Submitted:
07 July 2023
Posted:
07 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- What Life Cycle Extension Strategy (LCES) is suitable for digital CBM adoption?
- How does the digitalization of machines enable OEMs to innovate their BM?
2. Background
2.1. Digital CBMs for machine life cycle extension
2.2. Success stories
3. Materials and Methods
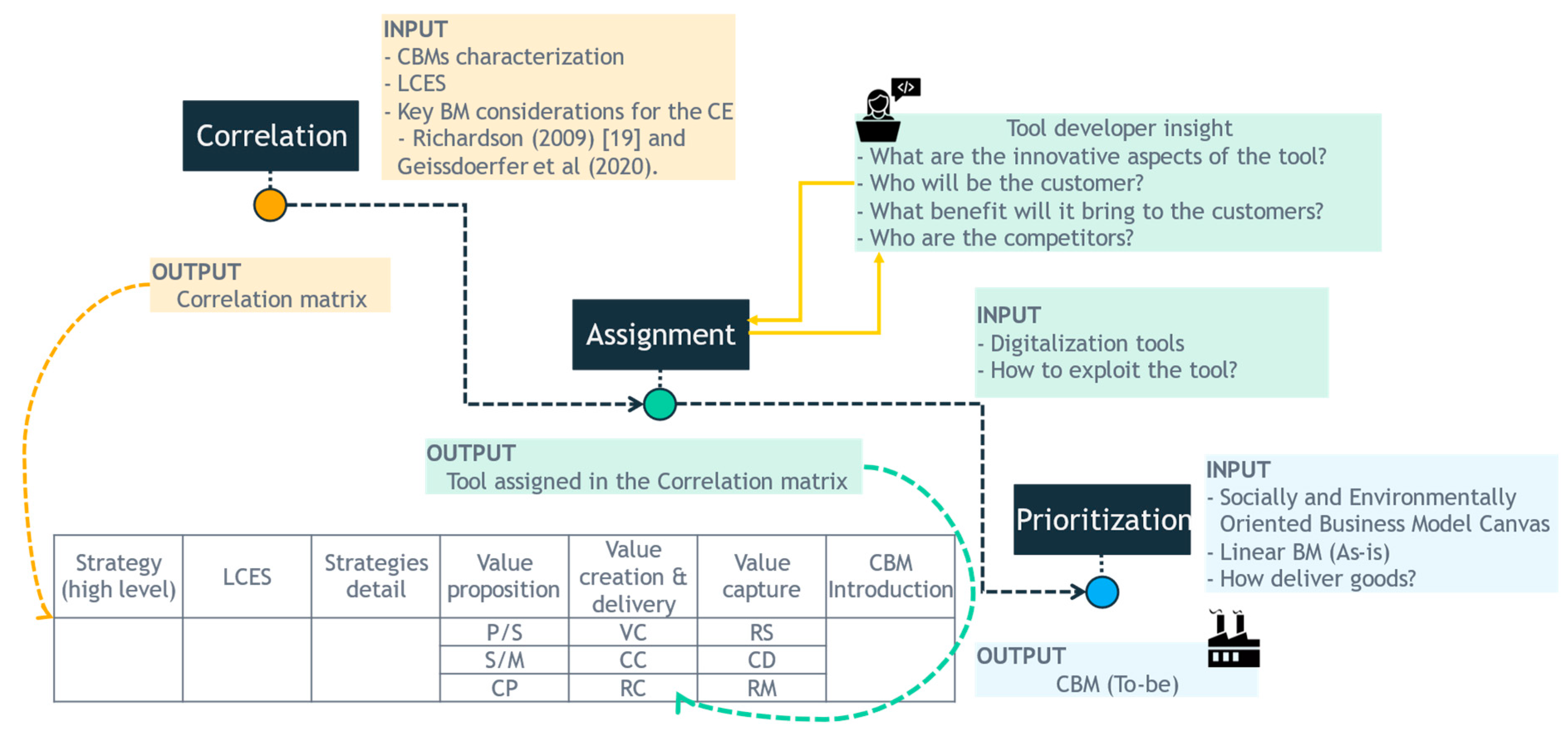
3.1. CBMs characterization
3.2. Correlation
3.3. Assignment
3.4. Prioritization
4. Results
4.1. Correlation matrix
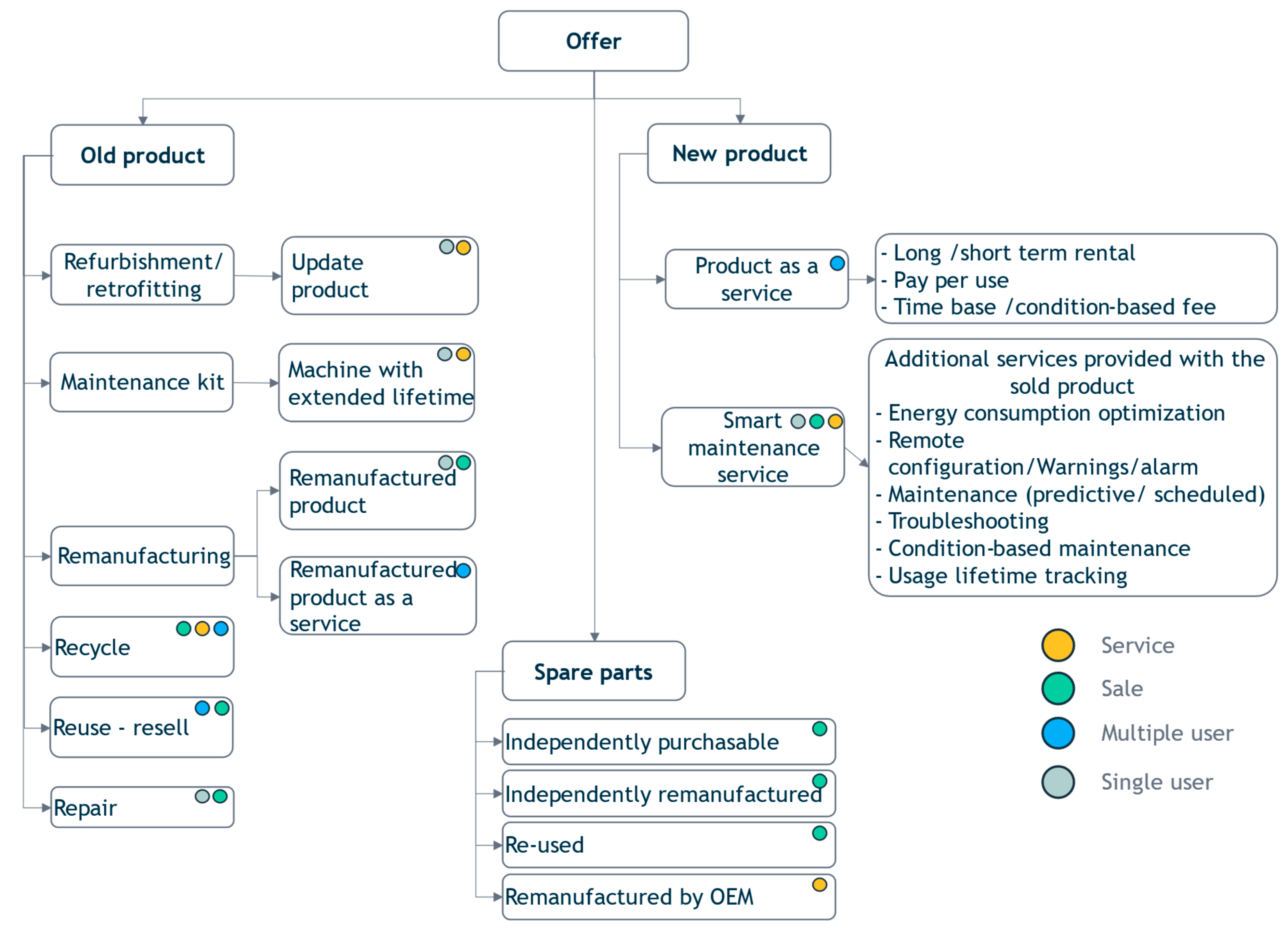
4.1.1. Reuse- Resell
4.1.2. Pay per use
4.1.3. Repair or corrective maintenance
4.1.4. Predictive maintenance
4.1.5. Time-based maintenance
4.1.6. Remanufacturing
4.1.7. Recondition
4.1.8. Refurbishment
4.1.9. Recycle & cannibalization
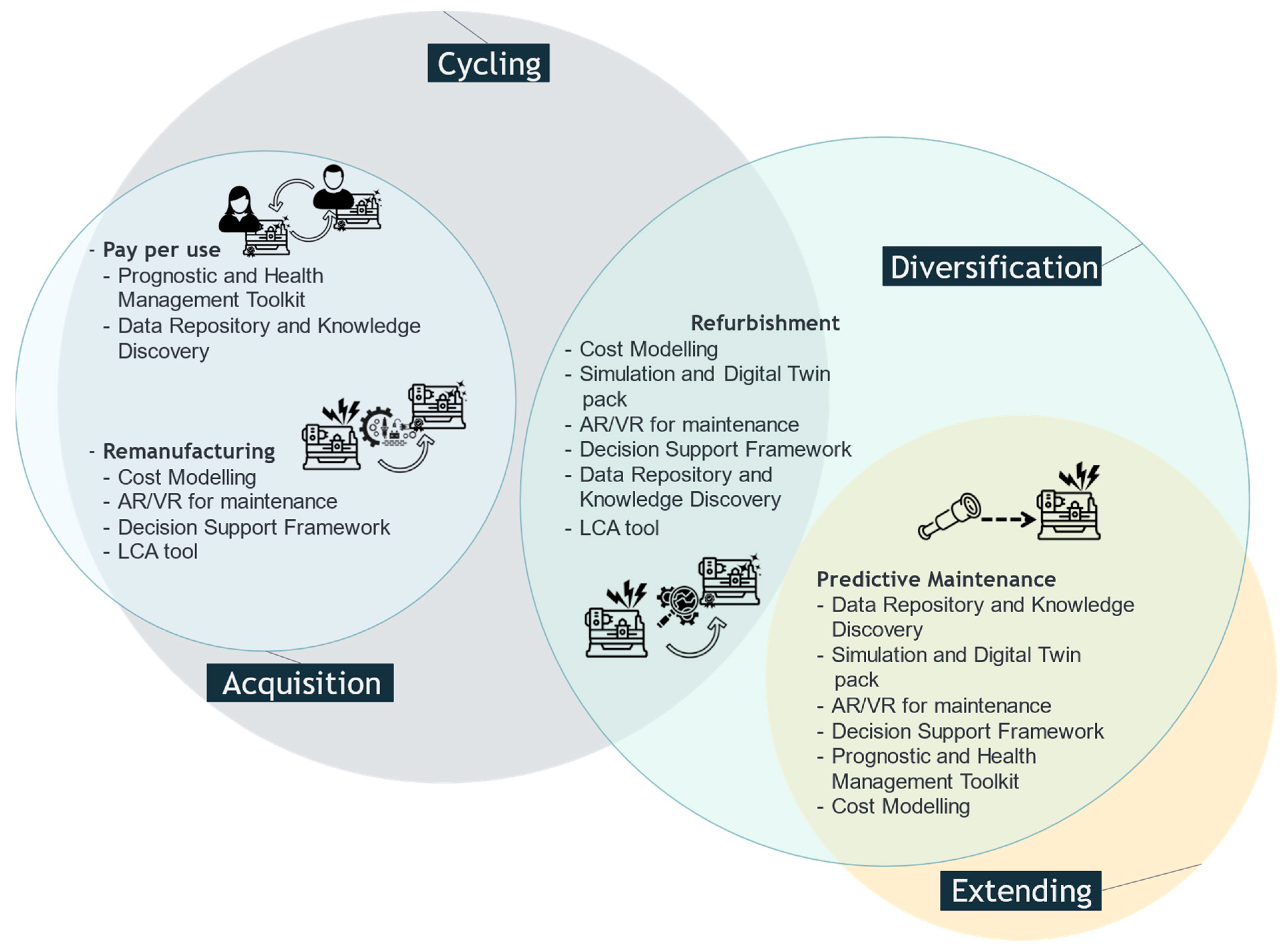
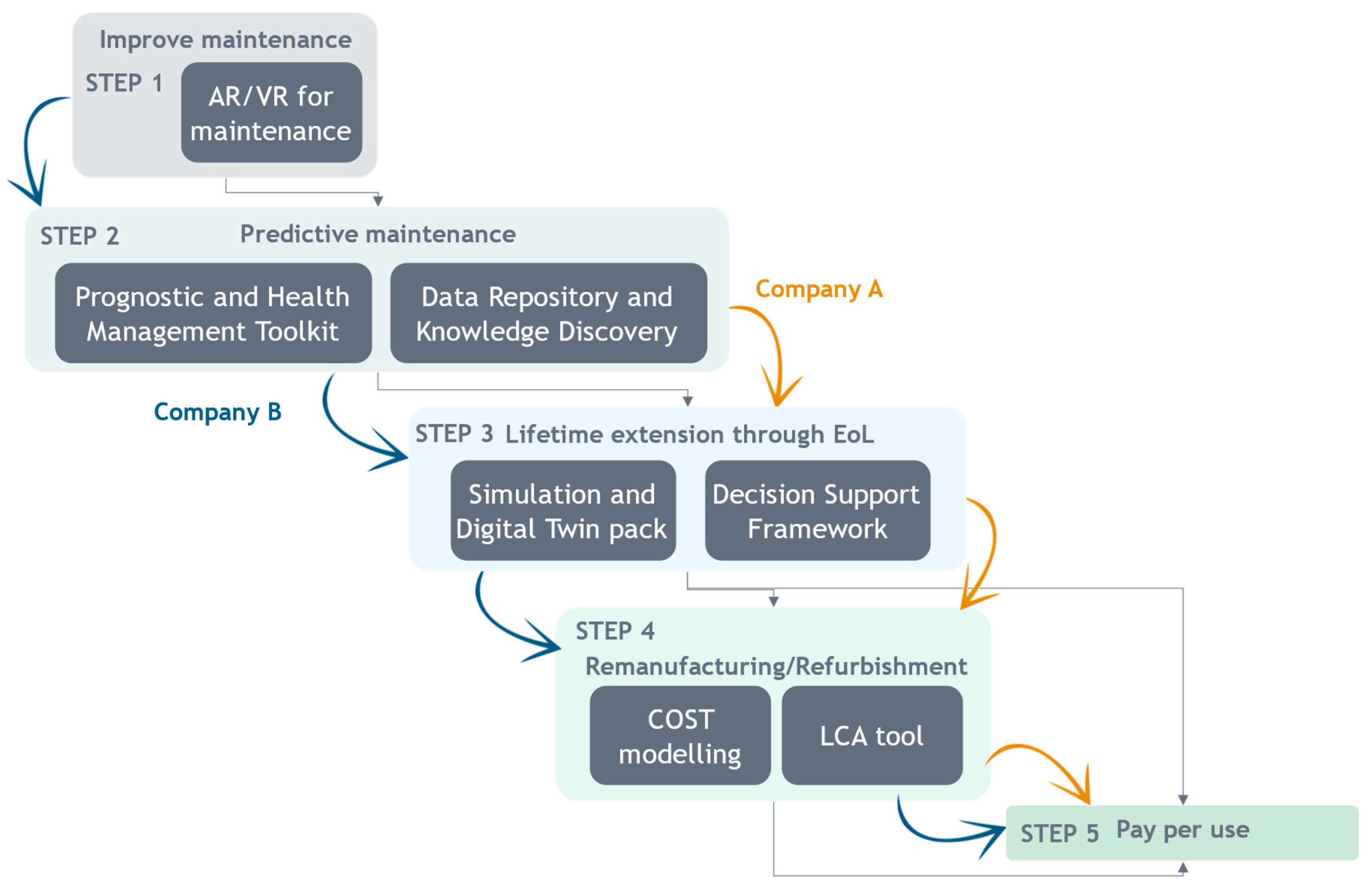
4.2. Business cases
- Segmenting the complex metamorphosis process from linear to CBMs
- Simplifying the transformation by tackling difficulties and changes little by little.
5. Discussion and conclusion
- It supports the exploitation of digitalization tools; with the advent of the fourth and fifth industrial revolutions [81] companies equip their products and processes with innovative tools. Their potentialities can be exploited more deeply and enlarged to a wider perspective with the support of the proposed approach. The correlation matrix as it has been developed in its general form, stands as a base to be specified for the single organization and thus digitalizing tools can be inserted between the core resources.
- It is based on qualitative evaluations, as it is purposed to support the very first decision-making steps.
- It is widely applicable in enterprises of different sectors, as the correlation matrix can be customized according to the peculiar needs and features of the involved organization.
- Economic sphere: only when a new practice expected by the exploited step is well-established and economically advantageous, the company may move to the following one; economical KPIs should not only observe the total revenues or incomes, derived from a certain LCE, rather might also evaluate the quantities of goods handles within that LCE.
- Environmental and social sphere: each step of the roadmap should be sustainable within all the pillars of sustainability, and benefits involving proper management of the resources (i.e., materials, EoL processes, waste reduction) and the impact of the organization on its employees and the surrounding citizenship should be quantified and reached, prior facing new challenges.
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
| 1 | H2020 project, grant agreement no. 869884. |
References
- Ertz, M.; Leblanc-Proulx, S.; Sarigöllü, E.; Morin, V. Made to break? A taxonomy of business models on product lifetime extension. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2019, 234, 867–880. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, S., Raghavendra, M. R. A., Kaminski, J., Pepin, H. Opportunities for industry 4.0 to support remanufacturing. Applied Sciences 2018, 8. [CrossRef]
- Lüdeke-Freund, F.; Gold, S.; Bocken, N.M.P. A Review and Typology of Circular Economy Business Model Patterns. J Ind Ecol 2019, 23, 36–61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rosa, P., Sassanelli, C., Urbinati, A., Chiaroni, D., & Terzi, S. Assessing relations between Circular Economy and Industry 4.0: a systematic literature review. International Journal of Production Research 2020, 58. [CrossRef]
- Fordal, J.M. , Schjølberg, P., Helgetun, H. et al. Application of sensor data based predictive maintenance and artificial neural networks to enable Industry 4.0. Adv. Manuf. 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöggl, J.P.; Rusch, M.; Stumpf, L.; Baumgartner, R.J. Implementation of digital technologies for a circular economy and sustainability management in the manufacturing sector. Sustainable Production and Consumption 2023, 35, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, F.; Rossi, M.; Germani, M. How de-manufacturing supports circular economy linking design and EoL - a literature review. J Manuf Syst 2022, 63, 118–133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hatcher, G. D.; Ijomah, W. L.; Windmill, J. F. C. Design for remanufacture: a literature review and future research needs. J Clean Prod 2011, 19, 2004–2014. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lahrour, Y; Brissaud, D. ; Zwolinski, P. The strategy for implementing remanufacturing process in a commercial enterprise, the case study of a French company. Procedia CIRP 2019, 80, 554–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Henry, M.; Bauwens, T.; Hekkert, M.; Kirchherr, J. A Typology of Circular Start-Ups: Analysis of 128 Circular Business Models. J Clean Prod 2020, 245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sassanelli, C.; Rosa, P.; Rocca, R.; Terzi, S. Circular Economy Performance Assessment Methods: A Systematic Literature Review. J Clean Prod 2019, 229, 440–53. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bocken, N.M.P.; de Pauw, I.; Bakker, C.; van der Grinten, B. Product Design and Business Model Strategies for a Circular Economy. J Ind Prod Eng 2016, 33, 308–20. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lopes de Sousa Jabbour, A.B.; Luiz, J.V.R.; Luiz, O.R.; Jabbour, C.J.C.; Ndubisi, N.O.; de Oliveira, J.H.C.; Horneaux, F.J. ; Circular Economy Business Models and Operations Management. J Clean Prod 2019, 235, 1525–39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fontana, A.; Barni, A.; Leone, D.; Spirito, M.; Tringale, A.; Ferraris, M.; Reis, J.; Goncalves, G. Circular Economy Strategies for Equipment Lifetime Extension: A Systematic Review, Sustainability 2021, 13, 1117. [CrossRef]
- Martin, P.; Guide, V.D.R.; Craighead, C.W. Supply Chain Sourcing in Remanufacturing Operations: An Empirical Investigation of Remake versus Buy. Decision Sci 2010, 41, 301–24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steinhilper, R.; Weiland, F. Exploring New Horizons for Remanufacturing an Up-to-Date Overview of Industries, Products and Technologies. Proc Cirp 2015, 29, 769–73. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dassisti, M.; Florio, G.; Maddalena, F. Cryogenic Delamination and Sustainability: Analysis of an Innovative Recycling Process for Photovoltaic Crystalline Modules. In Sustainable Design and Manufacturing, Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies; Campana, G., Howlett, R.J., Rossi, S., Cimatti, B., Eds.; 2017; Volume 68. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schöggl, J.P.; Rusch, M.; Stumpf, L.; Baumgartner, R.J. Implementation of difital technologies for a circular economy and sustainability management in the manufacturing sector. Sustainable Production and Consumption 2023, 35, 401–420. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, S.; Hughes, M.; Hodgkinson, I.; Hughes, P. Digital transformation of industrial businesses: A dynamic capability approach. Technovation 2022, 113. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baines T, W. Lightfoot H. Servitization of the manufacturing firm. Exploring the operations practices and technologies that deliver advanced services. Int J Oper Prod Manag 2013, 34, 2–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagoropoulos A, Pigosso DCA, McAloone TC. The Emergent Role of Digital Technologies in the Circular Economy: A Review. Procedia CIRP 2017, 64, 19–24. [CrossRef]
- Liebherr, Rental services for construction machines. Available online: https://www.liebherr.com/en/usa/about-liebherr/service-services/service-services.html (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Hilti. Our fleet management service. Available online: https://www.hilti.group/content/hilti/CP/XX/en/services/tool-services/fleet-management.html#nav/close (accessed on 15 December 2022).
- Cat Reman. Available online: https://www.caterpillar.com/en/brands/cat-reman.html (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Aston business School, case studies. Available online: https://www.advancedservicesgroup.co.uk/research/publications/case-studies (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Goodyear. Available online: https://news.goodyear.eu/goodyear-launches-digital-innovations-to-reduce-otr-costs/ (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Bosch eXchange. Available online: https://www.boschaftermarket.com/xrm/media/images/country_specific/it/xx_pdfs_28/parts_5/gamma_bosch_exchange.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Volvo. Available online: https://www.volvotrucks.com/en-en/news-stories/magazine-online/2018/may/remanufacturing-engines.html (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Schneider Electric. Available online: https://www.se.com/uk/en/ (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Valtra. (s.d.). Parts and services. Available online: https://www.valtra.co.uk/service/services-and-repair/spare-parts.html (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Tarmac. (s.d.). Available online: https://www.tarmacaerosave.aero/about-us (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Fairphone. (s.d.). Available online: Tratto da https://www.fairphone.com/it/impact/ (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Hyla Mobile. (s.d.). Available online: https://www.hylamobile.com/#content3 (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Taitonetti. Available online: https://taitonetti.fi/index.php?route=blog/article&path=2&article_id=15 (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- CCL North. (s.d.), Company publication. Available online: https://www.cclnorth.com/ (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Apple. Liam, an Innovation Story. Available online: https://www.apple.com/environment/pdf/Liam_white_paper_Sept2016.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Vonk, L. Paying attention to waste: Apple’s circular economy. Continuum 2018, 32, 745–757. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheung, W.M.; Marsh, R.; Griffin, P.W.; Newnes, L.B.; Mileham, A.R.; Lanham, J.D. Towards cleaner production: A roadmap for predicting product end-of-life costs at early design concept. Journal of Cleaner Production 2015, 87, 431–441. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Philips. (s.d.). Decoupling growth from resource consumption. Available online: https://www.philips.com/a-w/about/sustainability/circular-economy (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Hp. Sustainable Impact Report. Available online: https://www8.hp.com/h20195/v2/GetPDF.aspx/c05179523.pdf#page=1 (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Dell. (2018). Design for Environment. Available online: https://i.dell.com/sites/content/corporate/corp-comm/en/Documents/design-for-environment.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Motorola. (s.d.). Corporate Responsibility. Available online: https://www.motorola.com/us/about/corporate-responsibility-recycling (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Lowe, G.; Bogue, R. Design for disassembly: A critical twenty-first century discipline. Assembly Automation 2007, 27, 285–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kodak. Corporate Responsibility Report. Available online: https://www.kodak.com/content/products-brochures/Company/Kodak-2017-Corporate-Responsibility-Report.pdf (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Xerox. (s.d.). Prevent and manage waste. Available online: https://www.xerox.com/en-us/about/ehs/reduce-waste (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Canon. Environmental circulation. Available online: https://global.canon/en/environment/circulation.html (accessed on 16 December 2022 ).
- Opresnik, D.; Taisch, M. The manufacturer’s value chain as a service - the case of remanufacturing. Journal of Remanufacturing 2015, 5, 1–23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Matsumoto, M. Development of a simulation model for reuse businesses and case studies in Japan. Journal of Cleaner Production 2010, 18, 1284–1299. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enerkem. (s.d.). Carbon Recycling. Available online: https://enerkem.com/process-technology/carbon-recycling/ (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Clarios. (s.d.). The Clarios difference. Available online: https://www.clarios.com/products (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Renault. Renault optimizes the lifecycle of its electric vehicle batteries. Available online: https://group.renault.com/en/news-on-air/news/renault-optimizes-the-lifecycle-of-its-electric-vehicle-batteries/ (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- AB InBev. (s.d.). Driving Sustainable Packaging. Available online: https://www.ab-inbev.com/sustainability/circular-packaging/ (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Re Pack. (s.d.). Upgrade your unpacking. Available online: https://www.originalrepack.com/ (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Toner Plast. (s.d.). Cloose the loop. Available online: https://www.closetheloop.com.au/tonerplas/ (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Eldan Recycling. The best of tyre recycling. Available online: https://eldan-recycling.com/tyre-recycling/ (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Lehigh technologies. (s.d.). Micronized rubber powders. Available online: https://lehightechnologies.com/what_we_do/the_business_we_are_in/#gallery (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Timberland. (s.d.). Drive. Recycle. Wear. Available online: https://www.timberland.com/blog/archive/timberland-tires.html (accessed on 16 December 2022).
- Gulipac, S. Industrial Symbiosis: Building on Kalundborg's waste management experience. Renewable Energy Focus 2017, 17, 25–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciccarelli, M.; Papetti, A.; Cappelletti, F.; Brunzini, A.; Germani, M. Combining World Class Manufacturing system and Industry 4.0 technologies to design ergonomic manufacturing equipment. Int J Inter Design Manuf 2022, 16, 263–279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geissdoerfer, M.; Pieroni, M.P.P.; Pigosso, D.C.A.; Soufani, K. Circular business models: A review. J Clean Prod 2020, 277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schiavone, F.; Leone, D.; Caporuscio, A.; Lan, S. Digital servitization and new sustainable configurations of manufacturing systems. Technol Forecast Soci 2022, 176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sparviero, S. The Case for a Socially Oriented Business Model Canvas: The Social Enterprise Model Canvas. J Soc Entrepren 2019, 10, 232–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kin, S.T.M., Ong, S.K., Nee, A.Y.C. Remanufacturing process planning. Procedia CIRP 2014, 15, 189–194. [CrossRef]
- Zheng, Y., Liu, J., & Ahmad, R. A cost-driven process planning method for hybrid additive–subtractive remanufacturing. Journal of Manufacturing Systems 2020, 55, 248–263. [CrossRef]
- Poschmann, H., Brüggemann, H., & Goldmann, D. Disassembly 4.0: A Review on Using Robotics in Disassembly Tasks as a Way of Automation. Chemie-Ingenieur-Technik 2020, 92, 341–359. [CrossRef]
- Chierici, E., Copani, G. Remanufacturing with Upgrade PSS for New Sustainable Business Models. Procedia CIRP 2016. [CrossRef]
- Kurilova-Palisaitiene, J., Sundin, E. Toward pull remanufacturing: A case study on material and information flow uncertainties at a German engine remanufacturer. Procedia CIRP 2015, 26, 270–275. [CrossRef]
- Harivardhini, S., Murali Krishna, K., Chakrabarti, A. An Integrated Framework for supporting decision making during early design stages on end-of-life disassembly. Journal of Cleaner Production 2017, 168, 558–574. [CrossRef]
- Sitcharangsie, S., Ijomah, W., Wong, T. C. Decision makings in key remanufacturing activities to optimise remanufacturing outcomes: A review. Journal of Cleaner Production 2019, 232, 1465–1481. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, C., Hu, M., Di Maio, F., Sprecher, B., Yang, X., Tukker, A. An overview of the waste hierarchy framework for analyzing the circularity in construction and demolition waste management in Europe. Science of The Total Environment 2022, 803, 149892. [CrossRef]
- Butzer, S., Schötz, S., Steinhilper, R. Remanufacturing Process Assessment – A Holistic Approach. Procedia CIRP 2016, 52, 234–238. [CrossRef]
- Dassisti, M., Florio, G., Maddalena, F. Cryogenic Delamination and Sustainability: Analysis of an Innovative Recycling Process for Photovoltaic Crystalline Modules. Sustainable Design and Manufacturing 2017. Smart Innovation, Systems and Technologies 2017, 68, 11. [CrossRef]
- Yousef, S., Tatariants, M., Makarevičius, V., Lukošiūtė, S. I., Bendikiene, R., Denafas, G. A strategy for synthesis of copper nanoparticles from recovered metal of waste printed circuit boards. Journal of Cleaner Production 2018, 185, 653–664. [CrossRef]
- Peng, S., Li, T., Li, M., Guo, Y., Shi, J., Tan, G. Z., Zhang, H. An integrated decision model of restoring technologies selection for engine remanufacturing practice. Journal of Cleaner Production 2019, 206, 598–610. [CrossRef]
- Hu, Z., Qin, X., Shao, T. Welding Thermal Simulation and Metallurgical Characteristics Analysis in WAAM for 5CrNiMo Hot Forging Die Remanufacturing. Procedia Engineering 2017, 207, 2203–2208. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Ao, X., Cai, W., Jiang, Z., Zhang, H. A sustainability evaluation method integrating the energy, economic and environment in remanufacturing systems. Journal of Cleaner Production 2019, 239, 118100. [CrossRef]
- Huang, W., Jiang, Z., Wang, T., Wang, Y., Hu, X. Remanufacturing Scheme Design for Used Parts Based on Incomplete Information Reconstruction. Chinese Journal of Mechanical Engineering (English Edition) 2020, 33. [CrossRef]
- Wu, Z., Li, T., Li, Q., Shi, B., Li, X., Wang, X., Lu, H., Zhang, H. C. Process optimization of laser cladding Ni60A alloy coating in remanufacturing. Optics and Laser Technology 2019, 120. [CrossRef]
- Peng, H., Wang, H., Chen, D. Optimization of remanufacturing process routes oriented toward eco-efficiency. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering 2019, 14, 422–433. [CrossRef]
- Cappelletti, F., Rossi, M., Marasca M., Germani, M. De-manufacturing: identification of the best strategies through the environmental and economic evaluation. International Journal on Interactive Design and Manufacturing 2023. [CrossRef]
- Papetti, A., Ciccarelli, Scoccia, C., Palmieri, G., Germani, M. A human-oriented design process for collaborative robotics. International Journal of Computer Integrated Manufacturing 2022. [CrossRef]
| Strategy (high level) | LCES | Value proposition | CBM introduction |
|---|---|---|---|
| Cycling | Resell–Reuse | Used machine take back | Acquisition |
| Pay per use | Machine as a service (rent- subscription/pay per use) | ||
| Remanufactured machine as a service | |||
| Recondition | Reconditioned machine | ||
| Refurbish | Machine refurbishment | ||
| Back in box spare parts | Diversification | ||
| Cannibalization | Used machine take back | Acquisition | |
| Recycle | Used machine take back | ||
| Remanufacture | Remanufactured machines | ||
| Extending | Repair or Corrective Maintenance | Remote/automatic troubleshootingAR maintenance | Diversification |
| Spare parts/modules rent | |||
| Preventive M. | - Remote configuration, statistics and alarms- AR for maintenance | Diversification | |
| Predictive M. | - Remote configuration, statistics and alarms - AR for maintenance- Usage lifetime tracking | Diversification | |
| Time-based M. | Maintenance kit | Diversification |
| Value proposition | Value creation & delivery | Value capture | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P/S | Sell used full products or parts of it | VC | RSC management operations (take back) | RS | Revenues models based on used parts of product sale |
| S/M | Segment of existing or new customers | CC | Capacity management (demand and supply of products) | CD | - Machine disassembly/inspection/ri-assembly - Logistics costs |
| CP | Need machine but with lower initial investments | RC | Machine experts or specific tools able to understand the state of the part/product | RM | Sale |
| Value proposition | Value creation & delivery | Value capture | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P/S | Machine as a service | VC | - Services operations - SC/RSC management operations |
RS | - (Reman) machine is provided by time/activities - Lower cost of spare parts supply - Reimbursement from dismantlers |
| Remanufactured machine as a service | |||||
| S/M | Segment of existing or new customers | CC | - Machine maintenance - Capacity management |
CD | - Maintenance - Machine disassembly/inspection/ri-assembly - Logistics costs |
| - Machine maintenance - Capacity management - Machine remanufacturing | |||||
| CP | - pay only when the machine is needed - lower total cost of ownership and/or lower up-front investments - have functionality or temporary availability of products, no ownership |
RC | - Digital capabilities - Service network collaboration - Long-term customer relationship - Contract and customer relationship management |
RM | - Recurrent revenues from service temporary contracts - Pricing per unit of service (i.e., time, number of uses), rental or leasing rent |
| - Suppliers outsourcing and collaborations to close the loop - Disassembly, inspection, evaluation and assembly operations | |||||
| Value proposition | Value creation & delivery | Value capture | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P/S | TroubleshootingAR maintenance | VC | Support maintenance phase /service operations | RS | Revenues models based on service packages |
| Spare parts/modules rent | Revenues from storing services | ||||
| S/M | - Existing/new customers - Segments of customers in need of expertise in certain non-core activities, convenience |
CC | Knowledge of machine and failure cases | CD | Service maintenance costs |
| Cost for warehousing and maintaining spare modules in good condition | |||||
| CP | Willing to accelerate/ make maintenance simpler | RC | - Digital capabilities - Service network cooperation |
RM | - Recurrent revenues from customized service packages - Platform fees |
| Suppliers’ management | |||||
| Value proposition | Value creation & delivery | Value capture | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P/S | - Remote configuration, statistics and alarms - AR for maintenance - Usage lifetime tracking |
VC | Avoid physical interventions | RS | Revenues models based on service packages and/or tailored contracts |
| S/M | - Existing/new customers - Segments of customers in need of expertise in certain non-core activities, convenience |
CC | Knowledge of machine and failure cases | CD | Service maintenance costs |
| CP | Need to avoid unexpected failures | RC | - Digital capabilities - Service network cooperation |
RM | - Recurrent revenues from customized service packages - Platform fees |
| Value proposition | Value creation & delivery | Value capture | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| P/S | Maintenance kit | VC | Periodical shipment of maintenance kits to the customers | RS | Revenue models based on maintenance kit fee |
| S/M | -Segment of existing customers who wish to carry out maintenance autonomously - Segment of existing customers that did not buy original spare parts before |
CC | - Machine/customer localization- Orchestration of suppliers - Capacity management (demand and supply of products) |
CD | Maintenance kit logistics |
| CP | Need to avoid unexpected failures | RC | - Service network cooperation - Long-term customer relationship |
RM | Revenue from providing maintenance kit (time-based) |
| Value proposition | Value creation & delivery | Value capture | |||
| P/S | Remanufactured machines | VC | - RSC management (take back) and remanufacture operations - acquire spare parts from discarded products |
RS | - Reman machine is sold - Lower cost of spare parts supply - Additional revenues from residual values of products/materials |
| S/M | Segment of existing or new customers | CC | - Machine remanufacturing - Capacity management (demand and supply of products) |
CD | - Maintenance during guarantee - Machine disassembly/inspection/ri-assembly |
| CP | - lower total cost of ownership and/or lower up-front investments - Need machine in good condition, but with lower initial investments |
RC | - Suppliers outsourcing and collaborations to close the loop - Disassembly, inspection, evaluation and assembly operations |
RM | Revenue from high-quality products at lower prices |
| Value proposition | Value creation & delivery | Value capture | |||
| P/S | Reconditioned machines | VC | RSC management (take back) and remanufacture operations | RS | - Reconditioned machine is sold - Lower cost of spare parts supply - Additional revenues from residual values of products/materials |
| S/M | Segment of existing or new customers | CC | - Machines recondition - Capacity management (demand and supply of products) |
CD | - Maintenance during guarantee - Machine disassembly/inspection/re-assembly |
| CP | - Lower total cost of ownership and/or lower up-front investments, convenience - Need machine in good condition - also not as new-, but with lower initial investments |
RC | - Suppliers outsourcing and collaborations to close the loop - Disassembly, inspection, evaluation and assembly operations |
RM | Revenue from reconditioned products sold at lower prices |
| Value proposition | Value creation & delivery | Value capture | |||
| P/S | Machine refurbishment | VC | Refurbish machines as done in pilot cases | RS | Additional revenue through upgrade service |
| Back in box spare parts | - Provided low-price spare parts - Reimburse the client for returning old part - spare parts RSC management |
Remanufactured spare part selling | |||
| S/M | Segment of existing customers that want their machines to be upgrade | CC | Supply chain management (if upgraded occur outside the shopfloor where the machine is installed) | CD | Refurbishment cost + machine analysis status costs (+ reverse supply chain cost) |
| Segment of existing customers that did not buy original spare parts before | Spare parts refurbishment | - RSC, inspection, refurbishment costs - cost for spare part residual value reimbursement |
|||
| CP | Wish to have a keeping-up to times machine without investing a lot | RC | - Service network cooperation - Knowledge of machines + upgrading technologies |
RM | Payment of refurbishment service |
| Wish to pay less for maintenance but want guaranteed well-functioning spare parts | - Service network cooperation - Spare parts residue value estimation |
Bosch Exchange - back in box | |||
| Value proposition | Value creation & delivery | Value capture | |||
| P/S | Used machine take back | VC | - RSC operation - Suppliers outsourcing and collaborations (i.e., collectors) |
RS | - Additional revenues from residual values of products/materials - Savings with reduced costs for resource input |
| S/M | Segment of customers who bought machines years ago and are replacing/dismantling the machine | CC | - Machine/customer localization - Recycling flow management |
CD | Costs related to machine taking back (RSC) and preparing for recycle |
| CP | - Need to get rid of old machine in a sustainable way - Need a turnkey solution for machine dismantling |
RC | - Access to core/EoL products/ Selective disassembly - RSC |
RM | Revenue model based on direct sales or trade of resources |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





