bhaskaran, K.; Bacon, S.; Bates, C.; Morton, C.E.; Curtis, H.J.; Mehrkar, A.; Evans, D.; Inglesby, P.; et al. Factors Associated with COVID-19-Related Death Using OpenSAFELY. Nature 2020, 584, 430–436. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, X.; Xu, S.; Yu, M.; Wang, K.; Tao, Y.; Zhou, Y.; Shi, J.; Zhou, M.; Wu, B.; Yang, Z.; et al. Risk Factors for Severity and Mortality in Adult COVID-19 Inpatients in Wuhan. J. Allergy Clin. Immunol. 2020, 146, 110–118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamyshnyi, A.; Krynytska, I.; Matskevych, V.; Marushchak, M.; Lushchak, O. Arterial Hypertension as a Risk Comorbidity Associated with COVID-19 Pathology. Int. J. Hypertens. 2020, 2020, 8019360. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, F.; Zheng, K.I.; Wang, X.B.; Sun, Q.F.; Pan, K.H.; Wang, T.Y.; Chen, Y.P.; Targher, G.; Byrne, C.D.; George, J.; et al. Obesity Is a Risk Factor for Greater COVID-19 Severity. Diabetes Care 2020, 43, E72–E74. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valentino, M.S.; Marzuillo, P.; Esposito, C.; Bartiromo, M.; Nardolillo, M.; Villani, A.V.; Maresca, A.; Furcolo, G.; Guarino, S.; Miraglia Del Giudice, E.; et al. The Impact of COVID-19 Pandemic Lockdown on the Relationship between Pediatric MAFLD and Renal Function. J. Clin. Med. 2023, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- You, J.H.; Lee, S.A.; Chun, S.Y.; Song, S.O.; Lee, B.W.; Kim, D.J.; Boyko, E.J. Clinical Outcomes of COVID-19 Patients with Type 2 Diabetes: A Population-Based Study in Korea. Endocrinol. Metab. 2020, 35, 901–908. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dennis, J.M.; Mateen, B.A.; Sonabend, R.; Thomas, N.J.; Patel, K.A.; Hattersley, A.T.; Denaxas, S.; McGovern, A.P.; Vollmer, S.J. Type 2 Diabetes and COVID-19– Related Mortality in the Critical Care Setting: A National Cohort Study in England, March–July 2020. Diabetes Care 2021, 44, 50–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Petakh, P.; Kamyshna, I.; Nykyforuk, A.; Yao, R.; Imbery, J.F.; Oksenych, V.; Korda, M.; Kamyshnyi, A. Immunoregulatory Intestinal Microbiota and COVID-19 in Patients with Type Two Diabetes: A Double-Edged Sword. Viruses 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyshnyi, O.; Matskevych, V.; Lenchuk, T.; Strilbytska, O.; Storey, K.; Lushchak, O. Metformin to Decrease COVID-19 Severity and Mortality: Molecular Mechanisms and Therapeutic Potential. Biomed. Pharmacother. 2021, 144, 112230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sinha, P.; Matthay, M.A.; Calfee, C.S. Is a “Cytokine Storm” Relevant to COVID-19? JAMA Intern. Med. 2020, 180, 1152–1154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- de la Rica, R.; Borges, M.; Gonzalez-Freire, M. COVID-19: In the Eye of the Cytokine Storm. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 558898. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, J.F.-W.; Yuan, S.; Kok, K.-H.; To, K.K.-W.; Chu, H.; Yang, J.; Xing, F.; Liu, J.; Yip, C.C.-Y.; Poon, R.W.-S.; et al. A Familial Cluster of Pneumonia Associated with the 2019 Novel Coronavirus Indicating Person-to-Person Transmission: A Study of a Family Cluster. Lancet (London, England) 2020, 395, 514–523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baj, J.; Karakuła-Juchnowicz, H.; Teresiński, G.; Buszewicz, G.; Ciesielka, M.; Sitarz, R.; Forma, A.; Karakuła, K.; Flieger, W.; Portincasa, P.; et al. COVID-19: Specific and Non-Specific Clinical Manifestations and Symptoms: The Current State of Knowledge. J. Clin. Med. 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke-Galindo, I.; Falfán-Valencia, R. Genetics Insight for COVID-19 Susceptibility and Severity: A Review. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 622176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pairo-Castineira, E.; Clohisey, S.; Klaric, L.; Bretherick, A.D.; Rawlik, K.; Pasko, D.; Walker, S.; Parkinson, N.; Fourman, M.H.; Russell, C.D.; et al. Genetic Mechanisms of Critical Illness in COVID-19. Nat. 2020 5917848 2020, 591, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Negi, K.; Agarwal, M.; Pahuja, I.; Bhardwaj, B.; Rawat, M.; Bhaskar, A.; Dwivedi, V.P. Combating the Challenges of COVID-19 Pandemic: Insights into Molecular Mechanisms, Immune Responses and Therapeutics against SARS-CoV-2. Oxford open Immunol. 2023, 4, iqad001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fricke-Galindo, I.; Martínez-Morales, A.; Chávez-Galán, L.; Ocaña-Guzmán, R.; Buendía-Roldán, I.; Pérez-Rubio, G.; Hernández-Zenteno, R. de J.; Verónica-Aguilar, A.; Alarcón-Dionet, A.; Aguilar-Duran, H.; et al. IFNAR2 Relevance in the Clinical Outcome of Individuals with Severe COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 949413. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dieter, C.; de Almeida Brondani, L.; Lemos, N.E.; Schaeffer, A.F.; Zanotto, C.; Ramos, D.T.; Girardi, E.; Pellenz, F.M.; Camargo, J.L.; Moresco, K.S.; et al. Polymorphisms in ACE1, TMPRSS2, IFIH1, IFNAR2, and TYK2 Genes Are Associated with Worse Clinical Outcomes in COVID-19. Genes (Basel). 2022, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadler, A.J.; Williams, B.R.G. Interferon-Inducible Antiviral Effectors. Nat. Rev. Immunol. 2008, 8, 559–568. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kerr, I.M.; Brown, R.E.; Hovanessian, A.G. Nature of Inhibitor of Cell-Free Protein Synthesis Formed in Response to Interferon and Double-Stranded RNA. Nature 1977, 268, 540–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, Q.; Zhang, Y.; Wu, L.; Niu, S.; Song, C.; Zhang, Z.; Lu, G.; Qiao, C.; Hu, Y.; Yuen, K.-Y.; et al. Structural and Functional Basis of SARS-CoV-2 Entry by Using Human ACE2. Cell 2020, 181, 894–904.e9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hoffmann, M.; Kleine-Weber, H.; Schroeder, S.; Krüger, N.; Herrler, T.; Erichsen, S.; Schiergens, T.S.; Herrler, G.; Wu, N.-H.; Nitsche, A.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Cell Entry Depends on ACE2 and TMPRSS2 and Is Blocked by a Clinically Proven Protease Inhibitor. Cell 2020, 181, 271–280.e8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shevchuk, O.; Pak, A.; Palii, S.; Ivankiv, Y.; Kozak, K.; Korda, M.; Vari, S.G. Blood ACE2 Protein Level Correlates with COVID-19 Severity. Severity 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Newsome, P.N.; Sarin, S.K.; Anstee, Q.M.; Targher, G.; Romero-Gomez, M.; Zelber-Sagi, S.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Dufour, J.-F.; Schattenberg, J.M.; et al. A New Definition for Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: An International Expert Consensus Statement. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 202–209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Sanyal, A.J.; George, J.; Sanyal, A.; Neuschwander-Tetri, B.; Tiribelli, C.; Kleiner, D.E.; Brunt, E.; Bugianesi, E.; Yki-Järvinen, H.; et al. MAFLD: A Consensus-Driven Proposed Nomenclature for Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease. Gastroenterology 2020, 158, 1999–2014.e1. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younossi, Z.M.; Koenig, A.B.; Abdelatif, D.; Fazel, Y.; Henry, L.; Wymer, M. Global Epidemiology of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease-Meta-Analytic Assessment of Prevalence, Incidence, and Outcomes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 73–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Powell, E.E.; Wong, V.W.-S.; Rinella, M. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Lancet (London, England) 2021, 397, 2212–2224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wong, V.W.-S.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Woo, J.; Abrigo, J.M.; Chan, C.K.-M.; Shu, S.S.-T.; Leung, J.K.-Y.; Chim, A.M.-L.; Kong, A.P.-S.; Lui, G.C.-Y.; et al. Impact of the New Definition of Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease on the Epidemiology of the Disease. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2021, 19, 2161–2171.e5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yilmaz, Y.; Byrne, C.D.; Musso, G. A Single-Letter Change in an Acronym: Signals, Reasons, Promises, Challenges, and Steps Ahead for Moving from NAFLD to MAFLD. Expert Rev. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2021, 15, 345–352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Younossi, Z.; Tacke, F.; Arrese, M.; Chander Sharma, B.; Mostafa, I.; Bugianesi, E.; Wai-Sun Wong, V.; Yilmaz, Y.; George, J.; Fan, J.; et al. Global Perspectives on Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Hepatology 2019, 69, 2672–2682. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ji, D.; Qin, E.; Xu, J.; Zhang, D.; Cheng, G.; Wang, Y.; Lau, G. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Diseases in Patients with COVID-19: A Retrospective Study. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 451–453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hegyi, P.J.; Váncsa, S.; Ocskay, K.; Dembrovszky, F.; Kiss, S.; Farkas, N.; Erőss, B.; Szakács, Z.; Hegyi, P.; Pár, G. Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease Is Associated With an Increased Risk of Severe COVID-19: A Systematic Review With Meta-Analysis. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 626425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Singh, A.; Hussain, S.; Antony, B. Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Clinical Outcomes in Patients with COVID-19: A Comprehensive Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Diabetes Metab. Syndr. Clin. Res. Rev. 2021, 15, 813–822. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tao, Z.; Li, Y.; Cheng, B.; Zhou, T.; Gao, Y. Risk of Severe COVID-19 Increased by Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. J. Clin. Gastroenterol. 2021, 55, 830. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Y.; Wang, Y.; Duan, G.; Yang, H. NAFLD Was Independently Associated with Severe COVID-19 among Younger Patients Rather than Older Patients: A Meta-Analysis. J. Hepatol. 2022. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mushtaq, K.; Khan, M.U.; Iqbal, F.; Alsoub, D.H.; Chaudhry, H.S.; Ata, F.; Iqbal, P.; Elfert, K.; Balaraju, G.; Almaslamani, M.; et al. NAFLD Is a Predictor of Liver Injury in COVID-19 Hospitalized Patients but Not of Mortality, Disease Severity on the Presentation or Progression – The Debate Continues. J. Hepatol. 2021, 74, 482–484. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchynskyi, M.; Kamyshna, I.; Oksenych, V.; Zavidniuk, N.; Kamyshnyi, A. The Intersection of COVID-19 and Metabolic-Associated Fatty Liver Disease: An Overview of the Current Evidence. Viruses 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pirola, C.J.; Sookoian, S. COVID-19 and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: Biological Insights from Multi-Omics Data. Liver Int. 2023, 43, 580–587. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Speliotes, E.K.; Yerges-Armstrong, L.M.; Wu, J.; Hernaez, R.; Kim, L.J.; Palmer, C.D.; Gudnason, V.; Eiriksdottir, G.; Garcia, M.E.; Launer, L.J.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Analysis Identifies Variants Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease That Have Distinct Effects on Metabolic Traits. PLoS Genet. 2011, 7, e1001324. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kozlitina, J.; Smagris, E.; Stender, S.; Nordestgaard, B.G.; Zhou, H.H.; Tybjærg-Hansen, A.; Vogt, T.F.; Hobbs, H.H.; Cohen, J.C. Exome-Wide Association Study Identifies a TM6SF2 Variant That Confers Susceptibility to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 352–356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Holmen, O.L.; Zhang, H.; Fan, Y.; Hovelson, D.H.; Schmidt, E.M.; Zhou, W.; Guo, Y.; Zhang, J.; Langhammer, A.; Løchen, M.-L.; et al. Systematic Evaluation of Coding Variation Identifies a Candidate Causal Variant in TM6SF2 Influencing Total Cholesterol and Myocardial Infarction Risk. Nat. Genet. 2014, 46, 345–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Santoro, N.; Zhang, C.K.; Zhao, H.; Pakstis, A.J.; Kim, G.; Kursawe, R.; Dykas, D.J.; Bale, A.E.; Giannini, C.; Pierpont, B.; et al. Variant in the Glucokinase Regulatory Protein (GCKR) Gene Is Associated with Fatty Liver in Obese Children and Adolescents. Hepatology 2012, 55, 781–789. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goffredo, M.; Caprio, S.; Feldstein, A.E.; D’Adamo, E.; Shaw, M.M.; Pierpont, B.; Savoye, M.; Zhao, H.; Bale, A.E.; Santoro, N. Role of TM6SF2 Rs58542926 in the Pathogenesis of Nonalcoholic Pediatric Fatty Liver Disease: A Multiethnic Study. Hepatology 2016, 63, 117–125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gorden, A.; Yang, R.; Yerges-Armstrong, L.M.; Ryan, K.A.; Speliotes, E.; Borecki, I.B.; Harris, T.B.; Chu, X.; Wood, G.C.; Still, C.D.; et al. Genetic Variation at NCAN Locus Is Associated with Inflammation and Fibrosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Morbid Obesity. Hum. Hered. 2013, 75, 34–43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parisinos, C.A.; Wilman, H.R.; Thomas, E.L.; Kelly, M.; Nicholls, R.C.; McGonigle, J.; Neubauer, S.; Hingorani, A.D.; Patel, R.S.; Hemingway, H.; et al. Genome-Wide and Mendelian Randomisation Studies of Liver MRI Yield Insights into the Pathogenesis of Steatohepatitis. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 241–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Grimaudo, S.; Amodio, E.; Pipitone, R.M.; Maida, C.M.; Pizzo, S.; Prestileo, T.; Tramuto, F.; Sardina, D.; Vitale, F.; Casuccio, A.; et al. PNPLA3 and TLL-1 Polymorphisms as Potential Predictors of Disease Severity in Patients With COVID-19. Front. cell Dev. Biol. 2021, 9, 627914. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valenti, L.; Jamialahmadi, O.; Romeo, S. Lack of Genetic Evidence That Fatty Liver Disease Predisposes to COVID-19. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 709–711. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Innes, H.; Buch, S.; Barnes, E.; Hampe, J.; Marjot, T.; Stickel, F. The Rs738409 G Allele in PNPLA3 Is Associated With a Reduced Risk of COVID-19 Mortality and Hospitalization. Gastroenterology 2021, 160, 2599–2601.e2. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bianco, C.; Baselli, G.; Malvestiti, F.; Santoro, L.; Pelusi, S.; Manunta, M.; Grasselli, G.; Bandera, A.; Scudeller, L.; Prati, D.; et al. Genetic Insight into COVID-19-Related Liver Injury. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2021, 41, 227–229. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, F. Receptor Recognition and Cross-Species Infections of SARS Coronavirus. Antiviral Res. 2013, 100, 246–254. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cui, N.; Tong, H.; Li, Y.; Ge, Y.; Shi, Y.; Lv, P.; Zhao, X.; Zhang, J.; Fu, G.; Zhou, Y.; et al. Role of Prealbumin in Predicting the Prognosis of Severely and Critically Ill COVID-19 Patients. Am. J. Trop. Med. Hyg. 2021, 105, 718–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, C.; Li, Y.; Guan, T.; Lai, Y.; Shen, Y.; Zeyaweiding, A.; Zhao, H.; Li, F.; Maimaiti, T. ACE2 Polymorphisms Associated with Cardiovascular Risk in Uygurs with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus. Cardiovasc. Diabetol. 2018, 17, 127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pouladi, N.; Abdolahi, S. Investigating the ACE2 Polymorphisms in COVID-19 Susceptibility: An in Silico Analysis. Mol. Genet. genomic Med. 2021, 9, e1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, P.; Zhu, L.; Cai, J.; Lei, F.; Qin, J.-J.; Xie, J.; Liu, Y.-M.; Zhao, Y.-C.; Huang, X.; Lin, L.; et al. Association of Inpatient Use of Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme Inhibitors and Angiotensin II Receptor Blockers With Mortality Among Patients With Hypertension Hospitalized With COVID-19. Circ. Res. 2020, 126, 1671–1681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamet, P.; Pausova, Z.; Attaoua, R.; Hishmih, C.; Haloui, M.; Shin, J.; Paus, T.; Abrahamowicz, M.; Gaudet, D.; Santucci, L.; et al. SARS-CoV-2 Receptor ACE2 Gene Is Associated with Hypertension and Severity of COVID 19: Interaction with Sex, Obesity, and Smoking. Am. J. Hypertens. 2021, 34, 367–376. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sienko, J.; Marczak, I.; Kotowski, M.; Bogacz, A.; Tejchman, K.; Sienko, M.; Kotfis, K. Association of ACE2 Gene Variants with the Severity of COVID-19 Disease-A Prospective Observational Study. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2022, 19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cafiero, C.; Rosapepe, F.; Palmirotta, R.; Re, A.; Ottaiano, M.P.; Benincasa, G.; Perone, R.; Varriale, E.; D’Amato, G.; Cacciamani, A.; et al. Angiotensin System Polymorphisms’ in SARS-CoV-2 Positive Patients: Assessment Between Symptomatic and Asymptomatic Patients: A Pilot Study. Pharmgenomics. Pers. Med. 2021, 14, 621–629. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, Y.; Li, Q.; Chen, J.; Liu, S.; Liu, S.; He, X.; Ling, Y.; Zheng, J.; Corpe, C.; Lu, H.; et al. Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 SNPs as Common Genetic Loci and Optimal Early Identification Genetic Markers for COVID-19. Pathog. (Basel, Switzerland) 2022, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martínez-Gómez, L.E.; Herrera-López, B.; Martinez-Armenta, C.; Ortega-Peña, S.; Camacho-Rea, M.D.C.; Suarez-Ahedo, C.; Vázquez-Cárdenas, P.; Vargas-Alarcón, G.; Rojas-Velasco, G.; Fragoso, J.M.; et al. ACE and ACE2 Gene Variants Are Associated With Severe Outcomes of COVID-19 in Men. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 812940. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, J.; Zou, H.; Corpe, C. An Observed Association between Angiotensin-Converting Enzyme 2 Polymorphisms and COVID-19 Severity in China. J. Infect. 2022, 84, e21–e22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernández-de-Las-Peñas, C.; Arendt-Nielsen, L.; Díaz-Gil, G.; Gómez-Esquer, F.; Gil-Crujera, A.; Gómez-Sánchez, S.M.; Ambite-Quesada, S.; Palomar-Gallego, M.A.; Pellicer-Valero, O.J.; Giordano, R. Genetic Association between ACE2 (Rs2285666 and Rs2074192) and TMPRSS2 (Rs12329760 and Rs2070788) Polymorphisms with Post-COVID Symptoms in Previously Hospitalized COVID-19 Survivors. Genes (Basel). 2022, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Takaoka, A. Interferons. Handb. Horm. Comp. Endocrinol. Basic Clin. Res. 2021, 447–452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Duncan, C.J.A.; Mohamad, S.M.B.; Young, D.F.; Skelton, A.J.; Leahy, T.R.; Munday, D.C.; Butler, K.M.; Morfopoulou, S.; Brown, J.R.; Hubank, M.; et al. Human IFNAR2 Deficiency: Lessons for Antiviral Immunity. Sci. Transl. Med. 2015, 7, 307ra154. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Buchynskyi, M.; Kamyshna, I.; Lyubomirskaya, K.; Moshynets, O.; Kobyliak, N.; Oksenych, V.; Kamyshnyi, A. Efficacy of Interferon Alpha for the Treatment of Hospitalized Patients with COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2023, 14, 250. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyshnyi, A.; Koval, H.; Kobevko, O.; Buchynskyi, M.; Oksenych, V.; Kainov, D.; Lyubomirskaya, K.; Kamyshna, I.; Potters, G.; Moshynets, O. Therapeutic Effectiveness of Interferon-A2b against COVID-19 with Community-Acquired Pneumonia: The Ukrainian Experience. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2023, 24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, D.; Yang, J.; Feng, B.; Lu, W.; Zhao, C.; Li, L. Mendelian Randomization Analysis Identified Genes Pleiotropically Associated with the Risk and Prognosis of COVID-19. J. Infect. 2021, 82, 126–132. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, B.M.; Hill, H.R. Role of Host Immune and Inflammatory Responses in COVID-19 Cases with Underlying Primary Immunodeficiency: A Review. J. Interf. cytokine Res. Off. J. Int. Soc. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2020, 40, 549–554. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Baranova, A.; Cao, H.; Zhang, F. Unraveling Risk Genes of COVID-19 by Multi-Omics Integrative Analyses. Front. Med. 2021, 8, 738687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, L.; Zhu, J.; Liu, D.; Sun, Y.; Wu, C. An Integrative Multiomics Analysis Identifies Putative Causal Genes for COVID-19 Severity. Genet. Med. Off. J. Am. Coll. Med. Genet. 2021, 23, 2076–2086. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Smieszek, S.P.; Polymeropoulos, V.M.; Xiao, C.; Polymeropoulos, C.M.; Polymeropoulos, M.H. Loss-of-Function Mutations in IFNAR2 in COVID-19 Severe Infection Susceptibility. J. Glob. Antimicrob. Resist. 2021, 26, 239–240. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Contoli, M.; Papi, A.; Tomassetti, L.; Rizzo, P.; Vieceli Dalla Sega, F.; Fortini, F.; Torsani, F.; Morandi, L.; Ronzoni, L.; Zucchetti, O.; et al. Blood Interferon-α Levels and Severity, Outcomes, and Inflammatory Profiles in Hospitalized COVID-19 Patients. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 648004. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schreiber, G. The Role of Type I Interferons in the Pathogenesis and Treatment of COVID-19. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 595739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- da Silva, R.P.; Gonçalves, J.I.B.; Zanin, R.F.; Schuch, F.B.; de Souza, A.P.D. Circulating Type I Interferon Levels and COVID-19 Severity: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Front. Immunol. 2021, 12, 657363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kristiansen, H.; Gad, H.H.; Eskildsen-Larsen, S.; Despres, P.; Hartmann, R. The Oligoadenylate Synthetase Family: An Ancient Protein Family with Multiple Antiviral Activities. J. Interf. cytokine Res. Off. J. Int. Soc. Interf. Cytokine Res. 2011, 31, 41–47. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fagone, P.; Nunnari, G.; Lazzara, F.; Longo, A.; Cambria, D.; Distefano, G.; Palumbo, M.; Nicoletti, F.; Malaguarnera, L.; Di Rosa, M. Induction of OAS Gene Family in HIV Monocyte Infected Patients with High and Low Viral Load. Antiviral Res. 2016, 131, 66–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Al-Ahmadi, W.; Al-Haj, L.; Al-Mohanna, F.A.; Silverman, R.H.; Khabar, K.S.A. RNase L Downmodulation of the RNA-Binding Protein, HuR, and Cellular Growth. Oncogene 2009, 28, 1782–1791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lin, R.-J.; Yu, H.-P.; Chang, B.-L.; Tang, W.-C.; Liao, C.-L.; Lin, Y.-L. Distinct Antiviral Roles for Human 2’,5’-Oligoadenylate Synthetase Family Members against Dengue Virus Infection. J. Immunol. 2009, 183, 8035–8043. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovanessian, A.G. On the Discovery of Interferon-Inducible, Double-Stranded RNA Activated Enzymes: The 2’-5’oligoadenylate Synthetases and the Protein Kinase PKR. Cytokine Growth Factor Rev. 2007, 18, 351–361. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hovnanian, A.; Rebouillat, D.; Levy, E.R.; Mattei, M.G.; Hovanessian, A.G. The Human 2’,5’-Oligoadenylate Synthetase-like Gene (OASL) Encoding the Interferon-Induced 56-KDa Protein Maps to Chromosome 12q24.2 in the Proximity of the 2’,5’-OAS Locus. Genomics 1999, 56, 362–363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mashimo, T.; Glaser, P.; Lucas, M.; Simon-Chazottes, D.; Ceccaldi, P.E.; Montagutelli, X.; Desprès, P.; Guénet, J.L. Structural and Functional Genomics and Evolutionary Relationships in the Cluster of Genes Encoding Murine 2’,5’-Oligoadenylate Synthetases. Genomics 2003, 82, 537–552. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mapping the Human Genetic Architecture of COVID-19. Nature 2021, 600, 472–477. [CrossRef]
- Banday, A.R.; Stanifer, M.L.; Florez-Vargas, O.; Onabajo, O.O.; Papenberg, B.W.; Zahoor, M.A.; Mirabello, L.; Ring, T.J.; Lee, C.-H.; Albert, P.S.; et al. Genetic Regulation of OAS1 Nonsense-Mediated Decay Underlies Association with COVID-19 Hospitalization in Patients of European and African Ancestries. Nat. Genet. 2022, 54, 1103–1116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sabater Molina, M.; Nicolás Rocamora, E.; Bendicho, A.I.; Vázquez, E.G.; Zorio, E.; Rodriguez, F.D.; Gil Ortuño, C.; Rodríguez, A.I.; Sánchez-López, A.J.; Jara Rubio, R.; et al. Polymorphisms in ACE, ACE2, AGTR1 Genes and Severity of COVID-19 Disease. PLoS One 2022, 17, e0263140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dorairaj, V.; Sulaiman, S.A.; Abu, N.; Abdul Murad, N.A. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD): Pathogenesis and Noninvasive Diagnosis. Biomedicines 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pafili, K.; Roden, M. Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) from Pathogenesis to Treatment Concepts in Humans. Mol. Metab. 2021, 50, 101122. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Romeo, S.; Kozlitina, J.; Xing, C.; Pertsemlidis, A.; Cox, D.; Pennacchio, L.A.; Boerwinkle, E.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Genetic Variation in PNPLA3 Confers Susceptibility to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nat. Genet. 2008, 40, 1461–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pirazzi, C.; Adiels, M.; Burza, M.A.; Mancina, R.M.; Levin, M.; Ståhlman, M.; Taskinen, M.-R.; Orho-Melander, M.; Perman, J.; Pujia, A.; et al. Patatin-like Phospholipase Domain-Containing 3 (PNPLA3) I148M (Rs738409) Affects Hepatic VLDL Secretion in Humans and in Vitro. J. Hepatol. 2012, 57, 1276–1282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salari, N.; Darvishi, N.; Mansouri, K.; Ghasemi, H.; Hosseinian-Far, M.; Darvishi, F.; Mohammadi, M. Association between PNPLA3 Rs738409 Polymorphism and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. BMC Endocr. Disord. 2021, 21, 125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. Meta-Analysis of the Influence of I148M Variant of Patatin-like Phospholipase Domain Containing 3 Gene (PNPLA3) on the Susceptibility and Histological Severity of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2011, 53, 1883–1894. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Salameh, H.; Hanayneh, M. Al; Masadeh, M.; Naseemuddin, M.; Matin, T.; Erwin, A.; Singal, A.K. PNPLA3 as a Genetic Determinant of Risk for and Severity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Spectrum. J. Clin. Transl. Hepatol. 2016, 4, 175–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vespasiani-Gentilucci, U.; Gallo, P.; Porcari, A.; Carotti, S.; Galati, G.; Piccioni, L.; De Vincentis, A.; Dell’Unto, C.; Vorini, F.; Morini, S.; et al. The PNPLA3 Rs738409 C > G Polymorphism Is Associated with the Risk of Progression to Cirrhosis in NAFLD Patients. Scand. J. Gastroenterol. 2016, 51, 967–973. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Luo, F.; Oldoni, F.; Das, A. TM6SF2: A Novel Genetic Player in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver and Cardiovascular Disease. Hepatol. Commun. 2022, 6, 448–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Smagris, E.; Gilyard, S.; BasuRay, S.; Cohen, J.C.; Hobbs, H.H. Inactivation of Tm6sf2, a Gene Defective in Fatty Liver Disease, Impairs Lipidation but Not Secretion of Very Low Density Lipoproteins. J. Biol. Chem. 2016, 291, 10659–10676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Que, S.; Zhou, L.; Zheng, S.; Romeo, S.; Mardinoglu, A.; Valenti, L. The Effect of the TM6SF2 E167K Variant on Liver Steatosis and Fibrosis in Patients with Chronic Hepatitis C: A Meta-Analysis. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 9273. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.-Y.; Liu, Z.; Li, L.; Wang, H.-J.; Wang, H. TM6SF2 Rs58542926 Is Related to Hepatic Steatosis, Fibrosis and Serum Lipids Both in Adults and Children: A Meta-Analysis. Front. Endocrinol. (Lausanne). 2022, 13, 1026901. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sookoian, S.; Pirola, C.J. Meta-Analysis of the Influence of TM6SF2 E167K Variant on Plasma Concentration of Aminotransferases across Different Populations and Diverse Liver Phenotypes. Sci. Rep. 2016, 6, 27718. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, M.; Li, Y.; Zhang, S.; Wang, X.; Shen, J.; Zhang, S. Interaction of TM6SF2 E167K and PNPLA3 I148M Variants in NAFLD in Northeast China. Ann. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, F.; Esmaili, S.; Rogers, G.B.; Bugianesi, E.; Petta, S.; Marchesini, G.; Bayoumi, A.; Metwally, M.; Azardaryany, M.K.; Coulter, S.; et al. Lean NAFLD: A Distinct Entity Shaped by Differential Metabolic Adaptation. Hepatology 2020, 71, 1213–1227. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Young, S.; Tariq, R.; Provenza, J.; Satapathy, S.K.; Faisal, K.; Choudhry, A.; Friedman, S.L.; Singal, A.K. Prevalence and Profile of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Lean Adults: Systematic Review and Meta-Analysis. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 953–972. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kozlitina, J. Genetic Risk Factors and Disease Modifiers of Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis. Gastroenterol. Clin. North Am. 2020, 49, 25–44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Y.-L.; Reeves, H.L.; Burt, A.D.; Tiniakos, D.; McPherson, S.; Leathart, J.B.S.; Allison, M.E.D.; Alexander, G.J.; Piguet, A.-C.; Anty, R.; et al. TM6SF2 Rs58542926 Influences Hepatic Fibrosis Progression in Patients with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Nat. Commun. 2014, 5, 4309. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wong, V.W.-S.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Tse, C.-H.; Chan, H.L.-Y. Prevalence of the TM6SF2 Variant and Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Chinese. J. Hepatol. 2014, 61, 708–709. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sookoian, S.; Castaño, G.O.; Scian, R.; Mallardi, P.; Fernández Gianotti, T.; Burgueño, A.L.; San Martino, J.; Pirola, C.J. Genetic Variation in Transmembrane 6 Superfamily Member 2 and the Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Histological Disease Severity. Hepatology 2015, 61, 515–525. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Aulchenko, Y.S.; Ripatti, S.; Lindqvist, I.; Boomsma, D.; Heid, I.M.; Pramstaller, P.P.; Penninx, B.W.J.H.; Janssens, A.C.J.W.; Wilson, J.F.; Spector, T.; et al. Loci Influencing Lipid Levels and Coronary Heart Disease Risk in 16 European Population Cohorts. Nat. Genet. 2009, 41, 47–55. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Willer, C.J.; Schmidt, E.M.; Sengupta, S.; Peloso, G.M.; Gustafsson, S.; Kanoni, S.; Ganna, A.; Chen, J.; Buchkovich, M.L.; Mora, S.; et al. Discovery and Refinement of Loci Associated with Lipid Levels. Nat. Genet. 2013, 45, 1274–1283. [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.-L.; Chen, H.; Wang, C.-L.; Liang, L. Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Children and Adolescence: From “Two Hit Theory” to “Multiple Hit Model”. World J. Gastroenterol. 2018, 24, 2974–2983. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.-C.; Chang, P.-F.; Chang, M.-H.; Ni, Y.-H. Genetic Variants in GCKR and PNPLA3 Confer Susceptibility to Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese Individuals. Am. J. Clin. Nutr. 2014, 99, 869–874. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tan, H.-L.; Zain, S.M.; Mohamed, R.; Rampal, S.; Chin, K.-F.; Basu, R.C.; Cheah, P.-L.; Mahadeva, S.; Mohamed, Z. Association of Glucokinase Regulatory Gene Polymorphisms with Risk and Severity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: An Interaction Study with Adiponutrin Gene. J. Gastroenterol. 2014, 49, 1056–1064. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Z.; Wen, J.; Tao, X.; Lu, B.; Du, Y.; Wang, M.; Wang, X.; Zhang, W.; Gong, W.; Ling, C.; et al. Genetic Variation in the GCKR Gene Is Associated with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Chinese People. Mol. Biol. Rep. 2011, 38, 1145–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zain, S.M.; Mohamed, Z.; Mohamed, R. Common Variant in the Glucokinase Regulatory Gene Rs780094 and Risk of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2015, 30, 21–27. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, J.; Zhao, Y.; Zhang, H.; Hua, W.; Jiao, W.; Du, X.; Rui, J.; Li, S.; Teng, H.; Shi, B.; et al. Contribution of Rs780094 and Rs1260326 Polymorphisms in GCKR Gene to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease: A Meta-Analysis Involving 26,552 Participants. Endocr. Metab. Immune Disord. Drug Targets 2021, 21, 1696–1708. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fischer, M.; Pleiss, J. The Lipase Engineering Database: A Navigation and Analysis Tool for Protein Families. Nucleic Acids Res. 2003, 31, 319–321. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lei, X.; Callaway, M.; Zhou, H.; Yang, Y.; Chen, W. Obesity Associated Lyplal1 Gene Is Regulated in Diet Induced Obesity but Not Required for Adipocyte Differentiation. Mol. Cell. Endocrinol. 2015, 411, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yuan, C.; Lu, L.; An, B.; Jin, W.; Dong, Q.; Xin, Y.; Xuan, S. Association Between LYPLAL1 Rs12137855 Polymorphism With Ultrasound-Defined Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Chinese Han Population. Hepat. Mon. 2015, 15, e33155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Wang, K.; Wang, Z.; Sun, X.; Zhong, L.; Deng, G.; Song, G.; Sun, B.; Peng, Z.; et al. Additive Effects of the Risk Alleles of PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 on Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) in a Chinese Population. Front. Genet. 2016, 7, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trejo, M.J.; Morrill, K.E.; Klimentidis, Y.C.; Garcia, D.O. Examining Genetic Associations with Hepatic Steatosis in Mexican-Origin Adults. Ann. Hepatol. 2023, 101120. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cai, W.; Weng, D.-H.; Yan, P.; Lin, Y.-T.; Dong, Z.-H.; Mailamuguli; Yao, H. Genetic Polymorphisms Associated with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Uyghur Population: A Case-Control Study and Meta-Analysis. Lipids Health Dis. 2019, 18, 14. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rotman, Y.; Koh, C.; Zmuda, J.M.; Kleiner, D.E.; Liang, T.J. The Association of Genetic Variability in Patatin-like Phospholipase Domain-Containing Protein 3 (PNPLA3) with Histological Severity of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2010, 52, 894–903. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansoor, S.; Maheshwari, A.; Di Guglielmo, M.; Furuya, K.; Wang, M.; Crowgey, E.; Molle-Rios, Z.; He, Z. The PNPLA3 Rs738409 Variant but Not MBOAT7 Rs641738 Is a Risk Factor for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Obese U.S. Children of Hispanic Ethnicity. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Nutr. 2021, 24, 455–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, S.L.; Li, Y.; Sheng, X.; Hom, V.; Xia, L.; Zhao, K.; Pooler, L.; Setiawan, V.W.; Lim, U.; Monroe, K.R.; et al. Genome-Wide Association Study of Liver Fat: The Multiethnic Cohort Adiposity Phenotype Study. Hepatol. Commun. 2020, 4, 1112–1123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hyysalo, J.; Stojkovic, I.; Kotronen, A.; Hakkarainen, A.; Sevastianova, K.; Makkonen, J.; Lundbom, N.; Rissanen, A.; Krauss, R.M.; Melander, O.; et al. Genetic Variation in PNPLA3 but Not APOC3 Influences Liver Fat in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2012, 27, 951–956. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Xing, C.; Tian, Z.; Ku, H.-C. Genetic Variant I148M in PNPLA3 Is Associated with the Ultrasonography-Determined Steatosis Degree in a Chinese Population. BMC Med. Genet. 2012, 13, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shang, X.-R.; Song, J.-Y.; Liu, F.-H.; Ma, J.; Wang, H.-J. GWAS-Identified Common Variants With Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Chinese Children. J. Pediatr. Gastroenterol. Nutr. 2015, 60, 669–674. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Xia, M.-F.; Ling, Y.; Bian, H.; Lin, H.-D.; Yan, H.-M.; Chang, X.-X.; Li, X.-M.; Ma, H.; Wang, D.; Zhang, L.-S.; et al. I148M Variant of PNPLA3 Increases the Susceptibility to Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Caused by Obesity and Metabolic Disorders. Aliment. Pharmacol. Ther. 2016, 43, 631–642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, C.-W.; Lin, H.-Y.; Shin, S.-J.; Yu, M.-L.; Lin, Z.-Y.; Dai, C.-Y.; Huang, J.-F.; Chen, S.-C.; Li, S.S.-L.; Chuang, W.-L. The PNPLA3 I148M Polymorphism Is Associated with Insulin Resistance and Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in a Normoglycaemic Population. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2011, 31, 1326–1331. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hudert, C.A.; Selinski, S.; Rudolph, B.; Bläker, H.; Loddenkemper, C.; Thielhorn, R.; Berndt, N.; Golka, K.; Cadenas, C.; Reinders, J.; et al. Genetic Determinants of Steatosis and Fibrosis Progression in Paediatric Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2019, 39, 540–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Krawczyk, M.; Rau, M.; Schattenberg, J.M.; Bantel, H.; Pathil, A.; Demir, M.; Kluwe, J.; Boettler, T.; Lammert, F.; Geier, A. Combined Effects of the PNPLA3 Rs738409, TM6SF2 Rs58542926, and MBOAT7 Rs641738 Variants on NAFLD Severity: A Multicenter Biopsy-Based Study. J. Lipid Res. 2017, 58, 247–255. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kitamoto, T.; Kitamoto, A.; Yoneda, M.; Hyogo, H.; Ochi, H.; Nakamura, T.; Teranishi, H.; Mizusawa, S.; Ueno, T.; Chayama, K.; et al. Genome-Wide Scan Revealed That Polymorphisms in the PNPLA3, SAMM50, and PARVB Genes Are Associated with Development and Progression of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Japan. Hum. Genet. 2013, 132, 783–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Costanzo, A.; Belardinilli, F.; Bailetti, D.; Sponziello, M.; D’Erasmo, L.; Polimeni, L.; Baratta, F.; Pastori, D.; Ceci, F.; Montali, A.; et al. Evaluation of Polygenic Determinants of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease (NAFLD) By a Candidate Genes Resequencing Strategy. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 3702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Valenti, L.; Al-Serri, A.; Daly, A.K.; Galmozzi, E.; Rametta, R.; Dongiovanni, P.; Nobili, V.; Mozzi, E.; Roviaro, G.; Vanni, E.; et al. Homozygosity for the Patatin-like Phospholipase-3/Adiponutrin I148M Polymorphism Influences Liver Fibrosis in Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatology 2010, 51, 1209–1217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Longo, M.; Meroni, M.; Paolini, E.; Erconi, V.; Carli, F.; Fortunato, F.; Ronchi, D.; Piciotti, R.; Sabatini, S.; Macchi, C.; et al. TM6SF2/PNPLA3/MBOAT7 Loss-of-Function Genetic Variants Impact on NAFLD Development and Progression Both in Patients and in In Vitro Models. Cell. Mol. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2022, 13, 759–788. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verrijken, A.; Beckers, S.; Francque, S.; Hilden, H.; Caron, S.; Zegers, D.; Ruppert, M.; Hubens, G.; Van Marck, E.; Michielsen, P.; et al. A Gene Variant of PNPLA3, but Not of APOC3, Is Associated with Histological Parameters of NAFLD in an Obese Population. Obesity (Silver Spring). 2013, 21, 2138–2145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lisboa, Q.C.; Nardelli, M.J.; Pereira, P. de A.; Miranda, D.M.; Ribeiro, S.N.; Costa, R.S.N.; Versiani, C.A.; Vidigal, P.V.T.; Ferrari, T.C. de A.; Couto, C.A. PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 Polymorphisms in Brazilian Patients with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 792–806. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zain, S.M.; Mohamed, R.; Mahadeva, S.; Cheah, P.L.; Rampal, S.; Basu, R.C.; Mohamed, Z. A Multi-Ethnic Study of a PNPLA3 Gene Variant and Its Association with Disease Severity in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hum. Genet. 2012, 131, 1145–1152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Uygun, A.; Ozturk, K.; Demirci, H.; Oztuna, A.; Eren, F.; Kozan, S.; Yilmaz, Y.; Kurt, O.; Turker, T.; Vatansever, S.; et al. The Association of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Genetic Polymorphisms: A Multicenter Study. Eur. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2017, 29, 441–447. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Idilman, R.; Karatayli, S.C.; Kabacam, G.; Savas, B.; Elhan, A.H.; Bozdayi, A.M. The Role of PNPLA3 (Rs738409) C>g Variant on Histological Progression of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Hepatol. forum 2020, 1, 82–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Zhao, Q.; Wu, K.; Fan, D. I148M Variant of PNPLA3 Confer Increased Risk for Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease Not Only in European Population, but Also in Chinese Population. Hepatology 2011, 54, 2275. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, H.; Wong, G.L.-H.; Whatling, C.; Chan, A.W.-H.; Leung, H.H.-W.; Tse, C.-H.; Shu, S.S.-T.; Chim, A.M.-L.; Lai, J.C.-T.; Yip, T.C.-F.; et al. Association of Genetic Variations with NAFLD in Lean Individuals. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2022, 42, 149–160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hotta, K.; Yoneda, M.; Hyogo, H.; Ochi, H.; Mizusawa, S.; Ueno, T.; Chayama, K.; Nakajima, A.; Nakao, K.; Sekine, A. Association of the Rs738409 Polymorphism in PNPLA3 with Liver Damage and the Development of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. BMC Med. Genet. 2010, 11, 172. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kawaguchi, T.; Sumida, Y.; Umemura, A.; Matsuo, K.; Takahashi, M.; Takamura, T.; Yasui, K.; Saibara, T.; Hashimoto, E.; Kawanaka, M.; et al. Genetic Polymorphisms of the Human PNPLA3 Gene Are Strongly Associated with Severity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Japanese. PLoS One 2012, 7, e38322. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, S.S.; Byoun, Y.-S.; Jeong, S.-H.; Woo, B.H.; Jang, E.S.; Kim, J.-W.; Kim, H.Y. Role of the PNPLA3 I148M Polymorphism in Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease and Fibrosis in Korea. Dig. Dis. Sci. 2014, 59, 2967–2974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, J.-H.; Cho, B.; Kwon, H.; Prilutsky, D.; Yun, J.M.; Choi, H.C.; Hwang, K.-B.; Lee, I.-H.; Kim, J.-I.; Kong, S.W. I148M Variant in PNPLA3 Reduces Central Adiposity and Metabolic Disease Risks While Increasing Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Liver Int. Off. J. Int. Assoc. Study Liver 2015, 35, 2537–2546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Chatterjee, A.; Basu, A.; Das, K.; Chowdhury, A.; Basu, P. Exome-Wide Scan Identifies Significant Association of Rs4788084 in IL27 Promoter with Increase in Hepatic Fat Content among Indians. Gene 2021, 775, 145431. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bhatt, S.P.; Nigam, P.; Misra, A.; Guleria, R.; Pandey, R.M.; Pasha, M.A.Q. Genetic Variation in the Patatin-like Phospholipase Domain-Containing Protein-3 (PNPLA-3) Gene in Asian Indians with Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Metab. Syndr. Relat. Disord. 2013, 11, 329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karoli, R.; Fatima, J.; Singh, P.S.; Siddiqi, Z.; Varshney, S.; Beg, M.S.; Khan, M.A. Association of Genetic Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease with Insulin Resistance-Are We Different? J. Assoc. Physicians India 2019, 67, 34–38. [Google Scholar]
- Kanth, V.V.R.; Sasikala, M.; Rao, P.N.; Steffie Avanthi, U.; Rao, K.R.; Nageshwar Reddy, D. Pooled Genetic Analysis in Ultrasound Measured Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Indian Subjects: A Pilot Study. World J. Hepatol. 2014, 6, 435–442. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Narayanasamy, K.; Karthick, R.; Panneerselvam, P.; Mohan, N.; Ramachandran, A.; Prakash, R.; Rajaram, M. Association of Metabolic Syndrome and Patatin-like Phospholipase 3 - Rs738409 Gene Variant in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease among a Chennai-Based South Indian Population. J. Gene Med. 2020, 22, e3160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Alam, S.; Islam, M.S.; Islam, S.; Mustafa, G.; Saleh, A.A.; Ahmad, N. Association of Single Nucleotide Polymorphism at PNPLA3 with Fatty Liver, Steatohepatitis, and Cirrhosis of Liver. Indian J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Indian Soc. Gastroenterol. 2017, 36, 366–372. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lee, G.H.; Phyo, W.W.; Loo, W.M.; Kwok, R.; Ahmed, T.; Shabbir, A.; So, J.; Koh, C.J.; Hartono, J.L.; Muthiah, M.; et al. Validation of Genetic Variants Associated with Metabolic Dysfunction-Associated Fatty Liver Disease in an Ethnic Chinese Population. World J. Hepatol. 2020, 12, 1228–1238. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Krawczyk, M.; Stachowska, E.; Milkiewicz, P.; Lammert, F.; Milkiewicz, M. Reduction of Caloric Intake Might Override the Prosteatotic Effects of the PNPLA3 p.I148M and TM6SF2 p.E167K Variants in Patients with Fatty Liver: Ultrasound-Based Prospective Study. Digestion 2016, 93, 139–148. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Koo, B.K.; Joo, S.K.; Kim, D.; Bae, J.M.; Park, J.H.; Kim, J.H.; Kim, W. Additive Effects of PNPLA3 and TM6SF2 on the Histological Severity of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. J. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. 2018, 33, 1277–1285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Akuta, N.; Kawamura, Y.; Arase, Y.; Suzuki, F.; Sezaki, H.; Hosaka, T.; Kobayashi, M.; Kobayashi, M.; Saitoh, S.; Suzuki, Y.; et al. Relationships between Genetic Variations of PNPLA3, TM6SF2 and Histological Features of Nonalcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Japan. Gut Liver 2016, 10, 437–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hernaez, R.; McLean, J.; Lazo, M.; Brancati, F.L.; Hirschhorn, J.N.; Borecki, I.B.; Harris, T.B.; Nguyen, T.; Kamel, I.R.; Bonekamp, S.; et al. Association between Variants in or near PNPLA3, GCKR, and PPP1R3B with Ultrasound-Defined Steatosis Based on Data from the Third National Health and Nutrition Examination Survey. Clin. Gastroenterol. Hepatol. Off. Clin. Pract. J. Am. Gastroenterol. Assoc. 2013, 11, 1183–1190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mazo, D.F.; Malta, F.M.; Stefano, J.T.; Salles, A.P.M.; Gomes-Gouvea, M.S.; Nastri, A.C.S.; Almeida, J.R.; Pinho, J.R.R.; Carrilho, F.J.; Oliveira, C.P. Validation of PNPLA3 Polymorphisms as Risk Factor for NAFLD and Liver Fibrosis in an Admixed Population. Ann. Hepatol. 2019, 18, 466–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Delik, A.; Akkız, H.; Dinçer, S. The Effect of PNPLA3 Polymorphism as Gain in Function Mutation in the Pathogenesis of Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. Indian J. Gastroenterol. Off. J. Indian Soc. Gastroenterol. 2020, 39, 84–91. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Petta, S.; Miele, L.; Bugianesi, E.; Cammà, C.; Rosso, C.; Boccia, S.; Cabibi, D.; Di Marco, V.; Grimaudo, S.; Grieco, A.; et al. Glucokinase Regulatory Protein Gene Polymorphism Affects Liver Fibrosis in Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease. PLoS One 2014, 9, e87523. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eslam, M.; Mangia, A.; Berg, T.; Chan, H.L.Y.; Irving, W.L.; Dore, G.J.; Abate, M.L.; Bugianesi, E.; Adams, L.A.; Najim, M.A.M.; et al. Diverse Impacts of the Rs58542926 E167K Variant in TM6SF2 on Viral and Metabolic Liver Disease Phenotypes. Hepatology 2016, 64, 34–46. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zhou, Y.; Llauradó, G.; Orešič, M.; Hyötyläinen, T.; Orho-Melander, M.; Yki-Järvinen, H. Circulating Triacylglycerol Signatures and Insulin Sensitivity in NAFLD Associated with the E167K Variant in TM6SF2. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 657–663. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grandone, A.; Cozzolino, D.; Marzuillo, P.; Cirillo, G.; Di Sessa, A.; Ruggiero, L.; Di Palma, M.R.; Perrone, L.; Miraglia Del Giudice, E. TM6SF2 Glu167Lys Polymorphism Is Associated with Low Levels of LDL-Cholesterol and Increased Liver Injury in Obese Children. Pediatr. Obes. 2016, 11, 115–119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mancina, R.M.; Sentinelli, F.; Incani, M.; Bertoccini, L.; Russo, C.; Romeo, S.; Baroni, M.G. Transmembrane-6 Superfamily Member 2 (TM6SF2) E167K Variant Increases Susceptibility to Hepatic Steatosis in Obese Children. Dig. liver Dis. Off. J. Ital. Soc. Gastroenterol. Ital. Assoc. Study Liver 2016, 48, 100–101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Liu, Z.; Peng, Z.; Liu, W. The TM6SF2 Rs58542926 T Allele Is Significantly Associated with Non-Alcoholic Fatty Liver Disease in Chinese. J. Hepatol. 2015, 62, 1438–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dongiovanni, P.; Petta, S.; Maglio, C.; Fracanzani, A.L.; Pipitone, R.; Mozzi, E.; Motta, B.M.; Kaminska, D.; Rametta, R.; Grimaudo, S.; et al. Transmembrane 6 Superfamily Member 2 Gene Variant Disentangles Nonalcoholic Steatohepatitis from Cardiovascular Disease. Hepatology 2015, 61, 506–514. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bale, G.; Steffie, A.U.; Ravi Kanth, V.V.; Rao, P.N.; Sharma, M.; Sasikala, M.; Reddy, D.N. Regional Differences in Genetic Susceptibility to Non-Alcoholic Liver Disease in Two Distinct Indian Ethnicities. World J. Hepatol. 2017, 9, 1101–1107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pan, L.; Huang, P.; Xie, X.; Xu, J.; Guo, D.; Jiang, Y. Metabolic Associated Fatty Liver Disease Increases the Severity of COVID-19: A Meta-Analysis. Dig. Liver Dis. 2021, 53, 153–157. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trottier, C.; Chabot, S.; Mann, K.K.; Colombo, M.; Chatterjee, A.; Miller, W.H.J.; Ward, B.J. Retinoids Inhibit Measles Virus in Vitro via Nuclear Retinoid Receptor Signaling Pathways. Antiviral Res. 2008, 80, 45–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trasino, S.E.; Tang, X.-H.; Jessurun, J.; Gudas, L.J. Obesity Leads to Tissue, but Not Serum Vitamin A Deficiency. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 15893. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Peter, A.; Kovarova, M.; Nadalin, S.; Cermak, T.; Königsrainer, A.; Machicao, F.; Stefan, N.; Häring, H.-U.; Schleicher, E. PNPLA3 Variant I148M Is Associated with Altered Hepatic Lipid Composition in Humans. Diabetologia 2014, 57, 2103–2107. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wen, J.; Nodzak, C.; Shi, X. QTL Analysis Beyond EQTLs. Methods Mol. Biol. 2020, 2082, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S.; Liu, Y.; Jiang, N.; Chen, J.; Leach, L.; Luo, Z.; Wang, M. Genome-Wide EQTLs and Heritability for Gene Expression Traits in Unrelated Individuals. BMC Genomics 2014, 15, 13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamyshna, I.; Pavlovych, L.; Pankiv, I.; Pankiv, V.; Kamyshnyi, A.I.; Kamyshna, L.; Pavlovych, I.; Pankiv, V.; Pankiv, A.K. Evaluation of the Influence of Single-Nucleotide Polymorphisms of Vitamin D Receptor ( Rs2228570 ), BDNF ( Rs6265 ), and NMDA ( Rs4880213 ) Genes on Gene Expression in Different Tissues. Int. J. Endocrinol. 2023, 19, 83–88. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kamyshna, I.I.; Pavlovych, L.B.; Sydorchuk, L.P.; Malyk, I. V; Kamyshnyi, A.M. BDNF Blood Serum Linkage with BDNF Gene Polymorphism (Rs6265) in Thyroid Pathology Patients in the West-Ukrainian Population. Endocr. Regul. 2021, 55, 193–203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kamyshna, I.I.; Pavlovych, L.B.; Kamyshnyi, A.M. Association between NMDA Gene Polymorphism (Rs4880213) and GRIN2B Blood Serum Levels in Thyroid Pathology Patients. J. Med. Life 2022, 15, 109–116. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dzhuryak, V.; Sydorchuk, L.; Sydorchuk, A.; Kamyshnyi, O.; Kshanovska, A.; Levytska, S.; Knut, R.; Sheremet, M.; Ivashchuk, S.; et al. Biointerface Research in Applied Chemistry. ultrasound 2020, 10, 5556–5563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lyubomirskaya, E.S.; Kamyshnyi, A.M.; Krut, Y.Y.; Smiianov, V.A.; Fedoniuk, L.Y.; Romanyuk, L.B.; Kravets, N.Y.; Mochulska, O.M. SNPs and Transcriptional Activity of Genes of Innate and Adaptive Immunity at the Maternal-Fetal Interface in Woman with Preterm Labour, Associated with Preterm Premature Rupture of Membranes. Wiad. Lek. 2020, 73, 25–30. [Google Scholar]
- Kamyshna, I.I.; Pavlovych, L.B.; Malyk, I.V.; Kamyshnyi, A.M. 25-OH Vitamin D Blood Serum Linkage with VDR Gene Polymorphism (Rs2228570) in Thyroid Pathology Patients in the West-Ukrainian Population. J. Med. Life 2021, 14, 549–556. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tapper, E.B.; Asrani, S.K. The COVID-19 Pandemic Will Have a Long-Lasting Impact on the Quality of Cirrhosis Care. J. Hepatol. 2020, 73, 441–445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gao, X.; Lv, F.; He, X.; Zhao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Zu, J.; Henry, L.; Wang, J.; Yeo, Y.H.; Ji, F.; et al. Impact of the COVID-19 Pandemic on Liver Disease-Related Mortality Rates in the United States. J. Hepatol. 2023, 78, 16–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
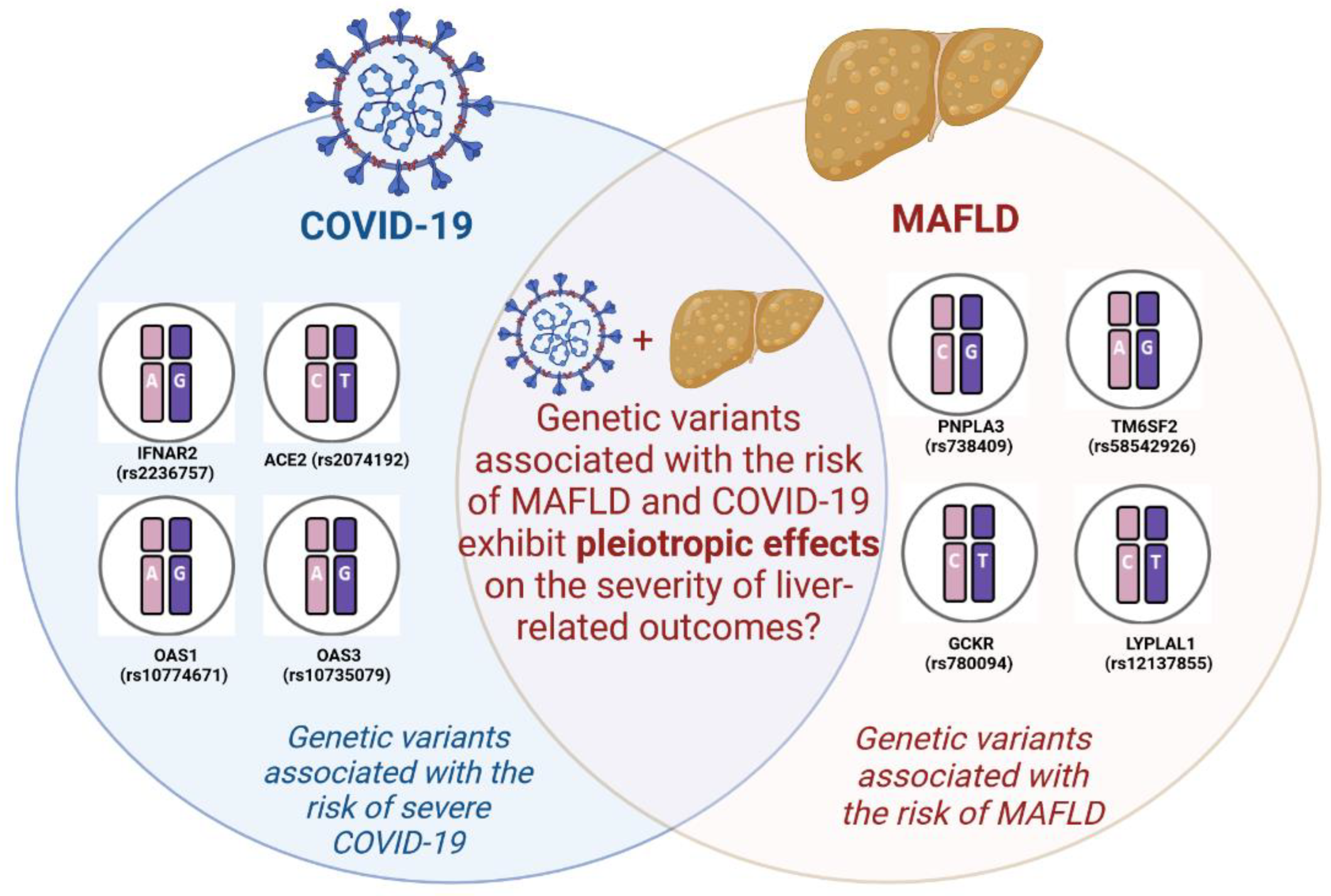
| Gene | SNP | The number of patients | SNP ’s effect | Significance | Features | Patient cohorts | References |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| PNPLA3 | rs738409 (C > G) (I148M) | 383 | Associated with an increased risk of severe COVID-19 outcomes | p = 0,035 (GG genotype) | Individuals harboring a GG genotype in the PNPLA3 gene may exhibit inherent upregulation of the NLRP3 inflammasome, rendering them more susceptible to tissue damage upon infection with SARS-CoV-2 | Italian populations | [44] |
| 1460 | Was not associated with the risk of severe COVID-19 | p > 0,1 | There appears to be an inclination towards protection against COVID-19 when considering the aforementioned genotype. These findings imply that the genetic inclination towards hepatic fat accumulation does not independently heighten the susceptibility to severe COVID-19. Moreover, this indicates that MAFLD does not assume a causal role in this particular condition | UK populations | [45] | ||
| 1585 | Associated with a lower risk of COVID-19 hospitalization and death | p = 0,027 (hospitalization); p = 0,037 (death) | On average, the presence of each additional G allele was associated with a notable decrease of 21% in the likelihood of COVID-19 hospitalization and a further decrease of 25% in the likelihood of COVID-19-related mortality | UK populations | [46] | ||
| 1397 | Was not associated with the risk of severe COVID-19 in hospitalized patients |
p = 0,46 | Intriguingly, a genetic predisposition to accumulate fat in the liver may paradoxically confer protection during the course of COVID-19 |
Hospital-based Fondazione IRCCS Ca' Granda cohort | [47] |
| Trait | CHR | Effective Allele | Tissue | Effect Size | p-value | Population | Sample Size | |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| GCKR rs780094 | ||||||||
| AC074117.1 | 2 | C | Fibroblast | -0,206732 | 3,23E-09 | MIX | 483 | |
| ATRAID | 2 | T | Blood | -0,20743 | 2,2E-13 | MIX | 2765 | |
| ATRAID | 2 | C | Blood-T cell CD8+ activated | 0,130598 | 0,00000114 | EAS | 416 | |
| ATRAID | 2 | C | Lymphocyte | 0,163788 | 0,0000466 | EUR | 368 | |
| EIF2B4 | 2 | C | Blood | -0,00922729 | 0,0000631 | MIX | 5257 | |
| EMILIN1 | 2 | T | Adipose-Subcutaneous | 0,24 | 0,00000333 | EUR | 770 | |
| GPN1 | 2 | C | Blood-T cell CD4+ activated | 0,188994 | 0,00000277 | EAS | 416 | |
| KRTCAP3 | 2 | T | Blood | -0,237548 | 6,3E-17 | MIX | 2765 | |
| KRTCAP3 | 2 | C | Blood-T cell CD4+ activated | 0,234009 | 0,0000181 | EAS | 416 | |
| NRBP1 | 2 | C | Lymphocyte | -0,141265 | 0,00000365 | EUR | 368 | |
| NRBP1 | 2 | C | Blood | -0,013931 | 2,04E-12 | MIX | 5257 | |
| NRBP1 | 2 | T | Blood | 0,153229 | 0,000000044 | MIX | 2765 | |
| NRBP1 | 2 | NA | Blood-Monocyte | 5,524902 | 6,21E-08 | EUR | 432 | |
| PPM1G | 2 | C | Adipose | -0,331022 | 0,0000007 | EUR | 434 | |
| SLC5A6 | 2 | T | Blood | 0,165322 | 4,7E-09 | MIX | 2765 | |
| SLC5A6 | 2 | NA | Blood-Monocyte | 0,233295 | 0,00000113 | MIX | 696 | |
| SNX17 | 2 | C | Blood-Monocytes CD14+ | -0,03898 | 0,00000409 | MIX | 197 | |
| SNX17 | 2 | T | Blood | 0,141788 | 0,00000034 | MIX | 2765 | |
| SNX17 | 2 | NA | Blood-Monocyte | 4,2447721 | 0,0000286 | EUR | 432 | |
| ZNF512 | 2 | C | Blood | 0,0147365 | 7,47E-08 | MIX | 5257 | |
| AC074117.1 | 2 | C | Fibroblast | -0,206732 | 3,23E-09 | MIX | 483 | |
| ATRAID | 2 | T | Blood | -0,20743 | 2,2E-13 | MIX | 2765 | |
| ATRAID | 2 | C | Blood-T cell CD8+ activated | 0,130598 | 0,00000114 | EAS | 416 | |
| ATRAID | 2 | C | Lymphocyte | 0,163788 | 0,0000466 | EUR | 368 | |
| PNPLA3 rs738409 | ||||||||
| SAMM50 | 22 | G | Blood-T cell CD8+ | -3,90455 | 9,44E-05 | EUR | 283 | |
| PNPLA3 | 22 | G | Skin | -0,13586 | 1,54E-06 | MIX | 605 | |
| SAMM50 | 22 | C | Blood | -0,07719 | 5,67E-106 | MIX | 5257 | |
| SAMM50 | 22 | G | Adipose-Subcutaneous | 0,188769 | 9,6E-07 | EUR | 385 | |
| AL031595.2 | 22 | G | Blood-Monocyte | 0,220815 | 0,00188 | EAS | 416 | |
| TM6SF2 rs58542926 | ||||||||
| ATP13A1 | 19 | G | Blood | 0,442548 | 3,13E-08 | EUR | 121 | |
| ATP13A1 | 19 | T | Blood-T cell CD4+ | 5,639089 | 1,71E-08 | EUR | 293 | |
| ATP13A1 | 19 | T | Blood-T cell CD8+ | 5,943743 | 2,79E-09 | EUR | 283 | |
| BORCS8 | 19 | T | Breast | -0,27489 | 4,48E-06 | MIX | 396 | |
| GATAD2A | 19 | C | Blood | -0,03402 | 5,07E-15 | MIX | 5257 | |
| GATAD2A | 19 | T | Blood | 0,163165 | 3,74E-06 | MIX | 670 | |
| MAU2 | 19 | T | Blood-T cell CD4+ | -4,67124 | 2,99E-06 | EUR | 293 | |
| MAU2 | 19 | T | Blood | -0,19358 | 6,75E-14 | MIX | 670 | |
| MAU2 | 19 | T | Blood | -0,18721 | 2,07E-07 | EUR | 369 | |
| TM6SF2 | 19 | T | Adipose-Subcutaneous | 0,32323 | 7,09E-05 | MIX | 581 | |
| YJEFN3 | 19 | T | Large Intestine-Colon | 0,200617 | 7,71E-05 | MIX | 318 | |
| LYPLAL1 rs12137855 | ||||||||
| LYPLAL1 | 1 | C | Lymphocyte | -0,122143 | 0,00085 | EUR | 368 | |
| LYPLAL1 | 1 | NA | Blood | -0,220481 | 0,000305 | EUR | 240 | |
| SLC30A10 | 1 | NA | Stem cell-iPSC | -0,143156 | 0,0313 | EUR | 215 | |
| LYPLAL1 | 1 | T | Blood-B cell | -2,04427 | 0,0409 | EUR | 45 | |
| RPS15AP12 | 1 | T | Adipose | 0,146055 | 0,0723 | EUR | 434 | |
| AC096642.1 | 1 | T | Artery-Tibial | -0,14702 | 1,58E-05 | MIX | 584 | |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





