Abstract The underlying mechanisms of secondary neuronal damage following intracerebellar hemorrhage are not yet clear. We aimed to study the possible mechanisms in the mediation of secondary neuronal damage following intracerebellar hemorrhage. ICbH was induced by collagenase type VII-S into mice in 2 phases (n=24/phase): 12 in control group, 12 in day 1 group, 12 in day 3 group and another 12 in day 7 group. All mice underwent locomotor assessment and subsequently sacrificed on day 1, day 3 and day 7 respectively. Cerebellum from phase one and phase two were taken to study morphological, immunohistochemistry and oxidative stress respectively. Mice behavior disturbed following ICbH at day 3 and y 7 as compared with control. Besides, NO increased-on day 1 post induction and suppressed on day 3 and 7. Expressions of SOD, CAT, nNOS, GPX1 and COX-2 were significantly raised on day 3. Morphological studies of the perihaematoma region and tissue showed neuronal damage occurred from day 1 onwards, peaked on day 3 and continued day 7. NO and expression of genes be correlating with morphological changes. Briefly, NO and oxidative stress has an important role in the cascade of secondary neuronal damage of the perihematomal region of ICbH.
1. Introduction
Intracerebral Hemorrhage (ICH) accounts for up to 20 – 30% in Asian countries population. 10% of this ICH are intracerebellar origin and nearly up to 50% of all cerebellar strokes [Tijjani Salihu et al., 2016, and Qureshi et al., 2009]. Most commonly affecting the elderly population – with an average age of more than sixty years. It is one of the most disastrous stroke subtypes which associated with high mortality, poor clinical outcome and less effective therapeutic options than other stroke subtypes [Broderick J et al.., 2007]. Primary brain injury after ICH is caused by the tissue disruption due to parenchymal blood accumulation and the mechanical damage associated with the mass effect [Mracsko et al.., 2014]. The unfavourable outcome usually associated with secondary damage to the brain tissue around the initial hematoma, attributable to the presence of intraparenchymal blood and may be dependent on secondary hematoma enlargement and perihematomal oedema, on top of the initial bleed mass effect [Aronowski et al., 2011]. Mortality rates have been decreasing for intracerebellar hemorrhage (ICbH) with vast improvement in clinical imaging and early surgical intervention. But, the long-term functional outcome for these patients remains unfavourable regardless of the mode of treatment – medically or surgically. The underlying pathophysiological mechanisms of secondary damages to neurons in ICbH is still not understood yet. But this has been frequently discussed for ICH and many authors have studied the effects of neuroinflammation in ICH. Neuroinflammation after ICH involves the early activation of astrocytes, release of proinflammatory mediators and the influx of peripheral leukocytes and has a major role in the pathophysiology of secondary brain damage. Another major components might be causing damage in perihaematoma region is via oxidative stress,nitric oxide process and glutamate and GABA regulation. [Mracsko et al., 2014].
Nitric oxide (NO) and Nitric Oxide Synthase (NOS) has been frequently discussed in connection to the ischemic infarctions – especially in those caused by vasospasm after episode of subarachnoid hemorrhage (SAH) [Jung et al., 2007 Vellimana et al., 2011]. NO not only serves as potent vasodilator, but also maintains endothelial function, preventing vascular smooth muscle cell growth, inhibiting platelet aggregation and blocking leukocyte adhesion [Li et al., 2011]. NO produced in the body by 3 isoforms of NOS – iNOS (inducible NOS or NOS2), eNOS (endothelial NOS or NOS3) and nNOS (neuronal NOS or NOS1). Different sites of expression and activity of these isoforms of NOS plays a critical role in the function of NO. nNOS is expressed in neuronal cell bodies and NO derived from nNOS (nNOS-NO) acts as important neurotransmitter associated with neuronal plasticity, memory formation, regulation of central nervous system blood flow, transmission of pain signals and neurotransmitter release. Overexpression of nNOS seen in conditions causing neuronal injury[Toda et al., 2009, 2003 and Garry et al., 2015].
In this study, we investigated the possibility of involvement of excitatory amino acid transporters mainly excitatory amino acid transporter 1 (EAAT1) also known as glutamate aspartate transporter (GLAST), glia fibrillary acidic protein (GFAP) and GABAA receptors α1 subunit (GABAAα1) in the perihematomal regions after ICbH. We induced ICbH using bacterial collagenase type VII to the cerebellum using stereotaxic surgery method onto Swiss Albino mice (Tijjani Salihu et al., 2016). Swiss Albino mice were chosen because of their all-purpose use in research and drug safety testing (Yong, Her, & Chen, 2018) and this model is known to be genetically engineered for the study of stroke mechanisms of injury (Yan, Chopp, & Chen, 2015). We chose the mice model because not many researches have been done in the cerebellum using mice, but more are done in the rat model (Krafft et al., 2012). This technique was first introduce by Rosenberg, Mun-Bryce, Wesley, & Komfeld, 1990 used by Lekic et al., 2011 and Tijjani Salihu et al., 2016. Furthermore, after induction of the ICbH the behavior of these mice was studied using the open field test (OFT) in the parameters of line crossing, rearing, time spent in periphery, immobility time and grooming. Ataxic tests were also done to show any ataxic behavior (Guyenet et al., 2010).
Glutamate levels are regulated in the CNS by a family of EAATs. EAAT1/GLAST is one of the transporters in this family and it is more robust in the cerebellum. Bregmann glia (BG), in the cerebellar express the EAAT/GLAST1 in extreme density’s, animals that have knocked out EAAT1/GLAST gene have disrupted cerebellar behavioral deficits and exacerbated responses to cerebellar injuries (Canul-Tec et al., 2017). GFAP is an intermediate filament in the astrocytic structure (Yoon, Walters, Paulsen, & Scarisbrick, 2017). When there is injury to the CNS, GFAP is up regulated in the astrocytes that play a role in activation, or reactive astrocytes that play a vital role in injury damage control (Luger et al., 2017). GABAA receptors are ionotropic receptors that play a vital role in the inhibition of excitation in the CNS (Enna, 2007). In the cerebellar they form by four types on interneurons activated by granule cells (Kaja et al., 2015). The receptor subunits including α1-6, β1-3, γ1-3 and δ. Major combinations are 2α1, 2β2 and 1γ2 subunits (Zimcikova, Simko, Karesova, Kremlacek, & Malakova, 2017). It is said that the α1 subunit variant is highly expressed throughout the brain and mice lacking α1 subunit exhibit marked loss of GABAA receptors. In conclusion this study is to understand the possibility of involvement of EAAT1, GFAP and GABAAα1 in the perihematomal regions of cerebellum after the induction intracerebellar hemorrhage in mice model.
In the CNS, EAAT 1, GFAP and GABAAα1 play major roles as glial transporters, receptors, and intermediate filament in the cytoskeleton of cells mostly in astrocytes and based on literature the role of EAAT1, GFAP and GABAAα1 involvement has not been studied yet in the secondary damage following ICbH in mice. Studies in the cerebrum were performed by Rosenberg, Mun-Bryce, Wesley, & Komfeld, 1990 studies on the cerebellum were performed by Lekic et al., 2011 and Tijjani Salihu et al., 2016 which they studied the behavior and morphological changes to the neurons at the perihematomal regions of the tissue. This study will help us to understand the mechanisms of secondary damage in the perihematomal regions of ICbH and whether EAAT1, GFAP and GABAAα1 may be involved in these mechanisms at the perihematomal regions of ICbH in mice model.
2. Materials and Methods:
2.1. Ethical Approval
All procedures followed the Guide for the care and Use of Laboratory Animals and approved by the Animal Care and Use Committee of Universiti Sains Malaysia, Health Campus (Animal ethics approval/2018/ (112)/ (924)).
2.2. Animal Preparation
Twenty-four (n = 48) age and weight matched adult male Swiss Albino mice with an average body weight of 25 - 32g were used. All mice were obtained, kept and maintained in the Animal Research and Service Centre (ARASC), Universiti Sains Malaysia, Health Campus, Kubang Kerian, Kelantan, Malaysia. The polypropylene cages (32cm x24cm x16cm) used as the living place. The bedding material that was used is wood shavings and changed at 2 to 3 days interval. Pellet diet and water ad libitum were supplied, and the mice exposed with 12 hourly light cycle via automated timed light.
2.3. Experimental Design
The animals were divided into 2 phases with 4 groups of animals: control (n = 12), day 1 ICbH (n = 12), day 3 ICbH (n = 12), day 7 ICbH (n = 12). In phase 1, animals underwent induction of ICbH, behavioural and ataxic studies that were done to the induced animals. In phase 2, ICbH animals perihematomal tissues were harvested and used for immunohistochemical studies.
2.4. Intracerebellar Haemorrhage Induction Mice Model
The mouse model of cerebellar haemorrhage, which was induced by collagenase type VII via injection, was adapted from an establish rat protocol and has been described previously in (Rosenberg, Mun-Bryce, Wesley, & Komfeld, 1990,Lekic et al., 2011,Tijjani Salihu et al., 2016). 24 age and weight matched adult male (25 - 32g) Swiss Albino mice were used. Aseptic technique was used for all surgeries. Mice were anesthetized with isoflurane (3% induction, 2% maintenance, 1l/min O2) and secured prone onto a stereotaxic frame (C.H. STOELTING Co. Stellar Stereotaxic Instrument, Model 51400, Lorton, VA) before making an incision over the scalp, the following stereotaxic coordinates were the measured from the bregma, to locate the deep cerebellar (paramedian) white matter tract: -5.8 mm (caudal), 2.0 mm (lateral), and 3.0 mm (deep). A borehole (1 mm) was drilled, and a 30-gauge needle was inserted. Collagenase type VII (0.4 U/µL, Sigma, St Louis, MO) was infused by microinfusion pump (rate = 0.4 µL/min, Harvard Apparatus, Holliston, MA). The syringe remained in place for 10 minutes to prevent back-leakage before being withdrawn. Then the borehole was sealed with bone wax (World Precision Instruments Inc.), incision was closed using Nexaband liquid topical tissue adhesive (Abbott Labs) and the animals could recover. The animals were given free access to food and water upon recovery from anaesthesia.
2.5. Pain Detection and Management
The mouse is taught to be in pain following these actions. Orbital constriction is narrowing of the orbital area, with tightly closed eyelids or an eye squeeze (denoted by wrinkle around eye) (Langford et al., 2010). Nose bulge is rounded extension of skin visible on the bridge of the nose. Cheek protuberance refers to convex look of the cheek muscle (between eye and whiskers) from their baseline position. Ear position refers to ears pulled apart and back from their baseline position or including vertical ridges that from owing to tips of the ears being drawn back. Whisker change is movement of whiskers from their baseline position either backward, against the face or forward, as if standing on the end; whiskers may also cluster together. Note that these features are indistinguishable to those observed in humans: orbital tightening, nose bulge and cheek bulge, supporting Darwin’s century-old prediction that facial expression are evolutionary conserved (Deuis, Dvorakova, & Vetter, 2017). Carprofen was given 5-10 mg/kg in water to the mice postoperatively.
2.6. Behavioural Assessment
Behavior assessments were conducted via assessment of locomotor activity of mice after collagenase injection in cerebellum performed. Assessment done daily once using following methods until the animals were sacrificed to harvest for its perihaematomal tissue.
2.6.1. Rotarod Test
This test was similar as wooden beam test to evaluate balancing abilities except the wooden beam or rod was rotated around its longitudinal axis by means of a DC electric motor (San Diego Instruments, San Diego, CA). The accelerating-rotarod test was programmed to accelerate 0 to 40 rpm in 4 min and then hold constant speed for another 1 minute. The maximum observation time was 5 minutes. The time that the mouse remained on the rotarod before falling was recorded. Data from 3 trials was averaged for each mouse. This method adapted from Colombel, C., et al. 2002 and Wei, P., et al. 2011.
2.6.2. Wooden beam test
This test was used to evaluate the balancing abilities of the mice when their motion was not limited. The apparatus consisted of a stationary wooden beam with a square section (3cm x 3cm), 50cm in length, placed 80cm above a foam carpet. At the onset of the trial, each animal was placed at the middle of the beam with its body axis being perpendicular to beam’s long axis. We then recorded the latency before falling and the maximum time fixed to 1 minute. This method adapted from Lekic, T., et al. 2011.
2.6.3. Wire suspension test
This test was used to evaluate the muscular strength of animals. The mice were hung by their two forepaws in the middle of a string (3mm diameter and 30cm length) which hung 80cm above the floor covered with foam carpet to cushion the falls. Latencies before the fall were measured and cut off time set maximum at 1 minute. This method adapted from Colombel, C., et al. 2002[
36] and Lekic, T., et al. 2011[Lekic et al., 2011].
2.6.4. Hole-Board Test
This test was used to evaluate the motor coordination of mice. The apparatus consists of a square wooden box (33cm x 33cm x 10cm) containing a floor with 16 holes (hole board). The hole measured 1cm deep and 2cm in diameter, arranged 4 x 4 array. The test done by placing animal at the centre of hole-board and then measure during a duration of 1-minute period, the number of fore- or hindlimb slips into the hole as well as the walking time in this period of 1-minute. This method was adapted from Colombel, C., et al. 2002 and Lorivel, T., et al. 2006.
2.7. Biochemical Studies
Animals in phase 2 were fatally anesthetized on their respective days for harvesting of perihaematoma tissue of cerebellum and harvested tissue kept into Protein (RIPA Lysis & Extraction Buffer) and RNA (TRIzol RNA Stabilization) Reagent. For biochemical study on nitric oxide assay, perihaematoma tissue which was kept inside RIPA was disrupted and homogenized with PBS and centrifuged at 10000 rpm for 20 minutes obtaining supernatant as samples. Protein concentration in the samples were measured by using Spectrophotometer NanoDrop 2000 (ThermoFisher Scientific, Wilmington, DE, USA) and its analysing software. Concentration of protein were analysed with absorption of the protein at 280nm and standard set as 1Abs = 1mg/mL concentration. Protein concentration of each sample from phase 2 were analysed and equal concentration of 250mg/mL was set as standard for each sample undergoing analysis of nitric oxide. Standard reagent of Nitric Oxide was prepared by serial dilution as per protocol in Colorimetric Nitric Oxide Assay Kit (Calbiochem, EMD Biosciences Inc, San Diego, CA, USA).
85μL of Standard Nitric Oxide Reagent and 5-85μL (with equal protein concentration of 250mg/mL) of samples were added into plate wells. Enough buffer was added to each sample to bring up the volume to 85μL. Nitric oxide is rapidly converted into nitrate and nitrite when kept into tissue stabilizers. Rate of conversion may vary substantially depending on the biological fluids and tissue culture media used. Hence for accurate analysis of total nitric oxide, one must analyse both nitrate and nitrite levels. Thus, Nitrate Reductase enzyme used to convert nitrate to nitrite prior to quantitation providing accurate determination of total nitric oxide. 10μL of reconstituted Nitrate Reductase was added to each well. 10μL of 2mM NADH (β – Nicotinamide Adenine Dinucleotide, reduced form) added into all the wells and plate were shaken at room temperature for 20 minutes. Subsequently, 50μL each of Colour Reagent #1 and Colour Reagent #2 was added to all the wells and shaken gently for 5 minutes at room temperature. Absorbance was read at 540nm under plate reader and results obtained.
2.8. Histological Studies
2.8.1. Brain tissue preservation preparation
Phosphate buffered saline (PBS) is a mixture of 1.09 g of sodium phosphate dibasic Na2HPO4 (Labo Chemie 0597100500, Labochemie PVT.LTD, India) with 0.32 g sodium phosphate monobasic NaH2PO4 (Sigma-Aldrich, 58282-500G, Sigma-Aldrich, USA) and 9 g of sodium chloride NaCl (Sigma-Aldrich 31434, Sigma-Aldrich USA) and diluted in 1000 ml of distilled water. Preparation of 4% paraformaldehyde solution (Labo Chemie, 0597100500, Labochemie PVT.LTD, India) with 3.2 g of sodium phosphate monobasic NaH2PO4 (Sigma-Aldrich 31434, Sigma-Aldrich, USA) that was diluted in 500 ml distilled water. Continuing the process, 500 ml distilled water was added into the Scott bottle (Duran, 10053294, Duran Group, Germany) making it a total of 1000 ml and heated to approximately 60 ⁰C using a hotplate stirrer (NUVE, MK418, NUVE Turkey), the 40 g of paraformaldehyde powder OH(CH2O)nH (n = 8-100) (Acros Organics, AC416780010, Fisher Scientific, USA) and 500 ml phosphate buffer (PB) solution was added, the temperature was maintained at 60 ⁰C until the cocktail dissolved which was indicated by its colourless presentation. Phosphate buffered (PB) solution 0.2 M was prepared by adding 10.94 g of sodium phosphate dibasic Na2HPO4.
2.8.2. Tissue collection and processing
Animals were fatally anesthetized with mild anaesthesia (sodium pentobarbital: 0.27 ml) (Dorminal, DIN 02333708 Alfasan, Woerden, Holland) followed by cardiovascular perfusion with 0.1 M ice-cold PBS pH 7 (Acros Organics, AC416780010, Fisher Scientific, USA) (phosphate buffered saline) for 2 minutes and followed by 4% paraformaldehyde pH 7 for pre-fixation of the tissues for 3 minutes. The brain was the carefully dissected out shown in Fig 3.5 and post fixed in the same fixative overnight in 4 ⁰C. Tissues were processed for paraffin embedding and sectioning. Paraffin sections were utilized for the study of GABAAα1, EAAT1 and GFAP.
Perfused and post-fixed brain tissues were processed in an automatic tissue processor. Paraffin blocks were the prepared by placing the tissue in the wax moulds followed by embedding. Serial coronal sections of 5µm thickness were obtained by sectioning the paraffin blocks with rotary microtome. Tissue slices were taken from the left hemisphere of the cerebellar after the induction of haemorrhage to the deep paramedian white matter. The tissue sections were mounted on a clear glass microscopy slide. To assess changes occurring in the perihematomal area at 1, 3, 7 days and control three coronal sections were taken from each animal (n = 6) for immunohistochemical studies done in Neuroscience Lab, Department of Neurosciences, School of Medical Sciences, Health Campus, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Kubang Kerian, Kelantan, Malaysia.
2.8.3. Immunohistochemical Staining
Immunohistochemical staining was conducted using HRP/DAB technique. The manufacturers protocol for the rabbit specific HRP/DAB detection kit, IHC kit (Abcam, AB64261, Abcam, UK) is labelled streptavidin-biotin immunoenzymatic antigen detection system that includes 3,3 diaminobenzidine (DAB) as a chromogen and haematoxylin as a counter stain, by referring the manufactures protocol. For the transporter, intermediate filament and receptor containing subunit staining, the tissues sections were deparaffinized, rehydrated, and rinsed in 0.1 M PBS buffer, followed by intubation with hydrogen peroxide blocking solution (Abcam, AB64218, Abcam, UK) for 10 minutes at room temperature in a dark place. The samples were then washed in 0.1 M PBS buffer and protein blocking solution (Abcam, AB64226, Abcam, UK) was applied on the tissue sections for 5 minutes at room temperature to block nonspecific background staining and washed with PBS buffer. The sections were then incubated overnight at 4 ⁰C with 70 µL of rabbit polyclonal primary antibodies to the GABAA α1 subunit, EAAT1/GLAST transporter and GFAP intermediate filament (Abcam, AB33299, Abcam, UK) at (1:100) dilution in the blocking buffer (Antibody diluents solution) (Dako, 50809, Dako, Denmark).
Following 24 hours, the sections from primary antibody tests were washed with PBS buffer and secondary antibodies containing biotinylated goat anti-rabbit were applied and incubated for 1 hour at room temperature, a rabbit specific HRP/DAB (ABC) Detection IHC kit (Abcam, AB64261, Abcam, UK) was used. After the incubation, the slides washed again in PBS buffer, streptavidin peroxidase, incubated for 15 minutes, and rinsed in PBS buffer again. One drop (30 µL) of DAB chromogen was added to 1.5 ml (50 drops) of DAB substrate, mixed by swirling, and applied to the tissue. After incubation for 5 minutes, the slides were rinsed with PBS buffer. A drop of Harris Haematoxylin stain (Labstain, N082/816, Labchem Sdn. Bhd., Malaysia) was then applied and the tissue was counterstained for 1 minute, rinsed with distilled water, mounted with Faramount aqueous mounting medium (ready to use) (Dako, 5302580, Dako, Denmark), and the covered with a coverslip (HmbG, G0543, HmbG Inc., Germany) (Wong et al., 2019). The staining was observed with a light microscope with an image analyser (Olympus Bx-14-32PO2, Olympus Corporation, Japan) with a 20x magnification field. The expression intensity observed and analysed qualitatively. These expressions was assessed by 3 blinded investigators from Department of Neurosciences, School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia, Health Campus, Kubang Kerian, Kelantan, Malaysia using a subjective scale of none, mild (+), moderate (++) and strong (+++) (Uysal et al., 2015).
2.9. Statistical Analysis
GraphPad version 8.01 was utilised for all statistical analysis. This data was expressed as mean and standard error mean (SEM). Statistical significance was analysed by one-way ANOVA and post hoc tests. Statistical significance is set at p < 0.05.
3. Results
3.1. Impairment in motor and balance coordination after induction of cerebellar hemorrhage
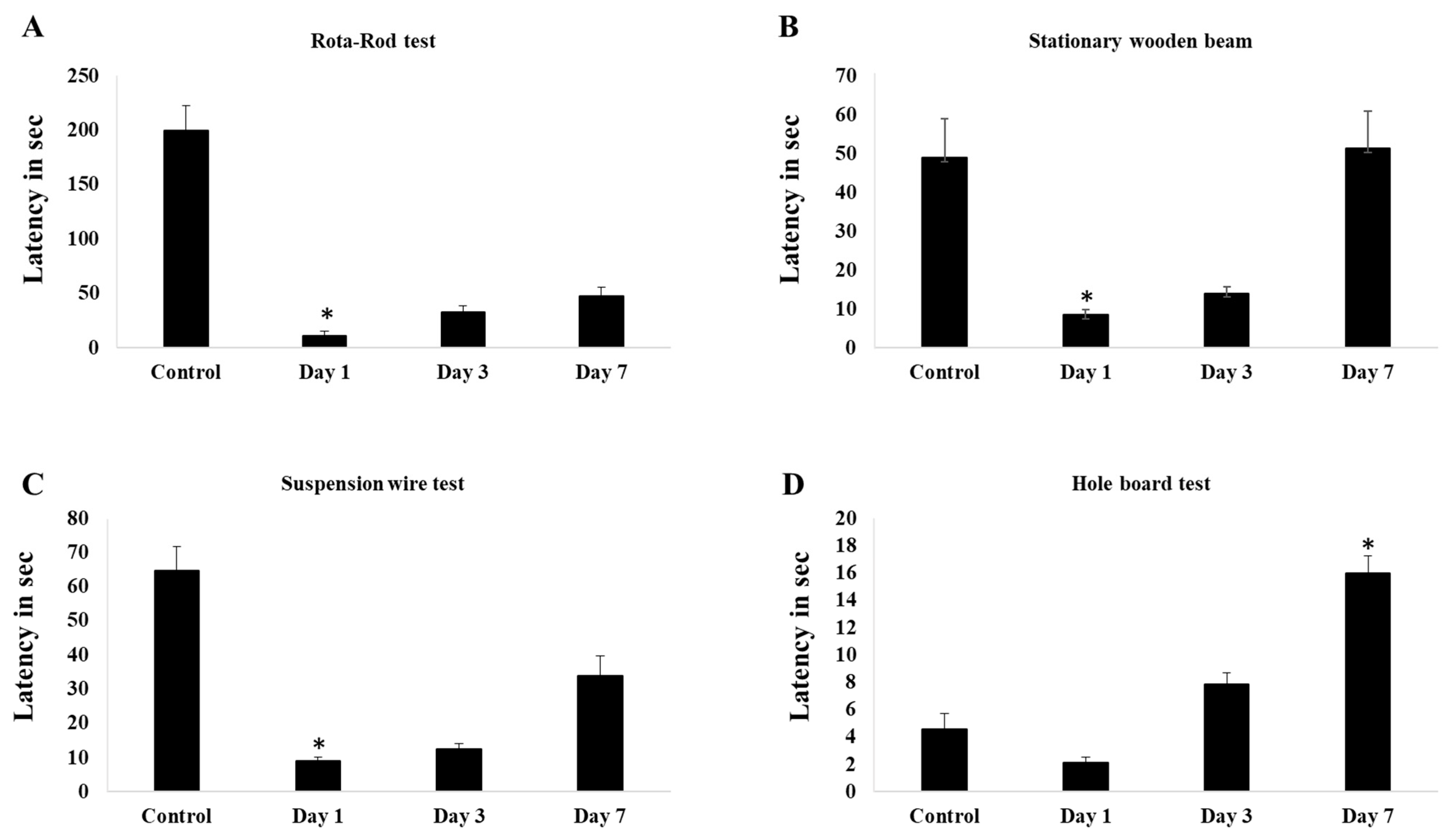
Induction of 0.4u of collagenase in cerebellum causes deficit in time in the latencies before falling in rota-rod test test after day-1 and improve a little bit in day-3. Significant improvement seen in day-7 and more or less shows similar value with control group
(Figure 1A). In stationary beam test, induction of collagenase causes significant deficit in walking time in both post day-1 and day-3 surgery. Improvement seen after 1-week of surgery and shows significant walking time higher than control group
(Figure 1B). Similarly, to hanging wire test, significant decrease in latencies before falling in stationary beam test shown by day-1 and day-3 post surgery and by a week, the value showed significant improvement
(Figure 1C). For hole-board test, day-7 post surgery mice showed high frequency of slips per minute and walking time compared to other groups
(Figure 1D)
3.2. Biochemical Assay
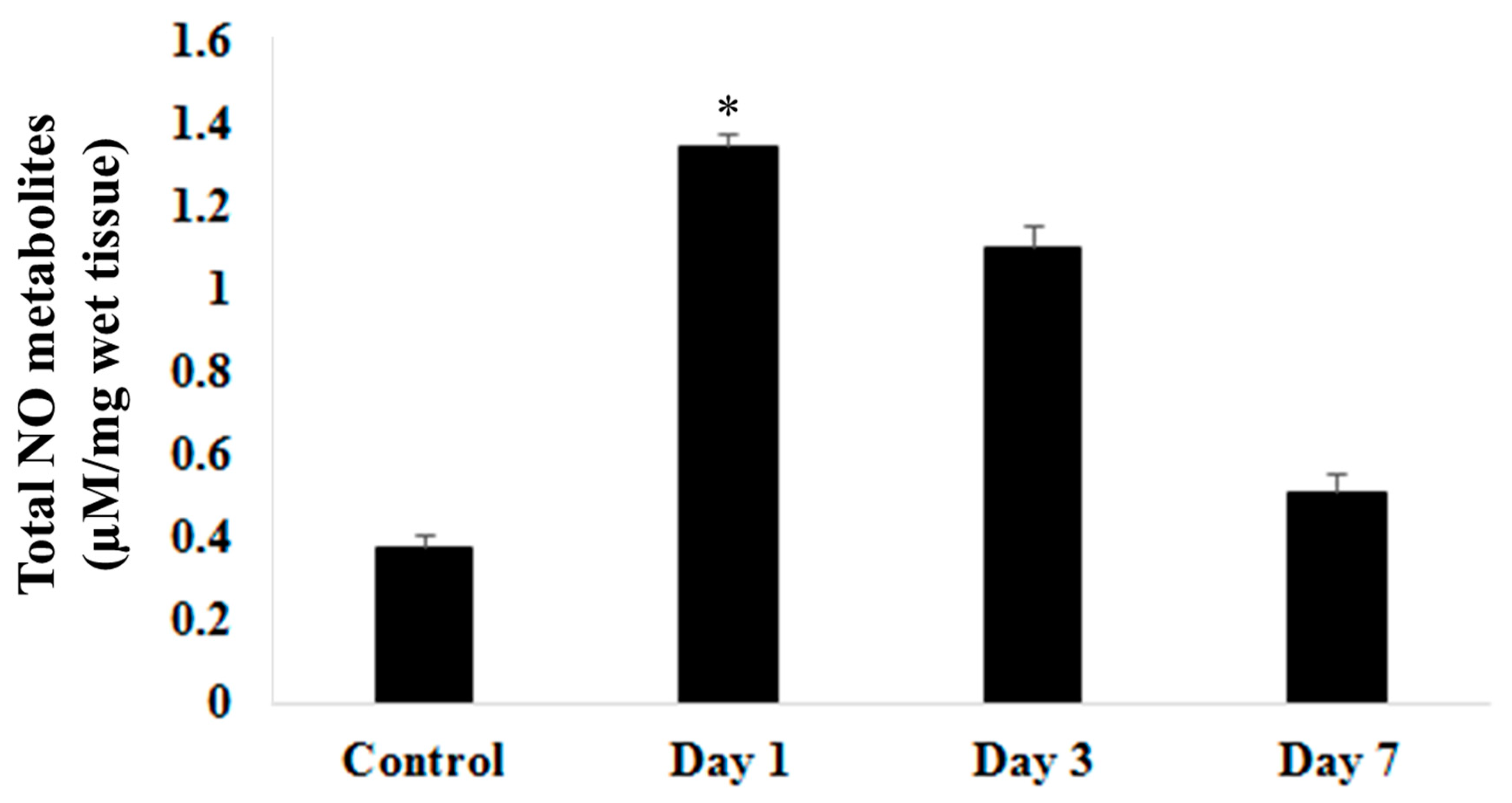
Biochemical studies on nitric oxide metabolites via Colorimetric Nitric Oxide Assay (
Figure 2) showed significantly (p<0.05) raised on day 1 post surgery. This level steadily decreases on day 3 and day 7 post induction of ICbH. Level of nitric oxide metabolites on day 7 post induction of haematoma was still higher than in control group may suggest ongoing insult to the perihaematomal region despite resolution of clot seen on day 7 group in the morphological study. When compared nitric oxide levels and locomotor assessment, nitric oxide levels were inversely proportionate to results of stationary beam test, wire suspension test and rotarod test. As the nitric oxide peaks on day 1, the latencies for above mentioned test were at lowest. Nitric oxide steadily decreases on day 3 and day 7, meanwhile latencies steadily increased on day 3 and day 7 groups.
3.3. Morphological changes
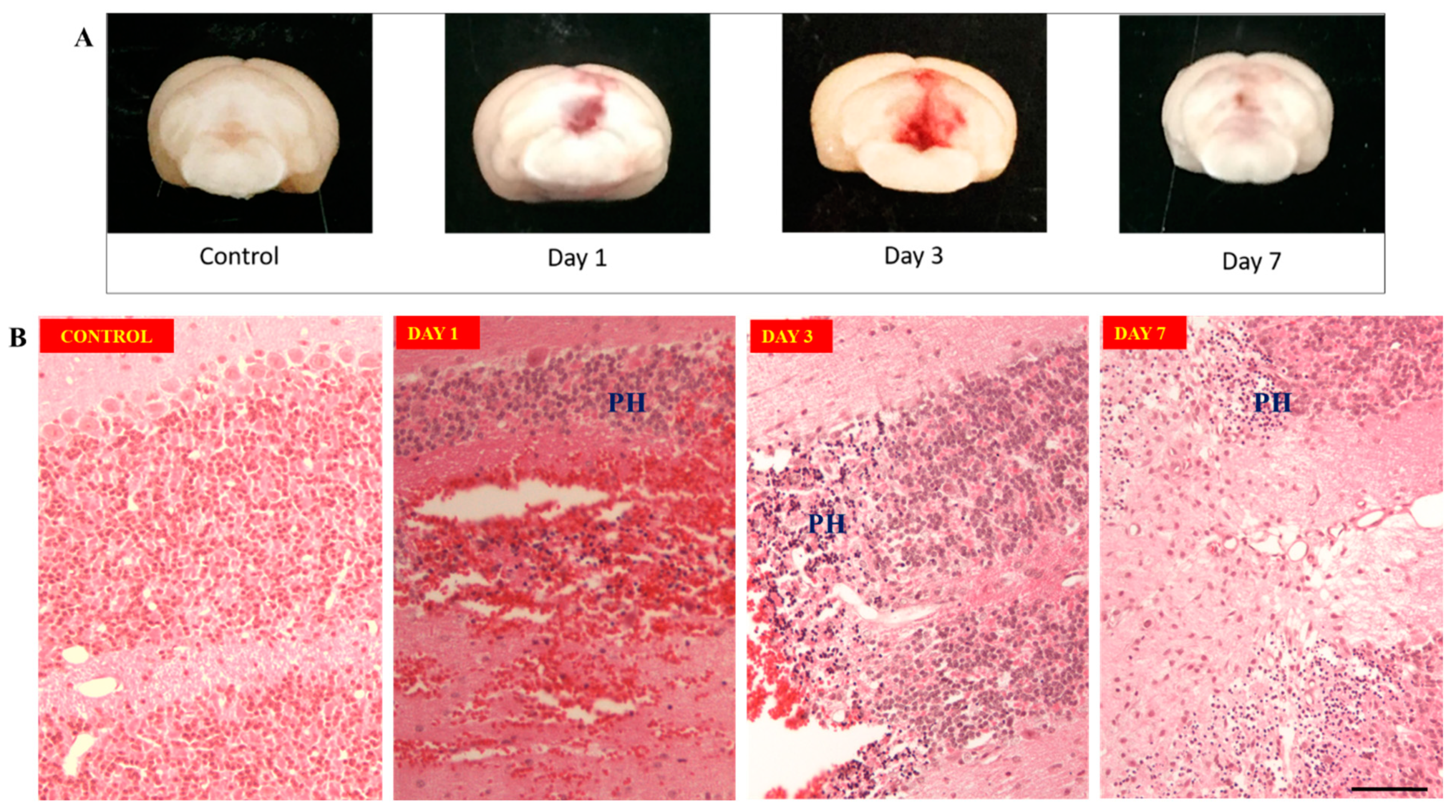
Morphological studies showed largest clot formation occurs on day 3
(Figure 3A) compared to day 1 post induction meanwhile clot resolution seen on day 7 after surgery. Hematoxylin and Eosin staining of perihaematoma tissue of cerebellum
(Figure 3B) on day 1 showed edema of granular cells forming dark round cells with lack of nucleolus. These changes of granular cells persisted from day 1 till day 7 specimens. On day 3, there was influx of pro-inflammatory cells, like microglia or macrophages at the region between perihaematoma and hematoma regions, on top of the neuronal damages seen from day 1. This became more organized on day 7.
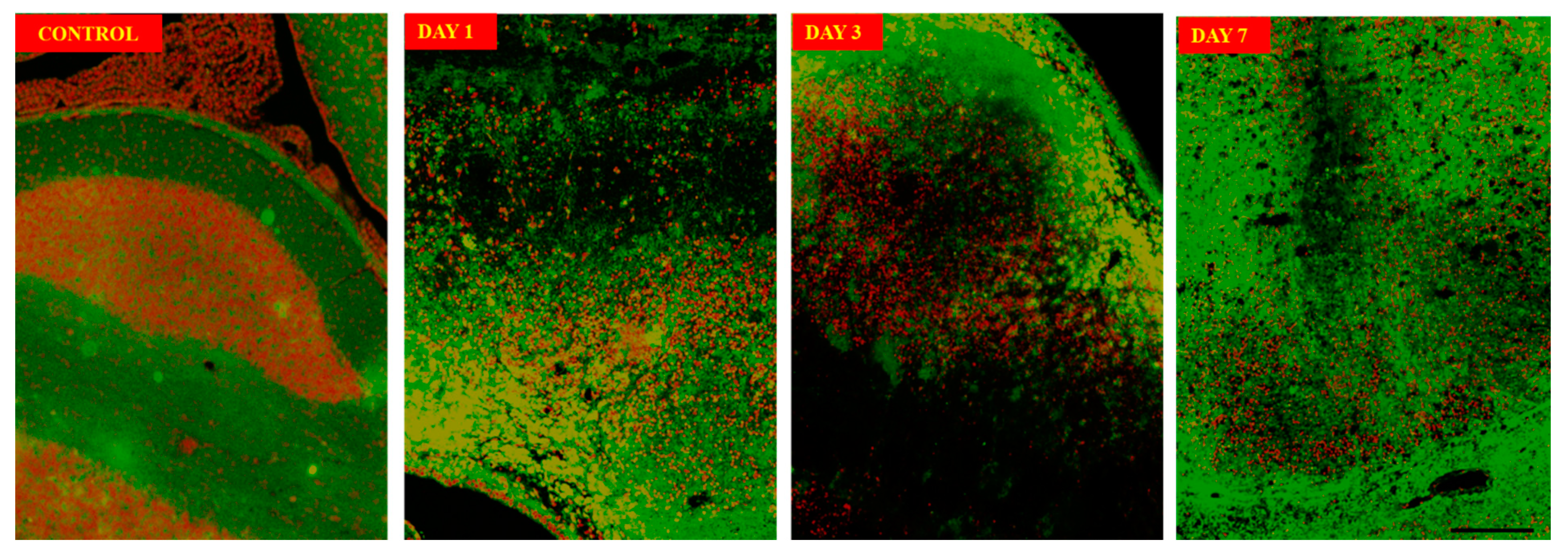
The neuronal structure using immunofluorescence imaging
(Figure 4) on day 3 sections showed neuronal damage characterized by damage to soma as well as axonal damages when compared with control sections. Annexin V-FITC/Propidium Iodide Assay
(Figure 4) on the perihaematomal tissue show most neuronal death or apoptosis occurs on day 1 to day 3. Apoptosis persist on day 7 but less in number. Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) image
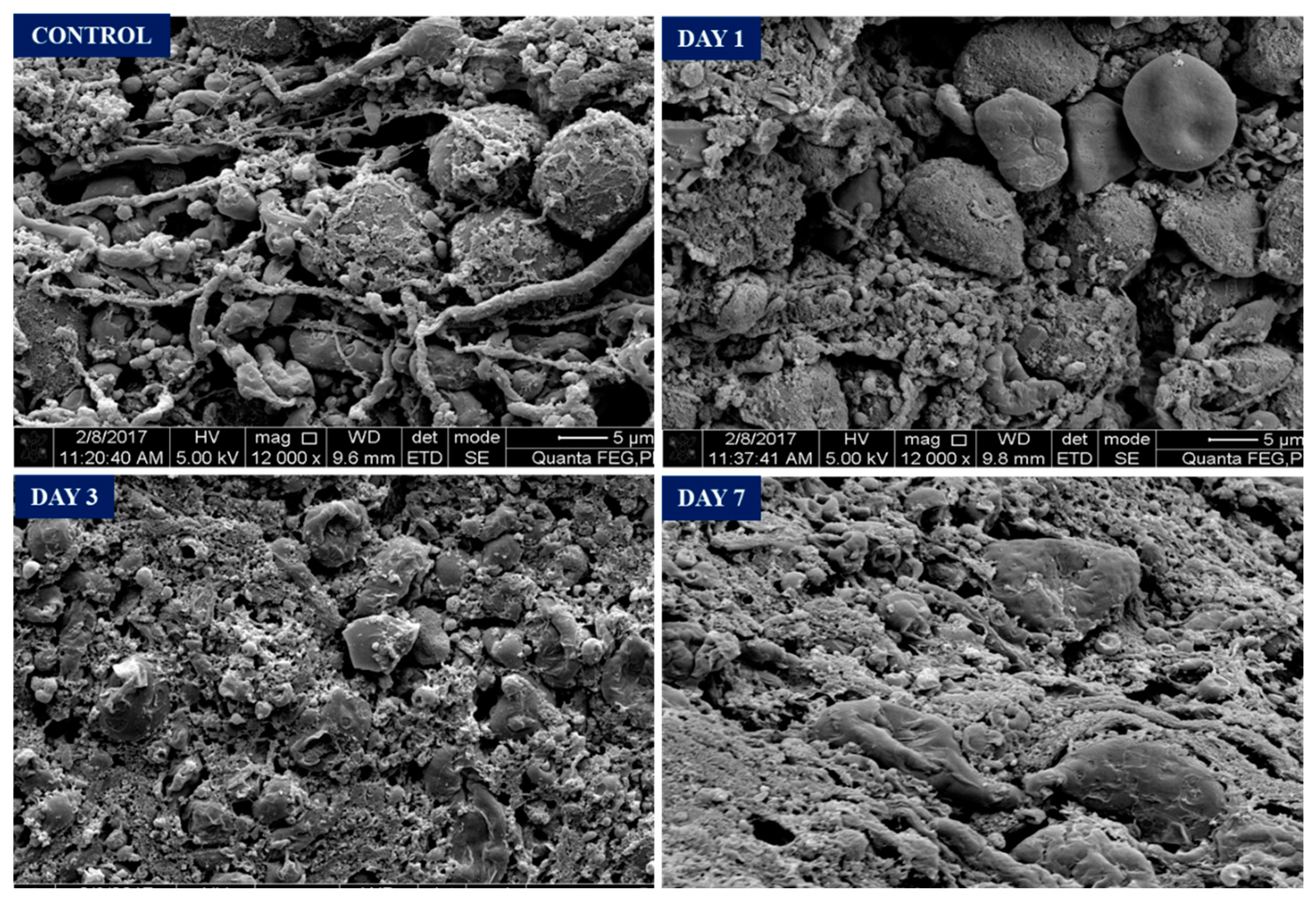
(Figure 5) in control group showed intact neuron cells with intact axons forming synapses. On day 1 post surgery, noticed there are disruptions of axonal and their synapses at the region close to haematoma. The neuronal cell body remains intact. On day 3, the neuronal cell body under goes shrinkage extensively in the perihaematomal region with no visible axons. Further degeneration occurs, and remnants of dead neurons were seen at perihaematoma tissue on day 7 along with macrophages clearing and reorganizing the tissue.
3.4. Immunohistochemistry
Results of the expression of GFAP (
Figure 6), EAAT1/GLAST (
Figure 7) and GABA
A α1 subunit in the mouse cerebellum sections divided between control, day 1, day 3 and day 7 in the perihematomal regions.
3.5. Oxidative stress markers by Molecular studies
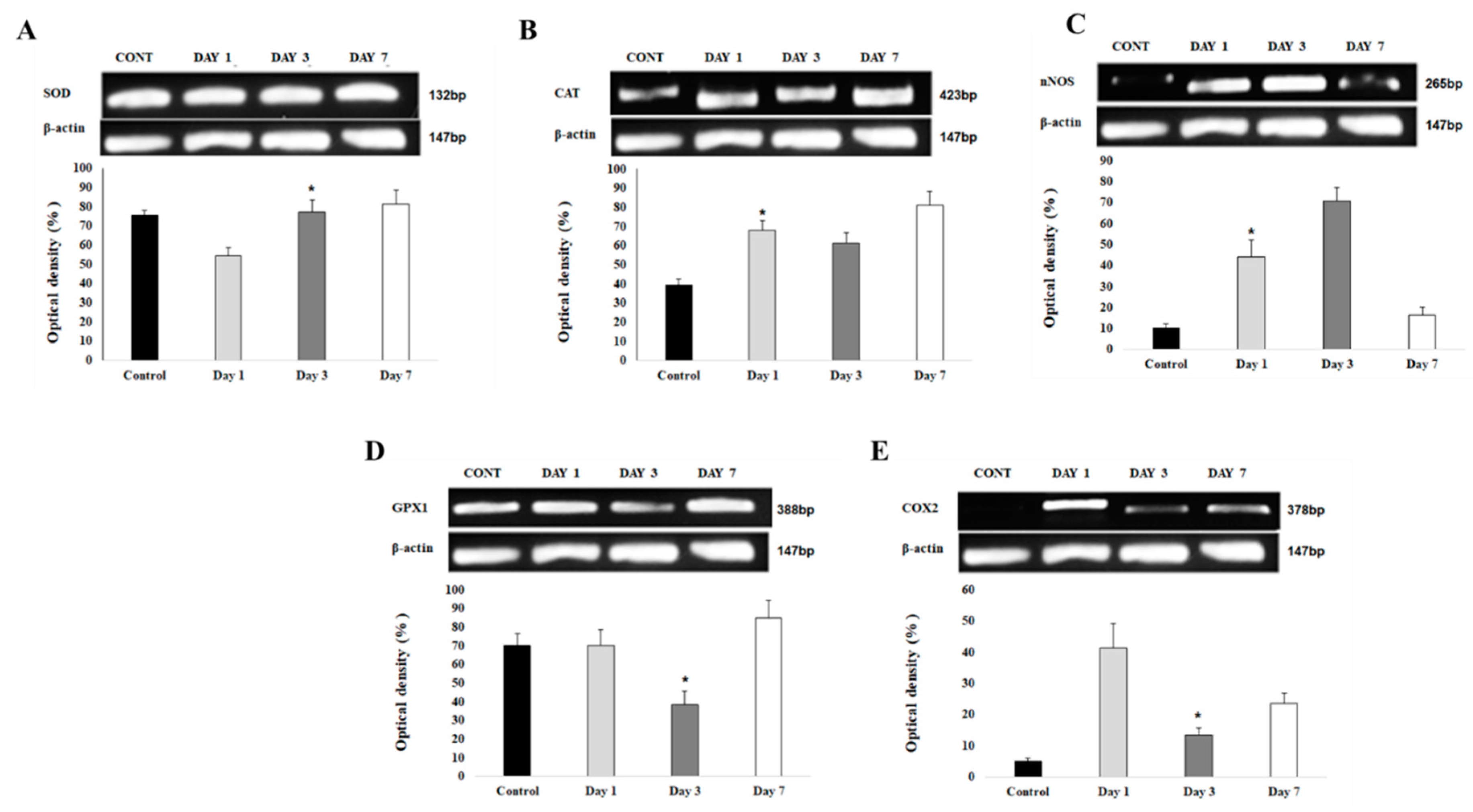
3.5.1. Upregulation of gene expression of antioxidants at day 7 post ICbH
Antioxidants such as SOD1 (
Figure 9A), catalase (
Figure 9B), and glutathione peroxidase (
Figure 9D) all show upregulation of gene expressions at day 7 post ICbH. However, each gene had low level of gene expressions at different times; SOD1 started at day 1 post ICbH, catalase and GPx1 at day 3 post ICbH.
3.5.2. Upregulation of gene expression of pro-oxidants at day 1 and 3 post ICbH
In contrast to antioxidants, pro-oxidants as COX2 (
Figure 9E) is upregulated at day 1 then downregulated by day 3 while another pro-oxidant, nNOS (Figure 9C) starts to upregulate at day 1 and continue significantly by day 3, then starts to downregulate by day 7 post-ICbH.
4. Discussion
Deterioration of neurological condition following ICbH persists days after onset of the hematoma. Surgical intervention by removal of the clot may have improved the overall survival rates but do not always achieve complete halt in the deterioration of neurological functions[Kirollos et al., 2001]. This could be possibly due to the secondary brain injury which occurs in the perihaematoma region of the ICbH. Number of previous studies have showed that secondary brain damage occurs as a result from interaction of cytotoxicity, excitotoxicity, oxidative stress, and inflammation from red blood cell lysis[Chaudhary et al., 2013]. In this study, we have analyzed the nitric oxide level in perihaematoma region as well as investigated the expression of neuroinflammatory marker genes to understand the propagation of secondary neuron damage in the perihaematoma region. From the nitric oxide (NO) results, we understood that NO increased on day 1 of ICbH but in day 3 and day 7 following ICbH, the NO level continuously reduced. This reduction of NO could be one of the key factors to trigger the secondary neuronal damage in ICbH as seen in the apoptosis assay and morphological data which suggests that neuronal damage occurs progressively till day 7 post ICbH.
Based on the literatures, NO serves as potent vasodilator and plays a major role in neuroprotection through regulation of cerebral blood flow in the central nervous system[Hlatky et al., 2003, Iqbal et al., 2016 and Kandasamy et al., 2013, Pautz et al., 2010]. Piknova et al., 2011 reported that administration of NO donor reversed blood flow in cerebellum. Hypoxia could be one of the reasons to reduce blood flow in perihaematomal of intracerebellar haemorrhage[Peers et al., 2007, Shiva et al., 2013 and Muthuraju et al., 2011]. Hence, the suppression in level of NO at day 3 and day 7, may lead to secondary neuronal damage through reduction in blood flow. But at the same time, NO can be converted into potent oxidant and cytotoxic agent. In pathophysiological condition, abundance of NO can react with reactive oxygen species like superoxide and forms peroxynitrite. Peroxynitrite is known to be a potent cytotoxic agent which contributes to apoptotic neuronal death in various acute injuries and neurodegenerative conditions. But there is an endogenous system to cope with toxic effects of peroxynitrate by means of peroxiredoxin (PRX). PRX plays major role as antioxidant in oxidative stress condition within the nervous system. There are 6 subfamilies of PRX has been identified in nervous system, which consist of PRX I – VI and all are being studied for use as antioxidants[Radi et al., 2013]. The use of PRX as a possible therapeutic agent to reduce secondary neuronal damages in ICbH needs to be investigated in future.
In our study, induction of ICbH using collagenase injection produced hemorrhagic lesion which is evident by morphological assessment at 24 hours, day 3 and day 7 after injection. We have obtained significant locomotor deficits after induction of ICbH compared to control group which we have assessed via battery of tests like stationary wooden beam test, wire suspension test, hole-board test and rotarod test[Colombel et al., 2022 and Lorivel et al., 2006]. Significant locomotor deficits which were observed can be associated with neuronal damage that has occurred secondary to ICbH. These deficits gradually improved over time on day 3 and almost back to baseline as per control group on day 7. This has been confirmed via morphological assessment whereby clot resolution seen on day 7 thus this causing improvement in the balancing abilities and muscular strength of the animals. Meanwhile, Zhu et al reported that in mouse ICH model, maximum deficit peaks on day 3 post induction. Our data suggest that maximum deficit peaks on day 1 post surgery for intracerebellar hemorrhage. This could possibly indicate that cerebellar neurons are more susceptible for damage compared to cerebral neurons. However, motor coordination assessed via hole-board test showed significant and gradual worsening from day 1 to day 7 with peak at day 7. Despite significant improvements in the walking time for hole-board test, the precision and coordination still impaired as observed by increase in number of slips. This is possible as cerebellum’s, one of main function is fine motor coordination which fine tunes the motor signals from the cerebral cortex before executing to limbs. Even though the resolution of clot occurs on day 7, but permanent damage has occurred to neurons of cerebellum causing persistent discoordination in motor movements[Morton et al., 2004 and Manto et al., 2012].
Neuronal damages were seen on morphological studies using Hematoxylin & Eosin (H&E) staining, Annexin V-FITC/Propidium Iodide staining and Scanning Electron Microscope (SEM) images. The neuronal damage starts on day 1 and persistent on day 3 and day 7. Neuron cells in the perihaematoma region were seen edematous from day 1 under H&E staining with further damage by lack of nucleolus is seen on day 1 till day 7. Ongoing death of neurons further confirmed by Annexin V-FITC/Propidium Iodide staining from day 1 to day 7 showing significant cell deaths up to day 7 on the perihaematoma region. Lekic and colleagues studied ICbH of rat model and found that significant reduction in purkinje cell density in cerebellum 30 days after the surgery[
34]. Few previous studies have obtained similar continuing neuronal degeneration in the perihaematomal area of basal ganglia hemorrhage mode [Wasserman J.K. et al., 2007 and Qureshi A.I. Et al., 2003]. But our results showed that neuronal degeneration in cerebellar hemorrhage model starts from day 1 post surgery and became more obvious on day 3 and reduces on day 7. Contrary to ICH models from basal ganglia region, where the peak degeneration occurs on day 1 and decline on day 3[Wasserman et al., 2007, 2008 and Qureshi et al., 2003]. To further visualize the damage of neurons in perihaematoma, we used SEM to see evolution of the damage that neurons undergo. It is clearly seen that axons and their synapses disrupt first on day 1 followed by shrinkage of cell body on day 3 and complete degeneration of neurons occurs on day 7. This supports the neuronal degenerations that occur in the perihaematoma region.
Information transfer in the brain relies on the functional balance between excitatory and inhibitory networks. At the level of individual neurons, this balance involves the maintenance of appropriate ratios of excitatory versus inhibitory synaptic inputs (Cirillo et al., 2020). The postsynaptic side harbors the postsynaptic density protein which is a multimeric scaffold that anchor NMDARs and AMPARs to the surface. Inhibitory synapses have adaptor protein gephyrin help to cluster GABA which are ionotropic GABAARs and metabotropic GABABRs and glycine receptors onto the postsynaptic surface (Qin et al., 2019). The disorders of the E/I imbalance implicitly lump together some vastly different disorders, such as epilepsy, schizophrenia and others because they share an excess of excitation. Meanwhile, in schizophrenia (SCZ) and autism spectrum disorders (ASD) imbalances may arise from problems in initial neural circuit formation or maintenance, as many of the genes derived from linkage and association studies code for proteins involved with these processes. In addition, post-mortem studies have discovered structural/functional changes in both glutamatergic excitatory and GABAergic inhibitory circuits in individuals with ASD and SCZ. In this study we focused on the expression of (EAAT1) also known as (GLAST), (GFAP) and (GABAAα1).
GFAP on day 1 and day 3 showed less expression as compared to day 7 indicates that more astroglia cells have been damaged due to the slowly expanding hematoma induced by the collagenase. The reactive astrocytes accumulate in the perihematomal region as early as 1–3 days after ICH onset (Chiu et al., 2017). GFAP has no special contribution in the normal nervous system but plays a vital role in the glial scar and the activation of astrocytes. Activation of astrocytes and expression of GFAP inhibits inflammatory response after injury, effectively limiting the damage within a controllable region, GFAP expression is greatest in reactive astrocytes proximal to CNS traumatic lesions, tapering in perilesional zones (McKeon & Benarroch, 2018). However, the introduction of collagenase in the cerebellum in this study had caused immediate astroglia cell damage and damage to the nerve tissue that induces intense proliferation and hypertrophy of astrocytes; these shifts are accompanied by accelerated synthesis of GFAP and fibrillogenesis. This phenomenon (is called astrocytosis) and is the main link in the development of reactive gliosis as the total glial response of the CNS to damage GFAP that is directly involved in (Tykhomyrov, Pavlova, & Nedzvetsky, 2016). Brenner, 2014 suggests increased GFAP expression is associated with hypoactivity and social deficits in mice, this can be seen in our study as the mice showed poor time spent in periphery and grooming results where on day 1 and day 3 the mice spent more time in the periphery suggesting that they prefer to be more towards the sides then in the centre and increased grooming habits day 7 (Brenner, 2014).
EAAT1/GLAST on day 1 and day 3 show less expression as compared to day 7. In this study, increased EAAT1/GLAST protein expression and function may not cause more glutamate release, but rather augment glutamate clearance. Several studies suggested that uptake of glutamate by EAAT1/GLAST played a neuroprotective role after ischemia (Fontana, 2015). Meanwhile, glutamate uptake of activated astrocytes is mainly performed by EAAT1/GLAST. A recent study showed that focal overexpression of EAAT1/GLAST significantly decreased ischemia-induced glutamate overflow, decreased cell death and improved behavioral recovery in a rat model of stroke. However, decreased glutamate transporter activity, due either to functional impairment or decreased EAAT1/GLAST protein expression can contribute to the accumulation of extracellular glutamate, one might hypothesize that the local astrocytic network tries to restore glutamate homeostasis but decompensates after injury-triggered elevations of extracellular glutamate thus “overloading” astrocytic uptake mechanisms. The EAAT1/GLAST knockout mice also display poor nesting behaviour and abnormal sociability (Watase et al., 1998, Sharp, Liu, Zhan, & Ander, 2008). This can be seen in the results of grooming and time spent in periphery whereby there is a drop in grooming behavior.
In another study, done by Sarac et al., 2009, several mechanisms such as loss of glial glutamine synthetase or loss of glutaminase in neurons in hippocampus in mesial temporal lobe epilepsy (MTLE), have been found and attributed to the mechanism for raised extra-cellular glutamate with lowered expression of EAAT1/GLAST and EAAT2/GLT-1 role to converted the glutamate to glutamine was slowed thus extracellular glutamate is increased leading to MTLE and the author also mentioned that downregulation of the EAAT1/GLAST transporters could be secondary to reduced neuronal glutamate transmission and release or downregulation of the transporters could in itself contribute to neuronal death by increasing extra-cellular glutamate concentrations leading to selective neurotoxicity towards MTLE. Furthermore, in another study the author mentioned, dysfunction of glutamate transport may contribute to high extracellular glutamate in the epileptogenic hippocampus. Impaired glutamate transport function has been reported in human epilepsy but remains controversial. Therefore, reduction of glutamate-mediated excitotoxicity is a potential strategy to prevent seizure-induced neuronal death and subsequent recurrent seizures. In our results we should that EAAT1/GLAST upregulated on day 7 but on day 1 and day 3 was lower. This could have led to secondary damage to the neurons while the EAAT1/GLAST transporters were low on day 1and day 3 and the conversion of glutamate to glutamine was not taking place so there was increased extracellular glutamate causing secondary damage to the neurons to occur.
GABAAα1 subunit on day 1 and day 3 showed increased expression, but day 7 showed a reduction of the expressed subunit. In this study GABAAα1 receptor containing subunit level in perihematomal area may vary depending on glutamate release and reuptake in perilesional tissue (Qin et al., 2019). Meanwhile it is highlighted in the temporal course of glutamate release and reuptake in perilesional tissue in traumatic brain injury (TBI) model. In “pericontusional” hippocampus, glutamine did not peak until day 3 implying a slower, ongoing glutamate release that may indicate that tissue remains viable beyond the initial injury. They also demonstrated a decrease in GABA on day 1 in lesioned tissue, but not deeper hippocampal tissue, which they proposed was due to decreased conversion of glutamate to GABA that leads to excitotoxicity (Colombel, Lalonde, & Caston, 2002). In another study, they found that changes in receptor containing subunit γ2, a subunit of GABAA receptors in rats at day 7 developed seizures following TBI (Kaja et al., 2015). Our results suggest that there could be a plausible event like this that happens in the ICbH model in mice whereby GABAAα1 receptor containing subunit expression causes a further tip of the balance between excitation to inhibition to become more excitatory, this may also be because GABA’s inhibitory effects in the adult brain is known to be reversed to excitatory by pathological conditions such as epilepsy and traumatic brain injury (TBI) (Ben-Ari, 2014). It is said that there are no major behavioural changes when α1 subunit is disrupted but these mice however exhibit a marked loss of GABAA receptor numbers and compensatory increases in the GABAA receptor α2 and α3 subunit in the forebrain (Savtchenko et al., 2015). Investigation conducted on the cerebellum showed that there was a dramatic increase of compensatory α3, α4 and α6 subunits in α1 knockout mice (Ogris et al., 2006).
Based on the results in this study, we conclude that ICbH causes motor deficits following ICbH. We also understand that the cerebellum is involved in the mediation of the motor behaviour following ICbH. In the perihematomal regions, ischemia may play a major part in the release of more glutamate, and when there is excess of glutamate in the synaptic cleft, this could cause damage to the neurons. Our findings concluded that level of glutamate could be regulate by EAAT1/GLAST to prevent the causation of excitotoxicity following ICbH in perihematomal regions. GFAP is present in the CNS when there is an insult to the brain and could be utilised as a marker because more expression of GFAP is present in ICH. Meanwhile GABAAα1 receptor containing subunit could not balance the inhibitory role in perihematomal regions.
In conclusion, we believe that NO and NOS pathway has an important role in cascade of secondary neuronal damage of the perihaematoma region of ICbH. By further investigating manipulation of NO and NOS pathway with exogenous NO donor, there is a therapeutic possibility in reducing the secondary neuronal damage in ICbH. It can serve as primary treatment in ICbH which does not require surgical evacuation or as an adjunct treatment after surgical evacuation of clot, to improve the post-operative neurological outcome in future. There is involvement of EAAT1/GLAST, GFAP and GABAAα1 in the perihematomal regions of the cerebellum after ICbH pertaining to secondary damage. Further, experiments need to be conducted to understand all other glutamate receptors and transporters and GABAA receptors in ICbH in mouse model. The present results give new insights to find therapies for minimizing secondary neuronal damage in ICbH.
Acknowledgements
We thank the Ministry of Science, Technology & Innovation Malaysia (MOSTI). This work has been supported by Project number: 06-05-13-SF0016, from the science fund of 2014. Also, we would like to thank the Director of the Hospital Universiti Sains Malaysia (HUSM) and School of Medical Sciences, Universiti Sains Malaysia (USM) for granting permission to the investigators to use all the related facilities and assets belong to USM during the process of conducting this research project. We also thank all the staff of Animal Research and Service Centre (ARASC), USM, Kubang Kerian, Kelantan for their technical support and help in this project.
Conflicts of Interest
The authors declare no conflict of interest.
References
- Aronowski J and Zhao X. (2011). Molecular pathophysiology of cerebral hemorrhage: secondary brain injury. Stroke, 42(6), 1781–1786. [CrossRef]
- Ben-Ari, Y. (2014, August 26). The GABA excitatory/inhibitory developmental sequence: A personal journey. Neuroscience, Vol. 279, pp. 187–219. 26 August. [CrossRef]
- Brenner, M. (2014). Role of GFAP in CNS injuries.
- Broderick J, Connolly S, Feldmann E, Hanley D, Kase C, and Krieger D. (2007). Guidelines for the management of spontaneous intracerebral hemorrhage in adults: 2007 update: a guideline from the American Heart Association/American Stroke Association Stroke Council, High Blood Pressure Research Council, and the Quality of Care and Outcomes in Research Interdisciplinary Working Group. Circulation, 116, 391–413. [CrossRef]
- Canul-Tec, J. C., Assal, R., Cirri, E., Legrand, P., Brier, S., Chamot-Rooke, J., & Reyes, N. (2017). Structure and allosteric inhibition of excitatory amino acid transporter 1. Nature, 544(7651), 446–451. 7651. [CrossRef]
- Chaudhary N, Gemmete JJ, Tompson BG, Xi G, and Pandey AS. (2013). Iron-potential therapeutic target in hemorrhagic stroke. World Neurosurgery, 79, 7–9. [CrossRef]
- Chiu, C.-D., Yao, N.-W., Guo, J.-H., Shen, C.-C., Lee, H.-T., Chiu, Y.-P., … Chang, C. (2017). Inhibition of astrocytic activity alleviates sequela in acute stages of intracerebral hemorrhage.
- Cirillo, J., Mooney, R. A., Ackerley, S. J., Alan Barber, P., Borges, V. M., Clarkson, A. N., … Byblow, W. D. (2020). Neurochemical balance and inhibition at the subacute stage after stroke. Journal of Neurophysiology, 123(5), 1775–1790. 5. [CrossRef]
- Colombel, C., Lalonde, R., & Caston, J. (2002). The effects of unilateral removal of the cerebellar hemispheres on motor functions and weight gain in rats. Brain Research, 950(1–2), 231–238. [CrossRef]
- Deuis, J. R., Dvorakova, L. S., & Vetter, I. (2017). Methods Used to Evaluate Pain Behaviors in Rodents. Front. Mol. Neurosci, 10, 284. (. [CrossRef]
- Eng, L. F., & Ghirnikar, R. S. (1994). GFAP and Astrogliosis. Brain Pathology, 4(3), 229–237. 3. [CrossRef]
- Enna, S. J. (2007). The GABA Receptors. In The GABA Receptors (pp. 1–21).
- Fedele, M. , Gualillo, O., & Vecchione, A. (2016). Editorial Animal Models of Human Pathology 2016.
- Garry, P.S., et al., The role of the nitric oxide pathway in brain injury and its treatment — From bench to bedside. Experimental Neurology, 2015. 263: p. 235-243. [CrossRef]
- Guyenet, S. J. , Furrer, S. A., Damian, V. M., Baughan, T. D., la Spada, A. R., & Garden, G. A. (2010). A simple composite phenotype scoring system for evaluating mouse models of cerebellar ataxia. Journal of Visualized Experiments, (39).
- Hlatky, R. , et al., Role of nitric oxide in cerebral blood flow abnormalities after traumatic brain injury. J Cereb Blood Flow Metab, 2003. 23(5): p. 582-8. [CrossRef]
- Iqbal, S. , et al., Inducible nitric oxide synthase (NOS-2) in subarachnoid hemorrhage: Regulatory mechanisms and therapeutic implications. Brain Circ, 2016. 2(1): p. 8-19. [CrossRef]
- Jung CS, Iuliano BA, Harvey White J, Espey MG, Oldfield EH, Pluta RM. (2004). Association between cerebrospinal fluid levels of asymmetric dimethyl L arginine, an endogenous inhibitor of endothelial nitric oxide synthase, and cerebral vasospasm in a primate model of subarachnoid hemorrhage. J Neurosurg, 101, 836 42.
- Kaja, S. , Payne, A. J., Nielsen, E., Thompson, C. L., van den Maagdenberg, A. M. J. M., Koulen, P., & Snutch, T. P. (2015). Differential cerebellar GABAA receptor expression in mice with mutations in CaV2.1 (P/Q-type) calcium channels. Neuroscience, 304, 198–208. [CrossRef]
- Kandasamy, R., et al., Cerebrospinal fluid nitric oxide metabolite levels as a biomarker in severe traumatic brain injury. International Journal of Neuroscience, 2013. 123(6): p. 385-391.Pautz, A., et al., Regulation of the expression of inducible nitric oxide synthase. Nitric Oxide, 2010. 23(2): p. 75-93. [CrossRef]
- Kirollos RW, Tyagi AK, Ross SA, van Hille PT, Marks PV. (2001). Management of spontaneous cerebellar hematomas: a prospective treatment protocol. Neurosurgery, 49, 1378–1387. [CrossRef]
- Krafft, P. R. , Rolland, W. B., Duris, K., Lekic, T., Campbell, A., Tang, J., & Zhang, J. H. (2012). Modeling intracerebral hemorrhage in mice: Injection of autologous blood or bacterial collagenase. Journal of Visualized Experiments. [CrossRef]
- Langford, D. J., Bailey, A. L., Chanda, M. L., Clarke, S. E., Drummond, T. E., Echols, S., … Mogil, J. S. (2010). Coding of facial expressions of pain in the laboratory mouse. Nature Methods, 7(6), 447–449. 7, 6, 447–449.
- Lee, F. H. F. , Zhang, H., Jiang, A., Zai, C. C., & Liu, F. (2018). Specific Alterations in Astrocyte Properties via the GluA2-GAPDH Complex Associated with Multiple Sclerosis. Scientific Reports, 8(1), 1–17. [CrossRef]
- Lekic, T., et al., Characterization of the Brain Injury, Neurobehavioral Profiles and Histopathology in a Rat Model of Cerebellar Hemorrhage. Exp Neurol, 2011. 227(1): p. 96-103. [CrossRef]
- Lekic, T., Rolland, W., Hartman, R., Kamper, J., Suzuki, H., Tang, J., & Zhang, J. H. (2011a). Characterization of the brain injury, neurobehavioral profiles, and histopathology in a rat model of cerebellar hemorrhage. Experimental Neurology, 227(1), 96–103. 1.
- Li, N., et al., Nitric oxide (NO) and asymmetric dimethylarginine (ADMA): their pathophysiological role and involvement in intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurol Res, 2011. 33(5): p. 541-8. [CrossRef]
- Lorivel, T. and P. Hilber, Effects of chlordiazepoxide on the emotional reactivity and motor capacities in the cerebellar Lurcher mutant mice. Behav Brain Res, 2006. 173(1): p. 122-8. [CrossRef]
- Luger, S., Witsch, J., Dietz, A., Hamann, G. F., Minnerup, J., Schneider, H., … Foerch, C. (2017). Glial fibrillary acidic protein serum levels distinguish between intracerebral hemorrhage and cerebral ischemia in the early phase of stroke. Clinical Chemistry, 63(1), 377–385. 1. [CrossRef]
- Manto, M., et al., Consensus Paper: Roles of the Cerebellum in Motor Control—The Diversity of Ideas on Cerebellar Involvement in Movement. The Cerebellum, 2012. 11(2): p. 457-487. [CrossRef]
- McKeon, A., & Benarroch, E. E. (2018). Glial fibrillary acid protein: Functions and involvement in disease. Neurology, 90(20), 925–930. [CrossRef]
- Morton, S.M. and A.J. Bastian, Cerebellar control of balance and locomotion. Neuroscientist, 2004. 10(3): p. 247-59.
- Mracsko, E. and R. Veltkamp, Neuroinflammation after intracerebral hemorrhage. Front Cell Neurosci, 2014. 8: p. 388. [CrossRef]
- Muthuraju, S., et al., Role of cholinergic markers on memory function of rats exposed to hypobaric hypoxia. Eur J Pharmacol, 2011. 672(1-3): p. 96-105. [CrossRef]
- Ogris, W., Lehner, R., Fuchs, K., Furtmuller, B., Hoger, H., Homanics, G. E., & Sieghart, W. (2006). Investigation of the abundance and subunit composition of GABAA receptor subtypes in the cerebellum of alpha1-subunit-deficient mice. Journal of Neurochemistry, 96(1), 136–147. [CrossRef]
- Peers, C., H.A. Pearson, and J.P. Boyle, Hypoxia and Alzheimer's disease. Essays in biochemistry, 2007. 43: p. 153-164. [CrossRef]
- Piknova, B., et al., The role of nitrite in neurovascular coupling. Brain Res, 2011. 1407: p. 62-8.
- Qin, L. , Actor-Engel, H. S., Woo, M. S., Shakil, F., Chen, Y. W., Cho, S., & Aoki, C. (2019). An Increase of Excitatory-to-Inhibitory Synaptic Balance in the Contralateral Cortico-Striatal Pathway Underlies Improved Stroke Recovery in BDNF Val66Met SNP Mice. Neurorehabilitation and Neural Repair, 33(12), 989–1002. [CrossRef]
- Qureshi AI, Mendelow AD, Hanley DF. Intracerebral haemorrhage. (2009). Lancet, 373, 1632–1644.
- Qureshi, A.I., et al., Apoptosis as a form of cell death in intracerebral hemorrhage. Neurosurgery, 2003. 52(5): p. 1041-7; discussion 1047-8.
- Raco A, Caroli E, Isidori A, Salvati M. (2003). Management of acute cerebellar infarction: one institution's experience. Neurosurgery, 53, 1061–1066.
- Radi, R., Peroxynitrite, a stealthy biological oxidant. J Biol Chem, 2013. 288(37): p. 26464-72. [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, G. A. (2011, April). Modeling of cerebellar hemorrhage. Experimental Neurology, Vol. 228, pp. 157–159. [CrossRef]
- Rosenberg, G. A., Mun-Bryce, S., Wesley, M., & Komfeld, M. (1990). Collagenase-induced intracerebral hemorrhage in rats. Stroke, 21(5), 801–807. [CrossRef]
- Shiva, S., Nitrite: A physiological store of nitric oxide and modulator of mitochondrial function. Redox Biology, 2013. 1(1): p. 40-44. [CrossRef]
- Tijjani Salihu A, Muthuraju S, Aziz Mohamed Yusoff A, Ahmad F, Zulkifli Mustafa M, Jaafar H, Idris Z, Rahman Izaini Ghani A, Malin Abdullah J. (2016). Mouse model of intracerebellar haemorrhage. Behav Brain Res, 1(312), 374-84. 312.
- Toda, N. and T. Okamura, The Pharmacology of Nitric Oxide in the Peripheral Nervous System of Blood Vessels. Pharmacological Reviews, 2003. 55(2): p. 271. [CrossRef]
- Toda, N., K. Ayajiki, and T. Okamura, Cerebral Blood Flow Regulation by Nitric Oxide: Recent Advances. Pharmacological Reviews, 2009. 61(1): p. 62. [CrossRef]
- Tykhomyrov, A. , Pavlova, A. S., & Nedzvetsky, V. S. (2016). Glial Fibrillary Acidic Protein (GFAP): on the 45th Anniversary of Its Discovery. Neurophysiology, 48(1), 54–71. [CrossRef]
- Vellimana, A.K. , et al., Endothelial nitric oxide synthase mediates endogenous protection against subarachnoid hemorrhage-induced cerebral vasospasm. Stroke, 2011. 42(3): p. 776-82. [CrossRef]
- Wasserman, J.K., H. Yang, and L.C. Schlichter, Glial responses, neuron death and lesion resolution after intracerebral hemorrhage in young vs. aged rats. European Journal of Neuroscience, 2008. 28(7): p. 1316-1328. [CrossRef]
- Watase, K., Hashimoto, K., Kano, M., Yamada, K., Watanabe, M., Inoue, Y., … Tanaka, K. (1998). Motor discoordination and increased susceptibility to cerebellar injury in GLAST mutant mice. European Journal of Neuroscience, 10(3), 976–988. 3. [CrossRef]
- Yan, T. , Chopp, M., & Chen, J. (2015, December 1). Experimental animal models and inflammatory cellular changes in cerebral ischemic and hemorrhagic stroke. Neuroscience Bulletin, Vol. 31, pp. 717–734. [CrossRef]
- Yong, K. S. M. , Her, Z., & Chen, Q. (2018, August 1). Humanized Mice as Unique Tools for Human-Specific Studies. Archivum Immunologiae et Therapiae Experimentalis, Vol. 66, pp. 245–266. [CrossRef]
- Yoon, H. , Walters, G., Paulsen, A. R., & Scarisbrick, I. A. (2017). Astrocyte heterogeneity across the brain and spinal cord occurs developmentally, in adulthood and in response to demyelination. PLoS ONE, 12(7). [CrossRef]
- Zimcikova, E. , Simko, J., Karesova, I., Kremlacek, J., & Malakova, J. (2017). Behavioral effects of antiepileptic drugs in rats: Are the effects on mood and behavior detectable in open-field test? [CrossRef]
Figure 1.
(A) shows the latency in seconds for rota-rod test, (B). shows the latency in seconds for stationary wooden bean walk, (C). shows latency in seconds for suspension wire test, (D). shows the latency in seconds for hole board test. The data shown following ICbH in the control, day-1, day-3 and day-7. One-way ANOVA test were used for the analysis of data from behavior studies. Post hoc difference differences between group means were tested using the Newman-Keuls test. Values of p ≤ 0.05 was considered as significant.
Figure 1.
(A) shows the latency in seconds for rota-rod test, (B). shows the latency in seconds for stationary wooden bean walk, (C). shows latency in seconds for suspension wire test, (D). shows the latency in seconds for hole board test. The data shown following ICbH in the control, day-1, day-3 and day-7. One-way ANOVA test were used for the analysis of data from behavior studies. Post hoc difference differences between group means were tested using the Newman-Keuls test. Values of p ≤ 0.05 was considered as significant.
Figure 2.
Total Nitric Oxide metabolites level in control, day 1, day 3 and day 7 following ICbH. One-way ANOVA tests were used for the analysis of data from biochemical studies. Post hoc difference differences between group means were tested using the Newman-Keuls test. Values of p ≤ 0.05 was considered as significant.
Figure 2.
Total Nitric Oxide metabolites level in control, day 1, day 3 and day 7 following ICbH. One-way ANOVA tests were used for the analysis of data from biochemical studies. Post hoc difference differences between group means were tested using the Newman-Keuls test. Values of p ≤ 0.05 was considered as significant.
Figure 3.
(A): Morphology of hematoma formation on control, day 1, day 3 and day 7 groups. Largest clot seen on day 3 after induction. Clot resolution seen on day 7. Figure 3 (B): Hematoxylin & Eosin staining of cerebellum tissue. Upper row: showing normal cerebellum tissue on control and hematoma formation on day 1. Lower row: Granular layer of cerebellum cortex on control and perihaematoma region – labelled PH (Perihaematoma), on day 1, day 3 and day 7.
Figure 3.
(A): Morphology of hematoma formation on control, day 1, day 3 and day 7 groups. Largest clot seen on day 3 after induction. Clot resolution seen on day 7. Figure 3 (B): Hematoxylin & Eosin staining of cerebellum tissue. Upper row: showing normal cerebellum tissue on control and hematoma formation on day 1. Lower row: Granular layer of cerebellum cortex on control and perihaematoma region – labelled PH (Perihaematoma), on day 1, day 3 and day 7.
Figure 4.
Annexin V-FITC/Propidium Iodide Assay showing progression of apoptosis of neurons from day 1 to day 7 compared to control.
Figure 4.
Annexin V-FITC/Propidium Iodide Assay showing progression of apoptosis of neurons from day 1 to day 7 compared to control.
Figure 5.
Scanning Electron Microscope Image. Normal neurons seen on control. Day 1 - axonal damage seen with some intact neuronal soma. Day 3 - shrinkage of neurons occupying in perihaematoma region. Day 7- Remnants of dead neurons and reorganization of perihaematoma tissue.
Figure 5.
Scanning Electron Microscope Image. Normal neurons seen on control. Day 1 - axonal damage seen with some intact neuronal soma. Day 3 - shrinkage of neurons occupying in perihaematoma region. Day 7- Remnants of dead neurons and reorganization of perihaematoma tissue.
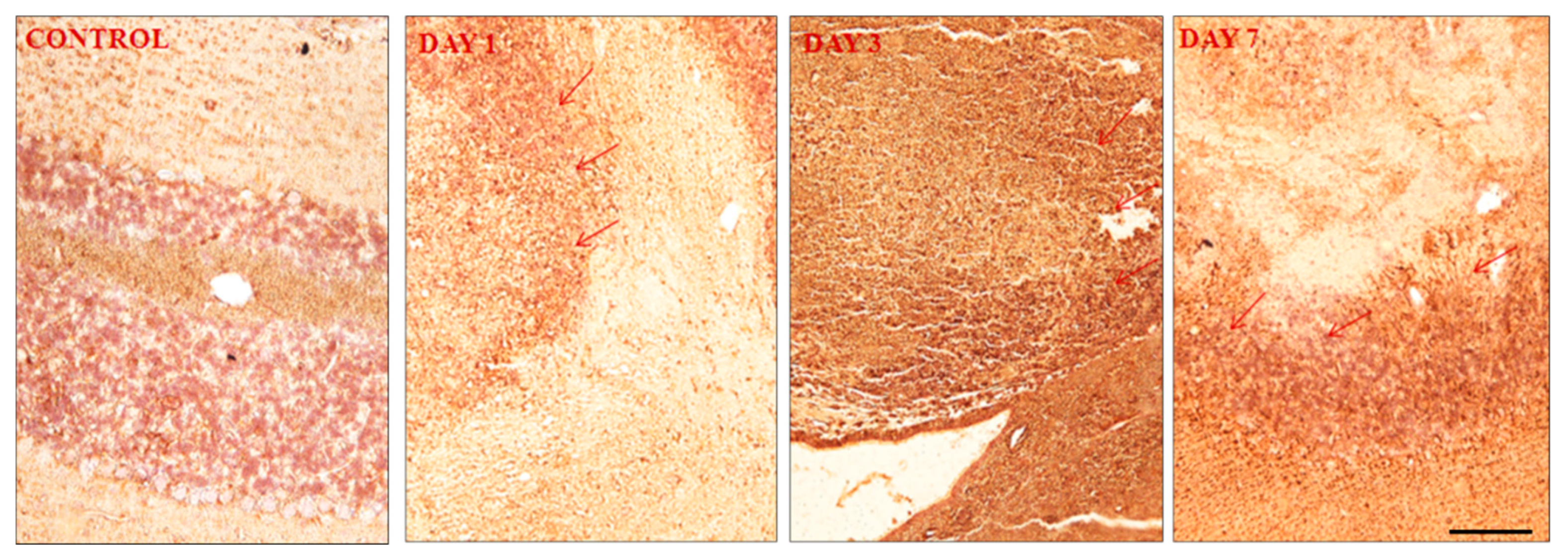
Figure 6.
Expression of GFAP following induction of hemorrhage in the cerebellum. Day 7 shows more GFAP expressions that day 3 and day 1. It indicates neurons under stress condition. Picture (A) shows no expression, (B) shows mild expression (+), (C) shows moderate expression (++) and (D) shows strong expression (+++). The cell and tissue were labelled with chromogen 3-3-diaminobenzidine (DAB). The red arrows show the area of expression that shows GFAP expression. 3 blinded investigators gave the same scale value on observation. Cohen kappa: 0.75. Scale bar = 50µm and 20x magnification was used.
Figure 6.
Expression of GFAP following induction of hemorrhage in the cerebellum. Day 7 shows more GFAP expressions that day 3 and day 1. It indicates neurons under stress condition. Picture (A) shows no expression, (B) shows mild expression (+), (C) shows moderate expression (++) and (D) shows strong expression (+++). The cell and tissue were labelled with chromogen 3-3-diaminobenzidine (DAB). The red arrows show the area of expression that shows GFAP expression. 3 blinded investigators gave the same scale value on observation. Cohen kappa: 0.75. Scale bar = 50µm and 20x magnification was used.
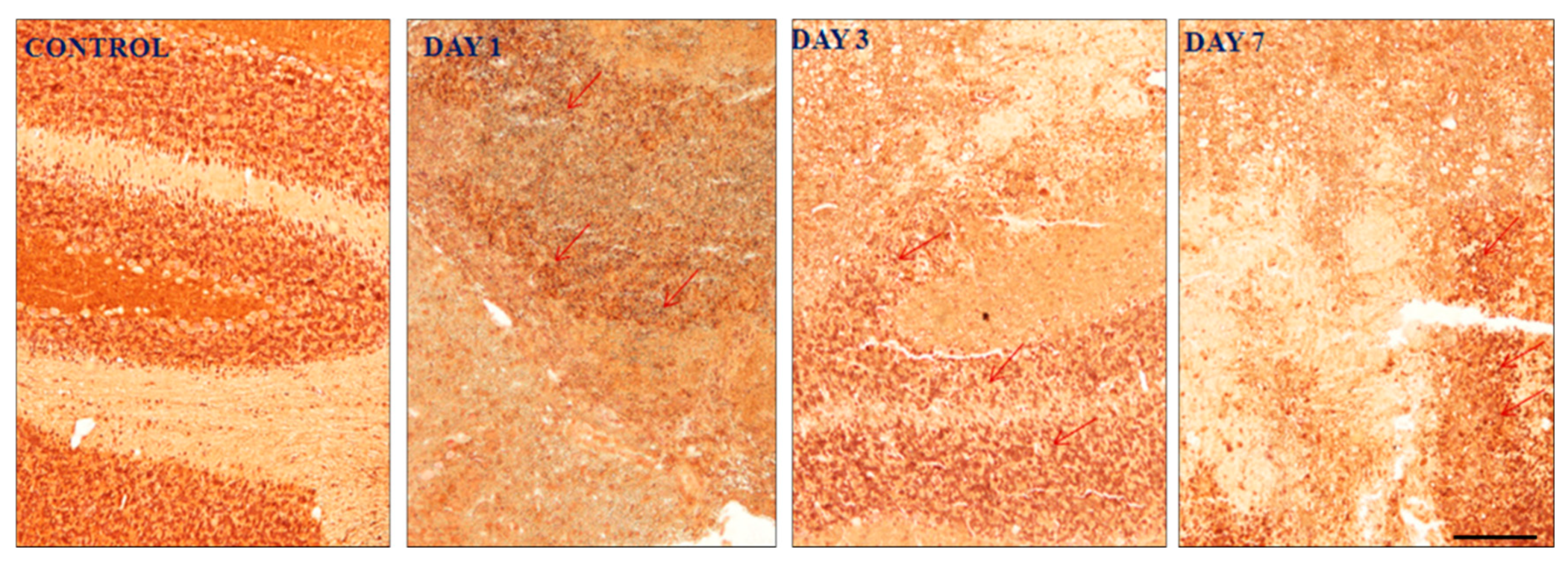
Figure 7.
Expression of EAAT1/GLAST following induction of haemorrhage in the cerebellum. Day 7 shows more EAAT1/GLAST expressions than day 3 and day 1. It indicates neuron under stress. Picture (A) showed no expression, (B) showed mild expression (+), (C) showed moderate expression (++) and (D) showed strong expression. The cell and tissue were labelled with chromogen 3-3-diaminobenzidine (DAB). The red arrows show the area of expression that shows EAAT1/GLAST expression. 3 blinded investigators gave the same scale value on observation. Cohen kappa: 0.75. Scale bar = 50µm and 20x magnification was used.
Figure 7.
Expression of EAAT1/GLAST following induction of haemorrhage in the cerebellum. Day 7 shows more EAAT1/GLAST expressions than day 3 and day 1. It indicates neuron under stress. Picture (A) showed no expression, (B) showed mild expression (+), (C) showed moderate expression (++) and (D) showed strong expression. The cell and tissue were labelled with chromogen 3-3-diaminobenzidine (DAB). The red arrows show the area of expression that shows EAAT1/GLAST expression. 3 blinded investigators gave the same scale value on observation. Cohen kappa: 0.75. Scale bar = 50µm and 20x magnification was used.
Figure 8.
Expression of GABAA α1 subunit following induction of haemorrhage in the cerebellum. Day 7 shows less GABAA α1 subunit expression that day 3 and day 1. It indicates neuron under stress condition. Pictures (A) showed no expression, (B) showed moderate expression (++), (C) showed strong expression (+++) and (D) showed mild expression (+). The cell and tissue were labelled with chromogen 3-3-diaminobenzidine (DAB). The red arrows show the area of expression that shows GABAA α1 subunit expression. 3 blinded investigators gave the same scale of value on observation. Cohen kappa: 0.75. Scale bar = 50µm and 20x magnification was used.
Figure 8.
Expression of GABAA α1 subunit following induction of haemorrhage in the cerebellum. Day 7 shows less GABAA α1 subunit expression that day 3 and day 1. It indicates neuron under stress condition. Pictures (A) showed no expression, (B) showed moderate expression (++), (C) showed strong expression (+++) and (D) showed mild expression (+). The cell and tissue were labelled with chromogen 3-3-diaminobenzidine (DAB). The red arrows show the area of expression that shows GABAA α1 subunit expression. 3 blinded investigators gave the same scale of value on observation. Cohen kappa: 0.75. Scale bar = 50µm and 20x magnification was used.
Figure 9.
(A). SOD1 gene expression at the perihematomal area after ICH. Gel electrophoresis analysis of SOD1 expression in the perihematomal area of brain section in control, day 1, 3 and 7 post ICbH. The bar graph shows the optical density values (in percentage to B-Actin) ± SD of SOD1 PCR product bands. (n=4), (B). Catalase gene expression at the perihematomal area after ICH. The bar graph shows the optical density values (in percentage to B-Actin) ± SD of catalase PCR product bands. (n=4), (C). nNOS gene expression at the perihematomal area after ICH. The bar graph shows the optical density values (in percentage to B-Actin) ± SD of nNOS PCR product bands. (n=4), (D). GPx1 gene expression at the perihematomal area after ICH. The bar graph shows the optical density values (in percentage to B-Actin) ± SD of GPx1 PCR product bands. (n=4), (E). COX2 gene expression at the perihematomal area after ICH. Gel electrophoresis analysis of COX2 expression in the perihematomal area of brain section in control, day 1, 3 and 7 post ICbH. The bar graph shows the optical density values (in percentage to B-Actin) ± SD of COX2 PCR product bands. (n=4).
Figure 9.
(A). SOD1 gene expression at the perihematomal area after ICH. Gel electrophoresis analysis of SOD1 expression in the perihematomal area of brain section in control, day 1, 3 and 7 post ICbH. The bar graph shows the optical density values (in percentage to B-Actin) ± SD of SOD1 PCR product bands. (n=4), (B). Catalase gene expression at the perihematomal area after ICH. The bar graph shows the optical density values (in percentage to B-Actin) ± SD of catalase PCR product bands. (n=4), (C). nNOS gene expression at the perihematomal area after ICH. The bar graph shows the optical density values (in percentage to B-Actin) ± SD of nNOS PCR product bands. (n=4), (D). GPx1 gene expression at the perihematomal area after ICH. The bar graph shows the optical density values (in percentage to B-Actin) ± SD of GPx1 PCR product bands. (n=4), (E). COX2 gene expression at the perihematomal area after ICH. Gel electrophoresis analysis of COX2 expression in the perihematomal area of brain section in control, day 1, 3 and 7 post ICbH. The bar graph shows the optical density values (in percentage to B-Actin) ± SD of COX2 PCR product bands. (n=4).
|
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (https://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).