Submitted:
05 July 2023
Posted:
06 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
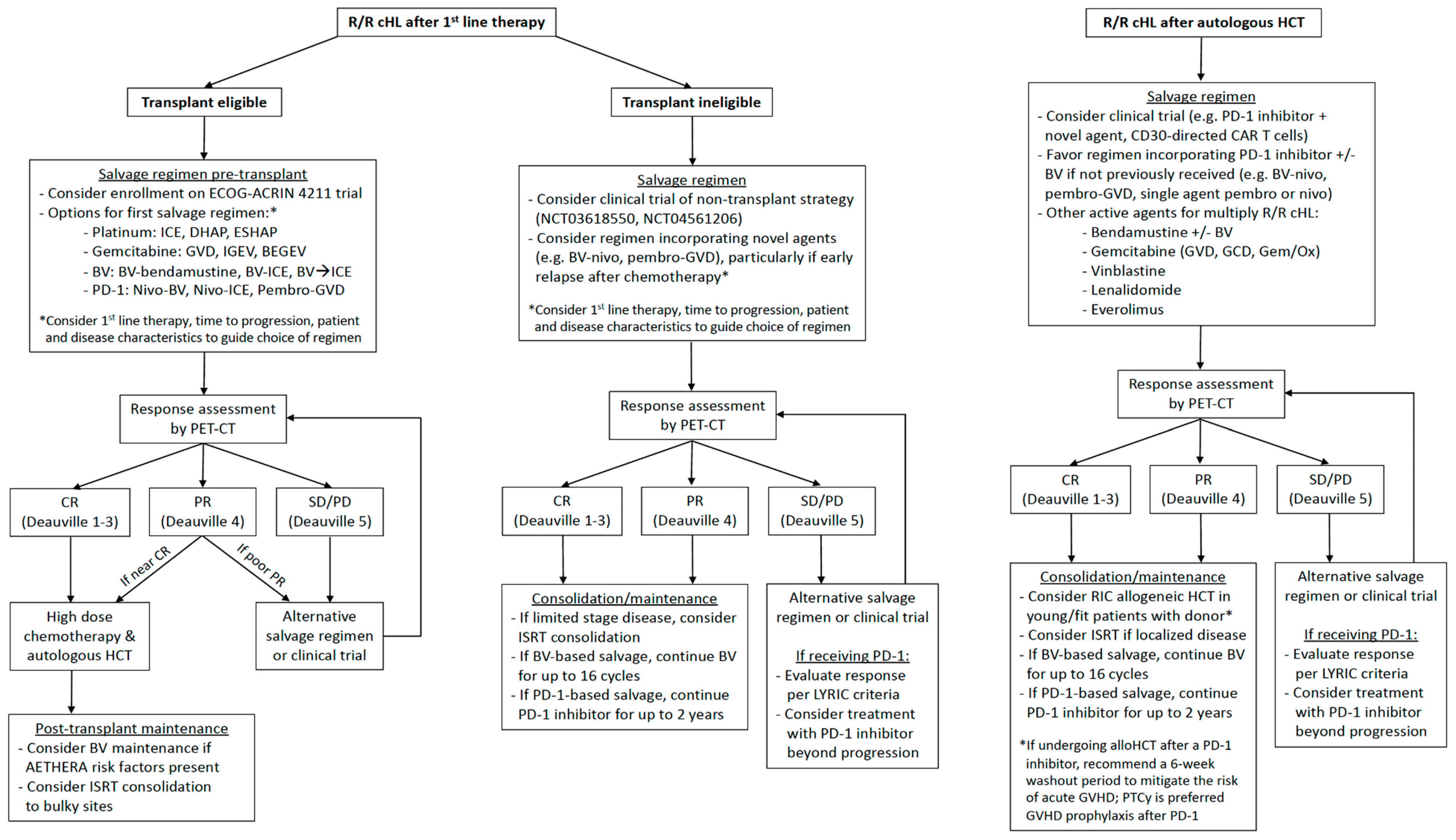
2. Management of Transplant Eligible Patients
2.1. Pre-transplant salvage therapy
2.1.1. Combination chemotherapy
2.1.2. BV-based regimens
2.1.3. PD-1 inhibitor-based regimens
2.1.4. Choosing salvage therapy pre-transplant
2.2. Post-transplant maintenance/consolidation
2.2.1. BV maintenance
2.2.2. PD-1 inhibitor maintenance
2.2.3. Radiotherapy consolidation
2.3. Does everyone with R/R cHL need a transplant?
3. Management of Transplant Ineligible Patients
3.1. Special considerations with PD-1 blockade
4. Treatment of relapse after AHCT
4.1. Allogeneic HCT
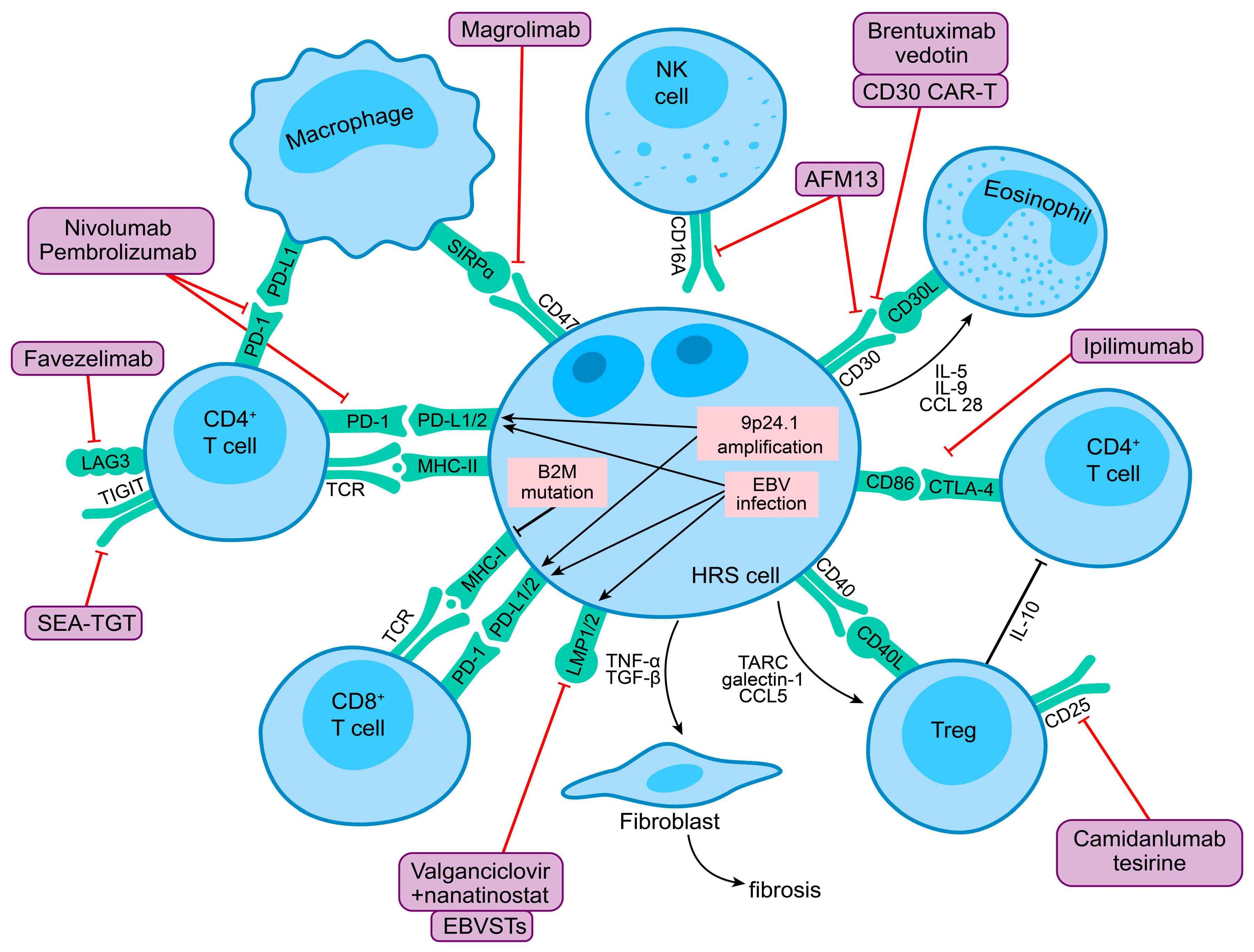
5. Novel immunotherapy approaches
5.1. PD-1 inhibitor combinations
5.1.1. PD-1 + CTLA-4 blockade
5.1.2. PD-1 + LAG-3 or TIM-3 blockade
5.1.3. PD-1 + CELMoD
5.1.4. PD-1 + BTK inhibitor
5.1.5. PD-1 + JAK inhibitor
5.1.6. PD-1 + Hypomethylating agent
5.1.7. PD-1 + HDAC inhibitor
5.1.8. PD-1 + CD47 blockade
5.1.9. PD-1 + CD30/CD16A bispecific antibody
5.2. Novel antibodies beyond PD-1
5.2.1. Anti-CD25 ADC
5.2.2. Anti-TIGIT antibody
5.3. Chimeric antigen receptor T-cell therapy
5.3.1. Autologous CD30 CAR-T
5.3.2. Allogeneic CD30.CAR EBVSTs
6. Conclusions and Future Directions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sasse, S.; Bröckelmann, P.J.; Goergen, H.; Plütschow, A.; Müller, H.; Kreissl, S.; Buerkle, C.; Borchmann, S.; Fuchs, M.; Borchmann, P.; et al. Long-Term Follow-Up of Contemporary Treatment in Early-Stage Hodgkin Lymphoma: Updated Analyses of the German Hodgkin Study Group HD7, HD8, HD10, and HD11 Trials. J Clin Oncol 2017, 35, 1999–2007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Luminari, S.; Fosså, A.; Trotman, J.; Molin, D.; d'Amore, F.A.; Enblad, G.; Berkahn, L.; Barrington, S.F.; Radford, J.; Federico, M.; et al. Long Follow-up of the Response-Adjusted Therapy for Advanced Hodgkin Lymphoma (RATHL) Trial (CRUK/07/033) Confirms the Safety of Both De-Escalation and Intensification of Chemotherapy. Blood 2022, 140, 766–767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borchmann, P.; Goergen, H.; Kobe, C.; Lohri, A.; Greil, R.; Eichenauer, D.A.; Zijlstra, J.M.; Markova, J.; Meissner, J.; Feuring-Buske, M.; et al. PET-guided treatment in patients with advanced-stage Hodgkin's lymphoma (HD18): final results of an open-label, international, randomised phase 3 trial by the German Hodgkin Study Group. Lancet 2017, 390, 2790–2802. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, S.M.; Radford, J.; Connors, J.M.; Długosz-Danecka, M.; Kim, W.-S.; Gallamini, A.; Ramchandren, R.; Friedberg, J.W.; Advani, R.; Hutchings, M.; et al. Overall Survival with Brentuximab Vedotin in Stage III or IV Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2022, 387, 310–320. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hoppe, R.T.; Advani, R.H.; Ai, W.Z.; Ambinder, R.F.; Armand, P.; Bello, C.M.; Benitez, C.M.; Chen, W.; Dabaja, B.; Daly, M.E.; et al. NCCN Guidelines® Insights: Hodgkin Lymphoma, Version 2.2022: Featured Updates to the NCCN Guidelines. J Natl Compr Cancer Netw 2022, 20, 322–334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eichenauer, D.A.; Aleman, B.M.P.; André, M.; Federico, M.; Hutchings, M.; Illidge, T.; Engert, A.; Ladetto, M. Hodgkin lymphoma: ESMO Clinical Practice Guidelines for diagnosis, treatment and follow-up. Ann Oncol 2018, 29, iv19–iv29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinner, M.A.; Sica, R.A.; Tamaresis, J.S.; Lu, Y.; Chang, C.; Lowsky, R.; Frank, M.J.; Johnston, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Muffly, L.; et al. Improved outcomes for relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma after autologous transplantation in the era of novel agents. Blood 2023, 141, 2727–2737. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Linch, D.C.; Winfield, D.; Goldstone, A.H.; Moir, D.; Hancock, B.; McMillan, A.; Chopra, R.; Milligan, D.; Hudson, G.V. Dose intensification with autologous bone-marrow transplantation in relapsed and resistant Hodgkin's disease: results of a BNLI randomised trial. Lancet 1993, 341, 1051–1054. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitz, N.; Pfistner, B.; Sextro, M.; Sieber, M.; Carella, A.M.; Haenel, M.; Boissevain, F.; Zschaber, R.; Müller, P.; Kirchner, H.; et al. Aggressive conventional chemotherapy compared with high-dose chemotherapy with autologous haemopoietic stem-cell transplantation for relapsed chemosensitive Hodgkin's disease: a randomised trial. Lancet 2002, 359, 2065–2071. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, C.H.; Nimer, S.D.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Trippett, T.; Hedrick, E.E.; Filippa, D.A.; Louie, D.; Gonzales, M.; Walits, J.; Coady-Lyons, N.; et al. A 2-step comprehensive high-dose chemoradiotherapy second-line program for relapsed and refractory Hodgkin disease: analysis by intent to treat and development of a prognostic model. Blood 2001, 97, 616–623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Barrington, S.F.; Mikhaeel, N.G.; Kostakoglu, L.; Meignan, M.; Hutchings, M.; Müeller, S.P.; Schwartz, L.H.; Zucca, E.; Fisher, R.I.; Trotman, J.; et al. Role of imaging in the staging and response assessment of lymphoma: consensus of the International Conference on Malignant Lymphomas Imaging Working Group. J Clin Oncol 2014, 32, 3048–3058. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, A.J.; Yahalom, J.; Kewalramani, T.; Maragulia, J.C.; Vanak, J.M.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Moskowitz, C.H. Pretransplantation functional imaging predicts outcome following autologous stem cell transplantation for relapsed and refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2010, 116, 4934–4937. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, C.H.; Kewalramani, T.; Nimer, S.D.; Gonzalez, M.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Yahalom, J. Effectiveness of high dose chemoradiotherapy and autologous stem cell transplantation for patients with biopsy-proven primary refractory Hodgkin's disease. Br J Haematol 2004, 124, 645–652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hertzberg, M.S.; Crombie, C.; Benson, W.; Taper, J.; Gottlieb, D.; Bradstock, K.F. Outpatient-based ifosfamide, carboplatin and etoposide (ICE) chemotherapy in transplant-eligible patients with non-Hodgkin's lymphoma and Hodgkin's disease. Ann Oncol 2003, 14 Suppl 1, i11–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josting, A.; Rudolph, C.; Reiser, M.; Mapara, M.; Sieber, M.; Kirchner, H.H.; Dörken, B.; Hossfeld, D.K.; Diehl, V.; Engert, A. Time-intensified dexamethasone/cisplatin/cytarabine: an effective salvage therapy with low toxicity in patients with relapsed and refractory Hodgkin's disease. Ann Oncol 2002, 13, 1628–1635. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Labrador, J.; Cabrero-Calvo, M.; Pérez-López, E.; Mateos, M.V.; Vázquez, L.; Caballero, M.D.; García-Sanz, R. ESHAP as salvage therapy for relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma. Ann Hematol 2014, 93, 1745–1753. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baetz, T.; Belch, A.; Couban, S.; Imrie, K.; Yau, J.; Myers, R.; Ding, K.; Paul, N.; Shepherd, L.; Iglesias, J.; et al. Gemcitabine, dexamethasone and cisplatin is an active and non-toxic chemotherapy regimen in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's disease: a phase II study by the National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Ann Oncol 2003, 14, 1762–1767. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, N.L.; Niedzwiecki, D.; Johnson, J.L.; Friedberg, J.W.; Johnson, K.B.; van Besien, K.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Cheson, B.D.; Canellos, G.P. Gemcitabine, vinorelbine, and pegylated liposomal doxorubicin (GVD), a salvage regimen in relapsed Hodgkin's lymphoma: CALGB 59804. Ann Oncol 2007, 18, 1071–1079. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.; Magagnoli, M.; Spina, M.; Pinotti, G.; Siracusano, L.; Michieli, M.; Nozza, A.; Sarina, B.; Morenghi, E.; Castagna, L.; et al. Ifosfamide, gemcitabine, and vinorelbine: a new induction regimen for refractory and relapsed Hodgkin's lymphoma. Haematologica 2007, 92, 35–41. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Santoro, A.; Mazza, R.; Pulsoni, A.; Re, A.; Bonfichi, M.; Zilioli, V.R.; Zanni, M.; Merli, F.; Anastasia, A.; Luminari, S.; et al. Five-year results of the BEGEV salvage regimen in relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv 2020, 4, 136–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Newland, A.M.; Li, J.X.; Wasco, L.E.; Aziz, M.T.; Lowe, D.K. Brentuximab vedotin: a CD30-directed antibody-cytotoxic drug conjugate. Pharmacotherapy 2013, 33, 93–104. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Francisco, J.A.; Cerveny, C.G.; Meyer, D.L.; Mixan, B.J.; Klussman, K.; Chace, D.F.; Rejniak, S.X.; Gordon, K.A.; DeBlanc, R.; Toki, B.E.; et al. cAC10-vcMMAE, an anti-CD30-monomethyl auristatin E conjugate with potent and selective antitumor activity. Blood 2003, 102, 1458–1465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Younes, A.; Gopal, A.K.; Smith, S.E.; Ansell, S.M.; Rosenblatt, J.D.; Savage, K.J.; Ramchandren, R.; Bartlett, N.L.; Cheson, B.D.; de Vos, S.; et al. Results of a pivotal phase II study of brentuximab vedotin for patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2012, 30, 2183–2189. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Gopal, A.K.; Smith, S.E.; Ansell, S.M.; Rosenblatt, J.D.; Savage, K.J.; Connors, J.M.; Engert, A.; Larsen, E.K.; Huebner, D.; et al. Five-year survival and durability results of brentuximab vedotin in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2016, 128, 1562–1566. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Palmer, J.M.; Martin, P.; Tsai, N.; Kim, Y.; Chen, B.T.; Popplewell, L.; Siddiqi, T.; Thomas, S.H.; Mott, M.; et al. Results of a Multicenter Phase II Trial of Brentuximab Vedotin as Second-Line Therapy before Autologous Transplantation in Relapsed/Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2015, 21, 2136–2140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, A.J.; Schöder, H.; Yahalom, J.; McCall, S.J.; Fox, S.Y.; Gerecitano, J.; Grewal, R.; Hamlin, P.A.; Horwitz, S.; Kobos, R.; et al. PET-adapted sequential salvage therapy with brentuximab vedotin followed by augmented ifosamide, carboplatin, and etoposide for patients with relapsed and refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma: a non-randomised, open-label, single-centre, phase 2 study. Lancet Oncol 2015, 16, 284–292. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, A.J.; Schoder, H.; Lee, J.; Davey, T.; Hancock, H.; Hamlin, P.A.; Horwitz, S.M.; Kumar, A.; Matasar, M.J.; Noy, A.; et al. Long-Term Follow-up Confirms Durability of Single-Agent Brentuximab Vedotin As Pre-Transplant Salvage for Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2019, 134, 1555–1555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, R.C.; Cassaday, R.D.; Smith, S.D.; Fromm, J.R.; Cowan, A.J.; Warren, E.H.; Shadman, M.S.; Shustov, A.; Till, B.G.; Ujjani, C.S.; et al. Dose-dense brentuximab vedotin plus ifosfamide, carboplatin, and etoposide for second-line treatment of relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma: a single centre, phase 1/2 study. Lancet Haematol 2021, 8, e562–e571. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kersten, M.J.; Driessen, J.; Zijlstra, J.M.; Plattel, W.J.; Morschhauser, F.; Lugtenburg, P.J.; Brice, P.; Hutchings, M.; Gastinne, T.; Liu, R.; et al. Combining brentuximab vedotin with dexamethasone, high-dose cytarabine and cisplatin as salvage treatment in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: the phase II HOVON/LLPC Transplant BRaVE study. Haematologica 2021, 106, 1129–1137. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Garcia-Sanz, R.; Sureda, A.; de la Cruz, F.; Canales, M.; Gonzalez, A.P.; Pinana, J.L.; Rodriguez, A.; Gutierrez, A.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; Sanchez-Gonzalez, B.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin and ESHAP is highly effective as second-line therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma patients (long-term results of a trial by the Spanish GELTAMO Group). Ann Oncol 2019, 30, 612–620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- LaCasce, A.S.; Bociek, R.G.; Sawas, A.; Caimi, P.; Agura, E.; Matous, J.; Ansell, S.M.; Crosswell, H.E.; Islas-Ohlmayer, M.; Behler, C.; et al. Three-year outcomes with brentuximab vedotin plus bendamustine as first salvage therapy in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2020, 189, e86–e90. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Green, M.R.; Monti, S.; Rodig, S.J.; Juszczynski, P.; Currie, T.; O'Donnell, E.; Chapuy, B.; Takeyama, K.; Neuberg, D.; Golub, T.R.; et al. Integrative analysis reveals selective 9p24.1 amplification, increased PD-1 ligand expression, and further induction via JAK2 in nodular sclerosing Hodgkin lymphoma and primary mediastinal large B-cell lymphoma. Blood 2010, 116, 3268–3277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Roemer, M.G.; Advani, R.H.; Ligon, A.H.; Natkunam, Y.; Redd, R.A.; Homer, H.; Connelly, C.F.; Sun, H.H.; Daadi, S.E.; Freeman, G.J.; et al. PD-L1 and PD-L2 Genetic Alterations Define Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma and Predict Outcome. J Clin Oncol 2016, 34, 2690–2697. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reinke, S.; Bröckelmann, P.J.; Iaccarino, I.; Garcia-Marquez, M.; Borchmann, S.; Jochims, F.; Kotrova, M.; Pal, K.; Brüggemann, M.; Hartmann, E.; et al. Tumor and microenvironment response but no cytotoxic T-cell activation in classic Hodgkin lymphoma treated with anti-PD1. Blood 2020, 136, 2851–2863. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cader, F.Z.; Schackmann, R.C.J.; Hu, X.; Wienand, K.; Redd, R.; Chapuy, B.; Ouyang, J.; Paul, N.; Gjini, E.; Lipschitz, M.; et al. Mass cytometry of Hodgkin lymphoma reveals a CD4+ regulatory T-cell–rich and exhausted T-effector microenvironment. Blood 2018, 132, 825–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagasaki, J.; Togashi, Y.; Sugawara, T.; Itami, M.; Yamauchi, N.; Yuda, J.; Sugano, M.; Ohara, Y.; Minami, Y.; Nakamae, H.; et al. The critical role of CD4+ T cells in PD-1 blockade against MHC-II–expressing tumors such as classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv 2020, 4, 4069–4082. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wienand, K.; Chapuy, B.; Stewart, C.; Dunford, A.J.; Wu, D.; Kim, J.; Kamburov, A.; Wood, T.R.; Cader, F.Z.; Ducar, M.D.; et al. Genomic analyses of flow-sorted Hodgkin Reed-Sternberg cells reveal complementary mechanisms of immune evasion. Blood Adv 2019, 3, 4065–4080. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vari, F.; Arpon, D.; Keane, C.; Hertzberg, M.S.; Talaulikar, D.; Jain, S.; Cui, Q.; Han, E.; Tobin, J.; Bird, R.; et al. Immune evasion via PD-1/PD-L1 on NK cells and monocyte/macrophages is more prominent in Hodgkin lymphoma than DLBCL. Blood 2018, 131, 1809–1819. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, S.M.; Lesokhin, A.M.; Borrello, I.; Halwani, A.; Scott, E.C.; Gutierrez, M.; Schuster, S.J.; Millenson, M.M.; Cattry, D.; Freeman, G.J.; et al. PD-1 blockade with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2015, 372, 311–319. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Engert, A.; Younes, A.; Fanale, M.; Santoro, A.; Zinzani, P.L.; Timmerman, J.M.; Collins, G.P.; Ramchandren, R.; Cohen, J.B.; et al. Nivolumab for Relapsed/Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma After Failure of Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation: Extended Follow-Up of the Multicohort Single-Arm Phase II CheckMate 205 Trial. J Clin Oncol 2018, 36, 1428–1439. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, R.; Zinzani, P.L.; Lee, H.J.; Armand, P.; Johnson, N.A.; Brice, P.; Radford, J.; Ribrag, V.; Molin, D.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; et al. Pembrolizumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: 2-year follow-up of KEYNOTE-087. Blood 2019, 134, 1144–1153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, A.F.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Bartlett, N.L.; Vose, J.M.; Ramchandren, R.; Feldman, T.A.; LaCasce, A.S.; Ansell, S.M.; Moskowitz, C.H.; Fenton, K.; et al. Interim results of brentuximab vedotin in combination with nivolumab in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 1183–1194. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Advani, R.H.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Bartlett, N.L.; Vose, J.M.; Ramchandren, R.; Feldman, T.A.; LaCasce, A.S.; Christian, B.A.; Ansell, S.M.; Moskowitz, C.H.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin in combination with nivolumab in relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: 3-year study results. Blood 2021, 138, 427–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, M.G.; Lee, H.J.; Palmer, J.M.; Chen, R.; Tsai, N.C.; Chen, L.; McBride, K.; Smith, D.L.; Melgar, I.; Song, J.Y.; et al. Response-adapted anti-PD-1-based salvage therapy for Hodgkin lymphoma with nivolumab alone or in combination with ICE. Blood 2022, 139, 3605–3616. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bryan, L.J.; Casulo, C.; Allen, P.B.; Smith, S.E.; Savas, H.; Dillehay, G.L.; Karmali, R.; Pro, B.; Kane, K.L.; Bazzi, L.A.; et al. Pembrolizumab Added to Ifosfamide, Carboplatin, and Etoposide Chemotherapy for Relapsed or Refractory Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Multi-institutional Phase 2 Investigator-Initiated Nonrandomized Clinical Trial. JAMA Oncol 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, A.J.; Shah, G.; Schöder, H.; Ganesan, N.; Drill, E.; Hancock, H.; Davey, T.; Perez, L.; Ryu, S.; Sohail, S.; et al. Phase II Trial of Pembrolizumab Plus Gemcitabine, Vinorelbine, and Liposomal Doxorubicin as Second-Line Therapy for Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2021, 39, 3109–3117. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rossi, C.; Gilhodes, J.; Maerevoet, M.; Herbaux, C.; Morschhauser, F.; Brice, P.; Garciaz, S.; Borel, C.; Ysebaert, L.; Obéric, L.; et al. Efficacy of chemotherapy or chemo-anti-PD-1 combination after failed anti-PD-1 therapy for relapsed and refractory hodgkin lymphoma: A series from lysa centers. Am J Hematol 2018, 93, 1042–1049. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Casadei, B.; Argnani, L.; Morigi, A.; Lolli, G.; Broccoli, A.; Pellegrini, C.; Nanni, L.; Stefoni, V.; Coppola, P.E.; Carella, M.; et al. Effectiveness of chemotherapy after anti-PD-1 blockade failure for relapsed and refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Cancer Med 2020, 9, 7830–7836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carreau, N.A.; Pail, O.; Armand, P.; Merryman, R.; Advani, R.H.; Spinner, M.A.; Herrera, A.; Chen, R.; Tomassetti, S.; Ramchandren, R.; et al. Checkpoint Blockade Treatment May Sensitize Hodgkin Lymphoma to Subsequent Therapy. Oncologist 2020, 25, 878–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Calabretta, E.; Guidetti, A.; Ricci, F.; Di Trani, M.; Monfrini, C.; Magagnoli, M.; Bramanti, S.; Maspero, D.; Morello, L.; Merli, M.; et al. Chemotherapy after PD-1 inhibitors in relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: Outcomes and clonal evolution dynamics. Br J Haematol 2022, 198, 82–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merryman, R.W.; Redd, R.A.; Nishihori, T.; Chavez, J.; Nieto, Y.; Darrah, J.M.; Rao, U.; Byrne, M.T.; Bond, D.A.; Maddocks, K.J.; et al. Autologous stem cell transplantation after anti-PD-1 therapy for multiply relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv 2021, 5, 1648–1659. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Saba, R.; Augustin, K.; Ryan, M.; Bartlett, N.L.; Cashen, A. Engraftment Syndrome in Patients with Relapsed Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma Who Received PD-1 Blockade Containing Salvage Therapy Followed By Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation. Transpl Cell Ther. 2022, 28, S406. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Park, J.J.; Lin, J.; Huang, E.; Schaar, D.G. The Impact of Prior Salvage Treatment With Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors on Hodgkin Lymphoma Patients Undergoing Autologous Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation: A Single-Center Experience. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2021, 21, e726–e730. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bai, B.; Wang, X.-X.; Gao, Y.; Li, P.-F.; He, H.-X.; Ping, L.-Q.; Huang, C.; Cai, Q.-C.; Huang, H.-Q. Prior anti-PD-1 therapy as a risk factor for life-threatening peri-engraftment respiratory distress syndrome in patients undergoing autologous stem cell transplantation. Bone Marrow Transplant 2021, 56, 1151–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.H.; Spinner, M.A.; David, K.; Bachanova, V.; Goyal, G.; Kahl, B.; Dorritie, K.; Azzi, J.; Kenkre, V.P.; Arai, S.; et al. Checkpoint inhibitor-based salvage regimens prior to autologous stem cell transplant improve event-free survival in relapsed/refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Am J Hematol 2023, 98, 464–471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S. H.; Spinner, M.A.; David, K.A.; Bachanova, V.; Goyal, G.; Saba, R.; Dorritie, K.A.; Azzi, J.M.; Harris, E.; Fusco, B.; et al. Outcomes of classic Hodgkin lymphoma, relapsed within one year of diagnosis, in the era of novel agents. J Clin Oncol 2022, 40, 7515–7515. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, C.H.; Walewski, J.; Nademanee, A.; Masszi, T.; Agura, E.; Holowiecki, J.; Abidi, M.H.; Chen, A.I.; Stiff, P.; Viviani, S.; et al. Five-year PFS from the AETHERA trial of brentuximab vedotin for Hodgkin lymphoma at high risk of progression or relapse. Blood 2018, 132, 2639–2642. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.H.; Smith, A.; Spinner, M. A.; Sykorova, A.; Bachanova, V.; Evens, A.M.; Goyal, G.; Kahl, B.; Dorritie, K.; Azzi, J.; et al. Efficacy of brentuximab consolidation by metabolic response in an international real-world cohort of classic Hodgkin lymphoma at high risk for progression after ASCT. Hematological Oncology 2023, 41, 361–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Chen, Y.B.; Redd, R.A.; Joyce, R.M.; Bsat, J.; Jeter, E.; Merryman, R.W.; Coleman, K.C.; Dahi, P.B.; Nieto, Y.; et al. PD-1 blockade with pembrolizumab for classical Hodgkin lymphoma after autologous stem cell transplantation. Blood 2019, 134, 22–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bachier, C.; Schade, H.; Zoghi, B.; Ramakrishnan, A.; Shah, N.N. A Phase II Single Arm Study of Nivolumab As Maintenance Therapy after Autologous Stem Cell Transplantation in Patients with Hodgkin Lymphoma at Risk of Relapse or Progression. Blood 2021, 138, 2455. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herrera, A.F.; Chen, L.; Nieto, Y.; Holmberg, L.; Johnston, P.; Mei, M.; Popplewell, L.; Armenian, S.; Cao, T.; Farol, L.; et al. Brentuximab vedotin plus nivolumab after autologous haematopoietic stem-cell transplantation for adult patients with high-risk classic Hodgkin lymphoma: a multicentre, phase 2 trial. Lancet Haematol 2023, 10, e14–e23. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jauhari, S.; Plastaras, J.; Lukens, J.; Maity, A.; Schuster, S.J.; Dwivedy Nasta, S. Consolidative Radiation Therapy Following Autologous Transplantation in Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Blood 2015, 126, 3195. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilke, C.; Cao, Q.; Dusenbery, K.E.; Bachanova, V.; Lazaryan, A.; Lee, C.K.; Yuan, J. Role of Consolidative Radiation Therapy After Autologous Hematopoietic Cell Transplantation for the Treatment of Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2017, 99, 94–102. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, A.J. Do all patients with primary refractory/first relapse of HL need autologous stem cell transplant? Hematology Am Soc Hematol Educ Program 2022, 2022, 699–705. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ding, K.; Liu, H.; Ma, J.; Yang, H.; Cao, L.; Wang, H.; Peng, H.; Shi, W.; Zhao, X.; Wu, W.; et al. Tislelizumab with gemcitabine and oxaliplatin in patients with relapsed or refractory classic Hodgkin lymphoma: a multicenter phase II trial. Haematologica 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Josting, A.; Nogová, L.; Franklin, J.; Glossmann, J.P.; Eich, H.T.; Sieber, M.; Schober, T.; Boettcher, H.D.; Schulz, U.; Müller, R.P.; et al. Salvage radiotherapy in patients with relapsed and refractory Hodgkin's lymphoma: a retrospective analysis from the German Hodgkin Lymphoma Study Group. J Clin Oncol 2005, 23, 1522–1529. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Goda, J.S.; Massey, C.; Kuruvilla, J.; Gospodarowicz, M.K.; Wells, W.; Hodgson, D.C.; Sun, A.; Keating, A.; Crump, M.; Tsang, R.W. Role of salvage radiation therapy for patients with relapsed or refractory hodgkin lymphoma who failed autologous stem cell transplant. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2012, 84, e329–335. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Constine, L.S.; Yahalom, J.; Ng, A.K.; Hodgson, D.C.; Wirth, A.; Milgrom, S.A.; Mikhaeel, N.G.; Eich, H.T.; Illidge, T.; Ricardi, U.; et al. The Role of Radiation Therapy in Patients With Relapsed or Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma: Guidelines From the International Lymphoma Radiation Oncology Group. Int J Radiat Oncol Biol Phys 2018, 100, 1100–1118. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kuruvilla, J.; Ramchandren, R.; Santoro, A.; Paszkiewicz-Kozik, E.; Gasiorowski, R.; Johnson, N.A.; Fogliatto, L.M.; Goncalves, I.; de Oliveira, J.S.R.; Buccheri, V.; et al. Pembrolizumab versus brentuximab vedotin in relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma (KEYNOTE-204): an interim analysis of a multicentre, randomised, open-label, phase 3 study. Lancet Oncol 2021, 22, 512–524. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zinzani, P.L.; Ramchandren, R.; Santoro, A.; Paszkiewicz-Kozik, E.; Gasiorowski, R.; Johnson, N.A.; de Oliveira, J.S.R.; Buccheri, V.; Perini, G.F.; Dickinson, M.; et al. Quality-of-life analysis of pembrolizumab vs brentuximab vedotin for relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood Adv 2022, 6, 590–599. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ansell, S.M.; Bröckelmann, P.J.; von Keudell, G.; Lee, H.J.; Santoro, A.; Zinzani, P.L.; Collins, G.P.; Cohen, J.B.; De Boer, J.P.; Kuruvilla, J.; et al. Nivolumab for relapsed or refractory (R/R) classical Hodgkin lymphoma (CHL) after autologous transplantation: 5-year overall survival from the phase 2 CheckMate 205 Study. Hematol Oncol 2021, 39. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Zinzani, P.L.; Lee, H.J.; Johnson, N.A.; Brice, P., Mrs; Radford, J.; Ribrag, V.; Molin, D.; Vassilakopoulos, T.P.; Tomita, A.; et al. Five-year follow-up of KEYNOTE-087: pembrolizumab monotherapy in relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Cheson, B.D.; Ansell, S.; Schwartz, L.; Gordon, L.I.; Advani, R.; Jacene, H.A.; Hoos, A.; Barrington, S.F.; Armand, P. Refinement of the Lugano Classification lymphoma response criteria in the era of immunomodulatory therapy. Blood 2016, 128, 2489–2496. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merryman, R.W.; Carreau, N.A.; Advani, R.H.; Spinner, M.A.; Herrera, A.F.; Chen, R.; Tomassetti, S.; Ramchandren, R.; Hamid, M.; Assouline, S.; et al. Impact of Treatment Beyond Progression with Immune Checkpoint Blockade in Hodgkin Lymphoma. Oncologist 2020, 25, e993–e997. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Moskowitz, A.J.; Perales, M.A.; Kewalramani, T.; Yahalom, J.; Castro-Malaspina, H.; Zhang, Z.; Vanak, J.; Zelenetz, A.D.; Moskowitz, C.H. Outcomes for patients who fail high dose chemoradiotherapy and autologous stem cell rescue for relapsed and primary refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2009, 146, 158–163. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaloyannidis, P.; Voutiadou, G.; Baltadakis, I.; Tsirigotis, P.; Spyridonidis, A.; Repousis, P.; Balta, A.; Tsimberis, S.; Karakasis, D.; Sakellari, I.; et al. Outcomes of Hodgkin's lymphoma patients with relapse or progression following autologous hematopoietic cell transplantation. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2012, 18, 451–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- von Tresckow, B.; Müller, H.; Eichenauer, D.A.; Glossmann, J.P.; Josting, A.; Böll, B.; Klimm, B.; Sasse, S.; Fuchs, M.; Borchmann, P.; et al. Outcome and risk factors of patients with Hodgkin Lymphoma who relapse or progress after autologous stem cell transplant. Leuk Lymphoma 2014, 55, 1922–1924. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Arai, S.; Fanale, M.; DeVos, S.; Engert, A.; Illidge, T.; Borchmann, P.; Younes, A.; Morschhauser, F.; McMillan, A.; Horning, S.J. Defining a Hodgkin lymphoma population for novel therapeutics after relapse from autologous hematopoietic cell transplant. Leuk Lymphoma 2013, 54, 2531–2533. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Desai, S.H.; Spinner, M.A.; Evens, A.M.; Bachanova, V.; Goyal, G.; Kahl, B.; Dorritie, K.; Azzi, J.; Kenkre, V.P.; Arai, S.; et al. Overall survival in classic Hodgkin lymphoma pts who progress after autologous stem cell transplant in the era of novel agents. Hematol Oncol 2023, 41, 366–368. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, A.J.; Hamlin, P.A., Jr.; Perales, M.A.; Gerecitano, J.; Horwitz, S.M.; Matasar, M.J.; Noy, A.; Palomba, M.L.; Portlock, C.S.; Straus, D.J.; et al. Phase II study of bendamustine in relapsed and refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2013, 31, 456–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Johnston, P.B.; Pinter-Brown, L.C.; Warsi, G.; White, K.; Ramchandren, R. Phase 2 study of everolimus for relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Exp Hematol Oncol 2018, 7, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Fehniger, T.A.; Larson, S.; Trinkaus, K.; Siegel, M.J.; Cashen, A.F.; Blum, K.A.; Fenske, T.S.; Hurd, D.D.; Goy, A.; Schneider, S.E.; et al. A phase 2 multicenter study of lenalidomide in relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2011, 118, 5119–5125. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spinner, M.A.; Kennedy, V.E.; Tamaresis, J.S.; Lavori, P.W.; Arai, S.; Johnston, L.J.; Meyer, E.H.; Miklos, D.B.; Muffly, L.S.; Negrin, R.S.; et al. Nonmyeloablative TLI-ATG conditioning for allogeneic transplantation: mature follow-up from a large single-center cohort. Blood Adv 2019, 3, 2454–2464. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Sharplin, K.M.; Ritchie, D.; Gottlieb, D.; Bilmon, I.; Panicker, S.; Kennedy, G.A.; Curley, C.; Purtill, D.; Cooney, J.; Doocey, R.; et al. An Australasian Bone Marrow Transplant Registry (ABMTR) Study of the Trends and Outcomes of Allogeneic Haematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation (HSCT) in Hodgkin Lymphoma between 2009-2019: Relapse Remains the Most Common Cause of Death Post Transplantation. Blood 2020, 136, 36–37. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merryman, R.W.; Castagna, L.; Giordano, L.; Ho, V.T.; Corradini, P.; Guidetti, A.; Casadei, B.; Bond, D.A.; Jaglowski, S.; Spinner, M.A.; et al. Allogeneic transplantation after PD-1 blockade for classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Leukemia 2021, 35, 2672–2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Merryman, R.W.; Kim, H.T.; Zinzani, P.L.; Carlo-Stella, C.; Ansell, S.M.; Perales, M.A.; Avigdor, A.; Halwani, A.S.; Houot, R.; Marchand, T.; et al. Safety and efficacy of allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell transplant after PD-1 blockade in relapsed/refractory lymphoma. Blood 2017, 129, 1380–1388. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Paul, S.; Zahurak, M.; Luznik, L.; Ambinder, R.F.; Fuchs, E.J.; Bolaños-Meade, J.; Wagner-Johnston, N.; Swinnen, L.J.; Schoch, L.; Varadhan, R.; et al. Non-Myeloablative Allogeneic Transplantation with Post-Transplant Cyclophosphamide after Immune Checkpoint Inhibition for Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma: A Retrospective Cohort Study. Biol Blood Marrow Transplant 2020, 26, 1679–1688. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Herbaux, C.; Merryman, R.; Devine, S.; Armand, P.; Houot, R.; Morschhauser, F.; Haverkos, B. Recommendations for managing PD-1 blockade in the context of allogeneic HCT in Hodgkin lymphoma: taming a necessary evil. Blood 2018, 132, 9–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Patel, S.S.; Weirather, J.L.; Lipschitz, M.; Lako, A.; Chen, P.H.; Griffin, G.K.; Armand, P.; Shipp, M.A.; Rodig, S.J. The microenvironmental niche in classic Hodgkin lymphoma is enriched for CTLA-4-positive T cells that are PD-1-negative. Blood 2019, 134, 2059–2069. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Armand, P.; Lesokhin, A.; Borrello, I.; Timmerman, J.; Gutierrez, M.; Zhu, L.; Popa McKiver, M.; Ansell, S.M. A phase 1b study of dual PD-1 and CTLA-4 or KIR blockade in patients with relapsed/refractory lymphoid malignancies. Leukemia 2021, 35, 777–786. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Diefenbach, C.S.; Hong, F.; Ambinder, R.F.; Cohen, J.B.; Robertson, M.J.; David, K.A.; Advani, R.H.; Fenske, T.S.; Barta, S.K.; Palmisiano, N.D.; et al. Ipilimumab, nivolumab, and brentuximab vedotin combination therapies in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma: phase 1 results of an open-label, multicentre, phase 1/2 trial. Lancet Haematol 2020, 7, e660–e670. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El Halabi, L.; Adam, J.; Gravelle, P.; Marty, V.; Danu, A.; Lazarovici, J.; Ribrag, V.; Bosq, J.; Camara-Clayette, V.; Laurent, C.; et al. Expression of the Immune Checkpoint Regulators LAG-3 and TIM-3 in Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. Clin Lymphoma Myeloma Leuk 2021, 21, 257–266.e253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lavie, D.; Johnson, N.; Borchmann, P.; Herrera, A.F.; Avigdor, A.; Gasiorowski, R.; Gregory, G.; Keane, C.; Vucinic, V.; Bazargan, M.; et al. An open-label phase 1/2 study of favezelimab plus pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed/refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma with/without previous anti-PD-1 treatment. Hematol Oncol 2023, 41, 364–366. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clancy-Thompson, E.; Perry, T.; Pryts, S.; Jaiswal, A.; Oganesyan, V.; Dyk, N.v.; Yang, C.; Garcia, A.; Yu, W.; Moynihan, J.; et al. 461 Generation of AZD7789, a novel PD-1 and TIM-3 targeting bispecific antibody, which binds to a differentiated epitope of TIM-3. J Immunother Cancer 2022, 10, A481–A481. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McDaniel, J.M.; Pinilla-Ibarz, J.; Epling-Burnette, P.K. Molecular action of lenalidomide in lymphocytes and hematologic malignancies. Adv Hematol 2012, 2012, 513702. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bond, D.A.; Wei, L.; Yildiz, V.; Reneau, J.; Sawalha, Y.; Christian, B.; Brammer, J.; Epperla, N.; Koff, J.; Dendorfer, A.; et al. Combination of the PD-1 inhibitor Nivolumab and Immunomodulatory Drug Lenalidomide in Relapsed Hodgkin and Large B-cell Lymphoma: Results from a Phase I/II Study. Hematol Oncol 2023, 41, 597–598. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dubovsky, J.A.; Beckwith, K.A.; Natarajan, G.; Woyach, J.A.; Jaglowski, S.; Zhong, Y.; Hessler, J.D.; Liu, T.-M.; Chang, B.Y.; Larkin, K.M.; et al. Ibrutinib is an irreversible molecular inhibitor of ITK driving a Th1-selective pressure in T lymphocytes. Blood 2013, 122, 2539–2549. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadani, M.; Balasubramanian, S.; Hari, P.N. Ibrutinib in Refractory Classic Hodgkin's Lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2015, 373, 1381–1382. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Badar, T.; Astle, J.; Kakar, I.K.; Zellner, K.; Hari, P.N.; Hamadani, M. Clinical activity of ibrutinib in classical Hodgkin lymphoma relapsing after allogeneic stem cell transplantation is independent of tumor BTK expression. Br J Haematol 2020, 190, e98–e101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hanel, W.; Shindiapina, P.; Bond, D.A.; Sawalha, Y.; Epperla, N.; Voorhees, T.; Welkie, R.L.; Huang, Y.; Behbehani, G.K.; Zhang, X.; et al. A Phase 2 Trial of Ibrutinib and Nivolumab in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin's Lymphoma. Cancers (Basel) 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tiacci, E.; Ladewig, E.; Schiavoni, G.; Penson, A.; Fortini, E.; Pettirossi, V.; Wang, Y.; Rosseto, A.; Venanzi, A.; Vlasevska, S.; et al. Pervasive mutations of JAK-STAT pathway genes in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2454–2465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Eric Van Den, N.; Marc, A.; Thomas, G.; Aspasia, S.; Corinne, H.; Amine, B.; Oumedaly, R.; Olivier, C.; Hervé, G.; Gregor, V.; et al. A phase II study of the oral JAK1/JAK2 inhibitor ruxolitinib in advanced relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Haematologica 2018, 103, 840–848. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bachanova, V.; Zak, J.; Cao, Q.; Maakaron, J.; Grzywacz, B.; Fletcher, C.; Ayyappan, S.; Hu, M.; Desai, S.; Felices, M.; et al. Phase 1 trial of Ruxolitinib combined with Nivolumab in patients relapsed/refractory Hodgkin lymphoma after failure of check-point inhibitor (CPI). Hematol Oncol 2023, 41, 582–582. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Svoboda, J.; Landsburg, D.L.; Nasta, S.D.; Barta, S.K.; Chong, E.A.; Carter, J.; Delp, G.; Duca, A.; Ballard, H.J.; Emanuel, S.A.; et al. Combination of everolimus and itacitinib in patients with Hodgkin lymphoma relapsed/refractory to brentuximab vedotin (BV) and checkpoint inhibitors (CPI). Hematol Oncol 2023, 41, 594–595. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pauken, K.E.; Sammons, M.A.; Odorizzi, P.M.; Manne, S.; Godec, J.; Khan, O.; Drake, A.M.; Chen, Z.; Sen, D.R.; Kurachi, M.; et al. Epigenetic stability of exhausted T cells limits durability of reinvigoration by PD-1 blockade. Science 2016, 354, 1160–1165. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghoneim, H.E.; Fan, Y.; Moustaki, A.; Abdelsamed, H.A.; Dash, P.; Dogra, P.; Carter, R.; Awad, W.; Neale, G.; Thomas, P.G.; et al. De Novo Epigenetic Programs Inhibit PD-1 Blockade-Mediated T Cell Rejuvenation. Cell 2017, 170, 142–157.e119. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G.; Wu, Y.; Wang, W.; Xu, J.; Lv, X.; Cao, X.; Wan, T. Low-dose decitabine enhances the effect of PD-1 blockade in colorectal cancer with microsatellite stability by re-modulating the tumor microenvironment. Cell Mol Immunol 2019, 16, 401–409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, X.; Li, Y.; Dong, L.; Chang, Y.; Zhang, X.; Wang, C.; Chen, M.; Bo, X.; Chen, H.; Han, W.; et al. Decitabine priming increases anti–PD-1 antitumor efficacy by promoting CD8+ progenitor exhausted T cell expansion in tumor models. J Clin Invest 2023, 133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nie, J.; Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Yang, Q.; Mei, Q.; Dong, L.; Li, X.; Liu, J.; Ku, W.; Zhang, Y.; et al. Addition of Low-Dose Decitabine to Anti-PD-1 Antibody Camrelizumab in Relapsed/Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2019, 37, 1479–1489. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Liu, Y.; Dong, L.; Li, X.; Yang, Q.; Brock, M.V.; Mei, Q.; Liu, J.; Chen, M.; Shi, F.; et al. Efficacy of Decitabine plus Anti-PD-1 Camrelizumab in Patients with Hodgkin Lymphoma Who Progressed or Relapsed after PD-1 Blockade Monotherapy. Clin Cancer Res 2021, 27, 2782–2791. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Borcoman, E.; Kamal, M.; Marret, G.; Dupain, C.; Castel-Ajgal, Z.; Le Tourneau, C. HDAC Inhibition to Prime Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors. Cancers (Basel) 2022, 14, 66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mei, M.G.; Chen, L.; Godfrey, J.; Song, J.Y.; Egelston, C.; budde, L.E.; Armenian, S.H.; Nikolaenko, L.; Nwangwu, M.; Guo, W.; et al. Pembrolizumab plus vorinostat is highly active in Hodgkin lymphoma, including patients refractory to prior PD-1 blockade. Blood 2023. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- von Keudell, G.; Sermer, D.; Vardhana, S.; Cho, D.; Biggar, E.; Moskowitz, A.J.; Kumar, A.; Batlevi, C.L.; Caron, P.; Hamilton, A.; et al. A Phase II Trial Investigating the Combination of Pembrolizumab (PEM) and Entinostat (ENT) in Relapsed and Refractory (R/R) Hodgkin Lymphoma (HL). Blood. 2020, 136, 2966. [Google Scholar]
- Haverkos, B.M.; Alpdogan, O.; Baiocchi, R.; Brammer, J.E.; Feldman, T.A.; Capra, M.; Brem, E.A.; Nair, S.M.; Scheinberg, P.; Pereira, J.; et al. Nanatinostat (Nstat) and Valganciclovir (VGCV) in Relapsed/Refractory (R/R) Epstein-Barr Virus-Positive (EBV +) Lymphomas: Final Results from the Phase 1b/2 VT3996-201 Study. Blood 2021, 138, 623. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chao, M.P.; Alizadeh, A.A.; Tang, C.; Myklebust, J.H.; Varghese, B.; Gill, S.; Jan, M.; Cha, A.C.; Chan, C.K.; Tan, B.T.; et al. Anti-CD47 antibody synergizes with rituximab to promote phagocytosis and eradicate non-Hodgkin lymphoma. Cell 2010, 142, 699–713. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López-Pereira, B.; Fernández-Velasco, A.A.; Fernández-Vega, I.; Corte-Torres, D.; Quirós, C.; Villegas, J.A.; Palomo, P.; González, S.; González, A.P.; Payer, Á.; et al. Expression of CD47 antigen in Reed-Sternberg cells as a new potential biomarker for classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Clin Transl Oncol 2020, 22, 782–785. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gholiha, A.R.; Hollander, P.; Löf, L.; Glimelius, I.; Hedstrom, G.; Molin, D.; Hjalgrim, H.; Smedby, K.E.; Hashemi, J.; Amini, R.-M.; et al. Checkpoint CD47 expression in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Br J Haematol 2022, 197, 580–589. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Steidl, C.; Lee, T.; Shah, S.P.; Farinha, P.; Han, G.; Nayar, T.; Delaney, A.; Jones, S.J.; Iqbal, J.; Weisenburger, D.D.; et al. Tumor-Associated Macrophages and Survival in Classic Hodgkin's Lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2010, 362, 875–885. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Scott, D.W.; Hong, F.; Kahl, B.S.; Fisher, R.I.; Bartlett, N.L.; Advani, R.H.; Buckstein, R.; Rimsza, L.M.; Connors, J.M.; et al. Tumor-associated macrophages predict inferior outcomes in classic Hodgkin lymphoma: a correlative study from the E2496 Intergroup trial. Blood 2012, 120, 3280–3287. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carey, C.D.; Gusenleitner, D.; Lipschitz, M.; Roemer, M.G.M.; Stack, E.C.; Gjini, E.; Hu, X.; Redd, R.; Freeman, G.J.; Neuberg, D.; et al. Topological analysis reveals a PD-L1-associated microenvironmental niche for Reed-Sternberg cells in Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2017, 130, 2420–2430. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stewart, B.J.; Fergie, M.; Young, M.D.; Jones, C.; Sachdeva, A.; Blain, A.; Bacon, C.M.; Rand, V.; Ferdinand, J.R.; James, K.R.; et al. Spatial and molecular profiling of the mononuclear phagocyte network in classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2023, 141, 2343–2358. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, J.; Wang, L.; Zhao, F.; Tseng, S.; Narayanan, C.; Shura, L.; Willingham, S.; Howard, M.; Prohaska, S.; Volkmer, J.; et al. Pre-Clinical Development of a Humanized Anti-CD47 Antibody with Anti-Cancer Therapeutic Potential. PLoS One 2015, 10, e0137345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Advani, R.; Flinn, I.; Popplewell, L.; Forero, A.; Bartlett, N.L.; Ghosh, N.; Kline, J.; Roschewski, M.; LaCasce, A.; Collins, G.P.; et al. CD47 Blockade by Hu5F9-G4 and Rituximab in Non-Hodgkin’s Lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2018, 379, 1711–1721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reusch, U.; Burkhardt, C.; Fucek, I.; Le Gall, F.; Le Gall, M.; Hoffmann, K.; Knackmuss, S.H.; Kiprijanov, S.; Little, M.; Zhukovsky, E.A. A novel tetravalent bispecific TandAb (CD30/CD16A) efficiently recruits NK cells for the lysis of CD30+ tumor cells. MAbs 2014, 6, 728–739. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pahl, J.H.W.; Koch, J.; Götz, J.J.; Arnold, A.; Reusch, U.; Gantke, T.; Rajkovic, E.; Treder, M.; Cerwenka, A. CD16A Activation of NK Cells Promotes NK Cell Proliferation and Memory-Like Cytotoxicity against Cancer Cells. Cancer Immunol Res 2018, 6, 517–527. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sasse, S.; Bröckelmann, P.J.; Momotow, J.; Plütschow, A.; Hüttmann, A.; Basara, N.; Koenecke, C.; Martin, S.; Bentz, M.; Grosse-Thie, C.; et al. AFM13 in patients with relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma: final results of an open-label, randomized, multicenter phase II trial. Leuk Lymphoma 2022, 63, 1871–1878. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bartlett, N.L.; Herrera, A.F.; Domingo-Domenech, E.; Mehta, A.; Forero-Torres, A.; Garcia-Sanz, R.; Armand, P.; Devata, S.; Izquierdo, A.R.; Lossos, I.S.; et al. A phase 1b study of AFM13 in combination with pembrolizumab in patients with relapsed or refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2020, 136, 2401–2409. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nieto, Y.; Banerjee, P.; Kaur, I.; Griffin, L.; Ganesh, C.; Barnett, M.; Bassett, R.; Kerbauy, L.; Basar, R.; Kaplan, M.; et al. Innate cell engager AFM13 combined with preactivated and expanded cord blood-derived NK cells for patients with double refractory CD30+ lymphoma. Blood, 2022, 138, 415. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hartley, J.A. The development of pyrrolobenzodiazepines as antitumour agents. Expert Opin Investig Drugs 2011, 20, 733–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Flynn, M.J.; Zammarchi, F.; Tyrer, P.C.; Akarca, A.U.; Janghra, N.; Britten, C.E.; Havenith, C.E.; Levy, J.N.; Tiberghien, A.; Masterson, L.A.; et al. ADCT-301, a Pyrrolobenzodiazepine (PBD) Dimer-Containing Antibody-Drug Conjugate (ADC) Targeting CD25-Expressing Hematological Malignancies. Mol Cancer Ther 2016, 15, 2709–2721. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hamadani, M.; Collins, G.P.; Caimi, P.F.; Samaniego, F.; Spira, A.; Davies, A.; Radford, J.; Menne, T.; Karnad, A.; Zain, J.M.; et al. Camidanlumab tesirine in patients with relapsed or refractory lymphoma: a phase 1, open-label, multicentre, dose-escalation, dose-expansion study. Lancet Haematol 2021, 8, e433–e445. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Carlo-Stella, C.; Ansell, S.; Zinzani, P.L.; Radford, J.; Maddocks, K.; Pinto, A.; Collins, G.P.; Bachanova, V.; Bartlett, N.; Bence-Bruckler, I.; et al. S201: Camidanlumab tesirine: Updated efficacy and safety in an open label, multicenter, phase 2 study of patients with relapsed or refractory classical Hodgkin lymphoma (R/R CHL). HemaSphere 2022, 6, 102–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, W.; Blessin, N.C.; Simon, R.; Kluth, M.; Fischer, K.; Hube-Magg, C.; Makrypidi-Fraune, G.; Wellge, B.; Mandelkow, T.; Debatin, N.F.; et al. Expression of the immune checkpoint receptor TIGIT in Hodgkin’s lymphoma. BMC Cancer 2018, 18, 1209. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Annibali, O.; Bianchi, A.; Grifoni, A.; Tomarchio, V.; Tafuri, M.; Verri, M.; Avvisati, G.; Crescenzi, A. A novel scoring system for TIGIT expression in classic Hodgkin lymphoma. Sci Rep 2021, 11, 7059. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Garralda, E.; Sanborn, R.E.; Minchom, A.R.; Davar, D.; Curigliano, G.; Ribrag, V.; Mehta, A.; Foss, F.M.; Zain, J.M.; Forero-Torres, A.; et al. SGNTGT-001: A phase 1 study of SEA-TGT, an effector-function enhanced monoclonal antibody (mAb), in advanced malignancies (trial in progress). J Clin Oncol 2021, 39, TPS2657–TPS2657. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.A.; Grover, N.S.; Beaven, A.W.; Lulla, P.D.; Wu, M.F.; Ivanova, A.; Wang, T.; Shea, T.C.; Rooney, C.M.; Dittus, C.; et al. Anti-CD30 CAR-T Cell Therapy in Relapsed and Refractory Hodgkin Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2020, 38, 3794–3804. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ahmed, S.; Flinn, I.W.; Mei, M.; Riedell, P.A.; Armand, P.; Grover, N.S.; Balyan, R.; Ding, C.; Myo, A.; Horak, I.D.; et al. Updated Results and Correlative Analysis: Autologous CD30.CAR-T-Cell Therapy in Patients with Relapsed or Refractory Classical Hodgkin Lymphoma (CHARIOT Trial). Blood 2022, 140, 7496–7497. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Quach, D.H.; Ramos, C.A.; Lulla, P.D.; Sharma, S.; Ganesh, H.R.; Nouraee, N.; Briones, Y.D.; Hadidi, Y.F.; Becerra-Dominguez, L.; Thakkar, S.G.; et al. CD30.CAR-Modified Epstein-Barr Virus-Specific T Cells (CD30.CAR EBVSTs) Provide a Safe and Effective Off-the-Shelf Therapy for Patients with CD30-Positive Lymphoma. Blood 2022, 140, 412–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramos, C.A.; Quach, D.H.; Lulla, P.D.; Rouce, R.H.; Sharma, S.; Ganesh, H.R.; Nouraee, N.; Briones, Y.D.; Becerra-Dominguez, L.; Thakkar, S.G.; et al. Off-the-shelf CD30.CAR-modified Epstein-Barr virus-specific T cells (CD30.CAR EBVSTs) provide a safe and effective therapy for patients with Hodgkin lymphoma (HL). Hematol Oncol 2023, 41, 83–85. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, S.; Gu, C.; Huang, L.; Wu, H.; Shi, J.; Zhang, Z.; Zhou, Y.; Zhou, J.; Gao, Y.; Liu, J.; et al. The third-generation anti-CD30 CAR T-cells specifically homing to the tumor and mediating powerful antitumor activity. Sci Rep 2022, 12, 10488. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Connors, J.M.; Jurczak, W.; Straus, D.J.; Ansell, S.M.; Kim, W.S.; Gallamini, A.; Younes, A.; Alekseev, S.; Illés, Á.; Picardi, M.; et al. Brentuximab Vedotin with Chemotherapy for Stage III or IV Hodgkin's Lymphoma. N Engl J Med 2018, 378, 331–344. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Herrera, A.F.; LeBlanc, M.; Castellino, S.M.; Li, H.; Rutherford, S.C.; Evens, A.M.; Davison, K.; Punnett, A.; Hodgson, D.; Parsons, S.K.; et al. Nivolumab(N)-AVD improves progression-free survival compared to brentuximab vedotin(BV)-AVD in advanced stage (AS) classic Hodgkin lymphoma (HL): results of SWOG S1826. Hematol Oncol 2023, 41, 33–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Roemer, M.G.M.; Redd, R.A.; Cader, F.Z.; Pak, C.J.; Abdelrahman, S.; Ouyang, J.; Sasse, S.; Younes, A.; Fanale, M.; Santoro, A.; et al. Major Histocompatibility Complex Class II and Programmed Death Ligand 1 Expression Predict Outcome After Programmed Death 1 Blockade in Classic Hodgkin Lymphoma. J Clin Oncol 2018, 36, 942–950. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Spina, V.; Bruscaggin, A.; Cuccaro, A.; Martini, M.; Di Trani, M.; Forestieri, G.; Manzoni, M.; Condoluci, A.; Arribas, A.; Terzi-Di-Bergamo, L.; et al. Circulating tumor DNA reveals genetics, clonal evolution, and residual disease in classical Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2018, 131, 2413–2425. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kurtz, D.M. Bringing circulating tumor DNA to the clinic in Hodgkin lymphoma. Haematologica 2021, 106, 5–6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moskowitz, A.J.; Schöder, H.; Gavane, S.; Thoren, K.L.; Fleisher, M.; Yahalom, J.; McCall, S.J.; Cadzin, B.R.; Fox, S.Y.; Gerecitano, J.; et al. Prognostic significance of baseline metabolic tumor volume in relapsed and refractory Hodgkin lymphoma. Blood 2017, 130, 2196–2203. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lynch, R.C.; Alig, S.; Ujjani, C.S.; Poh, C.; Warren, E.H.; Smith, S.D.; Shadman, M.; Shustov, A.; Till, B.; Raghunathan, V.M.; et al. T057: Circulating tumor DNA in classical Hodgkin lymphoma patients treated with pembrolizumab and chemotherapy: dynamic response assessment and correlation with baseline total metabolic tumor volume. HemaSphere 2022, 6, 26–27. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Regimen | Phase | N | CR rate | PFS (all patients) |
PFS (AHCT cohort) |
Median follow-up | Reference |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| BV → augmented ICE | 2 | 46 | 76% | 82% (3 years) | 82% (3 years) | 20 months | [26] |
| BV + ICE | 1/2 | 45 | 74% | 80% (2 years) | NR | 37 months | [28] |
| BV + DHAP | 2 | 55 | 81% | 74% (2 years) | NR | 27 months | [29] |
| BV + ESHAP | 1/2 | 66 | 70% | 71% (2 years) | NR | 27 months | [30] |
| BV + bendamustine | 1/2 | 55 | 74% | 63% (2 years) | 70% (2 years) | 21 months | [31] |
| Nivolumab + BV | 1/2 | 93 | 67% | 77% (3 years) | 91% (3 years) | 34 months | [43] |
| Nivolumab + ICE | 2 | 37 | 91% | 72% (2 years) | 94% (2 years) | 31 months | [44] |
| Pembrolizumab + ICE | 2 | 42 | 87% | 87% (2 years) | NR | 24 months | [45] |
| Pembrolizumab + GVD | 2 | 39 | 95% | 100% (1 year) | 100% (1 years ) | 14 months | [46] |
| Regimen | Therapeutic Target(s) | Phase | Patient population* | N | ORR | CRR | Median PFS | Median f/u | Ref |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Nivo + ipilimumab | PD1 + CTLA4 | 1 | 4 prior lines | 31 | 74% | 23% | NR | 18 mo. | [90] |
| Nivo + ipilimumab + BV | PD1 + CTLA4 + CD30 |
1/2 | 2 prior lines All PD1 naïve |
64 | 82% | 73% | NR | 20 mo. | [91] |
| Pembro + favezelimab | PD1 + LAG3 | 1/2 | PD1 naïve | 30 | 80% | 33% | 19.4 mo. | 32 mo. | [93] |
| Pembro + favezelimab | PD1 + LAG3 | 1/2 | PD1 refractory | 34 | 29% | 9% | 9.7 mo. | 35 mo. | [93] |
| Nivo + lenalidomide | PD1 + CELMoD | 1/2 | 3 prior lines 90% PD1 naïve |
10 | 70% | 30% | NR | -- | [96] |
| Nivo + ibrutinib | PD1 + BTK/ITK | 2 | 5 prior lines 59% prior PD1 |
17 | 52% | 29% | 17.3 mo. | 9 mo. | [100] |
| Nivo + ruxolitinib | PD1 + JAK1/2 | 1/2 | 4 prior lines 100% prior PD1 |
21 | 42% | 26% | 16.5 mo. | 21 mo. | [103] |
| Camrelizumab + decitabine | PD1 + HMA | 2 | PD1 naïve | 61 | 95% | 71% | NR | 15 mo. | [109] |
| Camrelizumab + decitabine | PD1 + HMA | 2 | PD1 refractory | 51 | 52% | 36% | 21.6 mo. | 39 mo. | [110] |
| Pembro + vorinostat | PD1 + HDACi | 1 | 3 prior lines 78% prior PD1 |
32 | 72% | 34% | 8.9 mo. | 33 mo. | [112] |
| Pembro + entinostat | PD1 + HDACi | 2 | 5 prior lines 55% prior PD1 |
22 | 86% | 45% | NR | 8 mo. | [113] |
| Pembro + AFM13 | PD1 + CD30/CD16A | 1 | 3 prior lines All PD1 naïve |
30 | 83% | 37% | -- | -- | [127] |
| AFM13 + umbilical cord blood derived NK cells | NK cells + CD30/CD16A | 1/2 | 6 prior lines 29% prior PD1 |
30 | 97% | 63% | NR | 8 mo. | [128] |
| Camidanlumab tesirine | CD25 | 1 | 5 prior lines 74% prior PD1 |
77 | 71% | 42% | 6.8 mo. | 9 mo. | [131] |
| Camidanlumab tesirine | CD25 | 2 | 5 prior lines 100% prior PD1 |
117 | 70% | 33% | 9.1 mo. | 11 mo. | [132] |
| CD30 CAR-T (RELY-30) | CD30 | 1/2 | 7 prior lines | 41 | 72% | 59% | 9 mo. | 18 mo. | [136] |
| CD30 CAR-T (CHARIOT) | CD30 | 2 | 6 prior lines | 15 | 73% | 60% | -- | -- | [137] |
| CD30 CAR.EBVSTs | CD30 + EBV | 1 | 5 prior lines | 16 | 75% | 38% | -- | -- | [139] |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




