Submitted:
01 July 2023
Posted:
04 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Antimicrobial Resistance: the current scenario
2. Diagnostic stewardship as a leverage in antimicrobial resistance
3. Drug target
3.1. The drug portfolio
3.2. Non-classical antimicrobial therapies
3.2.1. Monoclonal antibodies – The on-target molecule
3.2.2. Antimicrobial peptides: Arming the enemy
3.2.3. Aptamers - Emerging therapeutics
3.2.4. Phage therapy – the predator -prey re-visited

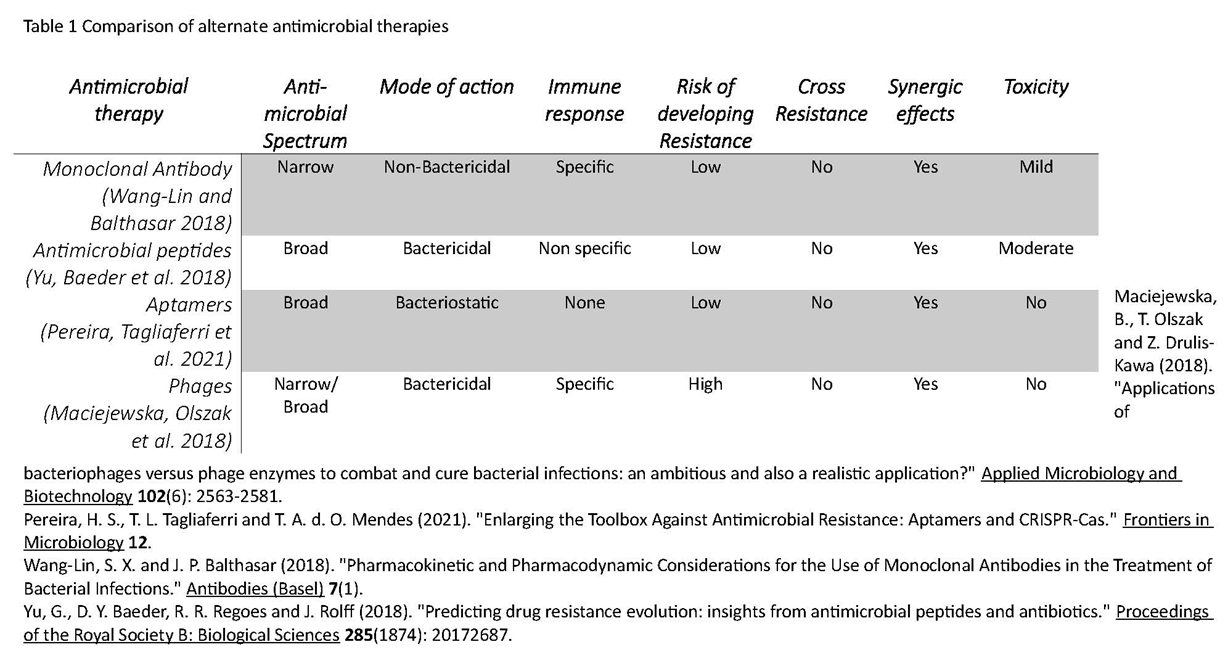
4. The Target - what is expected?
5. Phenotypic tests
5.1. Standard Antimicrobial susceptibility testing
5.1.1. Minimum inhibitory concentration
5.1.2. Mutation Prevention Concentration and Mutant Selection Window
5.2. In vivo altered susceptibility test
5.3. Cross resistance analysis
5.4. Synergy analysis
5.5. Dereplication - Antibiotic resistance platform
5.6. Biofilm eradication concentration
5.7. Phage dosing parameters
6. Genotypic assay
6.1. Non sequencing assay
6.2. Sequencing based assay
7. Companion diagnostics in infectious diseases
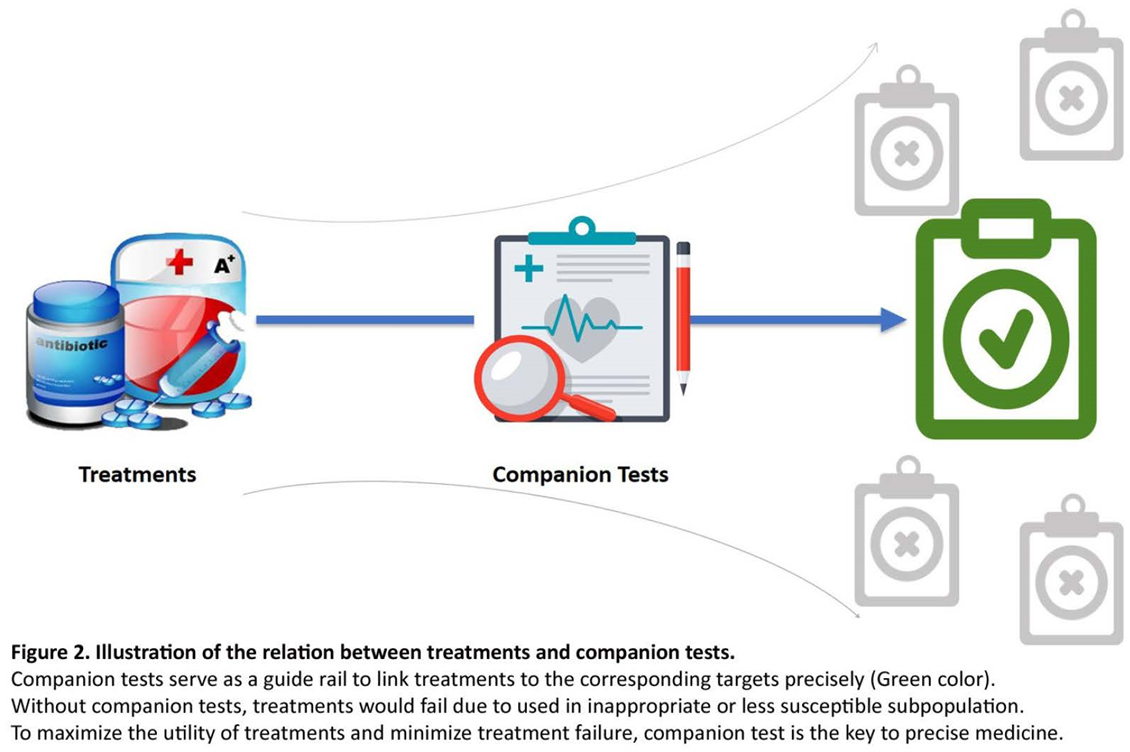
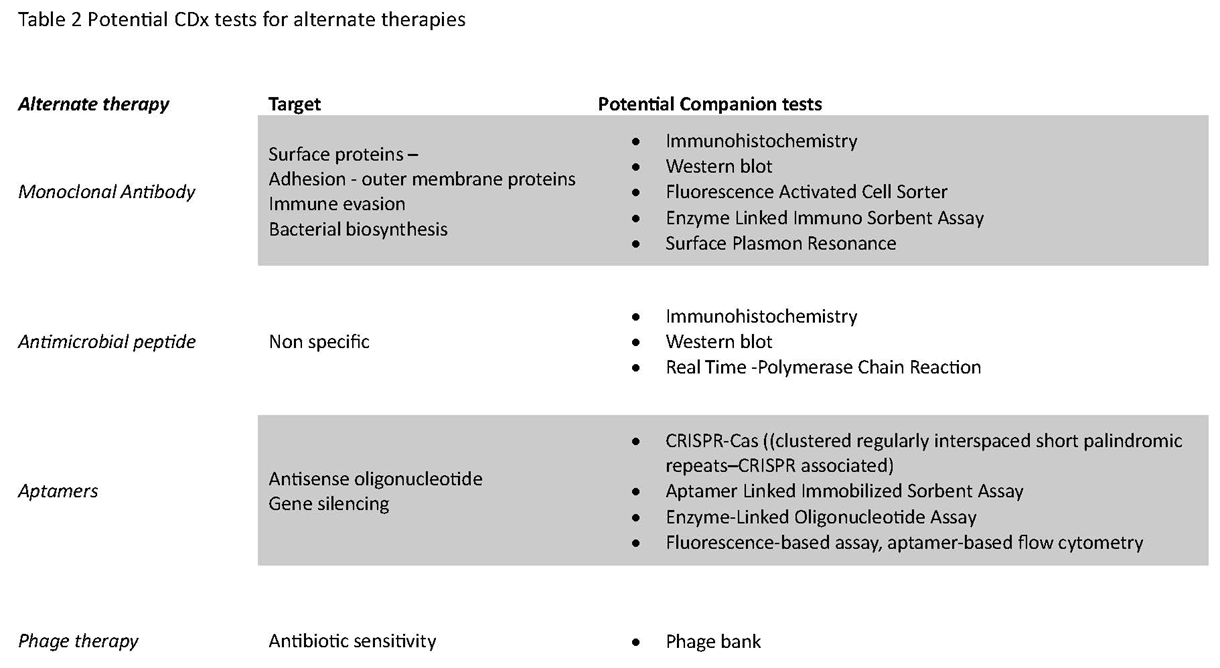
CDx with alternate therapies for infectious diseases
8. Conclusion
References
- https://www.pewtrusts.org/en/research-and-analysis/issue-briefs/2021/03/assessment-of-nontraditional-products-in-development-to-combat-bacterial-infections.
- WHO Guidelines Approved by the Guidelines Review Committee. Guidelines for the Treatment of Malaria. Geneva, World Health Organization.
- Aaron, S.D.; Ferris, W.; Henry, D.A.; Speert, D.P.; MacDONALD, N.E. Multiple Combination Bactericidal Antibiotic Testing for Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Infected with Burkholderia cepacia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 161, 1206–1212. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Abedon, S. (2011). "Phage therapy pharmacology: calculating phage dosing." Adv Appl Microbiol 77: 1-40.
- Afrasiabi, S.; Pourhajibagher, M.; Raoofian, R.; Tabarzad, M.; Bahador, A. Therapeutic applications of nucleic acid aptamers in microbial infections. J. Biomed. Sci. 2020, 27, 6–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Aguilar, J.L.; Varshney, A.K.; Pechuan, X.; Dutta, K.; Nosanchuk, J.D.; Fries, B.C. Monoclonal antibodies protect from Staphylococcal Enterotoxin K (SEK) induced toxic shock and sepsis by USA300Staphylococcus aureus. Virulence 2016, 8, 741–750. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ali, S. O., X. Q. Yu, G. J. Robbie, Y. Wu, K. Shoemaker, L. Yu, A. DiGiandomenico, A. E. Keller, C. Anude, M. Hernandez-Illas, T. Bellamy, J. Falloon, F. Dubovsky and H. S. Jafri (2019). "Phase 1 study of MEDI3902, an investigational anti-Pseudomonas aeruginosa PcrV and Psl bispecific human monoclonal antibody, in healthy adults." Clin Microbiol Infect 25(5): 629.e621-629.e626.
- Andersson, D.I.; Hughes, D.; Kubicek-Sutherland, J.Z. Mechanisms and consequences of bacterial resistance to antimicrobial peptides. Drug Resist. Updat. 2016, 26, 43–57. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- rdal, C., M. Balasegaram, R. Laxminarayan, D. McAdams, K. Outterson, J. H. Rex and N. Sumpradit (2020). "Antibiotic development — economic, regulatory and societal challenges." Nature Reviews Microbiology 18(5): 267-274.
- Band, V.I.; Crispell, E.K.; Napier, B.A.; Herrera, C.M.; Tharp, G.K.; Vavikolanu, K.; Pohl, J.; Read, T.D.; Bosinger, S.E.; Trent, M.S.; et al. Antibiotic failure mediated by a resistant subpopulation in Enterobacter cloacae. Nat. Microbiol. 2016, 1, 1–9. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, F. The 2010 Garrod Lecture: The dimensions of evolution in antibiotic resistance: ex unibus plurum et ex pluribus unum. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2011, 66, 1659–1672. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, F.; Negri, M. Challenges: Selective compartments for resistant microorganisms in antibiotic gradients. BioEssays 1997, 19, 731–736. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Baquero, F.; Negri, M.C.; I Morosini, M.; Blázquez, J. Selection of very small differences in bacterial evolution. Int. Microbiol. 1998, 1. [Google Scholar]
- Barbosa, C.; Trebosc, V.; Kemmer, C.; Rosenstiel, P.; Beardmore, R.; Schulenburg, H.; Jansen, G. Alternative Evolutionary Paths to Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance Cause Distinct Collateral Effects. Mol. Biol. Evol. 2017, 34, 2229–2244. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bayraç, A.T.; Donmez, S.I. Selection of DNA aptamers to Streptococcus pneumonia and fabrication of graphene oxide based fluorescent assay. Anal. Biochem. 2018, 556, 91–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Belanger, C.R.; Hancock, R.E.W. Testing physiologically relevant conditions in minimal inhibitory concentration assays. Nat. Protoc. 2021, 16, 3761–3774. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bikard, D.; Euler, C.W.; Jiang, W.; Nussenzweig, P.M.; Goldberg, G.W.; Duportet, X.; A Fischetti, V.; A Marraffini, L. Exploiting CRISPR-Cas nucleases to produce sequence-specific antimicrobials. Nat. Biotechnol. 2014, 32, 1146–1150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bonofiglio, L.; Gardella, N.; Mollerach, M. Application of Molecular Typing Methods to the Study of Medically Relevant Gram-Positive Cocci. 2012. [CrossRef]
- Boucher, H.W.; Talbot, G.H.; Bradley, J.S.; Edwards, J.E.; Gilbert, D.; Rice, L.B.; Scheld, M.; Spellberg, B.; Bartlett, J. Bad Bugs, No Drugs: No ESKAPE! An Update from the Infectious Diseases Society of America. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2009, 48, 1–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, D. G. (2017). 5.21 - New Drugs and Emerging Leads in Antibacterial Drug Discovery. Comprehensive Medicinal Chemistry III. S. Chackalamannil, D. Rotella and S. E. Ward. Oxford, Elsevier: 682-702.
- Burnham, K.L.; Davenport, E.E.; Radhakrishnan, J.; Humburg, P.; Gordon, A.C.; Hutton, P.; Svoren-Jabalera, E.; Garrard, C.; Hill, A.V.S.; Hinds, C.J.; et al. Shared and Distinct Aspects of the Sepsis Transcriptomic Response to Fecal Peritonitis and Pneumonia. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2017, 196, 328–339. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Buyck, J.M.; Plésiat, P.; Traore, H.; Vanderbist, F.; Tulkens, P.M.; Van Bambeke, F. Increased Susceptibility of Pseudomonas aeruginosa to Macrolides and Ketolides in Eukaryotic Cell Culture Media and Biological Fluids Due to Decreased Expression of oprM and Increased Outer-Membrane Permeability. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2012, 55, 534–542. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, B.J.; Payne, R.J.H. Bacteriophage Therapy and the Mutant Selection Window. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2008, 52, 4344–4350. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cairns, B.J.; Timms, A.R.; Jansen, V.A.A.; Connerton, I.F.; Payne, R.J.H. Quantitative Models of In Vitro Bacteriophage–Host Dynamics and Their Application to Phage Therapy. PLOS Pathog. 2009, 5, e1000253. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Caliendo, A.M.; Gilbert, D.N.; Ginocchio, C.C.; Hanson, K.E.; May, L.; Quinn, T.C.; Tenover, F.C.; Alland, D.; Blaschke, A.J.; Bonomo, R.A.; et al. Better Tests, Better Care: Improved Diagnostics for Infectious Diseases. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2013, 57, S139–S170. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Candia, J.; Cheung, F.; Kotliarov, Y.; Fantoni, G.; Sellers, B.; Griesman, T.; Huang, J.; Stuccio, S.; Zingone, A.; Ryan, B.M.; et al. Assessment of Variability in the SOMAscan Assay. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 1–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cantón, R.; Morosini, M.I. Emergence and spread of antibiotic resistance following exposure to antibiotics. FEMS Microbiol. Rev. 2011, 35, 977–991. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chan, B.K.; Abedon, S.T.; Loc-Carrillo, C. Phage cocktails and the future of phage therapy. Future Microbiol. 2013, 8, 769–783. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.B.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.B.; Ascierto, P.; Larkin, J.; Dummer, R.; Garbe, C.; Testori, A.; Maio, M.; et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chapman, P.B.; Hauschild, A.; Robert, C.; Haanen, J.B.; Ascierto, P.; Larkin, J.; Dummer, R.; Garbe, C.; Testori, A.; Maio, M.; et al. Improved survival with vemurafenib in melanoma with BRAF V600E mutation. N. Engl. J. Med. 2011, 364, 2507–2516. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chaudhry, W.N.; Concepción-Acevedo, J.; Park, T.; Andleeb, S.; Bull, J.J.; Levin, B.R. Synergy and Order Effects of Antibiotics and Phages in Killing Pseudomonas aeruginosa Biofilms. PLOS ONE 2017, 12, e0168615. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, C.; Clark, C.G.; Langner, S.; Boyd, D.A.; Bharat, A.; McCorrister, S.J.; McArthur, A.G.; Graham, M.R.; Westmacott, G.R.; Van Domselaar, G. Detection of Antimicrobial Resistance Using Proteomics and the Comprehensive Antibiotic Resistance Database: A Case Study. Proteom. – Clin. Appl. 2019, 14, e1800182. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, L.; Rashid, F.; Shah, A.; Awan, H.M.; Wu, M.; Liu, A.; Wang, J.; Zhu, T.; Luo, Z.; Shan, G. The isolation of an RNA aptamer targeting to p53 protein with single amino acid mutation. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2015, 112, 10002–10007. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, X.; Sun, Y.; Missiakas, D.; Schneewind, O. Staphylococcus aureus Decolonization of Mice With Monoclonal Antibody Neutralizing Protein A. J. Infect. Dis. 2018, 219, 884–888. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chuang, Y.-M.; Belchis, D.A.; Karakousis, P.C. The Polyphosphate Kinase Gene ppk2 Is Required for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Inorganic Polyphosphate Regulation and Virulence. mBio 2013, 4, e00039–13. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cload, S.T.; McCauley, T.G.; Keefe, A.D.; Healy, J.M.; Wilson, C. Properties of Therapeutic Aptamers. 2006, 363–416. [CrossRef]
- Coates, M., S. Blanchard and A. S. MacLeod (2018). "Innate antimicrobial immunity in the skin: A protective barrier against bacteria, viruses, and fungi." PLOS Pathogens 14(12): e1007353.
- Coers, J. Sweet host revenge: Galectins and GBPs join forces at broken membranes. Cell. Microbiol. 2017, 19, e12793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cornforth, D.M.; Diggle, F.L.; Melvin, J.A.; Bomberger, J.M.; Whiteley, M. Quantitative Framework for Model Evaluation in Microbiology Research Using Pseudomonas aeruginosa and Cystic Fibrosis Infection as a Test Case. Mbio 2020, 11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cox, G.; Sieron, A.; King, A.M.; De Pascale, G.; Pawlowski, A.C.; Koteva, K.; Wright, G.D. A Common Platform for Antibiotic Dereplication and Adjuvant Discovery. Cell Chem. Biol. 2017, 24, 98–109. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cruz, C.D.; Shah, S.; Tammela, P. Defining conditions for biofilm inhibition and eradication assays for Gram-positive clinical reference strains. BMC Microbiol. 2018, 18, 173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- A Cummings, L.; Kurosawa, K.; Hoogestraat, D.R.; SenGupta, D.J.; Candra, F.; Doyle, M.; Thielges, S.; A Land, T.; A Rosenthal, C.; Hoffman, N.G.; et al. Clinical Next Generation Sequencing Outperforms Standard Microbiological Culture for Characterizing Polymicrobial Samples. Clin. Chem. 2016, 62, 1465–1473. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Curren, E. J., J. D. Lutgring, S. Kabbani, D. J. Diekema, S. Gitterman, E. Lautenbach, D. J. Morgan, C. Rock, R. M. Salerno and L. C. McDonald (2021). "Advancing Diagnostic Stewardship for Healthcare-Associated Infections, Antibiotic Resistance, and Sepsis." Clinical Infectious Diseases 74(4): 723-728.
- Czaplewski, L.; Bax, R.; Clokie, M.; Dawson, M.; Fairhead, H.; Fischetti, V.A.; Foster, S.; Gilmore, B.F.; Hancock, R.E.W.; Harper, D.; et al. Alternatives to antibiotics—A pipeline portfolio review. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2016, 16, 239–251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dall, G.F.; Tsang, S.-T.J.; Gwynne, P.J.; MacKenzie, S.P.; Simpson, A.H.R.W.; Breusch, S.J.; Gallagher, M.P. Unexpected synergistic and antagonistic antibiotic activity against Staphylococcus biofilms. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2018, 73, 1830–1840. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- de la Fuente-Núñez, C.; Silva, O.N.; Lu, T.K.; Franco, O.L. Antimicrobial peptides: Role in human disease and potential as immunotherapies. Pharmacol. Ther. 2017, 178, 132–140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- De Sordi, L.; Khanna, V.; Debarbieux, L. The Gut Microbiota Facilitates Drifts in the Genetic Diversity and Infectivity of Bacterial Viruses. Cell Host Microbe 2017, 22, 801–808. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Di Somma, A.; Moretta, A.; Canè, C.; Cirillo, A.; Duilio, A. Antimicrobial and Antibiofilm Peptides. Biomolecules 2020, 10, 652. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dong, Y., X. Zhao, J. Domagala and K. Drlica (1999). "Effect of Fluoroquinolone Concentration on Selection of Resistant Mutants of Mycobacterium bovis BCG andStaphylococcus aureus." Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 43(7): 1756-1758.
- Doyle, C.R.; Moon, J.-Y.; Daily, J.P.; Wang, T.; Pirofski, L.-A. A Capsular Polysaccharide-Specific Antibody Alters Streptococcus pneumoniae Gene Expression during Nasopharyngeal Colonization of Mice. Infect. Immun. 2018, 86. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dua, P.; Kim, S.; Lee, D.-K. Nucleic acid aptamers targeting cell-surface proteins. Methods 2011, 54, 215–225. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Enright, M. C. and B. G. Spratt (1999). "Multilocus sequence typing." Trends in Microbiology 7(12): 482-487.
- Ersoy, S.C.; Heithoff, D.M.; Barnes, L.; Tripp, G.K.; House, J.K.; Marth, J.D.; Smith, J.W.; Mahan, M.J. Correcting a Fundamental Flaw in the Paradigm for Antimicrobial Susceptibility Testing. EBioMedicine 2017, 20, 173–181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fan, Y.; Cui, M.; Liu, Y.; Jin, M.; Zhao, H. Selection and characterization of DNA aptamers for constructing colorimetric biosensor for detection of PBP2a. Spectrochim. Acta Part A: Mol. Biomol. Spectrosc. 2019, 228, 117735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fantner, G.E.; Barbero, R.J.; Gray, D.S.; Belcher, A.M. Kinetics of antimicrobial peptide activity measured on individual bacterial cells using high-speed atomic force microscopy. Nat. Nanotechnol. 2010, 5, 280–285. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foucquier, J.; Guedj, M. Analysis of drug combinations: current methodological landscape. Pharmacol. Res. Perspect. 2015, 3, e00149. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Galarion, L.H.; Mohamad, M.; Alzeyadi, Z.; Randall, C.P.; O’neill, A.J. A platform for detecting cross-resistance in antibacterial drug discovery. J. Antimicrob. Chemother. 2021, 76, 1467–1471. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Geli, P., R. Laxminarayan, M. Dunne and D. L. Smith (2012). ""One-size-fits-all"? Optimizing treatment duration for bacterial infections." PLoS One 7(1): e29838.
- Gelman, D.; Yerushalmy, O.; Alkalay-Oren, S.; Rakov, C.; Ben-Porat, S.; Khalifa, L.; Adler, K.; Abdalrhman, M.; Coppenhagen-Glazer, S.; Aslam, S.; et al. Clinical Phage Microbiology: a suggested framework and recommendations for the in-vitro matching steps of phage therapy. Lancet Microbe 2021, 2, e555–e563. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Goel, A.K. Anti-Protective Antigen IgG Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay for Diagnosis of Cutaneous Anthrax in India. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2012, 19, 1238–1242. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ghosh, N.; Tomar, I.; Lukka, H.; Goel, A.K. Serodiagnosis of Human Cutaneous Anthrax in India Using an Indirect Anti-Lethal Factor IgG Enzyme-Linked Immunosorbent Assay. Clin. Vaccine Immunol. 2013, 20, 282–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gianvecchio, C.; Lozano, N.A.; Henderson, C.; Kalhori, P.; Bullivant, A.; Valencia, A.; Su, L.; Bello, G.; Wong, M.; Cook, E.; et al. Variation in Mutant Prevention Concentrations. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 42. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gibson, S.B.; Green, S.I.; Liu, C.G.; Salazar, K.C.; Clark, J.R.; Terwilliger, A.L.; Kaplan, H.B.; Maresso, A.W.; Trautner, B.W.; Ramig, R.F. Constructing and Characterizing Bacteriophage Libraries for Phage Therapy of Human Infections. Front. Microbiol. 2019, 10, 2537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gigante, V.; Sati, H.; Beyer, P. Recent advances and challenges in antibacterial drug development. ADMET DMPK 2022, 10, 147–151. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gootenberg, J. S., O. O. Abudayyeh, M. J. Kellner, J. Joung, J. J. Collins and F. Zhang (2018). "Multiplexed and portable nucleic acid detection platform with Cas13, Cas12a, and Csm6." Science 360(6387): 439-444.
- Altamirano, F.L.G.; Barr, J.J. Phage Therapy in the Postantibiotic Era. Clin. Microbiol. Rev. 2019, 32, e00066–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Green, L.S.; Jellinek, D.; Bell, C.; Beebe, L.A.; Feistner, B.D.; Gill, S.C.; Jucker, F.M.; Janjić, N. Nuclease-resistant nucleic acid ligands to vascular permeability factor/vascular endothelial growth factor. Chem. Biol. 1995, 2, 683–695. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groff, K.; Brown, J.; Clippinger, A.J. Modern affinity reagents: Recombinant antibodies and aptamers. Biotechnol. Adv. 2015, 33, 1787–1798. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Guilhelmelli, F.; Vilela, N.; Albuquerque, P.; Derengowski, L.d.S.; Silva-Pereira, I.; Kyaw, C.M. Antibiotic development challenges: the various mechanisms of action of antimicrobial peptides and of bacterial resistance. Front. Microbiol. 2013, 4, 353. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gullberg, E.; Cao, S.; Berg, O.G.; Ilbäck, C.; Sandegren, L.; Hughes, D.; Andersson, D.I. Selection of Resistant Bacteria at Very Low Antibiotic Concentrations. PLOS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1002158. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ha, N.-R.; Jung, I.-P.; La, I.-J.; Jung, H.-S.; Yoon, M.-Y. Ultra-sensitive detection of kanamycin for food safety using a reduced graphene oxide-based fluorescent aptasensor. Sci. Rep. 2017, 7, 40305. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Habets, M.G.J.L.; Brockhurst, M.A. Therapeutic antimicrobial peptides may compromise natural immunity. Biol. Lett. 2012, 8, 416–418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haines, M.E.K.; Hodges, F.E.; Nale, J.Y.; Mahony, J.; van Sinderen, D.; Kaczorowska, J.; Alrashid, B.; Akter, M.; Brown, N.; Sauvageau, D.; et al. Analysis of Selection Methods to Develop Novel Phage Therapy Cocktails Against Antimicrobial Resistant Clinical Isolates of Bacteria. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hall, A. R., D. D. Vos, V.-P. Friman, J.-P. Pirnay and A. Buckling (2012). "Effects of Sequential and Simultaneous Applications of Bacteriophages on Populations of Pseudomonas aeruginosa In Vitro and in Wax Moth Larvae." Applied and Environmental Microbiology 78(16): 5646-5652.
- Haney, E.F.; Straus, S.K.; Hancock, R.E.W. Reassessing the Host Defense Peptide Landscape. Front. Chem. 2019, 7, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Haney, E. F., M. J. Trimble, J. T. Cheng, Q. Vallé and R. E. W. Hancock (2018). "Critical Assessment of Methods to Quantify Biofilm Growth and Evaluate Antibiofilm Activity of Host Defence Peptides." Biomolecules 8(2): 29.
- He, Y.; Vines, R.R.; Wattam, A.R.; Abramochkin, G.V.; Dickerman, A.W.; Eckart, J.D.; Sobral, B.W.S. PIML: the Pathogen Information Markup Language. Bioinformatics 2004, 21, 116–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hede, K. Antibiotic resistance: An infectious arms race. Nature 2014, 509, S2–S3. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hjort, K., E. Fermér, P. C. Tang and D. I. Andersson (2022). "Antibiotic Minimal Selective Concentrations and Fitness Costs during Biofilm and Planktonic Growth." mBio 13(3): e0144722.
- Hudis, C.A. Trastuzumab — Mechanism of Action and Use in Clinical Practice. New Engl. J. Med. 2007, 357, 39–51. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jochumsen, N.; Marvig, R.L.; Damkiær, S.; Jensen, R.L.; Paulander, W.; Molin, S.; Jelsbak, L.; Folkesson, A. The evolution of antimicrobial peptide resistance in Pseudomonas aeruginosa is shaped by strong epistatic interactions. Nat. Commun. 2016, 7, 13002. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, J.; Nielsen, K. Companion Diagnostics: From Biomarkers to Diagnostics. 2017, 530–545. [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, J.T. Clinical application of companion diagnostics. Trends Mol. Med. 2015, 21, 405–407. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, J.T. Companion and Complementary Diagnostics: Clinical and Regulatory Perspectives. Trends Cancer 2016, 2, 706–712. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, J.T. Companion and complementary diagnostics: an important treatment decision tool in precision medicine. Expert Rev. Mol. Diagn. 2020, 20, 557–559. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jørgensen, J.; Nielsen, K. Companion Diagnostics: From Biomarkers to Diagnostics. 2017, 530–545. [CrossRef]
- Kadioglu, O.; Malczyk, A.H.; Greten, H.J.; Efferth, T. Aptamers as a novel tool for diagnostics and therapy. Investig. New Drugs 2015, 33, 513–520. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaper, J. B., J. P. Nataro and H. L. Mobley (2004). "Pathogenic Escherichia coli." Nat Rev Microbiol 2(2): 123-140.
- Kaplon, H.; Reichert, J.M. Antibodies to watch in 2019. mAbs 2018, 11, 219–238. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Karlsson, R., L. Gonzales-Siles, F. Boulund, L. Svensson-Stadler, S. Skovbjerg, A. Karlsson, M. Davidson, S. Hulth, E. Kristiansson and E. R. B. Moore (2015). "Proteotyping: Proteomic characterization, classification and identification of microorganisms – A prospectus." Systematic and Applied Microbiology 38(4): 246-257.
- Kaufmann, M.; Keppens, M.; Blair, E.D.; Unertl, K.M.; Field, J.R.; Price, L.; Peterson, J.F.; Jagga, Z.; Gupta, D.; Pirastu, N.; et al. A perspective analysis: companion diagnostics: an evolving paradigm in 21st century healthcare. Pers. Med. 2015, 12, 389–402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaur, H.; Bruno, J.G.; Kumar, A.; Sharma, T.K. Aptamers in the Therapeutics and Diagnostics Pipelines. Theranostics 2018, 8, 4016–4032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Keefe, A. D. and S. T. Cload (2008). "SELEX with modified nucleotides." Curr Opin Chem Biol 12(4): 448-456.
- Kiga, K.; Tan, X.-E.; Ibarra-Chávez, R.; Watanabe, S.; Aiba, Y.; Sato’o, Y.; Li, F.-Y.; Sasahara, T.; Cui, B.; Kawauchi, M.; et al. Development of CRISPR-Cas13a-based antimicrobials capable of sequence-specific killing of target bacteria. Nat. Commun. 2020, 11, 1–11. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Hatt, J.K.; Weigand, M.R.; Krishnan, R.; Pavlostathis, S.G.; Konstantinidis, K.T. Genomic and Transcriptomic Insights into How Bacteria Withstand High Concentrations of Benzalkonium Chloride Biocides. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kim, M.; Jo, Y.; Hwang, Y.J.; Hong, H.W.; Hong, S.S.; Park, K.; Myung, H. Phage-Antibiotic Synergy via Delayed Lysis. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2018, 84. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kobayashi, S.D.; Porter, A.R.; Freedman, B.; Pandey, R.; Chen, L.; Kreiswirth, B.N.; DeLeo, F.R. Antibody-Mediated Killing of Carbapenem-Resistant ST258 Klebsiella pneumoniae by Human Neutrophils. mBio 2018, 9, e00297–18. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kolovskaya, O.S.; Savitskaya, A.G.; Zamay, T.N.; Reshetneva, I.T.; Zamay, G.S.; Erkaev, E.N.; Wang, X.; Wehbe, M.; Salmina, A.B.; Perianova, O.V.; et al. Development of Bacteriostatic DNA Aptamers for Salmonella. J. Med. Chem. 2013, 56, 1564–1572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kouyos, R.D.; Wiesch, P.A.Z.; Bonhoeffer, S. On Being the Right Size: The Impact of Population Size and Stochastic Effects on the Evolution of Drug Resistance in Hospitals and the Community. PLOS Pathog. 2011, 7, e1001334. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kovacevic, K.D.; Gilbert, J.C.; Jilma, B. Pharmacokinetics, pharmacodynamics and safety of aptamers. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2018, 134, 36–50. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kubicek-Sutherland, J.Z.; Heithoff, D.M.; Ersoy, S.C.; Shimp, W.R.; House, J.K.; Marth, J.D.; Smith, J.W.; Mahan, M.J. Host-dependent Induction of Transient Antibiotic Resistance: A Prelude to Treatment Failure. EBioMedicine 2015, 2, 1169–1178. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lang, B.J.; Aaron, S.D.; Ferris, W.; Hebert, P.C.; MacDONALD, N.E. Multiple Combination Bactericidal Antibiotic Testing for Patients with Cystic Fibrosis Infected with Multiresistant Strains of Pseudomonas aeruginosa. Am. J. Respir. Crit. Care Med. 2000, 162, 2241–2245. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Langdon, A.; Crook, N.; Dantas, G. The effects of antibiotics on the microbiome throughout development and alternative approaches for therapeutic modulation. Genome Med. 2016, 8, 1–16. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lee, J.H.; Yigit, M.V.; Mazumdar, D.; Lu, Y. Molecular diagnostic and drug delivery agents based on aptamer-nanomaterial conjugates. Adv. Drug Deliv. Rev. 2010, 62, 592–605. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levin, B.R.; Bull, J.J. Population and evolutionary dynamics of phage therapy. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2004, 2, 166–173. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Levy, G. Pharmacologic target-mediated drug disposition. Clin. Pharmacol. Ther. 1994, 56, 248–252. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lijuan, C.; Xing, Y.; Minxi, W.; Wenkai, L.; Le, D. Development of an aptamer-ampicillin conjugate for treating biofilms. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2017, 483, 847–854. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- López, Y., M. Tato, D. Gargallo-Viola, R. Cantón, J. Vila and I. Zsolt (2019). "Mutant prevention concentration of ozenoxacin for quinolone-susceptible or -resistant Staphylococcus aureus and Staphylococcus epidermidis." PLOS ONE 14(10): e0223326.
- Louie, B., P. Mork, F. Martin-Sanchez, A. Halevy and P. Tarczy-Hornoch (2007). "Data integration and genomic medicine." Journal of Biomedical Informatics 40(1): 5-16.
- Luong, T., A. -C. Salabarria and D. R. Roach (2020). "Phage Therapy in the Resistance Era: Where Do We Stand and Where Are We Going?" Clinical Therapeutics 42(9): 1659-1680.
- Macia; Rojo-Molinero, E. ; Oliver, A. Antimicrobial susceptibility testing in biofilm-growing bacteria. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. 2014, 20, 981–990. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Magana, M.; Pushpanathan, M.; Santos, A.L.; Leanse, L.; Fernandez, M.; Ioannidis, A.; Giulianotti, M.A.; Apidianakis, Y.; Bradfute, S.; Ferguson, A.L.; et al. The value of antimicrobial peptides in the age of resistance. Lancet Infect. Dis. 2020, 20, e216–e230. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Makarova, O.; Johnston, P.; Rodriguez-Rojas, A.; El Shazely, B.; Morales, J.M.; Rolff, J. Genomics of experimental adaptation of Staphylococcus aureus to a natural combination of insect antimicrobial peptides. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 1–8. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Martinez, J. L. and F. Baquero (2000). "Mutation Frequencies and Antibiotic Resistance." Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 44(7): 1771-1777.
- McClure, N.S.; Day, T.; S. , M.N.; Troy, D.; G, Y.; D, B.; R, R.; J, R.; D, K.; A, R.; et al. A theoretical examination of the relative importance of evolution management and drug development for managing resistance. Proc. R. Soc. B: Boil. Sci. 2014, 281, 20141861. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mei, Q.; Ye, Y.; Zhu, Y.-L.; Cheng, J.; Chang, X.; Liu, Y.-Y.; Li, H.-R.; Li, J.-B. Testing the mutant selection window hypothesis in vitro and in vivo with Staphylococcus aureus exposed to fosfomycin. Eur. J. Clin. Microbiol. Infect. Dis. 2014, 34, 737–744. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Meinert, E., A. Alturkistani, D. Luo, K. Foley, C. Lam, A. Carter, D. Seyfried, J. Car and D. Brindley (2019). Chapter 25 - Current Status and Future Direction of Companion Diagnostics. Companion and Complementary Diagnostics. J. T. Jørgensen, Academic Press: 455-472.
- Mercer, D. K., C. S. Stewart, L. Miller, J. Robertson, V. M. S. Duncan and D. A. O’Neil (2019). "Improved Methods for Assessing Therapeutic Potential of Antifungal Agents against Dermatophytes and Their Application in the Development of NP213, a Novel Onychomycosis Therapy Candidate." Antimicrobial Agents and Chemotherapy 63(5): e02117-02118.
- Milne, C. P., J. P. Cohen and R. Chakravarthy (2015). "Market watch: Where is personalized medicine in industry heading?" Nat Rev Drug Discov 14(12): 812-813.
- Mokhtarzadeh, A.; Alibakhshi, A.; Hashemi, M.; Hejazi, M.; Hosseini, V.; de la Guardia, M.; Ramezani, M. Biodegradable nano-polymers as delivery vehicles for therapeutic small non-coding ribonucleic acids. J. Control. Release 2016, 245, 116–126. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morgan, D.J.; Malani, P.; Diekema, D.J. Diagnostic Stewardship—Leveraging the Laboratory to Improve Antimicrobial Use. JAMA 2017, 318, 607–608. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Motley, M.P.; Banerjee, K.; Fries, B.C. Monoclonal antibody-based therapies for bacterial infections. Curr. Opin. Infect. Dis. 2019, 32, 210–216. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, J.W.; A Vinks, A. Pharmacokinetic/Pharmacodynamic Modelling of Antibacterials In Vitro and In Vivo Using Bacterial Growth and Kill Kinetics. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 44, 201–210. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mouton, J.W.; A Vinks, A. Relationship Between Minimum Inhibitory Concentration and Stationary Concentration Revisited. Clin. Pharmacokinet. 2005, 44, 767–768. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mueller, M.; de la Peña, A.; Derendorf, H. Issues in Pharmacokinetics and Pharmacodynamics of Anti-Infective Agents: Kill Curves versus MIC. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 369–377. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nadon, C.; Van Walle, I.; Gerner-Smidt, P.; Campos, J.; Chinen, I.; Concepcion-Acevedo, J.; Gilpin, B.; Smith, A.M.; Kam, K.M.; Perez, E.; et al. PulseNet International: Vision for the implementation of whole genome sequencing (WGS) for global food-borne disease surveillance. Wkly. releases (1997–2007) 2017, 22. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nagy, E., G. Nagy, C. A. Power, A. Badarau and V. Szijártó (2017). Anti-bacterial Monoclonal Antibodies. Recombinant Antibodies for Infectious Diseases. T. S. Lim. Cham, Springer International Publishing: 119-153.
- Nahm, F.S. Receiver operating characteristic curve: overview and practical use for clinicians. Korean J. Anesthesiol. 2022, 75, 25–36. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nang, S. C., Y. -W. Lin, A. Petrovic Fabijan, R. Y. K. Chang, G. G. Rao, J. Iredell, H.-K. Chan and J. Li "Pharmacokinetics/pharmacodynamics of phage therapy: a major hurdle to clinical translation." Clinical Microbiology and Infection.
- Negri, M. C., M. Lipsitch, J. Blázquez, B. R. Levin and F. Baquero (2000). "Concentration-dependent selection of small phenotypic differences in TEM beta-lactamase-mediated antibiotic resistance." Antimicrob Agents Chemother 44(9): 2485-2491.
- Nizet, V. (2017). "The Accidental Orthodoxy of Drs. Mueller and Hinton." EBioMedicine 22: 26-27.
- O'Toole, G. A. (2011). "Microtiter dish biofilm formation assay." J Vis Exp(47).
- Ong, P.Y.; Ohtake, T.; Brandt, C.; Strickland, I.; Boguniewicz, M.; Ganz, T.; Gallo, R.L.; Leung, D.Y. Endogenous Antimicrobial Peptides and Skin Infections in Atopic Dermatitis. New Engl. J. Med. 2002, 347, 1151–1160. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Orchard, S., H. Hermjakob, R. K. Julian Jr., K. Runte, D. Sherman, J. Wojcik, W. Zhu and R. Apweiler (2004). "Common interchange standards for proteomics data: Public availability of tools and schema. Report on the Proteomic Standards Initiative Workshop, 2nd Annual HUPO Congress, Montreal, Canada, 8–11th 03." PROTEOMICS 4(2): 490-491. 20 October.
- Güngör). .(.; Gürkan, P.; Özçelik, B.; Oyardı,. Synthesis and antimicrobial activities of new higher amino acid Schiff base derivatives of 6-aminopenicillanic acid and 7-aminocephalosporanic acid. J. Mol. Struct. 2016, 1106, 181–191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Palliyil, S.; Downham, C.; Broadbent, I.; Charlton, K.; Porter, A.J. High-Sensitivity Monoclonal Antibodies Specific for Homoserine Lactones Protect Mice from Lethal Pseudomonas aeruginosa Infections. Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 2014, 80, 462–469. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Payne, R.J.; Jansen, V.A. Understanding Bacteriophage Therapy as a Density-dependent Kinetic Process. J. Theor. Biol. 2001, 208, 37–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pegram, A. and J. Bloomfield (2015). "Infection prevention and control." Nurs Stand 29(29): 37-42.
- Fabijan, A.P.; Lin, R.C.; Ho, J.; Maddocks, S.; Zakour, N.L.b.; Iredell, J.R. Safety of bacteriophage therapy in severe Staphylococcus aureus infection. Nat. Microbiol. 2020, 5, 465–472. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Picard, F.J.; Bergeron, M.G. Rapid molecular theranostics in infectious diseases. Drug Discov. Today 2002, 7, 1092–1101. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qiao, J.; Meng, X.; Sun, Y.; Li, Q.; Zhao, R.; Zhang, Y.; Wang, J.; Yi, Z. Aptamer-based fluorometric assay for direct identification of methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus from clinical samples. J. Microbiol. Methods 2018, 153, 92–98. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramadan, A.A. Bacterial typing methods from past to present: A comprehensive overview. Gene Rep. 2022, 29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Regoes, R.R.; Wiuff, C.; Zappala, R.M.; Garner, K.N.; Baquero, F.; Levin, B.R. Pharmacodynamic Functions: a Multiparameter Approach to the Design of Antibiotic Treatment Regimens. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2004, 48, 3670–3676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rex, J. H. and M. A. Pfaller (2002). "Has Antifungal Susceptibility Testing Come of Age?" Clinical Infectious Diseases 35(8): 982-989.
- Ribeiro da Cunha, B., L. Fonseca and C. Calado (2019). "Antibiotic Discovery: Where Have We Come from, Where Do We Go?" Antibiotics 8: 45.
- Rodriguez-Gonzalez, R.A.; Leung, C.Y.; Chan, B.K.; Turner, P.E.; Weitz, J.S. Quantitative Models of Phage-Antibiotic Combination Therapy. mSystems 2020, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rodríguez-Rojas, A.; Baeder, D.Y.; Johnston, P.; Regoes, R.R.; Rolff, J. Bacteria primed by antimicrobial peptides develop tolerance and persist. PLOS Pathog. 2021, 17, e1009443. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rollenske, T., V. Szijarto, J. Lukasiewicz, L. M. Guachalla, K. Stojkovic, K. Hartl, L. Stulik, S. Kocher, F. Lasitschka, M. Al-Saeedi, J. Schröder-Braunstein, M. von Frankenberg, G. Gaebelein, P. Hoffmann, S. Klein, K. Heeg, E. Nagy, G. Nagy and H. Wardemann (2018). "Cross-specificity of protective human antibodies against Klebsiella pneumoniae LPS O-antigen." Nat Immunol 19(6): 617-624.
- Russell, T.M.; Green, L.S.; Rice, T.; Kruh-Garcia, N.A.; Dobos, K.; De Groote, M.A.; Hraha, T.; Sterling, D.G.; Janjic, N.; Ochsner, U.A. Potential of High-Affinity, Slow Off-Rate Modified Aptamer Reagents for Mycobacterium tuberculosis Proteins as Tools for Infection Models and Diagnostic Applications. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2017, 55, 3072–3088. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ryman, J. T. and B. Meibohm (2017). "Pharmacokinetics of Monoclonal Antibodies." CPT Pharmacometrics Syst Pharmacol 6(9): 576-588.
- Sanghera, S.; Orlando, R.; Roberts, T. ECONOMIC EVALUATIONS AND DIAGNOSTIC TESTING: AN ILLUSTRATIVE CASE STUDY APPROACH. Int. J. Technol. Assess. Heal. Care 2013, 29, 53–60. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheerens, H.; Malong, A.; Bassett, K.; Boyd, Z.; Gupta, V.; Harris, J.; Mesick, C.; Simnett, S.; Stevens, H.; Gilbert, H.; et al. Current Status of Companion and Complementary Diagnostics: Strategic Considerations for Development and Launch. Clin. Transl. Sci. 2017, 10, 84–92. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sefah, K.; Shangguan, D.; Xiong, X.; O'Donoghue, M.B.; Tan, W. Development of DNA aptamers using Cell-SELEX. Nat. Protoc. 2010, 5, 1169–1185. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shatila, F.; Yaşa. ; Yalçın, H.T. Inhibition of Salmonella enteritidis biofilms by Salmonella invasion protein-targeting aptamer. Biotechnol. Lett. 2020, 42, 1963–1974. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- imundić, A. M. (2009). "Measures of Diagnostic Accuracy: Basic Definitions." Ejifcc 19(4): 203-211.
- Stevens, D. L., Y. Ma, D. B. Salmi, E. McIndoo, R. J. Wallace and A. E. Bryant (2007). "Impact of antibiotics on expression of virulence-associated exotoxin genes in methicillin-sensitive and methicillin-resistant Staphylococcus aureus." J Infect Dis 195(2): 202-211.
- Stoltenburg, R., P. Krafčiková, V. Víglaský and B. Strehlitz (2016). "G-quadruplex aptamer targeting Protein A and its capability to detect Staphylococcus aureus demonstrated by ELONA." Sci Rep 6: 33812.
- Su, M.; Satola, S.W.; Read, T.D. Genome-Based Prediction of Bacterial Antibiotic Resistance. J. Clin. Microbiol. 2019, 57, 1–15. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sun, D.; Rubio-Aparicio, D.; Nelson, K.; Dudley, M.N.; Lomovskaya, O. Meropenem-Vaborbactam Resistance Selection, Resistance Prevention, and Molecular Mechanisms in Mutants of KPC-Producing Klebsiella pneumoniae. Antimicrob. Agents Chemother. 2017, 61. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tagliaferri, T.L.; Guimarães, N.R.; Pereira, M.d.P.M.; Vilela, L.F.F.; Horz, H.-P.; dos Santos, S.G.; Mendes, T.A.d.O. Exploring the Potential of CRISPR-Cas9 Under Challenging Conditions: Facing High-Copy Plasmids and Counteracting Beta-Lactam Resistance in Clinical Strains of Enterobacteriaceae. Front. Microbiol. 2020, 11, 578. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Toh, S.Y.; Citartan, M.; Gopinath, S.C.; Tang, T.-H. Aptamers as a replacement for antibodies in enzyme-linked immunosorbent assay. Biosens. Bioelectron. 2015, 64, 392–403. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres-Barceló, C.; Hochberg, M.E. Evolutionary Rationale for Phages as Complements of Antibiotics. Trends Microbiol. 2016, 24, 249–256. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Torres, M.D.T.; Sothiselvam, S.; Lu, T.K.; De La Fuente-Nunez, C. Peptide Design Principles for Antimicrobial Applications. J. Mol. Biol. 2019, 431, 3547–3567. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Trubenová, B.; Roizman, D.; Rolff, J.; Regoes, R.R. Modeling Polygenic Antibiotic Resistance Evolution in Biofilms. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 916035. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tsakiroglou, M.; Evans, A.; Pirmohamed, M. Leveraging transcriptomics for precision diagnosis: Lessons learned from cancer and sepsis. Front. Genet. 2023, 14, 1100352. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Turner, K.H.; Wessel, A.K.; Palmer, G.C.; Murray, J.L.; Whiteley, M. Essential genome of Pseudomonas aeruginosa in cystic fibrosis sputum. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2015, 112, 4110–4115. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Unckless, R. L. and B. P. Lazzaro (2016). "The potential for adaptive maintenance of diversity in insect antimicrobial peptides." Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society B: Biological Sciences 371(1695): 20150291.
- Varshney, A.K.; Kuzmicheva, G.A.; Bowling, R.A.; Sunley, K.M.; Bowling, R.A., Jr.; Kwan, T.-Y.; Mays, H.R.; Rambhadran, A.; Zhang, Y.; Martin, R.L.; et al. A natural human monoclonal antibody targeting Staphylococcus Protein A protects against Staphylococcus aureus bacteremia. PLoS ONE 2018, 13, e0190537. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visan, L.; Rouleau, N.; Proust, E.; Peyrot, L.; Donadieu, A.; Ochs, M. Antibodies to PcpA and PhtD protect mice against Streptococcus pneumoniae by a macrophage- and complement-dependent mechanism. Hum. Vaccines Immunother. 2017, 14, 489–494. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Visnapuu, A.; Van der Gucht, M.; Wagemans, J.; Lavigne, R. Deconstructing the Phage–Bacterial Biofilm Interaction as a Basis to Establish New Antibiofilm Strategies. Viruses 2022, 14, 1057. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vivekananda, J.; Salgado, C.; Millenbaugh, N.J. DNA aptamers as a novel approach to neutralize Staphylococcus aureus α-toxin. Biochem. Biophys. Res. Commun. 2014, 444, 433–438. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vogel, C.; Marcotte, E.M. Insights into the regulation of protein abundance from proteomic and transcriptomic analyses. Nat. Rev. Genet. 2012, 13, 227–232. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang-Lin, S.X.; Balthasar, J.P. Pharmacokinetic and Pharmacodynamic Considerations for the Use of Monoclonal Antibodies in the Treatment of Bacterial Infections. Antibodies 2018, 7, 5. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, H.-Y.; Hsieh, T.-T.; Chung, C.-R.; Chang, H.-C.; Horng, J.-T.; Lu, J.-J.; Huang, J.-H. Efficiently Predicting Vancomycin Resistance of Enterococcus Faecium From MALDI-TOF MS Spectra Using a Deep Learning-Based Approach. Front. Microbiol. 2022, 13, 821233. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Mao, B.; Wu, M.; Liang, J.; Deng, L. Influence of aptamer-targeted antibiofilm agents for treatment of Pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilms. Antonie van Leeuwenhoek 2017, 111, 199–208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Whaley, K.; Schwaeble, W. Complement and Complement Deficiencies. Semin. Liver Dis. 1997, 17, 297–310. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- White, R.R.; Shan, S.; Rusconi, C.P.; Shetty, G.; Dewhirst, M.W.; Kontos, C.D.; Sullenger, B.A. Inhibition of rat corneal angiogenesis by a nuclease-resistant RNA aptamer specific for angiopoietin-2. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. 2003, 100, 5028–5033. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wollein Waldetoft, K., J. Gurney, J. Lachance, P. A. Hoskisson and S. P. Brown (2019). "Evolving Antibiotics against Resistance: a Potential Platform for Natural Product Development?" mBio 10(6).
- Xiang, D.; Zheng, C.; Zhou, S.-F.; Qiao, S.; Tran, P.H.-L.; Pu, C.; Li, Y.; Kong, L.; Kouzani, A.Z.; Lin, J.; et al. Superior Performance of Aptamer in Tumor Penetration over Antibody: Implication of Aptamer-Based Theranostics in Solid Tumors. Theranostics 2015, 5, 1083–1097. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xiong, Y.; Zhang, J.; Yang, Z.; Mou, Q.; Ma, Y.; Xiong, Y.; Lu, Y. Functional DNA Regulated CRISPR-Cas12a Sensors for Point-of-Care Diagnostics of Non-Nucleic-Acid Targets. J. Am. Chem. Soc. 2019, 142, 207–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Xu, L.; Dai, Q.; Shi, Z.; Liu, X.; Gao, L.; Wang, Z.; Zhu, X.; Li, Z. Accurate MRSA identification through dual-functional aptamer and CRISPR-Cas12a assisted rolling circle amplification. J. Microbiol. Methods 2020, 173, 105917. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yu, G., D. Y. Baeder, R. R. Regoes and J. Rolff (2016). "Combination effects of antimicrobial peptides." Antimicrobial agents and chemotherapy 60(3): 1717-1724.
- Yu, G.; Baeder, D.Y.; Regoes, R.R.; Rolff, J. Predicting drug resistance evolution: insights from antimicrobial peptides and antibiotics. Proc. R. Soc. B Boil. Sci. 2018, 285, 20172687. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, R.; Xu, W.; Shao, S.; Wang, Q. Gene Silencing Through CRISPR Interference in Bacteria: Current Advances and Future Prospects. Front. Microbiol. 2021, 12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhao, X.; Drlica, K. Restricting the Selection of Antibiotic-Resistant Mutants: A General Strategy Derived from Fluoroquinolone Studies. Clin. Infect. Dis. 2001, 33, S147–S156. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, G.; Wang, Y.-S.; Peng, H.; Li, S.-J.; Sun, T.-L.; Shi, Q.-S.; Garcia-Ojalvo, J.; Xie, X.-B. Proteomic signatures of synergistic interactions in antimicrobials. J. Proteom. 2023, 270, 104743. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhou, J.; Rossi, J. Aptamers as targeted therapeutics: Current potential and challenges. Nat. Rev. Drug Discov. 2017, 16, 181–202. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).




