Submitted:
03 July 2023
Posted:
04 July 2023
You are already at the latest version
Abstract
Keywords:
Introduction
Hallmarks of the Tumour Microenvironment of Gliomas
- a)
- Cellular Armoury and the Blood Brain Barrier
- b)
- The Lymphocytic Milieu
- c)
- Immunosuppressive factors and immune evasion
Immunotherapy and the Interplay
- a)
- Immunotherapy Landscape in Glioma
- b)
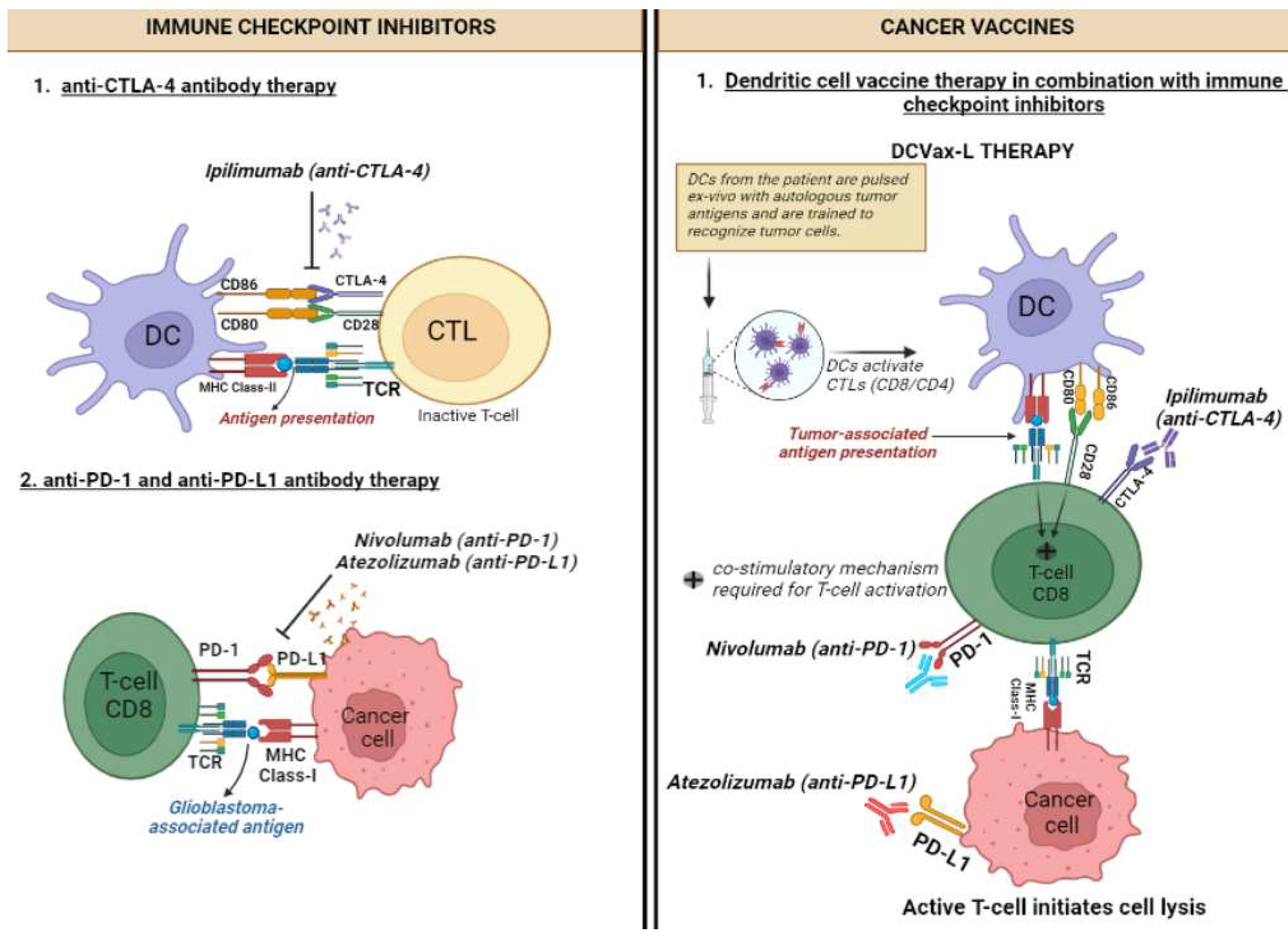
- Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors
- c)
- Therapeutic cancer vaccines
- d)
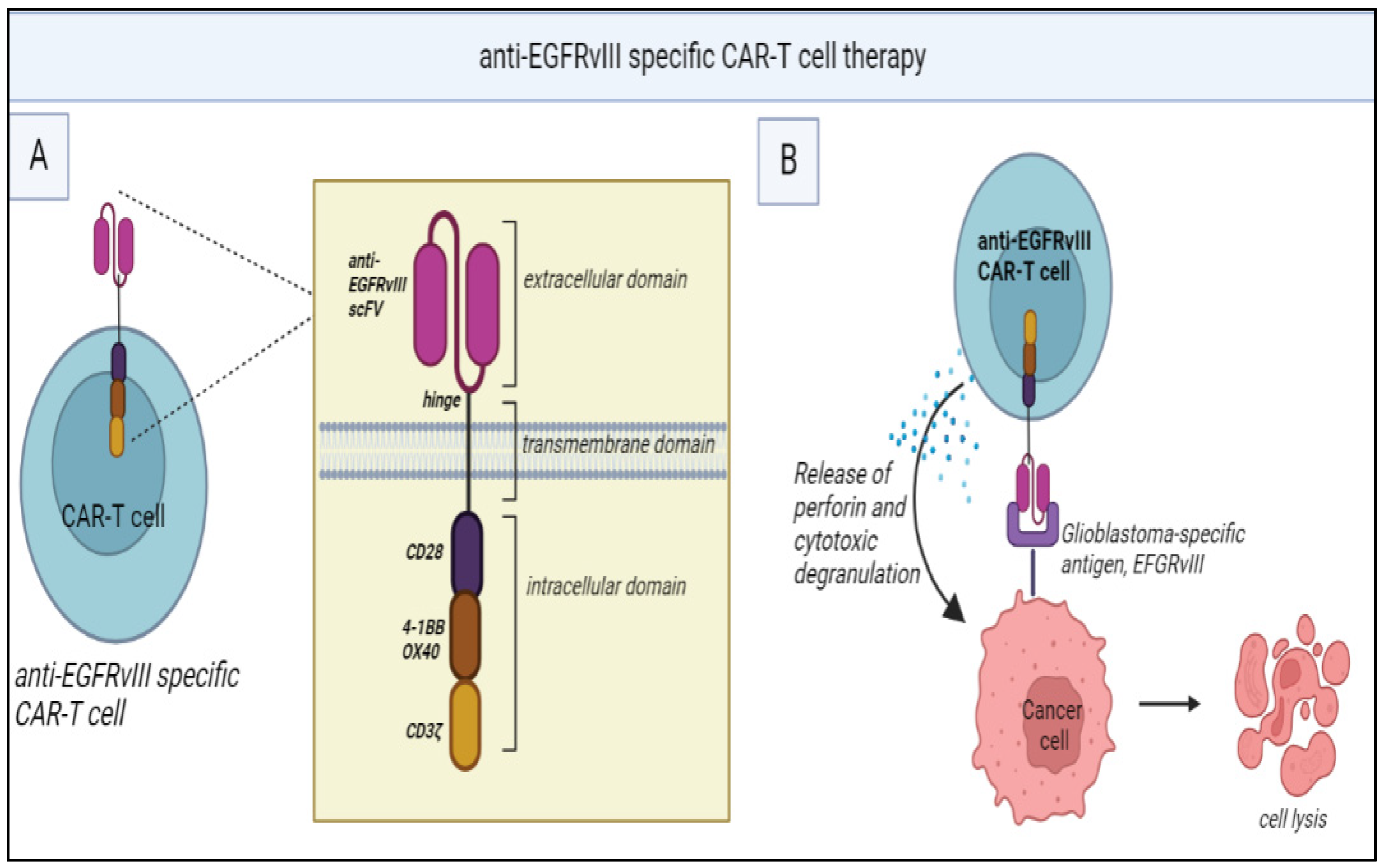
- Chimeric Antigen Receptor T and NK cells
- e)
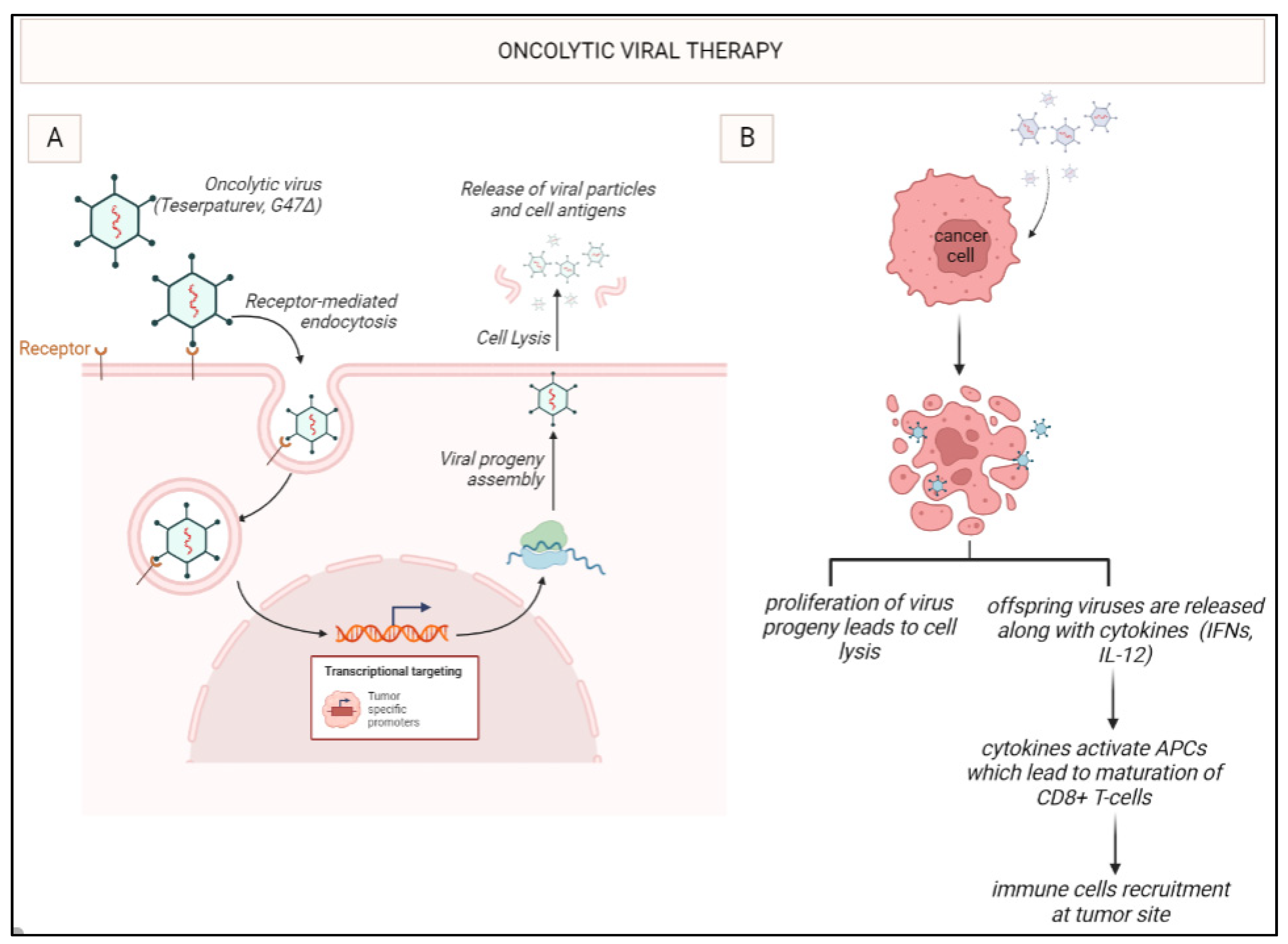
- Oncolytic virotherapy
Conclusions
Author Contributions
Funding
Conflicts of Interest
References
- Stupp, R.; Hegi, M.E.; Mason, W.P.; van den Bent, M.J.; Taphoorn, M.J.; Janzer, R.C.; Ludwin, S.K.; Allgeier, A.; Fisher, B.; Belanger, K.; et al. European Organisation for Research and Treatment of Cancer Brain Tumour and Radiation Oncology Groups; National Cancer Institute of Canada Clinical Trials Group. Effects of radiotherapy with concomitant and adjuvant temozolomide versus radiotherapy alone on survival in glioblastoma in a randomised phase III study: 5-year analysis of the EORTC-NCIC trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2009, 10, 459–466.
- Pollack, I.F.; Agnihotri, S.; Broniscer, A. Childhood brain tumors: current management, biological insights, and future directions. J. Neurosurg. Pediatr. 2019, 23, 261–273. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Ostrom, Q.T.; Cioffi, G.; Waite, K.; Kruchko, C.; Barnholtz-Sloan, J.S. CBTRUS Statistical Report: Primary Brain and Other Central Nervous System Tumors Diagnosed in the United States in 2014-2018. Neuro. Oncol. 2021, 23, iii–iii105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Louis, D.N.; Perry, A.; Wesseling, P.; Brat, D.J.; Cree, I.A.; Figarella-Branger, D.; Hawkins, C.; Ng, H.K.; Pfister, S.M.; Reifenberger, G.; et al. The 2021 WHO Classification of Tumors of the Central Nervous System: a summary. Neuro. Oncol. 2021, 23, 1231–1251. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Soeda, A.; Hara, A.; Kunisada, T.; Yoshimura, S.; Iwama, T.; Park, D.M. The evidence of glioblastoma heterogeneity. Sci. Rep. 2015, 5, 7979. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Rolle, C.E.; Sengupta, S.; Lesniak, M.S. Mechanisms of immune evasion by gliomas. Adv. Exp. Med. Biol. 2012, 746, 53–76. [Google Scholar] [PubMed]
- Magaña-Maldonado, R.; Chávez-Cortez, E.G.; Olascoaga-Arellano, N.K.; López-Mejía, M.; Maldonado-Leal, F.M.; Sotelo, J.; Pineda, B. Immunological Evasion in Glioblastoma. Biomed. Res. Int. 2016, 2016, 7487313. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Gieryng, A.; Pszczolkowska, D.; Walentynowicz, K.A.; Rajan, W.D.; Kaminska, B. Immune microenvironment of gliomas. Lab. Invest. 2017, 97, 498–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Groblewska, M.; Litman-Zawadzka, A.; Mroczko, B. The Role of Selected Chemokines and Their Receptors in the Development of Gliomas. Int. J. Mol. Sci. 2020, 21, 3704. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, Z.; Mou, L.; Pan, Y.; Feng, C.; Zhang, J.; Li, J. CXCL8 Promotes Glioma Progression By Activating The JAK/STAT1/HIF-1α/Snail Signaling Axis. Onco. Targets. Ther. 2019, 12, 8125–8138. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dapash, M.; Hou, D.; Castro, B.; Lee-Chang, C.; Lesniak, MS. The Interplay between Glioblastoma and Its Microenvironment. Cells. 2021, 10, 2257. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- DeCordova, S.; Shastri, A.; Tsolaki, A.G.; Yasmin, H.; Klein, L.; Singh, S.K.; Kishore, U. Molecular Heterogeneity and Immunosuppressive Microenvironment in Glioblastoma. Front. Immunol. 2020, 11, 1402. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Chen, H.; Li, M.; Guo, Y.; Zhong, Y.; He, Z.; Xu, Y.; Zou, J. Immune response in glioma's microenvironment. Innov. Surg. Sci. 2021, 5, 20190001. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, N.F.; Carter, T.J.; Ottaviani, D.; Mulholland, P. Harnessing the immune system in glioblastoma. Br. J. Cancer. 2018, 119, 1171–1181. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Pombo Antunes, A.R.; Scheyltjens, I.; Duerinck, J.; Neyns, B.; Movahedi, K.; Van Ginderachter, J.A. Understanding the glioblastoma immune microenvironment as basis for the development of new immunotherapeutic strategies. Elife. 2020, 9, e52176. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Price, G.; Bouras, A.; Hambardzumyan, D.; Hadjipanayis, C.G. Current knowledge on the immune microenvironment and emerging immunotherapies in diffuse midline glioma. EBioMedicine. 2021, 69, 103453. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lu-Emerson, C.; Snuderl, M.; Kirkpatrick, N.D.; Goveia, J.; Davidson, C.; Huang, Y.; Riedemann, L.; Taylor, J.; Ivy, P.; Duda, D.G.; et al. Increase in tumor-associated macrophages after antiangiogenic therapy is associated with poor survival among patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Neuro. Oncol. 2013, 15, 1079–1087. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Böttcher, J.P.; Reis e Sousa, C. The Role of Type 1 Conventional Dendritic Cells in Cancer Immunity. Trends. Cancer. 2018, 4, 784–792. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Grabowski, M.M.; Sankey, E.W.; Ryan, K.J.; Chongsathidkiet, P.; Lorrey, S.J.; Wilkinson, D.S.; Fecci, P.E. Immune suppression in gliomas. J. Neurooncol. 2021, 151, 3–12. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Hetze, S.; Sure, U.; Schedlowski, M.; Hadamitzky, M.; Barthel, L. Rodent Models to Analyze the Glioma Microenvironment. ASN. Neuro. 2021, 13, 17590914211005074. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lieberman, N.A.P.; DeGolier, K.; Kovar, H.M.; Davis, A.; Hoglund, V.; Stevens, J.; Winter, C.; Deutsch, G.; Furlan, S.N.; Vitanza, N.A.; et al. Characterization of the immune microenvironment of diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma: implications for development of immunotherapy. Neuro. Oncol. 2019, 21, 83–94. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Liau, L.M.; Ashkan, K.; Brem, S.; Campian, J.L.; Trusheim, J.E.; Iwamoto, F.M.; Tran, D.D.; Ansstas, G.; Cobbs, C.S.; Heth, J.A.; et al. Association of Autologous Tumor Lysate-Loaded Dendritic Cell Vaccination With Extension of Survival Among Patients With Newly Diagnosed and Recurrent Glioblastoma: A Phase 3 Prospective Externally Controlled Cohort Trial. JAMA. Oncol. 2023, 9, 112–121. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Dubois, L.G.; Campanati, L.; Righy, C.; D'Andrea-Meira, I.; Spohr, T.C.; Porto-Carreiro, I.; Pereira, C.M.; Balça-Silva, J.; Kahn, S.A.; DosSantos, M.F.; et al. Gliomas and the vascular fragility of the blood brain barrier. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2014, 8, 418. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Daneman, R.; Prat, A. The blood-brain barrier. Cold. Spring. Harb. Perspect. Biol. 2015, 7, a020412. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fecci, P.E.; Mitchell, D.A.; Whitesides, J.F.; Xie, W.; Friedman, A.H.; Archer, G.E.; Herndon, J.E. 2nd.; Bigner, D.D.; Dranoff, G.; Sampson, J.H. Increased regulatory T-cell fraction amidst a diminished CD4 compartment explains cellular immune defects in patients with malignant glioma. Cancer. Res. 2006, 66, 3294–3302.
- Fares, J.; Fares, M.Y.; Fares, Y. Natural killer cells in the brain tumor microenvironment: Defining a new era in neuro-oncology. Surg. Neurol. Int. 2019, 10, 43. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhang, L.; Yu, H.; Xue, Y.; Liu, Y. Decreased natural killer cells in diffuse intrinsic pontine glioma patients. Childs. Nerv. Syst. 2020, 36, 1345–1346. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Zarek, P.E.; Huang, C.T.; Lutz, E.R.; Kowalski, J.; Horton, M.R.; Linden, J.; Drake, C.G.; Powell, J.D. A2A receptor signaling promotes peripheral tolerance by inducing T-cell anergy and the generation of adaptive regulatory T cells. Blood. 2008, 111, 251–259. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jaschinski, F.; Rothhammer, T.; Jachimczak, P.; Seitz, C.; Schneider, A.; Schlingensiepen, K.H. The antisense oligonucleotide trabedersen (AP 12009) for the targeted inhibition of TGF-β2. Curr. Pharm. Biotechnol. 2011, 12, 2203–2213. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Christofides, A.; Kosmopoulos, M.; Piperi, C. Pathophysiological mechanisms regulated by cytokines in gliomas. Cytokine. 2015, 71, 377–384. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Shah, P.V.; Arrieta, V.A.; Lee-Chang, C.; Sonabend, A.M. Cancer Immunoediting in Gliomas: Recent Advances and Implications for Immunotherapy. J. Cell. Immunol. 2020, 2, 352–358. [Google Scholar]
- Al-Kharboosh, R.; ReFaey, K.; Lara-Velazquez, M.; Grewal, S.S.; Imitola, J.; Quiñones-Hinojosa, A. Inflammatory Mediators in Glioma Microenvironment Play a Dual Role in Gliomagenesis and Mesenchymal Stem Cell Homing: Implication for Cellular Therapy. Mayo. Clin. Proc. Innov. Qual. Outcomes. 2020, 4, 443–459. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Najem, H.; Khasraw, M.; Heimberger, A.B. Immune Microenvironment Landscape in CNS Tumors and Role in Responses to Immunotherapy. Cells. 2021, 10, 2032. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Shiravand, Y.; Khodadadi, F.; Kashani, S.M.A.; Hosseini-Fard, S.R.; Hosseini, S.; Sadeghirad, H.; Ladwa, R.; O'Byrne, K.; Kulasinghe, A. Immune Checkpoint Inhibitors in Cancer Therapy. Curr. Oncol. 2022, 29, 3044–3060. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Revythis, A.; Shah, S.; Kutka, M.; Moschetta, M.; Ozturk, M.A.; Pappas-Gogos, G.; Ioannidou, E.; Sheriff, M.; Rassy, E.; Boussios, S. Unraveling the Wide Spectrum of Melanoma Biomarkers. Diagnostics. (Basel). 2021, 11, 1341. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Boussios, S.; Rassy, E.; Samartzis, E.; Moschetta, M.; Sheriff, M.; Pérez-Fidalgo, J.A.; Pavlidis, N. Melanoma of unknown primary: New perspectives for an old story. Crit. Rev. Oncol. Hematol. 2021, 158, 103208. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Adeleke, S.; Haslam, A.; Choy, A.; Diaz-Cano, S.; Galante, J.R.; Mikropoulos, C.; Boussios, S. Microsatellite instability testing in colorectal patients with Lynch syndrome: lessons learned from a case report and how to avoid such pitfalls. Per. Med. 2022, 19, 277–286. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Reardon, D.A.; Brandes, A.A.; Omuro, A.; Mulholland, P.; Lim, M.; Wick, A.; Baehring, J.; Ahluwalia, M.S.; Roth, P. ; Bähr, O, et al. Effect of Nivolumab vs Bevacizumab in Patients With Recurrent Glioblastoma: The CheckMate 143 Phase 3 Randomized Clinical Trial. JAMA. Oncol. 2020, 6, 1003–1010.
- Ameratunga, M.; Pavlakis, N.; Wheeler, H.; Grant, R.; Simes, J.; Khasraw, M. Anti-angiogenic therapy for high-grade glioma. Cochrane. Database. Syst. Rev. 2018, 11, CD008218. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Stessin, A.M.; Clausi, M.G.; Zhao, Z.; Lin, H.; Hou, W.; Jiang, Z.; Duong, T.Q.; Tsirka, S.E.; Ryu, S. Repolarized macrophages, induced by intermediate stereotactic dose radiotherapy and immune checkpoint blockade, contribute to long-term survival in glioma-bearing mice. J. Neurooncol. 2020, 147, 547–555. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Omuro, A.; Brandes, A.A.; Carpentier, A.F.; Idbaih, A.; Reardon, D.A.; Cloughesy, T.; Sumrall, A.; Baehring, J.; van den Bent, M.; Bähr, O.; et al. Radiotherapy combined with nivolumab or temozolomide for newly diagnosed glioblastoma with unmethylated MGMT promoter: An international randomized phase III trial. Neuro. Oncol. 2023, 25, 123–134. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Scheffel, T.B.; Grave, N.; Vargas, P.; Diz, F.M.; Rockenbach, L.; Morrone, F.B. Immunosuppression in Gliomas via PD-1/PD-L1 Axis and Adenosine Pathway. Front. Oncol. 2021, 10, 617385. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Schalper, K.A.; Rodriguez-Ruiz, M.E.; Diez-Valle, R.; López-Janeiro, A.; Porciuncula, A.; Idoate, M.A.; Inogés, S.; de Andrea, C.; López-Diaz de Cerio, A.; Tejada, S.; et al. Neoadjuvant nivolumab modifies the tumor immune microenvironment in resectable glioblastoma. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 470–476. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cloughesy, T.F.; Mochizuki, A.Y.; Orpilla, J.R.; Hugo, W.; Lee, A.H.; Davidson, T.B.; Wang, A.C.; Ellingson, B.M.; Rytlewski, J.A.; Sanders, C.M.; et al. Neoadjuvant anti-PD-1 immunotherapy promotes a survival benefit with intratumoral and systemic immune responses in recurrent glioblastoma. Nat. Med. 2019, 25, 477–486. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Choi, S.; Ismail, A.; Pappas-Gogos, G.; Boussios, S. HPV and Cervical Cancer: A Review of Epidemiology and Screening Uptake in the UK. Pathogens. 2023, 12, 298. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Flores, J.E.; Thompson, A.J.; Ryan, M.; Howell, J. The Global Impact of Hepatitis B Vaccination on Hepatocellular Carcinoma. Vaccines. (Basel). 2022, 10, 793. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, M.J.; Svensson-Arvelund, J.; Lubitz, G.S.; Marabelle, A.; Melero, I.; Brown, B.D.; Brody, J.D. Cancer vaccines: the next immunotherapy frontier. Nat. Cancer. 2022, 3, 911–926. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Morales, A. Treatment of carcinoma in situ of the bladder with BCG: a phase II trial. Cancer. Immunol. Immunother. 1980, 9, 69–72. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Small, E.J.; Schellhammer, P.F.; Higano, C.S.; Redfern, C.H.; Nemunaitis, J.J.; Valone, F.H.; Verjee, S.S.; Jones, L.A.; Hershberg, R.M. Placebo-controlled phase III trial of immunologic therapy with sipuleucel-T (APC8015) in patients with metastatic, asymptomatic hormone refractory prostate cancer. J. Clin. Oncol. 2006, 24, 3089–3094. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Northwest Biotherapeutics. New Patient Inquiry. Available at https://nwbio.com/patients-information-form/ Accessed April 1, 2023.
- National Institute for Health and Care Excellence. DCVax-L for treating newly diagnosed glioblastoma multiforme [ID836]. Available at https://www.nice.org.uk/guidance/indevelopment/gid-ta10143 Accessed April 1, 2023.
- Neelapu, S.S.; Locke, F.L.; Bartlett, N.L.; Lekakis, L.J.; Miklos, D.B.; Jacobson, C.A.; Braunschweig, I.; Oluwole, O.O.; Siddiqi, T.; Lin, Y.; et al. Axicabtagene Ciloleucel CAR T-Cell Therapy in Refractory Large B-Cell Lymphoma. N. Engl. J. Med. 2017, 377, 2531–2544. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Maude, S.L.; Laetsch, T.W.; Buechner, J.; Rives, S.; Boyer, M.; Bittencourt, H.; Bader, P.; Verneris, M.R.; Stefanski, H.E.; Myers, G.D.; et al. Tisagenlecleucel in Children and Young Adults with B-Cell Lymphoblastic Leukemia. N. Engl. J. Med. 2018, 378, 439–448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Brown, C.E.; Alizadeh, D.; Starr, R.; Weng, L.; Wagner, J.R.; Naranjo, A.; Ostberg, J.R.; Blanchard, M.S.; Kilpatrick, J.; Simpson, J.; et al. Regression of Glioblastoma after Chimeric Antigen Receptor T-Cell Therapy. N. Engl. J. Med. 2016, 375, 2561–2569. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Weller, M.; Butowski, N.; Tran, D.D.; Recht, L.D.; Lim, M.; Hirte, H.; Ashby, L.; Mechtler, L.; Goldlust, S.A.; Iwamoto, F.; et al. ACT IV trial investigators. Rindopepimut with temozolomide for patients with newly diagnosed, EGFRvIII-expressing glioblastoma (ACT IV): a randomised, double-blind, international phase 3 trial. Lancet. Oncol. 2017, 18, 1373–1385.
- O'Rourke, D.M.; Nasrallah, M.P.; Desai, A.; Melenhorst, J.J.; Mansfield, K.; Morrissette, J.J.D.; Martinez-Lage, M.; Brem, S.; Maloney, E.; Shen, A.; et al. A single dose of peripherally infused EGFRvIII-directed CAR T cells mediates antigen loss and induces adaptive resistance in patients with recurrent glioblastoma. Sci. Transl. Med. 2017, 9, eaaa0984. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Bielamowicz, K.; Fousek, K.; Byrd, T.T.; Samaha, H.; Mukherjee, M.; Aware, N.; Wu, M.F.; Orange, J.S.; Sumazin, P.; Man, T.K.; et al. Trivalent CAR T cells overcome interpatient antigenic variability in glioblastoma. Neuro. Oncol. 2018, 20, 506–518. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Del Vecchio, C.A.; Giacomini, C.P.; Vogel, H.; Jensen, K.C.; Florio, T.; Merlo, A.; Pollack, J.R.; Wong, A.J. EGFRvIII gene rearrangement is an early event in glioblastoma tumorigenesis and expression defines a hierarchy modulated by epigenetic mechanisms. Oncogene. 2013, 32, 2670–2681. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Lin, Y.J.; Mashouf, L.A.; Lim, M. CAR T Cell Therapy in Primary Brain Tumors: Current Investigations and the Future. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 817296. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Marofi, F.; Achmad, H.; Bokov, D.; Abdelbasset, W.K.; Alsadoon, Z.; Chupradit, S.; Suksatan, W.; Shariatzadeh, S.; Hasanpoor, Z.; Yazdanifar, M.; et al. Hurdles to breakthrough in CAR T cell therapy of solid tumors. Stem. Cell. Res. Ther. 2022, 13, 140. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Jackson, S.; Meeks, C.; Vézina, A.; Robey, R.W.; Tanner, K.; Gottesman, M.M. Model systems for studying the blood-brain barrier: Applications and challenges. Biomaterials. 2019, 214, 119217. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Cherkassky, L.; Morello, A.; Villena-Vargas, J.; Feng, Y.; Dimitrov, D.S.; Jones, D.R.; Sadelain, M.; Adusumilli, P.S. Human CAR T cells with cell-intrinsic PD-1 checkpoint blockade resist tumor-mediated inhibition. J. Clin. Invest. 2016, 126, 3130–3144. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Priceman, S.J.; Tilakawardane, D.; Jeang, B.; Aguilar, B.; Murad, J.P.; Park, A.K.; Chang, W.C.; Ostberg, J.R.; Neman, J.; Jandial, R.; et al. Regional Delivery of Chimeric Antigen Receptor-Engineered T Cells Effectively Targets HER2+ Breast Cancer Metastasis to the Brain. Clin. Cancer. Res. 2018, 24, 95–105. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Mulazzani, M.; Fräßle, S.P.; von Mücke-Heim, I.; Langer, S.; Zhou, X.; Ishikawa-Ankerhold, H.; Leube, J.; Zhang, W.; Dötsch, S.; Svec, M.; et al. Long-term in vivo microscopy of CAR T cell dynamics during eradication of CNS lymphoma in mice. Proc. Natl. Acad. Sci. U S A. 2019, 116, 24275–24284. [Google Scholar]
- Newick, K.; O'Brien, S.; Moon, E.; Albelda, S.M. CAR T Cell Therapy for Solid Tumors. Annu. Rev. Med. 2017, 68, 139–152. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Singh, K.; Hotchkiss, K.M.; Patel, K.K.; Wilkinson, D.S.; Mohan, A.A.; Cook, S.L.; Sampson, J.H. Enhancing T Cell Chemotaxis and Infiltration in Glioblastoma. Cancers. (Basel). 2021, 13, 5367. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Wang, G.; Wang, W. Advanced Cell Therapies for Glioblastoma. Front. Immunol. 2022, 13, 904133. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Vivier, E.; Tomasello, E.; Baratin, M.; Walzer, T.; Ugolini, S. Functions of natural killer cells. Nat. Immunol. 2008, 9, 503–510. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Burger, M.C.; Zhang, C.; Harter, P.N.; Romanski, A.; Strassheimer, F.; Senft, C.; Tonn, T.; Steinbach, J.P.; Wels, W.S. CAR-Engineered NK Cells for the Treatment of Glioblastoma: Turning Innate Effectors Into Precision Tools for Cancer Immunotherapy. Front. Immunol. 2019, 10, 2683. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Lim, J.; Park, Y.; Ahn, J.W.; Sim, J.; Kang, S.J.; Hwang, S.; Chun, J.; Choi, H.; Kim, S.H.; Chun, D.H.; et al. Autologous adoptive immune-cell therapy elicited a durable response with enhanced immune reaction signatures in patients with recurrent glioblastoma: An open label, phase I/IIa trial. PloS. One. 2021, 16, e0247293. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Liu, E.; Marin, D.; Banerjee, P.; Macapinlac, H.A.; Thompson, P.; Basar, R.; Nassif Kerbauy, L.; Overman, B.; Thall, P.; Kaplan, M.; et al. Use of CAR-Transduced Natural Killer Cells in CD19-Positive Lymphoid Tumors. N. Engl. J. Med. 2020, 382, 545–553. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ramanathan, A.; Lorimer, I.A.J. Engineered cells as glioblastoma therapeutics. Cancer. Gene. Ther. 2022, 29, 156–166. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Beier, C.P.; Kumar, P.; Meyer, K.; Leukel, P.; Bruttel, V.; Aschenbrenner, I.; Riemenschneider, M.J.; Fragoulis, A.; Rümmele, P.; Lamszus, K.; et al. The cancer stem cell subtype determines immune infiltration of glioblastoma. Stem. Cells. Dev. 2012, 21, 2753–2761. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kaufman, H.L.; Kohlhapp, F.J.; Zloza, A. Oncolytic viruses: a new class of immunotherapy drugs. Nat. Rev. Drug. Discov. 2015, 14, 642–662. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Fudaba, H.; Wakimoto, H. Oncolytic virus therapy for malignant gliomas: entering the new era. Expert. Opin. Biol. Ther. 2023, 23, 269–282. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Qi, Z.; Long, X.; Liu, J.; Cheng, P. Glioblastoma microenvironment and its reprogramming by oncolytic virotherapy. Front. Cell. Neurosci. 2022, 16, 819363. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Todo, T.; Ito, H.; Ino, Y.; Ohtsu, H.; Ota, Y.; Shibahara, J.; Tanaka, M. Intratumoral oncolytic herpes virus G47∆ for residual or recurrent glioblastoma: a phase 2 trial. Nat. Med. 2022, 28, 1630–1639. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bieler, A.; Mantwill, K.; Holzmüller, R.; Jürchott, K.; Kaszubiak, A.; Stärk, S.; Glockzin, G.; Lage, H.; Grosu, A.L.; Gansbacher, B.; et al. Impact of radiation therapy on the oncolytic adenovirus dl520: implications on the treatment of glioblastoma. Radiother. Oncol. 2008, 86, 419–427. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kieran, M.W.; Goumnerova, L.; Manley, P.; Chi, S.N.; Marcus, K.J.; Manzanera, A.G.; Polanco, M.L.S.; Guzik, B.W.; Aguilar-Cordova, E.; Diaz-Montero, C.M.; et al. Phase I study of gene-mediated cytotoxic immunotherapy with AdV-tk as adjuvant to surgery and radiation for pediatric malignant glioma and recurrent ependymoma. Neuro. Oncol. 2019, 21, 537–546. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Bai, Y.; Chen, Y.; Hong, X.; Liu, X.; Su, X.; Li, S.; Dong, X.; Zhao, G.; Li, Y. Newcastle disease virus enhances the growth-inhibiting and proapoptotic effects of temozolomide on glioblastoma cells in vitro and in vivo. Sci. Rep. 2018, 8, 11470. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Kleijn, A.; van den Bossche, W.; Haefner, E.S.; Belcaid, Z.; Burghoorn-Maas, C.; Kloezeman, J.J.; Pas, S.D.; Leenstra, S.; Debets, R.; de Vrij, J.; et al. The Sequence of Delta24-RGD and TMZ Administration in Malignant Glioma Affects the Role of CD8+T Cell Anti-tumor Activity. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics. 2017, 5, 11–19. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef] [PubMed]
- Wang, G.; Zhang, Z.; Zhong, K.; Wang, Z.; Yang, N.; Tang, X.; Li, H.; Lu, Q.; Wu, Z.; Yuan, B.; et al. CXCL11-armed oncolytic adenoviruses enhance CAR-T cell therapeutic efficacy and reprogram tumor microenvironment in glioblastoma. Mol. Ther. 2023, 31, 134–153. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Samson, A.; Scott, K.J.; Taggart, D.; West, E.J.; Wilson, E.; Nuovo, G.J.; Thomson, S.; Corns, R.; Mathew, R.K.; Fuller, M.J.; et al. Intravenous delivery of oncolytic reovirus to brain tumor patients immunologically primes for subsequent checkpoint blockade. Sci. Transl. Med. 2018, 10, eaam7577. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zadeh, G.; Daras, M.; Cloughesy, T.F.; Colman, H.; Kumthekar, P.U.; Chen, C.C.; Aiken, R.; Groves, M.D.; Ong, S.; Ramakrishna, R.; et al. LTBK-04. Phase 2 Multicenter Study of the Oncolytic Adenovirus DNX-2401 (tasadenoturev) in Combination with Pembrolizumab for Recurrent Glioblastoma; Captive Study (KEYNOTE-192). Neuro. Oncol. 2020, 22, ii237.
- Chalise, L.; Kato, A.; Ohno, M.; Maeda, S.; Yamamichi, A.; Kuramitsu, S.; Shiina, S.; Takahashi, H.; Ozone, S.; Yamaguchi, J.; et al. Efficacy of cancer-specific anti-podoplanin CAR-T cells and oncolytic herpes virus G47Δ combination therapy against glioblastoma. Mol. Ther. Oncolytics. 2022, 26, 265–274. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Zhu, G.; Zhang, J.; Zhang, Q.; Jin, G.; Su, X.; Liu, S.; Liu, F. Enhancement of CD70-specific CAR T treatment by IFN-γ released from oHSV-1-infected glioblastoma. Cancer. Immunol. Immunother. 2022, 71, 2433–2448. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
- Ma, R.; Lu, T.; Li, Z.; Teng, K.Y.; Mansour, A.G.; Yu, M.; Tian, L.; Xu, B.; Ma, S.; Zhang, J.; et al. An Oncolytic Virus Expressing IL15/IL15Rα Combined with Off-the-Shelf EGFR-CAR NK Cells Targets Glioblastoma. Cancer. Res. 2021, 81, 3635–3648. [Google Scholar] [CrossRef]
| Cell type | Function within the tumour microenvironment (TME) |
|---|---|
| Glioma cells |
|
| Tumour-associated macrophages and microglia (TAMs) |
|
| Regulatory T (Treg) cells |
|
| Natural kills (NK) cells |
|
| Dendritic cells (DCs) |
|
| Myeloid-derived suppressor cells (MDSCs) |
|
| Immunotherapy | Description |
|---|---|
| Immune checkpoint inhibitors (ICIs) | Monoclonal antibodies that block either the programmed cell death protein 1 (PD-1) or cytotoxic T-lymphocyte-associated protein 4 (CTLA-4) pathways, resulting in the activation of T cells to target cancer cells |
| Cancer vaccines | Immunogenic agents designed to stimulate antigen presentation and immune activation against cancer cells |
| T-cell therapies | T cells are genetically engineered to express chimeric antigen receptors (CARs) that can recognize specific tumour antigens |
| Oncolytic virotherapy (OVT) | Engineered viruses selectively infect and kill cancer cells, inducing an immune response against tumour antigens |
Disclaimer/Publisher’s Note: The statements, opinions and data contained in all publications are solely those of the individual author(s) and contributor(s) and not of MDPI and/or the editor(s). MDPI and/or the editor(s) disclaim responsibility for any injury to people or property resulting from any ideas, methods, instructions or products referred to in the content. |
© 2023 by the authors. Licensee MDPI, Basel, Switzerland. This article is an open access article distributed under the terms and conditions of the Creative Commons Attribution (CC BY) license (http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/).





