Submitted:
04 July 2023
Posted:
04 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
1. Introduction
2. Materials and Methods
2.1. Materials
2.2. Biosorbents characterization
2.3. Biosorption experiments
2.4. Modeling of experimental data
3. Results and discussion
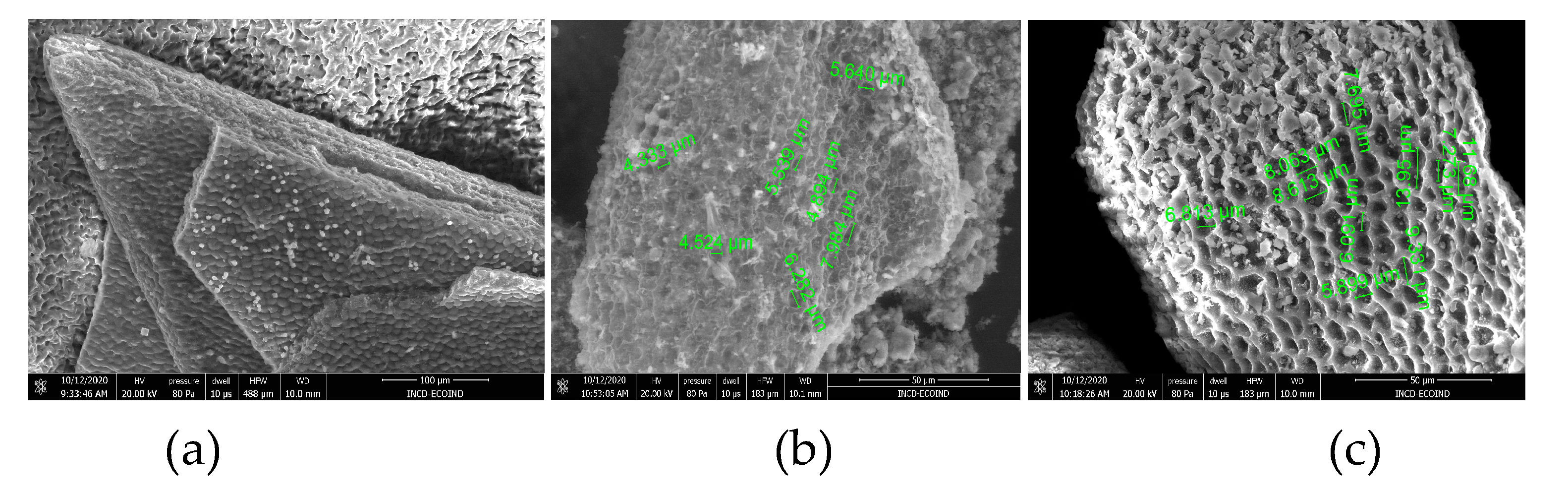
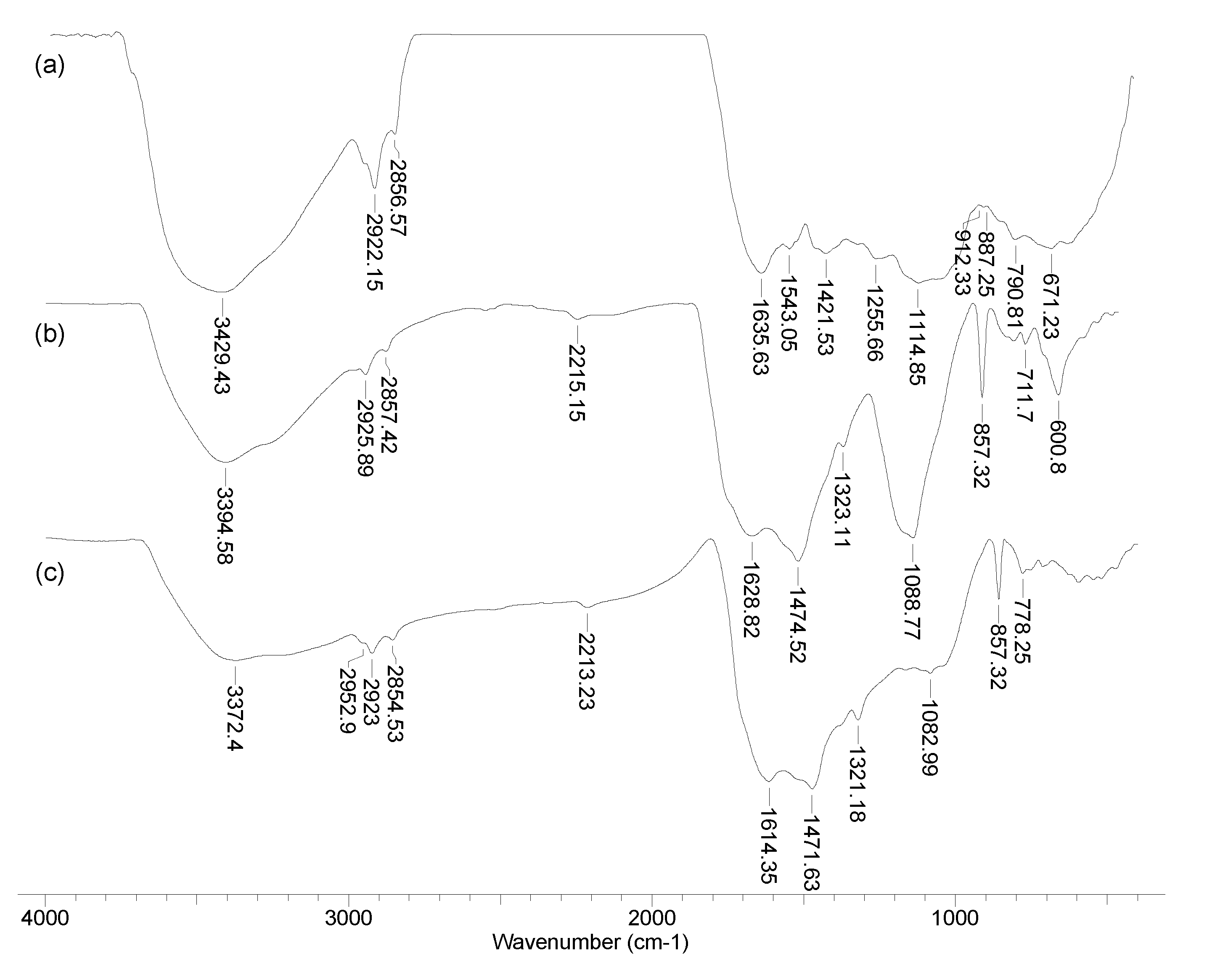
3.1. Structural particularities of the biosorbents
3.2. Kinetics of Cu(II) ions biosorption
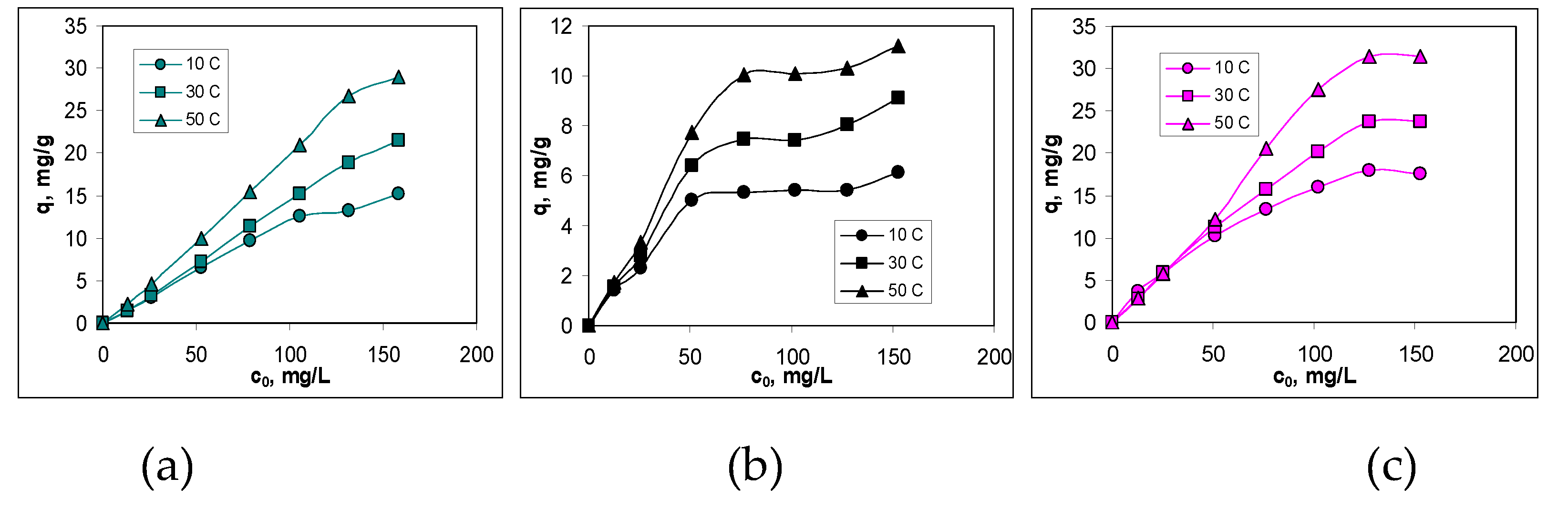
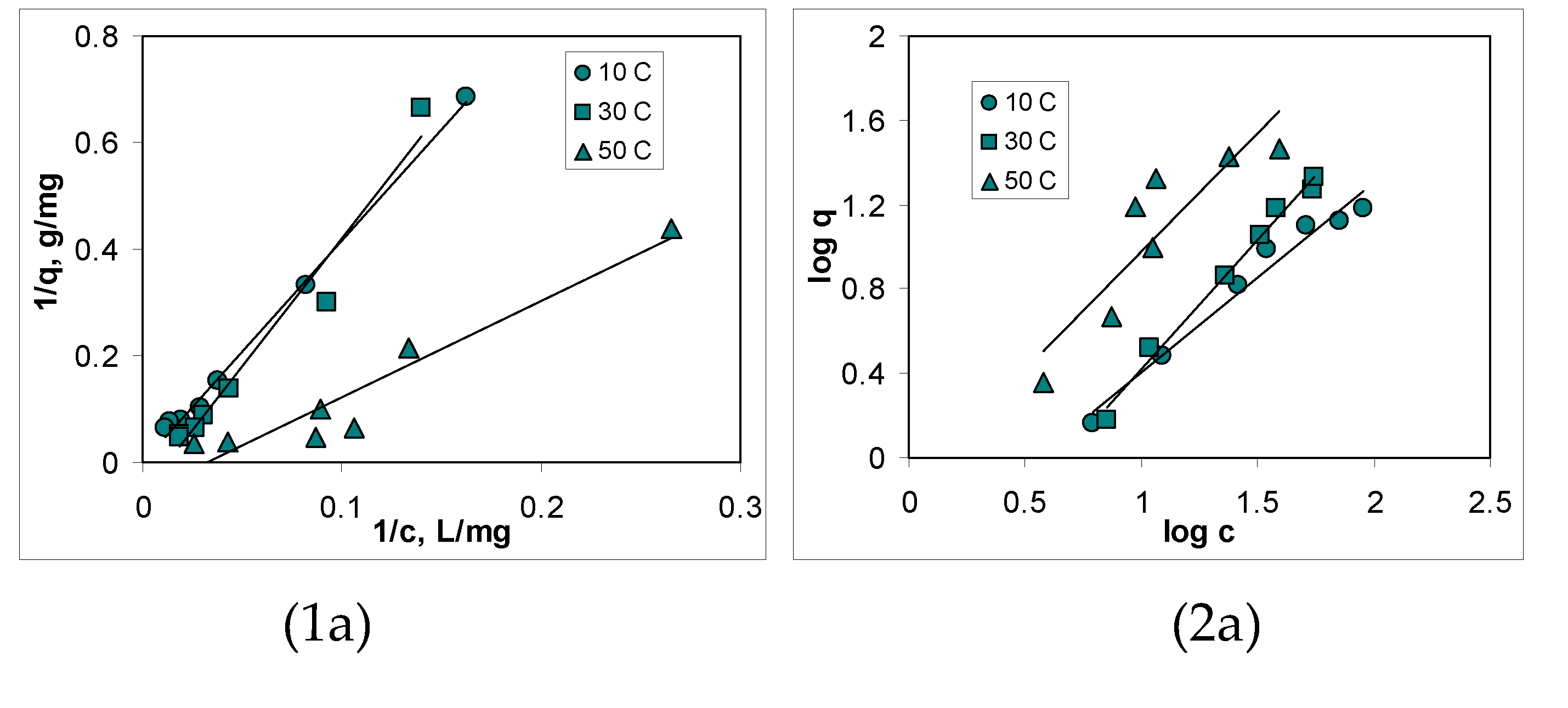
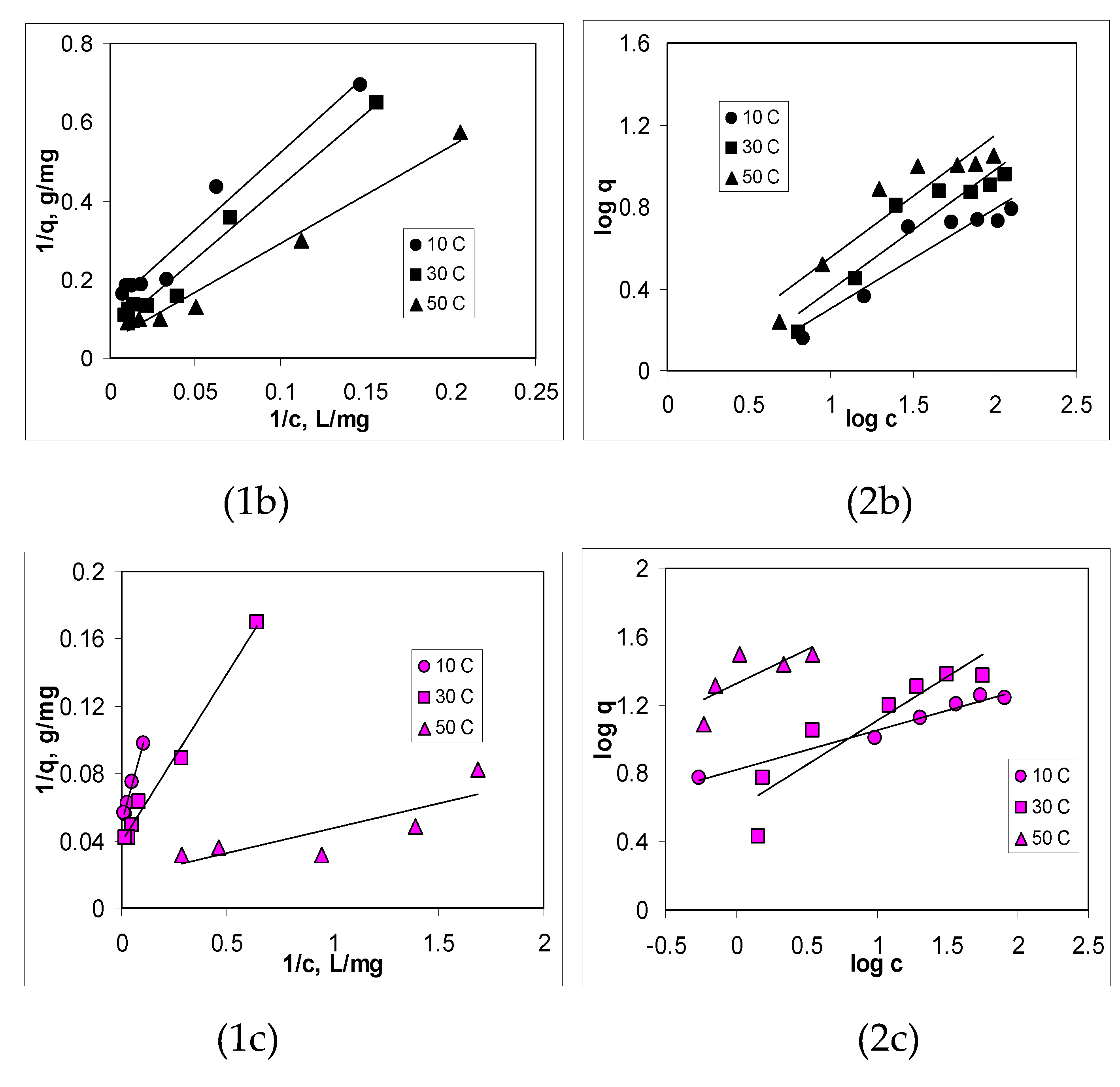
3.3. Isotherms of Cu(II) ions biosorption
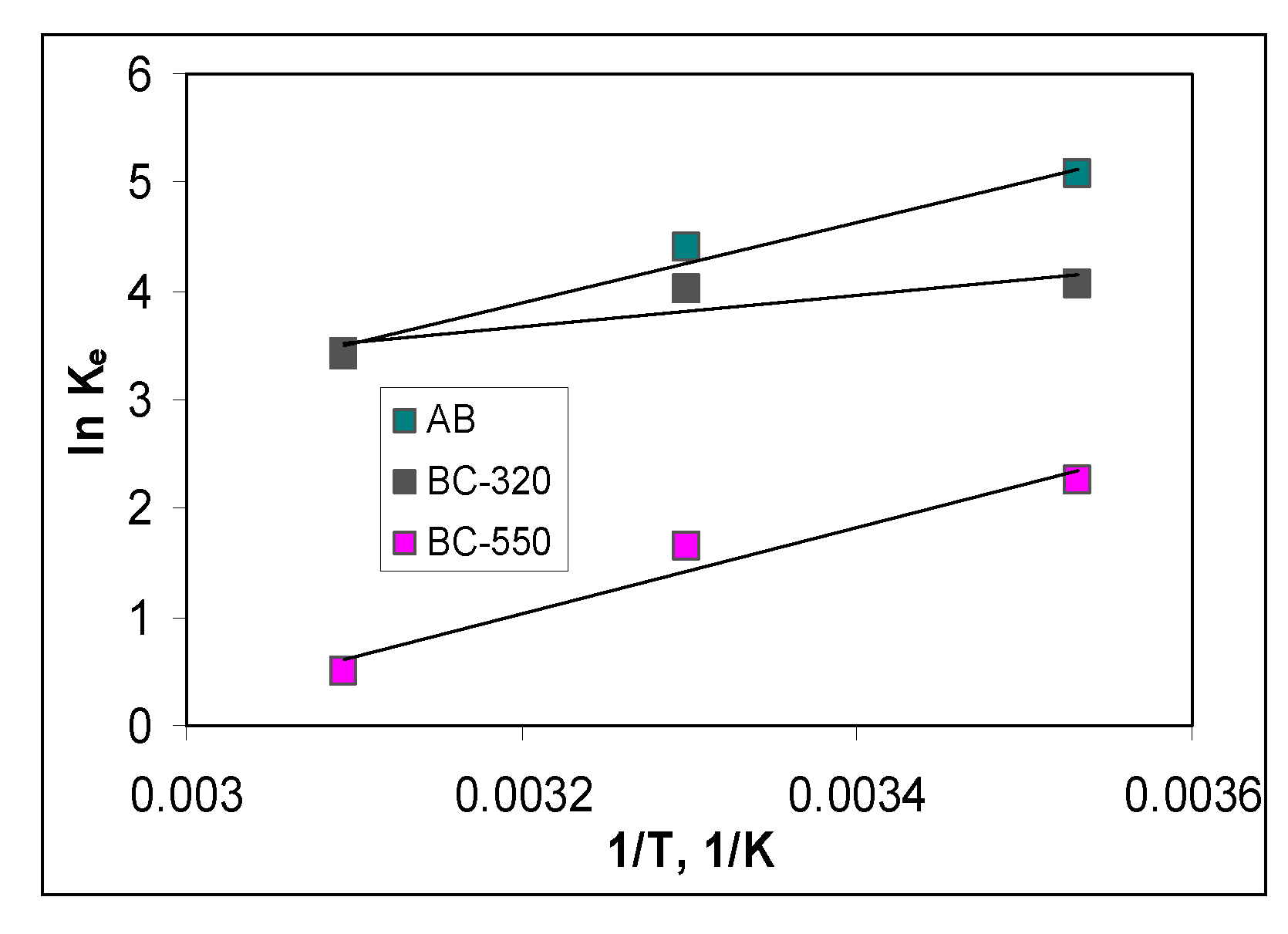
3.4. Thermodynamic parameters of Cu(II) ions biosorption
5. Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Data Availability Statement
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Sarode, S.; Upadhyay, P.; Khosa, M.A.; Mak, T.; Shakir, A.; Song, S.; Ullah, A. Overview of wastewater treatment methods with special focus on biopolymer chitin-chitosan. Int. J. Biol. Macromol. 2019, 121, 1086–1100. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E. Advantages and disadvantages of techniques used for wastewater treatment. Environm. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 145–155. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Nowicka, B. Heavy metal–induced stress in eukaryotic algae—mechanisms of heavy metal toxicity and tolerance with particular emphasis on oxidative stress in exposed cells and the role of antioxidant response. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2022, 29, 16860–16911. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ackova, D.G. Heavy metals and their general toxicity on plants. Plant Sci. Today 2018, 5, 15–19. [Google Scholar]
- Behera, M.; Nayak, J.; Banerjee, S.; Chakrabortty, S.; Tripathy, S.K. A review on the treatment of textile industry waste effluents towards the development of efficient mitigation strategy: An integrated system design approach. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2021, 105277. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Varjani, S.; Joshi, R.; Srivastava, V.K.; Ngo, H.H.; Guo, W. Treatment of wastewater from petroleum industry: current practices and perspectives. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2020, 27, 27172–27180. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bashir, A.; Malik, L.A.; Ahad, S.; Manzoor, T.; Bhat, M.A.; Dar, G.N.; Pandith, A.H. Removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous system by ion-exchange and biosorption methods. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 729–754. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Saleh, T.A.; Mustaqeem, M.; Khaled, M. Water treatment technologies in removing heavy metal ions from wastewater: A review. Environ. Nanotechn. Monit. Manag. 2022, 17, 100617. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Vijayaraghavan, K.; Balasubramanian, R. Is biosorption suitable for decontamination of metal-bearing wastewaters? A critical review on the state-of-the-art of biosorption processes and future directions. J. Environ. Manag. 2015, 160, 283–296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Crini, G.; Lichtfouse, E.; Wilson, L.D.; Morin-Crini, N. Conventional and non-conventional adsorbents for wastewater treatment. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 195–213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cheng, S.Y.; Show, P.L.; Lau, B.F.; Chang, J.S.; Ling, T.C. New Prospects for Modified Algae in Heavy Metal Adsorption. Trends Biotechnol., 2019, 37, 1255–1268. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- El-Sayed, S.; Hyun-Seog, R.; Subhabrata, D.; Moonis, A.K.; Abou-Shanab, R.A.I.; Chang, S.W.; Jeon, B.H. Algae as a green technology for heavy metals removal from various wastewater. World J. Microbiol. Biotechnol. 2019, 35, 75–94. [Google Scholar]
- Fawzy, M.A. Biosorption of copper ions from aqueous solution by Codium vermilara: Optimization, kinetic, isotherm and thermodynamic studies. Adv. Power Technol. 2020, 31, 3724–3735. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Li, R.; Zhang, T.; Zhong, H.; Song, W.; Zhou, Y.; Yin, X. Bioadsorbents from algae residues for heavy metal ions adsorption: chemical modification, adsorption behaviour and mechanism. Environ. Technol. 2021, 42, 3132–3143. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramesh, B.; Saravanan, A.; Senthil Kumar, P.; Yaashikaa, P.R.; Thamarai, P.; Shaji, A.; Rangasamy, G. A review on algae biosorption for the removal of hazardous pollutants from wastewater: Limiting factors, prospects and recommendations. Environ. Poll. 2023, 327, 121572. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jayakumar, V.; Govindaradjane, S.; Rajamohan, N.; Rajasimman, M. Biosorption potential of brown algae, Sargassum polycystum, for the removal of toxic metals, cadmium and zinc. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2022, 29, 41909–41922. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dulla, J.B.; Tamana, M.R.; Boddu, S.; Pulipati, K.; Srirama, K. Biosorption of copper(II) onto spent biomass of Gelidiella acerosa (brown marine algae): optimization and kinetic studies. Appl. Water Sci. 2020, 10, 56–66. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liu, Z.; Xu, Z.; Xu, L.; Buyong, F.; Chay, T.C.; Cai, Y.; Hu, B.; Zhu, Y.; Wang, X. Modifed biochar: synthesis and mechanism for removal of environmental heavy metals. Carbon Res. 2022, 1, 8–29. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tomczyk, A.; Sokołowska, Z.; Bogut, P. Biochar physicochemical properties: pyrolysis temperature and feedstock kind effects. Rev. Environ. Sci. Biotechnol. 2020, 19, 191–215. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khan, A.A.; Gul, J.; Naqvi, S.R.; Ali, J.; Farooq, W.; Liaqat, R.; Al Mohamadi, H.; Stepanec, L.; Juchelkov, D. Recent progress in microalgae-derived biochar for the treatment of textile industry wastewater. Chemosphere 2022, 306, 135565. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gupta, S.; Sireesha, S.; Sreedhar, I.; Patel, C.M.; Anitha, K.L. Latest trends in heavy metal removal from wastewater by biochar based sorbents. J. Water. Proc. Eng. 2020, 38, 101561. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, A.; Sharma, R.; Pant, D.; Malaviya, P. Engineered algal biochar for contaminant remediation and electrochemical applications. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 774, 145676. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Khandgave, S.S.; Sreedhar, I. A mini-review on engineered biochars as emerging adsorbents in heavy metal removal. Mat. Today: Proceedings, 2023, 72, 19–26. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wu, J.; Wang, T.; Wang, J.; Zhang, Y.; Pan, W.P. A novel modified method for the efficient removal of Pb and Cd from wastewater by biochar: Enhanced the ion exchange and precipitation capacity. Sci. Total Environ. 2021, 754, 142150. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, S.; Kwak, J.H.; Islam, S.; Naeth, M.A.; El-Din, M.G.; Chang, S.X. Biochar surface complexation and Ni(II), Cu(II), and Cd(II) adsorption in aqueous solutions depend on feedstock type. Sci. Total Environ. 2020, 712, 136538. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Foroutan, R.; Mohammadi, R.; Farjadfard, S.; Esmaeili, H.; Saberi, M.; Sahebi, S.; Dobaradaran, S.; Ramavandi, B. Characteristics and performance of Cd, Ni, and Pb bio-adsorption using Callinectes sapidus biomass: real wastewater treatment. Environ. Sci. Poll. Res. 2019, 26, 6336–6347. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, T.; Da, T.; Ma, Y. Reasonable calculation of the thermodynamic parameters from adsorption equilibrium constant. J. Molec. Liq. 2021, 322, 114980. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Moreira, V.R.; Lebron, Y.A.R.; Freire, S.J.; Santos, L.V.S.; Palladino, F.; Jacob, R.S. Biosorption of copper ions from aqueous solution using Chlorella pyrenoidosa: Optimization, equilibrium and kinetics studies. Microchem. J. 2019, 145, 119–129. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ho, Y.S.; McKay, G. Pseudo-second-order model for sorption processes. Process Biochem. 1999, 34, 451–465. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, J.; Guo, X. Rethinking of the intraparticle diffusion adsorption kinetics model: Interpretation, solving methods and applications. Chemosphere 2022, 309, 136732. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Tan, K.L.; Hameed, B.H. Insight into the adsorption kinetics models for the removal of contaminants from aqueous solutions. J. Taiwan Inst. Chem. Eng. 2017, 74, 25–48. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chong, K.H.; Volesky, B. Description of two-metal biosorption equilibria by Langmuir-type models. Biotechnol. Bioeng. 1995, 47, 451–460. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Rangabhashiyam, S.; Anu, N.; Nandagopal Giri, M.S.; Selvaraju, N. Relevance of isotherm models in biosorption of pollutants by agricultural by-products. J. Environ. Chem. Eng. 2014, 2, 398–414. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ozer, A.; Ozer, D.; Ozer, A. The adsorption of copper (II) ions on dehydrated wheat bran: Determination of the equilibrium and thermodynamic parameter. Process Biochem. 2004, 39, 2183–2191. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lima, E.C.; Gomes, A.A.; Tran, H.N. Comparison of the nonlinear and linear forms of the van't Hoff equation for calculation of adsorption thermodynamic parameters (ΔS° and ΔH°). J. Molec. Liq. 2020, 311, 113315. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Sahmoune, M.N. ; Evaluation of thermodynamic parameters for adsorption of heavy metals by green adsorbents. Environ. Chem. Lett. 2019, 17, 697–704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Dean, J.A. Handbook of Analytical Chemistry, Mc-Grow Hill Inc., New York, USA, 1995.
- Syeda, H.I.; Sultan, I.; Razavi, K.S.; Yap, P.S. Biosorption of heavy metals from aqueous solution by various chemically modified agricultural wastes: A review. J. Water. Proc. Eng. 2022, 46, 102446. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Yang, X.; Wan, Y.; Zheng, Y.; He, F.; Yu, Z.; Huang, J.; Wang, H.; Ok, S.; Jiang, Y.; Gao, B. Surface functional groups of carbon-based adsorbents and their roles in the removal of heavy metals from aqueous solutions: a critical review. Chem. Eng. J. 2019, 366, 608–621. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Menezes, J.M.C.; da Silva Bento, A.M.; de Paula Filho, F.J.; da Costa, J.G.M.; Melo Coutinho, H.D.; Pereira Teixeira, R.N. Kinetic and thermodynamic study of copper (II) IONS biosorption by Caryocar Coriaceum Wittm bark. Sust. Chem. Pharm. 2021, 19, 100364. [Google Scholar]
- Menezes, J.M.C.; da Silva Bento, A.M.; da Silva, J.H.; de Paula Filho, F.J.; da Costa, J.G. M.; Coutinho, H.D.M.; Pereira Teixeira, R.N. Equilibrium, kinetics and thermodynamics of lead (II) adsorption in bioadsorvent composed by Caryocar coriaceum Wittm barks. Chemosphere 2020, 261, 128144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kadiri, L. , Lebkiri, A., Rifi, E.H., Ouass, A., Essaadaoui, Y., Lebkiri, I., Mathematical modeling and thermodynamic study of copper (II) removal from aqueous solution by Coriandrum Sativum seeds. Mediterr. J. Chem. 2019, 7, 478–490. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ciobanu, A.A.; Munteanu, L.; Vasile, G.; Bulgariu, L. Evaluation of the biosorption performance of marine green algae biomass (Ulva lactuca sp. ) in the removal of inorganic pollutants. Bull. I.P.Iasi 2023, 69, 93–104. [Google Scholar]


| Kinetic model | Parameter | AB | BC-320 | BC-550 |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| PFO | R2 | 0.9069 | 0.8331 | 0.8802 |
| qe, mg/g | 1.50 | 2.29 | 1.37 | |
| k1, 1/min | 0.0139 | 0.0142 | 0.0137 | |
| PSO | R2 | 0.9999 | 0.9994 | 0.9998 |
| qe, mg/g | 5.67 | 4.62 | 5.93 | |
| k2, g/mg min | 0.0529 | 0.0299 | 0.0609 | |
| IPD | R21 | 0.9777 | 0.9869 | 0.9046 |
| c1, mg/L | 2.38 | 2.21 | 5.09 | |
| kdiff,1, mg/g min1/2 | 0.5251 | 0.7321 | 0.1852 | |
| R22 | 0.7273 | 0.9068 | 0.9416 | |
| c2, mg/L | 5.27 | 3.44 | 5.81 | |
| kdiff,2, mg/g min1/2 | 0.0201 | 0.0789 | 0.0201 |
| Biosorbent | Parameter | 10 °C | 30 °C | 50 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.9637 | 0.9962 | 0.9879 | |
| AB | qmax, mg/g | 18.46 | 26.98 | 37.18 |
| KL, L/g | 0.0063 | 0.0123 | 0.0323 | |
| R2 | 0.9669 | 0.9791 | 0.9804 | |
| BC-320 | qmax, mg/g | 7.73 | 14.84 | 32.31 |
| KL, L/g | 0.0173 | 0.0182 | 0.0330 | |
| R2 | 0.9874 | 0.9887 | 0.9855 | |
| BC-550 | qmax, mg/g | 20.12 | 25.77 | 55.56 |
| KL, L/g | 0.1056 | 0.1934 | 0.6135 |
| Biosorbent | Parameter | 10 °C | 30 °C | 50 °C |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| R2 | 0.9698 | 0.9879 | 0.7862 | |
| AB | n | 1.90 | 1.81 | 1.12 |
| KF, L/g | 0.3277 | 0.1516 | 0.7409 | |
| R2 | 0.8721 | 0.8877 | 0.8764 | |
| BC-320 | n | 2.07 | 1.69 | 1.68 |
| KF, L/g | 0.6745 | 0.6350 | 0.9084 | |
| R2 | 0.7993 | 0.8470 | 0.8599 | |
| BC-550 | n | 4.31 | 2.94 | 2.51 |
| KF, L/g | 6.6420 | 3.9319 | 2.1101 |
| Biosorbent | 10 °C | 30 °C | 50 °C |
|---|---|---|---|
| AB | 13.73 | 20.07 | 27.66 |
| BC-320 | 5.75 | 11.04 | 24.03 |
| BC-550 | 14.97 | 22.17 | 41.33 |
| Biosorbent | Temperature, °C | ΔG0, kJ/mol | ΔH0, kJ/mol | ΔS0, kJ/mol K |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 10 | -11.93 | |||
| AB | 30 | -11.09 | 11.47 | 0.96 |
| 50 | -9.22 | |||
| 10 | -10.09 | |||
| BC-320 | 30 | -9.55 | 10.02 | 1.16 |
| 50 | -9.16 | |||
| 10 | -15.29 | |||
| BC-550 | 30 | -14.14 | 7.98 | 1.41 |
| 50 | -13.13 |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





