Submitted:
04 July 2023
Posted:
06 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Fish Maintenance
2.2. Chemicals
2.3. Experimental Design
2.4. Behavioral Tests
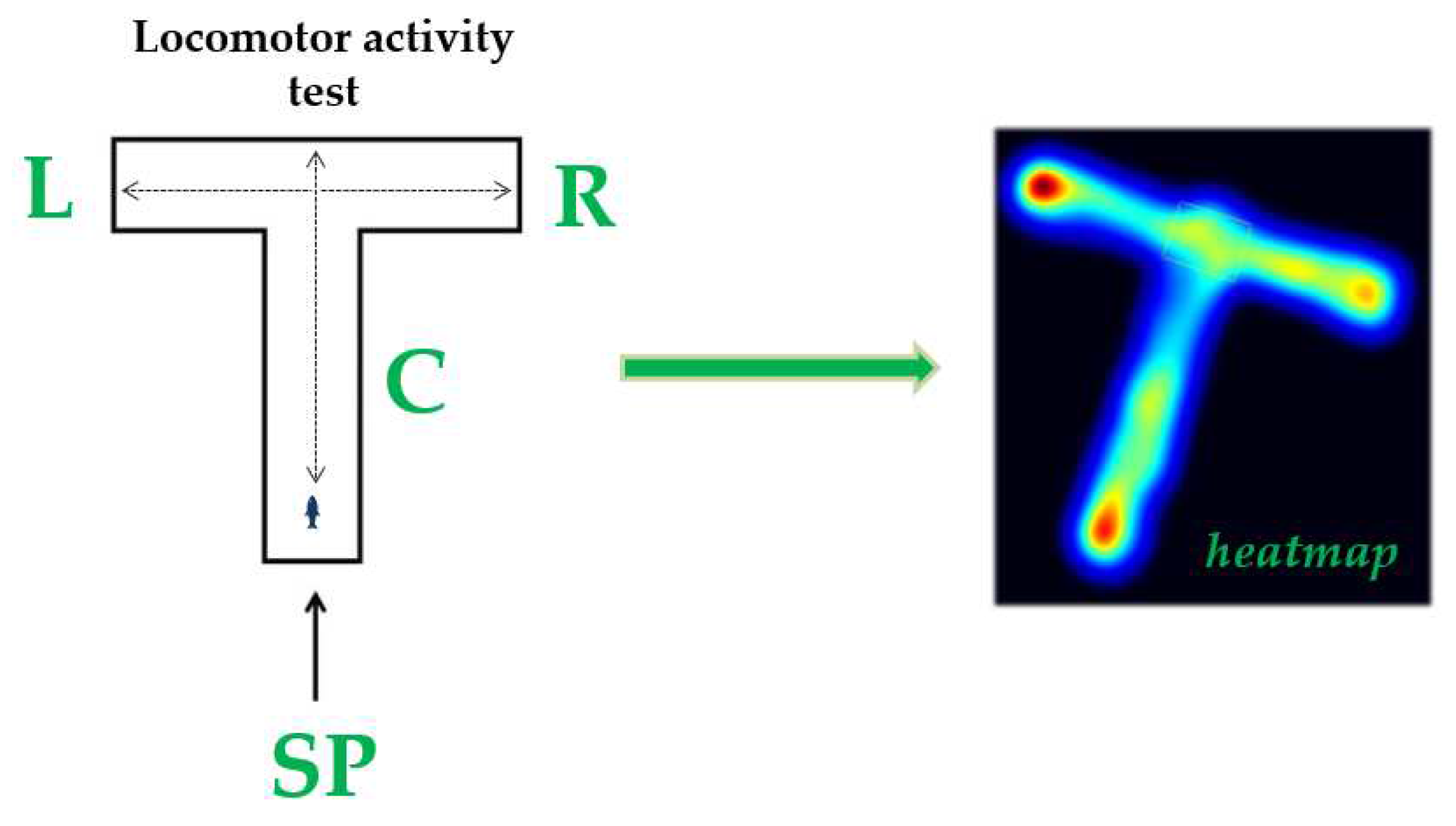
2.4.1. Locomotor Activity Test
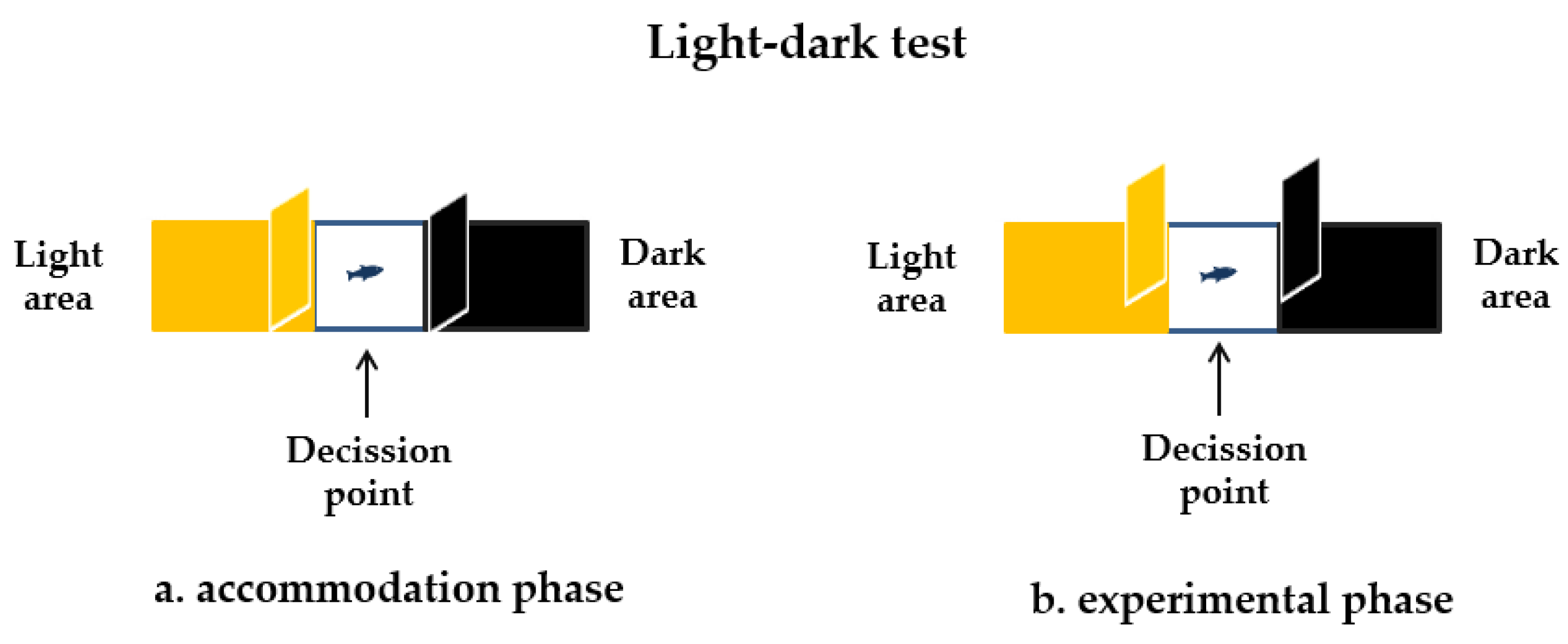
2.4.2. The Light-Dark Test
2.5. Assessment of Histological Changes
2.6. Statistical Analysis
2.7. Ethical Approval
3. Results
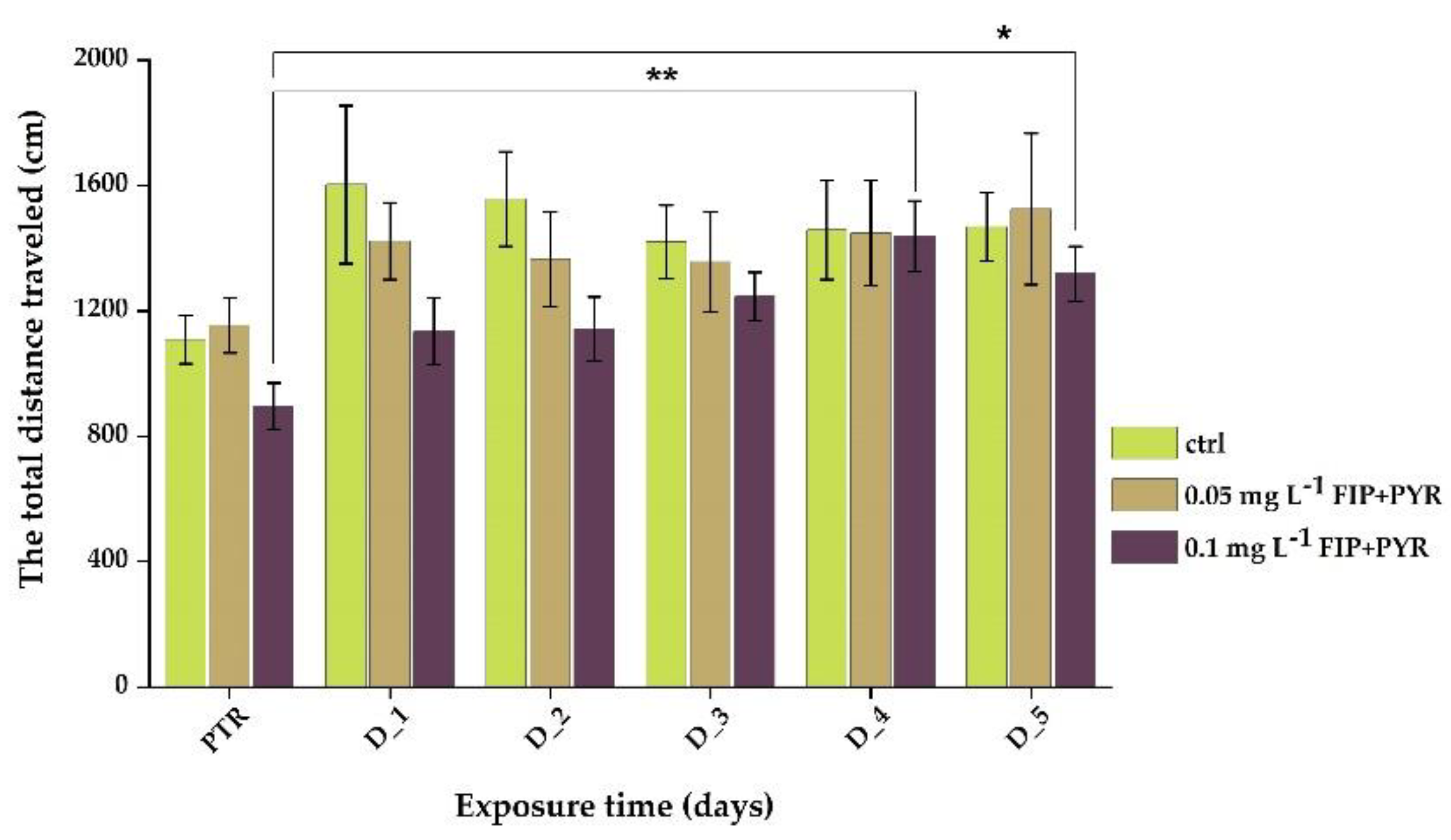
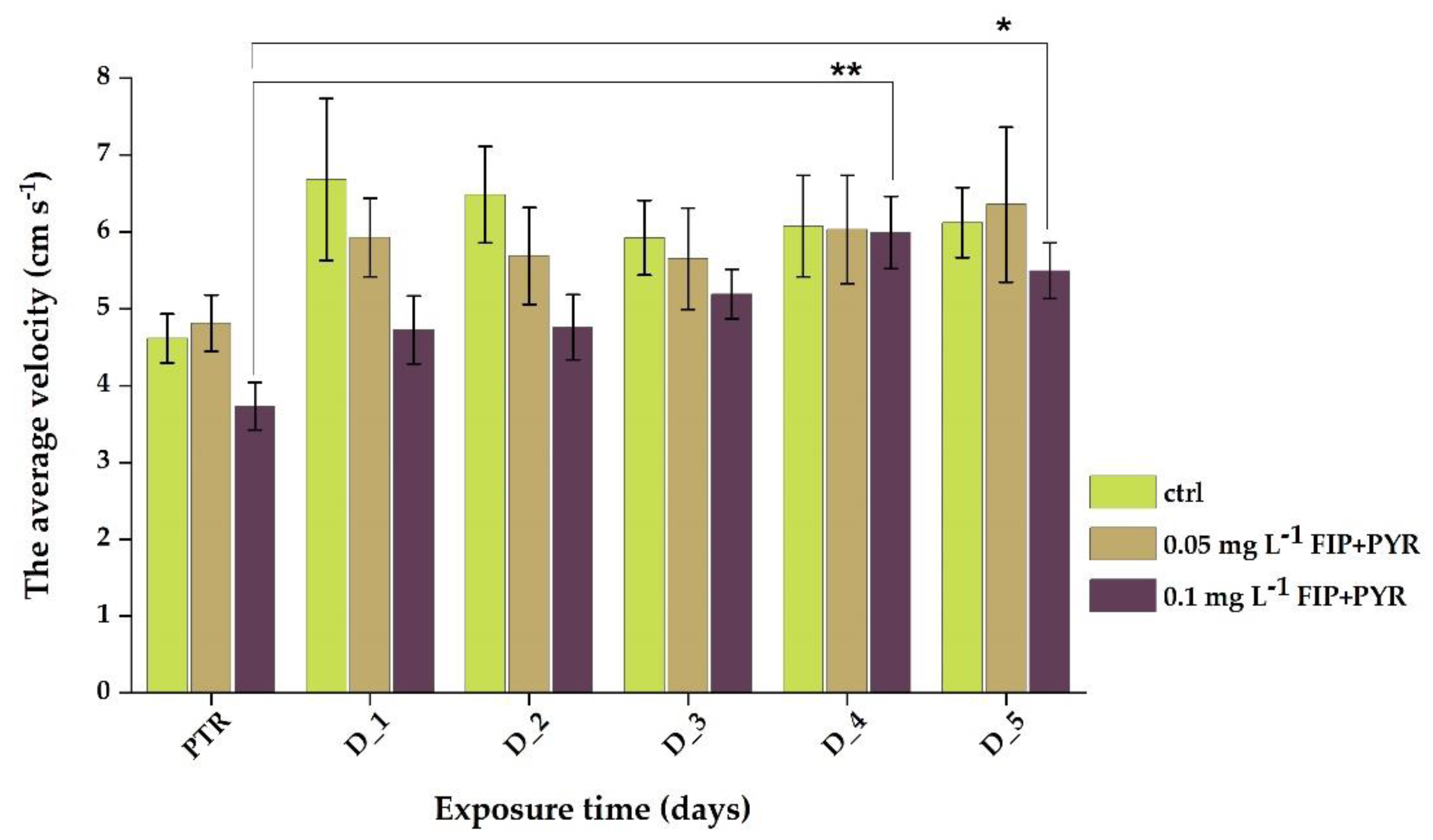
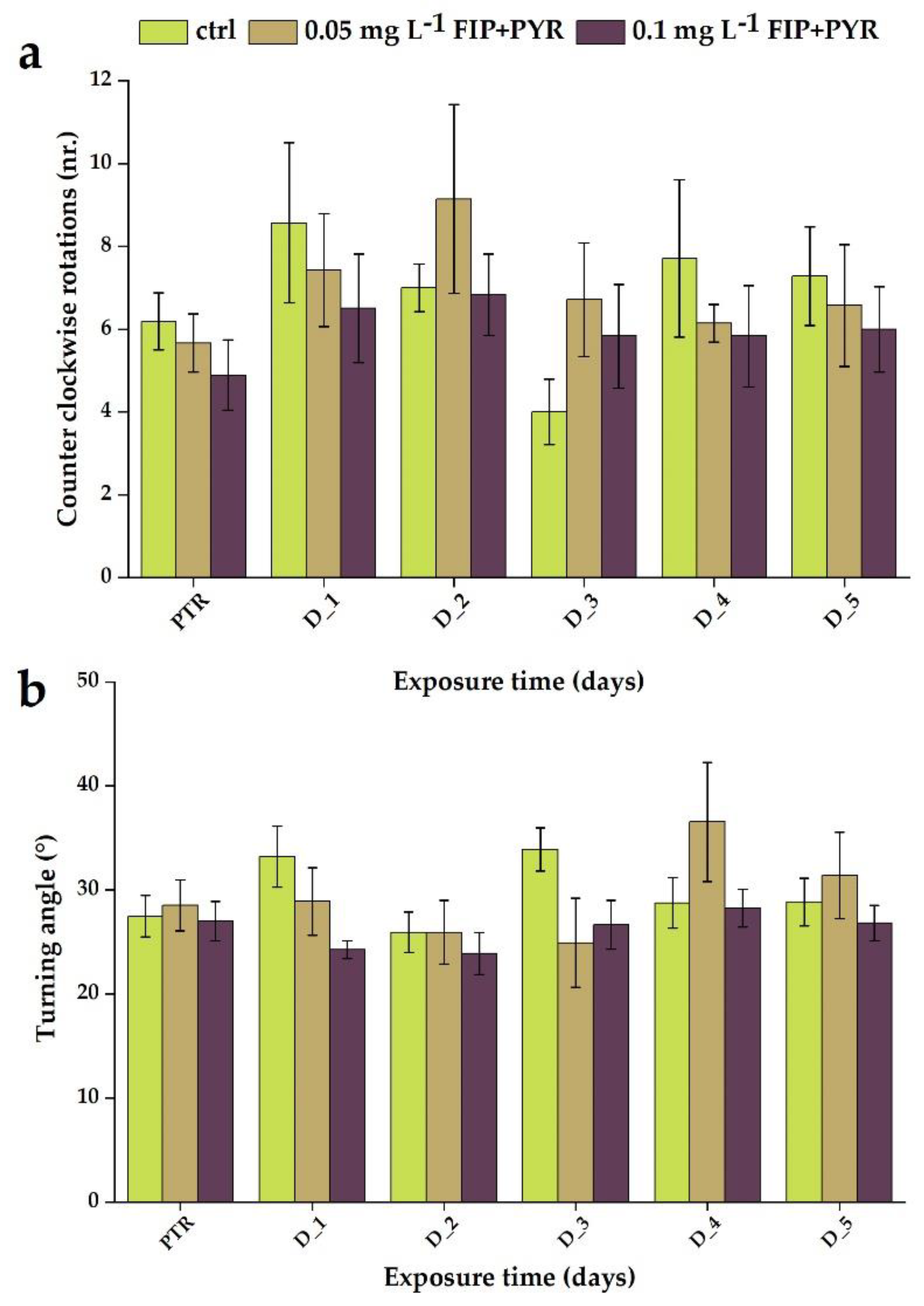
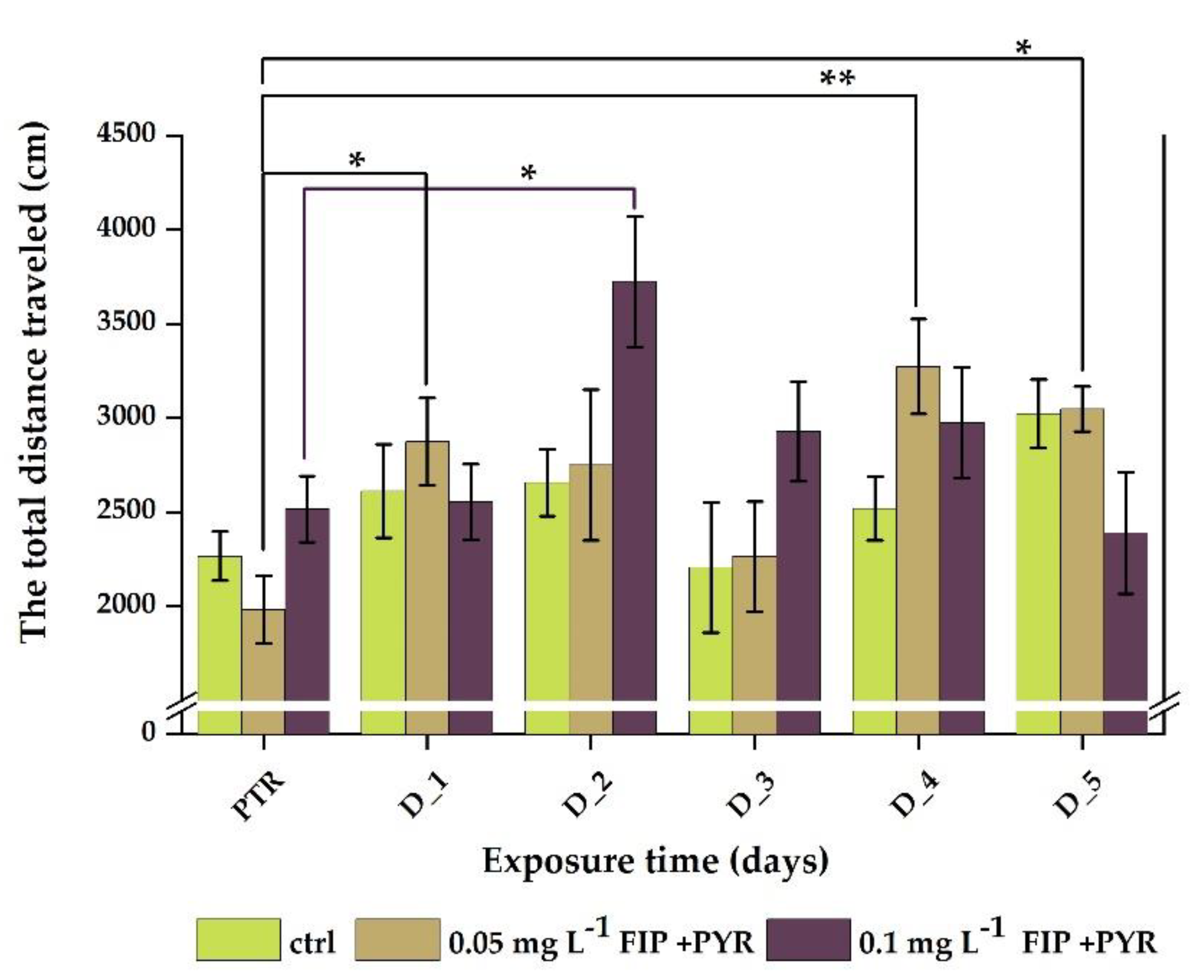
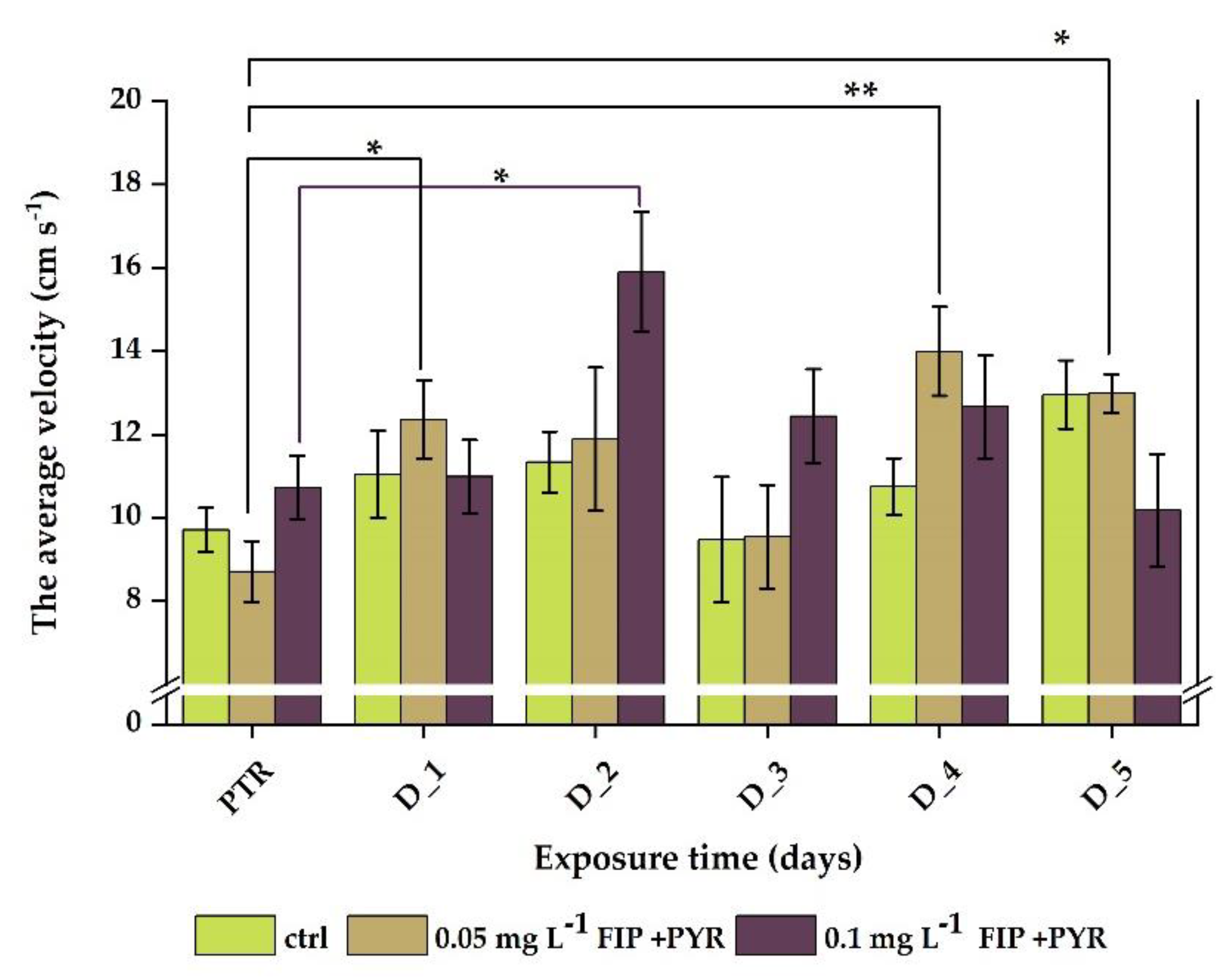
3.1. Impaired Locomotor Activity after Chronic Exposure to Pesticide Mixture
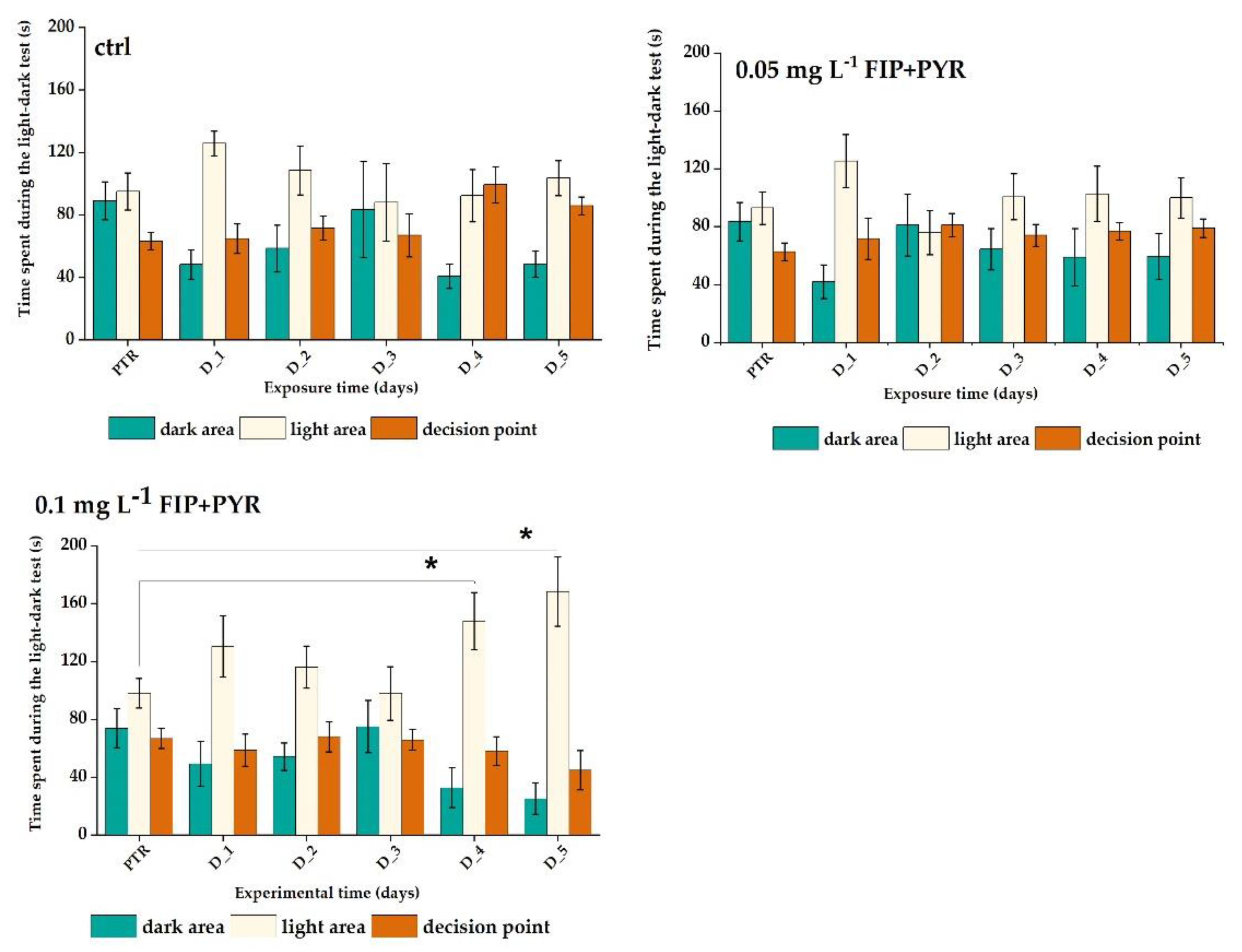
3.2. Increased Anxiety Level of Zebrafish
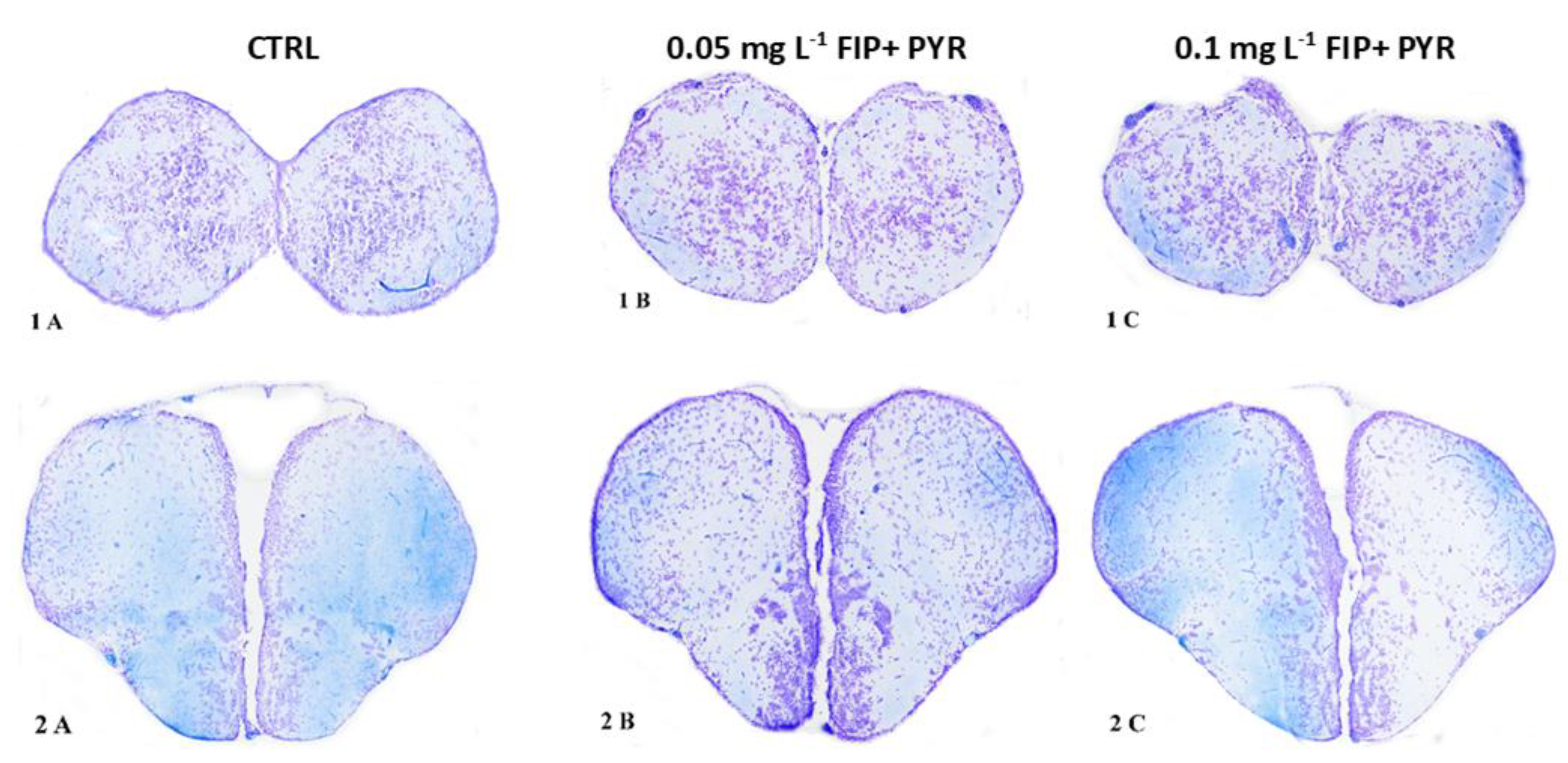
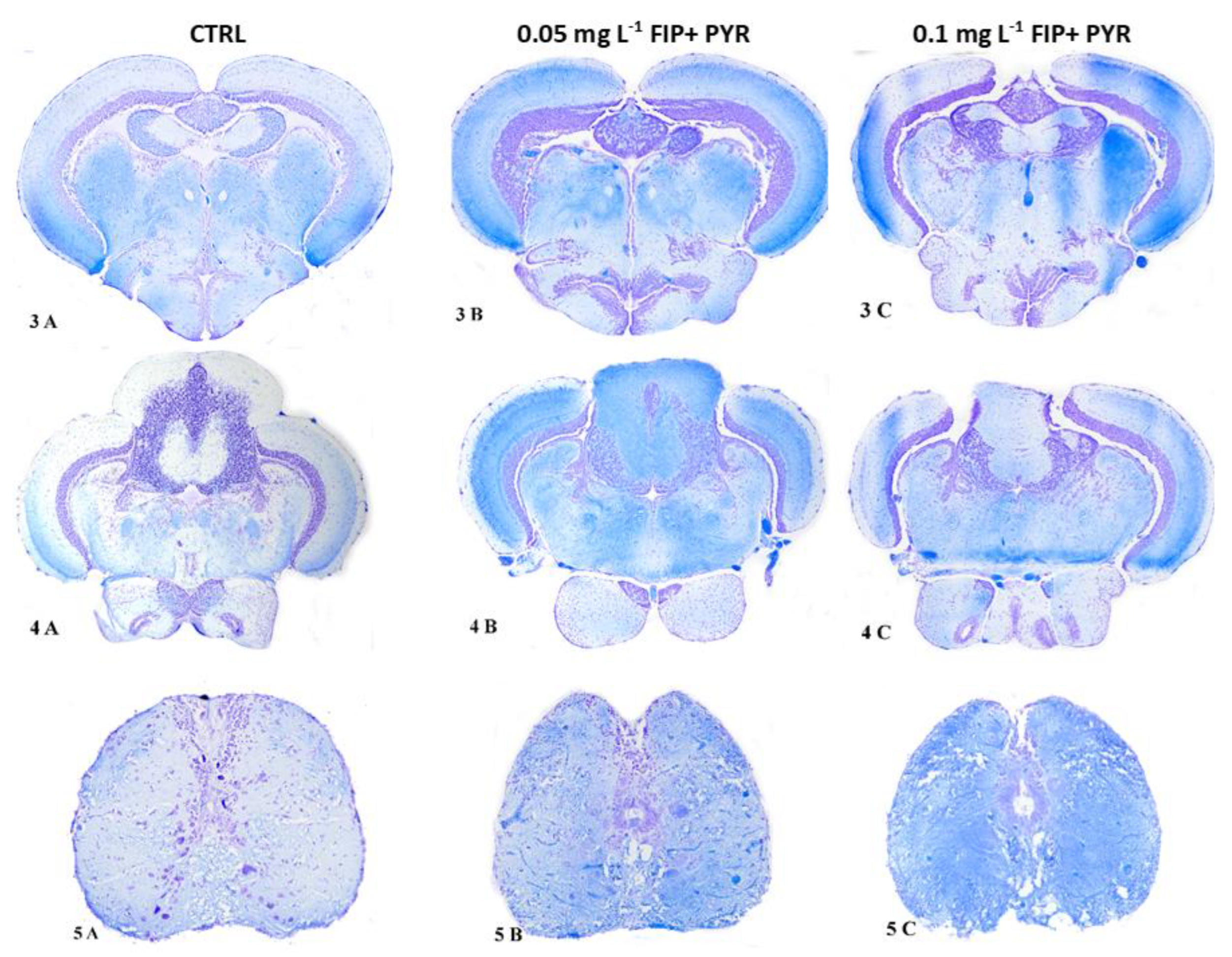
3.3. Histological Alterations
4. Discussion
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Institutional Review Board Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Tudi, M.; Daniel Ruan, H.; Wang, L.; Lyu, J.; Sadler, R.; Connell, D.; Chu, C.; Phung, D.T. Agriculture development, pesticide application and its impact on the environment. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2021, 18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Pathak, V.M.; Verma, V.K.; Rawat, B.S.; Kaur, B.; Babu, N.; Sharma, A.; Dewali, S.; Yadav, M.; Kumari, R.; Singh, S.; et al. Current status of pesticide effects on environment, human health and it’s eco-friendly management as bioremediation: A comprehensive review. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 962619. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Serrão, J.E.; Plata-Rueda, A.; Martínez, L.C.; Zanuncio, J.C. Side-effects of pesticides on non-target insects in agriculture: a mini-review. Naturwissenschaften 2022, 109, 17. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kim, K.-H.; Kabir, E.; Jahan, S.A. Exposure to pesticides and the associated human health effects. Sci. Total Environ. 2017, 575, 525–535. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Authority, E.F.S. Conclusion on the peer review of the pesticide risk assessment for bees for the active substance imidacloprid. EFSA J. 2013, 11, 3068. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Donley, N. The USA lags behind other agricultural nations in banning harmful pesticides. Environ. Heal. 2019, 18, 44. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sadaria, A.M.; Labban, C.W.; Steele, J.C.; Maurer, M.M.; Halden, R.U. Retrospective nationwide occurrence of fipronil and its degradates in U.S. wastewater and sewage sludge from 2001-2016. Water Res. 2019, 155, 465–473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hodgson, E. Chapter 9 - Biotransformation of Individual Pesticides: Some Examples. In; Hodgson, E.B.T.- P.B. and D., Ed.; Academic Press: Boston, 2012; pp. 195–208 ISBN 978-0-12-385481-0.
- Fent, G.M. Fipronil. In; Wexler, P.B.T.-E. of T. (Third E., Ed.; Academic Press: Oxford, 2014; pp. 596–597 ISBN 978-0-12-386455-0.
- Bhatt, P.; Gangola, S.; Ramola, S.; Bilal, M.; Bhatt, K.; Huang, Y.; Zhou, Z.; Chen, S. Insights into the toxicity and biodegradation of fipronil in contaminated environment. Microbiol. Res. 2023, 266, 127247. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tingle, C.C.D.; Rother, J.A.; Dewhurst, C.F.; Lauer, S.; King, W.J. Fipronil: environmental fate, ecotoxicology, and human health concerns. Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol. 2003, 176, 1–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, X.; Martínez, M.A.; Wu, Q.; Ares, I.; Martínez-Larrañaga, M.R.; Anadón, A.; Yuan, Z. Fipronil insecticide toxicology: oxidative stress and metabolism. Crit. Rev. Toxicol. 2016, 46, 876–899. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, R.C.; Anadón, A. Chapter 42 - Fipronil. In; Gupta, R.C.B.T.-V.T. (Third E., Ed.; Academic Press, 2018; pp. 533–538 ISBN 978-0-12-811410-0.
- Ohi, M.; Dalsenter, P.R.; Andrade, A.J.M.; Nascimento, A.J. Reproductive adverse effects of fipronil in Wistar rats. Toxicol. Lett. 2004, 146, 121–127. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mossa, A.-T.H.; Swelam, E.S.; Mohafrash, S.M.M. Sub-chronic exposure to fipronil induced oxidative stress, biochemical and histopathological changes in the liver and kidney of male albino rats. Toxicol. reports 2015, 2, 775–784. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kartheek, R.M.; David, M.; Mossa, A.-T.H.; Swelam, E.S.; Mohafrash, S.M.M. Assessment of fipronil toxicity on Wistar rats: A hepatotoxic perspective. Toxicol. Reports 2018, 5, 448–456. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Terçariol, P.R.G.; Godinho, A.F. Behavioral effects of acute exposure to the insecticide fipronil. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2011, 99, 221–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mahmoud, Y.K.; Ali, A.A.; Abdelrazek, H.M.A.; Aldayel, T.S.; Abdel-Daim, M.M.; El-Menyawy, M.A.I. Neurotoxic effect of fipronil in male wistar rats: ameliorative effect of l-arginine and l-carnitine. Biology (Basel). 2021, 10. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Kitulagodage, M.; Isanhart, J.; Buttemer, W.A.; Hooper, M.J.; Astheimer, L.B. Fipronil toxicity in northern bobwhite quail Colinus virginianus: reduced feeding behaviour and sulfone metabolite formation. Chemosphere 2011, 83, 524–530. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Arslan, P.; Günal, A.Ç. Does fipronil affect on aquatic organisms? physiological, biochemical, and histopathological alterations of non-target freshwater mussel species. Water 2023, 15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ferreira, M.; De Oliveira, P.R.; Denardi, S.E.; Bechara, G.H.; Mathias, M.I.C. Action of the chemical agent fipronil (active ingredient of acaricide Frontline®) on the liver of mice: an ultrastructural analysis. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2012, 75, 197–205. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Clasen, B.; Loro, V.L.; Cattaneo, R.; Moraes, B.; Lópes, T.; de Avila, L.A.; Zanella, R.; Reimche, G.B.; Baldisserotto, B. Effects of the commercial formulation containing fipronil on the non-target organism Cyprinus carpio: implications for rice-fish cultivation. Ecotoxicol. Environ. Saf. 2012, 77, 45–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ishaaya, I.; Horowitz, A.R. Pyriproxyfen, a novel insect growth regulator for controlling whiteflies: mechanisms and resistance management. Pestic. Sci. 1995, 43, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sullivan, J.J.; Goh, K.S. Environmental fate and properties of pyriproxyfen. J. Pestic. Sci. 2008, 33, 339–350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Devillers, J. Fate of Pyriproxyfen in Soils and Plants. Toxics 2020, 8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- World Health Organization - Pyriproxyfen in drinking-water: use for vector control in drinking-water sources and containers. 2008.
- Moura, L.; de Nadai, B.L.; Corbi, J.J. One does not simply apply larvicides: Aedes aegypti from Araraquara (Brazil) has reduced susceptibility to pyriproxyfen. Vet. Parasitol. Reg. Stud. Reports 2023, 41, 100875. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shahid, A.; Zaidi, S.D.-E.-S.; Akbar, H.; Saeed, S. An investigation on some toxic effects of pyriproxyfen in adult male mice. Iran. J. Basic Med. Sci. 2019, 22, 997–1003. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Mehrnoush, G.; Mehrdad, S.; Saeid, K.H.A. Effect of pyriproxyfen on function and tissue of testis in adult rat. Int. J. Curr. Res. Rev. 2013, 5, 66–74. [Google Scholar]
- Caixeta, E.S.; Silva, C.F.; Santos, V.S.V.; Olegário de Campos Júnior, E.; Pereira, B.B. Ecotoxicological assessment of pyriproxyfen under environmentally realistic exposure conditions of integrated vector management for Aedes aegypti control in Brazil. J. Toxicol. Environ. Health. A 2016, 79, 799–803. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Azevedo, R.D.S.; Falcão, K.V.G.; Assis, C.R.D.; Martins, R.M.G.; Araújo, M.C.; Yogui, G.T.; Neves, J.L.; Seabra, G.M.; Maia, M.B.S.; Amaral, I.P.G.; et al. Effects of pyriproxyfen on zebrafish brain mitochondria and acetylcholinesterase. Chemosphere 2021, 263, 128029. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Costa, L.G.; Giordano, G.; Guizzetti, M.; Vitalone, A. Neurotoxicity of pesticides: a brief review. Front. Biosci. 2008, 13, 1240–1249. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abreu-Villaça, Y.; Levin, E.D. Developmental neurotoxicity of succeeding generations of insecticides. Environ. Int. 2017, 99, 55–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Richardson, J.R.; Fitsanakis, V.; Westerink, R.H.S.; Kanthasamy, A.G. Neurotoxicity of pesticides. Acta Neuropathol. 2019, 138, 343–362. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Oliveira, P.R.; Bechara, G.H.; Denardi, S.E.; Oliveira, R.J.; Mathias, M.I.C. Cytotoxicity of fipronil on mice liver cells. Microsc. Res. Tech. 2012, 75, 28–35. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Badgujar, P.C.; Chandratre, G.A.; Pawar, N.N.; Telang, A.G.; Kurade, N.P. Fipronil induced oxidative stress involves alterations in SOD1 and catalase gene expression in male mice liver: Protection by vitamins E and C. Environ. Toxicol. 2016, 31, 1147–1158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Abdel-Daim, M.M.; Abdeen, A. Protective effects of rosuvastatin and vitamin E against fipronil-mediated oxidative damage and apoptosis in rat liver and kidney. Food Chem. Toxicol. an Int. J. Publ. Br. Ind. Biol. Res. Assoc. 2018, 114, 69–77. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Awad, M.A.; Ahmed, Z.S.O.; AbuBakr, H.O.; Elbargeesy, G.A.E.-F.H.; Moussa, M.H.G. Fipronil induced oxidative stress in neural tissue of albino rat with subsequent apoptosis and tissue reactivity. Acta Histochem. 2021, 123, 151764. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghaffar, A.; Hussain, R.; Abbas, G.; Kalim, M.; Khan, A.; Ferrando, S.; Gallus, L.; Ahmed, Z. Fipronil (Phenylpyrazole) induces hemato-biochemical, histological and genetic damage at low doses in common carp, Cyprinus carpio (Linnaeus, 1758). Ecotoxicology 2018, 27, 1261–1271. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Maharajan, K.; Muthulakshmi, S.; Nataraj, B.; Ramesh, M.; Kadirvelu, K. Toxicity assessment of pyriproxyfen in vertebrate model zebrafish embryos (Danio rerio): A multi biomarker study. Aquat. Toxicol. 2018, 196, 132–145. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shahid, A.; Saher, M. Repeated exposure of pyriproxyfen to pregnant female mice causes developmental abnormalities in prenatal pups. Environ. Sci. Pollut. Res. Int. 2020, 27, 26998–27009. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Spitsbergen, J.M.; Kent, M.L. The state of the art of the zebrafish model for toxicology and toxicologic pathology research advantages and current limitations. Toxicol. Pathol. 2003, 31 Suppl, 62–87. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Parng, C.; Roy, N.M.; Ton, C.; Lin, Y.; McGrath, P. Neurotoxicity assessment using zebrafish. J. Pharmacol. Toxicol. Methods 2007, 55, 103–112. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Choi, T.-Y.; Choi, T.-I.; Lee, Y.-R.; Choe, S.-K.; Kim, C.-H. Zebrafish as an animal model for biomedical research. Exp. Mol. Med. 2021, 53, 310–317. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Audira, G.; Sampurna, B.P.; Juniardi, S.; Liang, S.-T.; Lai, Y.-H.; Hsiao, C.-D. A Versatile setup for measuring multiple behavior endpoints in zebrafish. Inventions 2018, 3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rafferty, S.A.; Quinn, T.A. A beginner’s guide to understanding and implementing the genetic modification of zebrafish. Prog. Biophys. Mol. Biol. 2018, 138, 3–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, Y.; Jia, Z.; Zhang, S.; He, X. Progress in gene-editing technology of zebrafish. Biomolecules 2021, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Robea, M.A.; Jijie, R.; Nicoara, M.; Plavan, G.; Ciobica, A.S.; Solcan, C.; Audira, G.; Hsiao, C.-D.; Strungaru, S.-A. Vitamin C attenuates oxidative stress and behavioral abnormalities triggered by fipronil and pyriproxyfen insecticide chronic exposure on zebrafish juvenile. Antioxidants (Basel, Switzerland) 2020, 9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Commission Recommendation Guidelines for the accommodation and care of animals used for experimental and other scientific purposes (notified under document number C(2007) 2525). Off. J. Eur. Union 2007, 50.
- Avdesh, A.; Chen, M.; Martin-Iverson, M.T.; Mondal, A.; Ong, D.; Rainey-Smith, S.; Taddei, K.; Lardelli, M.; Groth, D.M.; Verdile, G.; et al. Regular care and maintenance of a zebrafish (Danio rerio) laboratory: an introduction. J. Vis. Exp. 2012, e4196–e4196. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aleström, P.; D’Angelo, L.; Midtlyng, P.J.; Schorderet, D.F.; Schulte-Merker, S.; Sohm, F.; Warner, S. Zebrafish: Housing and husbandry recommendations. Lab. Anim. 2019, 54, 213–224. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Araujo, J.; Maximino, C.; de Brito, T.M.; da Silva, A.W.B.; Oliveira, K.R.M.; de Jesus Oliveira Batista, E.; Morato, S.; Herculano, A.M.; Gouveia, A. Behavioral and pharmacological aspects of anxiety in the light/dark preference test bt - Zebrafish Protocols for Neurobehavioral Research. In; Kalueff, A. V, Stewart, A.M., Eds.; Humana Press: Totowa, NJ, 2012; pp. 191–202 ISBN 978-1-61779-597-8.
- Directive 63 The protection of animals used for scientific purposes. Off. J. Eur. Union 2010, 53.
- Koslowski, S.; Latapy, C.; Auvray, P.; Blondel, M.; Meijer, L. Long-term fipronil treatment induces hyperactivity in female mice. Int. J. Environ. Res. Public Health 2020, 17, 1579. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Reichel, J.M.; Nissel, S.; Rogel-Salazar, G.; Mederer, A.; Käfer, K.; Bedenk, B.T.; Martens, H.; Anders, R.; Grosche, J.; Michalski, D.; et al. Distinct behavioral consequences of short-term and prolonged GABAergic depletion in prefrontal cortex and dorsal hippocampus. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2015, 8, 452. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gusso, D.; Reolon, G.K.; Gonzalez, J.B.; Altenhofen, S.; Kist, L.W.; Bogo, M.R.; Bonan, C.D. Pyriproxyfen exposure impairs cognitive parameters and alters cortisol levels in zebrafish. Front. Behav. Neurosci. 2020, 14, 103. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Li, P.; Akk, G. The insecticide fipronil and its metabolite fipronil sulphone inhibit the rat alpha1beta2gamma2L GABA(A) receptor. Br. J. Pharmacol. 2008, 155, 783–794. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Ghit, A.; Assal, D.; Al-Shami, A.S.; Hussein, D.E.E. GABAA receptors: structure, function, pharmacology, and related disorders. J. Genet. Eng. Biotechnol. 2021, 19, 123. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Eadie, A.; Vasquez, I.C.; Liang, X.; Wang, X.; Souders, C.L. 2nd; El Chehouri, J.; Hoskote, R.; Feswick, A.; Cowie, A.M.; Loughery, J.R.; et al. Residual molecular and behavioral effects of the phenylpyrazole pesticide fipronil in larval zebrafish (Danio rerio) following a pulse embryonic exposure. Comp. Biochem. Physiol. Part D. Genomics Proteomics 2020, 36, 100743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Jabłońska-Trypuć, A. Pesticides as inducers of oxidative stress. React. Oxyg. Species 2017, 3, 96–110. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mani, S.; Jain, A.; Gulati, A.; Tyagi, S.; Pal, K.V.; Jaiswal, H.; Singh, M. Oxidative stress: a potential link between pesticide exposure and early-life neurological disorders bt - free radical biology and environmental toxicity. In; Kesari, K.K., Jha, N.K., Eds.; Springer International Publishing: Cham, 2021; pp. 209–251 ISBN 978-3-030-83446-3.
- Sule, R.O.; Condon, L.; Gomes, A. V. A Common feature of pesticides: oxidative stress-the role of oxidative stress in pesticide-induced toxicity. Oxid. Med. Cell. Longev. 2022, 2022, 5563759. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ullah, R.; Zuberi, A.; Ullah, S.; Ullah, I.; Dawar, F. Cypermethrin induced behavioral and biochemical changes in Mahseer, Tor putitora. J. Toxicol. Sci. 2014, 39, 829–836. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nataraj, B.; Hemalatha, D.; Rangasamy, B.; Maharajan, K.; Ramesh, M. Hepatic oxidative stress, genotoxicity and histopathological alteration in fresh water fish Labeo rohita exposed to organophosphorus pesticide profenofos. Biocatal. Agric. Biotechnol. 2017, 12, 185–190. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Amin, K.A.; Hashem, K.S. Deltamethrin-induced oxidative stress and biochemical changes in tissues and blood of catfish (Clarias gariepinus): antioxidant defense and role of alpha-tocopherol. BMC Vet. Res. 2012, 8, 45. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Valko, M.; Leibfritz, D.; Moncol, J.; Cronin, M.T.D.; Mazur, M.; Telser, J. Free radicals and antioxidants in normal physiological functions and human disease. Int. J. Biochem. Cell Biol. 2007, 39, 44–84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, C.; Qian, Y.; Zhang, X.; Chen, F.; Zhang, Q.; Li, Z.; Zhao, M. A metabolomic study of fipronil for the anxiety-like behavior in zebrafish larvae at environmentally relevant levels. Environ. Pollut. 2016, 211, 252–258. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Farder-Gomes, C.F.; Fernandes, K.M.; Bernardes, R.C.; Bastos, D.S.S.; Martins, G.F.; Serrão, J.E. Acute exposure to fipronil induces oxidative stress, apoptosis and impairs epithelial homeostasis in the midgut of the stingless bee Partamona helleri Friese (Hymenoptera: Apidae). Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145679. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wu, C.-H.; Lu, C.-W.; Hsu, T.-H.; Wu, W.-J.; Wang, S.-E. Neurotoxicity of fipronil affects sensory and motor systems in zebrafish. Pestic. Biochem. Physiol. 2021, 177, 104896. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Park, H.; Lee, J.-Y.; Park, S.; Song, G.; Lim, W. Developmental toxicity of fipronil in early development of zebrafish (Danio rerio) larvae: Disrupted vascular formation with angiogenic failure and inhibited neurogenesis. J. Hazard. Mater. 2020, 385, 121531. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stehr, C.M.; Linbo, T.L.; Incardona, J.P.; Scholz, N.L. The developmental neurotoxicity of fipronil: notochord degeneration and locomotor defects in zebrafish embryos and larvae. Toxicol. Sci. 2006, 92, 270–278. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nourshargh, S.; Alon, R. Leukocyte migration into inflamed tissues. Immunity 2014, 41, 694–707. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schmitt, C.; Strazielle, N.; Ghersi-Egea, J.-F. Brain leukocyte infiltration initiated by peripheral inflammation or experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis occurs through pathways connected to the CSF-filled compartments of the forebrain and midbrain. J. Neuroinflammation 2012, 9, 187. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.-K.; Kwan, J.S.-K.; Wong, G.T.-C.; Yi, Z.-N.; Ma, A.C.-H.; Chang, R.C.-C. Leukocyte invasion of the brain after peripheral trauma in zebrafish (Danio rerio). Exp. Mol. Med. 2022, 54, 973–987. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Skelly, D.T.; Griffin, É.W.; Murray, C.L.; Harney, S.; O’Boyle, C.; Hennessy, E.; Dansereau, M.-A.; Nazmi, A.; Tortorelli, L.; Rawlins, J.N.; et al. Acute transient cognitive dysfunction and acute brain injury induced by systemic inflammation occur by dissociable IL-1-dependent mechanisms. Mol. Psychiatry 2019, 24, 1533–1548. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bevilaqua, F.; Sachett, A.; Chitolina, R.; Garbinato, C.; Gasparetto, H.; Marcon, M.; Mocelin, R.; Dallegrave, E.; Conterato, G.; Piato, A.; et al. A mixture of fipronil and fungicides induces alterations on behavioral and oxidative stress parameters in zebrafish. Ecotoxicology 2020, 29, 140–147. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Type of Tank | Temperature (°C) | pH | Salinity | Conductivity (µS cm-1) | Ammonia (mg L-1) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Housing tank | 26 | 7.6 | 0.26 | 551 | 0.05 |
| Experimental tank | 25 ± 0.5 | 7.4 | 0.25 | 553 | 0.04 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





