Submitted:
05 July 2023
Posted:
07 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
- We developed a high-performing system for real-time estimation of multi-person pose synchronization, detecting body synchronization across diverse visual inputs to calculate synchronization metrics. It leverages Lightweight OpenPose for efficient pose estimation, achieving a performance of 5-6 frames per second on a regular CPU. By analyzing pre-recorded rehearsal videos of jazz musicians, we extract 17 body synchronization metrics, encompassing arm, leg, and head movements. These metrics serve as features for our deep learning model. The system incorporates a robust synchronization metric, enabling accurate detection across various pose orientations.
- To assess the relationship between facial emotions and team entanglement, we compute the Pearson correlation between facial emotions and various body synchrony scores. Additionally, we conduct a regression analysis over the time series data, using body synchrony scores as predictors and facial emotions as dependent variables. This approach allows us to estimate the impact of body synchrony on facial emotions, providing deeper insights into the connection between team dynamics and emotional expressions.
- We propose a machine learning pipeline to predict the collective emotions of Jazz musicians using body synchrony scores to achieve accurate and interpretable results.
2. Related Work
2.1. Emotions
2.2. Facial Emotion Recognition (FER)
3. Methodology
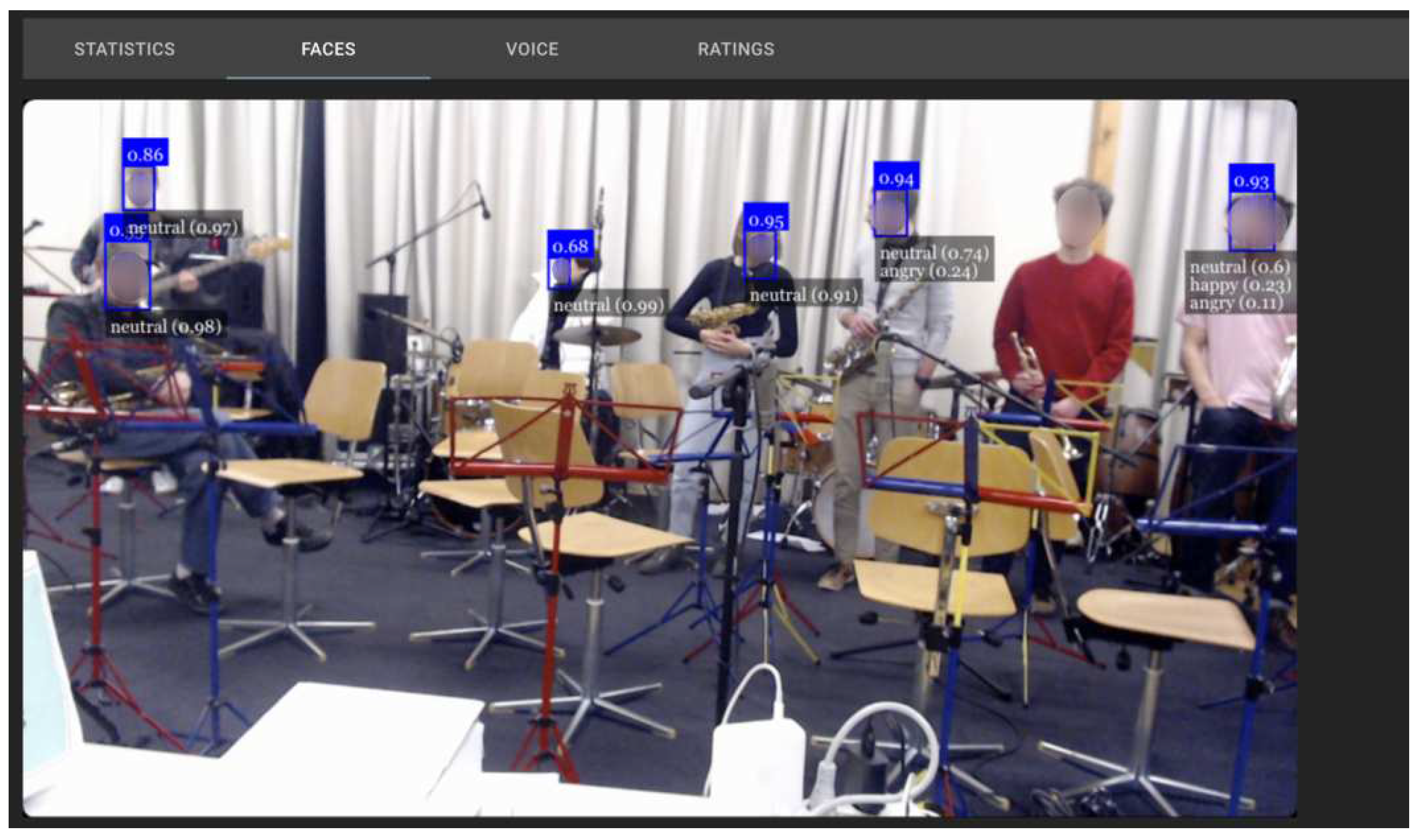
3.1. Extracting FER Time Series Data
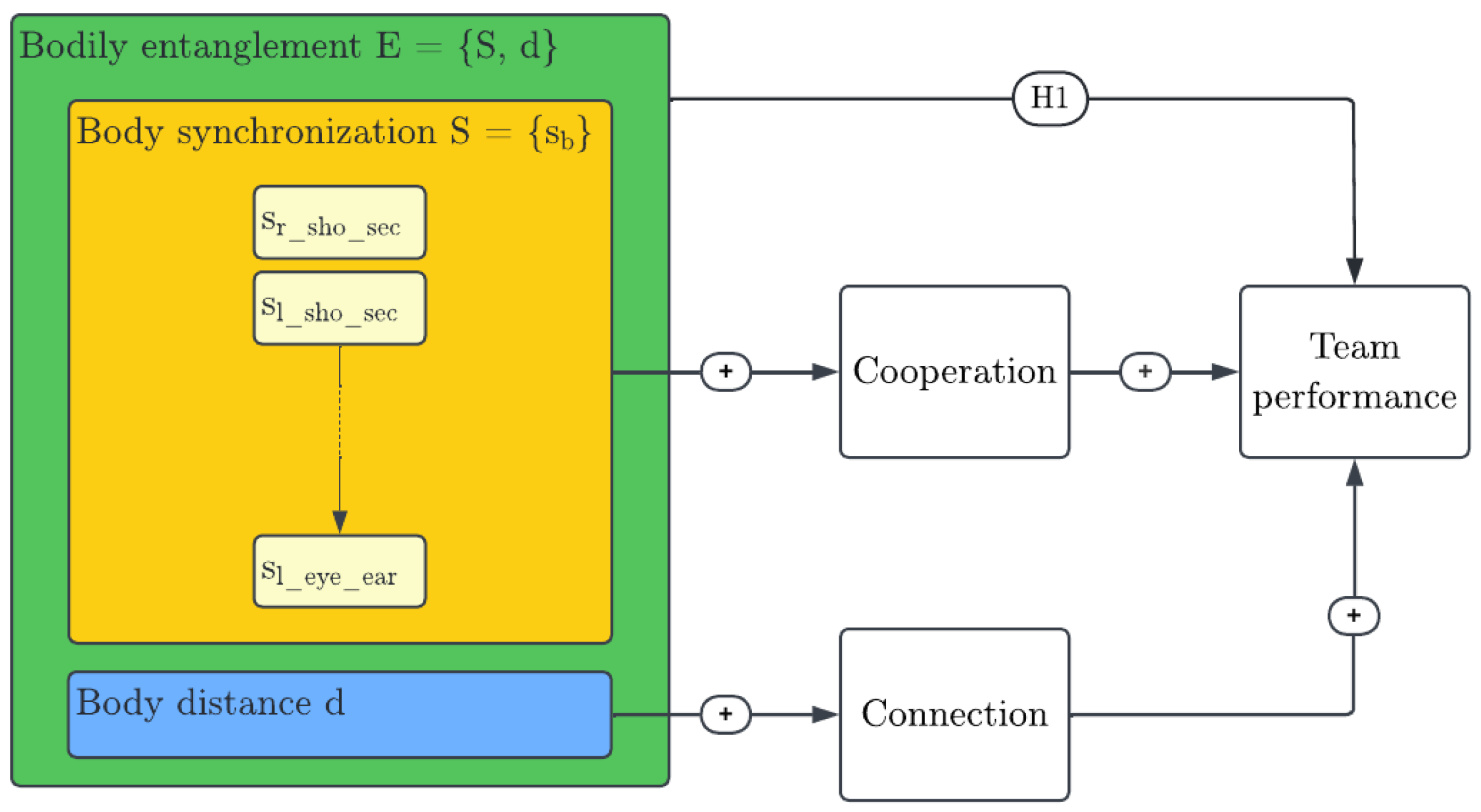
3.2. Team Entanglement
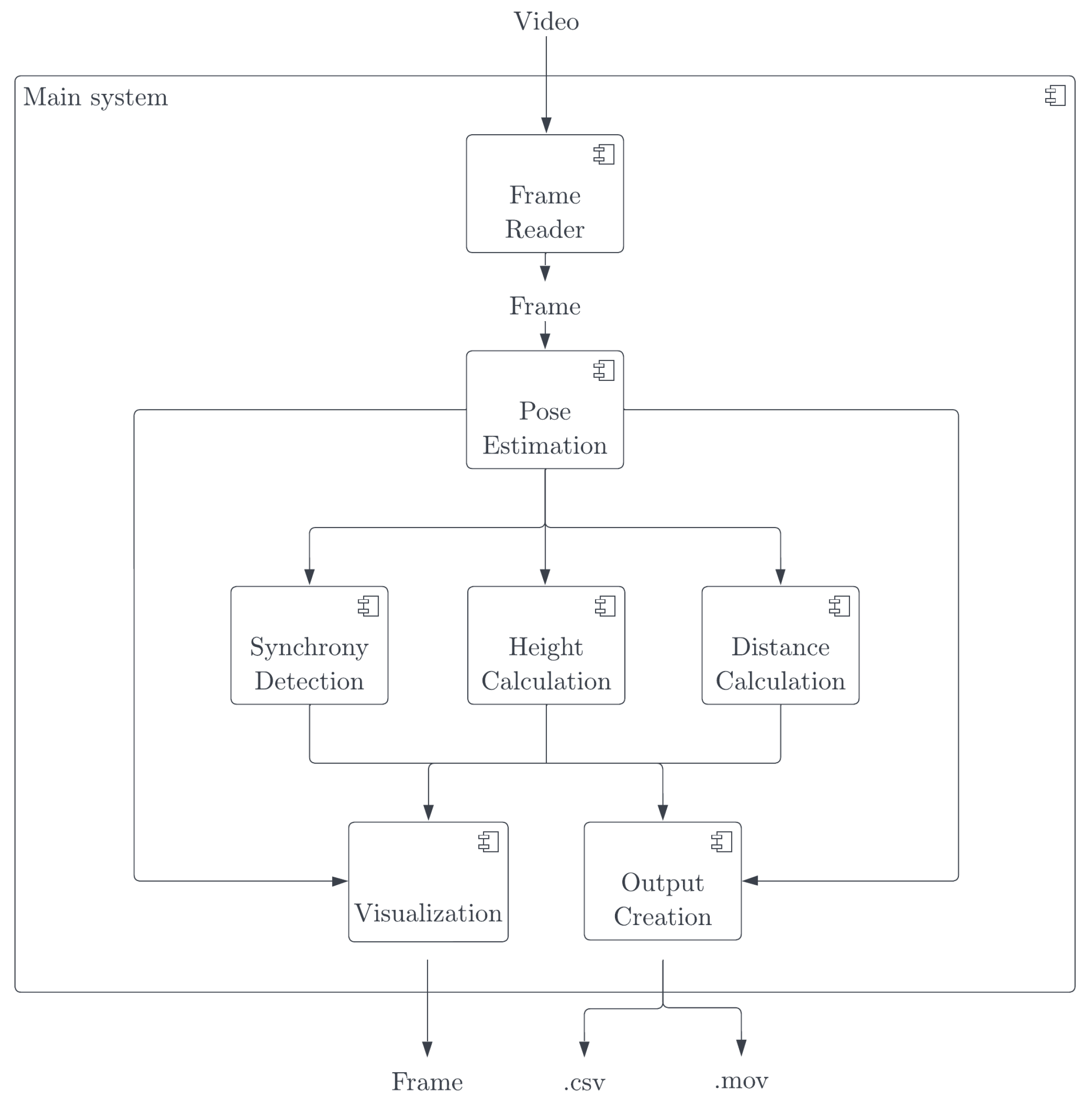
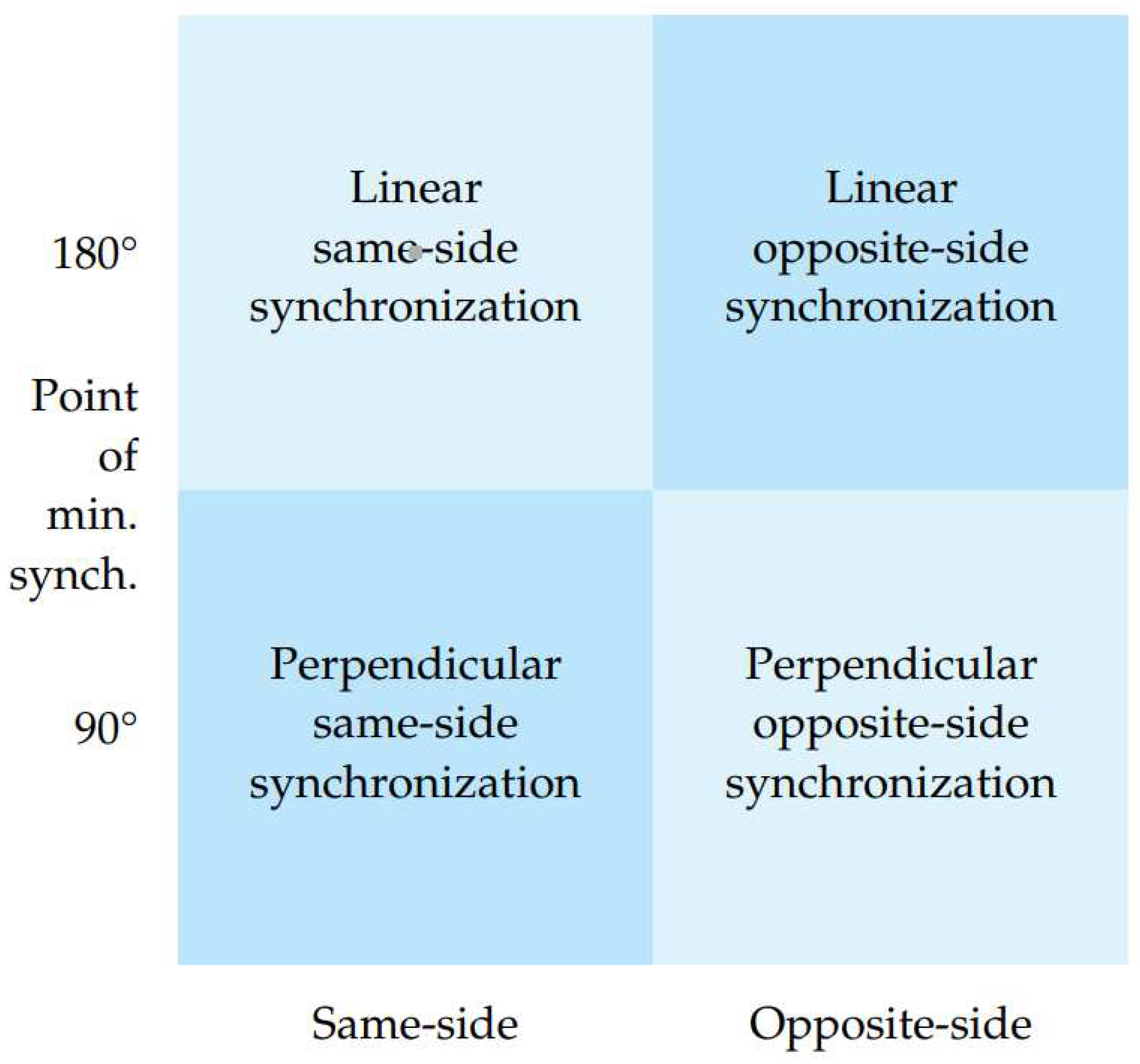
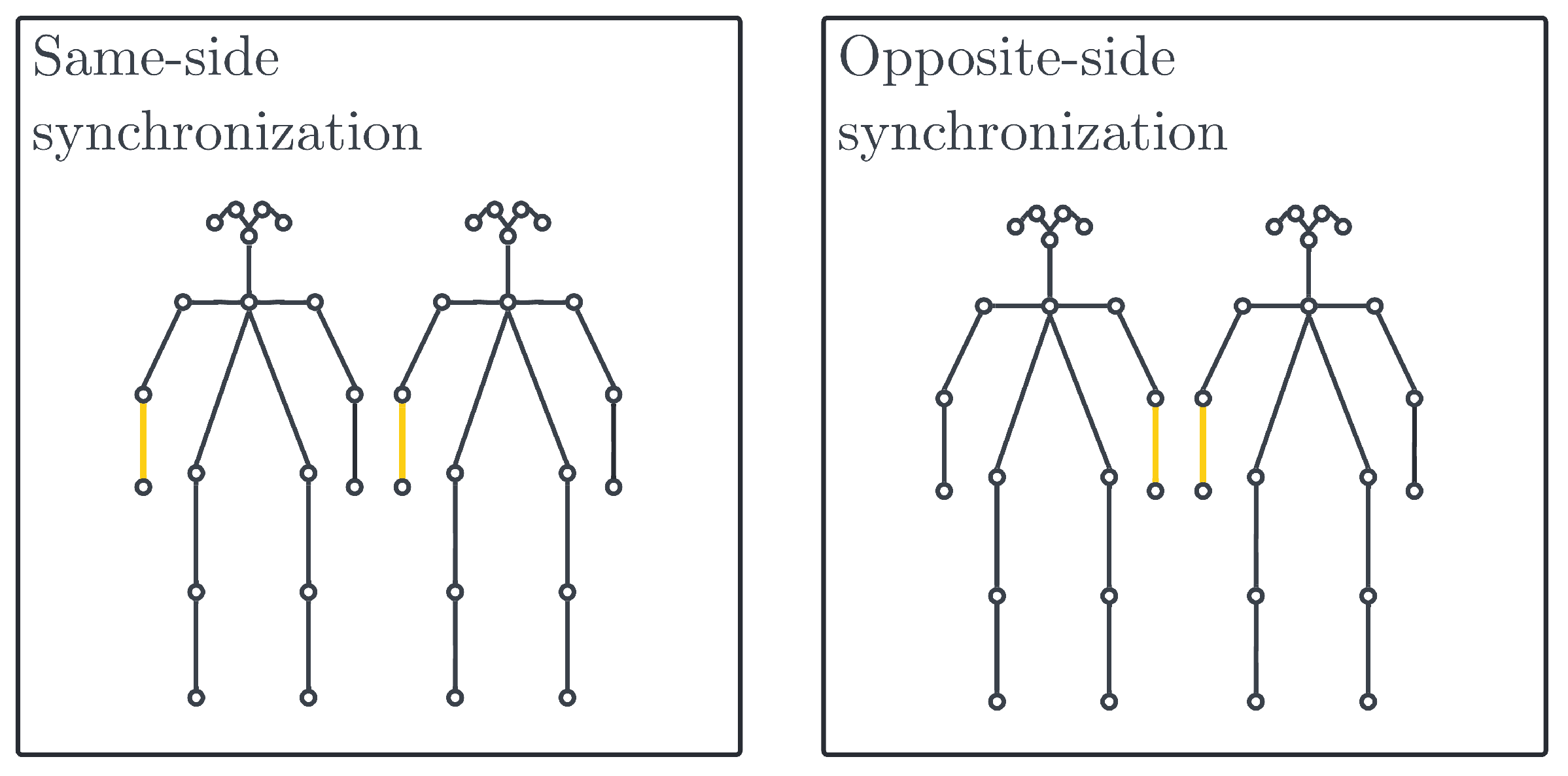
3.3. Real-Time Estimation of Multi-Person Pose Synchronization
3.3.1. Pose Estimation
3.3.2. Synchronization Calculation
3.3.3. Distance
3.4. Data Extraction & Pre-Processing
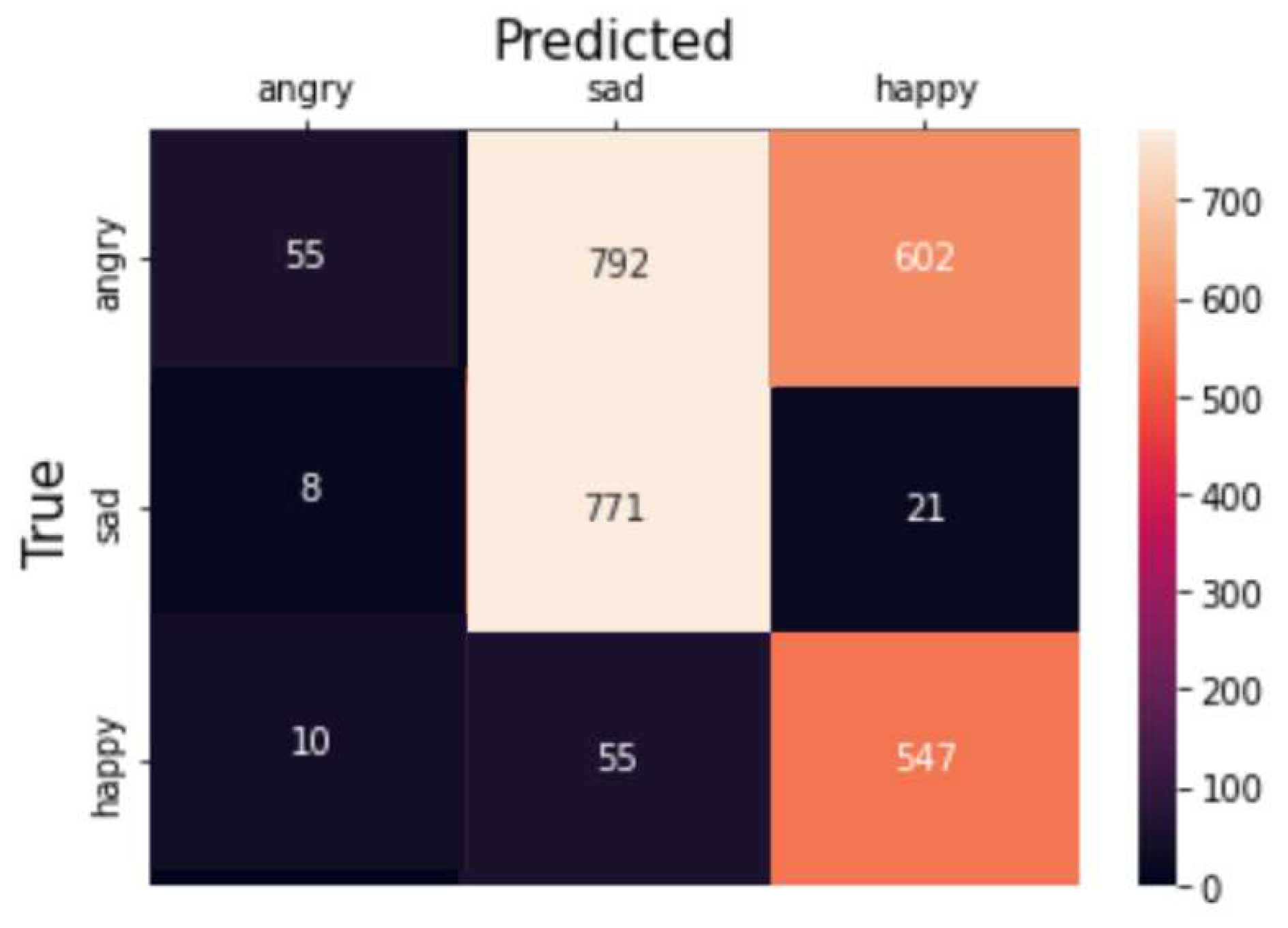
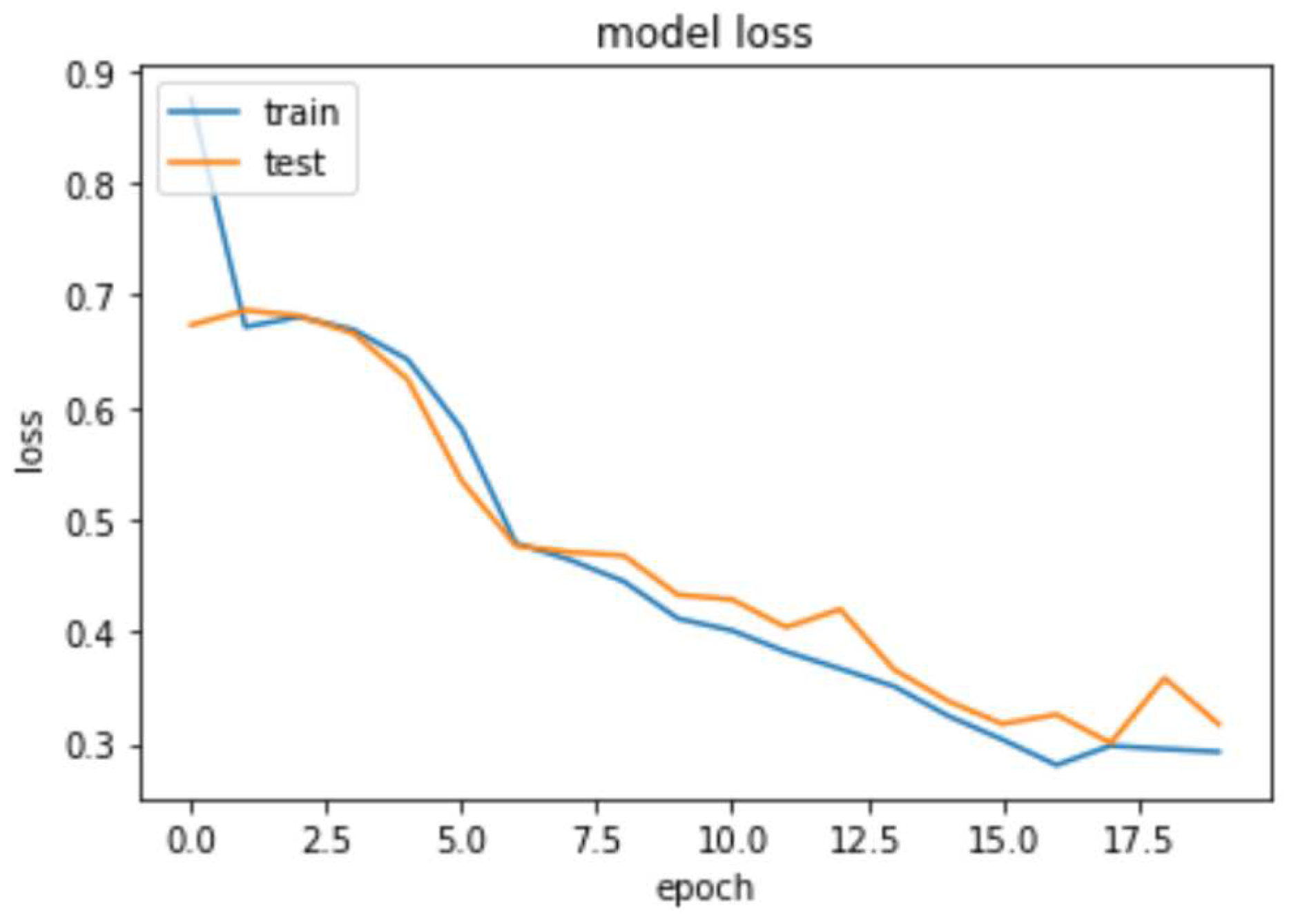
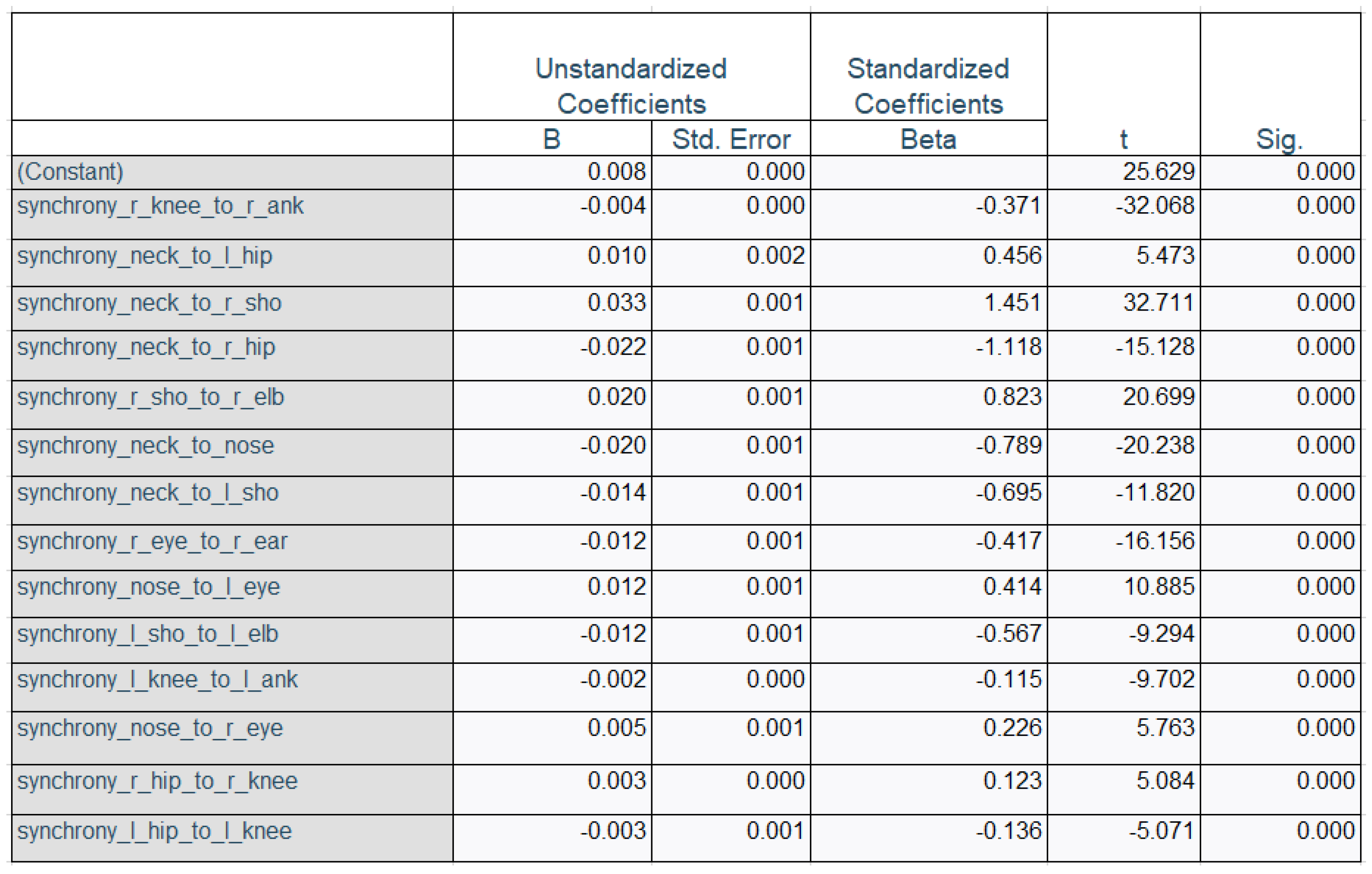
4. Results
4.1. Correlation Analysis
4.2. Regression Analysis
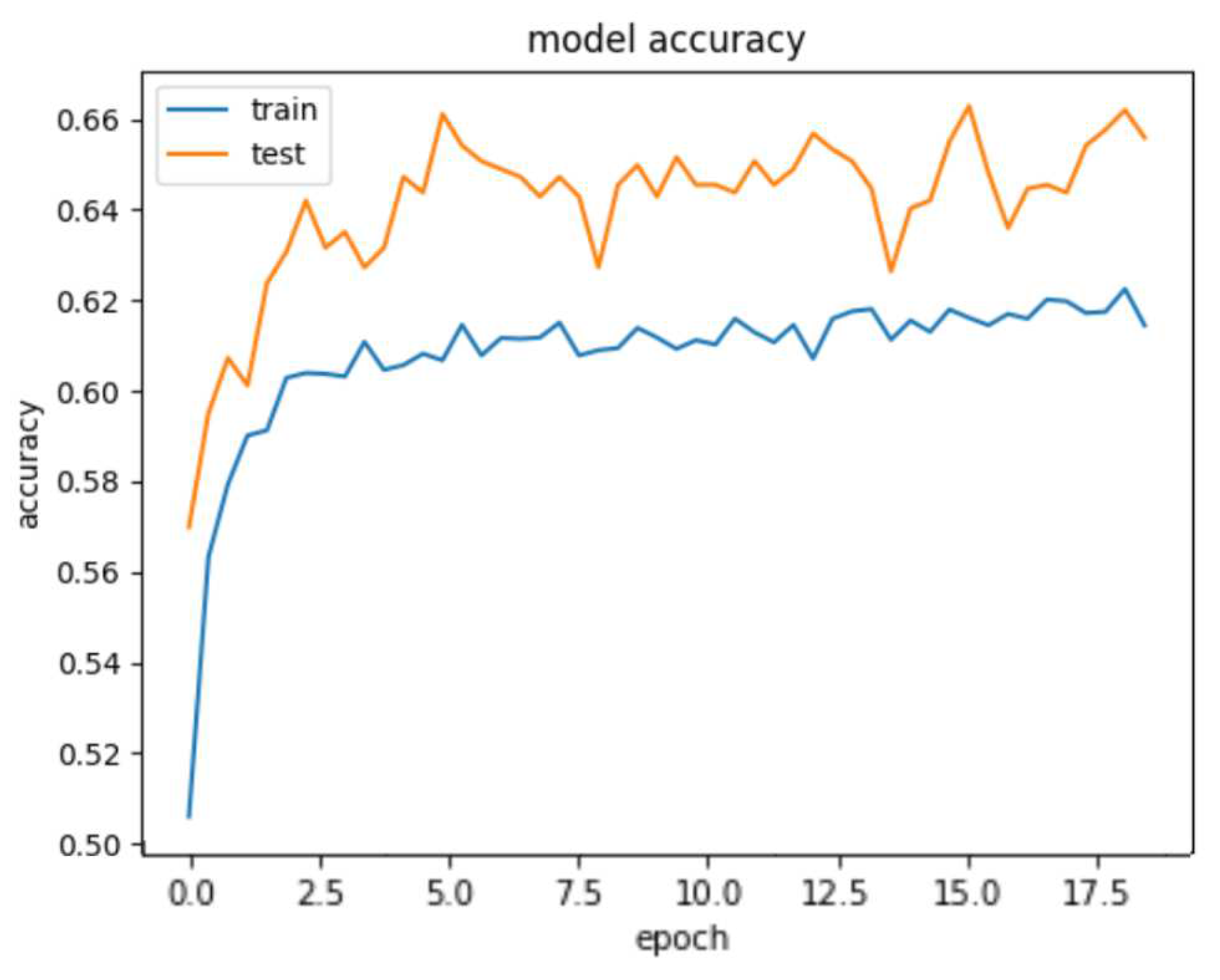
4.3. Deep Learning Model
5. Discussion
6. Limitations
7. Future Work & Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Usman, M.; Latif, S.; Qadir J., Using deep autoencoders for facial expression recognition, 13th International Conference on Emerging Technologies (ICET), Islamabad, Pakistan (2007), pp. 1-6, . [CrossRef]
- Guo, R.; Li, S.; He, L.; Gao, W.; Qi, H.; Owens, G., Pervasive and unobtrusive emotion sensing for human mental health, 7th International Conference on Pervasive Computing Technologies for Healthcare and Workshops, Venice (2013), pp. 436-439, http://dx.doi.org/10.4108/icst.pervasivehealth.2013.252133.
- De Nadai, S. et al., Enhancing safety of transport by road by on-line monitoring of driver emotions, 11th System of Systems Engineering Conference (SoSE), Kongsberg, Norway (2016), pp. 1-4, . [CrossRef]
- Verschuere, B.; Crombez, G.; Koster, E. H.W.; Uzieblo, K., Psychopathy and Physiological Detection of Concealed Information: A review. Psychologica Belgica (2006), 46(1-2), p. 99-116, . [CrossRef]
- Goldenberg, A.; Garcia, D.; Suri, G.; Halperin, E.; Gross, J., The Psychology of Collective Emotions (2017), http://dx.doi.org/10.31219/osf.io/bc7e6.
- Kerkeni, L.; Serrestou, Y.; Raoof, K.; Cléder, C.; Mahjoub, M.; Mbarki, M. (2019), Automatic Speech Emotion Recognition Using Machine Learning, http://dx.doi.org/10.5772/intechopen.84856.
- Ali, M.; Mosa, A.H.; Machot, F.A.; Kyamakya, K. (2018), Emotion Recognition Involving Physiological and Speech Signals: A Comprehensive Review. In: Recent Advances in Nonlinear Dynamics and Synchronization. Studies in Systems, Decision and Control, vol 109. Springer, Cham, . [CrossRef]
- Czarnocki, J., "Will new definitions of emotion recognition and biometric data hamper the objectives of the proposed AI Act?," International Conference of the Biometrics Special Interest Group (BIOSIG), Darmstadt, Germany (2021), pp. 1-4, . [CrossRef]
- Galesic, M. et al., Beyond collective intelligence: Collective adaptation. J R Soc Interface (2023), https://royalsocietypublishing.org/doi/10.1098/rsif.2022.0736.
- Li, S.; Deng, W., "Deep Facial Expression Recognition: A Survey," in IEEE Transactions on Affective Computing, vol. 13, no. 3, pp. 1195-1215, 1 July-Sept (2022), . [CrossRef]
- Schindler, K.; Van Gool, L.; de Gelder, B., Recognizing emotions expressed by body pose: A biologically inspired neural model. Neural networks : the official journal of the International Neural Network Society (2008), 1238-46, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.neunet.2008.05.003.
- Yang, Z.; Kay, A.; Li, Y.; Cross, W.; Luo, J., (2021) Pose-based Body Language Recognition for Emotion and Psychiatric Symptom Interpretation. 294-301, http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/ICPR48806.2021.9412591.
- Chartrand, T. L.; Bargh, J. A., “The chameleon effect: the perception-behavior link and social interaction.” Journal of personality and social psychology 76 6, (1999): 893-910, . [CrossRef]
- Chu, D. A., “Athletic training issues in synchronized swimming.” Clinics in sports medicine 18 2, (1999): 437-45, ix, .
- Kramer, R., Sequential effects in Olympic synchronized diving scores. Soc., (2017) . [CrossRef]
- Zhou, Z.; Xu, A.; Yatani, K., Syncup: Vision-based practice support for synchronized dancing. Proc. ACM Interact. Mob. Wearable Ubiquitous Technol., 5(3), Sep (2021), . [CrossRef]
- Balconi, M.; Cassioli, F.; Fronda, G.; Venutelli, M., (2019), Cooperative leadership in hyperscanning. Brain and body synchrony during manager-employee interactions. Neuropsychological Trends. 23-44, http://dx.doi.org/10.7358/neur-2019-026-bal2.
- Ravreby, I.; Yeshurun, Y., Liking as a balance between synchronization, complexity, and novelty. Scientific Reports (2022). 12. 3181, http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/s41598-022-06610-z.
- Yun, K.; Watanabe, K.; Shimojo, S., Interpersonal body and neural synchronization as a marker of implicit social interaction. Scientific reports. 2. 959, (2012), http://dx.doi.org/10.1038/srep00959.
- Gloor, P.; Zylka, M.; Fronzetti, A.; Makai, M., (2022), ’Entanglement’ - a new dynamic metric to measure team flow, Social Networks. 70. 100-111, http://dx.doi.org/10.1016/j.socnet.2021.11.010.
- Glowinski, D.; Camurri, A.; Volpe, G.; Dael, N.; Scherer K., Technique for automatic emotion recognition by body gesture analysis Proc. of Computer Vision and Pattern Recognition Workshops (2008), http://dx.doi.org/10.1109/CVPRW.2008.4563173.
- Van Delden, J., (2022), Real-Time Estimation of Multi-Person Pose Synchronization using OpenPose. Master Thesis, TUM Technical University of Munich, Department of Informatics.
- Colombetti, G.; "From affect programs to dynamical discrete emotions", Philosophical Psychology (2009), 407–425, . [CrossRef]
- Ekman, P.; Friesen, W. V., Constants across cultures in the face and emotion, Journal of personality and social psychology 17 2 (1971): 124-9, . [CrossRef]
- Plutchik, R., “The nature of emotions: Human emotions have deep evolutionary roots, a fact that may explain their complexity and provide tools for clinical practice.”, American Scientist, 2001, 89(4), 344-350.
- Posner, J.; Russell, J.; Peterson, B. (2005), The circumplex model of affect: An integrative approach to affective neuroscience, cognitive development, and psychopathology. Development and Psychopathology, 17(3), 715-734, . [CrossRef]
- Ambady, N.; Weisbuch, M., (2010), “Non verbal behavior”, In Handbook of Social Psychology, Vol. 1, 5th ed, (pp. 464–497), http://dx.doi.org/10.1002/9780470561119.socpsy001013.
- Rule, N.; Ambady, N. (2010), First Impressions of the Face: Predicting Success, Social and Personality Psychology Compass, 4(8), 506–516, . [CrossRef]
- Purves, D.; Augustine, G.; Fitzpatrick, D., Katz, L., LaMantia, A.; McNamara, J.; Williams, S., (2001), Neuroscience 2nd Edition. https://www.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/books/NBK10799/.
- Mehta, D.; Siddiqui, M.; Javaid, A., Recognition of Emotion Intensities Using Machine Learning Algorithms: A Comparative Study. Sensors (Basel). (2019) Apr 21;19(8):1897, . [CrossRef]
- Happy, S.; George, A.; and Routray, A., (2012), Realtime facial expression classification system using local binary patterns, in 4th International Conference on Intelligent Human Computer Interaction (2012), (pp. 1-5), IEEE, . [CrossRef]
- Ghimire, D.; Lee, J.(2013), Geometric Feature-based facial expression recognition in image sequences using multi-class Adaboost and Support Vector Machines, Sensors, 13(6), 7714-7734, . [CrossRef]
- Jung, H.; Lee, S.; Yim, J.; Park, S.; Kim, J. (2015), Joint fine-tuning in deep neural networks for facial expression recognition, In Proceedings of the IEEE International Conference on Computer Vision (pp. 2983-2991), . [CrossRef]
- Jain, D.; Zhang, Z.; Huang, K., (2017) Multiangle Optimal Pattern-based Deep Learning for Automatic Facial Expression Recognition, Pattern Recognition Letters, . [CrossRef]
- Kahou, S. et al. (2013), Combining modality specific deep neural networks for emotion recognition in video, in Proceedings of the 15th ACM on International Conference on Multimodal Interaction (pp.543-550), . [CrossRef]
- Bhave, A.; Renold, F.; Gloor, P., Using Plants as Biosensors to Measure the Emotions of Jazz Musicians, Handbook of Social Computing (2023), Edward Elgar Publishing.
- Page, P.; Kilian, K.; Donner, M., (2021), Enhancing Quality of Virtual Meetings through Facial and Vocal Emotion Recognition, COINs seminar paper summer semester, University of Cologne.
- Elkins, A.N.; Muth, E.R.; Hoover, A.W.; Walker, A.D.; Carpenter, T.L.; Switzer, F.S., Physiological compliance and team performance. Appl Ergon (2009) Nov;40(6):997-1003, . [CrossRef]
- Stevens, R.; Gorman, J.; Amazeen, P.; Likens, A.; Galloway, T., The organizational neurodynamics of teams. Nonlinear dynamics, psychology, and life sciences, 17:67–86, 01 (2013), https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/23244750/.
- Bakker, A., Flow among music teachers and their students: The crossover of peak experiences. Journal of Vocational Behavior (2005), 66(1):26–44, . [CrossRef]
- Dang, Q.; Yin, J.; Wang, B.; Zheng, W., Deep learning based 2D human pose estimation: A survey, in Tsinghua Science and Technology, vol. 24, no. 6, pp. 663-676, Dec. (2019), . [CrossRef]

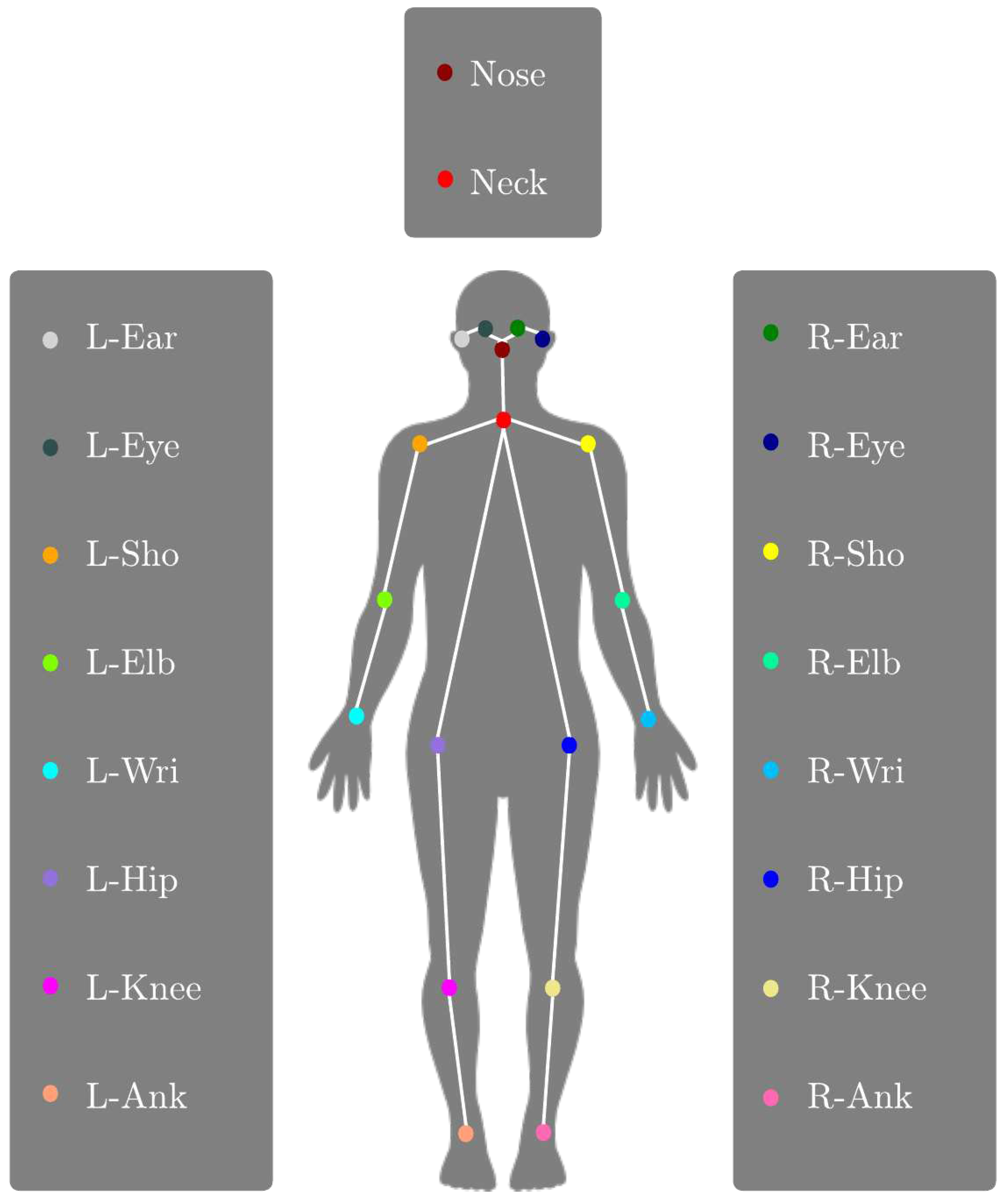

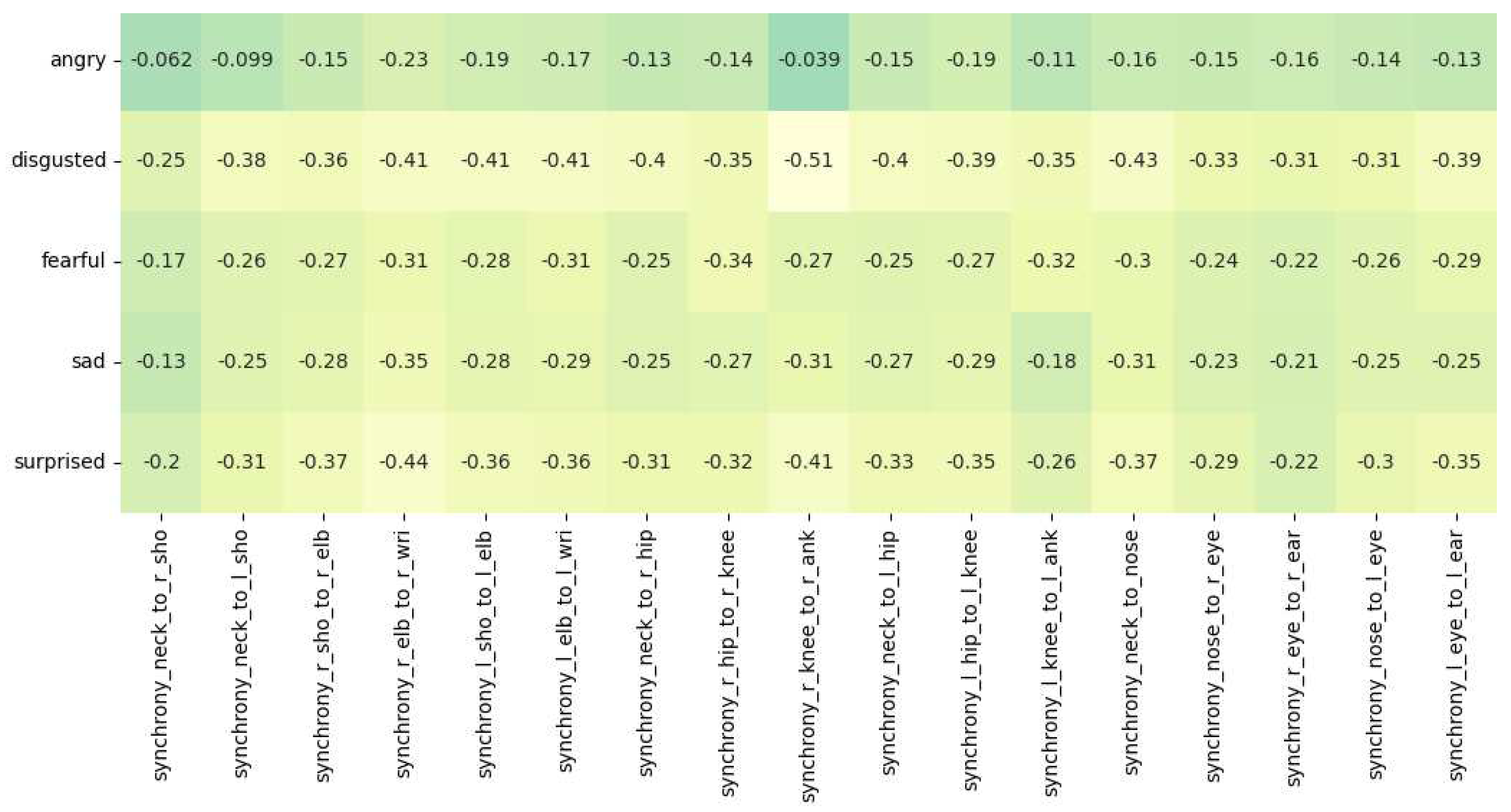
| Body Part | Keypoint Vector |
|---|---|
| Right Shoulder Section | neck → r_sho |
| Left Shoulder Section | neck → l_sho |
| Right Upper Arm | r_sho → r_elb |
| Right Lower Arm | r_elb → r_wri |
| Left Upper Arm | l_sho → l_elb |
| Left Lower Arm | l_elb → l_wri |
| Right Upper Bodyline | neck → r_hip |
| Right Upper Leg | r_hip → r_knee |
| Right Lower Leg | r_knee → r_ank |
| Left Upper Bodyline | neck → l_hip |
| Left Upper Leg | l_hip → l_knee |
| Left Lower Leg | l_knee → l_ank |
| Neck Section | neck → nose |
| Right Nose to Eye Section | nose → r_eye |
| Right Eye to Ear Section | r_eye → r_ear |
| Left Nose to Eye Section | nose → l_eye |
| Left Eye to Ear Section | l_eye → l_ear |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





