Submitted:
05 July 2023
Posted:
06 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Numerical Methodology
2.1. CFD
2.2. DEM
2.3. CFD-DEM Coupling
2.4. Coarse Graining
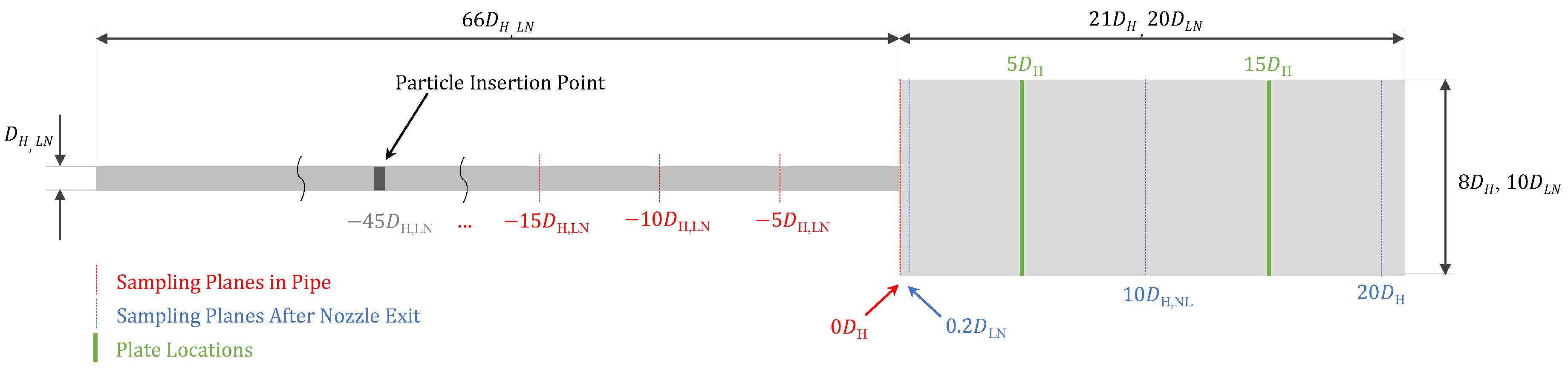
3. Simulation Setup
3.1. Generalized CFD Setup
3.2. Generalized DEM Setup
3.3. Hardalupas Et al. DEM Setup
3.4. Lau and Nathan DEM Setup
3.5. Coupling Setup
4. Results and Discussion
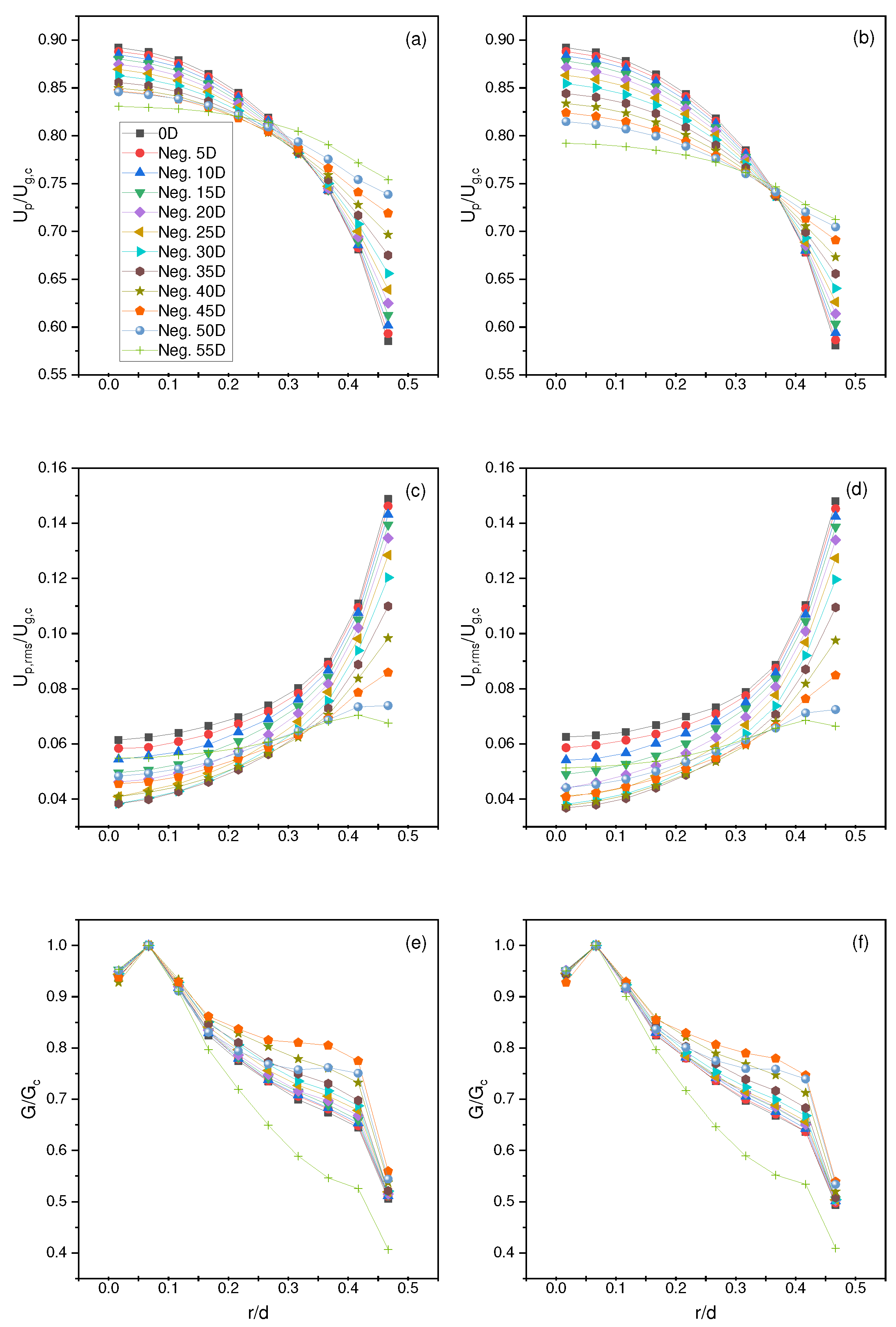
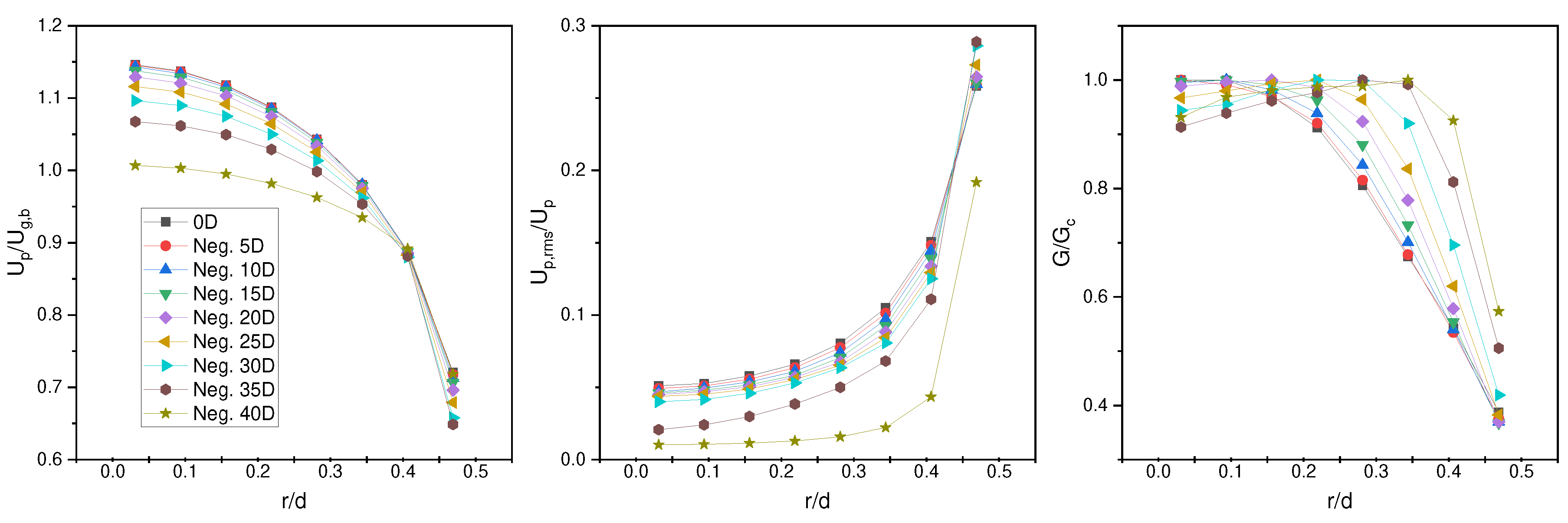
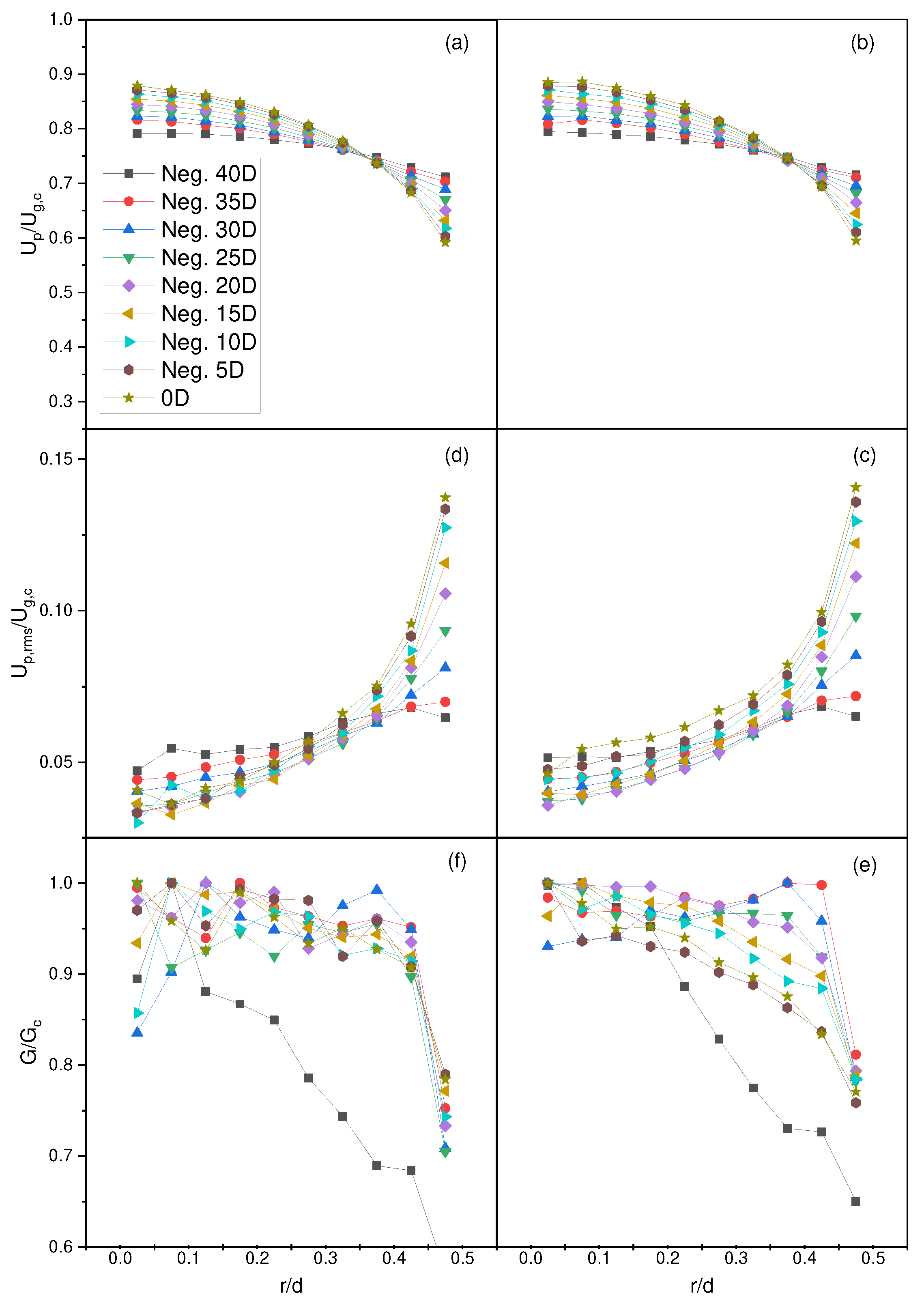
4.1. Particle Full Development
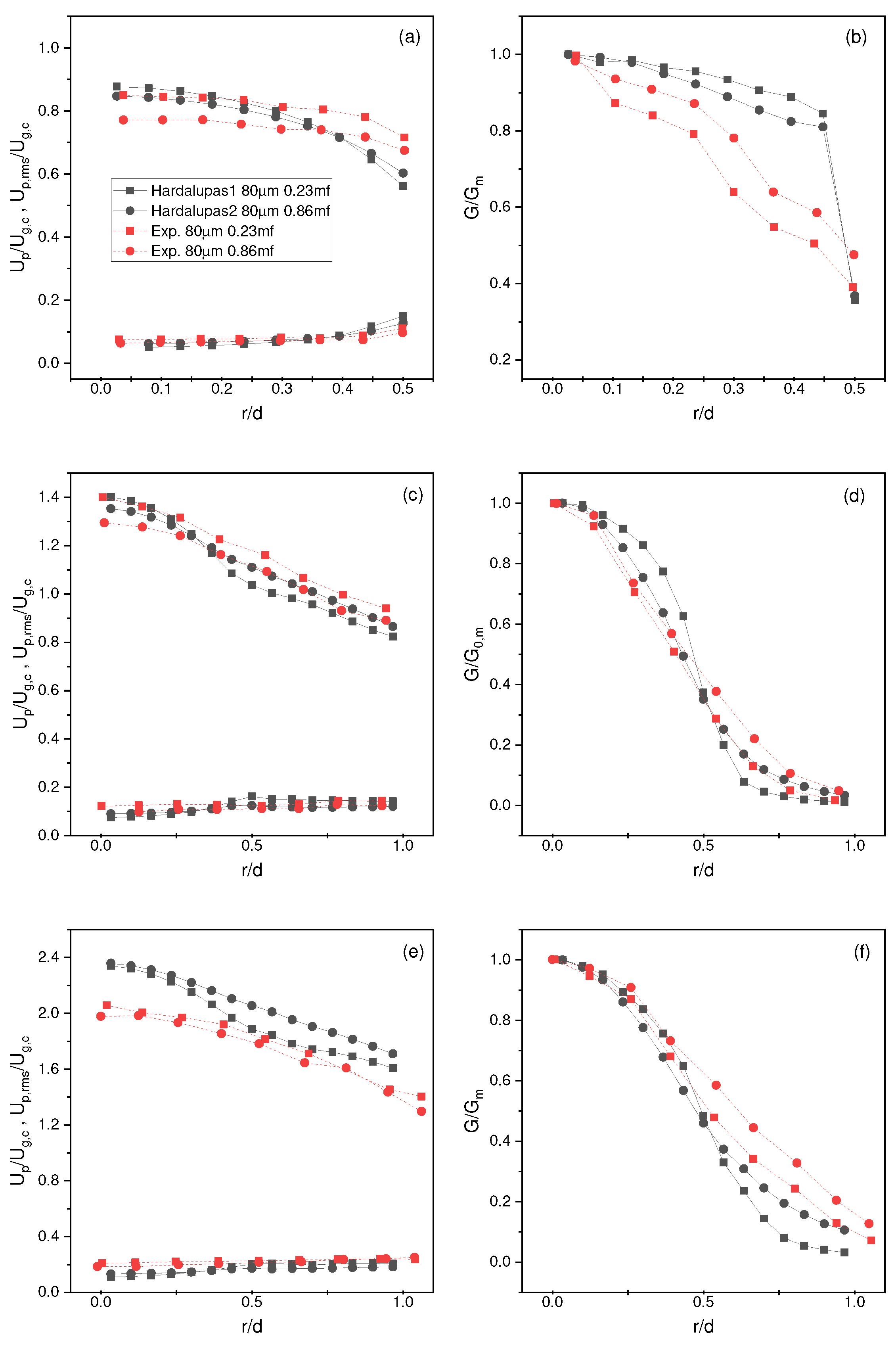
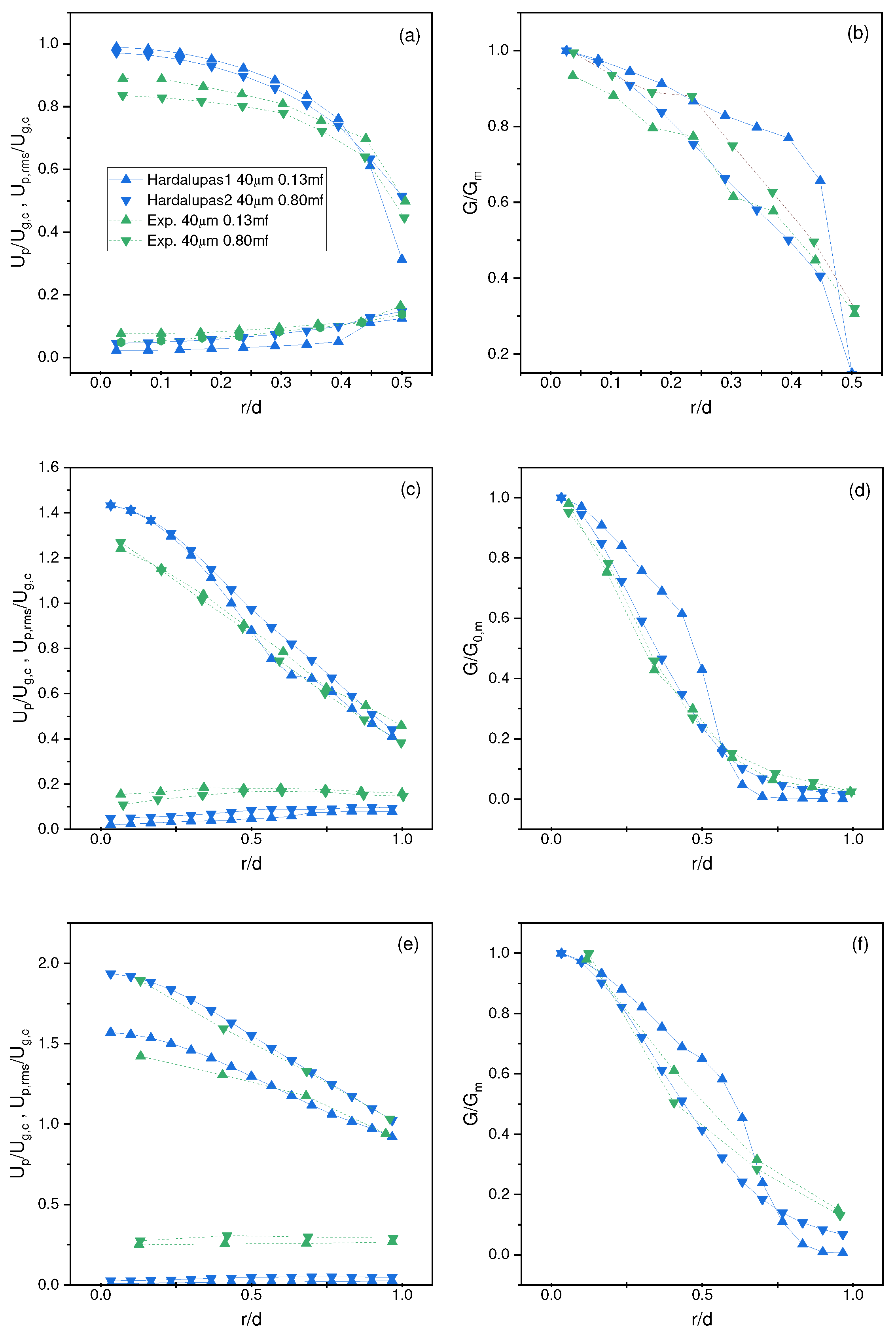
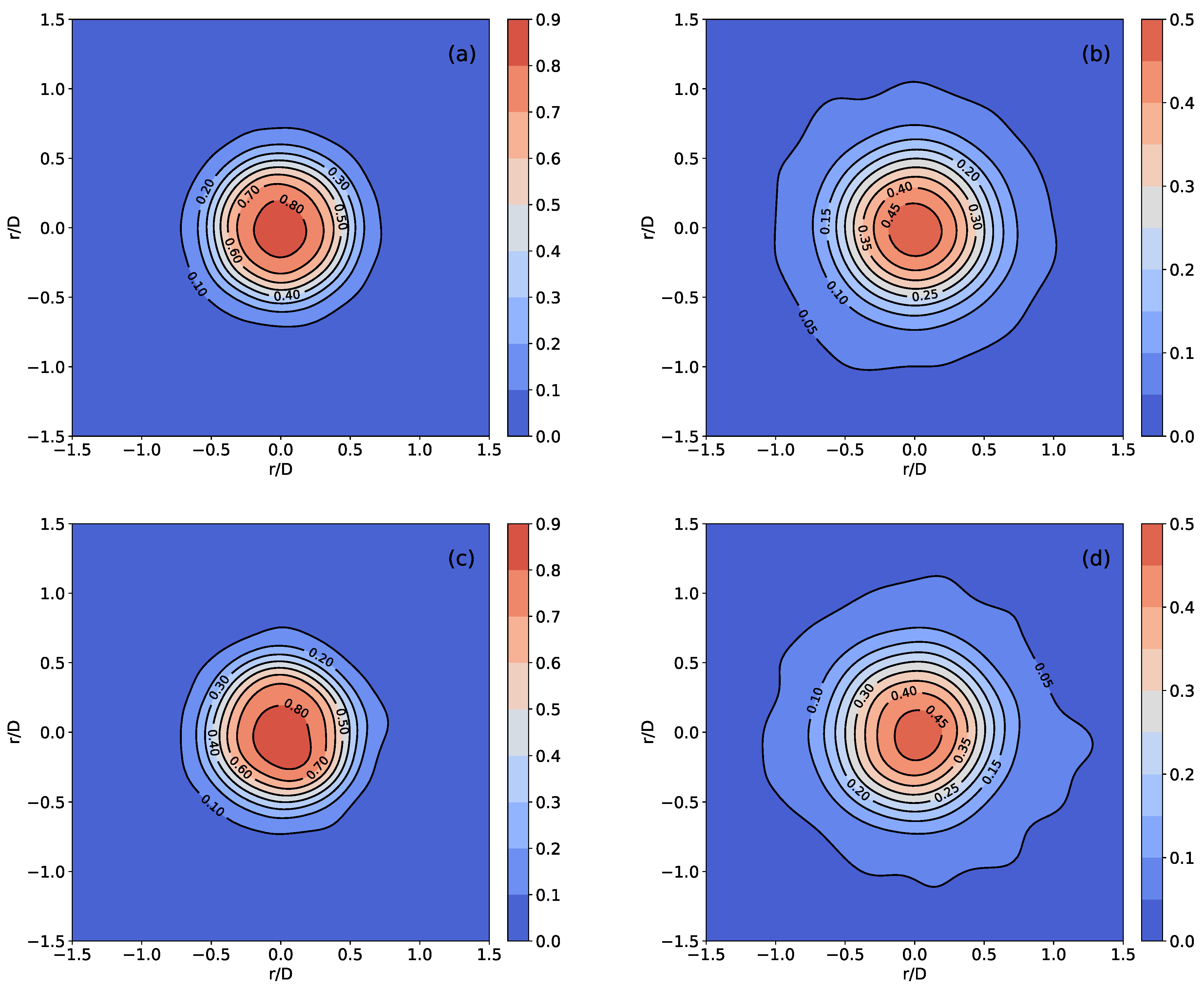
4.2. Hardalupas Et al. Results
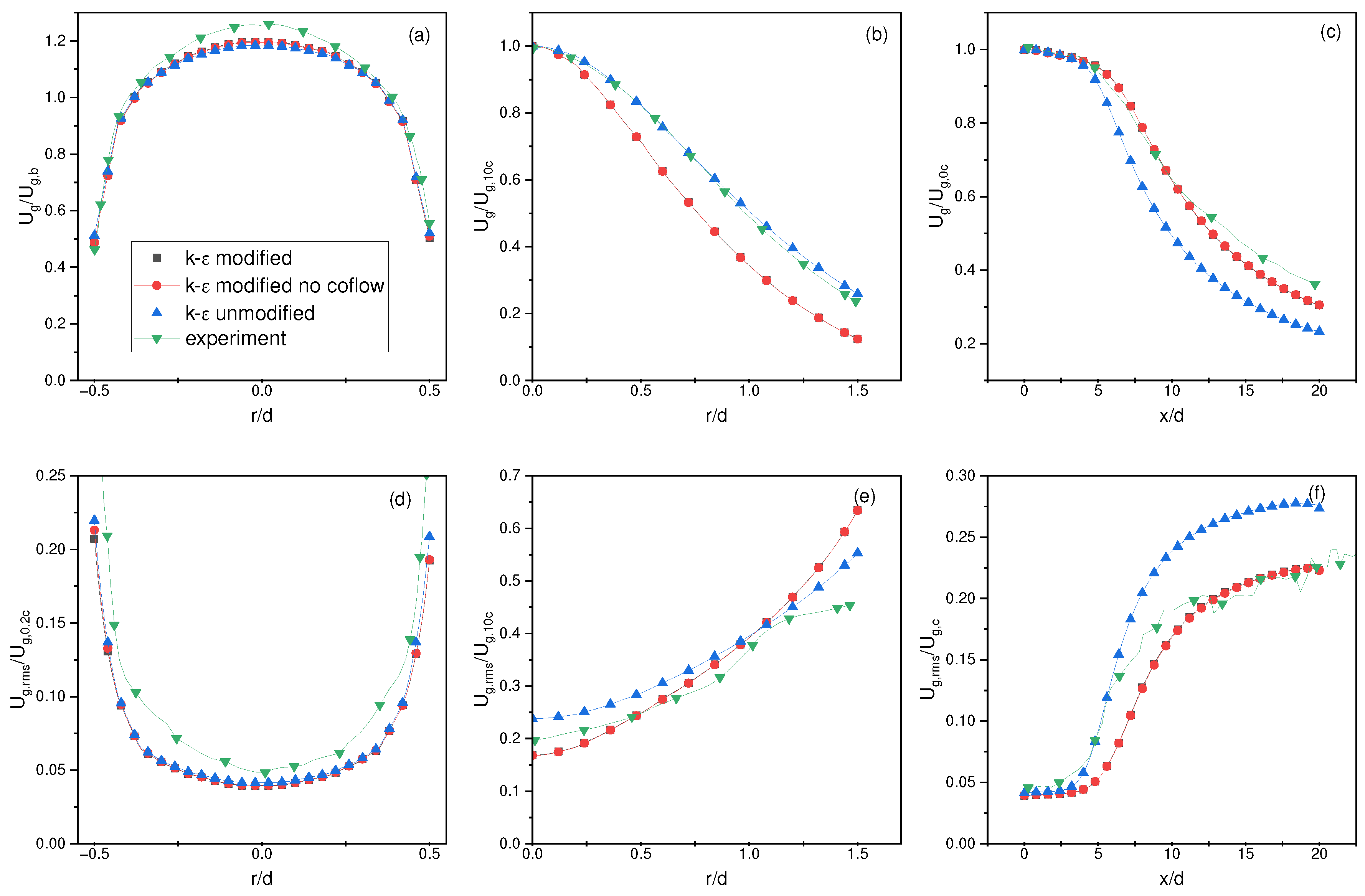
4.3. Lau and Nathan Single-Phase Results
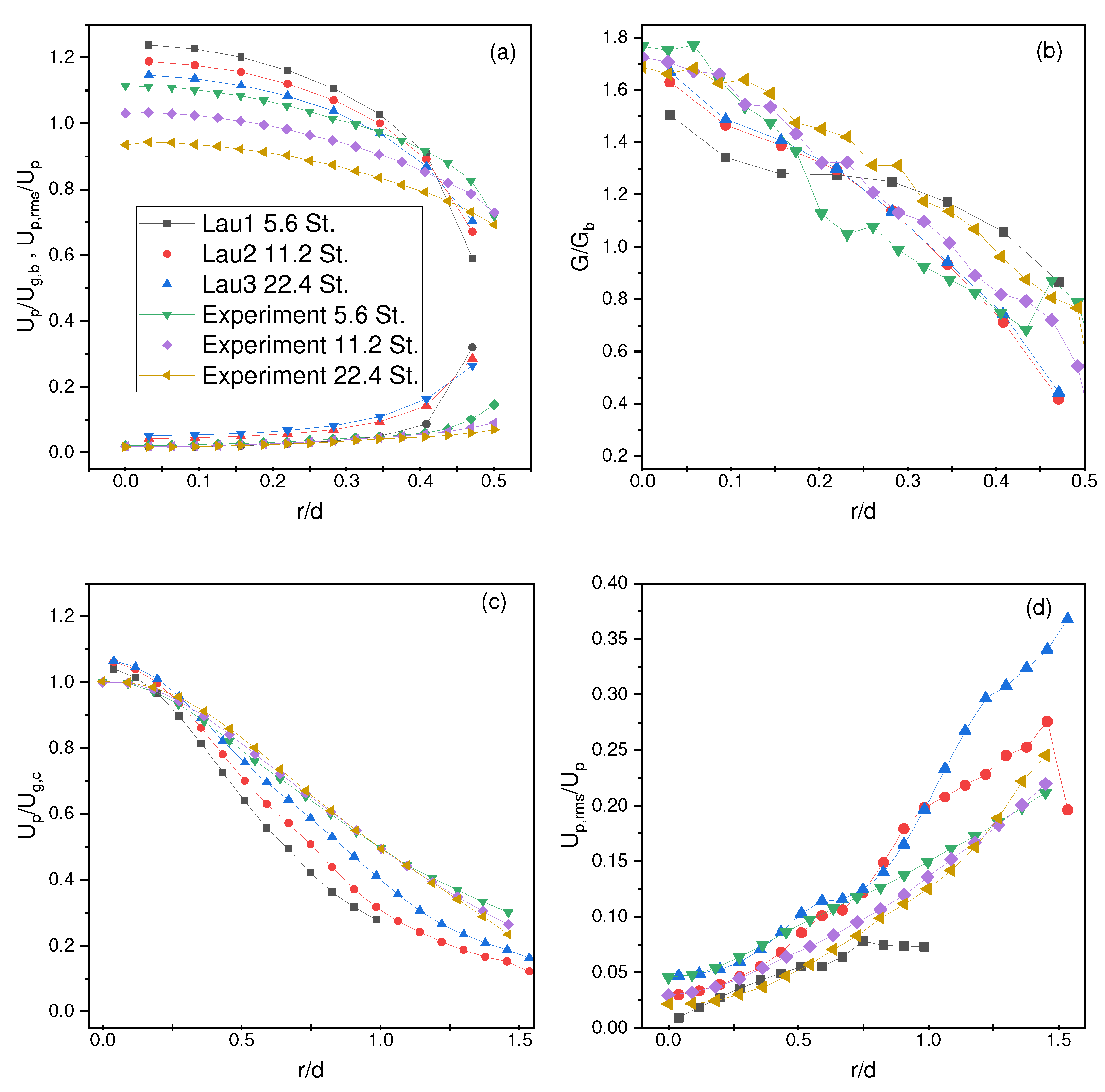
4.4. Lau and Nathan Results
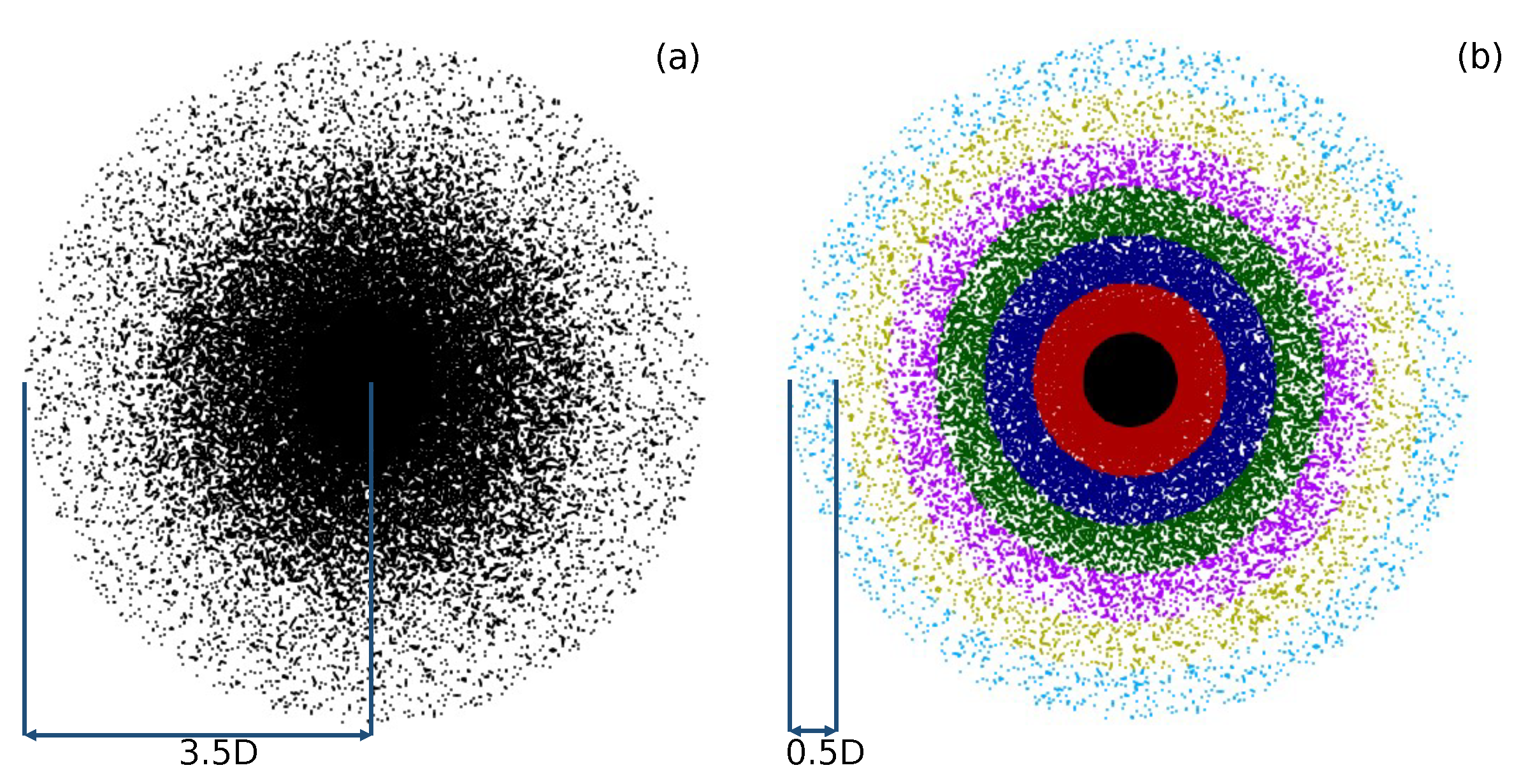
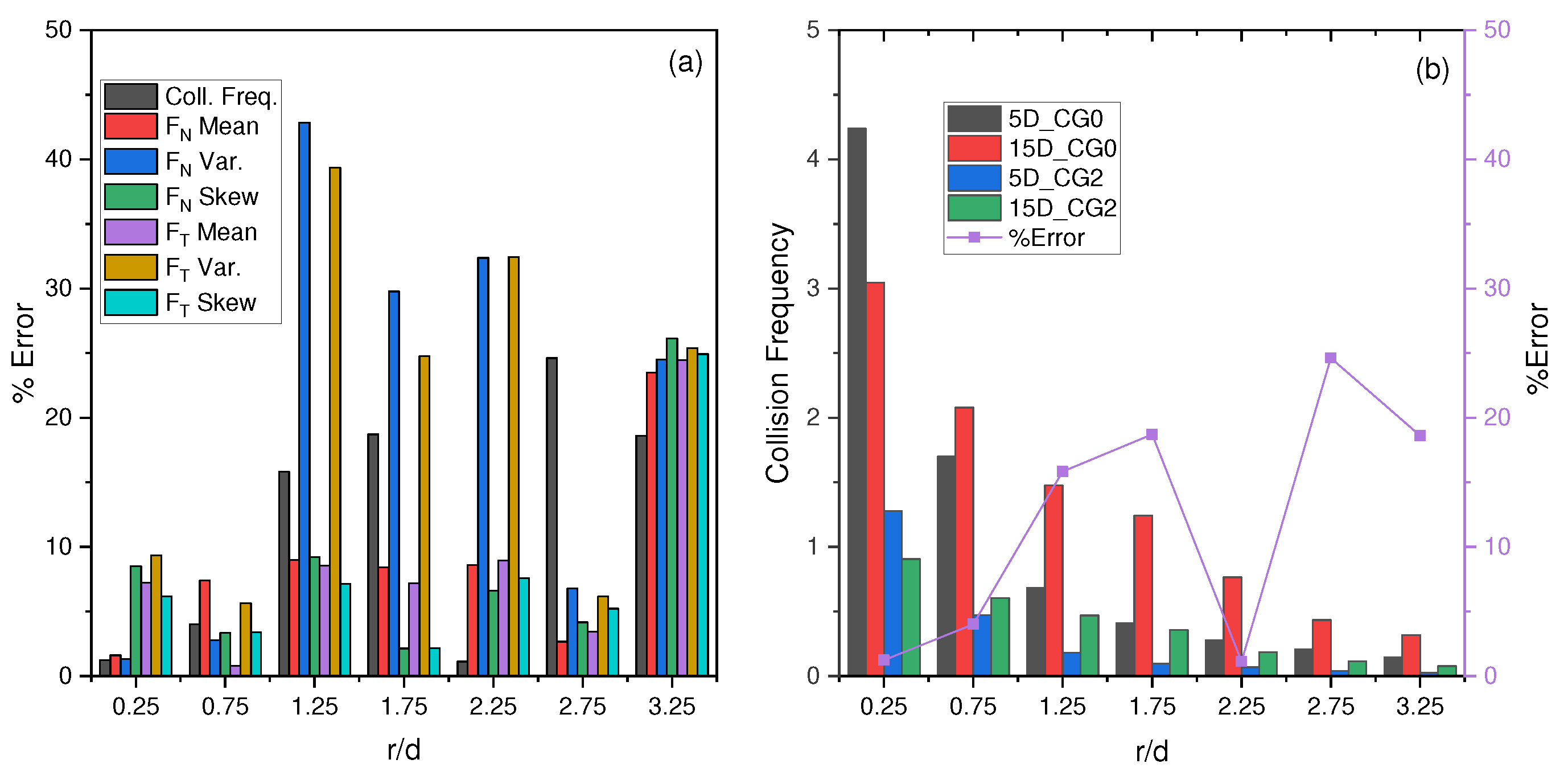
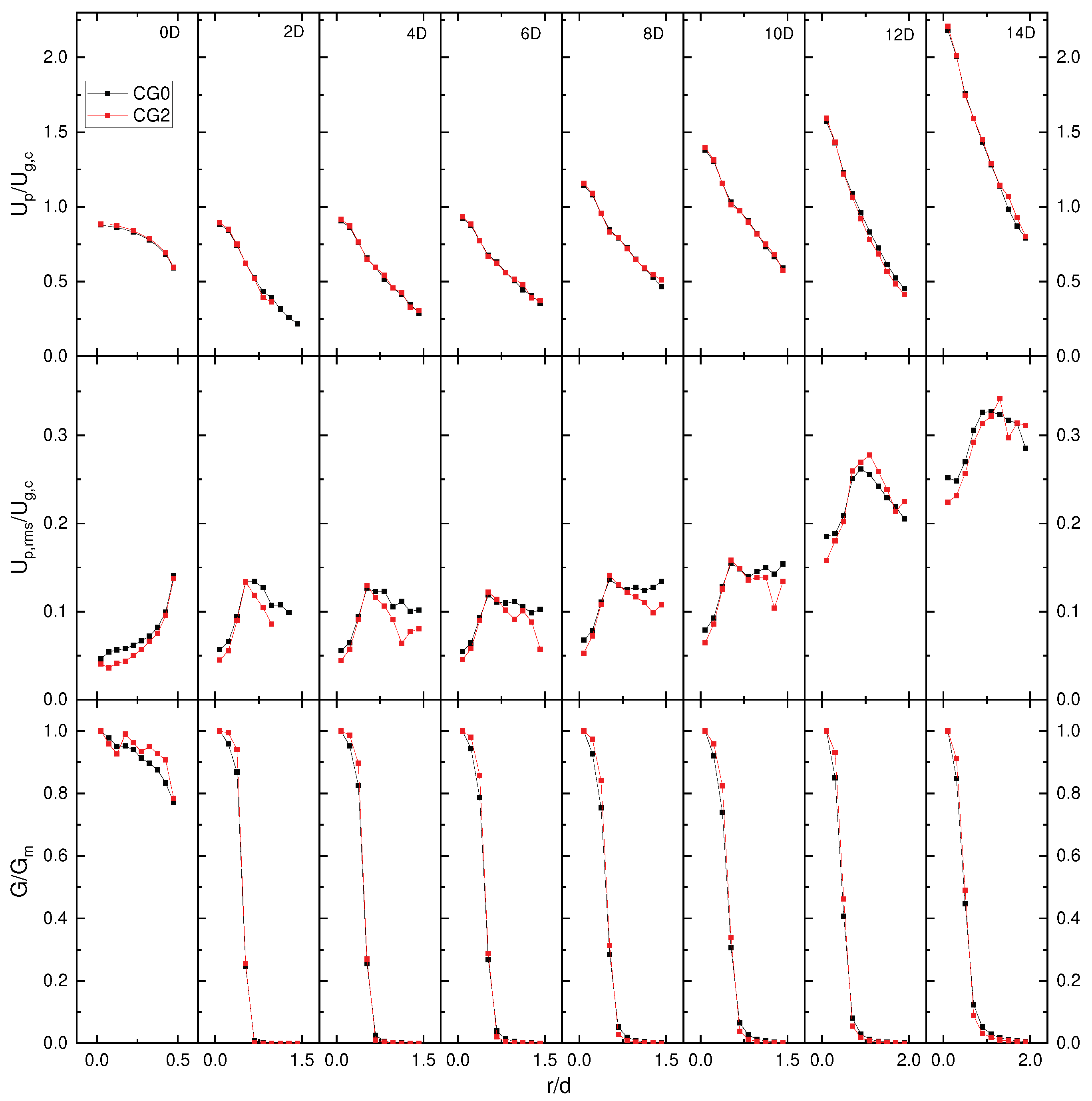
4.5. Coarse Graining Results
5. Conclusion
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
Nomenclature
| liquid volume fraction, | |
| volume of fluid inside of a cell | |
| volume of particles inside of a cell | |
| volume of the cell | |
| total solid volume inside of a cell | |
| density of the fluid | |
| density of the particle | |
| velocity of the liquid | |
| average solid velocity inside of the cell | |
| particle velocity | |
| variable to change between model A (Set II) and model B (Set I) of CFD-DEM formulation | |
| p | pressure |
| liquid phase stress tensor | |
| implicit momentum coupling term | |
| f | explicit force term |
| summation of all forces inside of a cell | |
| k | fluid turbulent kinetic energy |
| fluid turbulent dissipation | |
| fluid viscosity | |
| fluid turbulent viscosity | |
| k- constant | |
| k- constant | |
| k- constant | |
| k- constant | |
| deviatoric part of the fluid stress tensor | |
| Kronecker delta | |
| particle mass | |
| g | gravity vector |
| pressure force | |
| viscous force | |
| lift force acting on the particle | |
| particle-particle interaction force | |
| particle-wall interaction force | |
| drag force | |
| moment of inertia of the particle | |
| rotational velocity of the particle | |
| torque acting on the particle | |
| normal contact force | |
| tangential contact force | |
| normal stiffness coefficient | |
| normal damping coefficient | |
| normal overlap distance | |
| normal relative velocity | |
| tangential stiffness coefficient | |
| tangential damping coefficient | |
| tangential overlap distance | |
| tangential relative velocity | |
| used for the calculation of drag to further simplify the equation | |
| relative velocity between the fluid and the solid, | |
| a coefficient of drag | |
| diameter the grain | |
| coarse grain factor | |
| shape factor | |
| particle Reynolds number | |
| particle shape factor | |
| fluid viscosity | |
| equivalent Young’s modulus | |
| equivalent particle radius | |
| particle radius on collision | |
| particle Young’s modulus for collisions | |
| Poisson’s ratio for collisions | |
| Poisson’s ratio for collisions | |
| grain (parcel) radius | |
| particle radius | |
| un-scaled (no coarse graining) system | |
| coarse graining factor of 2 | |
| non-dimensional wall distance | |
| non-dimensional velocity defined as the near-wall velocity divided by the shear velocity | |
| Collision frequency statistic for unscaled system using 5D plate | |
| Collision frequency statistic for unscaled system using 15D plate | |
| Collision frequency statistic for scaled system using 5D plate | |
| Collision frequency statistic for scaled system using 15D plate | |
| Normal or tangential force statistic for unscaled system using 5D plate | |
| Normal or tangential force statistic for unscaled system using 15D plate | |
| Normal or tangential force statistic for scaled system using 5D plate | |
| Normal or tangential force statistic for scaled system using 15D plate |
Appendix A
References
- Hardalupas, Y.; Taylor, A.; Whitelaw, J. Velocity and particle-flux characteristics of turbulent particle-laden jets. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London. A. Mathematical and Physical Sciences 1989, 426, 31–78. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, Y.; Lockwood, F.C. Velocity measurements in a particle laden turbulent free jet. Combustion and Flame 1981, 40, 333–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- McComb, W.; Salih, S. Measurement of normalised radial concentration profiles in a turbulent aerosol jet, using a laser-doppler anemometer. Journal of Aerosol Science 1977, 8, 171–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Modarress, D.; Wuerer, J.; Elghobashi, S. An Experimental Study of a Turbulence Round Two-Phase Jet. Chemical Engineering Communications 1984, 28, 341–354. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Popper, J.; Abuaf, N.; Hetsroni, G. Velocity measurements in a two-phase turbulent jet. International Journal of Multiphase Flow 1974, 1, 715–726. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shuen, J.S. A Theoretical and Experimental Investigation of Dilute Particle-Laden Turbulent Gas Jets (two-Phase Flow). Ph.D., The Pennsylvania State University, United States – Pennsylvania, 1984.
- Lau, T.C.W.; Nathan, G.J. The effect of Stokes number on particle velocity and concentration distributions in a well-characterised, turbulent, co-flowing two-phase jet. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2016, 809, 72–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fernandes, C.; Semyonov, D.; Ferrás, L.L.; Nóbrega, J.M. Validation of the CFD-DPM solver DPMFoam in OpenFOAM® through analytical, numerical and experimental comparisons. Granular Matter 2018, 20, 64. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karimi, M.; Mostoufi, N.; Zarghami, R.; Sotudeh-Gharebagh, R. A new method for validation of a CFD–DEM model of gas–solid fluidized bed. International Journal of Multiphase Flow 2012, 47, 133–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kloss, C.; Goniva, C.; Hager, A.; Amberger, S.; Pirker, S. Models, algorithms and validation for opensource DEM and CFD-DEM. Progress in Computational Fluid Dynamics, An International Journal 2012, 12, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mansouri, A.; Arabnejad, H.; Shirazi, S.; McLaury, B. A combined CFD/experimental methodology for erosion prediction. Wear 2015, 332-333, 1090–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nguyen, V.; Nguyen, Q.; Liu, Z.; Wan, S.; Lim, C.; Zhang, Y. A combined numerical–experimental study on the effect of surface evolution on the water–sand multiphase flow characteristics and the material erosion behavior. Wear 2014, 319, 96–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pozzetti, G.; Peters, B. A numerical approach for the evaluation of particle-induced erosion in an abrasive waterjet focusing tube. Powder Technology 2018, 333, 229–242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, Q.; Huang, Q.; Sun, X.; Zhang, J.; Karimi, S.; Shirazi, S.A. Large Eddy Simulation of Slurry Erosion in Submerged Impinging Jets. Volume 3: Computational Fluid Dynamics; Micro and Nano Fluid Dynamics. American Society of Mechanical Engineers, 2020, p. V003T05A040. [CrossRef]
- Bazdidi-Tehrani, F.; Zeinivand, H. Presumed PDF modeling of reactive two-phase flow in a three dimensional jet-stabilized model combustor. Energy Conversion and Management 2010, 51, 225–234. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, D.; Miskovic, S. Analysis of Coupled CFD-DEM Simulations in Dense Particle-Laden Turbulent Jet Flow. Volume 2: Fluid Mechanics; Multiphase Flows; American Society of Mechanical Engineers: Virtual, Online, 2020. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wilcox, D.C. Turbulence modeling for CFD, 3rd ed.; Number Book, Whole in 1, DCW Industries: La Cãnada, Calif, 2006. [Google Scholar]
- Pope, S.B. An explanation of the turbulent round-jet/plane-jet anomaly. AIAA Journal 1978, 16, 279–281. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Faghani, E.; Saemi, S.D.; Maddahian, R.; Farhanieh, B. On the effect of inflow conditions in simulation of a turbulent round jet. Archive of Applied Mechanics 2011, 81, 1439–1453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Givi, P.; Ramos, J. On the calculation of heat and momentum transport in a round jet. International Communications in Heat and Mass Transfer 1984, 11, 173–182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgans, R.C.; Dally, B.B.; Nathan, G.J.; Lanspeary, P.V.; Fletcher, D.F. Applications of the Revised Wilcox 1998 K-Omega Turbulence Model To A Jet In Co-Flow. CFD in the Minerals and Process Industries, 1999, p. 6.
- Launder, B.E.; Spalding, D.B. The numerical computation of turbulent flows. Computer Methods in Applied Mechanics and Engineering 1974, 3, 269–289. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weaver, D.S.; Mišković, S. A Study of RANS Turbulence Models in Fully Turbulent Jets: A Perspective for CFD-DEM Simulations. Fluids 2021, 6. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bogusławski, L.; Popiel, C.O. Flow structure of the free round turbulent jet in the initial region. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 1979, 90, 531–539. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- GmbH, D.C. About CFDEM(R)coupling; CFDEMresearch GmbH, 2017.
- Zhou, Z.Y.; Kuang, S.B.; Chu, K.W.; Yu, A.B. Discrete particle simulation of particle–fluid flow: model formulations and their applicability. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2010, 661, 482–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Verlet, L. Computer "Experiments" on Classical Fluids. I. Thermodynamical Properties of Lennard-Jones Molecules. Physical Review 1967, 159, 98–103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Otsubo, M.; O’Sullivan, C.; Shire, T. Empirical assessment of the critical time increment in explicit particulate discrete element method simulations. Computers and Geotechnics 2017, 86, 67–79. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, A.; Di Maio, F.P. Comparison of contact-force models for the simulation of collisions in DEM-based granular flow codes. Chemical Engineering Science 2004, 59, 525–541. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, A.; Di Maio, F.P. An improved integral non-linear model for the contact of particles in distinct element simulations. Chemical Engineering Science 2005, 60, 1303–1312. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Andrews, M.; O’Rourke, P. The multiphase particle-in-cell (MP-PIC) method for dense particulate flows. International Journal of Multiphase Flow 1996, 22, 379–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Renzo, A.; Napolitano, E.; Di Maio, F. Coarse-Grain DEM Modelling in Fluidized Bed Simulation: A Review. Processes 2021, 9, 279. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Radl, S.; Radeke, C.; Khinast, J.G.; Sundaresan, S. Parcel-Based Approach for the Simulation of Gas-Particle Flows. CFD;, 2011; p. 11.
- Nasato, D.S.; Goniva, C.; Pirker, S.; Kloss, C. Coarse Graining for Large-scale DEM Simulations of Particle Flow – An Investigation on Contact and Cohesion Models. Procedia Engineering 2015, 102, 1484–1490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishigaki, M.; Abe, S.; Sibamoto, Y.; Yonomoto, T. Influence of mesh non-orthogonality on numerical simulation of buoyant jet flows. Nuclear Engineering and Design 2017, 314, 326–337. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weller, H.G.; Tabor, G.; Jasak, H.; Fureby, C. A tensorial approach to computational continuum mechanics using object-oriented techniques. Computers in Physics 1998, 12, 620. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaroslav, S. Contribution to investigation of turbulent mean-flow velocity profile in pipe of circular cross-section. 35th Meeting of Departments of Fluid Mechanics and Thermomechanics;, 2016; p. 020010. [CrossRef]
- Kalitzin, G.; Medic, G.; Iaccarino, G.; Durbin, P. Near-wall behavior of RANS turbulence models and implications for wall functions. Journal of Computational Physics 2005, 204, 265–291. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Xiao, Y.; Liu, Y.; Shi, Y. Effect of Young’s modulus on DEM results regarding transverse mixing of particles within a rotating drum. Powder Technology 2017, 318, 507–517. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lommen, S.; Schott, D.; Lodewijks, G. DEM speedup: Stiffness effects on behavior of bulk material. Particuology 2014, 12, 107–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lorenz, A.; Tuozzolo, C.; Louge, M.Y. Measurements of impact properties of small, nearly spherical particles. Experimental Mechanics 1997, 37, 292–298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sandeep, C.S.; Luo, L.; Senetakis, K. Effect of Grain Size and Surface Roughness on the Normal Coefficient of Restitution of Single Grains. Materials 2020, 13, 814. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tang, H.; Song, R.; Dong, Y.; Song, X. Measurement of Restitution and Friction Coefficients for Granular Particles and Discrete Element Simulation for the Tests of Glass Beads. Materials 2019, 12, 3170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lau, T.C.; Nathan, G.J. Influence of Stokes number on the velocity and concentration distributions in particle-laden jets. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2014, 757, 432–457. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ergun, S. Fluid Flow through Packed Columns. Chemical Engineering Process 1952, 48, 89–94. [Google Scholar]
- Wen, C.Y.; Yu, Y. Mechanics of fluidization. Chemical Engineering Progress Symposium Series 1966, 62, 100–111. [Google Scholar]
- Zhu, H.; Zhou, Z.; Yang, R.; Yu, A. Discrete particle simulation of particulate systems: Theoretical developments. Chemical Engineering Science 2007, 62, 3378–3396. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Latzko, H. Warmubergang an einem Turbulenten. Z. Angew 1921, Math, 268–290. [Google Scholar]
- Mena, S.E.; Curtis, J.S. Experimental data for solid–liquid flows at intermediate and high Stokes numbers. Journal of Fluid Mechanics 2020, 883, A24. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hu, G.; Hu, Z.; Jian, B.; Liu, L.; Wan, H. On the Determination of the Damping Coefficient of Non-linear Spring-dashpot System to Model Hertz Contact for Simulation by Discrete Element Method. Journal of Computers 2011, 6, 984–988. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Simulation | Particle | Particle | Mass | Gas Exit | Reynolds | Stokes |
| Name | Diameter, | Density, | Loading | Velocity, | Number | Number |
| Hardalupas1 | 80 | 2950 | 0.23 | 13 | 13000 | 50 |
| Hardalupas2 | 80 | 2950 | 0.86 | 13 | 13000 | 50 |
| Hardalupas3 | 40 | 2420 | 0.13 | 13 | 13000 | 10.27 |
| Hardalupas4 | 40 | 2420 | 0.80 | 13 | 13000 | 10.27 |
| Lau1 | 40 | 1200 | 0.40 | 12 | 10000 | 5.6 |
| Lau2 | 40 | 1200 | 0.40 | 24 | 20000 | 11.2 |
| Lau3 | 40 | 1200 | 0.40 | 48 | 40000 | 22.4 |
| Experiment | Number | Orthogonality | Orthogonality | Skew | Average |
| Cells | Max | Average | Max | ||
| Hardalupas et al. [1] | 3806397 | 21.9 | 2.9 | 0.5 | 24 |
| Lau and Nathan [7] | 3440578 | 25.8 | 3.1 | 0.5 | 24-76 |
| Location | Velocity | Pressure | Eddy Viscosity | Kinetic Energy | Epsilon |
| Wall | No Slip | Zero Gradient | Spalding Wall Func. | Zero Gradient | Epsilon Wall Func. |
| Inlet | Zero Gradient | Calculated | |||
| Outlet | Entrainment Vel. | Total Pressure | Calculated | Zero Gradient | Zero Gradient |
| Initial Freestream | Uniform 0 | Uniform 0 | 0 |
| Simulation | Inlet Velocity | Fluctuating | DEM | %Rayleigh, %Hertz |
| Name | (45D), | Velocity, | Time-Step, s | |
| Hardalupas1 | ||||
| Hardalupas2 | ||||
| Hardalupas3 | ||||
| Hardalupas4 | ||||
| Lau1 | ||||
| Lau2 | ||||
| Lau3 |
| Ratio | Col. Freq. | Mean | Var. | Skew | Mean | Var. | Skew |
| CG0 | 1.22 | 0.70 | 0.64 | 1.38 | 0.73 | 0.56 | 1.12 |
| CG2 | 1.25 | 0.68 | 0.62 | 1.42 | 0.75 | 0.55 | 1.10 |
| %Error | 2.39 | 3.10 | 3.78 | 3.56 | 3.81 | 1.04 | 1.23 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





