Submitted:
27 June 2023
Posted:
07 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
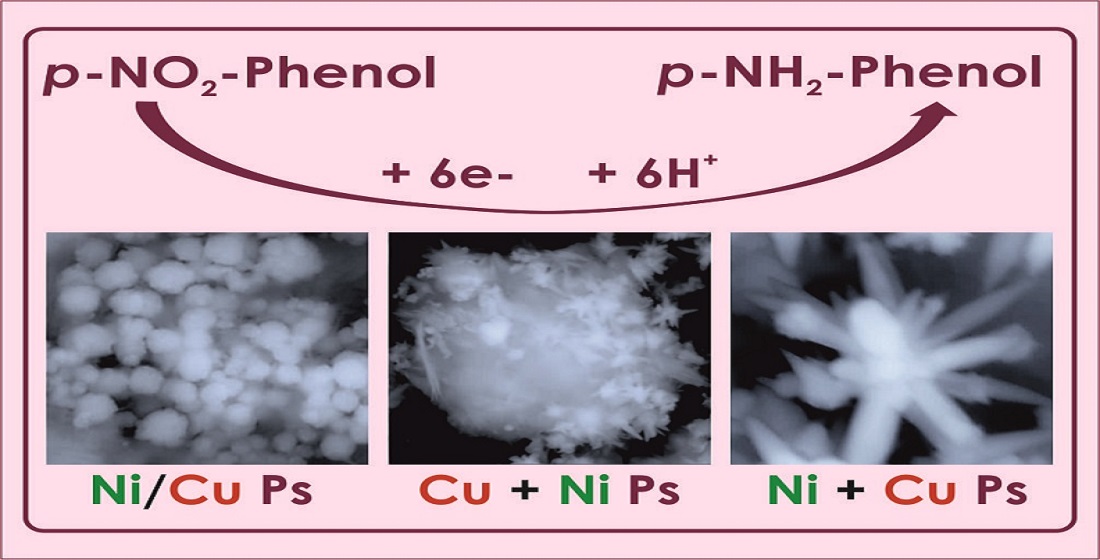

Keywords:
1. Introduction
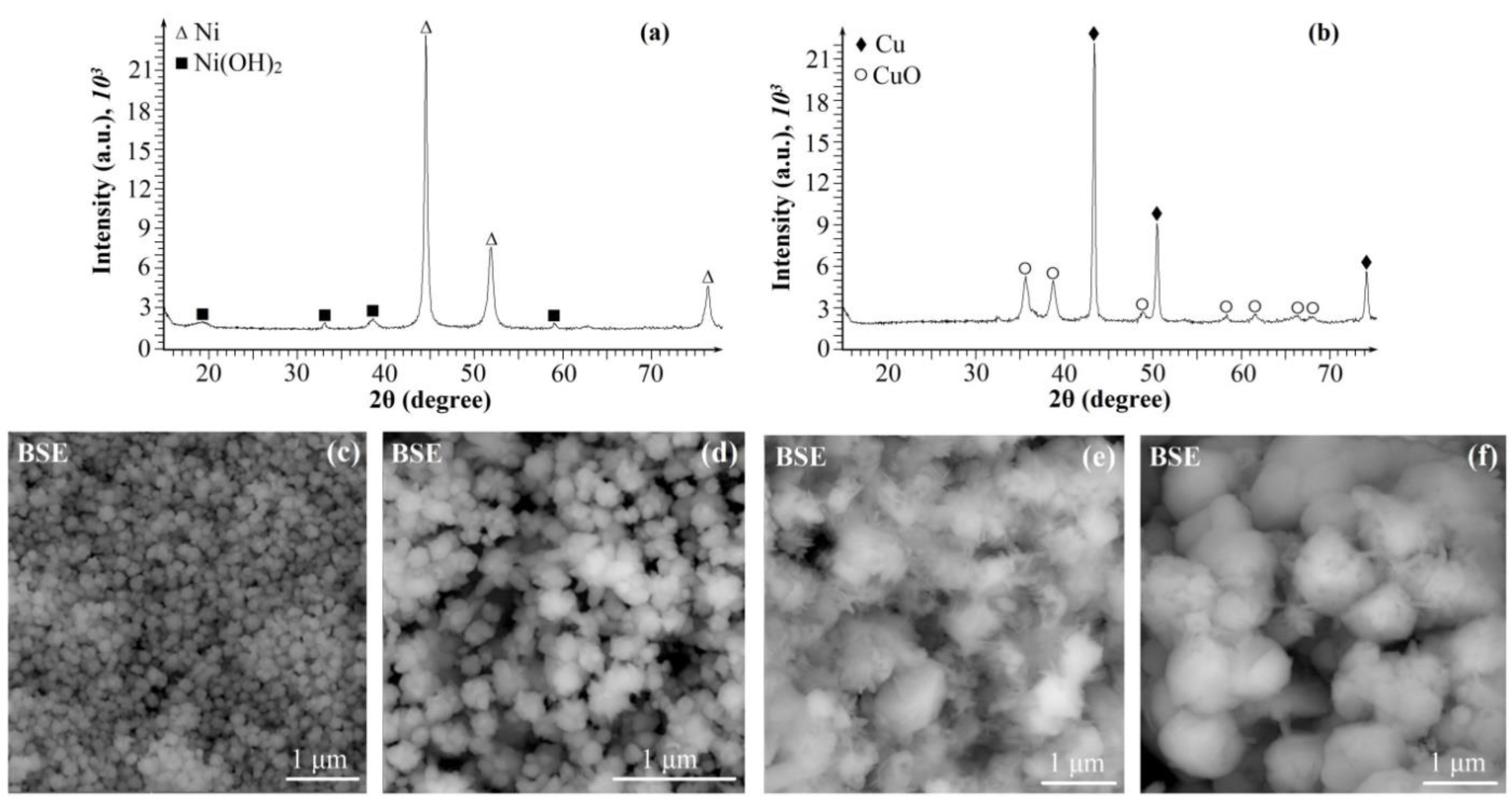
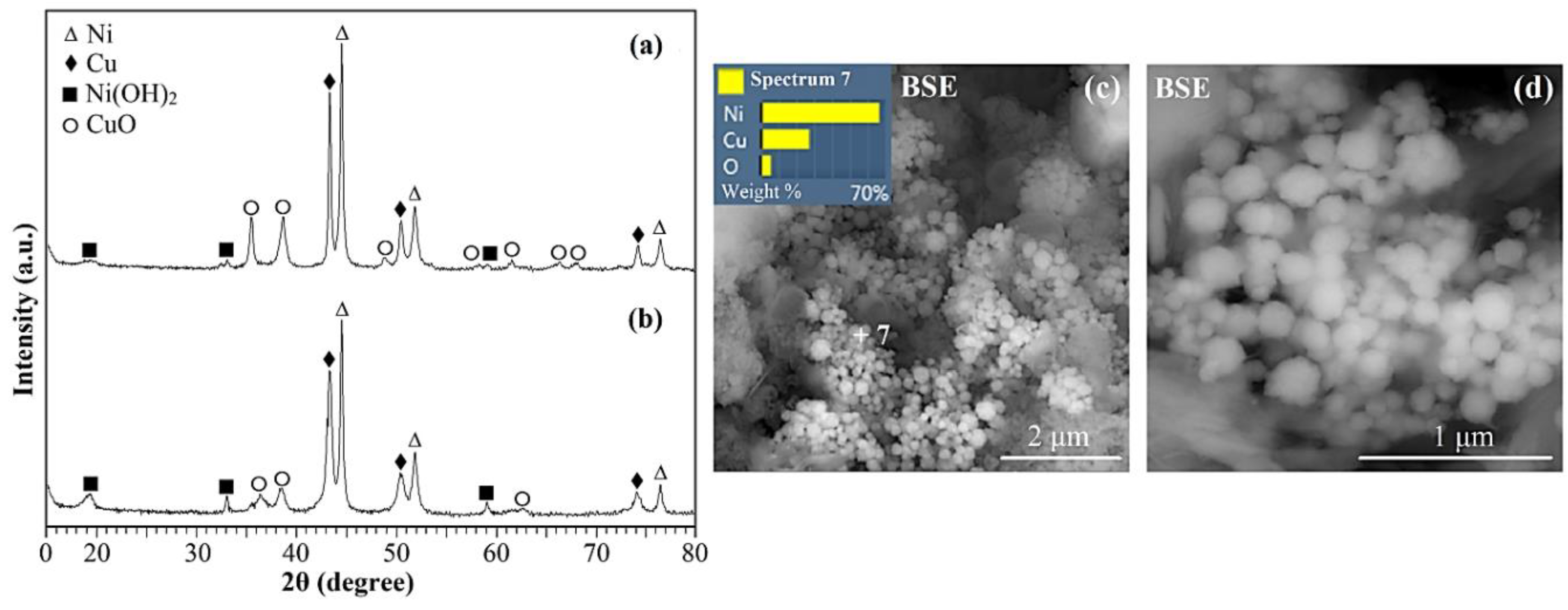
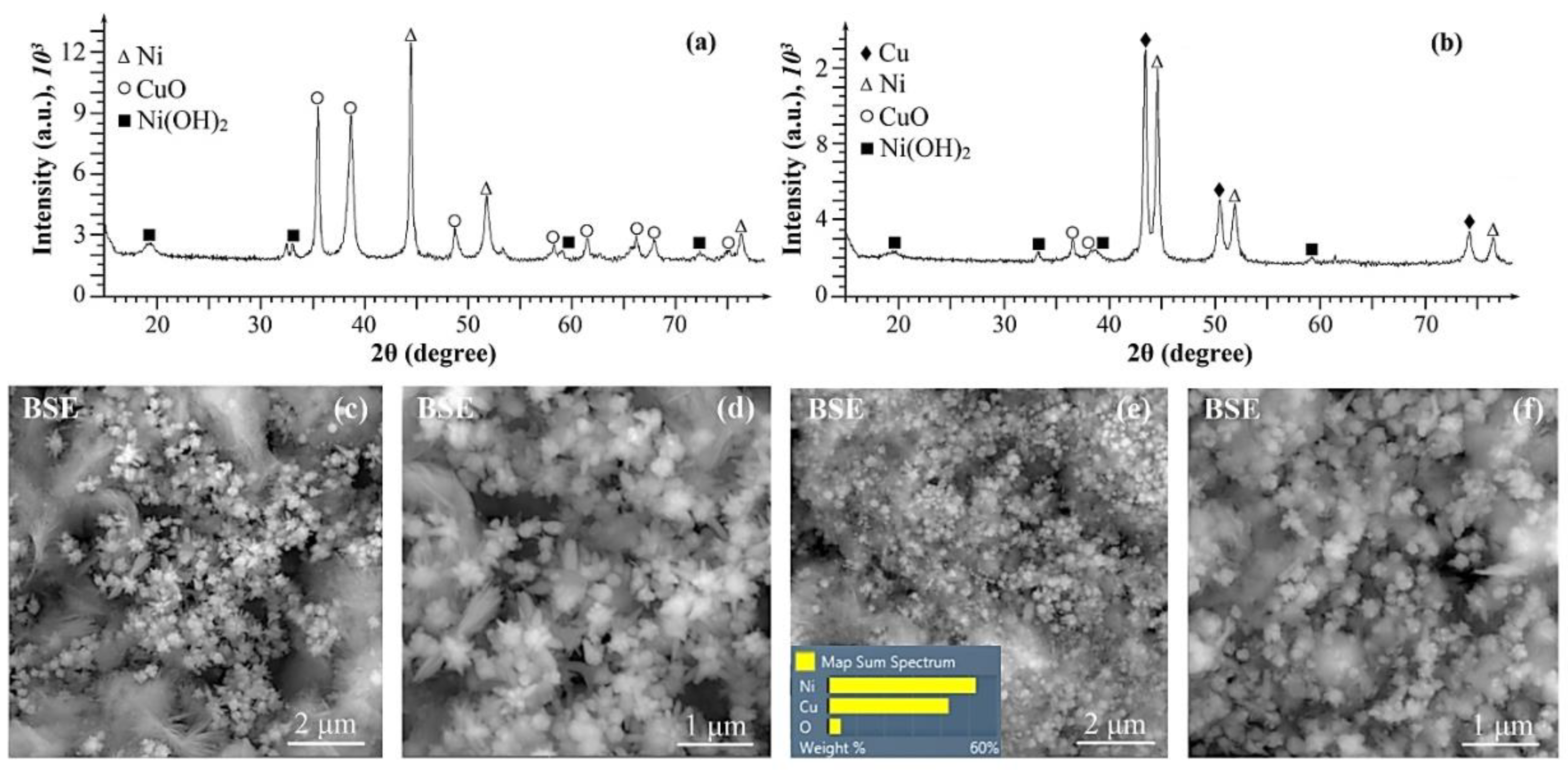
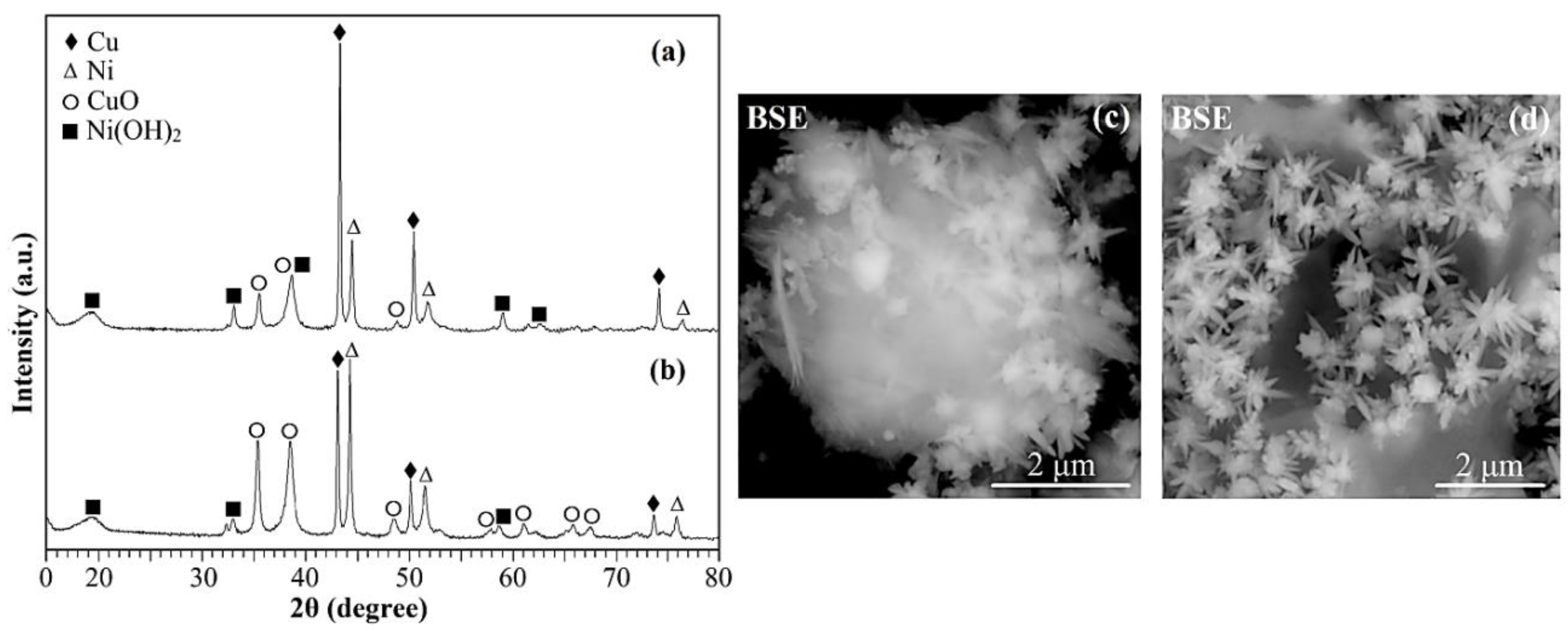
2. Results and discussion
3. Experimental Section
3.1. Ni-Cu particles synthesis
3.2. Electrocatalytic experiments
3.3. Physical-Chemical Investigations
4. Conclusions
Supplementary Materials
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Liu, X.; Wang, D.; Li, Y. Synthesis and catalytic properties of bimetallic nanomaterials with various architectures. Nano Today 2012, 7, 448-466. [CrossRef]
- Gilroy, K.D.: Ruditskiy, A.; Peng, H.-C.; Qin, D.; Xia, Y. Bimetallic Nanocrystals: Syntheses, Properties, and Applications. Chem. Rev. 2016, 116, 10414-10472. [CrossRef]
- Qiu, J.: Nguyen, Q.N.; Lyu, Z.; Wang, Q.; Xia,Y. Bimetallic Janus Nanocrystals: Syntheses and Applications. Adv. Mater. 2022, 34, 2102591. [CrossRef]
- Zhai, Y.; Han,,P.; Yun, Q.; Ge, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, Y.; Zhang, H. Phase engineering of metal nanocatalysts for electrochemical CO2 reduction. eScience. 2022, 2, 467-485. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Zhang, Z.; Zhang, X.; Zhang, J. Novel bimetallic Cu/Ni core-shell NPs and nitrogen doped GQDs composites applied in glucose in vitro detection. Public Library of Sciences One. 2019, 14, e0220005. [CrossRef]
- Yamauchi, T.; Tsukahara, Y.; Sakata, T.; Mori, H.; Yanagida, T.; Kawaic, T.; Wada, Y. Magnetic Cu-Ni (core-shell) nanoparticles in a one-pot reaction under microwave irradiation. Nanoscale. 2010, 2, 515-523. [CrossRef]
- Senapati, S.; Srivastava, S.K.; Singh, S.B.; Mishra, H.N. Magnetic Ni/Ag core-shell nanostructure from prickly Ni nanowire precursor and its catalytic and antibacterial activity. J. Mater. Chem. 2012, 14, 6899-6906. [CrossRef]
- Yang, C.; Xue, W.; Yin, H.; Lu, Z.; Wang, A.; Shen, L.; Jiang, Y. Hydrogenation of 3-nitro-4-methoxy-acetylaniline with H2 to 3-amino-4-methoxy-acetylaniline catalyzed by bimetallic copper/nickel nanoparticles. New J. Chem. 2017, 41, 3358-3366. [CrossRef]
- Hashemizadeh, S.; Biglari, M. Cu:Ni bimetallic nanoparticles: facile synthesis, characterization and its application in photodegradation of organic dyes. J. Materials Science: Materials in Electronics. 2018, 29, 13025-13031. [CrossRef]
- Fang, Y.; Zeng, X.; Chen, Y.; Ji, M.; Zheng, H.; Xu, W.; Peng, D.-L. Cu@Ni core–shell nanoparticles prepared via an injection approach with enhanced oxidation resistance for the fabrication of conductive films. Nanotechnology. 2020, 31, 355601. [CrossRef]
- Phinjaroenphan, R.; Boonserm, K.; Rattanasuporn, S. Preparation and Characterization of Bimetallic Cu-Ni and-or Ni-Cu core-shell Nanoparticles. Naresuan University Journal: Science and Technology. 2021, 29, 54-63. https:// doi.org/10.14456/nujst.2021.16. [CrossRef]
- Guo, X.; Xue, F.; Xu, S.; Shen, S.; Liu, M. Coupling Photothermal Effect into Efficient Photocatalytic H-2 Production by Using a Plate-like Cu@Ni Core-shell Co catalyst. ChemCatChem. 2020, 12, 2745-2751. [CrossRef]
- Hu, H.; Zhang, D.; Yu, W.; Sugawara, K.; Guo, T. Monodisperse and 1D Cross-Linked Multi-branched Cu@Ni Core-Shell Particles Synthesized by Chemical Reduction. J. Electronic Mater. 2014, 43, 2548-2552. [CrossRef]
- Gong, Z.; Ma, T.; Liang, F. Syntheses of magnetic blackberry-like Ni@Cu@Pd nanoparticles for efficient catalytic reduction of organic pollutants. J. Alloys Compd. 2021, 873, 159802. [CrossRef]
- Kytsya, A.R.; Bazylyak, L.I.; Zavaliy, I.Y.; Verbovytskyy, Y.V.; Zavalij, P. Synthesis, structure and hydrogenation properties of Ni-Cu bimetallic nanoparticles. Appl. Nanosci. 2022, 12, 1183-1190. [CrossRef]
- Wei, H.; Xue, Q.; Li, A.; Wan, T.; Huang, Y.; Cui, D.; Pan, D.; Dong, B.; Wei, R.; Naik, N.; Guo, Z. Dendritic core-shell copper-nickel alloy@metal oxide for efficient non-enzymatic glucose detection. Sensors and Actuators B: Chemical. 2021, 337, 129687. [CrossRef]
- Romanovskii, V.I.; Khort, A.A.; Podbolotov, K.B.; Sdobnyakov, N.Y.; Myasnichenko, V.S.; Sokolov, D.N. One-step synthesis of polymetallic nanoparticles in air invironment. Izv. Vyssh. Uchebn. Zaved. Khim. Khim. Technol. 2018, 61, 42-47. https://doi.org/10.6060/ivkkt.20186109-10.5867a. [CrossRef]
- Zhao, P.; Feng, X.; Huang, D.; Yang, D.; Astruc, D. Basic concepts and recent advances in nirophenol reduction by gold and other transition metal nanoparticles. Coord. Chem. Rev. 2015, 287, 114-136. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, W.; Tan, F.; Wang, W.; Qiu, X.; Qiao, X.; Chen, J. Facile, template-free synthesis of silver nanodendrites with high catalytic activity for the reduction of p-nitrophenol. J. Hazard. Mater. 2012, 217-218, 36-42. [CrossRef]
- Negrete-Vergara, C.; Alvarez-Alcalde, D.; Moya, S.A.; Paredes-Garcia, V.; Fuentes, S.; Venegas-Yazigi, D. Selective hydrogenation of aromatic nitro compounds using unsupported nickel catalysts. ChemistrySelect. 2022, 7, e202200220. [CrossRef]
- Li, Y.; Cao, Y.; Jia, D. Enhanced catalytic hydrogenation activity of Ni/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposite prepared by a solid-state method. J. Nanopart. Res. 2018, 20, 8. [CrossRef]
- Ding, J.; Chen, L.; Shao, R.; Wu, J.; Dong, W. Catalytic hydrogenation of p-nitrophenol to produce p-aminophenol over a nickel catalyst supported on active carbon. Reac. Kinet. Mech. Cat. 2012, 106, 225-232. [CrossRef]
- Kӓstner, C.; Thünemann, A.F. Catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol using silver nanoparticles with adjustable activity. Langmuir. 2016, 32, 7383-7391. [CrossRef]
- Din, M.I.; Khalid, R.; Hussain, Z.; Hussain, T.; Mujahid, A.; Najeeb, J.; Izhar, F. Nanocatalytic assemblies for catalytic reduction of nitrophenols: A critical review. Critical Reviews in Analytical Chemistry. 2020, 50, 322-338. [CrossRef]
- Sun, L.; Deng, Y.; Yang, Y.; Xu, Z.; Xie, K.; Liao, L. Preparation and catalytic activity of magnetic bimetallic nickel/copper nanowires. RSC Adv. 2017, 7, 17781-17787. [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.M.; Soboleva, Y.A.; Visurkhanova, Y.A.; Muldakhmetov, Z. Electrochemical synthesis of Fe–Cu composites based on copper(II) ferrite and their electrocatalytic properties. Rus. J. Electrochem. 2020, 56, 533-543. [CrossRef]
- Ivanova, N.M.; Muldakhmetov, Z.M.; Soboleva, E.A.; Visurkhanova, Y.A.; Zhivotova, T.S. Metal-carbon composites based on carbonized melamine-formaldehyde polymer and their electrocatalytic properties. Rus. J. Electrochem. 2022, 58, 946-956. [CrossRef]
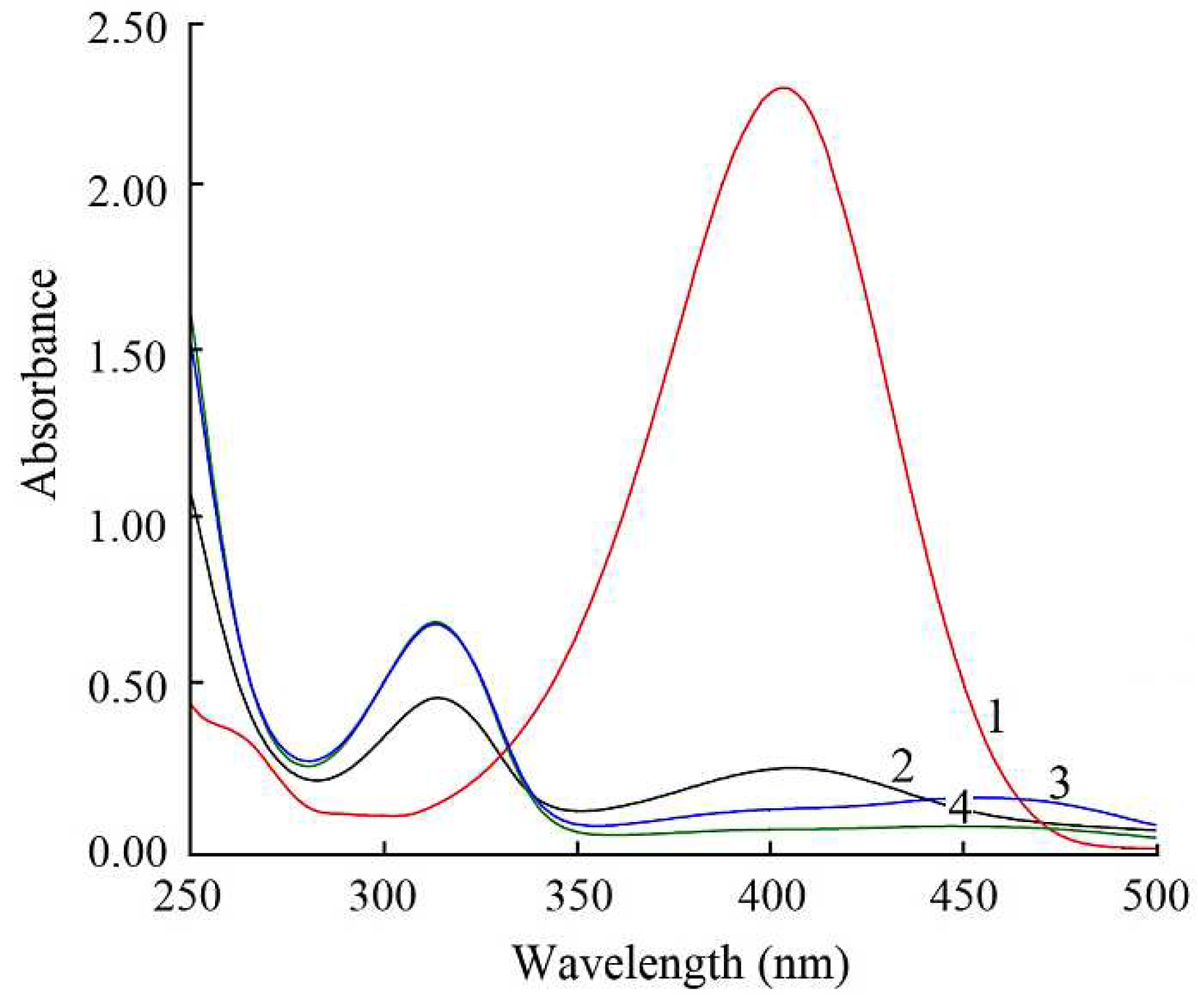
| Ni, Cu and Ni-Cu particles |
Metal content in 1 g of particles, g | Specific surface area, m2/g |
V H2, mL | Electrocatalytic hydrogenation of p-NPh | |||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Ni | Cu | W, mL Н2/min | α, % | Faradaic efficiency, % | |||||
| α = 0.25 | α = 0.5 | α = 0.5 | α = 0.75 | ||||||
| Сu cathode | - | - | - | - | 5.4 | 4.7 | 92.3 | 27.14 | 17.27 |
| Ni | 0.94 | - | 18.8 ± 0.2 | 15.7 | 16.7 | 16.6 | 100.0 | 95.27 | 86.24 |
| Ni | 0.47 | - | 8.4 | 12.6 | 12.0 | 100.0 | 69.11 | 60.09 | |
| Cu | - | 0.90 | 6.7 ± 0.1 | 120.1 | 17.2 | 16.7 | 100.0 | 96.10 | 86.24 |
| Cu | - | 0.45 | 58.2 | 15.8 | 15.0 | 100.0 | 86.02 | 72.87 | |
| Ni/Cu-1 | 0.46 | 0.46 | 11.7 ± 0.1 | 80.9 | 17.0 | 16.8 | 100.0 | 96.24 | 85.64 |
| Ni/Cu + PVA-1 | 0.48 | 0.48 | 15.4 ± 0.1 | 55.7 | 15.7 | 15.3 | 100.0 | 88.13 | 73.31 |
| Ni/Cu-2 | 0.41 | 0.41 | 13.8 ± 0.1 | 135.7 | 16.2 | 15.5 | 100.0 | 89.29 | 73.06 |
| Ni/Cu + PVA-2 | 0.45 | 0.45 | - | 111.2 | 12.4 | 11.8 | 100.0 | 67.52 | 59.63 |
| Cu/Ni-1 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 45.5 ± 0.1 | 59.4 | 15.5 | 15.0 | 99.8 | 86.15 | 73.14 |
| Cu/Ni + PVA-1 | 0.40 | 0.40 | - | 34.2 | 7.0 | 5.7 | 100.0 | 32.74 | 24.55 |
| Cu/Ni-2 | 0.42 | 0.42 | 30.8 ± 0.4 | 81.6 | 14.0 | 13.2 | 99.9 | 80.17 | 75.86 |
| Cu/Ni + PVA-2 | 0.49 | 0.49 | - | 17.1 | 12.8 | 12.2 | 100.0 | 70.06 | 62.16 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





