Submitted:
05 July 2023
Posted:
06 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Zn neurotoxicity
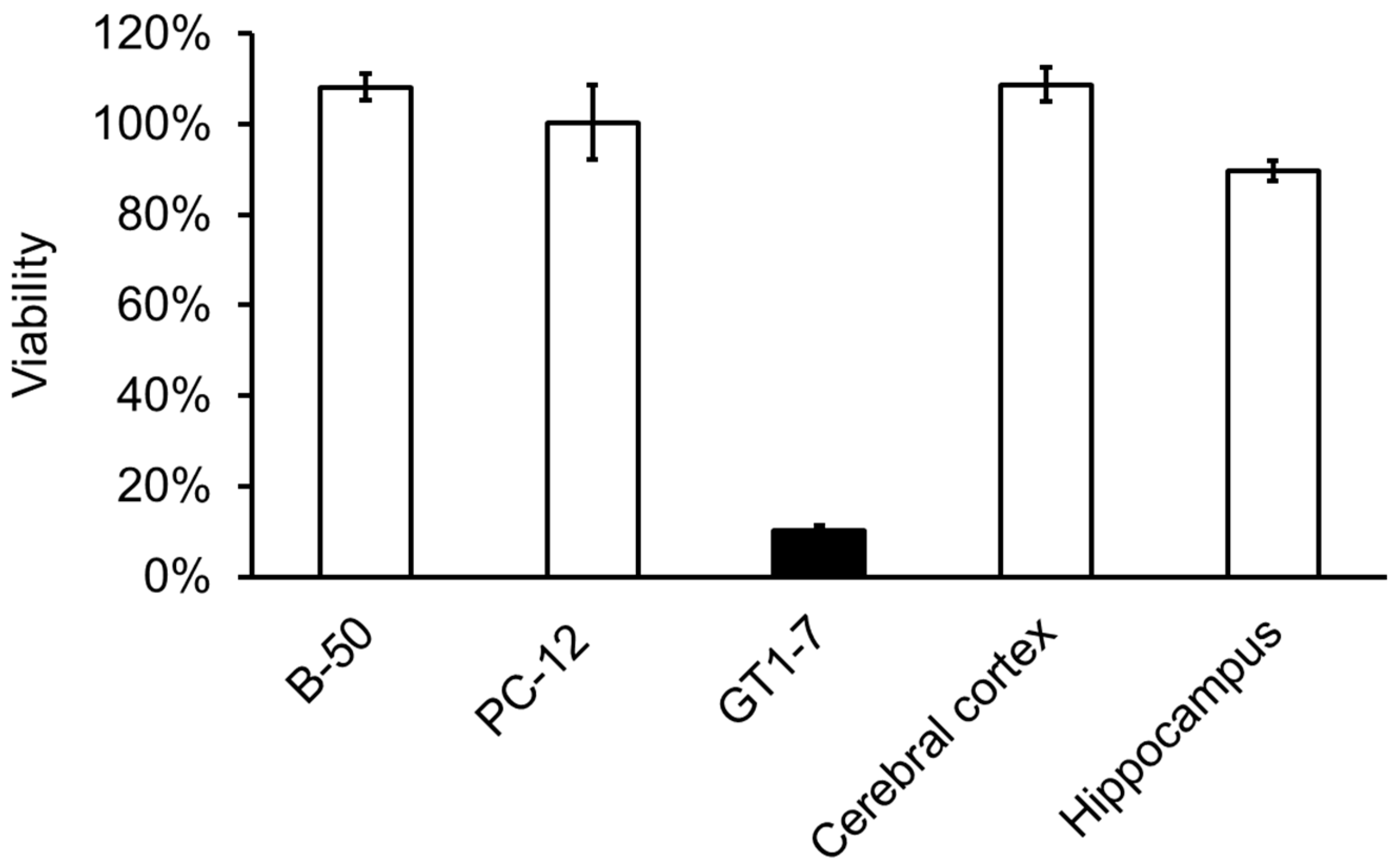
2.1. Usefulness of GT1-7 cells in the study of Zn2+-induced neurotoxicity
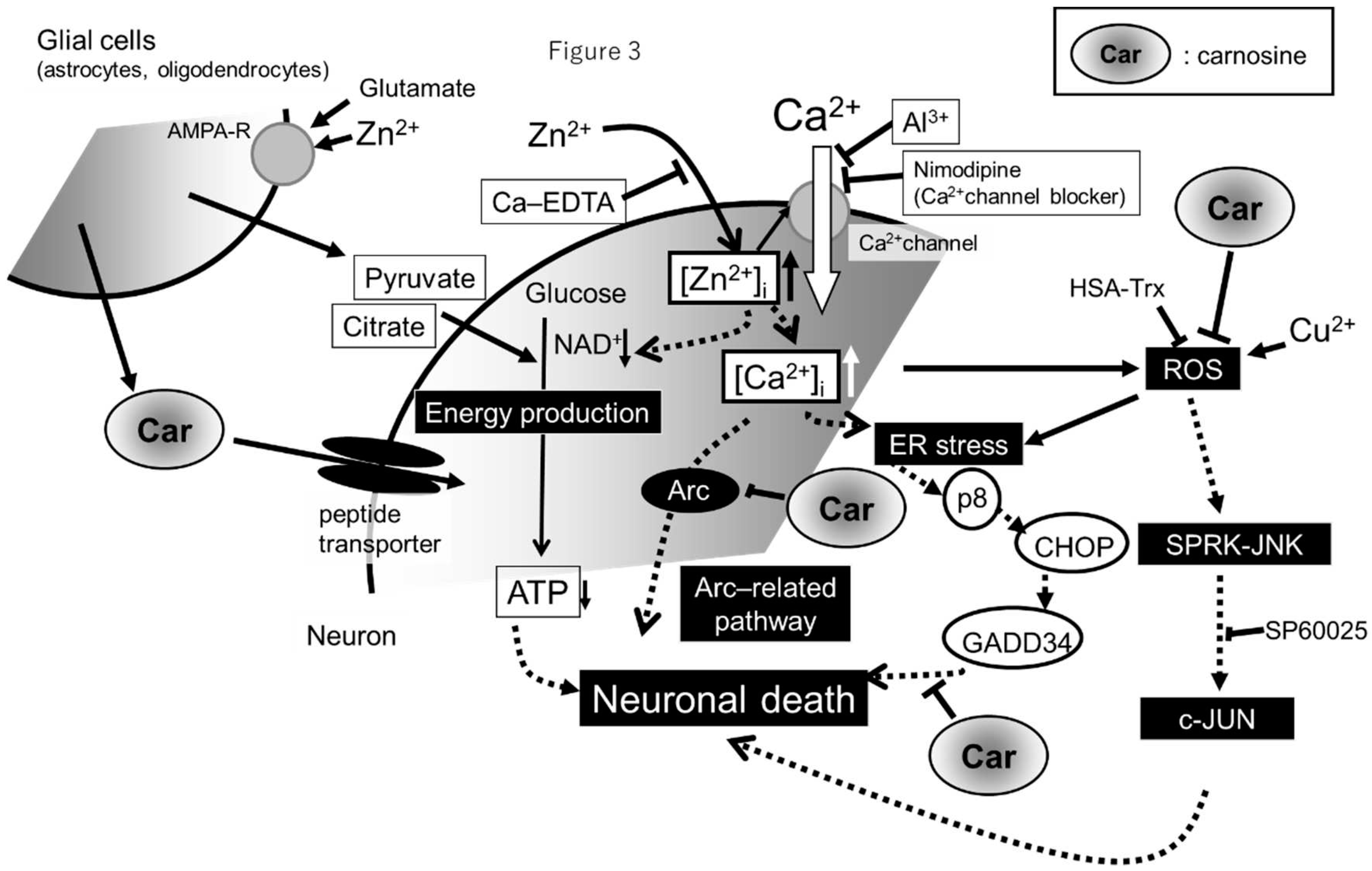
2.2. Molecular mechanism of Zn2+-induced GT1-7 cytotoxicity
2.3. neurodegenerative diseases and Zn
3. Carnosine can be a therapeutic agent for cerebrovascular dementia
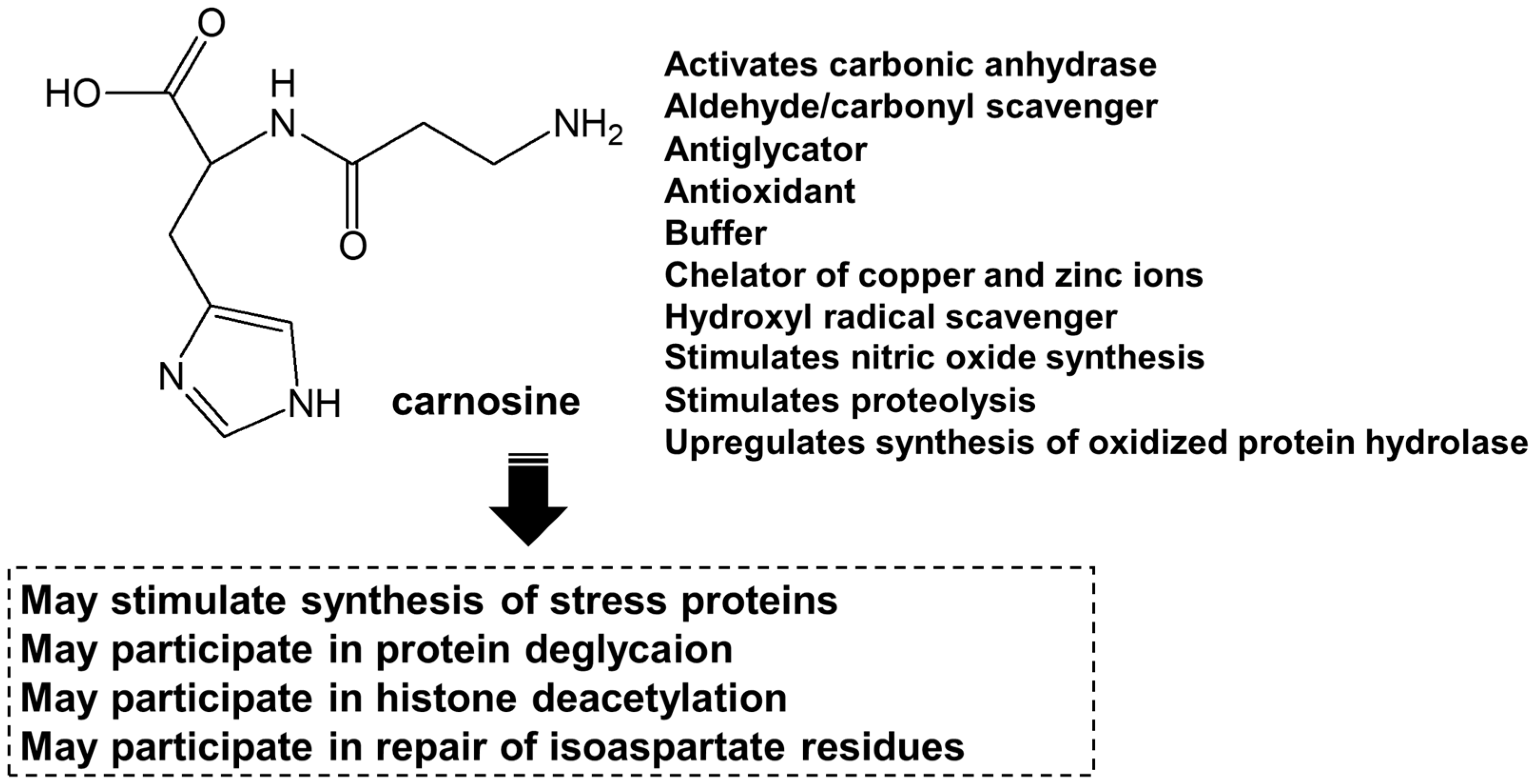
3.1. Carnosine
3.2. Carnosine in the brain
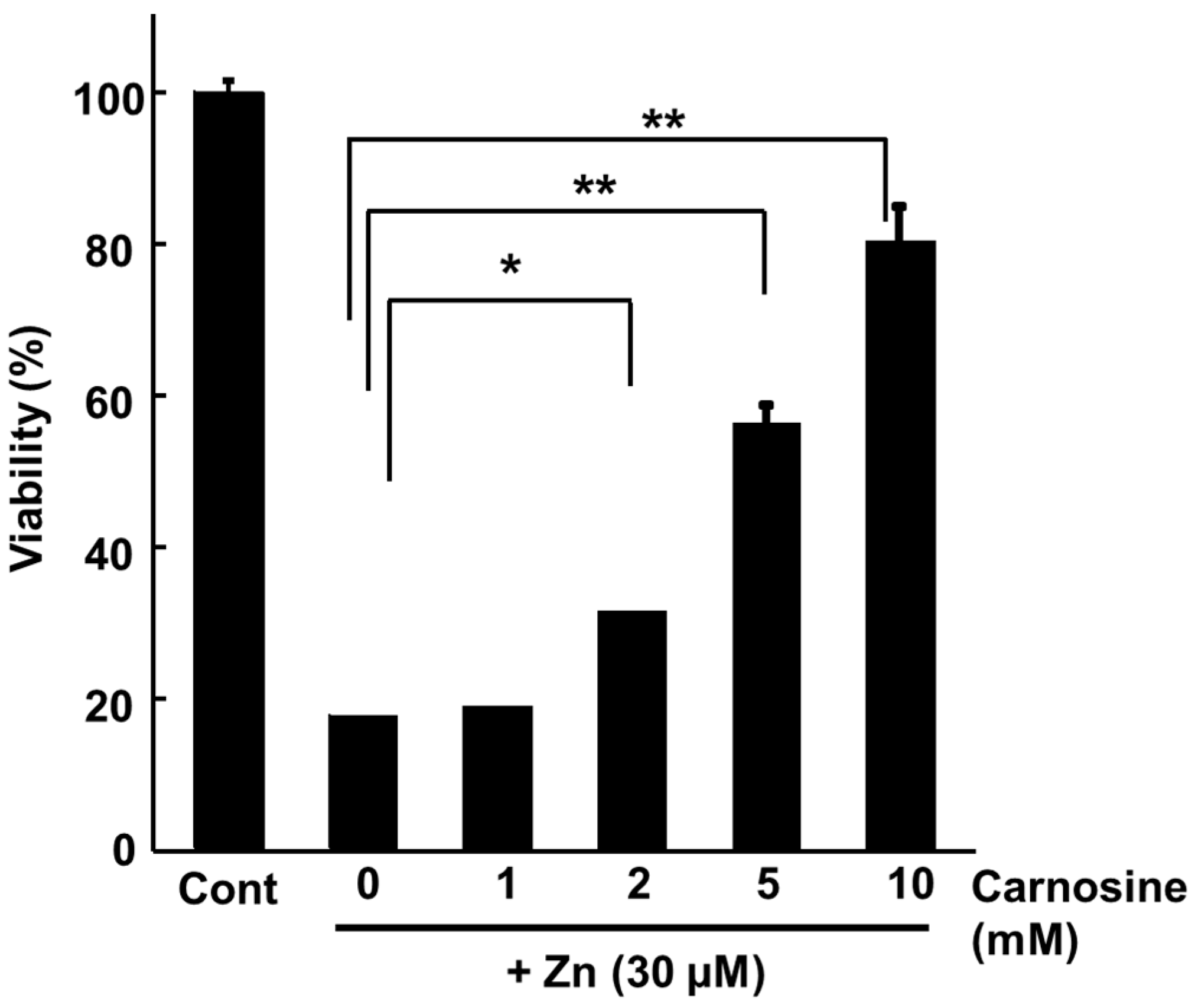
3.3. Carnosine suppresses Zn-induced neuronal death
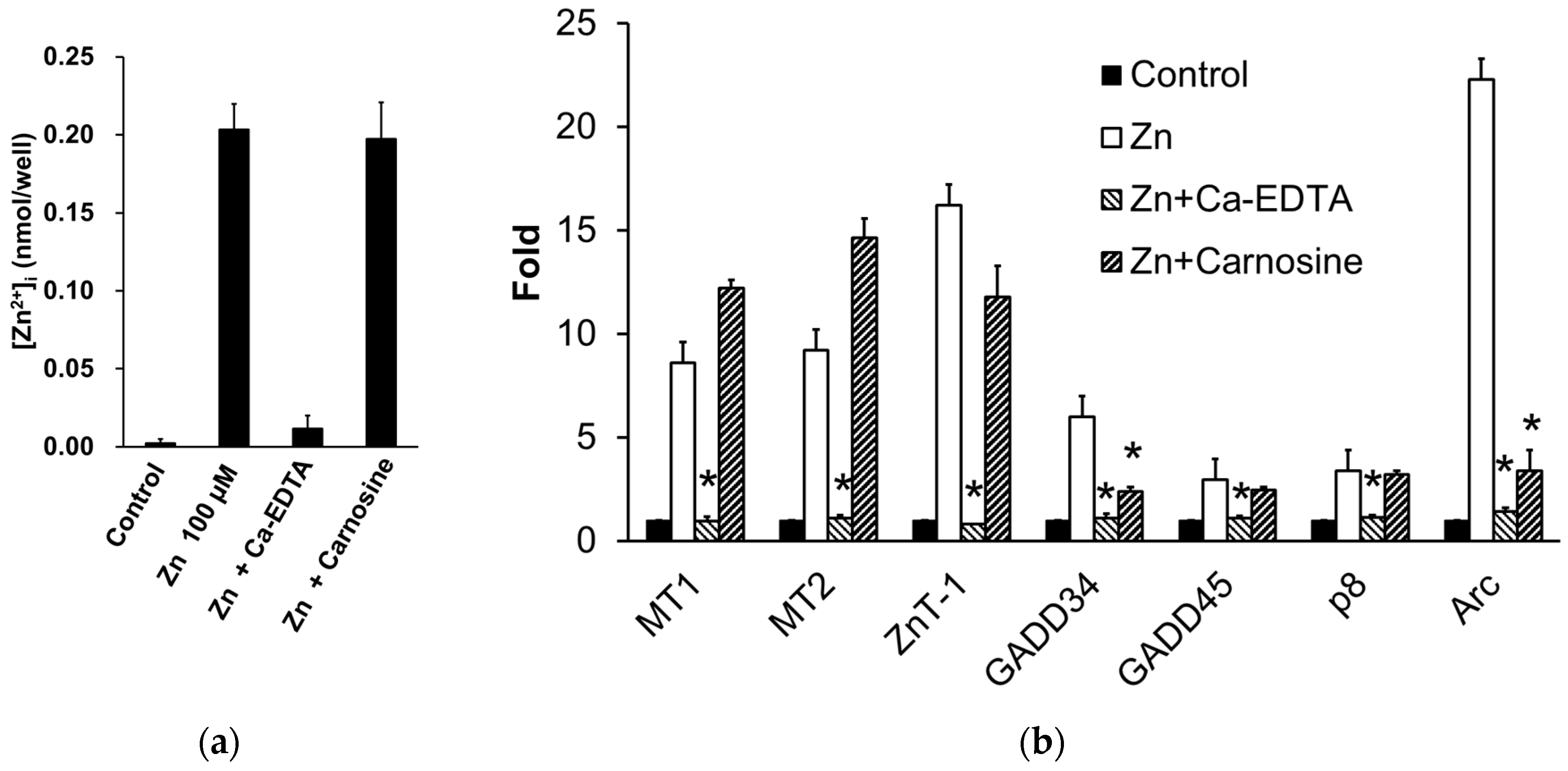
3.4. Potential uses of carnosine and its derivative as supplements
4. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Informed Consent Statement
Data Availability Statement
Acknowledgments
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Hambidge, M. Human zinc deficiency. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1344S–1349S. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Weiss, J.H., Sensi, S.L., Koh, J.Y. Zn(2+): a novel ionic mediator of neural injury in brain disease. Trends Pharmacol. Sci. 2000, 21, 395–401. [CrossRef]
- Nishio, R., Morioka, H., Takeuchi, A., Saeki, N., Furuhata, R., Katahira, M., Chinenn, T., Tamura, H., Tamano, H., Takeda, A. Intracellular hydrogen peroxide produced by 6-hydroxydopamine is a trigger for nigral dopaminergic degeneration of rats via rapid influx of extracellular Zn2. Neurotoxicology 2022, 89, 1–8.
- World Health Organization. Dementia. Fact sheets of WHO. Available online: https://www.who.int/news-room/fact-sheets/detail/dementia (accessed on 1 June 2023).
- Cao, Q., Tan, C.-C., Xu, W., Hu, H., Cao, X.-P., Dong, Q., Tan, L., Yu, J.-T. The prevalence of dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. J. Alzheimer’s Dis. 2020, 73, 1157–1166. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Selkoe, D.J. The molecular pathology of Alzheimer’s disease. Neuron 1991, 6, 487–498. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brás, I.C., Dominguez-Meijide, A., Gerhardt, E., Koss, D., Lázaro, D.F., Santos, P.I., Vasili, E., Xylaki, M., Outeiro, T.F. Synucleinopathies: where we are and where we need to go. J. Neurochem. 2020, 153, 433–454.
- Iadecola, C. The pathobiology of vascular dementia. Neuron 2013, 80, 844–866. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pagano, G., Ferrara, N., Brooks, DJ., Pavese, N. Age at onset and Parkinson disease phenotype. Neurology 2016, 86, 1400–1407. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kalia, LV., Lang, AE. Parkinson’s disease. Lancet 2015, 386, 896–912. [CrossRef]
- Erekat, NS. Apoptosis and its Role in Parkinson’s Disease. In Stoker, TB., Greenland, JC., Eds.; Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects. Codon Publications: Brisbane, Australia. 2018; pp. 65–82. [Google Scholar]
- Macchi, B., Di Paola, R., Marino-Merlo, F., Felice, MR., Cuzzocrea, S., Mastino, A. Inflammatory and cell death pathways in brain and peripheral blood in Parkinson’s disease. CNS Neurol. Disord. Drug Targets. 2015, 14, 313–324. [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M., Tanaka, K.I., Kato-Negishi, M. Zinc, carnosine, and neurodegenerative diseases. Nutrients 2018, 10, 147. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.I., Shimoda, M., Kasai, M., Ikeda, M., Ishima, Y., Kawahara, M. Involvement of SAPK/JNK signaling pathway in copper enhanced zinc-induced neuronal cell death. Toxicol. Sci. 2019, 169, 293–302. [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M., Konoha, K., Nagata, T., Sadakane, Y. Protective substances against zinc-induced neuronal death after ischemia: carnosine as a target for drug of vascular type of dementia. Recent Pat. CNS Drug Discov. 2007, 2, 145–149.
- Sadakane, Y., Konoha, K., Nagata, T., Kawahara, M. Protective activity of the extracts from Japanese eel (Anguilla japonica) against zinc-induced neuronal cell death: carnosine and an unknown substance. Trace Nutrient Res. 2007, 24, 98–105.
- Hipkiss, A.R. On the relationship between energy metabolism, proteostasis, aging and Parkinson’s disease: possible causative role of methylglyoxal and alleviative potential of carnosine. Aging Dis. 2017, 8, 334–345. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boldyrev, A.A., Aldini, G., Derave, W. Physiology and pathophysiology of carnosine. Physiol Rev. 2013, 93, 1803–1845. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- De Marchis, S., Modena, C., Peretto, P., Migheli, A., Margolis, F.L., Fasolo, A. Carnosine-related dipeptides in neurons and glia. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2000, 65, 824–833.
- Frederickson, C.J., Suh, S.W, Silva, D., Frederickson, C.J., Thompson, R.B. Importance of zinc in the central nervous system: the zinc-containing neuron. J. Nutr. 2000, 130, 1471S–1483S. [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M., Kato-Negishi, M., Kuroda, Y. Pyruvate blocks zinc-induced neurotoxicity in immortalized hypothalamic neurons. Cell Mol. Neurobiol., 2002, 22, 87–93. [CrossRef]
- Koyama, H., Konoha, K., Sadakane, Y., Ohkawara, S., Kawahara, M. Zinc neurotoxicity and the pathogenesis of vascular-type dementia: Involvement of calcium dyshomeostasis and carnosine. J. Clin. Toxicol., 2012, S3, 002.
- Mellon, P.L., Windle J.J., Goldsmith P.C., Padula C.A., Roberts J.L., Weiner R.I. Immortalization of hypothalamic GnRH neurons by genetically targeted tumorigenesis. Neuron 1990, 5, 1–10. [CrossRef]
- Mahesh, V.B., Zamorano, P., De Sevilla, L., Lewis, D., Brann, D.W. Characterization of ionotropic glutamate receptors in rat hypothalamus, pituitary and immortalized gonadotropin-releasing hormone (GnRH) neurons (GT1-7 cells). Neuroendocrinology 1999, 69, 397–407. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K., Kawahara, M. Copper enhances zinc-induced neurotoxicity and the endoplasmic reticulum stress response in a neuronal model of vascular dementia. Front Neurosci. 2017, 11, 58.
- Konoha, K., Sadakane, Y., Kawahara, M. Effects of gadolinium and other metal on the neurotoxicity of immortalized hypothalamic neurons induced by zinc. Biomed. Res. Trace Elem. 2004, 15, 275–277.
- Büsselberg, D., Platt, B., Haas, H.L., Carpenter, D.O. Voltage gated calcium channel currents of rat dorsal root ganglion (DRG) cells are blocked by Al3+. Brain Res. 1993, 622, 163–168. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, M., Kato-Negishi, M., Hosoda, R., Imamura, L., Tsuda, M., Kuroda, Y. Brain-derived neurotrophic factor protects cultured rat hippocampal neurons from aluminum maltolate neurotoxicity. J. Inorg. Biochem. 2003, 97, 124–131. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Tanaka, K.-I., Shimoda, M., Kawahara, M. Pyruvic acid prevents Cu2+/Zn2+-induced neurotoxicity by suppressing mitochondrial injury. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2018, 495, 1335–1341. [CrossRef]
- Cai, A.L., Zipfel, G.J., Sheline, C.T. Zinc neurotoxicity is dependent on intracellular NAD levels and the sirtuin pathway. Eur. J. Neurosci. 2006, 24, 2169–2176. [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.Y., Kim, Y.H., Koh, J.Y. Protection by pyruvate against transient forebrain ischemia in rats. J. Neurosci. 2001, 21, RC171. [CrossRef]
- Sheline, C.T., Behrens, M.M., Choi, D.W. Zinc-induced cortical neuronal death: Contribution of energy failure attributable to loss of NAD(+) and inhibition of glycolysis. J. Neurosci. 2000, 20, 3139–3154. [CrossRef]
- Sensi, S.L., Ton-That, D., Sullivan, P.G., Jonas, E.A., Gee, K.R., Kaczmarek, L.K., Weiss, J.H. Modulation of mitochondrial function by endogenous Zn2+ pools. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. USA 2003, 100, 6157–6162.
- Kawahara, M., Sadakane, Y., Koyama, H., Konoha, K., Ohkawara, S. D-histidine and L-histidine attenuate zinc-induced neuronal death in GT1-7 cells. Metallomics 2013, 5, 453–460. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mizuno, D., Konoha-Mizuno, D., Mori, M., Sadakane, Y., Koyama, H., Ohkawara, S., Kawahara, M. Protective activity of carnosine and anserine against zinc-induced neurotoxicity: a possible treatment for vascular dementia. Metallomics 2015, 7, 1233–1239. [CrossRef]
- Higo, T., Kozo, H., Hisatsune, C., Nukina, N., Hashikawa, T., Hattori, M., Nakamura, T., Mikoshiba, K. Mechanism of ER stress-induced brain damage by IP(3) receptor. Neuron 2010, 68, 865–878. [CrossRef]
- Kaneko, M., Imaizumi, K., Saito, A., Kanemoto, S., Asada, R., Matsuhisa, K., Ohtake, Y. ER stress and disease: toward prevention and treatment. Biol. Pharm. Bull. 2017, 40, 1337–1343.
- Sano, R., Reed, J.C. ER stress-induced cell death mechanisms. Biochim. Biophys. Acta 2013, 1833, 3460–3470. [CrossRef]
- Becker J.S., Matusch A, Palm C, Salber D, Morton K.A., Becker J.S. Bioimaging of metals in brain tissue by laser ablation inductively coupled plasma mass spectrometry (LA-ICP-MS) and metallomics. Metallomics 2010, 2, 104–111. [CrossRef]
- Kawahara M., Kato-Negishi M, Tanaka K. Cross talk between neurometals and amyloidogenic proteins at the synapse and the pathogenesis of neurodegenerative diseases. Metallomics 2017, 9, 619–633. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Yang, Y., Liu, L., Naik, I., Braunstein, Z., Zhong, J., Ren, B. Transcription factor C/EBP homologous protein in health and diseases. Front Immunol. 2017, 8, 1612. [CrossRef]
- Paschen, W., Hayashi, T., Saito, A., Chan, P.H. GADD34 protein levels increase after transient ischemia in the cortex but not in the CA1 subfield: implications for post-ischemic recovery of protein synthesis in ischemia-resistant cells. J. Neurochem. 2004, 90, 694–701. [CrossRef]
- Tanaka, K.I., Shimoda, M., Chuang, V.T.G., Nishida, K., Kawahara, M., Ishida, T., Otagiri, M., Maruyama, T., Ishima, Y. Thioredoxin-albumin fusion protein prevents copper enhanced zinc-induced neurotoxicity via its antioxidative activity. Int. J. Pharm. 2018, 535, 140–147. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dent, P., Yacoub, A., Contessa, J., Caron, R., Amorino, G., Valerie, K., Hagan, M.P., Grant, S., Schmidt-Ullrich, R. Stress and radiation-induced activation of multiple intracellular signaling pathways. Radiat. Res. 2003, 159, 283–300. [CrossRef]
- Dandekar, A., Mendez, R., Zhang, K. Cross talk between ER stress, oxidative stress, and inflammation in health and disease. Methods Mol. Biol. 2015, 1292, 205–214.
- Papaconstantinou, J. The role of signaling pathways of inflammation and oxidative stress in development of senescence and aging phenotypes in cardiovascular disease. Cells 2019, 8, 1383. [CrossRef]
- Konno, T., Melo, E.P., Chambers, J.E., Avezov, E. Intracellular sources of ROS/H2O2 in health and neurodegeneration: spotlight on endoplasmic reticulum. Cells 2021, 10, 233. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Nakano, Y., Shimoda, M., Okudomi, S., Kawaraya, S., Kawahara, M., Tanaka, K.-I. Seleno-L-methionine suppresses copper-enhanced zinc-induced neuronal cell death via induction of glutathione peroxidase. Metallomics 2020, 12, 1693–1701. [CrossRef]
- Jiang, H., Song, N., Jiao, Q., Shi, L., Du, X. Iron pathophysiology in parkinson diseases. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2019, 1173, 45–66.
- Kawahara, M., Mizuno, D., Koyama, H., Konoha, K., Ohkawara, S., Sadakane, Y. Disruption of zinc homeostasis and the pathogenesis of senile dementia. Metallomics 2014, 6, 209–219. [CrossRef]
- Stork, C.J., Li, Y.V. Elevated cytoplasmic free zinc and increased reactive oxygen species generation in the context of brain injury. Acta Neurochir. Suppl. 2016, 121, 347–353.
- Kalaria, R.N. The pathology and pathophysiology of vascular dementia. Neuropharmacology 2018, 134, 226–239. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pendlebury, S.T., Rothwell, P.M. Prevalence, incidence, and factors associated with pre-stroke and post-stroke dementia: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Lancet Neurol. 2009, 8, 1006–1018. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Frederickson, C.J., Klitenick, M.A., Manton, W.I., Kirkpatrick, J.B. Cytoarchitectonic distribution of zinc in the hippocampus of man and the rat. Brain Res. 1983, 27, 335–339.
- Koh, J.Y., Suh, S.W., Gwag, B.J., He, Y.Y., Hsu, C.Y., Choi, D.W. The role of zinc in selective neuronal death after transient global cerebral ischemia. Science 1996, 272, 1013–1016. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Calderone, A., Jover, T., Mashiko, T., Noh, K.M., Tanaka, H., Bennett, M.V., Zukin, R.S. Late calcium EDTA rescues hippocampal CA1 neurons from global ischemia-induced death. J. Neurosci. 2004, 24, 9903–9913. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitamura, Y., Iida, Y., Abe, J., Mifune, M., Kasuya, F., Ohta, M., Igarashi, K., Saito, Y., Saji, H. Release of vesicular Zn2+ in a rat transient middle cerebral artery occlusion model. Brain Res. Bull. 2006, 69, 622–625. [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z., Shi, W., Zhao, Y., Ji, X., Liu, K.J. Zinc accumulation in mitochondria promotes ischemia-induced BBB disruption through Drp1-dependent mitochondria fission. Toxicol. Appl. Pharmacol. 2019, 377, 114601. [CrossRef]
- Konnova, EA., Swanberg M. Animal Models of Parkinson’s Disease. In Stoker, TB., Greenland, JC., Eds.; Parkinson’s Disease: Pathogenesis and Clinical Aspects. Codon Publications: Brisbane, Australia. 2018; pp. 83–106.
- Rodriguez-Pallares, J., Parga, J.A., Joglar, B., Guerra, M.J., Labandeira-Garcia J.L. The mitochondrial ATP-sensitive potassium channel blocker 5-hydroxydecanoate inhibits toxicity of 6-hydroxydopamine on dopaminergic neurons. Neurotox. Res. 2009, 15, 82–95. [CrossRef]
- Jonsson, G. Chemical neurotoxins as denervation tools in neurobiology. Annu. Rev. Neurosci. 1980, 3, 169–187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tamano, H., Morioka, H., Nishio, R., Takeuchi, A., Takeda. A. Blockade of rapid influx of extracellular Zn2+ into nigral dopaminergic neurons overcomes Paraquat-induced Parkinson’s disease in rats. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 4539–4548. [CrossRef]
- Tamano, H., Nishio, R., H. Morioka, Furuhata, R., Komata, Y., Takeda. A. Paraquat as an environmental risk factor in Parkinson’s disease accelerates age-related degeneration via rapid influx of extracellular Zn2+ into nigral dopaminergic neurons. Mol. Neurobiol. 2019, 56, 7789–7799. [CrossRef]
- Fisher, A.B. Redox signaling across cell membranes. Antioxid. Redox Signal. 2009, 11, 1349–1356. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Hara, Y., Wakamori, M., Ishii, M., Maeno, E., Nishida, M., Yoshida, T., Yamada, H., Shimizu, S., Mori, E., Kudoh, J., Shimizu, N., Kurose, H., Okada, Y., Imoto, K., Mori. Y. LTRPC2 Ca2+-permeable channel activated by changes in redox status confers susceptibility to cell death. Mol. Cell 2002, 9, 163–173.
- Kubota, M., Kobayashi, N., Sugizaki, T., Shimoda, M., Kawahara M., Tanaka K. Carnosine suppresses neuronal cell death and inflammation induced by 6-hydroxydopamine in an in vitro model of Parkinson’s disease. PLoS One 2020, 15, e0240448.
- Sadakane, Y., Konoha, K., Kawahara, M. Protective activity of mango (Mangifera indica L.) fruit against a zinc-induced neuronal cell death is independent of its antioxidant activity. Trace Nutr. Res. 2005, 22, 73–79.
- Everaert, I., Mooyaart, A., Baguet, A., Zutinic, A., Baelde, H., Achten, E., Taes, Y., De Heer, E., Derav, W. Vegetarianism, female gender and increasing age, but not CNDP1 genotype, are associated with reduced muscle carnosine levels in humans. Amino Acids. 2011, 40, 1221–1229. [CrossRef]
- Derave, W., Everaert, I., Beeckman, S., Baguet, A. Muscle carnosine metabolism and beta-alanine supplementation in relation to exercise and training. Sports. Med. 2010, 40, 247–263. [CrossRef]
- Bakardjiev, A., Bauer, K. Biosynthesis, release, and uptake of carnosine in primary cultures. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2000, 65, 779–782.
- Harris, R.C., Wise, J.A., Price, K.A., Kim, H.J., Kim, C.K., Sale, C. Determinants of muscle carnosine content. Amino Acids 2012, 43, 5–12.
- Gariballa, A.E., Sinclair, A.J. Carnosine: physiological properties and therapeutic potential. Age Ageing 2000, 29, 207–210. [CrossRef]
- A Boldyrev, A., Aldini, G., Derave, W. Physiology and pathophysiology of carnosine. Physiol. Rev. 2013, 93, 1803–1845. [CrossRef]
- Mori, M., Mizuno, D., Konoha-Mizuno, K., Sadakane, Y., Kawahara M. Carnosine concentration in the muscle of thoroughbred horses and its implications in exercise performance. Trace Nutrients Res. 2015, 32, 49–53.
- Kawai, M., Minami, Y., Sayama, Y., Kuwano, A., Hiraga, A., Miyata H. Muscle Fiber Population and Biochemical Properties of Whole Body Muscles in Thoroughbred Horses. Anat. Rec. (Hoboken) 2009, 292, 1663–1669. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abe, H. Role of histidine-related compounds as intracellular proton buffering constituents in vertebrate muscle. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2000, 65, 757–765. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Sale, C., G Artioli, G., Gualano, B., Saunders., M Hobson, R., C Harris, R.Carnosine: from exercise performance to health. Amino Acids 2013, 44, 1477–1491.
- Quesnele, JJ., Laframboise, MA., Wong, JJ., Kim, P., Wells, GD., The effects of beta-alanine supplementation on performance: a systematic review of the literature. Int. J. Sport. Nutr. Exerc. Metab. 2014, 24, 14–27.
- Dubois, V.D., Bastawrous, A. N-acetylcarnosine (NAC) drops for age-related cataract. Cochrane Database Syst. Rev. 2017, 2, CD009493.
- Matsukura, T., Tanaka, H. Applicability of zinc complex of L-carnosine for medical use. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2000, 65, 817–823.
- Kimura, K., Nakano, Y., Sugizaki, T., Shimoda, M., Kobayashi, N., Kawahara, M., Tanaka, K.I. Protective effect of polaprezinc on cadmium-induced injury of lung epithelium. Metallomics 2019, 11, 1310–1320.
- Baslow, M.H., Suckow, R.F., Berg, M.J., Marks, N., Saito, M., Bhakoo, K.K. Differential expression of carnosine, homocarnosine and N-acetyl-L-histidine hydrolytic activities in cultured rat macroglial cells. J. Mol. Neurosci. 2001, 17, 351–359. [CrossRef]
- Tiedje, KE., Stevens, K., Barnes, S., Weaver, DF. β-Alanine as a small molecule neurotransmitter. Neurochem. Int. 2010, 57, 177–188. [CrossRef]
- Wang, H., Fei, YJ., Ganapathy, V., Leibach FH. Electrophysiological characteristics of the proton-coupled peptide transporter PEPT2 cloned from rat brain. Am. J. Physiol. 1998, 275, C967–C975. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lopachev, AV., Abaimov, DA., Filimonov, IS., Kulichenkova, KN., Fedorova, TN. An assessment of the transport mechanism and intraneuronal stability of L-carnosine. Amino Acids 2022, 54, 1115–1122. [CrossRef]
- Bonfanti, L., Peretto, P., De Marchis, S., Fasolo, A. Carnosine-related dipeptides in the mammalian brain. Prog. Neurobiol. 1999, 59, 333–353. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bakardjiev, A. Carnosine and beta-alanine release is stimulated by glutamatergic receptors in cultured rat oligodendrocytes. Glia 1998, 24, 346–351. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mori, M., Mizuno, D., Konoha-Mizuno, K., Sadakane, Y., Kawahara, M. Quantitative analysis of carnosine and anserine in foods by performing high performance liquid chromatography. Biomed. Res. Trace Elem. 2015, 26, 147–152.
- Kawahara, M., Sadakane Y., Mizuno K., Kato-Negishi M., Tanaka K. Carnosine as a possible drug for zinc-induced neurotoxicity and vascular dementia. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 2570. [CrossRef]
- Biffo, S., Grillo, M., Margolis, F.L. Cellular localization of carnosine-like and anserine-like immunoreactivities in rodent and avian central nervous system. Neuroscience 1990, 35, 637–651. [CrossRef]
- Margolis, F.L., Grillo, M. Axoplasmic transport of carnosine (β-alanyl-L-histidine) in the mouse olfactory pathway. Neurochem. Res. 1977, 2, 507–519. [CrossRef]
- Harding, J., Graziadei, P.P., Monti Graziadei, G.A., Margolis, F.L. Denervation in the primary olfactory pathway of mice. IV. Biochemical and morphological evidence for neuronal replacement following nerve section. Brain Res. 1977, 132, 11–28. [CrossRef]
- Harding, J., Margolis, F.L. Denervation in the primary olfactory pathway of mice. III. Effect on enzymes of carnosine metabolism. Brain Res. 1976, 110, 351–360. [CrossRef]
- Baran, E.J. Metal complexes of carnosine. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2000, 65, 789–797. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Trombley, P.Q., Horning, M.S., Blakemore, L.J. Interactions between carnosine and zinc and copper: implications for neuromodulation and neuroprotection. Biochemistry (Mosc) 2000, 65, 807–816.
- Corona, C., Frazzini, V., Silvestri, E., Lattanzio, R., La Sorda, R., Piantelli, M., Canzoniero, L.M., Ciavardelli, D., Rizzarelli, E., Sensi, S.L. Effects of dietary supplementation of carnosine on mitochondrial dysfunction, amyloid pathology, and cognitive deficits in 3xTg-AD mice. PLoS ONE 2011, 6, e17971.
- Caruso, G., Fresta, C.G., Musso, N., Giambirtone, M., Grasso, M., Spampinato, S.F., Merlo, S., Drago, F., Lazzarino, G., Sortinom, M.A., et al. Carnosine prevents Aβ-induced oxidative stress and inflammation in microglial cells: a key role of TGF-β. Cells 2019, 8, 64. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kawahara, M., Koyama, H., Nagata, T., Sadakane, Y. Zinc, copper, and carnosine attenuate neurotoxicity of prion fragment PrP106-126. Metallomics 2011, 3, 726–734. [CrossRef]
- Ommati, M.M., Heidari, R., Ghanbarinejad, V., Aminian, A., Abdoli, N., Niknahad, H. The neuroprotective properties of carnosine in a mouse model of manganism is mediated via mitochondria regulating and antioxidative mechanisms. Nutr. Neurosci. 2020, 23, 731–743. [CrossRef]
- Berezhnoy, D.S., Stvolinsky, S.L., Lopachev, A.V., Devyatov, A.A., Lopacheva, O.M., Kulikova, O.I., Abaimov, D.A., Fedorova, T.N. Carnosine as an effective neuroprotector in brain pathology and potential neuromodulator in normal conditions. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 139–150. [CrossRef]
- Ferreiro, E., Baldeiras, I., Ferreira, I.L., Costa, R.O., Rego, A.C., Pereira C.F., Oliveira C.R. Mitochondrial- and endoplasmic reticulum-associated oxidative stress in Alzheimer’s disease: from pathogenesis to biomarkers. Int. J. Cell. Biol. 2012, 2012, 735206.
- Moskalev, A.A., Smit-McBride, Z., Shaposhnikov, M.V., Plyusnina, E.N., Zhavoronkov, A., Budovsky, A., Tacutu, R., E Fraifeld, V. Gadd45 proteins: relevance to aging, longevity and age-related pathologies. Ageing Res. Rev. 2012, 11, 51–66.
- Korb, E., Finkbeiner S. Arc in synaptic plasticity: from gene to behavior. Trends Neurosci. 2011, 34, 591–598. [CrossRef]
- Zhang, X., Song, L., Cheng, X., Yang, Y., Luan, B., Jia, L., Xu, F., Zhang, Z. Carnosine pretreatment protects against hypoxia-ischemia brain damage in the neonatal rat model. Eur. J. Pharmacol. 2011, 667, 202–207. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.S., Han, K.H., Shin, J.A., Park, J.H., Song, K.Y., Kim, D.H. The neuroprotective effects of carnosine in early stage of focal ischemia rodent model. J. Korean Neurosurg. Soc. 2014, 55, 125–130. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Noguchi, K., Ali, T.F.S., Miyoshi, J., Orito, K., Negoto, T., Biswas, T., Taira, N., Koga, R., Okamoto, Y., Fujita, M., et al. Neuroprotective effects of a novel carnosine-hydrazide derivative on hippocampal CA1 damage after transient cerebral ischemia. Eur. J. Med. Chem. 2019, 163, 207–214. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Davis, C.K., Laud, P.J., Bahor, Z., Rajanikant, G.K., Majid, A. Systematic review and stratified meta-analysis of the efficacy of carnosine in animal models of ischemic stroke. J. Cereb. Blood Flow Metab. 2016, 36, 1686–1694. [CrossRef]
- Tomonaga, S., Hayakawa, T., Yamane, H., Maemura, H., Sato, M., Takahata, Y., Morimatsu, F., Furuse, M. Oral administration of chicken breast extract increases brain carnosine and anserine concentrations in rats. Nutr. Neurosci. 2007, 10, 181–186. [CrossRef]
- Hoffman, J.R., Rathmacher, J.A., Robinson, J., Gepner, Y., Cohen, H. Effect of β-alanine supplementation on carnosine and histidine content in the hippocampus of 14-month-old rats. Appl. Physiol. Nutr. Metab. 2019, 44, 1112–1115. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Araminia, B., Shalbafan, M., Mortezaei, A., Shirazi, E., Ghaffari, S., Sahebolzamani, E., Mortazavi, S.H., Shariati, B., Ardebili, M.E., Aqamolaei, A., et al. L-Carnosine combination therapy for major depressive disorder: a randomized, double-blind, placebo-controlled trial. J. Affect. Disord. 2020, 267, 131–136.
- Hisatsune, T., Kaneko, J., Kurashige, H., Cao, Y., Satsu, H., Totsuka, M., Katakura, Y., Imabayashi, E., Matsuda, H. Effect of anserine/carnosine supplementation on verbal episodic memory in elderly people. J. Alzheimers Dis. 2016, 50, 149–159. [CrossRef]
- Masuoka, N., Yoshimine, C., Hori, M., Tanaka, M., Asada, T., Abe, K., Hisatsune, T. Effects of anserine/carnosine supplementation on mild cognitive impairment with APOE4. Nutrients 2019, 11, 1626. [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Oppermann, H., Heinrich, M., Birkemeyer, C., Meixensberger, J., Gaunitz, F. The proton-coupled oligopeptide transporters PEPT2, PHT1 and PHT2 mediate the uptake of carnosine in glioblastoma cells. Amino Acids 2019, 51, 999–1008. [CrossRef]
- Hata, J., Ohara, T., Katakura, Y., Shimizu, K., Yamashita, S., Yoshida, D., Honda, T., Hirakawa, Y., Shibata, M., Sakata, S., et al. Association between serum β-alanine and risk of dementia. Am. J. Epidemiol. 2019, 188, 1637–1645.
- Stuerenburg, H.J. The roles of carnosine in aging of skeletal muscle and in neuromuscular diseases. Biochemistry 2000, 65, 862–865. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- J Anderson, E., Vistoli, G., A Katunga, L., Funai, K., Regazzoni, L., Monroe, T.B., Gilardoni, E., Cannizzaro, L., Colzani, M., De Maddis, D., Rossoni, G., Canevotti, R., Gagliardi, S., Carini, M., Aldini G. A carnosine analog mitigates metabolic disorders of obesity by reducing carbonyl stress. J. Clin. Invest. 2018, 128, 5280–5293.
- de Jager, S., Vermeulen, A., De Baere, S., Van der Stede, T., Lievens, E., Croubels, S., Jäger, R., Purpura, M., Bourgois, JG., Derave, W. Acute balenine supplementation in humans as a natural carnosinase-resistant alternative to carnosine. Sci Rep. 2023, 13, 6484. [CrossRef]
- Kawahara, M., Konoha, K. Drugs for prevention or treatment of vascular dementia [Translated from Japanese]. JP5382633, 11 October 2013. 11 October.
- Kawahara, M., Konoha, K. Drugs for prevention or treatment of vascular dementia [Translated from Japanese]. JP5294194, 21 June 2013.
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




